Abstract
Anaerobic digestion (AD) represents an advantageous solution for the treatment and valorization of organic waste and wastewater. To be suitable for energy purposes, biogas generated in AD must be subjected to proper upgrading treatments aimed at the removal of carbon dioxide and other undesirable gases. Pressurized anaerobic digestion (PDA) has gained increasing interest in recent years, as it allows the generation of a high-quality biogas with a low CO2 content. However, high pressures can cause some negative impacts on the AD process, which could be accentuated by feedstock characteristics. Until now, few studies have focused on the application of PAD to the treatment of real waste. The present work investigated, for the first time, the performance of the pressurized anaerobic digestion of raw compost leachate. The study was conducted in a lab-scale pressurized CSTR reactor, working in semi-continuous mode. Operating pressures from the atmospheric value to 4 bar were tested at organic loading rate (OLR) values of 20 and 30 kgCOD/m3d. In response to the rise in operating pressure, for both OLR values tested, a decrease of CO2 content in biogas was observed, whereas the CH4 fraction increased to values around 75% at 4 bar. Despite this positive effect, the pressure growth caused a decline in COD removal from 88 to 62% in tests with OLR = 20 kgCOD/m3d. At OLR = 30 kgCOD/m3d, an overload condition was observed, which induced abatements of about 56%, regardless of the applied pressure. With both OLR values, biogas productions and specific methane yields decreased largely when the pressure was brought from atmospheric value to just 1 bar. The values went from 0.33 to 0.27 LCH4/gCODremoved at 20 kgCOD/m3d, and from 0.27 to 0.18 LCH4/gCODremoved at 30 kgCOD/m3d. Therefore, as the pressure increased, although there was an enhanced biogas quality, the overall amount of methane was lowered. The pressured conditions did not cause substantial modification in the characteristics of digestates.
1. Introduction
Energy consumption increases every year with technological and social development causing significant environmental impacts. In recent years, the exploitation of organic waste as a source to produce energy and to recover chemical compounds has gained increasing interest [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Among the different technologies, anaerobic digestion (AD) is widely used [1,2,7,8,9], as it represents a sustainable approach to obtain biofuel and bioproducts from the treatment of wet biomass [8,9,10]. AD evolves according to a series of biochemical reactions involving different groups of microorganisms [3]. A wet digestate and biogas are generated because of the organic matter degradation under anaerobic conditions. Digestate can be generally used for agronomic purposes, due to its high nutrient content [11,12,13,14,15]. Biogas is a mixture mainly composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with a lower heating value (LHV) of about 21.5 MJ/m3 [14]. It also contains traces of other non-condensable gases such as H2S, H2, N2, NH3, O2, CO, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and steam [13,14,16]. Biogas composition varies according to the type of feedstock and the process conditions. Generally, the content of CH4 ranges between 55 and 65%, while the fraction of CO2 is between 35 and 40%. However, CO2 percentage can reach 50%, which leads to a reduction in the LHV value [17].
The use of biogas for energy purposes requires the application of effective upgrading treatments to remove CO2 and other undesirable gases [4,13,15,18]. These treatments permit the production of biogas with a CH4 content greater than 95% [4,13,15,19,20,21]. Upgrading technologies such as adsorption, high-pressure washing, high-pressure adsorption, cryogenic separation, and membrane separation are widely used in current practices [4,13,15,20,22]. However, these technologies are affected by high costs, clogging and foaming phenomena, water and energy consumption, and process complexity [4,13,15].
In particular, the high costs for biogas upgrading make biomethane less attractive than other biofuels [23]. In recent years, a lot of research has been carried out to reduce the drawbacks related to the purification of biogas. In this regard, pressurized anaerobic digestion (PAD) has attracted great attention [23,24,25,26]. In pressurized anaerobic digestion the pressure of the biogas is gradually autogenerated during fermentation. Therefore, PAD processes are carried out at pressures greater than atmospheric, which allows the obtainment of a biogas with a high methane fraction and a low carbon dioxide content [23,27]. This is due to the different properties of CH4 and CO2. Methane has a very low solubility in water and mainly remains in the gaseous phase, regardless of the pressure conditions in the digester. CO2 is characterized by greater solubility that significantly grows with increasing pressure [28,29]. Consequently, the pressure rise causes a greater solubilization of carbon dioxide in the liquid phase, which results in a biogas with a higher CH4 fraction and a greater LHV value than that generated under atmospheric conditions. PAD processes have so far been tested within the pressure range of 1–100 bar [30,31].
Merkel et al. [29] observed a CH4 growth from 79.08% at 10 bar, to 90.45% at 50 bar. Lindeboom et al. [27] monitored CH4 yields between 90% and 95% at pressures up to 90 bar. Bär et al. [32] found that the two-stage high-pressure digestion in biofilm reactors significantly improves the biogas quality at high operating pressure. In particular, methane fractions up to 85% were achieved at an operating pressure of 25 bar, whereas a CH4 percentage of 93% was detected by feeding the methanogenesis reactor with permeate from a microfiltration pretreatment [32]. Chen et al. [25,33] detected an increase in the CH4 fraction from 66.2 to 74.5% by raising the pressure from 1 to 9 bar, during the treatment of grass silage leachate in two-stage pressurized reactors. In addition to the generation of a biogas with a high CH4 content, PAD could potentially improve the characteristics of the digestate. Indeed, high pressures in the reactors promote the solubilization of nutrient compounds in the liquid phase [19,33,34]. In agreement with this statement, Latif et al. [34] detected an enhancement in soluble phosphate concentration working at 6 bar. Despite these benefits, PAD may suffer from some negative aspects. In particular, the greater CO2 solubilization could lead to an excessive reduction of pH, inhibiting the methanogens activity [25]. This is particularly relevant when wastes with a considerable content of easily degradable substrates are digested. On the other hand, some studies have postulated that high levels of total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) in the feedstock could lead to the formation of ammonia sufficient to increase the buffer capacity, and to hinder the pH drop induced by the CO2 solubilization [19]. Other works have stated that the accumulating pressure impacts on microorganism consortium cause the inhibition of the methane production yield [35]. These considerations make clear the need for further research to assess the actual performance of PAD in relation to the type and characteristics of the waste to be digested.
