Abstract
Deep learning is emerging in many industrial sectors in hand with big data analytics to streamline production. In the biomanufacturing sector, big data infrastructure is lagging compared to other industries. A promising approach is to combine deep neural networks (DNN) with prior knowledge in hybrid neural network (HNN) workflows that are less dependent on the quality and quantity of data. This paper reviews published articles over the past 30 years on the topic of HNN applications to bioprocesses. It reveals that HNNs have been applied to various bioprocesses, including microbial cultures, animal cells cultures, mixed microbial cultures, and enzyme biocatalysis. HNNs have been applied for process analysis, process monitoring, development of software sensors, open- and closed-loop control, batch-to-batch control, model predictive control, intensified design of experiments, quality-by-design, and recently for the development of digital twins. Most previous HNN studies have combined shallow feedforward neural networks (FFNNs) with physical laws, such as macroscopic material balance equations, following the semiparametric design principle. Only recently, deep HNNs based on deep FFNNs, convolution neural networks (CNN), long short-term memory (LSTM) networks and physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) have been reported. The biopharma sector is currently a major driver but applications to biologics quality attributes, new modalities, and downstream processing are significant research gaps.
1. Introduction
The use of mathematical models for bioprocess monitoring, optimization, and control has a long history in tandem with the progress in computation power and process analytical technology [1]. As early as the mid-1970s, Cooney et al. reported an unstructured bioprocess model (elemental material balances combined with macroscopic material balances and off-gas analysis) for computer-based bioprocess monitoring and control [2]. Over the years, bioprocess models became more detailed and computationally intensive with e.g., the emergence of genome-scale models (GEMs) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) [1]. With the advent of Industry 4.0, mathematical modeling is taking a prominent role in biomanufacturing more than ever before. Companies are investing on bioprocess digital twins (DTs) that rely on high-fidelity mathematical models with different levels of integration with the physical process [3]. Machine learning (ML) techniques are being applied to large collections of biological and process data to extract valuable process insights [4]. Historically, bioprocess modeling has been hindered by the lack of fundamental knowledge compared to other engineering fields. Due to this limitation, ML techniques that do not require fundamental knowledge are gaining popularity for bioprocess digitalization [5,6,7].
ML is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) dedicated to data-based modeling methods and algorithms that learn with experience [8]. The “learning with experience” feature is at the heart of the Industry 4.0 smart factories vision. Within ML, artificial neural networks (ANNs) are currently the most popular technique in bioprocessing, followed by ensemble learning, multivariate data analysis, support vector machines, and gaussian processes [7]. The emergence of deep learning with the publication of the adaptive moment estimation method (ADAM) [9], has significantly contributed to their growing interest for process digitalization [10]. Despite their rising popularity, DNNs have several disadvantages in relation to mechanistic modeling. They require large datasets (big data) for training due to their typically large number of parameters. DNNs trained on sparse and noisy data are prone to overfitting and poor generalization [11]. They are less transparent, as their structure and parameters have no physical meaning. Moreover, they often violate first principles, such as mass or energy conservation laws, due to their loose structure and their overfitting propensity.
In the case of bioprocesses, it is rarely the case that prior knowledge or process data are sufficient per se to develop a reliable mathematical model. To overcome this limitation, some authors have proposed methods to combine ANNs with prior knowledge in HNN modeling workflows. Psichogios and Ungar proposed the combination of ANNs with first principles equations to model a fed-batch bioreactor [12]. The HNN model consisted of a shallow feedforward neural network (FFNN) (with a single hidden layer) connected in series with a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) derived from macroscopic material balances. The authors compared HNN modeling, Kalman filtering, nonlinear programming (NLP), and fully ANNs for predictive modeling and state estimation. The indirect training method using sensitivity equations was introduced in this study, which allowed for training the FFNN by error backpropagation in a similar fashion to a fully FFNN. The authors concluded that extended Kalman filtering and NLP estimation performed better than the hybrid approach when a detailed mechanistic model was available. When, however, the mechanistic model was incomplete or unreliable, the hybrid model outperformed the Kalman filtering and NLP estimation. The key messages of this pioneering study were: (1) effective indirect training of the FFNN using the sensitivity method; (2) hybrid models are more flexible (better interpolation) than fully mechanistic models; and (3) hybrid models have better generalization properties and are easier to interpret than fully neural network models [12].
Shortly after, Thompson and Kramer conducted a study in which they applied a hybrid model to a fed-batch penicillin fermentation [13]. The hybrid model consisted of a radial basis function network (RBFN) connected in parallel with a mechanistic kinetic model to calculate specific kinetic rates. The RBFN worked as residual model to correct the output of the fundamental kinetic model. The kinetic rates were then fed to the bioreactor material balance equations (connected in series with the kinetic models). This pioneering study framed hybrid models as parallel and/or serial semiparametric mathematical structures that may grow in complexity depending on prior knowledge. They also concluded that less data are required for parameter estimation, and more accurate and consistent predictions of the hybrid model are obtained in comparison to the fully mechanistic or fully ANN models [13].
Schubert and coauthors studied the application of hybrid models for state and parameter estimation, feed rate optimization (open-loop control problem), and closed-loop control of a fed-batch baker’s yeast process [14,15]. While Psichogios and Ungar [12] and Thompson and Kramer [13] used synthetic data, Schubert et al. addressed a real-life problem [15]. The hybrid model consisted of a simultaneously serial and parallel structure composed of an FFNN (with 12 inputs, a single hidden layer with 10 nodes, and 3 outputs), dynamical ODEs, and a fuzzy expert system to decide on which process conditions the FFNN predictions are reliable. This pioneering study pointed out, for the first time, to the need of reliability monitoring of the neural network outputs outside the training domain and to adjust the model accordingly. A simple rule-based expert system was adopted for this purpose. It was concluded that process optimization and control based on hybrid models have a higher benefit/cost ratio than other methodologies [15].
Since these pioneering studies, a large number of bioprocess HNN models have been reported, highlighting the potential of this technique for bioprocess digitalization. In this paper, we present a systematic literature review and meta-analysis focused on the application of HNNs to bioprocesses. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, basic hybrid modeling methods are overviewed. In Section 3, the methodology adopted in this review is briefly presented and further detailed as Supplementary Materials (Supplementary File S1). In Section 4, the application of HNNs to bioprocesses is overviewed. Finally, in Section 5 and Section 6, future perspectives are discussed, and final conclusions are drawn.
2. What Is Hybrid Neural Network Modeling?
HNN modeling may be defined as the combination of ANNs with prior knowledge in a common mathematical structure. According to Thompson and Kramer [13], there are two main approaches to embodying prior knowledge in neural network models, namely design and training approaches. In design approaches, prior knowledge dictates the structure of the model. Prior knowledge is used to define the ANN topology (e.g., number of layers, types of layers, types of nodes), for modularization of the network, or to include nonnetwork mathematical equations (e.g., physical laws) in tandem with the ANN model. In training approaches, the prior knowledge dictates the parameter estimation problem either in the form of variable constraints, network weights constraints, or the definition of the loss function. In both design and training approaches, the inclusion of prior knowledge reduces data dependency: in design approaches, the dimension of the parameter space is reduced (i.e., the ANN is smaller, and the number of weights is lower), whereas in training approaches, the feasible region of the parameter space is reduced. In both cases, the training becomes less sensitive to sparse and noisy data and the final model improves its descriptive and predictive power in relation to a fully ANN model.
2.1. Design Approaches
In design approaches, prior knowledge shapes the structure of the HNN model. Design approaches may be further subdivided into modular and semiparametric design. In modular design, the overall model is decoupled into smaller interconnected modules. A biochemical process typically comprehends several interconnected unit operations. Instead of a large ANN to describe the full process, smaller ANNs may be interconnected to match process topology (prior knowledge). Whereas in a single ANN, all input nodes are connected to all output nodes, in modular ANNs, the connectivity is sparser, the number of parameters is reduced, and the data requirements are therefore also reduced. The modular ANN model is also more transparent, as the input/outputs variables of the modules have physical meaning. The hierarchical neural network model proposed by Mavrovouniotis and Chang is an example of modular ANN design [16]. A more recent example is the knowledge-based ANN concept proposed in [17].
The most frequently reported approach is semiparametric design (Figure 1A,B), in which physical laws are directly incorporated in the model structure. Instead of a large ANN, a smaller one is combined with physical laws in the form of a semiparametric model. Semiparametric models combine per definition parametric and nonparametric functions in the same model structure. Parametric functions are derived from prior knowledge of first principles, well-established mechanisms, and/or empirical correlations. They have a fixed mathematical structure and a fixed number of parameters with physical interpretation. On the contrary, ANNs are nonparametric functions entirely derived from process data. They have a loose structure without physical interpretation. Both model components are trained together.
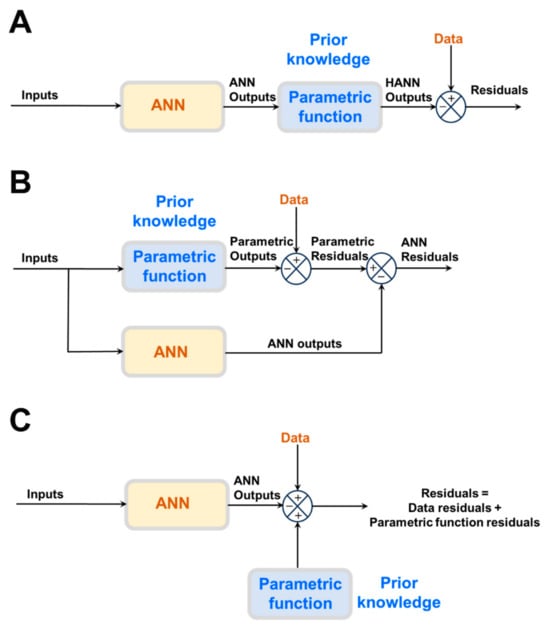
Figure 1.
