Synergistic Hypolipidemic and Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactobacillus and Spirulina platensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Algae Cultivation
2.3. Preparation of Cell Lysate
2.4. Experimental Design for Mice Feeding with L. plantarum and L. casei and Spirulina platensis
2.4.1. Animals
2.4.2. Blood Sampling and Biochemical Assays
2.4.3. Histopathological Examination
2.4.4. Assessment of Complete Blood Count (CBC)
2.4.5. Analysis of Myeloid Cells with Flow Cytometry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Lactobacillus and Spirulina Treatment on Body Weight
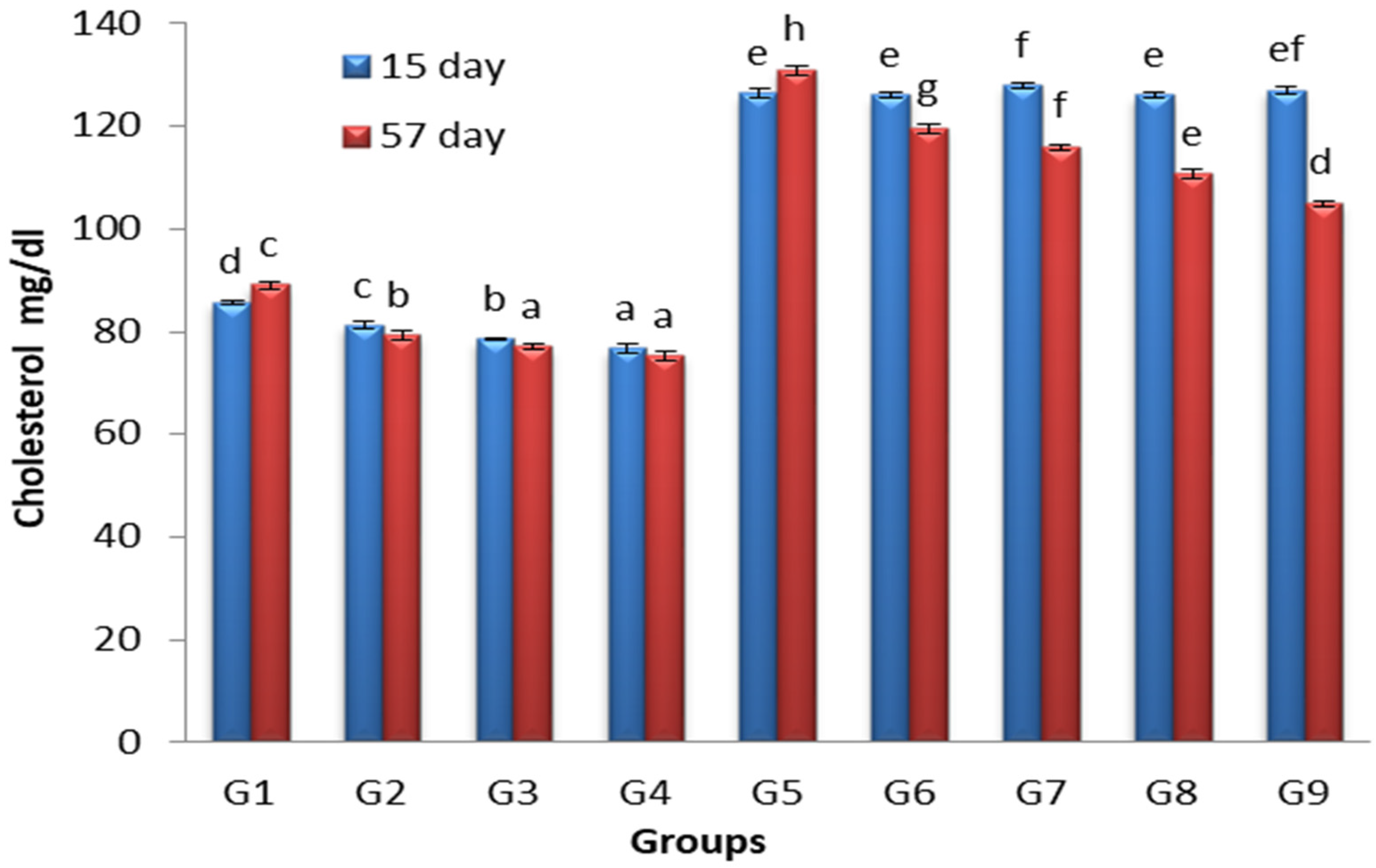
3.2. Effects of Lactobacillus and Spirulina Treatment on Cholesterol Levels
3.3. Effects of Lactobacillus and Spirulina Treatment on TG Level
3.4. Effects of Lactobacillus and Spirulina Treatment on High-Density Lipoprotein Level (HDL)
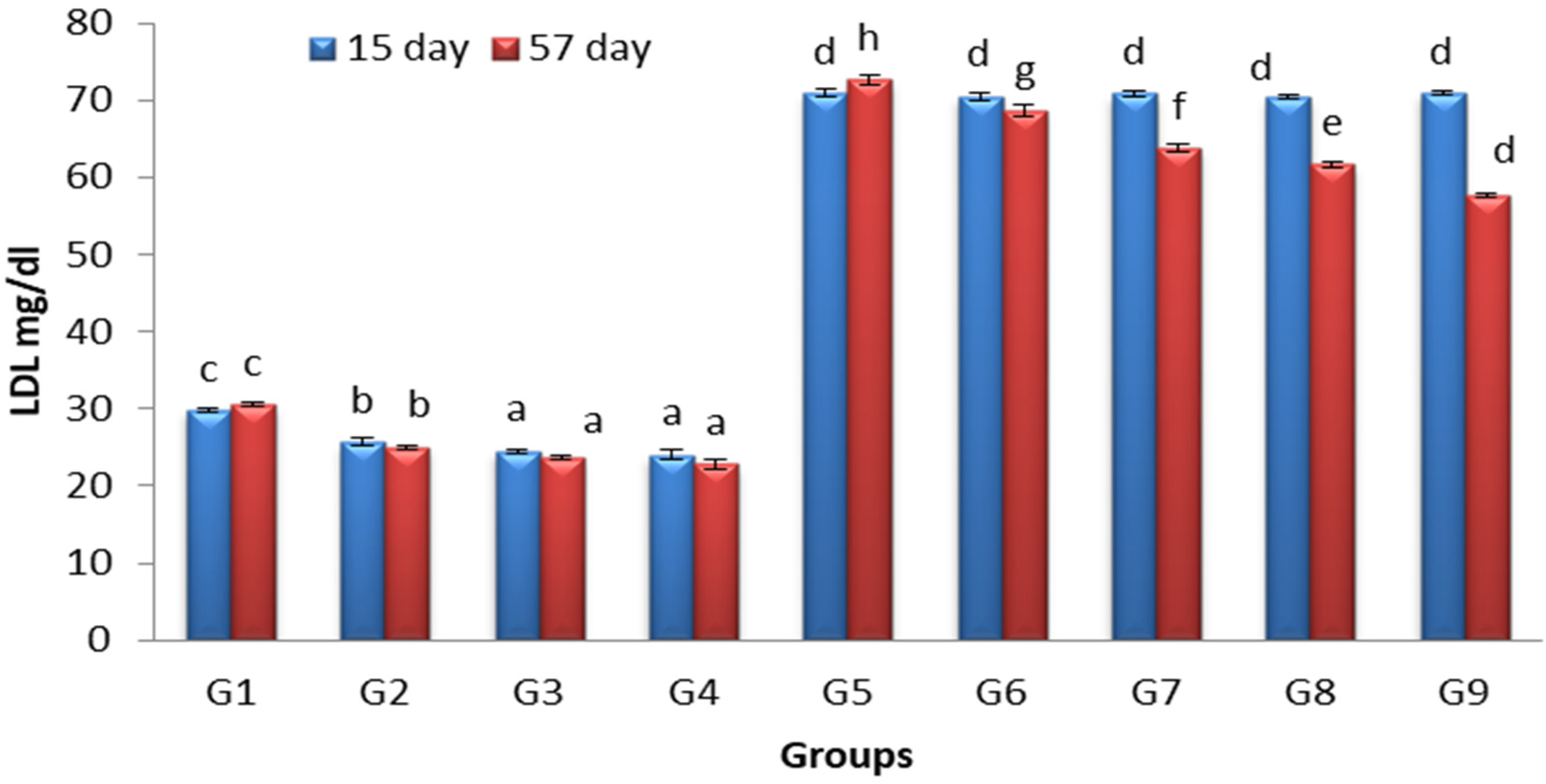
3.5. Effects of Lactobacillus and Spirulina Treatment on Low-Density Lipoprotein Level (LDL)
3.6. Complete Blood Count
3.7. Analysis of Myeloid Cells with Flow Cytometry
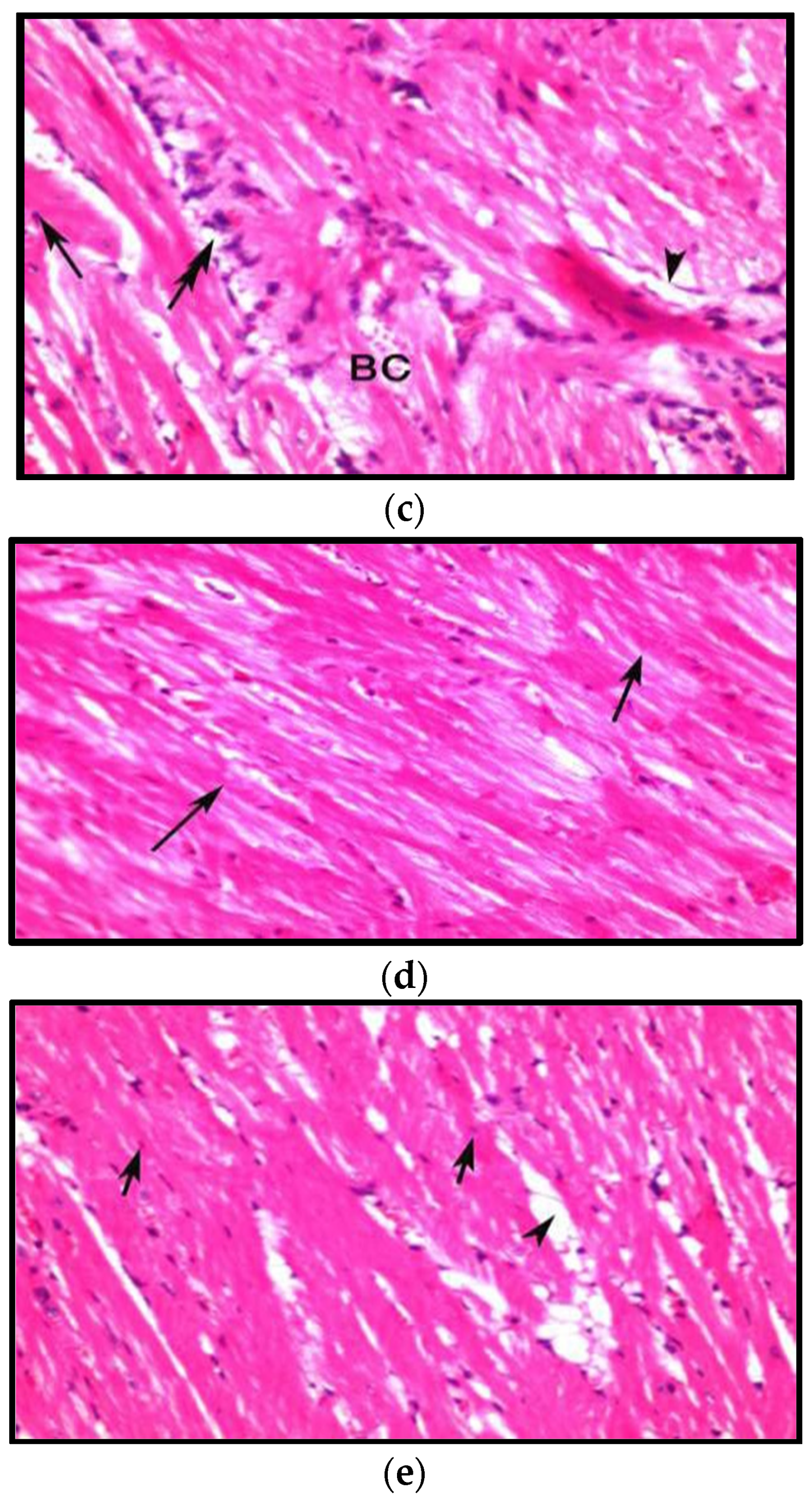
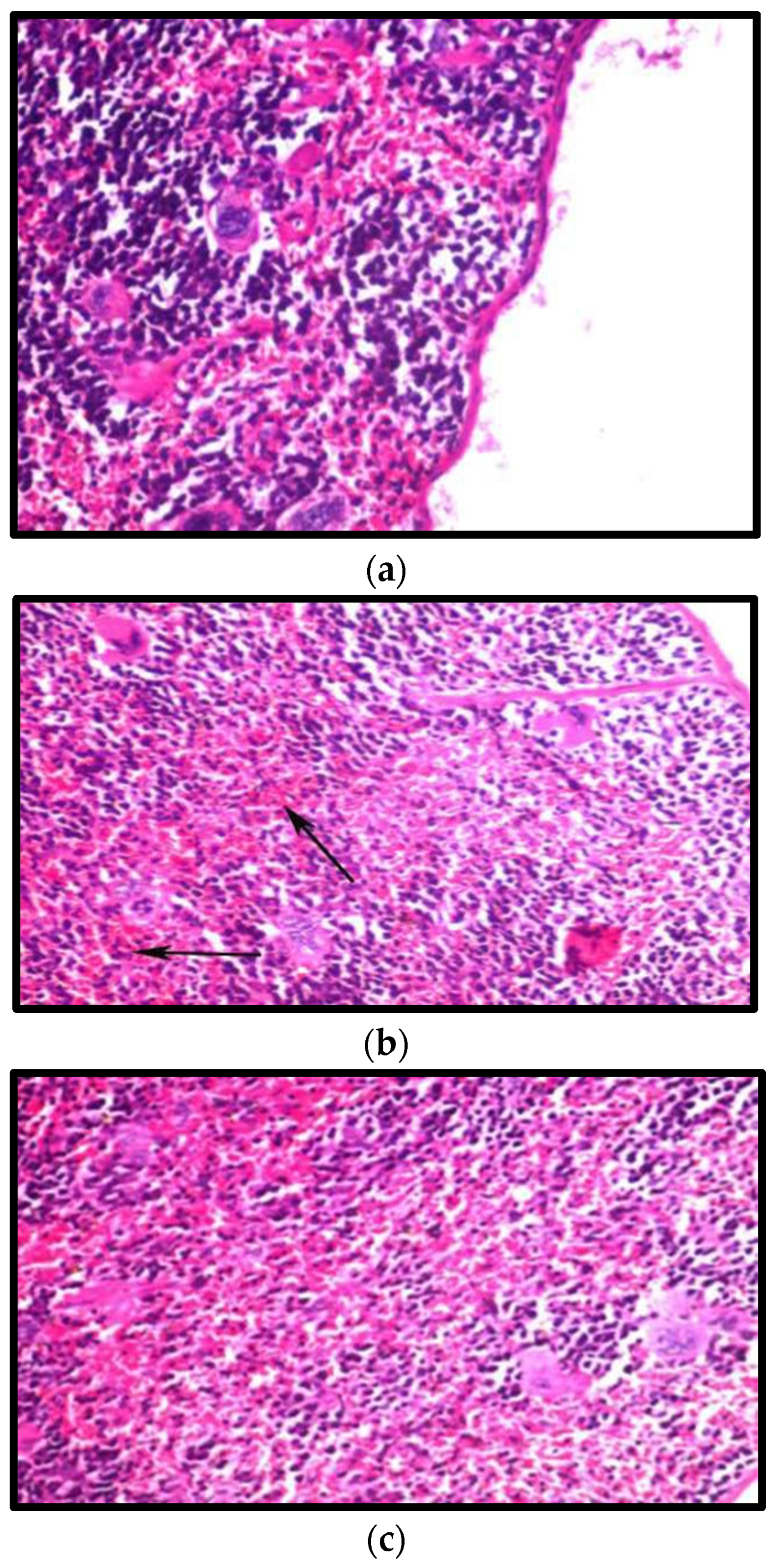
3.8. Histopathological Examination
3.8.1. Effects on Heart
3.8.2. Effect on the Spleen
3.8.3. Effects on Aorta
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navar-Boggan, A.M.; Peterson, E.D.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Neely, B., Sr.; Sniderman, A.D.; Pencina, M.J. Hyperlipidemia in Early Adulthood Increases Long-Term Risk of Coronary Heart Disease. Circulation 2015, 131, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armitage, J. The safety of statins in clinical practice. Lancet 2007, 7, 1781.e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Chiou, J. Potential Benefits of Probiotics and Prebiotics for Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunremi, O.R.; Sanni, A.I.; Agrawal, R. Hypolipidaemic and antioxidant effects of functional cereal-mix produced with probiotic yeast in rats fed high cholesterol diet. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 742.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdó, T.; García-Santos, J.A.; Bermúdez, M.G.; Campoy, C. The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota:mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitetta, L.; Vitetta, G.; Hall, S. Immunological Tolerance and Function: Associations Between Intestinal Bacteria, Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Phages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ananya, A.K.; Kamal, K.; Ahmad, I.Z. Cyanobacteria “the blue green algae” and its novel applications: A brief review. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Res. 2014, 7, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Celekli, A.; Alslibi, Z.A.; Bozkurt, H. Use of spirulina in probiotic fermented milk products. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 6, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Gyenis, B.; Szigeti, J.; Molnar, N.; Varga, L. Use of dried microalgal biomasses to stimulate acid production and growth of Lactobacillus plantarum and Enterococcus faecium in milk. Acta Agrar. Kapos. 2005, 9, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Moln´ar, N.; Gyenis, B.; Varga, L. Influence of a powdered Spirulina platensis biomass on acid production of lactococci in milk. Milchwissenschaft 2005, 60, 380–382. [Google Scholar]
- Watanuki, H.; Ota, K.; Malina, A.C.; Tassakka, A.R.; Kato, T.; Sakai, M. Immunostimulant effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, C.; Garg, A.P.; Prakash, D. Prebiotic efficiency of blue green algae on probiotics microorganisms. J. Microbiol. Exp. 2017, 4, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoda, M.; El-Halafawy, K.; El-Soda, M.A.E. Functionalities of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Egyptian Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrouk, C. Contribution a L’etude D’une Cyanobacterie: Influence de Divers Facteurs Physiques et Chimiques sur la Croissance et la Photosynthese de Spirulina Maxima (Setchell et Gardner) Geitler. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris, Paris, France, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Tchernyshyov, I.; Semenza, G.L.; Dang, C.V. HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osman, S.M.; Hussein, M.A. Purslane seeds fixed oil as a functional food in treatment of obesity induced by high fat diet in obese diabetic mice. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 5, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fossati, P.; Prencipe, L. Serum triglycerides determined colorimetrically with an enzyme that produces hydrogen peroxide. Clin. Chem. 1982, 28, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeg, R.; Ziegenohrm, J. Kinetic enzymatic method forautomated determination of total cholesterol in serum. J. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 1798–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.F.; Stone, S.; Ellis, S.; Collwell, J.A. Cholesterol determination in high density lipoproteins separated by three different methods. Clin. Chem. 1977, 23, 882–886. [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Frederickson, D.S. Estimation of concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 449–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, G.D.; Stevens, A.; Turner, D.R. Theory and Practice of Pathological Technique, 4th ed.; Churchill Livingston: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, H.M. Practical Flow Cytometry, 4th ed.; Wiley-Liss: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Snedcor, G.W.; Cochran, W.G. Statistical Methods, 7th ed.; The Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1982; p. 507. [Google Scholar]