Until now, PAD has been mainly tested in the digestion of synthetic substrates [24,27], activated sludge [34], and silage waste [19,25,26,29,33]. In the present work, the pressurized anaerobic digestion of compost leachate, generated by the aerobic stabilization of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste, was investigated. This is a new contribution to the development of PAD as, to the best of our knowledge, no previous work has focused on the treatment of compost leachate in pressurized digesters. This type of wastewater is produced in large quantities worldwide, and has peculiar characteristics such as a high content of organic matter with considerable aliquots of volatile fatty acids (VFA), acidic pH, high salinity, etc. [1,36,37]. The experiments were conducted on a pilot plant, working in semi-continuous mode under mesophilic conditions. The study assessed the effects of pressure increase, at different organic load rate (OLR) values, on process performance. Biogas composition, specific biogas yield (SBY), specific methane yield (SMY) and the main process parameters such as pH, VFA/alkalinity ratio, nutrients concentrations, etc., were evaluated in response to the pressure change. In addition, the characteristics of the produced digestates were analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this study, compost leachate from a tunnel composting facility located in Rende near Cosenza (Calabria Region, Italy) was used as feedstock. Activated sludge, collected from the recirculation line of the wastewater treatment plant of Lamezia Terme (Calabria Region, Italy) and maintained in anaerobic conditions for 15 days, was used as inoculum for the AD start-up. This operation mode was selected on the basis of our previous works, which proved the applicability of activated sludge for the inoculation of an anaerobic digestion process [1,5]. The samples were stored in 30 L tanks at 4 °C, to avoid any degradation.
2.2. Pressurized Pilot Plant
The PDA tests were performed using a laboratory pilot-plant designed and built in the Laboratory of Sanitary and Environmental Engineering of the University of Calabria. The pilot plant was composed of a completely stirred tank reactor (CSTR), and some auxiliary devices (biogas measurement system, heating device, connecting pipelines, and data acquisition system) (Figure 1a). The digester consisted of a 3 L cylindrical reactor, made of stainless steel 316 and wrapped in an insulated heating jacket, able to withstand high operating pressures (up to 40 bar). The overall unit was hermetically closed by a top flange provided with a nozzle pipe suitable for feeding the leachate and collecting the digestate (Figure 1b). The digester was equipped with a vertical steel mixer powered by a gear motor. Mesophilic conditions (37 °C) were maintained by a heating device connected to the reactor. The pressure inside the reactor was controlled by a system of adjustable valves.
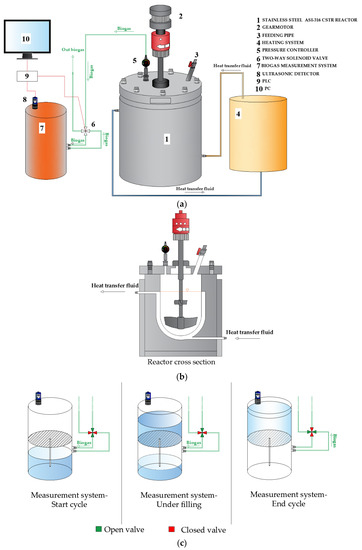
Figure 1.
PAD laboratory pilot plant (a); reactor cross section (b); biogas measurement system (c).
The produced biogas was left inside the reactor until the set pressure value was reached. At the required pressure, the excess biogas was extracted from the reactor.
The biogas measurement system consisted of a vertical cylindrical PVC tank divided into two equal septa, communicating with each other by a pipe (Figure 1c). In the lower septum, two silicone pipes were connected to a two-way solenoid valve that allowed the inlet and outlet of the biogas (Figure 1c). The system operated as described below.
The produced biogas flowed from the digester in the lower septum, which was initially filled with water. The volume of biogas progressively displaced the water from the lower to the upper septum. Therefore, the lower septum was gradually filled with biogas and, simultaneously, the upper septum became filled with water. Once the maximum level was reached, the solenoid valve discharged the biogas from the lower septum and the system returned to the initial condition. The water level in the upper compartment was measured by an ultrasonic sensor (Microsonic® mic + 25/DIU/TC; Microsonic GmbH, Dortmund, Germany), equipped with integrated temperature compensation. The sensor sent an analogue signal to the PLC (Arduino® Mega 250; Arduino, Turin, Italy) that switched it into biogas volume.
2.3. PDA Experimental Set-Up
The effects of the pressure increase on the AD performance at high OLR values were investigated. In particular, five operating pressures, from atmospheric to 4 bar, and two different organic loading rate (OLR) values, 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d, were tested.
The OLR were selected to investigate PAD in an optimal condition (20 kgCOD/m3d) and in an unfavorable state (30 kgCOD/m3d). In fact, our previous studies proved that, under atmospheric conditions, the digestion of compost leachate can efficiently evolve up to a high OLR of about 25 kgCOD/m3d, beyond which the performance rapidly deteriorates [1].
Before performing the pressurized tests, the reactor was inoculated with activated sludge that was maintained in anaerobic conditions for 15 days. After the preliminary phase, the CSTR was started in semi-continuous mode keeping the working volume at 1.5 L. The organic loading rate was gradually increased up to 20 kgCOD/m3d. Subsequently, holding the OLR of 20 kgCOD/m3d, the pressure was increased stepwise from the atmospheric value up to 4 bar. At this pressure, the OLR was then brought to 30 kgCOD/m3d. Finally, keeping the last OLR constant, decreasing pressures were applied until the atmospheric value was re-established. For each OLR, the values of pressure were maintained for two weeks. The average values of the parameters monitored during these two weeks were assumed and presented in the following sections.
