Abstract
Pectinolytic enzymes are related enzymes that hydrolyze pectic substances. Pectinolytic enzymes are of great interest in industrial applications for softening fruits, extracting and clarifying juices, extracting olive oil, retting textile fibers, preparing gel, and isolating protoplasts. The current work presents acidic extracellular pectinase production using low-cost agro-industrial waste with the indigenously isolated novel strain Aspergillus cervinus. Two fungal isolates, ARS2 and ARS8, with maximum pectinase activity, 41.88 ± 1.57 IU/mL and 39.27 ± 1.14 IU/mL, respectively, were screened out of 27 isolates from decayed fruit peels (orange, banana, and lemon) and soil containing decomposed vegetables. The isolate ARS2, identified as Aspergillus cervinus by molecular characterization, showed the highest pectinase activity of 43.05 ± 1.38IU/mL during screening and was further used for media component screening and optimization studies. To understand their effect on pectinase activity, one-factor-at-a-time (OFAT) studies were conducted on carbon sources, nitrogen sources, and mineral salts. The OFAT results showed the highest pectinase activity for orange peel (carbon source) at 44.51 ± 1.33 IU/mL, peptone (nitrogen source) at 45.05 ± 1.04 IU/mL, and NaH2PO4 (mineral salts) at 43.21 ± 1.12 IU/mL. The most significant media components screened by the Plackett–Burman (PB) design based on the p-value, Pareto chart, and main effect plot, were orange peel (p < 0.001), peptone (p < 0.001), NaH2PO4 (p < 0.001), and KH2PO4 (p < 0.001), which were further optimized using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Central Composite Design (CCD). The optimization results for the media components showed a maximum pectinase activity of 105.65 ± 0.31 IU/mL for 10.63 g orange peel, 3.96 g/L peptone, 2.07 g/L KH2PO4, and 2.10 g/L NaH2PO4. Thus, it was discovered that the indigenously isolated novel strain Aspergillus cervinus ARS2 was able to successfully produce a significant amount of pectinase using agro-industrial waste. Therefore, it can be considered for the large-scale optimized production of pectinase to meet industrial demands.
1. Introduction
Pectinases are a division of enzymes that catalyze the degradation of pectic substances into galacturonic acid [1]. Pectic substances are complex acidic polysaccharides having a backbone of galacturonic acid residues connected by α-1-4 glycosidic linkages [2]. Pectinases are divided based on their mode of action in turning pectic substances into pectin lyase (EC 4.2.2.10), polygalacturonase (EC 3.2.1.15), pectate lyase (EC 4.2.2.2), and pectinesterase (EC 3.1.1.11) [3]. The pectinase’s share in global industrial enzyme production is 10% [4] and it is expected to continue to increase in market size to 450.3 million dollars by 2028, as per the global pectinase market research report. It is reported that the pectinolytic enzymes share in global food enzymes is around 25% [5]. The biotechnological applications of the pectinase enzyme are in the fruit industry and concern the degumming of plant blast fibers, retting flax and vegetable fibers, bioscouring of cotton fibers, coffee and tea fermentation, pulp and paper industry, haze removal from wines, extraction of vegetable oil, and wastewater treatment [6,7,8,9,10,11].
These pectinases are produced from microbial or other sources, such as plants, nematodes, and insects. Different microbial sources, such as fungi, yeasts, and bacteria, have been involved in the production of pectinases using solid-state fermentation (SSF) and submerged fermentation (SmF). Many researchers have worked on different fungal strains for pectinase production such as Aspergillus sojae [12,13], Aspergillus niger [14,15,16,17,18], Aspergillus fumigates [19,20], Aspergillus sydowii [10], Aspergillus tubingensis [21], Aspergillus carbonarius [22], Aspergillus parvisclerotigenus [23], Aspergillus oryzae [24], Penicillium oxalicum [25], Penicillium notatum and Coriolus versicolor [26], Penicillium chrysogenum [27], Fusarium proliferatum [28], Schizophyllum commune [29], Trichoderma harzianum [30], Rhizopus sp. [31], and Candida sp. [32]. The pectinase production by the Aspergillus cervinus species has not yet, to the best of our knowledge, been evidenced and reported by any researcher [33] was confirmed by the detailed literature review. The capability of the Aspergillus cervinus species to synthesize pectinase using solid-state fermentation must be studied and the production cost of the enzyme needs to be reduced by using optimization techniques and low-cost agro-industrial waste as substrate.
Agro-industrial wastes are obtained from the processing, production, and harvesting of cereal products, vegetables, trees, and fruits. They are produced in huge quantities globally and are either used as animal feed or burnt in the field [34]. Agro-industrial residues are rich in polymeric materials, such as lignin, cellulose, and pectin, which are used to manufacture industrial products such as microbial pigments, organic acids, biofuels, aroma compounds, enzymes, protein enriched feed, and bioactive secondary metabolites [35]. Since these residues are abundant in pectin, they can be used in the production of the pectinase enzyme [36].
Different agricultural and agro-industrial wastes such as orange peel, lemon peel, banana peel, wheat bran, apple pomace, sugarcane bagasse, soy bran, coffee waste, papaya peel, grape pomace, strawberry pomace, mango peel, satkara peel, used tea, pineapple peel, and sunflower heads have been reported as the substrates used for pectinase production using SSF [16,17,18,23,37,38]. Among these, orange peels, with their high pectin content, have been used as a low-cost substrate for pectinase production in both SSF and SmF [39,40]. In the process of orange juice production, about 50% (by wt) of orange fruits are disposed of as peels, seeds, membranes, and juice vesicles. The use of these by-products as substrates in SSF for enzyme production has solved the disposal problem [11]. A combination of sugarcane bagasse and citrus pulp was utilized for the production of pectinase in SSF with Aspergillus oryzae [24]. Citrus fruit waste and wheat bran were used for polygalacturonase production in SSF [12]. Orange pomace, a citrus waste, has been used for pectinase production in SSF using Aspergillus niger [41]. The enhanced production (36.88 U/mL) of exo-polygalacturonase and (0.62 U/mL) endo-polygalacturonase was reported from a Penicillium oxalicum strain utilizing orange peel as the carbon source [42]. Additionally, maximum polygalacturonase production (12.12 U/mL) was obtained from an Aspergillus flavus strain when using orange peels as substrate [43].
The production of microbial pectinase has been reported by both solid-state fermentation and submerged fermentation. Solid-state fermentation, when compared to submerged state fermentation, is an attractive process for the microbial production of enzymes. SSF involves the substrate without free water; only filamentous fungi can grow considerably in this process [44]. SSF has several advantages over SmF, such as a low capital cost, low energy expenses, cheaper downstream processing, low output of wastewater, non-aseptic conditions, usage of a large variety of matrices, high productivity, high product concentration, high reproducibility, no foam formation, less fermentation space, and simple fermentation media [45].
The use of different optimization techniques for the enhancement of the production of microbial pectinase has been reported by many researchers. The optimization of enzyme production by one-factor-at-a-time (OFAT) is a conventional method that is time-consuming and laborious. It does not take into consideration the interactions between factors. The use of statistical methods is an effective optimization approach. It allows for the rapid screening of a large number of experimental domains and reflects the role of all the components [46]. Response surface methodology (RSM) is an experimental approach for obtaining the optimum conditions for a multivariable system. It is used for the optimization of process and media components in SSF for pectinase production [47]. Optimization through response surface methodology (RSM) based on central composite design (CCD) resulted in a 2.65-fold increase in polygalacturonase production by Aspergillus fumigates R6 [25]. Optimization through RSM with CCD improved the yield of pectinase enzyme using Rhizopus sp. C4 under SSF [31]. The Plackett–Burman design (PB design) and fractional factorial design (FFD) indicated the main factors that affected the pectinase production and improved its production by Aspergillus giganteus in SSF [48].
Due to the extensive industrial applications of pectinases, there is a need for continuous research to address different challenges in the production and commercialization of pectinase enzymes. A higher production cost is one of the hurdles in the commercialization of new sources of enzymes [8]. The use of novel strains, cheap raw materials, a favorable fermentation environment, and efficient downstream processing can decrease the cost [37]. Another hurdle is the stability of the pectinase enzyme in severe temperatures, adverse pH environments, and organic solvents which has limited its application in commercial processes. Additionally, the expense incurred in broad applications of the pectinase enzyme is higher due to its unstable nature. Therefore, thermostable enzymes are gaining importance [49]. To further reduce the cost of the enzyme for its efficient use, efforts can be made to immobilize pectinases onto cost-effective materials using different techniques [50]. Another way to reduce the cost of enzyme production for a specific application is to isolate the strains that can produce pectinase along with other enzymes and use the mixture for different specific applications [33].
