Robust Control Based on Modeling Error Compensation of Microalgae Anaerobic Digestion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AD of Microalgae
2.2. MAD Model
2.3. Robust Control Design Based on MEC
- A.
- For optimization and control purposes of AD processes, usually in practice, only a relatively limited number of control actions are possible. These are mostly restricted to the input flow rate or the input of a particular substrate in the feed [19,20]. Therefore, this paper selects the dilution rate (directly related to the input flow rate) as the control input variable.
- B.
- The minimum and maximum control inputs are selected following previous studies on the operational behavior of the MAD model [30]. The maximum input flow rate must be chosen to prevent the washout condition.
3. Results
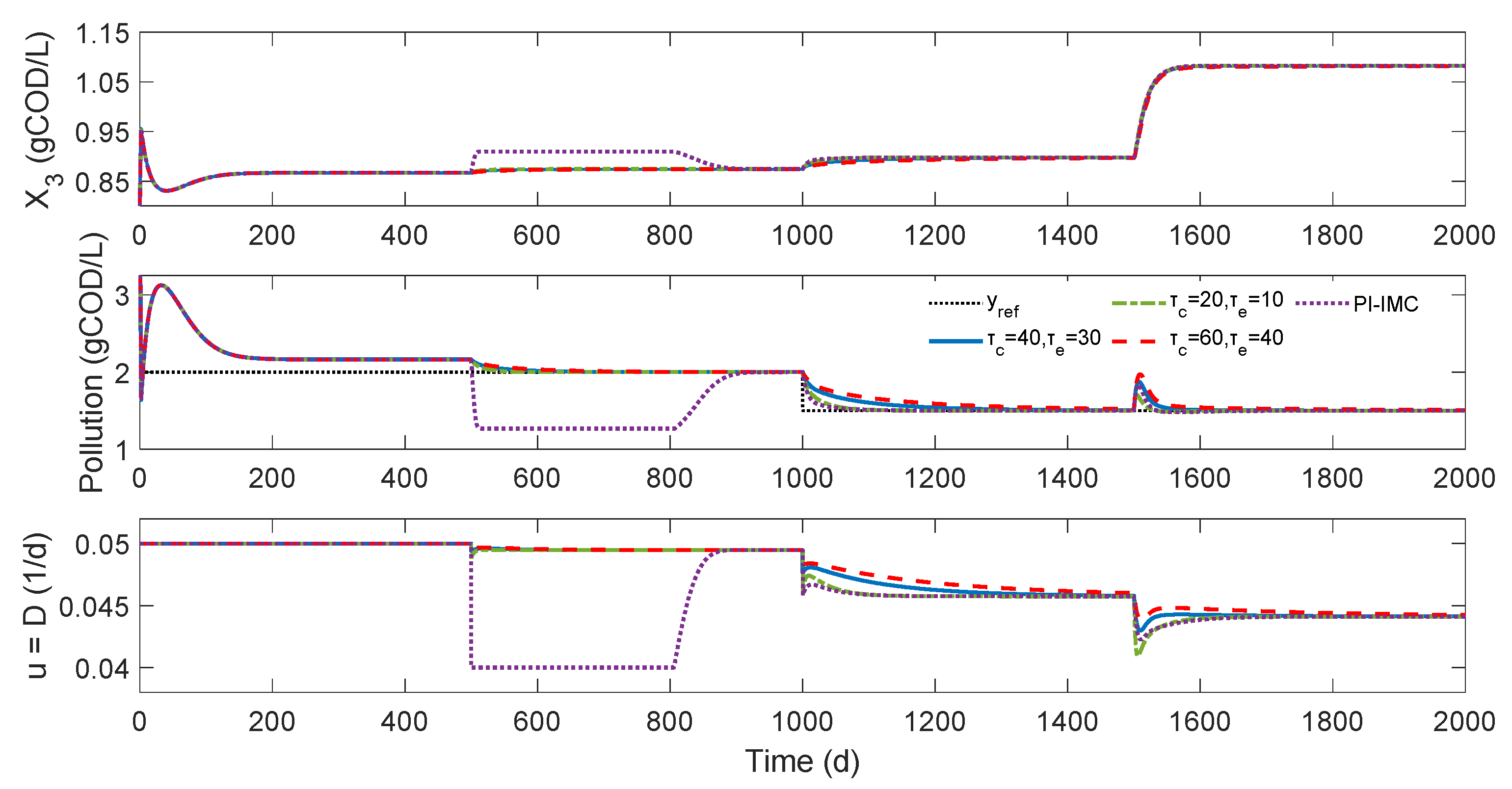
3.1. Control of the Organic Pollution Level
3.1.1. Control Problem
3.1.2. Numerical Results
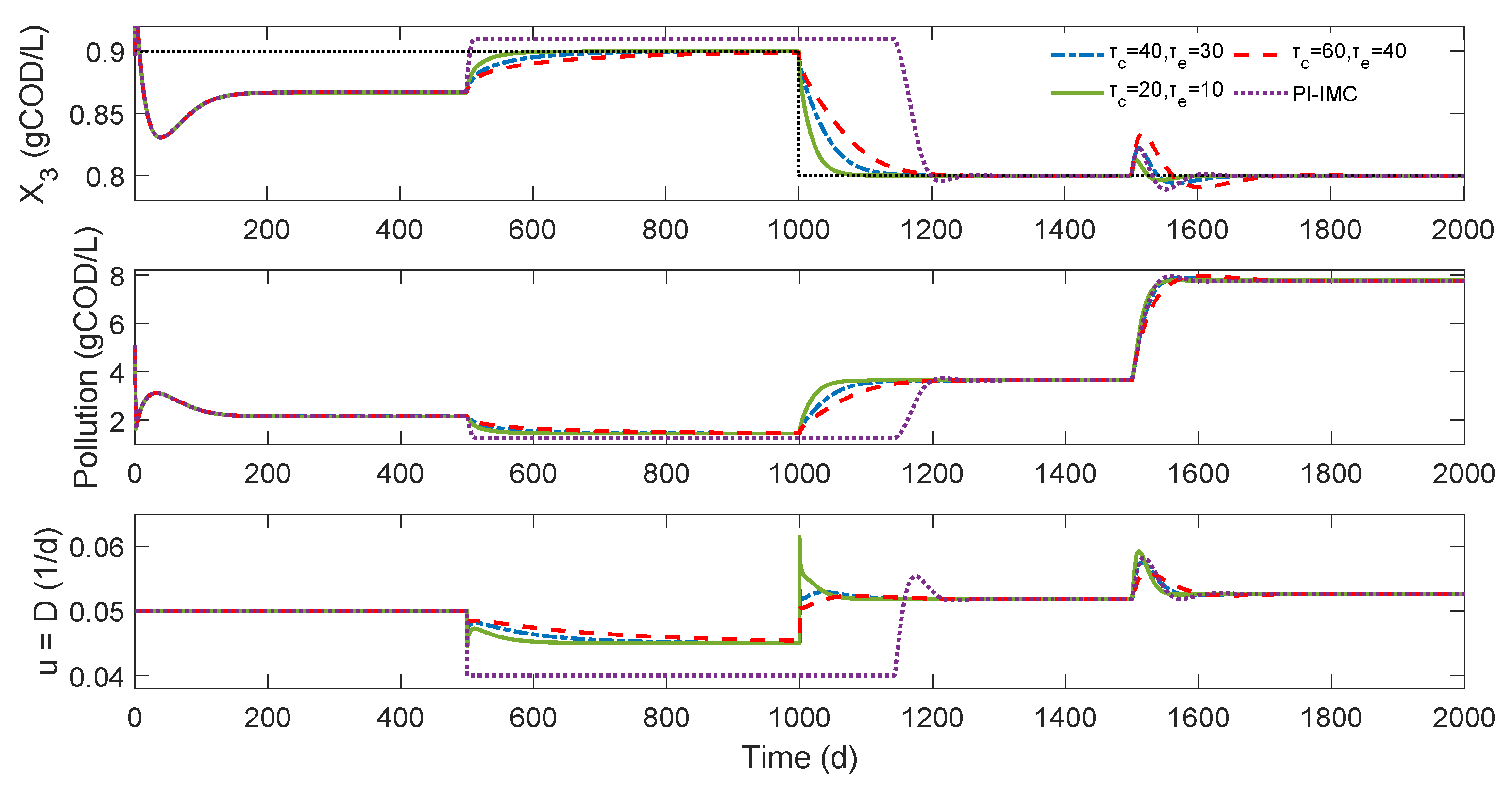
3.2. Control of the Methanogenic Biomass Concentration
3.2.1. Control Problem
3.2.2. Numerical Results
4. Discussion
- Dilution and Sin values: The AD operation is markedly influenced by the dilution rate and the substrate feed [19,20]. The observed values in the base and controlled process numerical simulation correspond to the region of lower organic pollution level and higher methanogenic biomass concentration according to the in-depth study presented by Khedim et al. [30] for the selected parameter values. As the substrate input feed increases and the dilution rate decreases, an increase in the methanogenic biomass concentration can achieve, as is shown in Figure 3 when the external perturbation is applied. Khedim et al. [30] suggest that the optimum yield of the MAD model in terms of biogas production was obtained for the following ranges [0.001–0.05] d−1, [0.03–30] gCOD/L of D, and Sin, respectively. Low dilution rates correspond to high HRT, allowing the active biomass population to remain in the reactor and not limiting the hydrolysis step.
- MEC closed-loop performance: The numerical results of the proposed controller on the benchmark MAD model demonstrate the capabilities and versatility of the MEC control approach when controlling the complex operation of AD. It is also noted that only two papers have addressed control designs for the AD of microalgae for the organic pollution level control problem [22,43]. In both cases, considering a possible error in that references in the time units (from hours to days) and sight differences between the values of some variables, the magnitude of the computed dilution rate is similar to the numerical assessment of two proposed nonlinear controllers based on feedback linearization and robust adaptive controllers. However, since both contributions include state and uncertain kinetic estimators, a fair comparison is not possible.