- Estadella, D.; Oyama, L.M.; Dâmaso, A.R.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Oller Do Nascimento, C.M. Effect of palatable hyperlipidic diet on lipid metabolism of sedentary and exercised Rats. Nutrition 2004, 20, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crovesy, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Ferreira, D.M.T.P.; Rosado, E.L.; Soares-Mota, M. Effect of Lactobacillus on body weight and body fat in overweight subjects: A systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Colica, C.; Boccuto, L.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aiello, V.; Romano, B.; De Lorenzo, A.; Izzo, A.A.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Obesity: A Role for Probiotics. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.-B.; Xin, S.-S.; Ding, L.-N.; Ding, W.-Y.; Hou, Y.-L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Zhang, X. The Potential Role of Probiotics in Controlling Overweight/Obesity and Associated Metabolic Parameters in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3862971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Bhat, A.G.; OKeefe, J. Effects of spirulina on weight loss and blood lipids: A review. Open Heart 2020, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Menghebilige; Bao, Q. Selection of potential probiotic lactobacilli for cholesterol-lowering properties and their effect on cholesterol metabolism in rats fed a high-lipid diet. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 95, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begley, M.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, J.M.; Bongers, R.S.; de Vos, W.M.; Kleerebezem, M. Functional analysis of four bile salt hydrolase and penicillin acylase family members in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4719–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabuchi, M.; Tamura, A.; Yamada, T.; Ishida, T.; Hosoda, M.; Hosono, A. Hypocholesterolemic effects of viable and heat-sterilized cells of Lactobacillus GG in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Milchwissenschaft 2004, 59, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.L.; Chen, H.; Ouyang, W.; Metz, T.; Prakash, S. Microencapsulated genetically engineered Lactobacillus plantarum 80 (pCBH1) for bile acid deconjugation and its implication in lowering cholesterol. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2004, 2004, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeun, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, S.Y.; Jun, H.J.; Park, H.J.; Seo, J.G. Hypocholesterolemic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum KCTC3928 by increased bile acid excretion in C57BL/6 mice. Nutrition 2010, 26, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir, I.; Chayoth, R.; Shany, S.; Stark, A.H.; Arad, S.M. Soluble poysacharides and biomass of red microalgae porphorydium species alter intestinal morphology and reduce serum cholesterol in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 48, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talayero, B.G.; Sacks, F.M. The Role of Triglycerides in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2011, 13, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, I.D.; Kim, S.-H.; Jeong, J.-W.; Lee, D.E.; Huh, C.-S.; Sim, J.-H.; Ahn, Y.-T. Triglyceride-Lowering Effects of Two Probiotics, Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032 and Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601, in a Rat Model of High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypertriglyceridemia. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.Y.; Kim, M.; Ahn, Y.T.; Sim, J.H.; Choi, I.D.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. The triglyceride-lowering effect of supplementation with dual probiotic strains, Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032: Reduction of fasting plasma lysophosphatidyl cholines in nondiabetic and hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazokopakis, E.E.; Starakis, I.K.; Papadomanolaki, M.G.; Mavroeidi, N.K.; Ganotakis, E.S. The hypolipidaemic effects of Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) supplementation in a Cretan population: A prospective study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.K.; Li, D.X.; Xiang, L.; Gong, X.J.; Kondo, Y.; Suzuki, I. Isolation of pancreatic lipase activity-inhibitory component of Spirulina platensis and it reduce postprandial triacylglycerolemia. Yakugaku Zasshi 2006, 126, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franczyk, B.; Rysz, J.; Ławinski, J.; Rysz-Górzynska, M.; Gluba-Brzózka, A. Is a High HDL-Cholesterol Level Always Beneficial? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasut, C.; Tirawat, Y.; Kesika, P.; Thangalee, S.; Peerajan, S.; Chaiyasut, K.; Sittiprapaporn, P. Effect of Lactobacillus paracasei HII01 supplementation on total cholesterol, and on the parameters of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, oxidative stress, inflammation and digestion in Thai hypercholesterolemic subjects. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wan, X.-Z.; Huang, Z.-R.; Liu, B.; Zhao, C. Regulatory Efficacy of the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Microalgae Spirulina platensis on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in High- Fat Diet Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ooi, L.-G.; Liong, M.-T. Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Probiotics and Prebiotics:A Review of in Vivo and in Vitro Findings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2499–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, S.; Shimizu, K.; Kaneko, H.; Shibayama, F.; Morikawa, K.; Kanamaru, Y.; Hirahashi, T.; Kato, T. A novel protein C-phycocyanin plays a crucial role in the hypocholesterolemic action of Spirulina platensis concentrate in rat. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sniderman, A.D.; Thanassoulis, G.T.; Navar, A.M.; Pencina, M.; Catapano, A.; Ference, B.A. Apolipoprotein B Particles and Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Ruan, Z. Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 8, e0178868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Kouchaki, E.; Salami, M.; Aghadavod, E.; Akbari, E.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Asemi, Z. The effects of probiotic supplementation on gene expression related to inflammation, insulin, and lipids in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, S.-H.; Kim, M.Y.; Sok, D.E. Spirulina Prevents Atherosclerosis by Reducing Hypercholesterolemia in Rabbits Fed a High-Cholesterol Diet. J. Nut. Sci. Vita. 2010, 56, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboderin, F.I.; Oyetayo, V.O. Haematological Studies of Rats Fed Different Doses of Probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum, Isolated from Fermenting Corn Slurry. Pak. J. Nutr. 2006, 5, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Nasirian, F.; Mesbahzadeh, B.; Maleki, S.A.; Mogharnasi, M.; Kor, N.M. The effects of oral supplementation of Spirulina platensis microalgae on hematological parameters in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 5238. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, D.C.; Tachibana, L.; Iwashita, M.K.P.I.; Nakandakare, I.B.; Romagosa, E.; Seriani, R.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Probiotic supplementation causes hematological changes and improves non-specific immunity in Brycon amazonicus. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2020, 42, e52473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korčok, D.J.; Tršić-Milanoviće, N.; Ivanović, N.; Đorđević, B. Development of Probiotic Formulation for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pacheco, J.M.; Yilmaz, M.; Rice, L. How low is too low: Statininduced hemolysis. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-R.A.; Hotten, D.F.; Malakhau, Y.; Volker, E.; Ghio, A.J.; Noble, P.W.; Kraft, M.; Hollingsworth, J.W.; Gunn, M.D.; Tigh, R.M. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Myeloid Cells in Human Blood, Bronchoalveolar Lavage, and Lung Tissues. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duque, G.A.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Heyman, M. Effets des probiotiques sur le système immunitaire: Mécanismes d’action potentiels. Cah. Nutr. Diét. 2007, 42, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.H.; Balachandran, P.; Christensen, O. Enhancement of natural killer cell activity in healthy subjects by Immulina, a Spirulina extract enriched for Braun-type lipoproteins. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 802–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, F.; Teng, B. Immunostimulatory Effects of Polysaccharides from Spirulina platensis In Vivo and Vitro and Their Activation Mechanism on RAW246.7 Macrophages. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soehnlein, O.; Drechsler, M.; Hristov, M.; Weber, C. Functional alterations of myeloid cell subsets in hyperlipidaemia:relevance for atherosclerosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 4293–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vareille-Delarbre, M.; Miquel, S.; Garcin, S.; Bertran, T.; Balestrino, D.; Evrard, B. Immunomodulatory effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on inflammatory response induced by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 2019, 87, e00570-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laino, J.; Villena, J.; Kanmani, P.; Kitazawa, H. Immunoregulatory effects triggered by lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides: New insights into molecular interactions with host cells. Microorganisms 2016, 4, E27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AL-Aameli, M.H.; Al-Taee, R.A.M.; Alsalame, H.A. Histological & Physiological Alternations in the Aorta & Heart in Relation with Cholesterol Diet in Male Albino Rat. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2019, 13, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghzadeh, J.; Vakili, A.; Sameni, H.R.; Shadnoush, M.; Bandegi, A.-R.; Khorasan, M.Z. The Effect of Oral Consumption of Probiotics in Prevention of Heart Injury in a Rat Myocardial Infarction Model: A Histopathological, Hemodynamic and Biochemical Evaluation. Iran. Biomed. J. 2017, 21, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naghashpour, M.; Cualing, H. Splenomegaly with sea-blue histiocytosis, dyslipidemia, and nephropathy in a patient with lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: A clinicopathologic correlation. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2009, 58, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokryazdan, P.; Jahromi, M.F.; Liang, J.B.; Kalavathy, R.; Sieo, C.C.; Ho, Y.W. Safety Assessment of Two New Lactobacillus Strains as Probiotic for Human Using a Rat Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nabi, X.-H.; Ma, C.-Y.; Manaer, T.; Heizati, M.; Wulazibieke, B.; Aierken, L. Anti-atherosclerotic effect of traditional fermented cheese whey in atherosclerotic rabbits and identification of probiotics. J. Altern Complement Med. 2016, 16, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





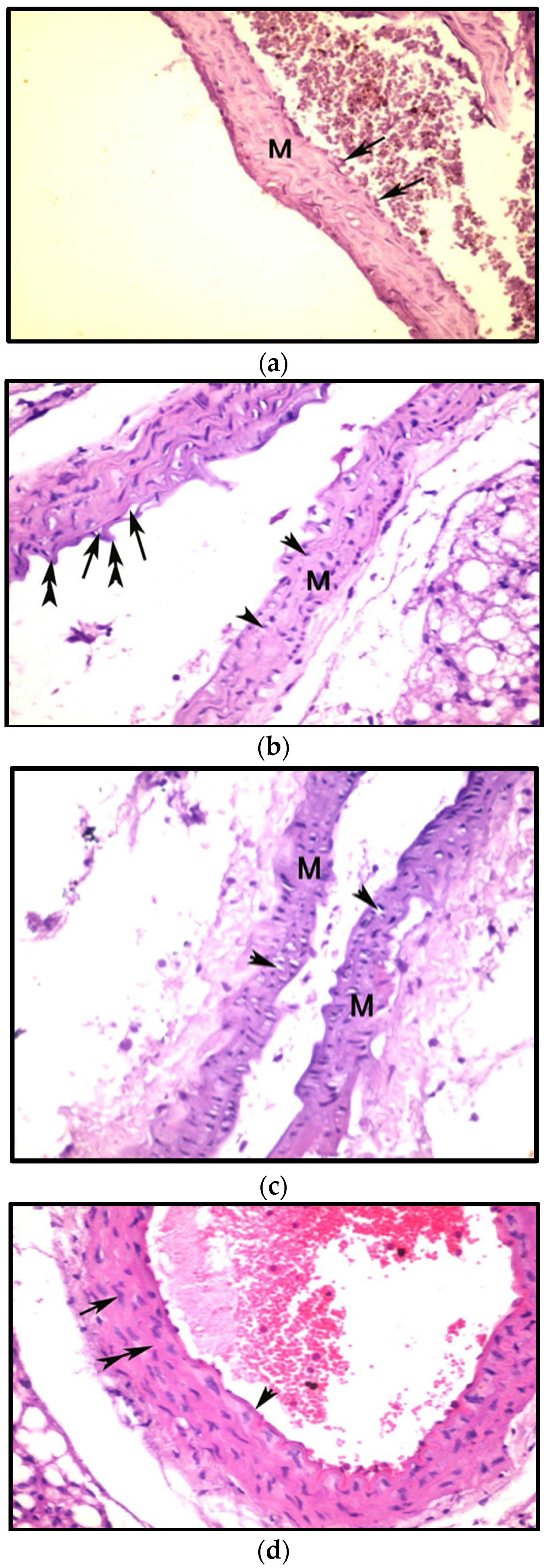
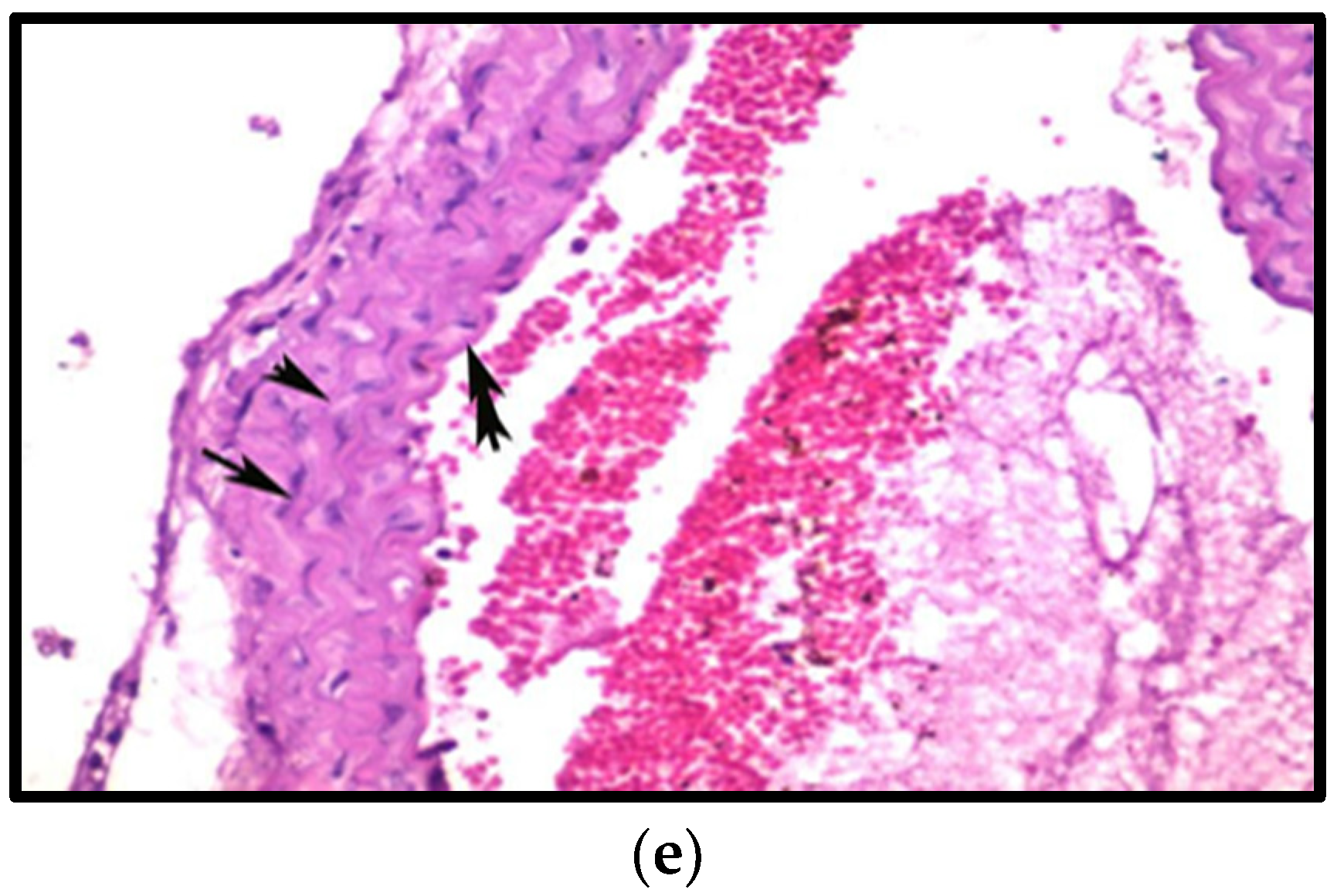
| Parameter | Days | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | G9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hb (g/dL) | 15 | 8.5 ± 0.288 a | 9.6 ± 0.23 ab | 10.3 ± 0.05 bc | 10.7 ± 0.12 bcd | 11.5 ± 0.12 cde | 11.3 ± 0.17 cde | 12 ± 0.28 e | 11.4 ± 0.29 cde | 11.7 ± 0.12 de |
| 57 | 8.9 ± 0.284 a | 10.2 ± 0.12 abc | 10.9 ± 0.1 bcd | 11.2 ± 0.14 cd | 12.1 ± 0.12 d | 11.2 ± 0.18 cd | 11.7 ± 0.23 d | 11.3 ± 0.26 cd | 9.6 ± 0.19 ab | |
| RBC (M/μL) | 15 | 3 ± 0.12 a | 3.4 ± 0.06 ab | 3.6 ± 0.05 ab | 3.7 ± 0.06 ab | 3.9 ± 0.06 ab | 3.8 ± 0.05 b | 4.2 ± 0.11 ab | 3.8 ± 0.12 ab | 4.1 ± 0.06 ab |
| 57 | 3.2 ± 0.12 a | 3.5 ± 0.06 a | 3.7 ± 0.03 a | 3.9 ± 0.06 a | 4.16 ± 0.08 a | 3.8 ± 0.08 a | 4.03 ± 0.08 a | 3.7 ± 0.08 a | 3.4 ± 0.03 a | |
| HCT (%) | 15 | 26 ± 0.01 a | 29.4 ± 0.01 b | 31.2 ± 0.01 c | 32.1 ± 0.01 cd | 33.8 ± 0.01 ef | 32.9 ± 0.01 cd | 36.4 ± 0.01 g | 33.5 ± 0.01 de | 35.5 ± 0.01 fg |
| 57 | 27 ± 0.01 a | 30.3 ± 0.01 b | 32.6 ± 0.01 c | 33.8 ± 0.01 de | 35.7 ± 0.01 f | 33.1 ± 0.01 cde | 34.9 ± 0.01 ef | 32.6 ± 0.01 cd | 29.7 ± 0.01 b | |
| MCH (pg) | 15 | 28.3 ± 0.15 a | 28.3 ± 0.18 a | 28.6 ± 0.32 a | 28.9 ± 0.15 a | 29.5 ± 0.12 a | 29.7 ± 0.03 a | 28.6 ± 0.12 a | 29.5 ± 0.13 a | 28.5 ± 0.15 a |
| 57 | 28.1 ± 0.4 a | 29.1 ± 0.15 ab | 28.9 ± 0.01 ab | 28.8 ± 0.05 ab | 28.9 ± 0.27 ab | 29.3 ± 0.27 ab | 29.1 ± 0.08 ab | 30 ± 0.26 b | 28 ± 0.29 a | |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 15 | 32.7 ± 0.12 ab | 32.5 ± 0.23 a | 33 ± 0.37 ab | 33.3 ± 0.17 bc | 33.9 ± 0.14 c | 34.2 ± 0.03 c | 32.9 ± 0.08 ab | 34.1 ± 0.15 c | 32.9 ± 0.12 ab |
| 57 | 32.3 ± 0.49 a | 33.6 ± 0.17 b | 33.4 ± 0.03 b | 33.2 ± 0.09 b | 33.6 ± 0.3 b | 33.8 ± 0.32 b | 33.6 ± 0.09 b | 34.6 ± 0.26 c | 32.4 ± 0.32 a | |
| MCV (fL) | 15 | 86.7 ± 0.06 a | 86.7 ± 0.05 a | 86.7 ± 0.05 a | 86.7 ± 0.05a | 86.7 ± 0.03 a | 86.7 ± 0.03 a | 86.6 ± 0.04 a | 86.7 ± 0.08 a | 86.7 ± 0.05 a |