Different methods to embody prior knowledge in HNN models: (A) Serial semiparametric hybrid structure. (B) Parallel semiparametric hybrid structure. (C) Physics-informed neural network structure.
Semiparametric HNN models can be classified as serial or parallel (Figure 1A,B). In serial structures (Figure 1A), the parametric equations (prior knowledge) cover only some parts of the process. The ANN has the job of learning from data the cause–effect relationships of those process parts lacking prior knowledge. One example of a serial semiparametric structure is the Psichogios and Ungar bioreactor hybrid model [12], where an FFNN (nonparametric model that calculates bioreaction kinetics) is connected in series with macroscopic material balance equations (parametric model). Other examples are the general bioreactor hybrid model [18] and the neural ordinary differential equation (neural ODE) model [19,20].
In the case of parallel semiparametric structures (Figure 1B), a full parametric model stemming from prior knowledge exists that, however, is not sufficiently accurate to describe the process. The ANN runs in parallel to compensate for parametric model inaccuracies. The parametric model takes priority in describing the process outputs. Firstly, the parametric model parameters are estimated to minimize the model–process mismatch. Then, the residuals of the parametric model are calculated over the data input space. If the residuals contain relevant information beyond the noise level, an ANN is trained to extract the cause–effect relationship from the parametric model residuals. The size of the ANN compensator is inversely proportional to the explained data variance using the parametric model. In limit, if the explained variance is sufficiently high, then the ANN compensator is not needed. Conversely, if the explained variance is negative, then the parametric model should be removed since a fully ANN will perform better than the hybrid structure. Examples of parallel semiparametric hybrid models are provided by, e.g., Côté et al. [21], Piron et al. [22] and Peres et al. [23]. The bioreactor model proposed by Thompson and Krameris simultaneously parallel and serial [13]. The biological kinetics are described with a Monod-type kinetic model (parametric) connected in parallel with a RBFN (nonparametric) compensator. The RBFN performs an additive correction of the Monod-type kinetic model outputs. The corrected kinetics are then connected in series with macroscopic material balances (parametric) in a similar way to the model reported by Psichogios and Ungar [12].
2.2. Training Approaches
Prior knowledge may also be incorporated in HNN models through the training method. It may dictate constraints on process variables, e.g., concentrations or reaction rates of irreversible reactions must be positive. Variable inequality constraints, network weights inequality constraints, and loss function regularizers may be introduced in the training method to enforce such desired output behavior [13]. Several methods have been developed to enforce ANN output monotonicity, convexity, concavity, or smoothness by adding parameter constraints and loss function regularizers [24,25]. More recently, physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) have emerged for modeling CFD problems based on the Navier–Stokes equations [26] or partial differential equations (PDEs) in general. The innovative aspect of PINNs is that physical equations are embodied in a “pure” ANN structure via the training approach (Figure 1C). PINNs use a DNN to parameterize state variables over independent variables (time and spatial coordinates). Automatic differentiation (AD) is applied to obtain partial derivatives of the state variables in time and spatial coordinates and to calculate a PDE’s agreement error (the terms on the right and left sides of the PDEs equations must agree with each other). Two different sets of residuals are simultaneously minimized during the training: (i) the measurement residuals between calculated and measured state variables; (ii) the Navier–Stokes PDEs agreement (physics) residuals. PINNs have been shown to converge to PDEs solutions obtained using numerical discretization methods. Moreover, PINNs have been shown to seamlessly integrate data and mathematical models in flow problems [27]. A key advantage of PINNs in relation to semiparametric HNNs is that numerical integration, or any other numerical method inherent to the parametric model, are avoided. This may be a substantial advantage in the case of PDEs and stiff systems of ODEs. Possible disadvantages are, however, that the exact mapping of the physical laws to the DNN structure is not guaranteed and that the physical laws may not be obeyed in case of extrapolation.
2.3. General Bioreactor Hybrid Model
Since the pioneering works by Psichogios and Ungar [12], Thompson and Kramer [13], and Schubert et al. [14,15], attempts were made to propose a bioreactor HNN structure that covers a wide range of problems [18,28,29,30,31]. The general bioreactor hybrid model (Figure 2) is a serial semiparametric structure that combines an ANN and a system of ODEs with information feedback. Prior knowledge is represented by a system of ODEs derived from macroscopic material balances and/or intracellular material balances. These may be divided into a state–space model and a measurement model that computes observable process outputs. The ANN is used to model cell properties (lacking fundamental knowledge) as a function of the process state and exogenous inputs. The observable outputs are compared with training examples under a supervised learning scheme.
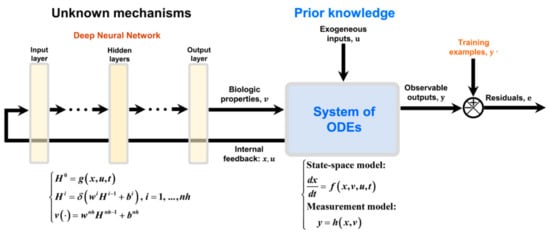
Figure 2.
General deep hybrid model for bioreactor systems. The model has parametric functions (functions f(.) and h(.)) with fixed mathematical structure; typically material/energy balance equations). Some process properties, v, lacking mechanistic explanation are modelled using a feedforward neural network (FFNN) as a function of the process state, x; exogenous inputs, u; and time, t. FFNN is a nonparametric function with loose structure that must be identified from process data given the absence of explanatory mechanisms for that particular part of the process. The model is dynamic in nature with state vector, x, and observable outputs, y, changing over time.
As reviewed in the next section, most previous studies have adopted a shallow HNN configuration based on three-layers FFNNs (with a single hidden layer with tanh activation function) connected in series with material balance equations. Shallow HNNs are typically trained in a least squares sense employing the Levenberg–Marquardt optimization algorithm. The computation of gradients follows the indirect sensitivity method originally proposed by Psichogios and Ungar [12] and detailed by Oliveira [18]. Sensitivity equations are required because the observable outputs, y, are not directly linked to the ANN outputs, v. Cross-validation is adopted to prevent overfitting. Recently, the general bioreactor HNN has been extended to deep multilayered FFNNs and deep learning [30,32,33]. Multiple hidden layers with rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation functions were adopted, connected in series with material balance equations. The ADAM algorithm [9] was applied to train the deep HNN in a weighted least squares sense. The objective function gradients were computed using modified semidirect sensitivity equations, thereby significantly reducing the CPU time [30]. Stochastic regularization based on random training examples and ANN weights dropout was adopted to mitigate overfitting. Deep HNN modeling was shown to systematically generalize better than shallow HNN modeling.
3. Systematic Literature Review
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) methodology was adopted in order to have a more structured vision of the literature produced on the application of HNNs to bioprocesses. The articles were selected based on a selection algorithm and the PRISMA flow diagram instructions [34,35], which are divided in four categories:
- -
- Scopus: The algorithm initially retrieved 481 publications from the Scopus database, and after screening, 94 relevant cases were obtained.
- -
- Web of Science (WoS): The algorithm initially retrieved 251 publications from the WoS database, and after screening, 84 relevant cases were obtained.
- -
- From the well-known authors’ search, 825 publications were extracted, and after screening, 66 relevant cases were obtained.
- -
- From backward citation, 74 relevant cases were obtained.
After merging the articles and deletion of duplicates, 185 publications were selected for keyword analysis, covering journal and conference papers published before September 2023. Figure 3 shows the evolution of the number of papers over time. The first paper was published in 1992 [12], followed by consistent growth, a peak in 2004 (15 papers), and a decline until 2015–2016. The number of papers is currently surging again.
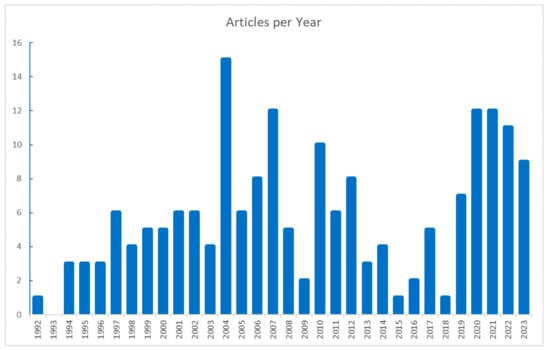
Figure 3.
Number of HNN bioprocess modeling publications from January 1992 until September 2023.
Among the 185 papers, the ten most cited papers are listed in Table 1. Keyword analysis showed that HNNs were first applied to microbial cultures for the production of baker’s yeast, bioethanol, and antibiotics. In the last decade, keywords such as “design of experiments”, “critical process parameters”, “process analytical technology”, “digital twins”, and “big data” have appeared. These are now hot topics for the application of HNNs to bioprocesses, especially in the biopharma sector. Only recently has the “deep learning” keyword appeared explicitly or implicitly in connection with hybrid modeling [30,32,33,36,37,38,39]. Further details of the PRISMA analysis are provided as Supplementary Materials (Supplementary File S1, Supplementary Figures S1–S7 and Supplementary Table S1). In what follows, the produced literature is critically overviewed.

