Flavor Characteristics of Navel Orange Wine Fermented by Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 and Angel Yeast SY
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strains and Materials
2.2. Vinification Process
2.3. Single-Factor Experimental Design for Co-Fermentation Conditions
2.4. Determination of Colony Count and Basic Physicochemical Indicators during the Fermentation Process
2.5. Chemical Analysis
2.5.1. Determination of Alcohol Content, Organic Acids and Amino Acids
2.5.2. Quantification of Volatile Compounds
2.6. Determination of Total Phenols, Total Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Electronic Nose and Electronic Eye Measurements of Fermented Navel Orange Wine
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Response Surface of Fermented Navel Orange Wine
3.2. Changes in Fundamental Indicators during the Fermentation Process
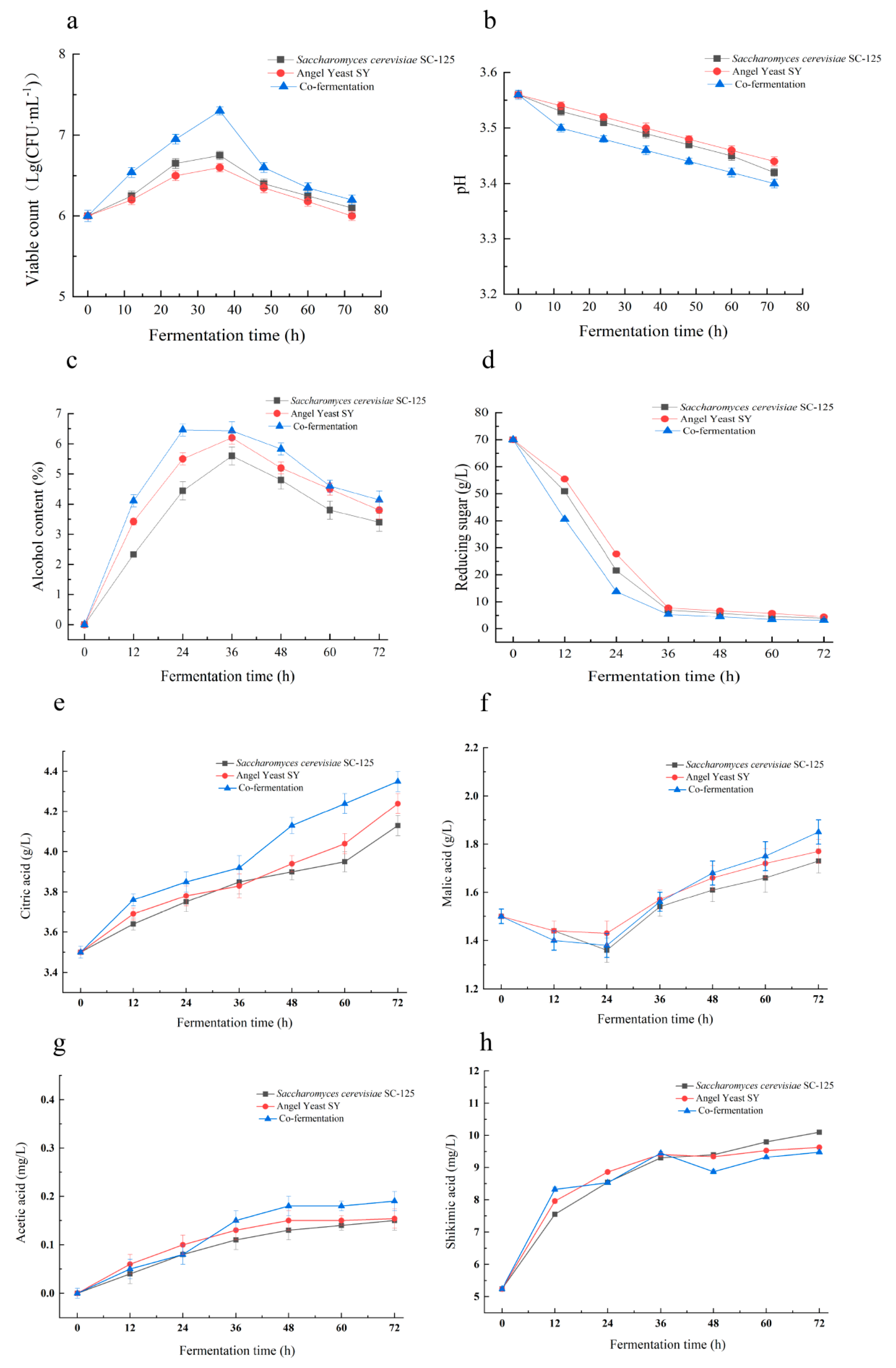
3.2.1. Changes in Microbial Colony Counts and pH during Fermentation
3.2.2. Changes in Alcohol Content and Reducing Sugars
3.2.3. Changes in Organic Acids
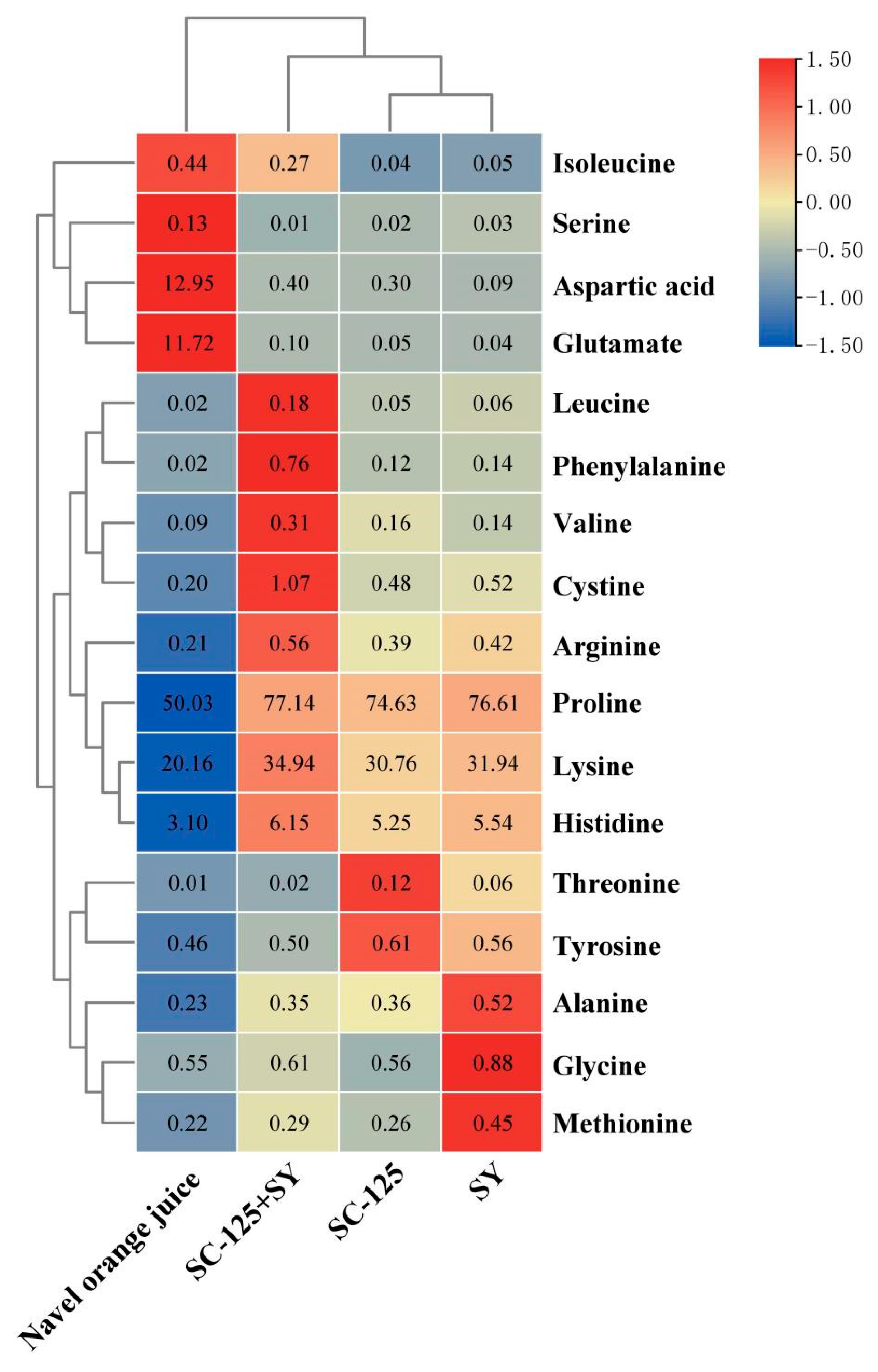
3.3. Changes in Amino Acids before and after Fermentation
3.4. Analysis of Volatile Compounds before and after Fermentation
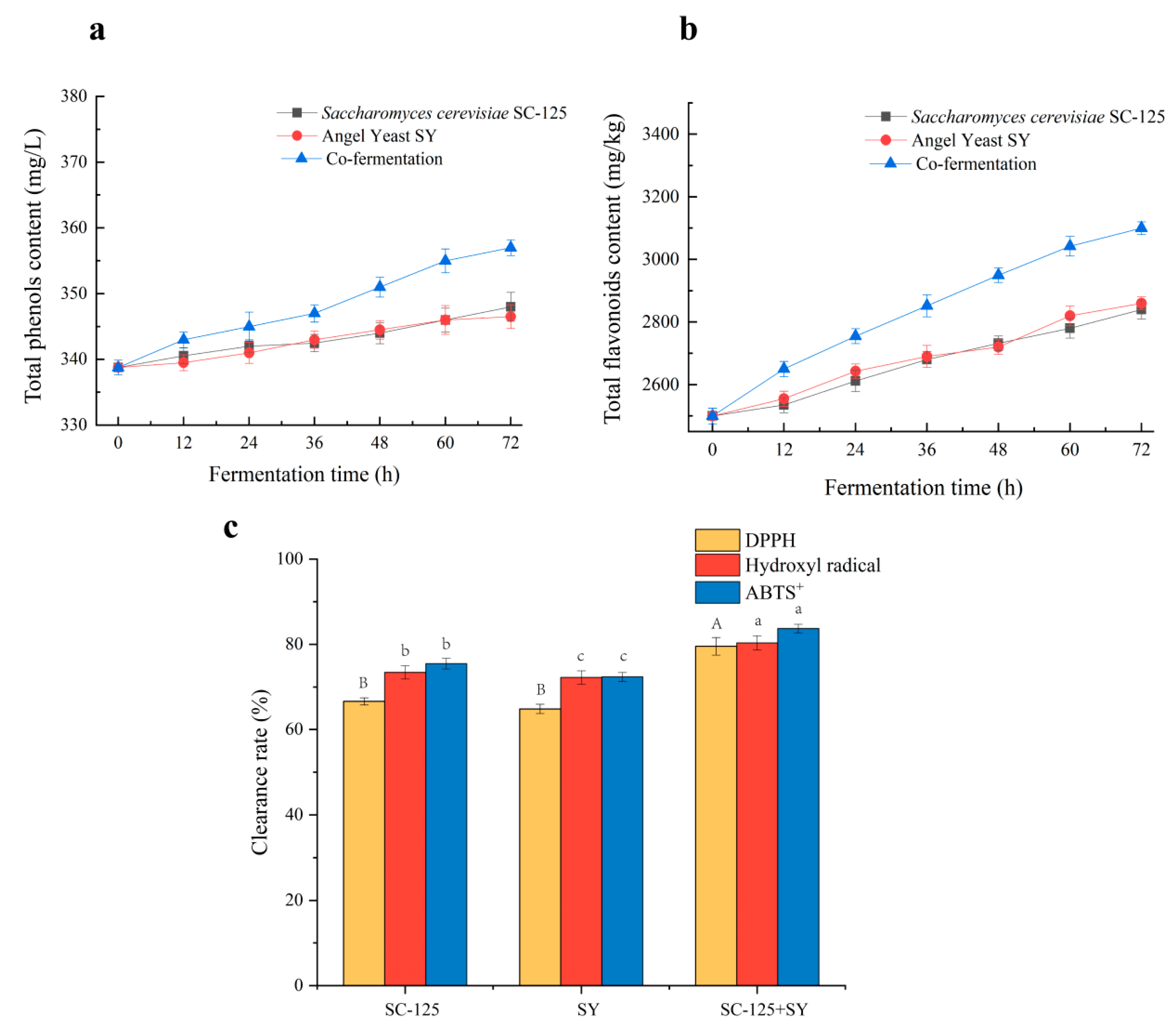
3.5. Changes in Total Phenols and Total Flavonoids and In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