Therefore, keeping all this in view, the current work focused on the use of novel strains, low-cost substrates, and favorable operating conditions and optimization techniques for the low-cost production of the pectinase enzyme which could overcome one of the obstacles in the commercialization of the enzyme. The present paper mainly focuses on the isolation and screening of a new potent pectinase-producing fungus from local environmental conditions. The use of this isolated novel fungal species for pectinase production using low-cost agro-industrial waste, in addition to optimization of the media components, has shown the enhanced production of pectinase using RSM-CCD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Software Used
All the media components were purchased from HiMedia Laboratories, Mumbai, India. All other chemicals, such as organic solvents, mineral salts, and buffer components, were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals Private Limited, Delhi, India. Minitab 17 Statistical Software (Minitab, LLC, State College, PA, USA) was used for the statistical optimization of pectinase production.
2.2. Isolation and Screening of Pectinolytic Fungi
In total, 27 different fungal isolates were isolated from samples taken from decayed fruit peels (orange, banana, and lemon) and soil containing decomposed vegetables brought from a local vegetable market-Durgadbail, Hubballi, Dharwad District, Karnataka, India. For the isolation of fungi, serial dilution and spread plate methods were used. All the fungal isolates were screened for pectinase activity using the pectin agar medium of composition (g/L): pectin, 5; peptone, 5; yeast extract, 5; KH2PO4, 2.5; NaCl, 2.5; and agar, 16 [51]. The pectinolytic activity of the isolates was evaluated by the zone of clearance (halo) and pectinase activity. In addition, these isolates were preserved on potato dextrose agar (PDA) slants and periodically sub-cultured.
2.3. Production of Pectinase
Inoculum was prepared in the modified medium proposed by Darah et al. [52] consisting of (g/100 mL): yeast extract (YE), 0.3; peptone, 0.5; FeSO4·7H2O, 0.01; NaH2PO4, 0.5; CaCl2·2H2O, 0.01; KCl, 0.5; KH2PO4, 0.1; ZnSO4·7H2O, 0.002; MgSO4·7H2O, 0.5; and Pectin, 5. The media was sterilized, cooled, and inoculated with a loop full of culture. It was incubated at 37 °C for 10 days until the spores were produced. Then, 15 mL of the moisture solution at pH 5.0 with a composition of (g/100 mL): yeast extract (YE), 0.3; peptone, 0.5; FeSO4·7H2O, 0.01; NaH2PO4, 0.5; CaCl2·2H2O, 0.01; KCl, 0.5; KH2PO4, 0.1; MgSO4·7H2O, 0.5; and ZnSO4·7H2O, 0.002, was added to 10 g of 2 mm uniformly sized dried orange peel powder (substrate) obtained from a sieve shaker (Universal Instruments, India). It was sterilized, cooled, and inoculated with 106 cells/mL inoculum and uniformly mixed. This inoculated flask was incubated at 37 °C for 5 days. A 100 mL quantity of 0.1 M citrate buffer (pH 4.5) was added to the fermented solids and kept in the shaker incubator for 3 h at 37 °C and 130 rpm. The fermented solids and the biomass were removed by filtration using a muslin cloth. The obtained filtrate was further centrifuged at 4 °C, 10,000 rpm, for 15 min. The supernatant, obtained from centrifugation, was taken for enzyme assay.
2.4. Pectinase Activity
The pectinase activity was estimated by measuring the release of reducing groups (galacturonic acid) in the reaction mixture containing the pectinase enzyme and 1% citrus pectin as a substrate. The pectin was hydrolyzed by pectinase into galacturonic acid units, and the quantification of hydrolysis of the pectin substrate was carried out by the 3, 5-Dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) reagent assay method described by Miller [53]. The reaction mixture consisted of 1% pectin in 0.1 M citrate buffer (pH 4.5) and pectinase enzyme and was incubated for 1 h. To this reaction mixture, DNS reagent was added and kept in a water bath for 10 min. The reaction mixture was then cooled and the absorbance was measured using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu 1900, Kyoto, Japan) at 540 nm. The reducing sugars convert 3, 5-Dinitrosalicylic acid, under an alkaline condition, to 3-amino-5-nitrosalicylic acid, an orange-yellowish compound that has an absorption maximum at 540 nm. A standard graph of D-galacturonic acid was prepared to check the enzyme activity. One international unit of enzymatic activity (IU) was defined as the quantity of enzyme which produced one µmol of galacturonic acid per minute under assay conditions. Enzyme activity (EA) in (IU/mL) was calculated using Equation (1) [54].
where ‘v’ represents the enzyme volume, ‘194.1’ represents the molecular weight of galacturonic acid, and ‘t’ represents the reaction time in min.
2.5. Molecular Identification of the Isolate ARS2
The isolate ARS2 identification was done at the National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms (NCIM), NCL, Pune, India, by the 18S rRNA sequencing method. A spin column kit was used to extract chromosomal DNA. Amplification of the fungal 18S rRNA gene (1500 bp) [55] was done using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in a thermal cycler using primer NS1_NS4_Seq178_ARS2. It was thenpurified by using Exonuclease I—Shrimp Alkaline Phosphatase.The purified ampliconswere sequenced in an ABI 3500xLgenetic analyzer (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). CHROMASLITE version 1.5 (Technelysium Pty Ltd., South Brisbane, QLD, Australia) was used to edit the sequencing files which were analyzed by the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST).The National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database was used to obtain the closest culture sequence based on the local similarity between sequences [56]. Further, for the accurate prediction of species and evolutionary relationships, multiple sequence alignment, and phylogenetic tree analysis were done. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Kimura 2-parameter method and are in units of the number of base substitutions per site. The analysis involved 16 nucleotide sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA6.
2.6. One-Factor-at-a-Time (OFAT) Studies of Media Components
To understand the influence of various media components on pectinase production by isolated fungi ARS2, OFAT studies were conducted. The effect of various carbon sources, nitrogen sources, and mineral salts on pectinase activity was studied [23]. The composition of different carbon sources is reported by previous studies; the orange peel contains approximately carbohydrates, 53.27; protein, 9.73; fibers, 14.19; ash, 5.17; and lipids, 8.70 g/100 g dry peel [57]. The apple peel consists of carbohydrates, 59.96; protein, 2.80; fibers, 13.95; ash, 1.39; and lipids, 9.96 g/100 g dry peel [57]. The banana peel composition is made up of carbohydrates, 43.40; protein, 10.44; lipid, 8.40; and ash, 12.45 g/100 g dry peel [57]. The composition of sweet lime peel contains carbohydrates,12.07; protein, 12.26; fat, 0.16; and fibers, 4.34 g/100 g dry peel [58]. The carrot peel composition is made up of carbohydrates, 9.68; protein, 1.65; fat, 0.3; and ash, 0.6 g/100 g dry peel [59]. The lemon peel consists of carbohydrates, 30.74; protein, 3.59; fat, 0.3; ash, 1.79; and fibers, 4.78 g/100 g dry peel [60]. The carbon sources considered for the study were 10 g of 2 mm dried, powdered, and sieved peels of apple, banana, carrot, lemon, sweet lime, and orange stored in different 250 mL conical flasks. The moisture solution used was of the composition (g/100 mL): yeast extract (YE), 0.3; peptone, 0.5; FeSO4·7H2O, 0.01; NaH2PO4, 0.5; CaCl2·2H2O, 0.01; KCl, 0.5; KH2PO4, 0.1; MgSO4·7H2O, 0.5; and ZnSO4·7H2O, 0.002. Based on optimum pectinase activity, a particular carbon source was fixed, and the effect on different nitrogen sources was studied. In each conical flask containing 10 g of a selected carbon source, a moisture solution was added containing one nitrogen source of 0.5 g/100 mL and other mineral salts with concentrations as mentioned in the moisture solution. Based on the optimum pectinase activity, a particular nitrogen source was selected to study further the effect of different mineral salts on pectinase activity. To study the effect of different mineral salts, each flask containing 10 g of selected carbon source was added, and a moisture solution was prepared by including one nitrogen and one mineral salt in the media of respective concentration as mentioned in the moisture solution. All the experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.7. Screening of Media Components by Plackett–Burman Design
Plackett–Burman design was used to screen the most significant media components that play a vital role in the production of pectinase [16]. Based on the OFAT analysis, the low and high levels of carbon sources, nitrogen sources, and mineral salts were fixed. A total of six different carbon sources were screened through twelve experimental runs using the PB design, keeping other components of the media constant. Carbon sources (2 mm size) considered for screening were the peels of oranges, lemons, sweet lemons, apples, bananas, and carrots. These carbon sources vary from low levels (−1) to high levels (+1), as indicated in Table 1. The experimental trials were designed using Minitab 17 software. Varying amounts of the solid substrate (carbon source) were taken in 12 different flasks. The moisture content was fixed to 100% by a moisture solution (mineral salt solution). The flasks were sterilized at 121 °C for 20 min and, upon cooling, inoculated with a 3% spore suspension containing approximately106 spores/mL. After mixing, the flasks were incubated at 37 °C for 6 days. Samples were collected after 6 days and were assayed for pectinase activity. The PB design results were generated by Minitab 17 software. Similarly, ten different nitrogen sources and seven different mineral salts were screened (using orange peel as a carbon source) through twelve experimental runs, each with a low level (−1) and a high level (+1), as indicated in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively.