Table 1.
Ten most cited HNN bioprocess modeling publications.
4. Applications of HNNs for Bioprocess Modeling
4.1. Microbial Culture
In the early years, hybrid models were mainly applied to traditional microbial processes such as baker’s yeast [14,15], antibiotics production [45] and beer/bioethanol production [46,47,48,49,50]. Preusting et al. addressed the historical penicillin process at the production scale [45]. The hybrid model structure was similar to that of Schubert et al. [15], using an expert system to weigh the outputs of the neural network and fundamental kinetic model depending on the reliability of the FFNN. This model was used to optimize (open-loop control problem) the large-scale production of penicillin using the in-house developed software tool HYBrid NETworks (HYBNET) [51].
Simutis et al. developed a simple hybrid model of S. cerevisiae showing successful predictive modeling of diacetyl formation during beer production in a production plant [52]. In the study by da Silva Henriques et al., a hybrid model for alcoholic Zymomonas mobilis fermentation was developed [50]. The model consisted of a three-layers FFNN (describing the kinetic rates) connected in series with macroscopic mass balance equations. Meleiro et al. applied a HNN for dynamic modeling and control of an industrial-scale S. cerevisiae fermentation process for bioethanol production [49]. They combined a three-layers FFNN with macroscopic material balances and simple Monod-type kinetics. The hybrid model provided online estimations of key process state variables and kinetic parameters based on reliable and easily accessible measurements. This enabled the implementation of efficient automatic control strategies [49]. Recently, hybrid modeling of bioethanol production was revisited by Da Silva Pereira et al. [53]. Bioethanol was produced using a flocculating yeast grown on cashew apple juice. A hybrid model was built consisting of three shallow FFNNs combined with mass balance equations (biomass, substrate, and product). Particle swarm optimization (PSO) was adopted to optimize bioethanol production (open-loop/dynamic optimization problem) at aid of the hybrid model, thereby achieving high yield and productivity.
Hybrid modeling of Pichia pastoris yeast for recombinant protein production was first attempted by Ferreira et al. [54]. The authors applied a serial HNN (three-layers FFNN combined with material balance equations in series) for dynamic modeling of P. pastoris GS115 expressing scFv in a pilot 50 L bioreactor. The hybrid model was subsequently employed for iterative batch-to-batch control, showing a fourfold titer improvement after four optimization cycles. Batch-to-batch control using hybrid models and evolutionary programming was investigated in a simulation study by Teixeira et al. [55]. Constraining the optimization design space depending on the reliability of the FFNN was shown to be essential in ensuring stable convergence to the global optimum. Another important finding was that the hybrid model should not include “wrong” mechanisms, or otherwise, an offset to the global optimum is observed. Recently, hybrid modeling of P. pastoris was revisited by Pinto et al. using state-of-the-art deep learning methods [30]. FFNN networks with varying depths and ReLU nodes were combined with material balance equations in the form of deep HNNs. Deep learning techniques, namely ADAM, stochastic regularization, and depth-dependent weight initialization, were evaluated in a hybrid modeling context. The semidirect training method was proposed to reduce the CPU time of the sensitivity equations, which then become independent of the size and depth of the neural network. The CPU time for training deep HNN models was significantly reduced.
Recombinant E. coli was studied by von Stoch et al. [56,57], who introduced the methodology of intensified design of experiments (iDoE) coupled with dynamic hybrid modeling. This approach was applied to an industrial E. coli process expressing a therapeutic protein. iDoE is a dynamic design of experiments based on intraexperiment step changes of design factors (such as pH, temperature, and feed rates) and dynamic modeling. Contrary to standard DoE, different combinations of process conditions are explored stepwise in the same experiment. A serial hybrid dynamic model (FFNN + material balance equations) was adopted to capture the dynamic relationship between stepwise variations in design factors and process response variables. The authors concluded that intraexperimental variations in process conditions could reduce the number of experiments by a factor, which in limit would be equivalent to the number of intraexperimental variations per experiment. Bayer et al. further explored the iDoE methodology in a 20 L fed-batch E. coli process expressing hSOD [58]. The hybrid model could accurately predict the endpoint biomass concentration and product titer as well as the respective time-resolved trajectories [58]. These studies emphasized the potential of hybrid modeling to address the challenges of process analytical technology (PAT) and quality by design (QbD) in the biopharma sector.
Hybrid modeling of biopolymer production by bacteria has been investigated in several studies [59,60,61,62]. One of the first HNN studies addressing Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production by bacteria was reported by Peres et al. [60]. A competitive hybrid structure was applied where a gating system was trained with the expectation maximization (EM) algorithm to learn in which regions of the input space the FFNN performs better than the competing mechanistic model. This hybrid approach was further detailed in a follow-up paper applied to baker’s yeast [63]. Production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) by Ralstonia eutropha was investigated by Patnaik et al. [64]. The authors demonstrated the superiority of the hybrid model (H-model) to the neural-cum-dispersion model (D-model) and to the neural network model (N-model). Recently, Luna et al. developed an HNN model with four layers of five nodes to describe the continuous production of PHA by Pseudomonas putida GPo1 [65]. The hybrid model was shown to describe the process in a wide range of operating conditions, including single and dual nutrient-limited growth conditions.
4.2. Animal Cell Culture
Animal cells are ubiquitous in the biopharmaceutical industry and are gaining momentum in the hybrid modeling community [58,66,67,68,69,70,71]. One of the first hybrid modeling studies of mammalian cell culture was reported by Dors et al. [72]. Fu and Barford (reported one of the first consistent HNN model applications to animal cell monoclonal antibody production [73]. The proposed HNN model predicted substrate consumption, toxic byproduct accumulation, cell growth, cell composition, and metabolic product formation [73]. The HNN produced a better result compared to the fully mechanistic model or fully artificial neural network model. Teixeira et al. developed a hybrid model for BHK-21 cells expressing the fusion glycoprotein IgG1-IL2 [74]. The HNN consisted of a simultaneously serial and parallel structure for dynamic predictive modeling. A shallow FFNN was connected in parallel with a fundamental kinetic model. The experience measure technique was adopted to automatically switch between the fundamental model and FFNN predictions depending on the reliability of the latter. The hybrid model was used to optimize the feeding strategy (dynamic optimization/open-loop control problem) of glucose and glutamine. Later, Teixeira et al. extended the HNN to incorporate knowledge of the metabolic network using the concept of elementary modes [44]. The resulting hybrid model predicted extracellular concentrations and intracellular fluxes simultaneously. The HNN was adopted for online optimizing control, which delivered a 10% titer increase in relation to the control experiment. This was one of the first attempts to include metabolic detail in hybrid models embedded in a model predictive control (MPC) scheme. Recently, Maton et alapplied a similar elementary modes HNN to a hybridoma HB-58 cell line [75]. Aehle et al. developed a serial hybrid model for online estimation of viable cell concentration in fed-batch CHO cultures [76]. The authors concluded that the HNN outperformed other data-based and model-based techniques. Narayanan et al. developed a serial hybrid model (FFNN with one hidden layer connected to material balances) for a CHO fed-batch process (81 batches in a 3.5 L bioreactor) [77]. They used the mass balance equation as the mechanistic part of the hybrid model to predict the process variables (substrate and metabolite concentration, cell density, and product concentration). The HNN showed high predictive power of CHO dynamics using only the initial and process conditions as inputs, in comparison to other statistical modeling methods. Kotidis et al. developed a complex serial hybrid model to describe N-glycosylation of recombinant proteins in CHO cultures [78]. The HNN utilized the extracellular concentration of metabolites and certain amino acids as inputs. A metabolic module calculated the specific growth rate and the specific antibody production rate. These rates were then fed to a nucleotide sugar donors module that calculated the respective intracellular concentration. The nucleotide sugar donors concentrations were then inputted to a four-layers FFNN, which calculated glycan distribution. The overall hybrid model simulated the glycoform distribution of four different proteins (two IgGs and two fusion proteins, EPO-Fc and Fc-DAO) expressed in three CHO cell lines (GS-CHO, CHO–K1, CHO–S). This study was one of the first to address hybrid modeling of glycosylation. As a follow-up to a previous E. coli study, Bayer et al. applied the same iDoE/hybrid modeling approach to reduce the validation burden of CHO cultures in a PAT and QbD context [79]. They also investigated the transferability of hybrid models along process scales (300 mL shaker scale and 15 L bioreactor). The authors concluded that a HNN trained on 300 mL bolus feeding shake flask DoE could be used to correctly estimate the cell behavior and product formation in a 15 L stirred tank bioreactor.