The feeding of the reactor and the extraction of the digestate were carried out manually. PDA tests lasted approximately five months, during which no additional chemicals were added. For each operating condition, a chemical–physical characterization of digestate was carried out.
2.4. Analytical Methods
Conductivity and pH were measured through benchtop analyzers (Crison BASIC 30 EC, Crison BASIC 20 pH; Hach Lange, Barcelona, Spain). Total solids (TS) and volatile solids (VS) were measured by weight analysis after drying the samples at 105 and 550 °C [38]. Alkalinity was measured by the potentiometric method [38]. Total COD and soluble COD were measured after digestion with potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7 0.5N) and volumetric titration with ammonium iron sulphate (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2∙6H2O [38]. Volatile fatty acids (VFA) were detected after distillation of the sample (VELP UDK 127 distillation unit; VELP Scientifica srl, Usmate, MB, Italy) and titration with sodium hydroxide (NaOH 0.01N) [38]. Ammonia nitrogen (N-NH4+), orthophosphates (P-PO43−) and sulphates (SO42−) were detected by spectrophotometric analysis with a UV-Vis (Thermo Spectronic Genesys 10uv; Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) [38]. Metals were determined, after calcination of the sample at 550 °C, with atomic absorption spectrophotometry (GBC 933 PLUS; GBC Scientific Equipment, Braeside, VIC, Australia) [38]. Each analysis was carried out in triplicate. The biogas production was detected at standard conditions. Methane percentage was detected daily after acidic gases and carbon dioxide neutralization through sodium hydroxide, as described in our previous work [1].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composting Leachate and Activated Sludge Characteristics
Composting leachate used in this study was characterized by a moderately acidic pH of 5.3, and by a notable conductivity value of around 5.6 mS/cm (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristics of raw compost leachate and activated sludge (d.l. detection limit).
A large amount of organic matter was detected with a COD concentration equal to 66.5 g/L and a soluble fraction of about 80%. Moreover, a very high content of volatile fatty acids (VFA), close to 15.2 gCH3COOH/L, was observed. The total Kjeldahl nitrogen concentration (TKN) resulted of about 1.5 gN/L, and the ammoniacal form was found to be 0.66 gN/L. Remarkable quantities of orthophosphate (P-PO43−) and sulphate (SO42−) were also measured. Due to the low pH value, dissolved metals such as Zinc (Zn), Nickel (Ni), Iron (Fe), Lead (Pb), and Manganese (Mn) were detected.
The characteristics presented above are representative of a leachate with a low maturation degree, generated in a composting process that evolved in micro-aerobic conditions. In fact, the values of total and solubilized COD indicate that the organic matter was not yet degraded. Furthermore, the large amount of VFA and the acidic pH suggested that the biological transformations evolved with lack of oxygen, similarly to the typical acid-acetogenic phases in fermentation processes.
The properties of inoculum were in line with the values of a typical activated sludge taken from the recirculation line of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. In particular, a total solids (TS) content of 10.8 g/L and a volatile fraction of 82% were found.
3.2. Performance of PAD
3.2.1. COD Removal
The characterization of the feedstock used during the experiments showed a high content of organic matter, which could lead to a notable biogas production. However, some of the leachate properties have the potential to hinder the evolution of the digestion process. Indeed, the acidic pH and the high level of VFA are adverse factors that can inhibit the methanogens activity. These negative effects can be overcome if an adequate buffer capacity is reached in the digester [1]. However, as previously described, the consequences of low pH values and great amounts of VFA could be even more marked in pressurized anaerobic digestion. The experiments conducted permitted to verify whether high-pressure digestion is suitable for the treatment of compost leachate.
In this regard, PAD tests were carried out at 20 and 30 kgCOD/m3d, varying the process pressure between the atmospheric value up to 4 bar. Under atmospheric conditions the removal yield was around 88 and 56% at 20 and 30 kgCOD/m3d, respectively (Figure 2). These values, in agreement with our previous work [1], confirmed that at atmospheric pressure, the anaerobic digestion of compost leachate significantly deteriorates when the OLR exceeds values of about 20 kgCOD/m3d. This deterioration of COD conversion is a clear consequence of a substrate overload condition. With the highest OLR applied, the organic matter abatement was independent of the operating pressure, and fluctuated between 50 and 60%. On the other hand, the detected results proved that the pressure growth causes a significant negative effect on COD degradation when the process operates under favorable OLR values. Indeed, at an OLR of 20 kgCOD/m3d, the pressure increase led to a decrease in COD removal efficiency from 88% at atmospheric pressure, to 62% at 4 bar (Figure 2).
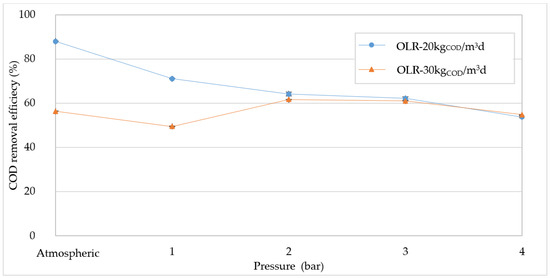
Figure 2.
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency at increasing pressures.
In particular, there was a marked reduction in COD yield in response to a slight pressure increase to just 1 bar. Above this value, a slower decreasing trend of the COD abatement was observed.
The adverse impact of pressure on COD removal was reported in previous studies [25,34,36,39]. Latif et al. [34], in a single-stage reactor, achieved COD removal efficiencies about 35 and 30% at 4 bar and 6 bar, respectively. Chen et al. [25] raised the working pressure to 9 bar and observed a worsening of the process performance at high OLR values and short hydraulic retention times.
3.2.2. Biogas Production and Composition
At OLR = 20 kgCOD/m3d, the trend of biogas production, as a function of process pressure (Figure 3), was generally consistent with the amounts of COD removed (Figure 2). Indeed, due to the substantial reduction in COD abatement with the pressure growth to 1 bar, the generated biogas showed a similar decrement. In particular, the biogas volume diminished by approximately 23% from 16.8 L, recorded at atmospheric pressure, to 12.8 L, at 1 bar. The production further decreased to about 10.4 L as the pressure increased to 4 bar (Figure 3).