Table 1.
The low and high levels of carbon sources used in the PB design.

Table 2.
The low and high levels of nitrogen sources used in the PB design.

Table 3.
The low and high levels of mineral salts used in the PB design.
2.8. Optimization of Pectinase Production Using Response Surface Methodology and Central Composite Design
The statistical optimization of the media components affecting the pectinase production was performed by CCD to increase the enzyme yield. The central composite design is an experimental design that is helpful in response surface methodology for framing a second order (quadratic) model for the response variable without using an entire three-level factorial experiment [61]. Using the results of OFAT and the PB design studies, the significant factors (orange peel, peptone, NaH2PO4, and KH2PO4) affecting pectinase production were further optimized using RSM-CCD. It comprised 31 runs at five levels (−α, −1, 0, 1, and +α) involving four significant media components based on the PB design results. The pectinase activity (response) was fitted by a second-order model to correlate the response to the independent parameters. Equation (2) indicates a general quadratic equation for RSM-CCD using four factors.
where Y indicates the response (enzyme activity) of the design, βo represents the model intercept, β1 to β4 represent the coefficients for linear terms, β11 to β44 represent quadratic coefficients, and β12to β34 represent the cross product coefficient indicating the interaction between parameters. A, B, C, and D represent different media components used for optimization. The values of different levels of independent parameters are shown in Table 4. The analysis of variance (ANOVA), Pareto chart, main effect plot, 3D response surface diagram, and 2D contour plot were obtained using Minitab 17 software.
Y = βo + β1A + β2B + β3C + β4D + β11A2 + β22B2 + β33C2 + β44D2 + β12AB + β13AC + β14AD + β23BC + β24BD + β34CD

Table 4.
The levels of media components used in RSM-CCD.
2.9. Model Validation
The solid-state fermentation media was prepared based on the optimal values of different media parameters obtained from the Minitab optimizer during optimization studies and was validated by conducting experiments in triplicate [38]. The experimental enzyme activity value was compared with the predicted value by the optimizer and the prediction error was calculated.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Screening of Pectinolytic Fungi
The samples taken from the soil containing decomposed vegetables and decayed fruit peels (orange, banana, and lemon) were used for the isolation of pectinolytic fungi. Twenty-seven isolates were obtained, out of which, seven isolates were screened for pectinase production by SSF by considering orange peel as substrate. Among the seven fungal isolates, ARS2 (41.88 ± 1.57 IU/mL) and ARS8 (39.27 ± 1.14 IU/mL) had the maximum pectinase activity, as indicated in Figure 1a. The enzyme activity of the two fungal isolates, ARS2 and ARS8, were compared at different incubation times. The enzyme activity of both the isolates was found to be maximized on the sixth day of incubation. However, ARS2 (43.05 ± 1.38 IU/mL) showed more pectinase activity than ARS8 (34.49 ± 1.27 IU/mL), as shown in Figure 1b. Therefore, ARS2 isolated from decayed orange peel was found to be the potential isolate and was considered for further studies. The isolated fungal strain ARS2 was characterized morphologically and found to be in the genus Aspergillus, as shown in Figure 2. In order to determine the species of the isolated strain, molecular characterization with 18S rRNA sequencing was performed.
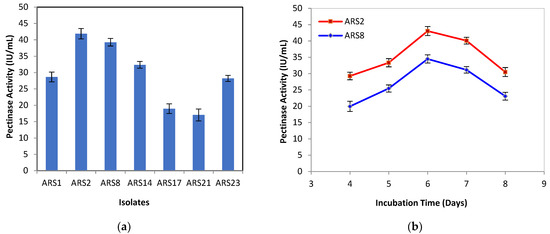
Figure 1.
Pectinase activity for (a) different isolates and (b) isolates ARS2 and ARS8 at different incubation times.
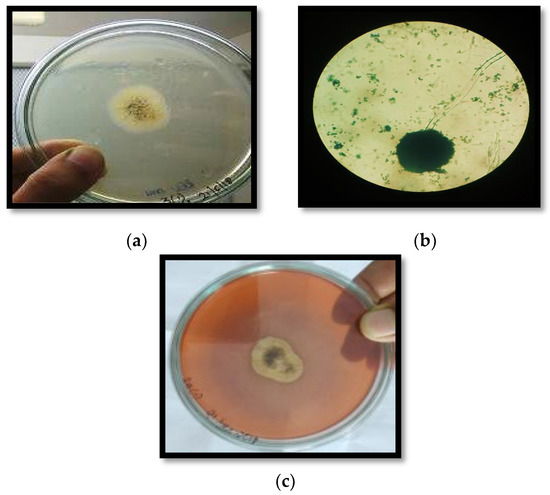
Figure 2.
Characterization of the isolate ARS2 (a) point inoculated, (b) lacto phenol cotton blue staining (40×) scale bar (100 μm), and (c) qualitativescreening based on the zone of clearance.
Darah et al. [52] reported the isolation of Aspergillus niger HFD5A-1 from rotten Malaysia oranges to produce the pectinase enzyme. Amilia et al. [51], in their research work, isolated Pencillium, Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Trichoderma species from the decayed peels of bananas and oranges and found orange peels as a potential source.
3.2. Molecular Characterization of the Isolate ARS2
The potential isolate ARS2 was identified using the 18S rRNA sequencing method. The 18S rRNA sequence of the ARS2 isolate was submitted to BLAST to extract the homologous sequence from the NCBI database. Further, the top homologous sequence was used to perform a multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis. The phylogram shown in Figure 3 shows that the ARS2 isolate is in close homology with AB0083971 Aspergillus cervinus. Hence, the isolate ARS2 was identified as Aspergillus cervinus. The sequence of the isolate ARS2 was submitted to the NCBI Genbank database, and accession number MN238704 was obtained. The isolate ARS2 belongs to the Aspergillus genus and cervinus species and is a member of the Trichocomaceae family. It includes species with radiate or short columnar, fawn-colored, and uniseriate conidial heads [62]. Aspergillus cervinus is reported to produce xanthocillin, terremutin, 5-toluquinone, dihydroxy-2, and sclerin [63]. Based on the extensive literature review, the present paper is the first research article on pectinase production by the Aspergillus cervinus strain.
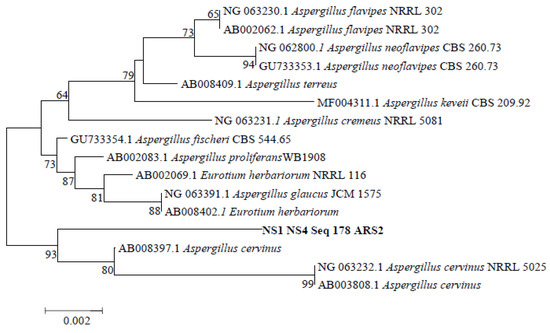
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree indicating the position of the isolate Aspergillus cervinus ARS2 compared to other species of the genus Aspergillus using 18S rRNA sequencing.