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demirbas, A. Biofuels securing the planet’s future energy needs. Energy Conv. Manag. 2009, 50, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, C. Biofuels. Current Biol. 2007, 17, R115–R119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.D. The promising future of microalgae: Current status, challenges, and optimization of a sustainable and renewable industry for biofuels, feed, and other products. Microbial Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, I.; Kumar, R.R.; Mutanda, T.; Bux, F. Biodiesel from microalgae: A critical evaluation from laboratory to large scale production. Appl. Energy 2013, 103, 444–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulz, O.; Gross, W. Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl. Microb. Biotech. 2004, 65, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun, R.; Singh, M.; Forde, G.M.; Danquah, M.K. Bioprocess engineering of microalgae to produce a variety of consumer products. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotech. Advan. 2013, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias Silva, C.E.; Bertucco, A. Bioethanol from microalgae and cyanobacteria: A review and technological outlook. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uggetti, E.; Passos, F.; Solé, M.; García, J.; Ferrer, I. Biogas from algae via anaerobic digestion. In Algae Biotechnology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 195–216. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q.; Chang, J.S.; Ho, S.H. Biohydrogen production from microalgae for environmental sustainability. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendruscolo, F. Starch: A potential substrate for biohydrogen production. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 39, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sialve, B.; Bernet, N.; Bernard, O. Anaerobic digestion of microalgae as a necessary step to make microalgal biodiesel sustainable. Biotech. Adv. 2009, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKennedy, J.; Sherlock, O. Anaerobic digestion of marine macroalgae: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresto, C.G.; Paletta, R.; Filippelli, P.; Galluccio, L.; de la Rosa, C.; Amaro, E.; Jauregi-Haza, U.; de Frias, J.A. Sargassum invasion in the caribbean: An opportunity for coastal communities to produce bioenergy based on biorefinery-an overview. Waste Biomass Valor. 2022, 13, 2769–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.d.L.; Fernandez-Araújo, O.d.Q.; Cammarota, M.C. Biogas from microalgae: An overview emphasizing pretreatment methods and their energy return on investment (EROI). Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.J.; Lewis, D.M.; Green, F.B. Anaerobic digestion of algae biomass: A review. Algal Res. 2014, 5, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekunle, K.F.; Okolie, J.A. A review of biochemical process of anaerobic digestion. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, P. Anaerobic waste treatment fundamentals. Part one: Chemistry and microbiology. Public Works 1964, 95, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, J.; Latrille, E.; Harmand, J.; Robles, A.; Ferrer, J.; Gaida, D.; Wolf, C.; Mairet, F.; Bernard, O.; Alcaraz-Gonzalez, V.; et al. Instrumentation and control of anaerobic digestion processes: A review and some research challenges. Rev. Env. Sci. Bio/Tech. 2015, 14, 615–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Gadhamshetty, V.; Nitayavardhana, S.; Khanal, S.K. Automatic process control in anaerobic digestion technology: A critical review. Biores. Technol. 2015, 193, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, H.; Abdullah, N.; Yuzir, A. Integration of microalgae biomass in biomethanation systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petre, E.; Selişteanu, D.; Roman, M. Control schemes for a complex biorefinery plant for bioenergy and biobased products. Biores. Tech. 2020, 295, 122245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, O. Hurdles and challenges for modelling and control of microalgae for CO2 mitigation and biofuel production. J. Process Cont. 2011, 21, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elalami, D.; Oukarroum, A.; Barakat, A. Anaerobic digestion and agronomic applications of microalgae for its sustainable valorization. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26444–26462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milledge, J.J.; Nielsen, B.V.; Maneein, S.; Harvey, P.J. A brief review of anaerobic digestion of algae for bioenergy. Energies 2019, 12, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Suárez, J.L.; Carreras, N. Use of microalgae residues for biogas production. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golueke, C.G.; Oswald, W.J.; Gotaas, H.B. Anaerobic digestion of algae. Appl. Microb. 1957, 5, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mairet, F.; Bernard, O.; Cameron, E.; Ras, M.; Lardon, L.; Steyer, J.P.; Chachuat, B. Three-reaction model for the anaerobic digestion of microalgae. Biotech. Bioeng. 