3.6. Electronic Nose and Electronic Eye Results Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Kan, C.N.; Wan, C.P.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.Y. Quality and biochemical changes of navel orange fruits during storage as affected by cinnamaldehyde-chitosan coating. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 129, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Bi, P.F.; Sun, N.; Gao, Z.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Guo, J. Characterization of different non-Saccharomyces yeasts via mono-fermentation to produce polyphenol-enriched and fragrant kiwi wine. Food Microbiol. 2021, 103, 103867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.Z.; Liu, X.Z.; Li, X.; Sheng, X.F.; Li, T.T.; Tang, W.Y.; Yu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.M. Effect of Hanseniaspora uvarum-Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mixed Fermentation on Aroma Characteristics of Rosa roxburghii Tratt, Blueberry, and Plum Wines. Molecules 2022, 27, 8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rego, E.S.B.; Rosa, C.A.; Freire, A.L.; Machado, A.M.D.; Gomes, F.D.O.; da Costa, A.S.P.; Mendonca, M.D.; Hernandez-Macedod, M.L.; Padilha, F.F. Cashew wine and volatile compounds produced during fermentation by non-Saccharomyces and Saccharomyces yeast. LWT 2020, 126, 109291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Wang, S.X.; Ren, L.X.; Li, D.N.; Ma, X.; Rong, Y.Z. Flavour characteristics of rice wine fermented with mixed starter by moulds and yeast strains. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 5791–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.P.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.W.; Ju, H.M.; Niu, C.; Song, Z.H.; Yuan, Y.H.; Yue, T.L. Assessment of chemical composition and sensorial properties of ciders fermented with different non-Saccharomyces yeasts in pure and mixed fermentations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 318, 108471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.J.; Chen, X.D.; Lin, R.; Xu, T.; Xiong, D.K.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.F. Quality Improvement in Apple Ciders during Simultaneous Co-Fermentation through Triple Mixed-Cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia kudriavzevii, and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Foods 2023, 12, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.P.; Zhu, H.; Tong, L.T.; Zhou, S.M.; Yang, R.H.; Niu, M. Volatile profiles of fresh rice noodles fermented with pure and mixed cultures. FRI 2019, 119, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Gao, J.Y.; Wang, S.C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, C.H.; Lan, Y.B.; Sun, X.; Li, S.X. Synergetic application of E-tongue and E-eye based on deep learning to discrimination of Pu-erh tea storage time. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2021, 187, 106297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, W.; Luo, X.L.; Sun, D.F. Analysis of Volatile Flavor Substances in the Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Lanmaoa asiatica Mushroom and Its Maillard Reaction Products Based on E-Nose and GC-IMS. Foods 2022, 11, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, C.Y.; Zheng, M.X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, W.L.; Tang, J. The Use of γ-Aminobutyric Acid-Producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 for Functional Fermented Beverage Production from Apple Juice. Foods 2022, 11, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QB/T 5188-2017; Brewing Red Yeast. Light Industry Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Ministry of Light Industry and Information Technology of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Zhou, Y.H.; Guo, W.C.; Ji, T.K.; Du, R.Y. Low-cost and handheld detector on soluble solids content and firmness of kiwifruit. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T15038-2006; General Analytical Methods for Wine and Fruit Wine. National Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China. Available online: https://www.winesofchile.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/National_Standard_of_the_People_s_Republic_of_China_Wines.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2006).