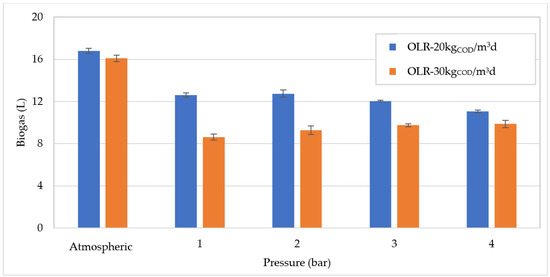
Figure 3.
Biogas production at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d.
At OLR = 30 kgCOD/m3d, despite the lower yield in COD degradation, the volume of biogas produced by operating at atmospheric pressure (16 L) was quite similar to that detected at 20 kgCOD/m3d (Figure 3). This can be explained by the fact that the overall amount of COD converted in atmospheric conditions was analogous with the two OLR values tested. With the growth in pressure there was a stabilization of the biogas production, and the values ranged between 9.28 and 9.87 L. The results presented above indicate that, as the pressure grows, the organic matter digestion and the biogas production deteriorate, and this effect is more marked at 20 kgCOD/m3d. On the other hand, the quality of biogas was notably improved by the increase in pressure. Indeed, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, at increasing pressure a linear increase in CH4 percentage was detected for both applied OLR values. In particular, the methane fraction grew by approximately 12–14% from the percentage of 62% at atmospheric pressure, to 74–76% at 4 bar (Figure 4 and Figure 5). The enhancement in methane fraction can be attributed to the higher solubilization of CO2 at increasing pressure generated in the reactor. This was confirmed by the progressive decrease in the CO2 aliquot in the biogas. The improvement in biogas composition represents an undoubted advantage of PAD processes which was proven in several previous works. In particular, Lindeboom et al. [24] observed an increase in methane from 49 ± 2% up to a maximum of 73 ± 2% at 5 bar in the digestion of starch. The authors found that no further improvement in biogas composition occurred at pressures above 5 bar. Other works, however, reported an enhancement in biogas quality at pressures above 10 bar. Merkle et al. [29] observed an increase in CH4 content to over 90% at 50 bar, by treating leachate of grass and maize silage.
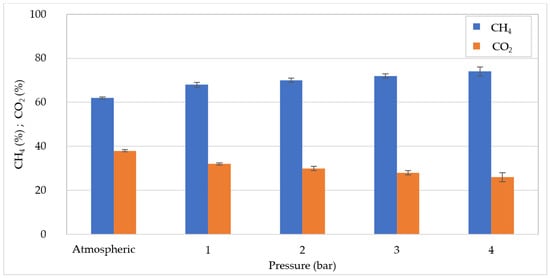
Figure 4.
CH4 and CO2 percentages at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d.
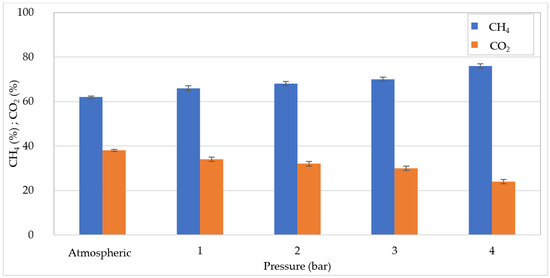
Figure 5.
CH4 and CO2 percentages at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 30 kgCOD/m3d.
In our experiments, despite the enhancement in biogas quality, the overall amount of methane decreased with the pressure rise. Indeed, the reduction in the volume of produced biogas was not compensated by the increase in the CH4 fraction. Therefore, higher pressures in the reactor led to lower methane yields.
The worsening of the process performance was confirmed by the trends of the specific biogas yield (SBY) and of the specific methane yield (SMY) (Figure 6 and Figure 7), defined as the volume produced per gram of COD removed.
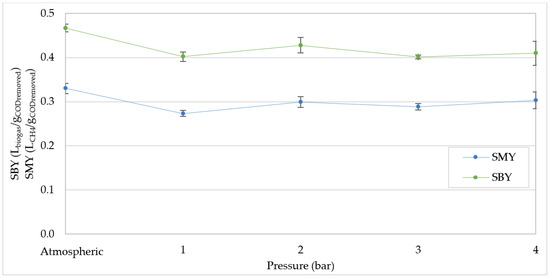
Figure 6.
Specific biogas yield (SBY) and specific methane yield (SMY) at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d.
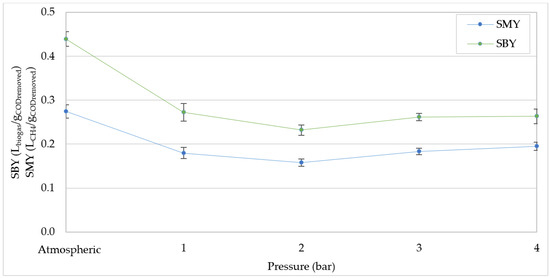
Figure 7.
Specific biogas yield (SBY) and specific methane yield (SMY) at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 30 kgCOD/m3d.
In particular, at an OLR of 20 kgCOD/m3d, in agreement with our previous work, the SMY was around 0.33 LCH4/gCODremoved operating in atmospheric conditions (Figure 6). This value is quite close to the stoichiometric yield at 37 °C, equal to 0.4 LCH4/gCODremoved, which confirms the high efficiency obtainable on the digestion of compost leachate, even at such a high OLR value [1,3]. There was a consistent decrease in SMY and SBY, bringing the pressure to 1 bar while, beyond this value, the variations were not significant.