2013, 109, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Bona, A.; Ferretti, G.; Ficara, E.; Malpei, F. LFT modelling and identification of anaerobic digestion. Cont. Eng. Practice 2015, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedim, Z.; Benyahia, B.; Cherki, B.; Sari, T.; Harmand, J. Effect of control parameters on biogas production during the anaerobic digestion of protein-rich substrates. Appl. Math. Modelling 2018, 61, 351–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Adaptive control of feedback linearizable systems: A modelling error compensation approach. Int. J. Robust Nonlin. Cont. 1999, 9, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Jara, M.; Flores-Mejia, H.; Velasco-Perez, A.; Puebla, H. Robust control framework based on input-output models enhanced with uncertainty estimation. Studies Inform. Cont. 2021, 30, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simutis, R.; Lübbert, A. Bioreactor control improves bioprocess performance. Biotech. J. 2015, 10, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoutidis, P.; Zachar, M.; Jogwar, S.S. Sustainability and process control: A survey and perspective. J. Process Cont. 2016, 44, 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R. Control of biotechnological processes. In Encyclopedia of Systems and Control; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 298–305. [Google Scholar]
- Rathore, A.S.; Mishra, S.; Nikita, S.; Priyanka, P. Bioprocess control: Current progress and future perspectives. Life 2021, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, T.; Inaba, T.; Aizawa, H.; Mayumi, D.; Sakata, S.; Charfi, A.; Hori, T. Unexpected diversity of acetate degraders in anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating organic solid waste revealed by high-sensitivity stable isotope probing. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalena, J.A.; Ballesteros, M.; González-Fernandez, C. Efficient anaerobic digestion of microalgae biomass: Proteins as a key macromolecule. Molecules 2018, 23, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigon, J.C.; Matteau-Lebrun, F.; Abdou, R.H.; McGinn, P.J.; O’Leary, S.J.; Guiot, S.R. Screening microalgae strains for their productivity in methane following anaerobic digestion. Appl. Energy 2013, 108, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Estrada, L.; Longoria, A.; Arenas, E.; Moreira, J.; Okoye, P.U.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.; Sebastian, P.J. A review on current trends in biogas production from microalgae biomass and microalgae waste by anaerobic digestion and co-digestion. BioEnergy Res. 2022, 15, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairet, F.; Bernard, O.; Ras, M.; Lardon, L.; Steyer, J.P. Modeling anaerobic digestion of microalgae using ADM1. Biores. Technol. 2011, 102, 6823–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayen, T.; Mairet, F.; Martinon, P.; Sebbah, M. Analysis of a periodic optimal control problem connected to microalgae anaerobic digestion. Optimal Cont. Appl. Methods 2015, 36, 750–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petre, E.; Roman, M.; Selişteanu, D. Nonlinear estimation and control schemes for a complex anaerobic digestion of microalgae with unknown kinetics and inputs. Biores. Technol. 