4.3. Mixed Microbial Cultures
Mixed microbial cultures (MMCs) are of widespread use in waste treatment plants and commonly termed as activated sludge. Reducing wastewater treatment costs has long been of interest, and modeling has proven an essential tool in optimizing wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). Due to the intrinsic complexity of WWTPs, some researchers combined artificial neural network with other methods or models to estimate and/or control process parameters. Côté et al. reported one of the first studies where a HNN was applied to a WWTP [21]. A mechanistic model was combined with a three-layers FFNN in parallel. The FFNN was used to extract cause–effect patterns from the mechanistic model residuals, thereby correcting its outputs (residual modeling strategy). The parallel coupling of the mechanistic model with the FFNN provided more accurate simulations of five key variables of the activated sludge process. Zhao et al. developed a hybrid dynamic model of a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) consisting of a simplified mechanistic model and a FFNN connected in parallel, also following the residual modeling approach [80]. Anderson et al. applied different hybrid mechanistic/FFNN models for dynamic modeling of WWTPs and process control [81]. They concluded that hybrid models do not necessarily produce superior control results. Sung Lee et al. applied a parallel hybrid model to a full-scale WWTP [41]. The authors reported more accurate predictions with good extrapolation properties of the HNN compared with other modeling approaches. Fang and Dai developed a simple hybrid model for chemical oxygen demand (COD) prediction [82]. Azwar et al. proposed a hybrid FFNN/proportional integral controller of dissolved oxygen concentration in a SBR [83]. The hybrid control scheme consisted of a basic FFNN controller in parallel with a proportional integral (PI) controller. This approach was shown to outperform other nonhybrid control schemes. Peres et al. reported a hybrid modular model applied to a phosphorous removal WWTP [84]. The hybrid model consisted of a mixture of experts (ME) network and a gating system connected in series with material balance equations. This serial/parallel hybrid structure with competing expert networks was trained with the EM algorithm. The final ME network was shown to better represent the cellular kinetic structure, which resulted in higher accuracy and generalization capacity of the hybrid model. Xiao et al. developed a hybrid model of dark fermentation for biohydrogen production. A NARX-BP hybrid neural network consisting of a two-stage model was developed, which combined NARX (nonlinear autoregressive exogenous) and BP-NN (backpropagation neural network). The model could predict biogas production with high accuracy [85]. Cheng et al. proposed a complex hybrid model that combined the activated sludge model (ASM) (knowledge-based model) and deep neural networks (data-based model) [39]. For the latter, a convolutional neural network (CNN) was combined with a long short-term memory network (LSTM). The CNN was used to extract data spatial features whereas the LSTM was used to extract temporal features. The integration of knowledge- and data-based models in parallel was achieved with an FFNN model connected in series. This complex hybrid model was applied to a sewage treatment plant. It showed an improvement in prediction accuracy in comparison with the typical existing models. The authors also proved the hybrid model’s stability by applying it to different datasets. Their paper is one of the first hybrid modeling studies incorporating state-of-the-art deep neural networks and ADAM training.
4.4. Enzymatic Biocatalysis
Enzyme reaction mechanisms can be quite complex and difficult to model mechanistically. A few studies applied HNNs to enzymatic conversion processes. van Can et al. investigated the enzymatic conversion of penicillin G to 6-ami-nopenicillanic acid (6APA) and phenyl acetic acid (PhAH) by penicillin acylase [86,87]. The extrapolation properties of hybrid models combining FFNNs, white-box kinetics and macroscopic material balance equations were investigated. It was concluded that when the macroscopic material balances are correctly formulated, the identification data only cover the amplitude domain of the rate terms without taking into account the future frequency domain of the complete model. Silva et al. developed a hybrid model of penicillin G acylase immobilized in chitosan for the production of amoxicillin [88]. Three kinetic models were compared, namely a mechanistic, a semiempirical, and a HNN model. It was shown that the HNN could accurately predict the reaction rates for conditions where the semiempirical model failed (e.g., at low substrate concentrations occurring at the end of the fed-batch industrial process). This study did not explicitly consider the reaction–diffusion problem typically occurring in immobilized catalysis.
4.5. Downstream Applications
The keyword analysis in this review clearly shows that only a few hybrid modeling publications have addressed downstream unit operations. One of the early studies was that by Piron et al., who applied a parallel HNN model to crossflow microfiltration in a baker’s yeast process [22]. The HNN consisted of a static FFNN connected in parallel with a dynamic material balance equation. They concluded that a recurrent neural network provided better approximation of process dynamics than the HNN and questioned the validity of the material balance equation. Santos et al. developed a similar parallel HNN model to describe the transport of solvents through nanofiltration membranes [89]. The authors concluded that most used mechanistic models are not sufficiently general to cover a wide range of membrane–solvent systems. To overcome this limitation, membrane and solvent molecular descriptors were incorporated in a parallel semiparametric HNN, where a static FFNN corrected the outputs of a mechanistic solution–diffusion model [89]. Rajabzadeh et al. estimated the filtration time and total solids concentration in the biomass leachate in a reverse osmosis process [90]. They applied an FFNN with four neurons in a single hidden layer. The standard Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm was chosen to train the FFNN. The model predicted more than 80% rejection efficiency of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and silica (for three types of biomass leachate samples) in the reverse osmosis permeate. Nagrath et al. applied HNN models to represent complex preparative chromatographic systems, thereby significantly reducing the computational time required for simulation and optimization [91]. Other recent applications of HNN models in chromatography are optimization, cleaning, and resin aging [67,69,92]. Narayanan et al. compared an HNN model with a mechanistic (lumped) kinetic model [93]. They benchmarked these models in a simulation experiment, and the results showed a higher prediction accuracy of the HNN model [93].
5. Future Perspectives
5.1. From Shallow to Deep HNNs for Bioprocess Operation
As discussed previously, the number of HNN publications showed a first peak in 2004 followed by a decline and is now growing again (Figure 3). Neural network applications to bioprocesses have shown similar publication trends, with a first “explosion” in the 1980s/early 1990s followed by a prolonged decline. The resurgence of neural networks was triggered by advances in deep learning, particularly the publication of the ADAM in 2014, which enabled the efficient training of complex multilayered topologies such as CNNs and LSTMs.
Most of the hybrid semiparametric studies published so far have applied very simple shallow neural networks, namely three-layers FFNNs. With a delay, hybrid modeling is starting to incorporate more complex neural network topologies and deep learning. Cheng and coauthors reported a multilayered HNN workflow for a wastewater treatment process that combined a mechanistic model, a convolutional neural network (CNN), an LSTM, and an FFNN [39]. Shah et al. proposed a serial semiparametric deep HNN for an industrial fermentation process [38]. The model applied a multilayered FFNN that was trained by the traditional nondeep Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm [38]. Bangi et al. recently proposed the universal differential equations (UDE) method based on deep FFNNs and applied it to a Saccharomyces cerevisiae batch fermentation process [36]. The UDE approach is, however, similar to a serial semiparametric HNN modeling problem [36]. Merkelbach et al. developed a software package called HybridML that uses TensorFlow for artificial neural network deep learning and Casadi to integrate ODEs [37]. Pinto et al. recently compared traditional shallow hybrid modeling (using Levenberg–Marquardt training coupled with indirect sensitivities, cross-validation, and the tanh activation function) with a deep hybrid modeling framework based on the ADAM, semidirect sensitivities, stochastic regularization, multiple hidden layers, and ReLU activation functions [30,94]. The deep hybrid models systematically outperformed the shallow hybrid models both in terms of predictive power and computational cost. A significant result was that for the same problem, the deep HNN systematically generalized better than the shallow HNN.
Given their predictive advantage, deep HNNs have been embedded in model predictive control (MPC) schemas [95,96,97,98]. Bhadriraju et al. used sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics (SINDy) coupled with a DNN surrogate model for system identification [95]. The DNN model was then embedded in a MPC of a continuous stirred tank reactor [95]. Similarly, Shah et al. developed DNN surrogate models trained on data generated from physical models (simulated under different operating conditions) that were used to design MPCs. The authors showed that LSTM–ANN-based MPCs are able to drive the process to the desired set-point [98]. Bangi et al. proposed a control Lyapunov–barrier function-based MPC based on a deep HNN [96]. The deep HNN consisted of a system of ODEs with a DNN correction term. The stability conditions of the control loop were derived using Lyapunov stability theory. This pioneering study concluded that the control loop is stable provided that the error of the deep HNN is small and bounded. The proposed MPC scheme was validated with a simulation experiment of a continuous stirred tank reactor [96]. Using a similar approach, Shah et al. applied an HNN-derived MPC controller to maximize profitability of an industry-scale fermentation process and showed that it is possible to increase productivity and decrease plant operating costs [97].
Given the clear advantages, an “explosion” of deep hybrid modeling bioprocess applications for process monitoring, optimization, and control will likely follow in the near future, incorporating state-of-the-art DNN topologies and deep learning algorithms hybridized with physical laws.
5.2. Narrowing the Gap between Hybrid Modeling and Systems Biology
With the emergence of systems biology in the early 2000s [99], several genome-scale models (GEM) have been reconstructed for industrially relevant cell factories. GEMs represent the most complete set of metabolic reactions and metabolites reconstructed from the annotated universe of gene-to-protein relationships. This explosion in structural detail of cell factories is hardly present in the hybrid modeling field. Hybrid model topologies embodying detailed mechanistic models are almost absent in the literature. The penetration of systems biology tools in routine bioprocess operations will likely challenge novel hybrid modeling methods and applications that incorporate more mechanistic detail [31]. GEMs represent a major progress in the understanding of the reaction structure of a given organism, but they are incomplete and difficult to deploy in practice. Recently, the combination of ML and constraint-based modeling (mechanistic) has been proposed to fill this gap [100,101,102,103]. Faure and coauthors proposed a hybrid ANN method that combines mechanistic layers, based on flux balance analysis (FBA), and ANN layers, trained on experimental data and/or FBA-generated data [104]. The proposed method improved the prediction of the growth rate of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas putida in different culture media.