| 57 | 86.7 ± 0.06 a | 86.7 ± 0.05 a | 86.6 ± 0.06 a | 86.6 ± 0.05 a | 85.98 ± 0.04 a | 86.5 ± 0.03 a | 86.6 ± 0.05 a | 86.6 ± 0.02 a | 86.6 ± 0.08 a | |
| WBC (×109/L) | 15 | 5 ± 0.06 a | 5.4 ± 0.12 b | 5.8 ± 0.12 c | 6.2 ± 0.05 d | 11.8 ± 0.08 e | 11.6 ± 0.1 e | 12.1 ± 0.1 f | 11.8 ± 0.1 e | 12.1 ± 0.1 f |
| 57 | 4.9 ± 0.08 a | 5.6 ± 0.12 b | 6 ± 0.12 c | 6.3 ± 0.06 d | 12 ± 0.2 i | 11 ± 0.1 h | 10.6 ± 0.1 g | 9.2 ± 0.1 f | 6.7 ± 0.1 e | |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 15 | 205 ± 0.9 a | 217 ± 0.98 b | 248 ± 0.88 c | 257.66 ± 0.9 c | 368 ± 0.8 d | 367 ± 0.9 d | 370 ± 0.9 d | 368.66 ± 0.8 d | 369.66 ± 0.9 d |
| 57 | 204 ± 0.8 a | 232 ± 0.7a | 253.66 ± 0.8 ab | 257.6 ± 0.89 ab | 370 ± 0.8 c | 335 ± 0.9 bc | 309 ± 0.9 a | 290.66 ± 0.8 abc | 216.33 ± 0.99 a |
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | G9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD11b − Ly6G+ | 3 ± 0.1 a | 3.84 ± 0.1 b | 4.74 ± 0.2 c | 5.8 ± 0.1 d | 14.2 ± 0.2 i | 11.9 ± 0.4 h | 10.5 ± 0.2 g | 9.66 ± 0.1 f | 7.5 ± 0.2 e |
| CD11b + Ly6G+ | 5.1 ± 0.1a | 5.9 ± 0.1 b | 6.35 ± 0.1 c | 6.7 ± 0.05 d | 45.2 ± 0.6 i | 42.8 ± 0.9 h | 41.5 ± 0.2 g | 37.26 ± 0.2 f | 24.2 ± 0.1 e |
| CD11b + Ly6G− | 0.7 ± 0.04 a | 0.9 ± 0.02 b | 1.72 ± 0.04 c | 3 ± 0.11 d | 25.8 ± 0.6 i | 23.8 ± 0.17 h | 21.8 ± 0.3 g | 20.5 ± 0.2 f | 12.9 ± 0.1 e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamouda, R.A.; Hamza, H.A.; Salem, M.L.; Kamal, S.; Alhasani, R.H.; Alsharif, I.; Mahrous, H.; Abdella, A. Synergistic Hypolipidemic and Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactobacillus and Spirulina platensis. Fermentation 2022, 8, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050220
Hamouda RA, Hamza HA, Salem ML, Kamal S, Alhasani RH, Alsharif I, Mahrous H, Abdella A. Synergistic Hypolipidemic and Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactobacillus and Spirulina platensis. Fermentation. 2022; 8(5):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050220
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamouda, Ragaa A., Hanafy A. Hamza, Mohammed L. Salem, Shymaa Kamal, Reem Hasaballah Alhasani, Ifat Alsharif, Hoda Mahrous, and Asmaa Abdella. 2022. "Synergistic Hypolipidemic and Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactobacillus and Spirulina platensis" Fermentation 8, no. 5: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050220
APA StyleHamouda, R. A., Hamza, H. A., Salem, M. L., Kamal, S., Alhasani, R. H., Alsharif, I., Mahrous, H., & Abdella, A. (2022). Synergistic Hypolipidemic and Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactobacillus and Spirulina platensis. Fermentation, 8(5), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050220