3.3. One-Factor-at-a-Time Studies of Media Components
3.3.1. Effect of Carbon Sources
A one-factor-at-a-time study of media components was conducted to know the level of each parameter affecting the enzyme activity and was further used in the PB design and RSM-CCD. The use of purified pectin as the carbon source is uneconomical, so the agro-industrial residues were considered economical and used for large-scale pectinase production. Different agro-industrial wastes such as apple peel, banana peel, lemon peel, orange peel, carrot peel, and sweet lime peel were used and tested for pectinase production. It can be inferred that orange peel offered the maximum enzyme activity (around 44.51 ± 1.33 IU/mL), followed by lemon peel (42.45 ± 0.88 IU/mL), carrot peel (41.31 ± 0.96 IU/mL), banana peel (31.70 ± 1.34 IU/mL), sweet lime peel (31.60 ± 1.33 IU/mL), and apple peel (16.61 ± 1.01 IU/mL), as shown in Figure 4a. Among different carbon sources, the orange peel was observed to be a potential carbon source for pectinase production. This might be due to the high pectin content and the presence of other nutrients, such as minerals, fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, in orange peels [64]. Since the substrate plays a vital role in defining the economics of an enzyme production process, different agricultural substrates were considered by several workers for pectinase production.
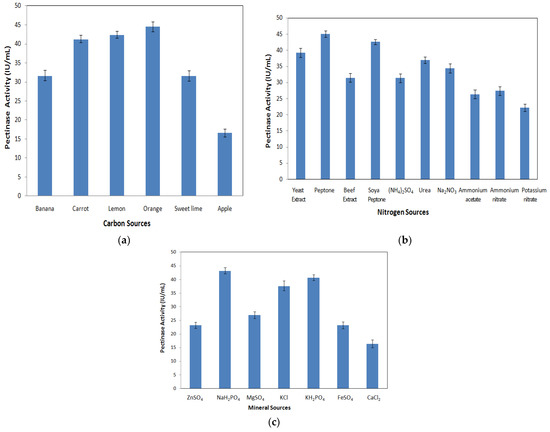
Figure 4.
Pectinase activity of Aspergillus cervinus ARS2 for different (a) carbon sources, (b) nitrogen sources, and (c) mineral sources.
The research work by Mrudula and Anitharaj [65] showed an optimum pectinase production with Aspergillus niger and orange peels as a carbon source, which supports the present findings. Darah et al. [52] reported that a medium supplemented with citrus pectin showed maximum pectinase activity (1.66 U/mL) when using Aspergillus niger HFD5A-1. Sethi et al. [66] showed increased pectinase production using banana peels as a carbon source with Aspergillus terreus NCFT4269.10. Govindaraji and Vuppu [67] reported orange peel as responsible for the highest pectinase activity (45.93 U/mL) with a novel strain, Streptomyces fumigatiscleroticus VIT-SP4, which supports the present findings. Ahmed and Awad [27] observed the highest pectinase activity (0.48 U/mL) for orange peels as the carbon source with Pencillium chrysogenum MF318506. Finally, Satapathy et al. [23] found pectinase activity of 1366 ± 36.71 U/mL using Aspergillus parvisclerotigenus KX928754 with apple pomace as the carbon source.
3.3.2. Effect of Nitrogen Sources
The different nitrogen sources considered for OFAT studies were organic nitrogen sources (soya peptone, yeast extract, peptone, and beef extract) and inorganic nitrogen sources (potassium nitrate, urea, (NH4)2SO4, Na2NO3, ammonium acetate, ammonium nitrate, and potassium nitrate). From Figure 4b, it was observed that both organic and inorganic nitrogen sources influenced enzyme production. In the current study, peptone showed a maximum pectinase activity (45.05 ± 1.04 IU/mL), followed by soya peptone (42.57 ± 0.80 IU/mL), yeast extract (39.23 ± 1.38 IU/mL), and beef extract (31.43 ± 1.35 IU/mL). In the case of inorganic nitrogen sources, urea showed the maximum pectinase activity (36.96 ± 0.99 IU/mL), followed by Na2NO3 (34.44 ± 1.41 IU/mL), (NH4)2SO4 (31.34 ± 1.39 IU/mL), ammonium nitrate (27.36 ± 1.37 IU/mL), ammonium acetate (26.32 ± 1.36 IU/mL), and potassium nitrate (22.19 ± 1.13 IU/mL). Results show that organic nitrogen sources served as a better nitrogen supplement for the enhancement of pectinase activity with Aspergillus cervinus. This may be due to the hydrolysis of the organic nitrogen sources, their mineral components, and other growth factors of the fungi into constituents that can be easily incorporated into the cellular metabolism. The inhibitory nature of different nitrogen sources may be due to the disturbance in the balance between carbon and nitrogen sources in the medium. Because of this, the pH control of the system is lost [68]. Mathew et al. [69] reported maximum polygalacturonase production by Pencillium SPC-F 20 using organic nitrogen sources and Rangarajan et al. [70] observed organic nitrogen sources were better when compared with inorganic nitrogen sources for pectinase production using Aspergillus niger.
In the current study, peptone showed the highest enzyme activity, which may be due to the presence of minerals and micronutrients that provide critical nutritional support for cell growth and proliferation. Akhter et al. [71] claimed peptone (organic nitrogen) increased the pectinase yield. Darah et al. [52] reported that a medium supplemented with peptone gave the highest pectinase yield (1.95 U/mL) with Aspergillus niger HFD5A-1. Sethi et al. [66] reported peptone as the best organic nitrogen source for the highest pectinase activity, which is in line with the present findings. The same researcher also reported ammonium persulfate as the best inorganic nitrogen source, which increased pectinase activity by about three-fold. Amin et al. [26], in their research work, found glycine as the suitable nitrogen source for polygalacturonase using Penicillium notatum, while ammonium sulfate favored the enzyme production of polygalacturonase with Coriolus versicolor. In the previous study done by Satapathy et al. [23], peptone exhibited maximum enzyme activity (1623.51 ± 13.93 U/mL) when using Aspergillus parvisclerotigenus KX928754.
3.3.3. Effect of Mineral Salts
The influence of mineral salts such as ZnSO4, NaH2PO4, MgSO4, KCl, KH2PO4, FeSO4, and CaCl2 on pectinase production was evaluated. Figure 4c reveals that the maximum enzyme activity (43.21 ± 1.12 IU/mL) was obtained for NaH2PO4, followed by KH2PO4 (40.70 ± 1.03 IU/mL), KCl (37.67 ± 1.81 IU/mL), MgSO4 (26.99 ± 1.24 IU/mL), FeSO4 (23.24 ± 1.25 IU/mL), ZnSO4 (23.23 ± 1.12 IU/mL), and CaCl2 (16.47 ± 1.40 IU/mL). Among different mineral salts, NaH2PO4 was found to be a potential mineral salt for the production of the pectinase enzyme due to its role in maintaining osmotic flux, membrane transport, and the release of enzymes from cells. Additionally, it may be due to the increased regulation of respective genes at the transcriptional level [16]. Since pectinase is a metallo enzyme, it is activated in the presence of particular metals [26]. Mahesh et al. [72] reported KH2PO4 as the potential mineral salt that gave the maximum pectinase activity with Aspergillus niger. According to Amin et al. [26], MnSO4 mineral salt significantly increased the enzyme production of Pencillium notatum and CaCO3 stimulated the enzyme activity of Coriolus versicolor.
3.4. Screening of Media Components by Plackett–Burman Design
3.4.1. Screening of Carbon Sources
To screen different carbon sources, nitrogen sources, and mineral salts, a PB design was used to identify significant variables affecting the pectinase activity (response) with two-factor interactions. A total of 12 experiments were designed by Minitab 17 software for screening six different carbon sources (Table 5 and Table 6), ten different nitrogen sources (Table 7 and Table 8), and seven different mineral salts (Table 9 and Table 10) and to identify the factors playing a significant role on pectinase activity.

Table 5.
The PB design matrix for carbon sources with the response.

Table 6.
The ANOVA table for the PB design of carbon sources.

Table 7.
The PB design matrix for nitrogen sources with the response.

Table 8.
The ANOVA table for the PB design of nitrogen sources.

Table 9.
The PB design matrix for mineral salts with the response.

Table 10.
The ANOVA table for the PB design of mineral salts.