By working at OLR = 30 kgCOD/m3d and atmospheric pressure, there was a worse conversion of the organic matter, and lower SMY and SBY were detected than those achieved at 20 kgCOD/m3d (Figure 6 and Figure 7). The yields underwent a reduction of about 35% with the pressure rise to 1 bar (Figure 7), beyond which SMY and SBY oscillated around 0.18 LCH4/gCODremoved and 0.25 L/gCODremoved, respectively. Consistent with our results, Chen et al. [25] found a notable attenuation of the specific methane yield between 1.5 bar to 9 bar, when the OLR was raised over to 15 kgCOD/m3d. Li et al. [40] observed a production yield at a pressure of 3 bar, significantly higher than that detected at 10 bar. Lemmer et al. [26] found a decrease in the SMY in the digestion of grass/maize-silage from 303.8 ± 47.2 mL/gCODadded to 258.0 ± 45.3 mL/gCODadded, at increasing pressure from 1 bar to 9 bar. The same authors [39] reported a stable value of the specific yields between 10 and 30 bar. These statements suggest that the greatest negative effects on SMY occur at moderate increases in pressure, and then the specific productions tend to stabilize. In particular, our results showed that the reduction in SMY and SBY mainly occurred at 1 bar.
3.2.3. pH and VFA/Alkalinity
Generally, the deterioration of digestion performance is attributed to the decrease in pH caused by the greater CO2 solubilization with increasing pressure. Moreover, this phenomenon can favor the activity of acetogenic bacteria leading to an accumulation of VFA in the reactor [24], which further accentuates the acidification of digesting mixture. Clearly, such an effect could cause the inhibition of methanogens and, therefore, lower methane production. Our results confirmed the reduction in pH with the pressure growth, and decreasing linear trends were detected for both OLR values tested (Figure 8). At OLR = 30 kgCOD/m3d the pH values were always lower than those measured at 20 kgCOD/m3d (Figure 8), as a consequence of higher levels of VFA. In fact, as shown in Figure 9, at atmospheric pressure the VFA reached a value around 7.5 gCH3COOH/L, while the concentration was below 6 gCH3COOH/L at 20 kgCOD/m3d. The higher amount of VFA found at OLR = 30 kgCOD/m3d corresponded to a greater value of VFA/Alkalinity that overcame 0.45 gCH3COOH/gCaCO3 (Figure 10). These values are representative of an overload condition (excessive OLR value) that justifies the lower digestion performance detected at atmospheric pressure. With increasing pressure, both the VFA concentrations and VFA/Alkalinity ratio increased. Therefore, under overload conditions (30 kgCOD/m3d) the pressure increase aggravates the digestion upset by promoting the accumulation of volatile fatty acids. However, with an organic load of 20 kgCOD/m3d, the pH values (Figure 8) were significantly higher compared with those monitored at 30 kgCOD/m3d and, furthermore, the concentration of volatile fatty acids did not show a significant accumulation with the operating pressure (Figure 9). Consistent with the trend of VFA, the values of VFA/Alkalinity were always below 0.41 gCH3COOH/gCaCO3 (Figure 10). According to our previous study, these values are tolerable in the digestion of compost leachate in CSTR systems without the occurrence of inhibition effects [1]. Based on these considerations, at OLR = 20 kgCOD/m3d the deterioration in biogas production with increasing pressure is not related to acidification conditions. Therefore, it can be affirmed that, contrarily to that hypothesized in some literature reports, the pressurized conditions in the digestion of waste with a high content of easily degradable substrates, such as compost leachate, do not cause detrimental acidification of mixture if suitable OLR values are applied.
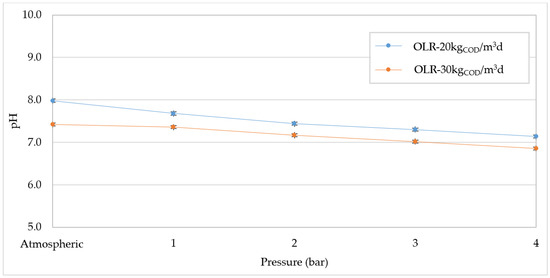
Figure 8.
pH values at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d.
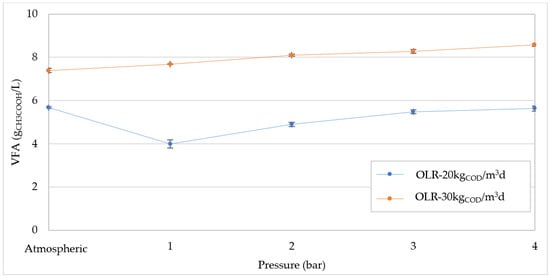
Figure 9.
Volatile fatty acids (VFA) trends at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d.
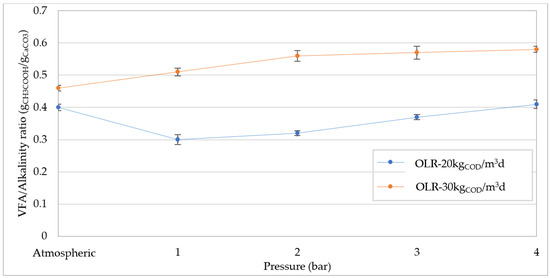
Figure 10.
Volatile fatty acids/Alkalinity ratio at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d.
Other mechanisms probably play a role in the adverse effects of pressure on the evolution of digestion. Some authors argued that high-pressure conditions can reduce the hydrolytic capacity of the system, which would be consistent with the lack of VFA accumulation. Other research took into consideration the effects of pressure in microbial community and microbial activity. Under pressurized conditions, a lower diversity and richness in microbial species was observed. Abe and Horikoshi [41] reported that the growth rates of piezosensitive microbes drop with the pressure. At high pressures, Li et al. [40] found a low abundance of Archea able to use the hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis pathways. This condition can negatively impact the direct interspecies electron transfer (DIET) mechanism [42], unbalancing the syntrophic relationship between the microbial community and worsening the overall digestion performance.