Lee and coauthors proposed a hybrid individual-based population model (IBPM) in order to study cell-to-cell heterogeneity [105]. IBPM parameters obey to probability density functions (PDFs) that are difficult to identify from data. An FFNN was used as a surrogate model of the PDFs, thereby reducing the computational cost of parameter identification. The proposed approach was applied to a tumor necrosis factor-α signaling network. Lee and coauthors proposed a hybrid modeling approach to describe signal transduction networks. The hybrid model combined a system of ODEs of network nodes (e.g., proteins) with a DNN correction term [106]. The authors applied this methodology to a simplified apoptosis network and to a lipopolysaccharide-induced NFkB signaling network.
An important tool for facilitating the widespread use of hybrid biological models will be the encoding in systems biology markup language (SBML). Pinto and coauthors recently developed a standalone Python tool that greatly facilitates the hybridization of mechanistic SBML models and ANNs [32]. This tool uses symbolic mathematics for the conversion of existing mechanistic models in SBML into hybrid models that combine mechanistic functions with ANNs. It applies symbolic differentiation to automatically generate sensitivity equations for the computation of gradients during training. Furthermore, after training, such hybrid models can be stored in public databases in SBML format. The upgrade of SBML models to hybrid models was illustrated with three well-known literature case studies: the Escherichia coli threonine synthesis model, the P58IPK signal transduction model, and the yeast glycolytic oscillations model [33].
5.3. Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs)
The integration of deep ANNs and the Navier–Stokes equations (or systems of partial differential equations in general) has evolved to a subfield known as physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) [26,27,107]. The simulation of fluid flow using numerical discretization requires complex mesh generation methods that are cost-prohibitive for high-dimensional problems. PINNs are formulated as a fully DNN to parameterize state variables over independent variables (time and spatial coordinates). Automatic differentiation (AD) is adopted to obtain partial derivatives of the state variables in time and spatial coordinates. Two different sets of residuals are minimized during the training process: (i) the residuals between calculated and measured state variables are minimized (measurement residuals); (ii) the Navier–Stokes equations residuals are also minimized (physics residuals). PINNs can thus be trained on experimental data and on additional information of the underlying physical laws, for example, at random points in the continuous space–time domain. Such physics-informed learning allows for seamlessly integrating data and PDEs in complex flow problems [108]. Moreover, specialized DNN topologies that automatically satisfy some of the physical constraints for better accuracy, faster training, and improved generalization may be designed. This is in contrast with traditional DNN models that typically allow for good fitting of a system, but their prediction may be inconsistent when performing extrapolation [109].
Given their potential, PINNs are a growing research field and new applications are being developed in material science, medicine, geography, and also bioprocessing [80,108,110]. Recently, Cui and coauthors developed a PINN model to describe the fed-batch cultivation of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells [111]. The authors used a mechanistic kinetic model to train a PINN to capture the dynamics of CHO cultivations. Mowbray and coauthors proposed a physics-informed hybrid modeling and reinforcement learning (RL) framework for bioprocess kinetics identification [7]. The authors trained the model on a fermentation synthetic dataset under the constraint of kinetic parameters physical bounds. The RL served to identify the best-suited model structure. This approach correctly identified the underlying kinetic structures and showed high prediction accuracy (average error of 1.3%). Rogers and coauthors proposed a PINN framework to infer time-varying kinetic parameters [112]. The framework was used to investigate known kinetics and its time-varying trajectories while simultaneously identifying the optimal hybrid model structure. The performance of this PINN framework was tested on several bioprocess simulation experiments.
Lagergren and coauthors also proposed an extension of PINNs to include biological information known as biologically informed neural networks (BINNs) [113]. The authors used a BINN to approximate in vitro biological experiments. The BINN was trained on sparse data with varying initial cell densities and the knowledge of the governing reaction–diffusion partial differential equations were used as constraints. The authors were able to use the model to discover a previously unconsidered biological mechanism that describes delayed population responses.
5.4. HNNs for Biopharma 4.0
HNN applications in the biopharma sector are currently increasing, particularly for process monitoring and control [114,115,116,117] and QbD [57,58,70,71,118] within the PAT framework. Significant achievements have been reported in process validation using HNNs and iDOE for E. coli and CHO culture [56,66]. There is, however, a clear gap in the application to new modalities such as cell-based therapies and nucleotide-based therapies. Most published studies still focus on yield and productivity of upstream processes. Very few studies incorporate critical quality attributes (CQAs) of biotherapeutics related to molecular properties such as glycosylation patterns [78], charge variants, and aggregates.
Industry 4.0 [117,119], big data [117,120], and digital twin [67,121] are recently added subjects that introduce new concepts that challenge the application of HNN modeling to the digitalization of biopharmaceutical processes. A digital twin is a virtual replica of the physical process that combines real-time data from sensors and other sources with advanced analytics to create a digital counterpart that mirrors the behavior and characteristics of the physical process. Digital twins allow for monitoring, analysis, and optimization of the physical process, enabling better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and improved performance. Deep HNNs are very promising for the development of high-fidelity digital twins as they seamlessly combine the learning from experience feature with constant physical laws. This allows, in principle, for reducing the parameter dimension space, decreasing data dependency, and implementing more focused learning schemes of critical (more variable) process parts.
A major future challenge is the implementation of “platform HNNs”. Platform HNNs should bear the capacity to learn from experience across different molecules and/or therapies. For platform models, a multiscale vision is needed, which links the molecular properties of the target biologic, the host cell biology, and the macroscopic scale of the production equipment. HNN modeling is, in principle, a strong candidate for addressing such complex modeling problems.
5.5. Downstream Processing
The present literature review shows that most applications of HNN models are found in upstream operation steps, with just a few in downstream operation steps. This could be explained by the availability of well-established mechanistic models of many downstream unit operations, which are generally less complex than bioreaction unit operations. However, many critical process parameters, such as mass and energy transfer coefficients, are directly linked with material properties at the molecular level, which are difficult to model in the continuum mechanics macroscopic world. Deep ANNs could be a valuable tool to deploy microphysics-informed transport flux representations applicable to continuum mechanics [122]. There is thus significant potential in applying HNNs for filtration, adsorption, chromatography, membrane separation, lyophilization, supercritical CO2 extraction, crystallization, and many more downstream unit operations.
A deep hybrid modeling approach based on time series transformers (TST) has been developed and showcased with a crystallization process [123,124,125]. Time series transformers consist of multiple encoder/decoder blocks that include multi-head attention and an FFNN. A k-dimensional process state tensor, with present and past observations, forms the input to the model. The output is a v-dimensional state tensor for predicting the future process state [123,124]. The authors concluded that there is an improvement in accuracy and interpretability of a TST-based hybrid framework compared to DNNs in a crystallization process. The authors also showed that the TST model has a powerful transfer learning capability. They trained a TST model (CrystalGPT) with a dataset from different crystallizers operating under various scenarios, showing a superior transfer learning than state-of-the-art LSTMs. By coupling the CrystalGPT with a model predictive controller, they reduced the variance in setpoint tracking to 1% [125].
In the case of chromatography processes, Narayanan et al. noted that the lack of accurate knowledge of adsorption isotherms and mass transfer kinetics may limit the applicability of mechanistic modeling [68]. The authors compared a hybrid semiparametric model (ANNs + material balance equations) with the lumped kinetic model approach in a chromatography process of industrial relevance. Both methods were compared using an in silico-generated dataset and an experimental dataset. The authors concluded that the HNN had two- to threefold lower prediction error than the mechanistic model. Learning complex adsorption isotherms from breakthrough data has been successfully achieved using the proposed HNN approach [93,126].
Subraveti et al. recently applied the concept of PINNs to model chromatography steps [127]. The authors concluded that PINNs can effectively predict elution curves in complex nonlinear, binary chromatography, with minimal data requirements. Specifically, no isotherm information was required to train the models [127]. PINNs are likely to take a prominent role in the scaleup of many downstream steps in the near future. Process scaleup is nontrivial in many downstream steps (e.g., Bourlès et al. [128]). Smyth et al. emphasized the difficulties in collecting informative datasets in production facilities due to regulatory constraints [129]. Lab- or pilot-scale data are more easily accessible but not necessarily representative of the production scale. Building computational fluid dynamics models based on PINNs could greatly facilitate the scaleup of such downstream unit operations.
As for upstream steps, HNNs are being considered for the development of digital twins of downstream unit operations. Krippl et al. applied an HNN model to predict the flux evolution and duration in crossflow ultrafiltration processes for various proteins, membrane types, input parameters, and filtration modes [67]. The prediction accuracy of the HNN was shown to be higher than the mechanistic film theory model. The authors concluded that this HNN could be used as a high-fidelity digital twin with the ability to predict the physical process under varying input parameters and different operation modes [67].