The results of the ANOVA, shown in Table 6, for carbon sources indicated that the model p-value (<0.001) is <0.05, indicating significance. The p-values of different carbon sources, i.e., orange peel (<0.001), lemon peel (<0.001), sweet lemon peel (<0.001), banana peel (0.035), and apple peel (0.002), indicated that they are also significant media components and have a significant effect on pectinase activity. The p-value of carrot peel is 0.493 (and thus greater than 0.05) which indicates that it is insignificant, as also indicated by the Pareto chart shown in Figure 5a. From the regression analysis, the R2–coefficient of determination was calculated as 90.23% (0.9023) for pectinase activity, which is closer to 1, indicating the linearity of the model. The experimental R2 agrees with the adjusted R2 and predicted R2 (Table 6), indicating the significance of the model.
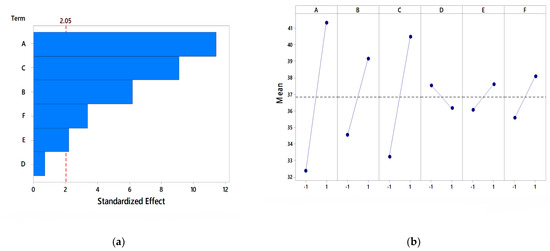
Figure 5.
Analysis of the PB design for carbon sources (a) Pareto chart, (b) main effect plot.
The Pareto chart was used as a tool for analyzing the significant parameters in the PB design. The Pareto chart separates highly significant factors by identifying the factor which has the greater effect on the response (enzyme activity). In the present analysis, except carrot peel, all factors are significant, with orange peel as the most significant parameter at a 95% confidence level, as shown in Figure 5a. Thus, orange peel was further used for optimization studies using RSM-CCD. Main effect plots are used to show the average response (enzyme activity) for each media component. In the main effect plots, as indicated in Figure 5b, the average response for orange peel was highest and at a higher level compared to the other carbon sources. This indicates that orange peel has a significant effect on pectinase activity. The main effect plot of banana peel and carrot peel is nearer to horizontal, which shows less impact on enzyme activity. Amin et al. [26] found wheat bran as the significant carbon source for pectinase production with Pencillium notatum and Coriolus versicolor and Ahmed et al. [16] reported satkara peel as the significant carbon source for pectinase production with Aspergillus niger-ATCC 1640 using the PB design.
3.4.2. Screening of Nitrogen Sources
The PB design was used to screen different nitrogen sources to recognize the significant variables affecting the response (enzyme activity).
For nitrogen source screening, the ANOVA table, as shown in Table 8 indicated that the model p-value (<0.001) is <0.05, which indicates that it is significant. Further p-values of nitrogen sources, i.e., urea (<0.001), yeast extract (<0.001), peptone (<0.001), beef extract (0.010), and soya peptone (<0.001), are significant parameters and have a significant effect on pectinase activity. The p-value for Na2NO3 (0.284), (NH4)2SO4 (0.254), ammonium nitrate (0.968), ammonium acetate (0.643), and potassium nitrate (0.584) are greater than 0.05, indicating insignificant parameters also seen in the Pareto chart analysis in Figure 6a. From the regression analysis, the R2–coefficient of determination was calculated as 97.79% (0.9779) for pectinase enzyme activity, which is closer to 1, indicating the linearity of the model. This explains that 97.79% of the variability of the response will be explained by the model. The adjusted R2 value is 0.9690, and the predicted R2 value of 0.9541 agrees with the experimental R2, thereby indicating the significance of the model.
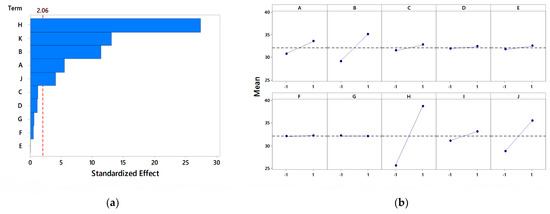
Figure 6.
Analysis of the PB design for nitrogen sources (a) Pareto chart, (b) main effect plot.
In the Pareto chart analysis, peptone, soya peptone, beef extract, and yeast extract were observed to be significant, with peptone as the most significant nitrogen source at a 95% confidence level, as shown in Figure 6a. Thus, peptone was further selected for optimization studies using RSM and CCD. In the main effect plot, as shown in Figure 6b, the average response for peptone was highest and at a higher level compared to the other nitrogen sources. This indicated that peptone has a significant effect on pectinase activity. The main effect plot of Na2NO3, (NH4)2SO4, ammonium nitrate, ammonium acetate, and potassium nitrate are nearer to horizontal, indicating a negligible effect on the enzyme activity. Ortiz et al. [48] found (NH4)2SO4 as a significant nitrogen source for pectinase production using the PB design with Aspergillus giganteus. Enshasy et al. [73] reported (NH4)2SO4 as the significant nitrogen source using the PB design for pectinase production with Aspergillus niger.
3.4.3. Screening of Mineral Salts
The PB design was used to screen different mineral salts to recognize the significant variables affecting the response (enzyme activity).
The ANOVA table for mineral salts shown in Table 10 indicates that the model p-value (<0.001) is less than 0.05, indicating that it is significant. Further p-values of mineral salts, i.e., KCl (<0.001), ZnSO4 (0.046), NaH2PO4 (<0.001), KH2PO4 (<0.001), and MgSO4 (<0.001), indicate significant media components thathave a significant effect on enzyme activity. The p-value for CaCl2 (0.845) and FeSO4 (0.345) were greater than 0.05, indicating insignificant parameters, as also represented by the Pareto chart shown in Figure 7a at a 95% confidence level. Based on the Pareto chart, NaH2PO4 was found to be the most significant and was considered for optimization using RSM-CCD. From the regression analysis, the R2–coefficient of determination was calculated as 87.70% (0.8770) for enzyme activity, which is closer to 1, indicating the linearity of the model. This explains that 87.70% of the variability of the response will be explained by the model. The adjusted R2 value is 0.8462, and the predicted R2 value of 0.7967 agrees with experimental R2, thereby indicating the significance of the model.
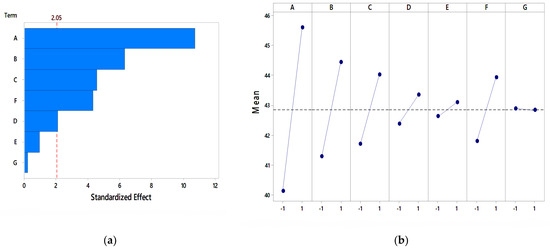
Figure 7.
Analysis of the PB for mineral salts (a) Pareto chart, (b) main effect plot.
In the main effect plots, as shown in Figure 7b, the average response for NaH2PO4 was highest and at a higher level compared to the other mineral salts. This indicated that NaH2PO4 had a significant effect on pectinase activity. The main effect plot of CaCl2 and FeSO4 is nearer to horizontal, which indicates a negligible effect on enzyme activity. Ortiz et al. [48] found CaCl2 and KH2PO4 as significant mineral salts by PB design for pectinase production with Aspergillus giganteus. Additionally, the PB design of media components conducted by Enshasy et al. [73] showed K2HPO4 as a significant mineral salt for pectinase production using Aspergillus niger.
3.5. Optimization of Pectinase Production
Optimization studies of the media components for determining the maximum pectinase activity of Aspergillus cervinus ARS2 were done by taking the following significant media components: orange peel, peptone, NaH2PO4, and KH2PO4. The CCD matrix and results of the experiment are shown in Table 11. The model given by Equation (3) indicates pectinase activity as a function of KH2PO4 (A), peptone (B), NaH2PO4 (C), and orange peel (D).
EA(IU/mL) = 1.16592 + 0.00089 A + 0.01182 B + 0.03634 C + 0.00642 D − 0.00772 A × A − 0.001115 B × B − 0.00917 C × C − 0.000302 D × D − 0.000197 A × B + 0.00855 A × C + 0.001323 A × D − 0.000767 B × C − 0.000095 B × D − 0.001129 C × D

Table 11.
The CCD matrix for the media components with the experimental and predicted response.