3.2.4. Sulphate (SO42−)
In general, high levels of sulfate in the digester promote the development of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB), which oxidize the organic matter using SO42− as an electron acceptor. The sulfate-reducing mechanism could induce positive effects in pressurized reactors, as the sulfate reduction generates alkalinity, which could counteract the digestate acidification. However, the development of SRB can upset the activity of methanogens, as the two groups of microorganisms compete with each other. Moreover, the reduction of sulfate generates sulfide, which can induce toxic effects on methane-producing Archea. These adverse effects are related to the COD/SO4 ratio, and a total or partial inhibition of methanogenesis might occur for values below 4 or between 4–10 gCOD/gSO4, respectively [1]. During our experiments, a sulphate amount able to cause the competition or inhibition phenomena was not reached. Indeed, the COD/SO4 always remained above 10. Moreover, no significant changes in sulfate concentration were observed with increasing pressure (Figure 11). Our results suggest that pressure increase does not have any influence on the sulfate degradation and SRB development. Previous works have reported that pressured conditions do not adversely affect the growth of sulphate-reducing bacteria [43,44].
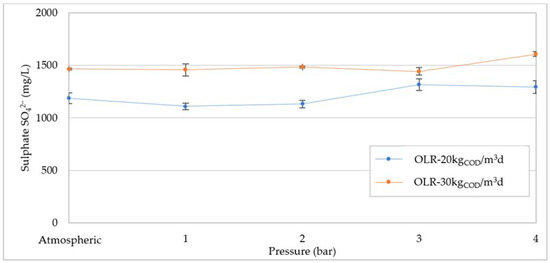
Figure 11.
Sulphate (SO42−) concentration at pressure increases for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d.
3.2.5. Ammonia Nitrogen (N-NH4+)
The presence of ammonia nitrogen is an important factor for a stable evolution of AD. Ammonia is generated by the breakdown of proteins and amino acids [3] and could reach harmful levels during the digestion of wastes with a high content of organic nitrogen. According to Hansen et al. [45], under thermophilic conditions, at pH 8 a free ammonia concentration of 1100 mg/L is toxic to anaerobic microorganisms. Khanal et al. [3] reported that an ammonium ion concentration above 3000 mg/L causes inhibitory effects, regardless of the operating conditions. On the other hand, some works considered a high ammonia nitrogen production beneficial in pressurized digesters, as it could increase the buffer capacity and hinder the acidification phenomena [26]. In our experiments, with an OLR of 20 kgCOD/m3d, the ammonium concentration increased by about 15%, as the pressure rose from the atmospheric value to 1 bar (Figure 12). Over 1 bar, the N-NH4+ slightly grew, reaching a maximum value of around 2100 mg/L. At OLR = 30 KgCOD/m3d, higher N-NH4+ values were detected in atmospheric conditions as a clear consequence of the increase in organic load, whereas a lower increase was monitored in response to the pressure growth. For each applied condition, the values of ammonium were quite high, but remained below the threshold considered able to cause inhibition effects [3]. Therefore, no negative impacts on biogas production can be attributed to the ammonia production. On the other hand, the increase in N-NH4+, which occurred mainly at 1 bar, did not avoid the pH from falling at increasing pressure. Based on these results, it can be affirmed that the generation of ammonia does not have a significant effect on the pressurized anaerobic digestion of compost leachate.
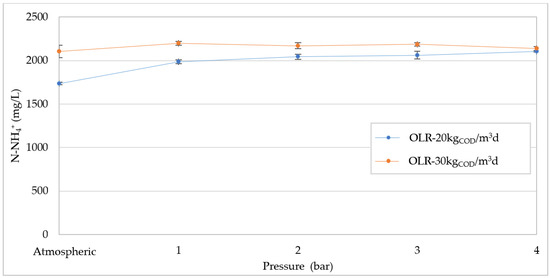
Figure 12.
Ammoniacal nitrogen (N-NH4+) concentration at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d.
3.2.6. Phosphate (P-PO43−)
During the AD process, only small amounts of nutrients are used for cell synthesis and, thus, most of the initial amount in the feedstock is released into the digestate [3]. Phosphorus generally remains in the liquid phase as orthophosphate ions. However, depending on the presence of metallic elements, PO43− could precipitate in the form of insoluble compounds such as Ca3(PO4)2, FePO4, AlPO4 or struvite (MgNH4PO4·6H2O) [12,46]. This phenomenon tends to occur on the surface of the pipelines which connect the various units (digesters, thickeners, etc.) and could cause the ducts obstruction. The high pressure in anaerobic digestion may enhance the phosphate solubility due to the increased CO2 concentration in the liquid phase. This helps to limit the adverse effect of the uncontrolled precipitation of phosphate. Moreover, after the pressurized digestion and the digestate thickening, the soluble PO43− in the liquid phase could be recovered through controlled precipitation treatments, in the form of valuable compounds such as struvite, which are potentially reusable as slow-release fertilizers [12]. The results of our investigations confirmed the increase in dissolved PO43− concentration in response to the pressure growth. As shown in Figure 13, no significant differences were found with the two applied OLR. In both cases, the phosphorus concentration linearly increased by about 35%, bringing the pressure from the atmospheric value to 4 bar. In agreement with these results, Latif et al. [34] found an enhancement in phosphate concentration from 51 to 73 mg/L, between 2 and 6 bar. Despite the increase in phosphorus solubility, it should be noted that the PO43− concentrations were quite low compared with the amount of P in the feedstock (Table 1). Therefore, under pressurized conditions, only a small enhancement in phosphorus solubilization can be reached.
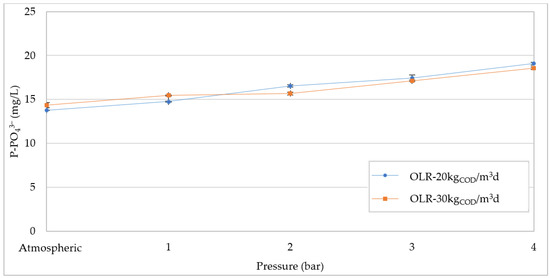
Figure 13.