6. Conclusions
In this paper, a systematic literature review on the application of HNN models to biological processes was presented using the PRISMA method, which shows a structured vision of the research developed on the subject. Statistical analysis regarding the number of articles, subject area of interest, and keyword occurrence in the last 30 years was performed. HNN modeling covers a wide range of microbial, animal cell, mixed microbial, and enzyme biocatalysis in different industries such as wastewater treatment, clean energy, biopolymers, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing. HNN models have mainly been applied for process analysis, process monitoring, open- and closed-loop control, batch-to-batch control, model predictive control, intensified design of experiments, and quality by design. Some recent “hot” topics such as big data, deep learning, Industry 4.0, and digital twins are major drivers of HNN applications, mainly in the biopharma sector. These topics will likely drive hybrid models to incorporate DNNs, deep learning methods, and systems biology models in the near future. The majority of HNN studies followed the semiparametric design approach where physical laws are directly incorporated in the model structure. Recently, the PINN framework has been proposed, which maps physical laws to the ANN structure during the training process. Both approaches will likely merge in a common framework whereby both methods are used simultaneously to incorporate prior knowledge in ANN models. A significant research gap is the application of HNNs to downstream operations. Some recent publications have addressed crystallization, membrane and chromatographic processes. There is significant potential for research in applying hybrid models to filtration, adsorption, chromatography, membrane separation, lyophilization, and many more. Closing this gap will likely enable HNNs to evolve towards plantwide digitalization platforms integrating multiple up- and downstream operations as the next big step in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation9100922/s1, Supplementary File S1: Systematic literature review method description and study limitations; Figure S1: PRISMA flow diagram summarizes the selection of the articles based on the algorithm; Figure S2: Subject areas of interest over the years based on the Scopus analytical reports; Figure S3: Author’s keywords occurrence analysis by year overlay visualization; Figure S4: All Keywords (author’s keywords and indexed keywords) Occurrence Over the Years; Figure S5: All keywords occurrence from 1992 until 2000 by year overlay visualization; Figure S6: All keywords occurrence from 2001 until 2010 by year overlay visualization; Figure S7: All keywords occurrence from 2011 until September 2023 by year overlay visualization; Table S1: Specifications of the first ten document sources that have published the highest number of articles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, investigation, visualization, resources, and writing—original draft preparation, R.A.; writing—review and editing, R.A., J.R.C.R. and R.O.; supervision, J.M.M. and R.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Associate Laboratory for Green Chemistry—LAQV, which is financed by national funds from FCT/MCTES (UIDB/50006/2020 and UIDP/50006/2020). This work received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement no. 101099487—BioLaMer-HORIZON-EIC-2022-PATHFINDEROPEN-01 (BioLaMer).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available as Supplementary Materials and openly available as “Mendeley Data” at https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/zmj5gkxbyf/1 (accessed on 20 September 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| Hybrid neural network | (HNN) |
| Genome-scale model | (GEM) |
| Monoclonal antibody | (mAb) |
| Design of experiments | (DOE) |
| Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses | (PRISMA) |
| Radial basis function network | (RBFN) |
| Nonlinear programming | (NLP) |
| Chinese hamster ovary | (CHO) |
| Proportional–integral–derivative controller | (PID controller) |
| Process analytical technology | (PAT) |
| Chemical oxygen demand | (COD) |
| Artificial neural network | (ANN) |
| Genetic algorithm | (GA) |
| Feedforward neural network | (FFNN) |
| Activated sludge model | (ASM) |
| Convolutional neural network | (CNN) |
| Long short-term memory neural network | (LSTM) |
| Particle swarm optimization | (PSO) |
| Nonlinear autoregressive exogenous | (NARX) |
| Backpropagation neural network | (BP-NN) |
| Quality by design | (QbD) |
| Poly(3-hydroxy alkanoates) | (PHA) |
| Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate | (PHB) |
| Adaptive moment estimation method | (ADAM) |
| Rectified linear unit | (ReLU) |
| Hyperbolic tangent | (tanh) |
| Physics-informed neural network | (PINN) |
| Universal differential equation | (UDE) |
| Biologically informed neural network | (BINN) |
| Time series transformers | (TST) |
References
- Noll, P.; Henkel, M. History and Evolution of Modeling in Biotechnology: Modeling & Simulation, Application and Hardware Performance. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 3309–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooney, C.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, D.I.C. Computer-aided Material Balancing for Prediction of Fermentation Parameters. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1977, 19, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udugama, I.; Öner, M.; Lopez, P.C.; Beenfeldt, C.; Bayer, C.; Huusom, J.K.; Gernaey, K.V.; Sin, G. Towards Digitalization in Bio-Manufacturing Operations: A Survey on Application of Big Data and Digital Twin Concepts in Denmark. Front. Chem. Eng. 2021, 3, 727152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-T.; Kristiani, E.; Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S. Big Data and Machine Learning Driven Bioprocessing—Recent Trends and Critical Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 372, 128625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helleckes, L.M.; Hemmerich, J.; Wiechert, W.; von Lieres, E.; Grünberger, A. Machine Learning in Bioprocess Development: From Promise to Practice. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowbray, M.; Vallerio, M.; Perez-Galvan, C.; Zhang, D.; Del Rio Chanona, A.; Navarro-Brull, F.J. Industrial Data Science—A Review of Machine Learning Applications for Chemical and Process Industries. React. Chem. Eng. 2022, 7, 1471–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowbray, M.; Savage, T.; Wu, C.; Song, Z.; Cho, B.A.; Del Rio-Chanona, E.A.; Zhang, D. Machine Learning for Biochemical Engineering: A Review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 172, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Kor, M.; Yitmen, I.; Alizadehsalehi, S. An Investigation for Integration of Deep Learning and Digital Twins towards Construction 4.0. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2023, 12, 461–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejani, M.M.; Ghatee, M. A Systematic Review on Overfitting Control in Shallow and Deep Neural Networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 6391–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psichogios, D.C.; Ungar, L.H. A Hybrid Neural Network-first Principles Approach to Process Modeling. AIChE J. 1992, 38, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.L.; Kramer, M.A. Modeling Chemical Processes Using Prior Knowledge and Neural Networks. AIChE J. 1994, 40, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, J.; Simutis, R.; Dors, M.; Havlík, I.; Lübbert, A. Hybrid Modelling of Yeast Production Processes—Combination of a Priori Knowledge on Different Levels of Sophistication. Chem. Eng. Technol. 1994, 17, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, J.; SIMUTIS, R.; Dors, M.; Havlik, I.; Lübbert, A.; LUBBERT, A.; Lübbert, A.; LUBBERT, A. Bioprocess Optimization and Control: Application of Hybrid Modelling. J. Biotechnol. 1994, 35, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrovouniotis, M.L.; Chang, S. Hierarchical Neural Networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1992, 16, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, H.P.N.; Mokhtarian, H.; Jafarian, H.; Dimassi, S.; Bakrani-Balani, S.; Hamedi, A.; Coatanéa, E.; Gary Wang, G.; Haapala, K.R. Knowledge-Based Design of Artificial Neural Network Topology for Additive Manufacturing Process Modeling: A New Approach and Case Study for Fused Deposition Modeling. J. Mech. Des. 2019, 141, 021705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R. Combining First Principles Modelling and Artificial Neural Networks: A General Framework. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2004, 28, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.T.Q.; Rubanova, Y.; Bettencourt, J.; Duvenaud, D. Neural Ordinary Differential Equations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07366. [Google Scholar]
- Rackauckas, C.; Ma, Y.; Martensen, J.; Warner, C.; Zubov, K.; Supekar, R.; Skinner, D.; Ramadhan, A.; Edelman, A. Universal Differential Equations for Scientific Machine Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.04385. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, M.; Grandjean, B.P.A.; Lessard, P.; Thibault, J. Dynamic Modelling of the Activated Sludge Process: Improving Prediction Using Neural Networks. Water Res. 1995, 29, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piron, E.; Latrille, E.; René, F. Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Crossflow Microfiltration Modelling: “Black-Box” and Semi-Physical Approaches. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1997, 21, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, J.; Oliveira, R.; Feyo De Azevedo, S. Knowledge Based Modular Networks for Process Modelling and Control. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2001, 25, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, R.; Wuthrich, M.V. Smoothness and Monotonicity Constraints for Neural Networks Using ICEnet. SSRN Electron. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, M.; Weber, T.; Gretton, A.; Mohamed, S. A Case for New Neural Network Smoothness Constraints. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 137, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-Informed Neural Networks: A Deep Learning Framework for Solving Forward and Inverse Problems Involving Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Karniadakis, G.E. NSFnets (Navier-Stokes Flow Nets): Physics-Informed Neural Networks for the Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2021, 426, 109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stosch, M.; Oliveira, R.; Peres, J.; Feyo De Azevedo, S. A Novel Identification Method for Hybrid (N)PLS Dynamical Systems with Application to Bioprocesses. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 10862–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; de Azevedo, C.R.; Oliveira, R.; von Stosch, M. A Bootstrap-Aggregated Hybrid Semi-Parametric Modeling Framework for Bioprocess Development. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Mestre, M.; Ramos, J.; Costa, R.S.; Striedner, G.; Oliveira, R. A General Deep Hybrid Model for Bioreactor Systems: Combining First Principles with Deep Neural Networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 165, 107952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.P.; Carinhas, N.; Dias, J.M.L.; Cruz, P.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Oliveira, R. Hybrid Semi-Parametric Mathematical Systems: Bridging the Gap between Systems Biology and Process Engineering. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 132, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Costa, R.S.; Alexandre, L.; Ramos, J.; Oliveira, R. SBML2HYB: A Python Interface for SBML Compatible Hybrid Modeling. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Ramos, J.R.C.; Costa, R.S.; Oliveira, R. A General Hybrid Modeling Framework for Systems Biology Applications: Combining Mechanistic Knowledge with Deep Neural Networks under the SBML Standard. AI 2023, 4, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 105906. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Guidelines and Guidance Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangi, M.S.F.; Kao, K.; Kwon, J.S. Il Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Hybrid Modeling of Lab-Scale Batch Fermentation for β-Carotene Production Using Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 179, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkelbach, K.; Schweidtmann, A.M.; Müller, Y.; Schwoebel, P.; Mhamdi, A.; Mitsos, A.; Schuppert, A.; Mrziglod, T.; Schneckener, S. HybridML: Open Source Platform for Hybrid Modeling. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 160, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Sheriff, M.Z.; Bangi, M.S.F.; Kravaris, C.; Kwon, J.S.-I.; Botre, C.; Hirota, J. Deep Neural Network-Based Hybrid Modeling and Experimental Validation for an Industry-Scale Fermentation Process: Identification of Time-Varying Dependencies among Parameters. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 441, 135643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Guo, Z.; Shen, Y.; Yu, K.; Gao, X. Knowledge and Data-Driven Hybrid System for Modeling Fuzzy Wastewater Treatment Process. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 7185–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stosch, M.; Oliveira, R.; Peres, J.; Feyo de Azevedo, S. Hybrid Semi-Parametric Modeling in Process Systems Engineering: Past, Present and Future. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2014, 60, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Jeon, C.O.; Park, J.M.; Chang, K.S. Hybrid Neural Network Modeling of a Full-Scale Industrial Wastewater Treatment Process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 78, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Li, D.; Cheng, C.; Lü, Z.-A.; Shen, Y. Simulation of Biomass Gasification with a Hybrid Neural Network Model. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, X. Optimization for High-Density Cultivation of Heterotrophic Chlorella Based on a Hybrid Neural Network Model. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 44, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.P.; Alves, C.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Oliveira, R. Hybrid Elementary Flux Analysis/Nonparametric Modeling: Application for Bioprocess Control. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preusting, H.; Noordover, J.; Simutis, R.; Lübbert, A. The Use of Hybrid Modelling for the Optimization of the Penicillin Fermentation Process. Chimia 1996, 50, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.C.; Alves, T.L.M.; Henriques, A.W.S.; Maciel Filho, R.; Lima, E.L. An Adaptive Optimal Control Scheme Based on Hybrid Neural Modelling. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1998, 22, S859–S862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.C.; Henriques, A.S.W.; Alves, T.L.M.; Maciel Filho, R.; Lima, E.L. Hybrid Neural Model for the Optimization of Fed-Batch Fermentations. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 1999, 16, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, L.H.P.; Da Costa, A.C.; Maciel Filho, R. Hybrid Neural Modeling of Bioprocesses Using Functional Link Networks. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. Part A Enzym. Eng. Biotechnol. 2002, 98–100, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meleiro, L.A.C.; Maciel Filho, R. State and Parameter Estimation Based on a Nonlinear Filter Applied to an Industrial Process Control of Ethanol Production. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2000, 17, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, A.W.D.; Da Costa, A.C.C.; Alves, T.L.M.L.M.; Lima, E.L.L.; Da Silva Henriques, A.W.; Da Costa, A.C.C.; Alves, T.L.M.L.M.; Lima, E.L.L.; Henriques, A.W.D.; Da Costa, A.C.C.; et al. A Hybrid Neural Model of Ethanol Production by Zymomonas Mobilis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1999, 77–79, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Simutis, R.; De Azevedo, S.F.; Lübbert, A. Hybnet, an Advanced Tool for Process Optimization and Control. IFAC Proc. 1998, 331, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simutis, R.; Oliveira, R.; Manikowski, M.; De Azevedo, S.F.; Lübbert, A. How to Increase the Performance of Models for Process Optimization and Control. J. Biotechnol. 1997, 59, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Pereira, A.; Pinheiro, Á.D.T.; Rocha, M.V.P.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Cartaxo, S.J.M. Hybrid Neural Network Modeling and Particle Swarm Optimization for Improved Ethanol Production from Cashew Apple Juice. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.R.; Dias, J.M.L.; Von Stosch, M.; Clemente, J.; Cunha, A.E.; Oliveira, R. Fast Development of Pichia Pastoris GS115 Mut+ Cultures Employing Batch-to-Batch Control and Hybrid Semi-Parametric Modeling. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.P.; Clemente, J.J.; Cunha, A.E.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Oliveira, R. Bioprocess Iterative Batch-to-Batch Optimization Based on Hybrid Parametric/Nonparametric Models. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Stosch, M.; Willis, M.J. Intensified Design of Experiments for Upstream Bioreactors. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Stosch, M.; Hamelink, J.-M.; Oliveira, R. Toward Intensifying Design of Experiments in Upstream Bioprocess Development: An Industrial Escherichia Coli Feasibility Study. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, B.; von Stosch, M.; Striedner, G.; Duerkop, M. Comparison of Modeling Methods for DoE-Based Holistic Upstream Process Characterization. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e1900551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, B.; Pohlodek, J.; Matschek, J.; Savchenko, A.; Carius, L.; Findeisen, R. Towards Risk-Aware Machine Learning Supported Model Predictive Control and Open-Loop Optimization for Repetitive Processes. IFAC Pap. 2021, 54, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; Koller, M.; Braunegg, G.; Horvat, P. Mathematical Modelling as a Tool for Optimized PHA Production. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2015, 29, 183–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P.R. Design Considerations in Hybrid Neural Optimization of Fed-Batch Fermentation for PHB Production by Ralstonia Eutropha. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, J.; Oliveira, R.; Serafim, L.S.; Lemos, P.; Reis, M.A.; Feyo de Azevedo, S. Hybrid Modelling of a PHA Production Process Using Modular Neural Networks. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2004, 18, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, J.; Oliveira, R.; de Azevedo, S.F. Bioprocess Hybrid Parametric/Nonparametric Modelling Based on the Concept of Mixture of Experts. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P.R. Neural and Hybrid Optimizations of the Fed-Batch Synthesis of Poly-β-Hydroxybutyrate by Ralstonia Eutropha in a Nonideal Bioreactor. Bioremediat. J. 2008, 12, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, M.F.; Ochsner, A.M.; Amstutz, V.; von Blarer, D.; Sokolov, M.; Arosio, P.; Zinn, M. Modeling of Continuous PHA Production by a Hybrid Approach Based on First Principles and Machine Learning. Processes 2021, 9, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, B.; Striedner, G.; Duerkop, M. Hybrid Modeling and Intensified DoE: An Approach to Accelerate Upstream Process Characterization. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 2000121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krippl, M.; Dürauer, A.; Duerkop, M. Hybrid Modeling of Cross-Flow Filtration: Predicting the Flux Evolution and Duration of Ultrafiltration Processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, H.; Behle, L.; Luna, M.F.; Sokolov, M.; Guillén-Gosálbez, G.; Morbidelli, M.; Butté, A. Hybrid-EKF: Hybrid Model Coupled with Extended Kalman Filter for Real-Time Monitoring and Control of Mammalian Cell Culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirrung, S.M.; van der Wielen, L.A.M.; van Beckhoven, R.F.W.C.; van de Sandt, E.J.A.X.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Ottens, M. Optimization of Biopharmaceutical Downstream Processes Supported by Mechanistic Models and Artificial Neural Networks. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stosch, M.; Davy, S.; Francois, K.; Galvanauskas, V.; Hamelink, J.-M.; Luebbert, A.; Mayer, M.; Oliveira, R.; O’Kennedy, R.; Rice, P.; et al. Hybrid Modeling for Quality by Design and PAT-Benefits and Challenges of Applications in Biopharmaceutical Industry. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stosch, M.; Hamelink, J.-M.; Oliveira, R. Hybrid Modeling as a QbD/PAT Tool in Process Development: An Industrial E. coli Case Study. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dors, M.; Simutis, R.; Lübbert, A. Advanced Supervision of Mammalian Cell Cultures Using Hybrid Process Models. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1995, 28, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.-C.; Barford, J.P. A Hybrid Neural Network—First Principles Approach for Modelling of Cell Metabolism. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1996, 20, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; Cunha, A.E.; Clemente, J.J.; Moreira, J.L.; Cruz, H.J.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Oliveira, R. Modelling and Optimization of a Recombinant BHK-21 Cultivation Process Using Hybrid Grey-Box Systems. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 118, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maton, M.; Bogaerts, P.; Vande Wouwer, A. Hybrid Dynamic Models of Bioprocesses Based on Elementary Flux Modes and Multilayer Perceptrons. Processes 2022, 10, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aehle, M.; Simutis, R.; Lübbert, A. Comparison of Viable Cell Concentration Estimation Methods for a Mammalian Cell Cultivation Process. Cytotechnology 2010, 62, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Narayanan, H.; Luna, M.F.; von Stosch, M.; Cruz Bournazou, M.N.; Polotti, G.; Morbidelli, M.; Butté, A.; Sokolov, M. Bioprocessing in the Digital Age: The Role of Process Models. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e1900172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotidis, P.; Kontoravdi, C. Harnessing the Potential of Artificial Neural Networks for Predicting Protein Glycosylation. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2020, 10, e00131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, B.; Duerkop, M.; Striedner, G.; Sissolak, B. Model Transferability and Reduced Experimental Burden in Cell Culture Process Development Facilitated by Hybrid Modeling and Intensified Design of Experiments. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 740215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hao, O.J.; McAvoy, T.J.; Chang, C.-H. Modeling Nutrient Dynamics in Sequencing Batch Reactor. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.S.; McAvoy, T.J.; Hao, O.J. Use of Hybrid Models in Wastewater Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Dai, L.