The statistical significance of the quadratic regression model was verified by the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Fisher’s test (F). The high value of ‘F’ and the low value of ‘p’ indicate the model is significant. The coefficient of determination (R2) for the model was found to be 85.98% (0.8598), which is close to 1, indicating the fitness of the model and a better correlation between the experimental and predicted enzyme activity. The R2 value in percentage (85.98%) indicates the variation in pectinase activity due to the independent parameters, and the remaining 14% is the total variation that cannot be explained by the model. The R2 predicted value of 0.7862 indicated a better correlation between the experimental and predicted enzyme activity. The R2 predicted value of 0.7862 is in agreement with the R2 adjusted value of 0.8347. The adjustedR2 fixes the R2 value based on the sample size and the number of parameters in the model. The adjustedR2 (0.8347) is smaller than the R2 (0.8598) because of the small sample size in the model.
From the ANOVA in Table 12, it was found that the linear effects/p-value of peptone (<0.001), orange peel (<0.001), and NaH2PO4 (<0.001) and interaction effects/p-value of KH2PO4 and NaH2PO4 (<0.001), KH2PO4and orange peel (<0.001), and NaH2PO4 and orange peel (0.002) and squared effect/p-value of all media components were highly significant for pectinase production as the p-values of all were less than 0.05. The linear effect of KH2PO4 (0.881) and interaction effects of KH2PO4and peptone (0.782), peptone and NaH2PO4 (0.283), and peptone and orange peel (0.426) were found to have no significance.

Table 12.
The ANOVA table for RSM-CCD.
The Pareto chart reports the significant media components affecting pectinase production as shown in Figure 8. The linear effect of KH2PO4 and interaction effect between peptone and NaH2PO4, peptone and orange peel, and peptone and KH2PO4 were found to be insignificant. The regression equation obtained from the analysis of RSM can be represented by 3-dimensional surface plots and 2-dimensional contour plots. Response surface curves are used to determine the optimum values of the components for maximum enzyme production and to know the interaction between the components. The effect of the two parameters on the enzyme activity is indicated by 3D surface plots and 2D contour plots, as shown in Figure 9.
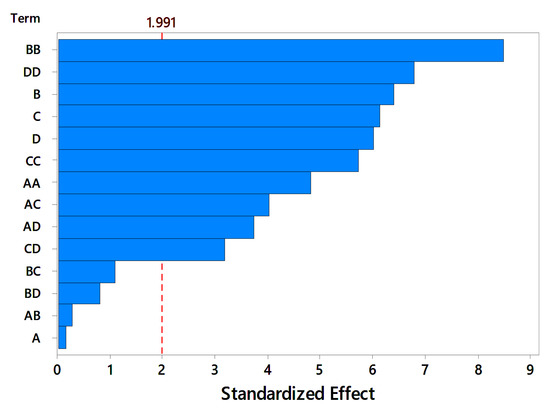
Figure 8.
Pareto chart showing the standardized effects of four variables.
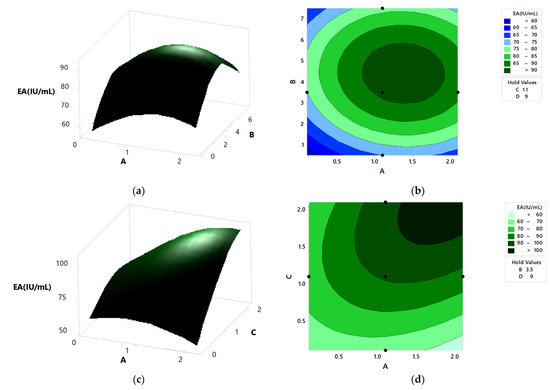
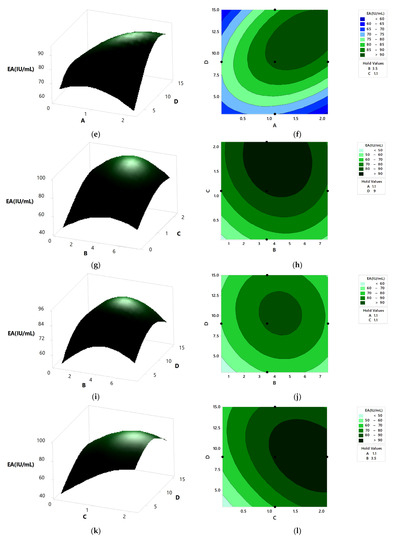
Figure 9.
The 3D surface plots and 2D contour plot showing the relative effect of media components on pectinase activity; (a,b) peptone and KH2PO4, (c,d) NaH2PO4 and KH2PO4, (e,f) orange Peel and KH2PO4, (g,h) NaH2PO4 and peptone, (i,j) orange peel and peptone, and (k,l) orange peel and NaH2PO4.
Figure 9a,b represents the relative effects of peptone (0.5–6.5 g/L) and KH2PO4 (0.1–2.1 g/L) on pectinase activity, while holding orange peel and NaH2PO4 constant at 9.0 g and 1.1 g/L, respectively. Pectinase production was maximum at the mid values of peptone and KH2PO4. With the increase in peptone and KH2PO4, there was an increase in pectinase activity, which reached the maximum at mid values and then decreased. Figure 9c,d shows the relative effects of KH2PO4 (0.1–2.1 g/L) and NaH2PO4 (0.1–2.1g/L) on pectinase activity when orange peel and peptone are kept constant at 9.0 g and 3.5 g/L, respectively. At the high value of NaH2PO4 and mid value of KH2PO4, enzyme production was the highest. The relative effects of KH2PO4 (0.1–2.1 g/L) and orange peel (3.0–15.0 g), keeping NaH2PO4 and peptone constant at 1.1 g/L and 3.5 g/L, respectively, are shown in Figure 9e,f. It was observed that the enzyme activity was maximized at a high value of orange peel and mid value of KH2PO4. From Figure 9g,h, it was found that the enzyme activity increased with the increase in peptone, reached the maximum, and then decreased. The highest enzyme activity was observed at a mid-value of peptone and high value of NaH2PO4, keeping orange peel and KH2PO4 constant at 9.0 g and 1.1 g/L, respectively. The relative effects of peptone and orange peel on enzyme activity, keeping both KH2PO4 and NaH2PO4 constant at 1.1 g/L, are shown in Figure 9i,j. There was an increase in the enzyme activity with the increase in the concentration of peptone and orange peel, which reached a maximum and then decreased. At mid values of peptone and orange peel, the enzyme activity was maximized. Figure 9k,l shows maximum enzyme activity at high values of NaH2PO4 and orange peel, where peptone and KH2PO4 were kept constant at 3.5 g/L and 1.1 g/L, respectively. The enzyme activity increased with the increase in both NaH2PO4 and orange peel.
The optimization results for media components obtained from the Minitab optimizer showed maximum pectinase activity of 105.65 ± 0.31 IU/mL for 10.63 g orange peel, 3.96 g/L peptone, 2.07 g/L KH2PO4, and 2.10 g/L NaH2PO4. Pectinase activity increased by 2.34 folds on optimization of the media components by RSM-CCD. Sharma et al. [74] observed an increase in enzyme activity by a novel strain Pseudozyma sp. SPJ from 71.19 IU/g to 1215.66 IU/g dry substrates when optimized by CCD, which showed a 17-fold increase in yield. Ajayi et al. [61] claimed an improvement in pectinase production by Aspergillus niger when the parameters were optimized by RSM and CCD. According to Govindaraji and Vuppu [67], the media optimization by RSM produced a maximum pectinase activity of 170.05 U/mL by an isolated novel strain, Streptomyces fumigatiscleroticus VIT-SP4, for orange pectin—0.75%, starch—1.17%, and yeast extract—2%. Ahmed and Rahman [27], in their work on optimization using the Box–Behken design (BBD), reported the highest pectinase activity of 1.292 U/mL, an increase of 6.04-fold at 4.5 g/L peptone and 2.5% orange peel. Ahmed et al. [16] reported the highest pectinase activity of 0.6178 μmol/mL using Aspergillus niger-ATCC 1640 under the BBD optimized conditions of (NH4)2SO4 (2.7 g/L), urea (0.5 g/L), and satkara peel (8.4 g/L).
3.6. Model Validation
To validate the model sufficiency, experiments were conducted in triplicate in the laboratory within the experimental range to verify the predicted optima. The experimental results were in concurrence with the predicted value and confirmed the model to be adequate. The optimal values of different media parameters were obtained from the Minitab optimizer, which is shown in Table 13. The predicted enzyme activity corresponding to these optimal values was 106.80 IU/mL, and the experimental value was 105.65 ± 0.31 IU/mL which was in line with the predicted value. The media optimization using RSM-CCD showed the enhancement in pectinase activity by 2.34 fold, and the model was found to be valid for the optimization process.