- Chen, L.C.; Xiang, W.L.; Liang, X.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, J. Fungal Biomarkers in Traditional Starter Determine the Chemical Characteristics of Turbid Rice Wine from the Rim of the Sichuan Basin, China. Foods 2023, 12, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupak, M.; Kocourek, V.; Kolouchova, I.; Hajslova, J. Rapid approach for the determination of alcoholic strength and overall quality check of various spirit drinks and wines using GC–MS. Food Control 2017, 80, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.C.; Tian, Y.X. Analysis of the formation mechanism of volatile and non-volatile flavor substances in corn wine fermentation based on high-throughput sequencing and metabolomics. FRI 2023, 165, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 30987-2020; Determination of Free Amino Acids in Plants. State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Aslan, E.; Aksu, A.; Korkmaz, N.E.; Taskin, O.S.; Caglar, N.B. Monitoring the antioxidant activities by extracting the polyphenolic contents of algae collected from the Bosphorus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.F.; Benjakul, S.; Sanmartin, C.; Ying, X.G.; Ma, L.K.; Xiao, G.S.; Yu, J.; Liu, G.Q.; Deng, S.G. Changes of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) during Storage, as Evaluated by Headspace Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry and Principal Component Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewkod, T.; Bovonsombut, S.; Tragoolpua, Y. Efficacy of kombucha obtained from greenoolong, and black teas on inhibition of pathogenic bacteria, antioxidation, and toxicity on colorectal cancer cell line. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Hua, J.L.; Wang, C. Anti-oxidation and anti-aging activity of polysaccharide from Malus micromoles Makino fruit wine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 121, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.X.; Xiong, J.J.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.Y.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Yuan, H.B.; Lou, X.M. Rapid identification of adulteration in raw bovine milk with soymilk by electronic nose and headspace-gas chromatography ion-mobility spectrometry. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, J.J.; Ye, M.L.; Zhang, J.H. Effect of six lactic acid bacteria strains on physicochemical characteristics, antioxidant activities and sensory properties of fermented orange juices. Foods 2022, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras-Lopez, M.J.; Cerezo, A.B.; Escudero-Lopez, B.; Cerrillo, I.; Berna, G.; Martin, F.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C.; Fernandez-Pachon, M.S. Changes in orange juice (poly) phenol composition induced by controlled alcoholic fermentation. Foods 2016, 8, 8151–8164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Xu, K.D.; Cai, R.; Yue, T.L.; Yuan, Y.H.; Gao, Z.P. Construction of recombinant Fusan yeasts for the production of cider with low alcohol and enhanced aroma. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Jussier, D.; Terrade, N.; Yada, Y.R.; Orduña, D.M.R. Kinetics of sugars, organic acids and acetaldehyde during simultaneous yeast-bacterial fermentations of white wine at different pH values. FRI 2010, 44, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Bao, X.M.; Li, Y.W.; Jiao, C.L.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Zhang, W.X.; Liu, W.F.; Shen, Y. Cloning and characterization of heterologous transporters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and identification of important amino acids for xylose utilization. Metab. Eng. 2015, 30, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Pérez, A.; Romero-González, R.; Frenich, G.A. Application of an innovative metabolomics approach to discriminate geographical origin and processing of black pepper by untargeted UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS analysis and mid-level data fusion. FRI 2021, 150, 110722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.R.; Xing, X.; Chu, Q.; Sun, S.Y.; Wang, P. Impact of co-culture of Lactobacillus plantarum and Oenoc occusoeniat different ratios on malolactic fermentation, volatile and sensory characteristics of mulberry wine. LWT 2022, 169, 113995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Li, R.T.; Wu, X.X.; Liu, S.X.; Shi, L. UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS-based quantitative lipidomics reveals the chemical changes of phospholipids during thermal processing methods of Tan sheep meat. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguela, J.M.; Vernhet, A.; Julien-Ortiz, A.; Sieczkowski, N.; Mouret, J.-R. Effect of grape must polyphenols on yeast metabolism during alcoholic fermentation. FRI 2019, 121, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.S.; Ren, X.J.; Wei, L.W.; Cao, X.H. Yonghong Ge, He Liu, Jianrong Li. Collaborative analysis on difference of apple fruits flavour using electronic nose and electronic tongue. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 26, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Polo, C.; Javier Montero, J.; Gómez-Polo, M.; Casado, M.A. Comparison of the CIELab and CIEDE 2000 Color Difference Formulas on Gingival Color Space. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 29, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, S. Combined Use of Lachancea thermotolerans and Schizosaccharomyces pombe in wine making: A review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.3 | 9 | 0.033 | 29.62 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A | 2.00 × 10−4 | 1 | 2.00 × 10−4 | 0.18 | 0.6851 | |
| B | 1.80 × 10−3 | 1 | 1.80 × 10−3 | 1.61 | 0.2452 | |
| C | 8.00 × 10−4 | 1 | 8.00 × 10−4 | 0.72 | 0.4257 | |
| AB | 1.23 × 10−3 | 1 | 1.23 × 10−3 | 1.1 | 0.3301 | |
| AC | 2.25 × 10−4 | 1 | 2.25 × 10−4 | 0.2 | 0.6673 | |
| BC | 4.23 × 10−3 | 1 | 4.23 × 10−3 | 3.78 | 0.0931 | |
| A2 | 0.098 | 1 | 0.098 | 87.25 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 0.032 | 1 | 0.032 | 28.66 | 0.0011 | |
| C2 | 0.13 | 1 | 0.13 | 118.26 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual | 7.83 × 10−3 | 7 | 1.12 × 10−3 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 2.55 × 10−3 | 3 | 8.50 × 10−4 | 0.64 | 0.6262 | |
| Pure Error | 5.28 × 10−3 | 4 | 1.32 × 10−3 | |||
| Cor Total | 0.31 | 16 |
| Navel Orange Wine | L | a | b | h | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 | 74.63 | 4.40 | 40.29 | 83.77 | 24.09 |
| Angel Yeast SY | 73.68 | 7.88 | 41.01 | 79.12 | 41.76 |
| Co-fermentation | 75.34 | 4.13 | 44.88 | 84.75 | 25.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ye, H.; Zou, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, B.; Wang, S.; Peng, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, W.; et al. Flavor Characteristics of Navel Orange Wine Fermented by Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 and Angel Yeast SY. Fermentation 2023, 9, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100872
Zhang Y, Ye H, Zou Y, He Z, Xu B, Wang S, Peng C, Zhou X, Zhang Q, Xiang W, et al. Flavor Characteristics of Navel Orange Wine Fermented by Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 and Angel Yeast SY. Fermentation. 2023; 9(10):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100872
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yingyue, Hong Ye, Yuting Zou, Zihan He, Bitao Xu, Su Wang, Chuanning Peng, Xuerui Zhou, Qing Zhang, Wenliang Xiang, and et al. 2023. "Flavor Characteristics of Navel Orange Wine Fermented by Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 and Angel Yeast SY" Fermentation 9, no. 10: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100872
APA StyleZhang, Y., Ye, H., Zou, Y., He, Z., Xu, B., Wang, S., Peng, C., Zhou, X., Zhang, Q., Xiang, W., Cai, T., & Tang, J. (2023). Flavor Characteristics of Navel Orange Wine Fermented by Saccharomyces cerevisiae SC-125 and Angel Yeast SY. Fermentation, 9(10), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100872