-K. Prediction Method for Wastewater COD Based on Hybrid Neural Network Model. Zhongguo Jishui Paishui/China Water Wastewater 2003, 19, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Azwar; Hussain, M.A.; Ramachandran, K.B. The Study of Neural Network-Based Controller for Controlling Dissolved Oxygen Concentration in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 28, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres, J.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.; Feyo de Azevedo, S.; Oliveira, R. Hybrid Modular Mechanistic/ANN Modelling of a Wastewater Phosphorus Removal Process. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2006, 21, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, C.; Ju, B.; Xu, H.; Sun, D.; Dang, Y. Estimation of In-Situ Biogas Upgrading in Microbial Electrolysis Cells via Direct Electron Transfer: Two-Stage Machine Learning Modeling Based on a NARX-BP Hybrid Neural Network. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Can, H.J.L.; Te Braake, H.A.B.; Bijman, A.; Hellinga, C.; Luyben, K.C.A.M.; Heijnen, J.J. An Efficient Model Development Strategy for Bioprocesses Based on Neural Networks in Macroscopic Balances: Part II. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 62, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Can, H.J.L.; Te Braake, H.A.B.; Dubbclman, S.; Hellinga, C.; Luyben, K.C.A.; Heijnen, J.J. Understanding and Applying the Extrapolation Properties of Serial Gray-Box Models. AIChE J. 1998, 44, 1071–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A.; Costa Neto, E.H.; Adriano, W.S.; Ferreira, A.L.O.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. Use of Neural Networks in the Mathematical Modelling of the Enzymic Synthesis of Amoxicillin Catalysed by Penicillin G Acylase Immobilized in Chitosan. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.C.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Oliveira, R.; Velizarov, S.; Crespo, J.G. Analysis of Solvent Flux through Nanofiltration Membranes by Mechanistic, Chemometric and Hybrid Modelling. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 300, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Ruzich, N.; Zendehboudi, S.; Rahbari, M. Biomass Leachate Treatment and Nutrient Recovery Using Reverse Osmosis: Experimental Study and Hybrid Artificial Neural Network Modeling. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 7155–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrath, D.; Messac, A.; Bequette, B.W.; Cramer, S.M. A Hybrid Model Framework for the Optimization of Preparative Chromatographic Processes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Briskot, T.; Hahn, T.; Baumann, P.; Hubbuch, J. Root Cause Investigation of Deviations in Protein Chromatography Based on Mechanistic Models and Artificial Neural Networks. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1515, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, H.; Seidler, T.; Luna, M.F.; Sokolov, M.; Morbidelli, M.; Butté, A. Hybrid Models for the Simulation and Prediction of Chromatographic Processes for Protein Capture. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1650, 462248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, J.; Ramos, J.R.C.; Costa, R.S.; Rossell, S.; Dumas, P.; Oliveira, R. Hybrid Deep Modeling of a CHO-K1 Fed-Batch Process: Combining First-Principles with Deep Neural Networks. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1237963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadriraju, B.; Bangi, M.S.F.; Narasingam, A.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Operable Adaptive Sparse Identification of Systems: Application to Chemical Processes. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangi, M.S.F.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Deep Hybrid Model-Based Predictive Control with Guarantees on Domain of Applicability. AIChE J. 2023, 69, e18012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Choi, H.-K.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Achieving Optimal Paper Properties: A Layered Multiscale KMC and LSTM-ANN-Based Control Approach for Kraft Pulping. Processes 2023, 11, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Sheriff, M.Z.; Bangi, M.S.F.; Kravaris, C.; Kwon, J.S.-I.; Botre, C.; Hirota, J. Multi-Rate Observer Design and Optimal Control to Maximize Productivity of an Industry-Scale Fermentation Process. AIChE J. 2023, 69, e17946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Systems Biology: A Brief Overview. Science 2002, 295, 1662–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, G.; Vijayakumar, S.; Yaneske, E.; Angione, C. Machine and Deep Learning Meet Genome-Scale Metabolic Modeling. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Berry, C.; Ghosh, P.; Fong, S.S. Recent Advances on Constraint-Based Models by Integrating Machine Learning. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 64, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; You, Q.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, L.; Lu, H.; Chen, Q. Advances and Applications of Machine Learning and Intelligent Optimization Algorithms in Genome-Scale Metabolic Network Models. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanufacturing 2023, 3, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.R.C.; Oliveira, G.P.; Dumas, P.; Oliveira, R. Genome-Scale Modeling of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells by Hybrid Semi-Parametric Flux Balance Analysis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, L.; Mollet, B.; Liebermeister, W.; Faulon, J.-L. A Neural-Mechanistic Hybrid Approach Improving the Predictive Power of Genome-Scale Metabolic Models. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Jayaraman, A.; Kwon, J.S.I. Identification of Cell-to-Cell Heterogeneity through Systems Engineering Approaches. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Jayaraman, A.; Kwon, J.S. Development of a Hybrid Model for a Partially Known Intracellular Signaling Pathway through Correction Term Estimation and Neural Network Modeling. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Jagtap, A.D.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for High-Speed Flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 360, 112789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karniadakis, G.E.; Kevrekidis, I.G.; Lu, L.; Perdikaris, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, L. Physics-Informed Machine Learning. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 422–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, B. Hybrid Modeling in Bioprocess Dynamics: Structural Variabilities, Implementation Strategies, and Practical Challenges. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2023, 120, 2072–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, C.; Feng, Y.; Su, H.; Zhu, J. Physics-Informed Machine Learning: A Survey on Problems, Methods and Applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.08064. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.; Bertalan, T.S.; Ndahiro, N.; Khare, P.; Betenbaugh, M.; Maranas, C.; Kevrekidis, I.G. Data-Driven and Physics Informed Modelling of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Bioreactors. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.03257. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, A.W.; Cardenas, I.O.S.; Del Rio-Chanona, E.A.; Zhang, D. Investigating Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Bioprocess Hybrid Model Construction. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2023, 52, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, J.H.; Nardini, J.T.; Baker, R.E.; Simpson, M.J.; Flores, K.B. Biologically-Informed Neural Networks Guide Mechanistic Modeling from Sparse Experimental Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandenius, C.-F.; Gustavsson, R. Mini-Review: Soft Sensors as Means for PAT in the Manufacture of Bio-Therapeutics. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.P.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, P.M.; Carrondo, M.J.T. Advances in On-Line Monitoring and Control of Mammalian Cell Cultures: Supporting the PAT Initiative. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Stosch, M.; Oliveria, R.; Peres, J.; De Azevedo, S.F. Hybrid Modeling Framework for Process Analytical Technology: Application to Bordetella Pertussis Cultures. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargalo, C.L.; Udugama, I.; Pontius, K.; Lopez, P.C.; Nielsen, R.F.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Mansouri, S.S.; Bayer, C.; Junicke, H.; Gernaey, K.V. Towards Smart Biomanufacturing: A Perspective on Recent Developments in Industrial Measurement and Monitoring Technologies for Bio-Based Production Processes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 47, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Stosch, M.; Schenkendorf, R.; Geldhof, G.; Varsakelis, C.; Mariti, M.; Dessoy, S.; Vandercammen, A.; Pysik, A.; Sanders, M. Working within the Design Space: Do Our Static Process Characterization Methods Suffice? Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansana, J.; Joswiak, M.N.; Castillo, I.; Wang, Z.; Rendall, R.; Chiang, L.H.; Reis, M.S. Recent Trends on Hybrid Modeling for Industry 4.0. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2021, 151, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Thunéll, S.; Lindberg, U.; Jiang, L.L.; Trygg, J.; Tysklind, M.; Souihi, N.; Thunell, S.; Lindberg, U.; Jiang, L.L.; et al. A Machine Learning Framework to Improve Effluent Quality Control in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Savage, T.R.T.R.; Cho, B.A.B.A. Combining Model Structure Identification and Hybrid Modelling for Photo-Production Process Predictive Simulation and Optimisation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 3356–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniati, F.; Gregori, G. Learning Transport Processes with Machine Intelligence. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitapure, N.; Kwon, J.S. Introducing Hybrid Modeling with Time-Series-Transformers: A Comparative Study of Series and Parallel Approach in Batch Crystallization. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.05749. [Google Scholar]
- Sitapure, N.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Exploring the Potential of Time-Series Transformers for Process Modeling and Control in Chemical Systems: An Inevitable Paradigm Shift? Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 194, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitapure, N.; Kwon, J.S.-I. CrystalGPT: Enhancing System-to-System Transferability in Crystallization Prediction and Control Using Time-Series-Transformers. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 177, 108339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, H.; Luna, M.; Sokolov, M.; Arosio, P.; Butté, A.; Morbidelli, M. Hybrid Models Based on Machine Learning and an Increasing Degree of Process Knowledge: Application to Capture Chromatographic Step. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 10466–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subraveti, S.G.; Li, Z.; Prasad, V.; Rajendran, A. Can a Computer “Learn” Nonlinear Chromatography?: Experimental Validation of Physics-Based Deep Neural Networks for the Simulation of Chromatographic Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 5929–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlès, E.; de Lannoy, G.; Scutellà, B.; Fonseca, F.; Trelea, I.C.; Passot, S. Scale-up of Freeze-Drying Cycles, the Use of Process Analytical Technology (PAT), and Statistical Analysis; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 215–240. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, P.; de Lannoy, G.; Von Stosch, M.; Pysik, A.; Khan, A. Machine Learning in Research and Development of New Vaccines Products: Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the ESANN 2019—Proceedings, 27th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).