2019, 287, 121429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morari, M.; Zafiriou, E. Robust Process Control; Prentice Hall, Englewood-Cliffs: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, I.R.; Tempo, R. Robust control of uncertain systems: Classical results and recent developments. Automatica 2014, 50, 1315–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Olbrot, A.W.; Polis, M.P. Robust stabilization and robust performance using model reference control and modeling error compensation. IEEE Tran. Automatic Cont. 1994, 39, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puebla, H.; Hernandez-Martinez, E.; Hernandez-Suarez, R.; Ramirez-Muñoz, J.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. A simple feedback control approach for output modulation of spatiotemporal patterns in a class of tubular reactors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 17517–17528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puebla, H.; Roy, P.K.; Velasco-Perez, A.; Gonzalez-Brambila, M.M. Biological pest control using a model-based robust feedback. IET Syst. Biol. 2018, 12, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Cisneros, G.; Dochain, D.; Alvarez-Ramírez, J. Model based extremum-seeking controller via modelling-error compensation approach. J. Proc. Cont. 2019, 80, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgot, M.; Folch, M. Wastewater treatment and water reuse. Current Op. Env. Sci. Health 2018, 2, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogestad, S. Simple analytic rules for model reduction and PID controller tuning. J. Proc. Cont. 2003, 13, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Jara, M.; Velasco-Pérez, A.; Vian, J.; Vigueras-Carmona, S.E.; Puebla, H. Robust Control Based on Modeling Error Compensation of Microalgae Anaerobic Digestion. Fermentation 2023, 9, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010034
Rodríguez-Jara M, Velasco-Pérez A, Vian J, Vigueras-Carmona SE, Puebla H. Robust Control Based on Modeling Error Compensation of Microalgae Anaerobic Digestion. Fermentation. 2023; 9(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Jara, Mariana, Alejandra Velasco-Pérez, Jose Vian, Sergio E. Vigueras-Carmona, and Héctor Puebla. 2023. "Robust Control Based on Modeling Error Compensation of Microalgae Anaerobic Digestion" Fermentation 9, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010034
APA StyleRodríguez-Jara, M., Velasco-Pérez, A., Vian, J., Vigueras-Carmona, S. E., & Puebla, H. (2023). Robust Control Based on Modeling Error Compensation of Microalgae Anaerobic Digestion. Fermentation, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010034