Phosphate (P-PO43−) concentration at increasing pressures for organic load rate (OLR) of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d.
3.3. Digestate Characteristics
Table 2 shows the physical–chemical characteristics of the digestates obtained in the different operating conditions tested.

Table 2.
Digestate’s chemical–physical characteristics (measure unit (M.U.); detection limit (d.l.)).
High contents of fertilizing elements such as N-NH4+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and SO42− were found for all samples. These elements make the digestate a valuable matrix potentially exploitable in agronomic practices. Furthermore, in compliance with the recommendations for agricultural applications, digestates were characterized by low ratios between organic matter content and nitrogen (Table 2). This parameter is of great importance as it affects the availability of nitrogen in soil [1]. The orthophosphate content was small compared with the amount of nitrogen. The low content of the soluble phosphorus, as previously discussed, is mainly attributable to the precipitation of phosphate salts [1,3,34]. Therefore, the use of compost leachate digestate for fertilizing purposes would be more suitable in soils with sufficient amounts of phosphorus. The presence of hazardous metal ions, such as Pb, Ni and Zn, was negligible. Their concentrations were lower than those required by current fertilizer regulations [47]. These low concentrations were due to the pH values which allowed the precipitation of most of the metallic species present in the mixture. Overall, for most of the monitored parameters, a clear effect of the pressure increase on their release into the digestate was not found.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the pressurized anaerobic digestion of compost leachate was investigated. The experiments were carried out by testing operating pressures up to 4 bar, with organic load rates of 20 kgCOD/m3d and 30 kgCOD/m3d. The detected results confirmed that pressure growth leads to the production of biogas with an increase in the methane fraction and a decrease in CO2 content. At a pressure of 4 bar, a percentage of methane of around 75% was reached for both OLR values tested. On the other hand, there was a general decline of the digestion performance under high pressure conditions. At 20 kgCOD/m3d, the COD removal was close to 88% at atmospheric pressure, and then decreased by about 35% as the pressure increased. At 30 kgCOD/m3d, the removal of organic load remained around a quite low value of 56%, which is representative of overload conditions.
Regardless of the applied organic load, biogas production and specific methane yield notably worsened as the pressure increased to 1 bar. In particular, the SMY values fell from 0.33 to 0.27 LCH4/gCODremoved, at 20 kgCOD/m3d, and from 0.27 to 0.18 LCH4/gCODremoved, at 30 kgCOD/m3d. As expected, the acidification of digestate was monitored at growing pressures. However, the magnitude of this phenomenon was not sufficient to justify the worsening of the digestion performance. Moreover, no adverse effects imputable to sulphates and ammonia compounds were identified. Therefore, the detected results suggested the occurrence of other effects such as the reduction of hydrolytic capability, or the alteration of microbial activity. An enhanced solubilization of nutrient compounds, such as orthophosphates, was observed with increasing pressures. However, the increase in PO43- was quite low up to a pressure of 4 bar. More generally, the pressure values did not substantially affect the chemical composition of the digestates, which showed characteristics compatible for agronomic utilization.
In conclusion, the digestion of compost leachate in pressurized reactors does not appear to be advantageous compared with digestion in atmospheric conditions. However, further studies, under different operating conditions (OLR, pressure values), are necessary to confirm these statements. Furthermore, additional research should be conducted to better clarify the mechanisms that mainly affect the biogas production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.; methodology, A.S. and C.L.; formal analysis, C.L. and G.M.C.; investigation, C.L.; data curation, A.S., C.L. and G.M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S. and C.L.; writing—review and editing, A.S. and C.L.; supervision, A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Siciliano, A.; Limonti, C.; Curcio, G.M.; Calabrò, V. Biogas Generation through Anaerobic Digestion of Compost Leachate in Semi-Continuous Completely Stirred Tank Reactors. Processes 2019, 7, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siciliano, A.; Stillitano, M.A.; Limonti, C. Energetic Valorization of Wet Olive Mill Wastes through a Suitable Integrated Treatment: H2O2 with Lime and Anaerobic Digestion. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanal, S. Anaerobic Biotechnology for Bioenergy Production: Principles and Applications; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barbera, E.; Menegon, S.; Banzato, D.; D’Alpaos, C.; Bertucco, A. From biogas to biomethane: A process simulation-based techno-economic comparison of different upgrading technologies in the Italian context. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Limonti, C.; Mehariya, S.; Molino, A.; Calabrò, V. Biofuel Production and Phosphorus Recovery through an Integrated Treatment of Agro-Industrial Waste. Sustainability 2018, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, M.V.; Salvador, R.; de Francisco, A.C.; Piekarski, C.M. Mapping of research lines on circular economy practices in agriculture: From waste to energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 109958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubando, A.T.; Felix, C.B.; Chen, W.-H. Biorefineries in circular bioeconomy: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehariya, S.; Patel, A.K.; Obulisamy, P.K.; Punniyakotti, E.; Wong, J.W. Co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge for methane production: Current status and perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y. A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic digestion: Research updates and tendencies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Stillitano, M.; De Rosa, S. Increase of the anaerobic biodegradability of olive mill wastewaters through a pre-treatment with hydrogen peroxide in alkaline conditions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 55, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfet, E.; Aubry, G.; Ramirez, A.A. Nutrient removal and recovery from digestate: A review of the technology. Biofuels 2018, 9, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Limonti, C.; Curcio, G.M.; Molinari, R. Advances in Struvite Precipitation Technologies for Nutrients Removal and Recovery from Aqueous Waste and Wastewater. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z.; Yu, X. Selection of appropriate biogas upgrading technology-a review of biogas cleaning, upgrading and utilisation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qian, G.; Zhong, L.; Guo, R.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Z.P. Effective bio-treatment of fresh leachate from pretreated municipal solid waste in an expanded granular sludge bed bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Vinh-Thang, H.; Ramirez, A.A.; Rodrigue, D.; Kaliaguine, S. Membrane gas separation technologies for biogas upgrading. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24399–24448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Cervantes, A.; Estrada, J.M.; Lebrero, R.; Muñoz, R. A comparative analysis of biogas upgrading technologies: Photosynthetic vs physical/chemical processes. Algal Res. 2017, 25, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Biogas Potential of Manure and Straw Mixtures. Energy Sources 2006, 28, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, L.A.; De Guido, G.; Consonni, S.; Bortoluzzi, G.; Gatti, M. From biogas to biomethane: How the biogas source influences the purification costs. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 409–414. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmer, A.; Chen, Y.; Wonneberger, A.-M.; Graf, F.; Reimert, R. Integration of a Water Scrubbing Technique and Two-Stage Pressurized Anaerobic Digestion in One Process. Energies 2015, 8, 2048–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niesner, J.; Jecha, D.; Stehlik, P. Biogas upgrading technologies: State of art review in European region. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 35, 517–522. [Google Scholar]
- Köppel, W.; Götz, M.; Graf, F. Biogas upgrading for injection into the gas grid. GWF Gas Erdgas 2009, 150, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Leonzio, G. Upgrading of biogas to bio-methane with chemical absorption process: Simulation and environmental impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scamardella, D.; De Crescenzo, C.; Marzocchella, A.; Molino, A.; Chianese, S.; Savastano, V.; Tralice, R.; Karatza, D.; Musmarra, D. Simulation and Optimization of Pressurized Anaerobic Digestion and Biogas Upgrading Using Aspen Plus. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 74, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeboom, R.E.; Ding, L.; Weijma, J.; Plugge, C.M.; van Lier, J.B. Starch hydrolysis in autogenerative high pressure digestion: Gelatinisation and saccharification as rate limiting steps. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 71, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rößler, B.; Zielonka, S.; Wonneberger, A.-M.; Lemmer, A. Effects of Organic Loading Rate on the Performance of a Pressurized Anaerobic Filter in Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion. Energies 2014, 7, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemmer, A.; Chen, Y.; Lindner, J.; Wonneberger, A.; Zielonka, S.; Oechsner, H.; Jungbluth, T. Influence of different substrates on the performance of a two-stage high pressure anaerobic digestion system. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeboom, R.E.F.; Fermoso, F.; Weijma, J.; Zagt, K.; Van Lier, J.B. Autogenerative high pressure digestion: Anaerobic digestion and biogas upgrading in a single step reactor system. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-K.; Chen, G.-J.; Han, G.-H.; Guo, X.-Q.; Guo, T.-M. Experimental study on the solubility of natural gas components in water with or without hydrate inhibitor. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2003, 207, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, W.; Baer, K.; Lindner, J.; Zielonka, S.; Ortloff, F.; Graf, F.; Kolb, T.; Jungbluth, T.; Lemmer, A. Influence of pressures up to 50 bar on two-stage anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, W.; Baer, K.; Haag, N.L.; Zielonka, S.; Ortloff, F.; Graf, F.; Lemmer, A. High-pressure anaerobic digestion up to 100 bar: Influence of initial pressure on production kinetics and specific methane yields. Environ. Technol. 2016, 38, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.; Lamb, J.J.; Hjelme, D.R.; Lien, K.M. Overview of recent progress towards in-situ biogas upgradation techniques. Fuel 2018, 226, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, K.; Merkle, W.; Tuczinski, M.; Saravia, F.; Horn, H.; Ortloff, F.; Graf, F.; Lemmer, A.; Kolb, T. Development of an innovative two-stage fermentation process for high-calorific biogas at elevated pressure. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 115, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rößler, B.; Zielonka, S.; Lemmer, A.; Wonneberger, A.-M.; Jungbluth, T. The pressure effects on two-phase anaerobic digestion. Appl. Energy 2014, 116, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.A.; Mehta, C.M.; Batstone, D.J. Enhancing soluble phosphate concentration in sludge liquor by pressurised anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2018, 145, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindeboom, R.E.F.; Shin, S.G.; Weijma, J.; van Lier, J.B.; Plugge, C.M. Piezo-tolerant natural gas-producing microbes under accumulating pCO2. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mokhtarani, N.; Bayatfard, A.; Mokhtarani, B. Full scale performance of compost’s leachate treatment by biological anaerobic reactors. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Azaïs, A.; Benkaraache, S.; Drogui, P.; Tyagi, R.D. Composting leachate: Characterization, treatment, and future perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 323–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association and Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Lemmer, A.; Merkle, W.; Baer, K.; Graf, F. Effects of high-pressure anaerobic digestion up to 30 bar on pH-value, production kinetics and specific methane yield. Energy 2017, 138, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Su, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H. High-calorific biogas production from anaerobic digestion of food waste using a two-phase pressurized biofilm (TPPB) system. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F.; Horikoshi, K. The biotechnological potential of piezophiles. Trends Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.; Fazzino, F.; Limonti, C.; Siciliano, A. Enhancement of Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge by Conductive Materials under High Volatile Fatty Acids-to-Alkalinity Ratios. Water 2021, 13, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallmeyer, J.; Boetius, A. Effects of Temperature and Pressure on Sulfate Reduction and Anaerobic Oxidation of Methane in Hydrothermal Sediments of Guaymas Basin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, A.; Jørgensen, B.B. Bacterial sulfate reduction in hydrothermal sediments of the Guaymas Basin, Gulf of California, Mexico. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.H.; Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B.K. Anaerobic digestion of swine manure: Inhibition by ammonia. Water Res. 1998, 32, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Stillitano, M.A.; Limonti, C.; Marchio, F. Ammonium Removal from Landfill Leachate by Means of Multiple Recycling of Struvite Residues Obtained through Acid Decomposition. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Parliament. Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Laying Down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of CE Marked Fertilising Products and Amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 (COM(2016)0157-C8-0123/2016-2016/0084(COD)); European Parliament: Strasbourg, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).