Table 13.
Media components optimal values for pectinase activity.
4. Conclusions
The present work reports the production of acidic extracellular pectinase for the first time using the indigenously isolated novel strain Aspergillus cervinus ARS2 and economic agro-industrial waste. The fungal isolate ARS2, isolated from decayed orange peels, showed maximum pectinase activity and was morphologically characterized as the Aspergillus genus. The isolated strain was molecularly characterized, and the 18S rRNA sequence was deposited in the NCBI Genbank with accession number MN238704. Based on the screening of different isolates, ARS2 was found to be the potential producer of the pectinase enzyme. The screening of media components by the PB design showed peptone, orange peel, NaH2PO4, and KH2PO4 as significant. Further statistical optimization by RSM-CCD revealed the maximum pectinase activity of 105.65 ± 0.31 IU/mL for 10.63 g orange peel, 3.96 g/L peptone, 2.07 g/L KH2PO4, and 2.10 g/L NaH2PO4. The statistical optimization of media components showed a 2.34-fold increase in pectinase production. This novel strain, Aspergillus cervinus ARS2, has shown better pectinase production than the previous strains reported. Therefore, it can be used for the large-scale production of the enzyme. The use of cheap agro-industrial waste and media optimization has reduced the cost of enzyme production. The future scope of research on pectinase may be focused on elucidating the molecular mechanism that regulates the enzyme secretions and the mechanism of action of distinctive pectinolytic microbes against different agro-industrial substrates. Future research may also focus on protein and genetic engineering to obtain broad-spectrum pectinase with high catalytic affinities and efficient microorganisms, respectively. The application of pectinase in the pharmaceutical and textile industries is the least explored and needs to be strengthened as well as its usage to be expanded.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R.S., S.V.D. and U.M.M.; Data curation, A.R.S. and S.A.; Formal analysis, A.B.M., M.H.M., U.M.M. and B.A.M.; Funding acquisition, A.B.M., A.A., M.H.M. and A.A.K.; Investigation, A.R.S. and S.V.D.; Methodology, A.R.S., S.A. and S.V.D.; Project administration, A.B.M., A.A., I.A.S. and A.A.K.; Resources, M.H.M. and I.A.S.; Software, A.R.S. and S.A.; Supervision, S.V.D. and U.M.M.; Visualization, B.A.M. and A.A.K.; Writing—original draft, A.R.S., S.A. and U.M.M.; and Writing—review and editing, A.A., S.V.D., M.H.M., I.A.S. and B.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through the Large Groups Project under grant number (RGP. 2/159/43/2022), as well as support from the AlMaarefa University researchers supporting program (TUMA-2021–36), AlMaarefa University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia; AlMaarefa University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; and the Department of Biotechnology, KLE Technological University, Hubballi, India, for providing support to this research work. The authors are also thankful to the National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms (NCIM), NCL, Pune, India, for molecular characterization activity.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Reid, I.; Ricard, M. Pectinase in paper making: Solving retention problems in mechanical pulps bleached with hydrogen peroxide. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummadi, S.N.; Kumar, D.S. Microbial pectic transeliminases. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combo, A.M.M.; Aguedo, M.; Goffin, D.; Wathelet, B.; Paquot, M. Enzymatic production of pectic oligosaccharides from polygalacturonic acid with commercial pectinase preparations. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, S.; Anju, M.; Aneesh, E.M.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Recent advancements in the production and applications of microbial pectinases-an overview. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumer, O.J.; Abate, D. Screening and molecular identification of pectinase producing microbes from coffee pulp. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2961767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.R.; Vohra, P.K.; Chopra, S.; Tewari, R. Applications of pectinases in the commercial sector: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, R. Apple juice clarification using fungal pectinolytic enzyme and gelatin. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 573–576. [Google Scholar]
- Jayani, R.S.; Saxena, S.; Gupta, R. Microbial Pectinolytic enzymes: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2931–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, R.; Siddalinga Murthy, K.R.; Sneha, G.; Shabana, S.; Syama, A.; Radhika, V. Partial purification and biochemical characterization of extracellular pectinase from Aspergillus niger isolated from groundnut seeds. J. Appl. Biosci. 2008, 9, 378–384. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Mandal, S.K. Optimization of processing parameters for production of pectinolytic enzymes from fermented pineapple residue of mixed Aspergillus species. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 5, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, H.; Gogus, N.; Tari, C.; Heerd, D.; Lahore, M.F. Optimization of the process parameters for the utilization of orange peel to produce polygalacturonase by solid-state fermentation from an Aspergillus sojae mutant strain. Turk. J. Biol. 2012, 36, 394–404. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/tbtkbiology/issue/11697/139664 (accessed on 30 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Heerd, D.; Yegin, S.; Taric, C.; Fernandez-Lahore, M. Pectinase enzyme—Complex production by Aspergillus spp., in solid state fermentation: A comparative study. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Tari, C. Valorization of wheat bran for the production of polygalacturonase in SSF of Aspergillus sojae. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 54, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, G.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, D. Production, purification and biochemical characterization of an exo-polygalacturonase from Aspergillus niger MTCC478 suitable for clarification of orange juice. 3Biotech 2017, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, M.K.; Nighojkar, A.; Nighojkar, S.; Kumar, A. Purification and characterization of polygalacturonase produced by Aspergillus niger AN07 in solid state fermentation. Can. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 1, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Rana, M.R.; Zzaman, W.; Ara, R.; Aziz, M. Optimization of substrate composition for pectinase production from Satkara (Citrus macroptera) peel using Aspergillus niger-ATCC 1640 in solid-state fermentation. Heliyon. 2021, 7, e08133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.A.; Lawal, B.; Salubi, A.E.; Onibokun, A.E.; Oniha, M.I.; Ajayi, O.M. Pectinase production by Aspergillus niger using pineapple peel pectin and its application in coconut oil extraction. In 4th International Conference on Science and Sustainable Development (ICSSD 2020) IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esawy, M.A.; Gamal, A.A.; Kamel, Z. Optimization of Aspergillus niger NRC1ami pectinase using citrus peel pectin, purification, and thermodynamic characterization of the free and modified enzyme. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, I.G.; Fontana, R.C.; Da Silveira, M.M. Influence of pH and temperature on the production of polygalacturonases by Aspergillus fumigates. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.Y.; Saad, W.Z.; Mohamad, R.; Tahir, P.M. Optimization of cultural conditions for polygalacturonase production by a newly isolated Aspergillus fumigates R6 capable of retting kenaf. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 97, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Song, Y.; Lin, Y.; Qin, Y. A new strain of Aspergillus tubingensis for high activity pectinase production. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakkeeran, E.; Kumar, U.S.; Subramaniam, R. Aspergillus carbonarius polygalacturonases purified by integrated membrane process and affinity precipitation for apple juice production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3293–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satapathy, S.; Soren, J.P.; Mondal, K.C.; Srivastava, S.; Pradhan, C.; Sahoo, S.L.; Thatoi, H.; Rout, J.R. Industrially relevant pectinase production from Aspergillus parvisclerotigenus KX928754 using apple pomace as the promising substrate. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2021, 15, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biz, A.; Finkler, A.T.J.; Pitol, L.O.; Medina, B.S.; Krieger, N.; Mitchell, D.A. Production of pectinases by solid state fermentation of a mixture of citrus waste and sugarcane bagasse in a pilot-scale packed bed bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 111, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tu, T.; Zhang, D.; Ma, R.; You, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, B.; Luo, H.; Xu, B. Two acidic, thermophilic GH28 polygalacturonase from Talaromyces leycettanus JCM 12802 with application potentials for grape juice clarification. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, F.; Bhatti, H.N.; Bilal, M.; Asgher, M. Multiple parameter optimizations for enhanced biosynthesis of exo-polygalacturonase enzyme and its application in fruit juice clarification. Int. J. Food Eng. 2017, 13, 20160256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.E.; Awad, H.M. Optimizing the production of pectinase of orange peel waste by penicillium chrysogenum MF318506 using response surface methodology in submerged fermentation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 11, e3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, A.N.; Mansoldo, F.R.P.; Godoy, M.G.; Firpo, R.M.; Cedrola, S.M.L.; Vermelho, A.B. Production of an endo-polygalacturonase from Fusarium proliferatum isolated from agro-industrial waste. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 38, 102199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, T.; Saman, T.; Irfan, M.; Anwar, F.; Ikram, M.S.; Tabassam, Q. Pectinase production from Schizophyllum commune through central composite design using citrus waste and its immobilization for industrial exploitation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, N.G.; Nabi, M.; Asgher, A.; Shah, H.; Sheikh, M.A.; Asad, M.J. Production of pectinase by Trichoderma harzianum in solid state fermentation of citrus peels. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Handa, S.; Sharma, N.; Pathania, S. Multiple parameter optimization for maximization of pectinase production by Rhizopus sp. C4 under solid state fermentation. Fermentation 2016, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Dutta, T.; Sheikh, J. Extraction of pectinase from Candida isolated from textile mill effluent and its application in bio-scouring of cotton. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 17, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, S.; Ayele, A. Pectinase from microorganisms and its industrial applications. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K. Potential risk and environmental benefits of waste derived from animal agriculture. In Agricultural Wastes Agriculture Issues and Policies Series; Ashworth, G.S., Azevedo, P., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Singh nee’ Nigam, P.; Pandey, A. Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilization; Springer Science + Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh Bari, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Farbeh, F. Optimizing endopectinase production from date pomace by Aspergillus niger PC5 using response surface methodology. Food Bioprod. Process. 2010, 88, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, M.K.; Nighojkar, S.; Kumar, A.; Nighojkar, A. Pectinolytic enzymes- solid state fermentation, assay methods and applications in fruit juice industries: A review. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez Pérez, J.; Chávez Arias, B.S.; de la Vega Quintero, J.C.; Zárate Baca, S.; Pais-Chanfrau, J.M. Multi-objective statistical optimization of pectinolytic enzymes production by an Aspergillus sp. on dehydrated coffee residues in solid-state fermentation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.M.; Ge, X.Y.; Zhang, W.G. Improvement of polygalacturonase production at high temperature by mixed culture of Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10085–10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Zia, M.A.; Hussain, M.A.; Akram, Z.; Naveed, M.T.; Nowrouzi, A. Bioprocessing of citrus waste peel for induced pectinase production by Aspergillus niger, its purification and characterization. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. 2016, 9, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Najafpour, G.D.; Mohammadi, M. Production of pectinases for quality apple juice through fermentation of orange pomace. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 4123–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.J.; Xia, J.L.; Shan, Y.; Nie, Z.Y.; Su, D.L.; Gao, Q.R.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.L. Optimizing production of pectinase from orange peel by Pencillium oxalicum PJ02 using response surface methodology. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, A.J.; Odunfa, S.A.; Olanbiwonninu, A.; Owoseni, M.C. Production of cellulose and pectinase from orange peels by fungi. Nat. Sci. 2012, 10, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, L.R.; Shet, A.R.; Achappa, S.; Desai, S.V.; Hombalimath, V.S.; Kallur, M.M. Statistical optimization of media components for xylanase production by Aspergillus spp. using solid state fermentation and its application in fruit juice clarification. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2021, 33, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.; Manan, M.A. Design aspects of solid state fermentation as applied to microbial bioprocessing. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 4, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavikatti, J.S.; Bodducharl, S.M.; Kamagond, R.S.; Desai, S.V.; Shet, A.R. Statistical optimisation of protease production using a freshwater bacterium Chryseobacterium cucumeris SARJS-2 for multiple industrial applications. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Haque, S.; Niwas, R.; Srivastava, A.; Pasupuleti, M.; Tripathi, C.K.M. Strategies for fermentation medium optimization: An In-depth review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, G.E.; Maria, C.; Mora, P.; Noseda, D.G.; Cazabat, G.; Saravalli, C.; Lopez, M.C.; Gil, G.P.; Blasco, M.; Alberto, E.O. Pectinase production by Aspergillus giganteus in solid state fermentation: Optimization, scale up, biochemical characterization and its application in olive-oil extraction. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, S.; Rout, J.R.; Kerry, R.G.; Thatoi, H.; Sahoo, S.L. Biochemical prospects of various microbial pectinase and pectin: An approachable concept in pharmaceutical bioprocessing. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, g.; Singh, A.; Kaur, A.; Singh, J.; Kaur, J.; Mahajan, R. Microbial pectinases: An ecofriendly tool of nature for industries. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amilia, K.R.; Sari, S.L.A.; Setyaningsih, R. Isolation and screening of pectinolytic fungi from orange (Citrus nobilis Tan.) and banana (Musa acuminata L.) fruit peel. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darah, I.; Haritharan, W.; Lim, S.H. Involvement of physicochemical parameters on pectinase production by Aspergillus niger HFD5A-1. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 7, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Coffman, A.M.; Ju, L.K. Development of reproducible assays for polygalacturonase and pectinase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2015, 72, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romelle, F.D.; Ashwini Rani, P.; Manohar, R.S. Chemical composition of some selected fruit peels. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 4, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarshini, S.; John, S. Analysis of Nutrient Content and Physicochemical Properties of Newly Developed Sweet Lime Peel Vinegar and Sweet Lime Fruit-Peel Combo Vinegar. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2014, 4, 260–262. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.; Muhammad, S.H.; Abdullah, I. Effect of pre-treatments and drying methods on dehydration and rehydration characteristics of carrot. Univers. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Nguyen, N.T.P.; Dinh, D.V.; Kieu, N.T.; Bach, L.G.; Phong, H.X.; Muoi, N.V.; Truc, T.T. Evaluate the chemical composition of peels and juice of seedless lemon (Citrus latifolia) grown in hau giang province, Vietnam. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.A.; Salubi, A.E.; Lawal, B.; Onibokun, A.E.; Ajayi, O.; Ogunieye, T.A. Optimization of pectinase productionby Aspergillus niger using central composite design. Afr. J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. 2018, 19, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gams, W.; Christensen, M.; Onions, A.H.; Pitt, J.I.; Samson, R.A. Infrageneric taxa of Aspergillus. In Advances in Penicillium and Aspergillus Systematics; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.J.; Varga, J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Jiang, X.Z.; Samson, R.A. Polyphasic taxonomy of Aspergillus section cervini. Stud. Mycol. 2016, 85, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kute, A.B.; Mohapatra, D.; Kotwaliwale, N.; Giri, S.K.; Sawant, B.P. Characterization of pectin extracted from orange peel powder using microwave-assisted and acid extraction methods. Agric. Res. 2020, 9, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrudula, S.; Anitharaj, R. Pectinase production in solid state fermentation by Aspergillus niger using orange peel as substrate. Glob. J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 6, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, B.K.; Nanda, P.K.; Sahoo, S. Enhanced production of pectinase by Aspergillus terreus NCFT 4269.10 using banana peels as substrate. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraji, P.K.; Vuppu, S. Characterisation of pectin and optimization of pectinase enzyme from novel Streptomyces fumigatiscleroticus VIT-SP4 for drug delivery and concrete crack-healing applications: An eco-friendly approach. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3529–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, R.; Kurup, G. Screening and isolation of pectinase from fruit and vegetable wastes and the use of orange waste as a substrate for pectinase production. Int. Res. J. Biol. 2013, 2, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, A.; Eldo, A.; Molly, A.G. Optimization of culture conditions for the production of thermostable polygalacturonase by Penicillium SPC-F 20. Int. J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 35, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangarajan, V.; Rajasekharan, M.; Ravichandran, R.; Sriganesh, K.; Vaitheeswaran, V. Pectinase production from orange peel extract and dried orange peel solid as substrates using Aspergillus niger. Int. J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 6, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, N.; Morshed, M.A.; Uddin, A.; Begum, F.; Sultan, T.; Azad, A.K. Production of pectinase by Aspergillus niger cultured in solid state media. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, N.; Vivek, R.; Arunkumar, M.; Balakumar, S. Statistical designing of enriched pectin extract medium for the enhanced production of pectinase by Aspergillus niger. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 666–672. [Google Scholar]
- Enshasy, H.A.; Elsayed, E.A.; Suhaimi, N.; Malek, R.A.; Esawy, M. Bioprocess optimization for pectinase production using Aspergillus niger in a submerged cultivation system. BMC Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, J.; Mandhan, R.P. Lucrative pectinase production by novel strain Pseudozyma sp. SPJ with statistical optimization techniques using agro-industrial residues. Front. Biol. 2014, 9, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).