Enhancing Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion by Optimization of Mixing Regimes Using Helical Ribbon Impeller
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Procedures
2.2. Inoculum Feeding, Substrates, and Sampling
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Gas Analysis
2.3.2. Volatile Fatty Acids
2.3.3. Total Solid (TS) and Organic TS Content
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Mixing Operation
2.4.1. Mechanical Mixing
2.4.2. Rheology
2.5. CFD Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
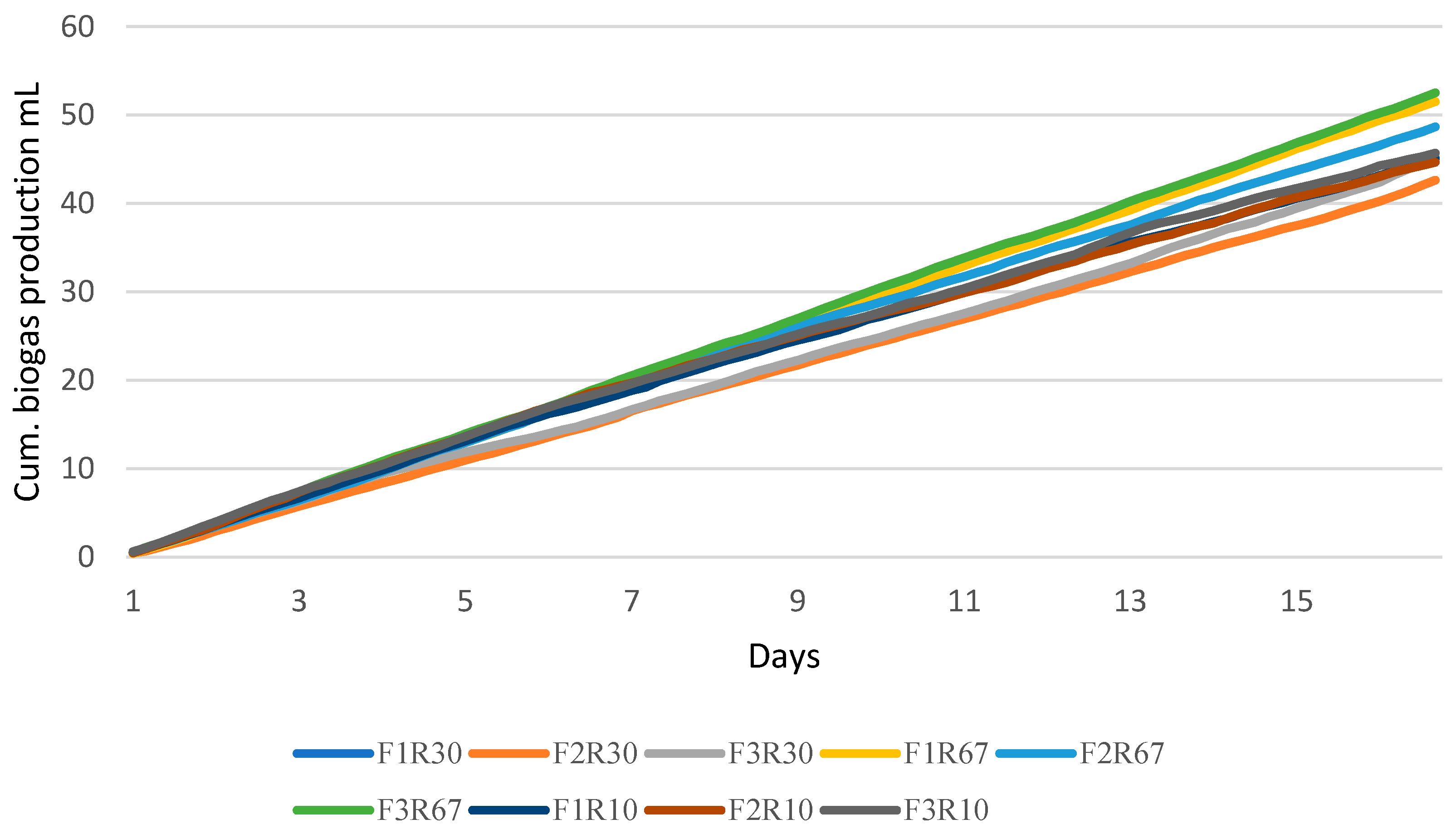
3.1. Startup Phase
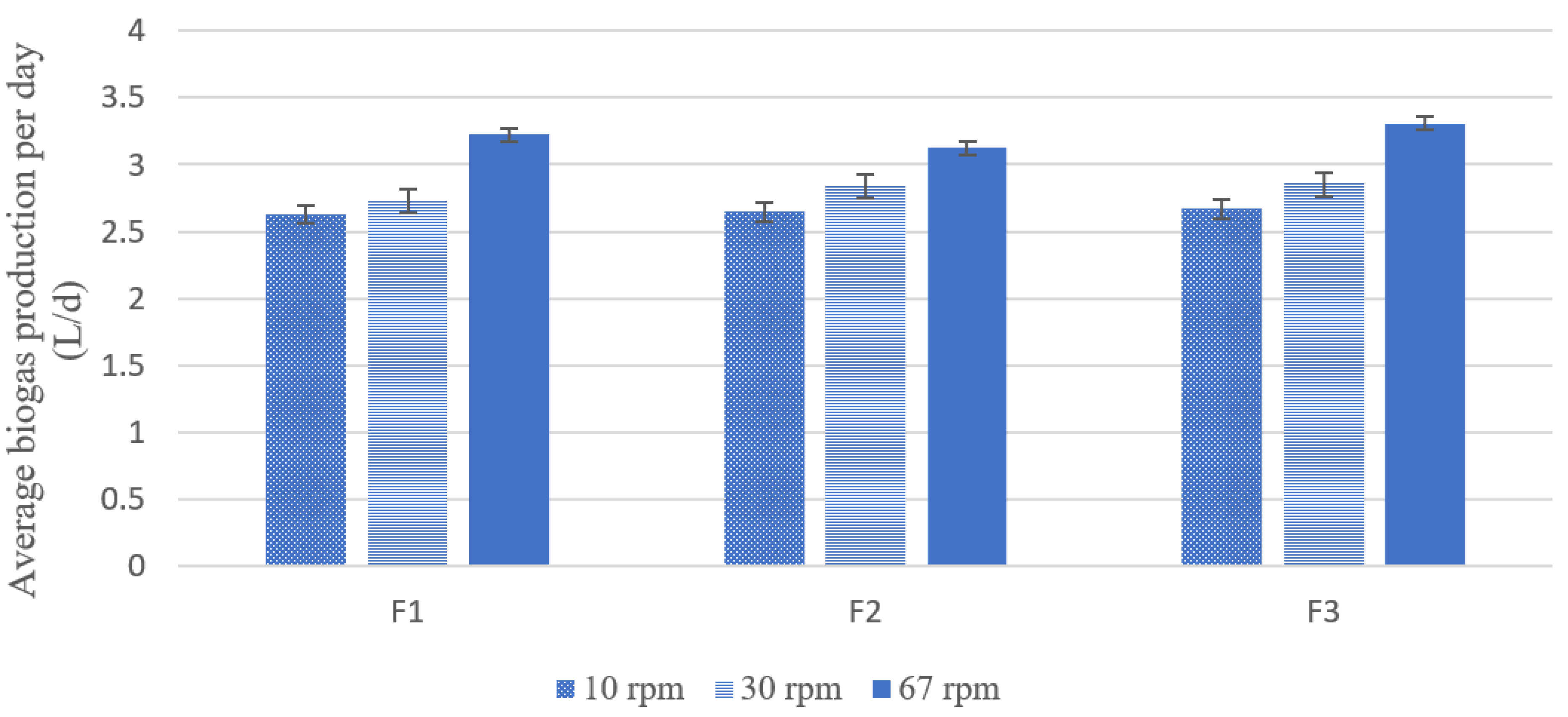
3.2. Effect of Mixing Intensity on Biogas Production Rate
3.3. Statistical Data Analysis
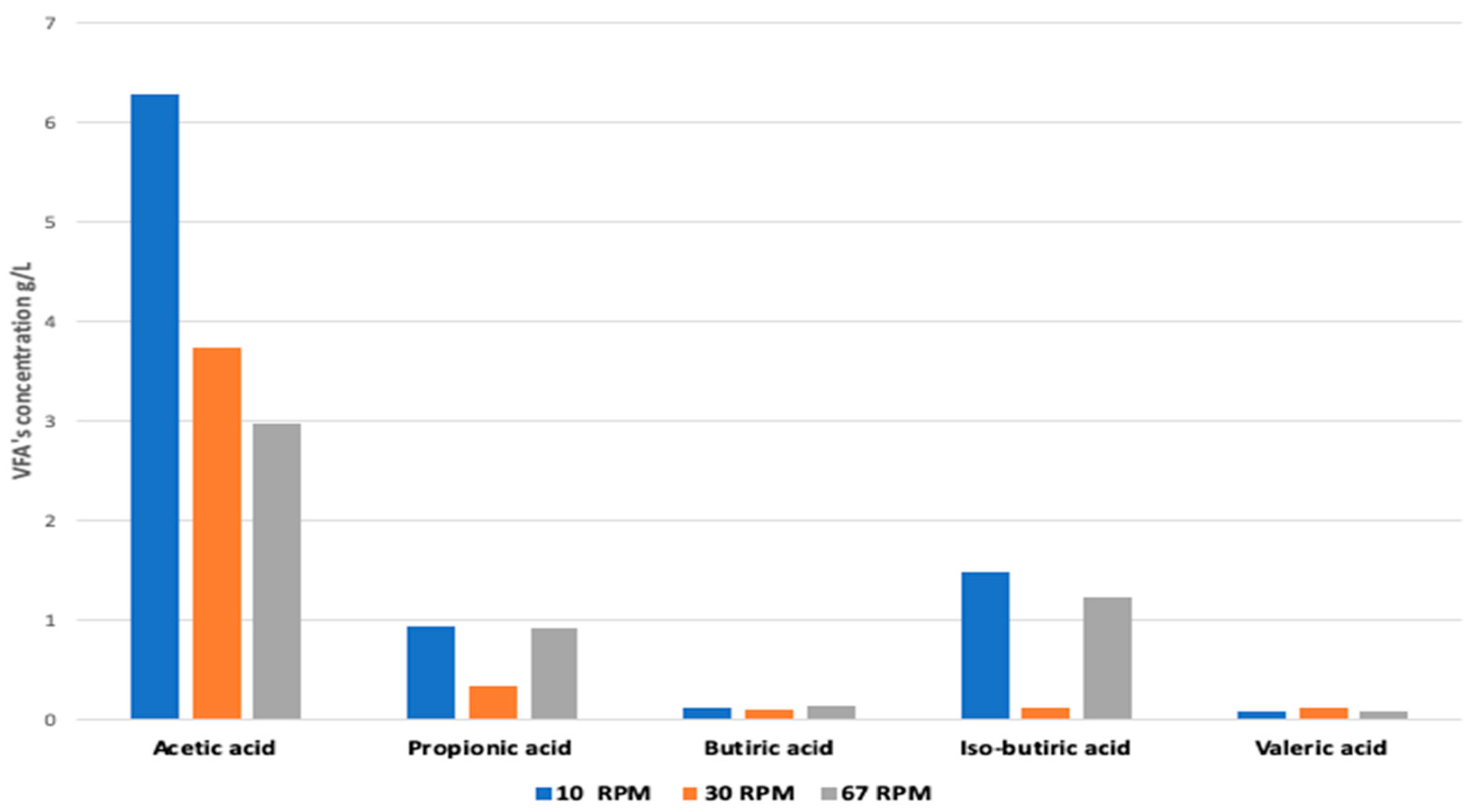
3.4. Effect of Mixing Regimes on VFA Accumulation
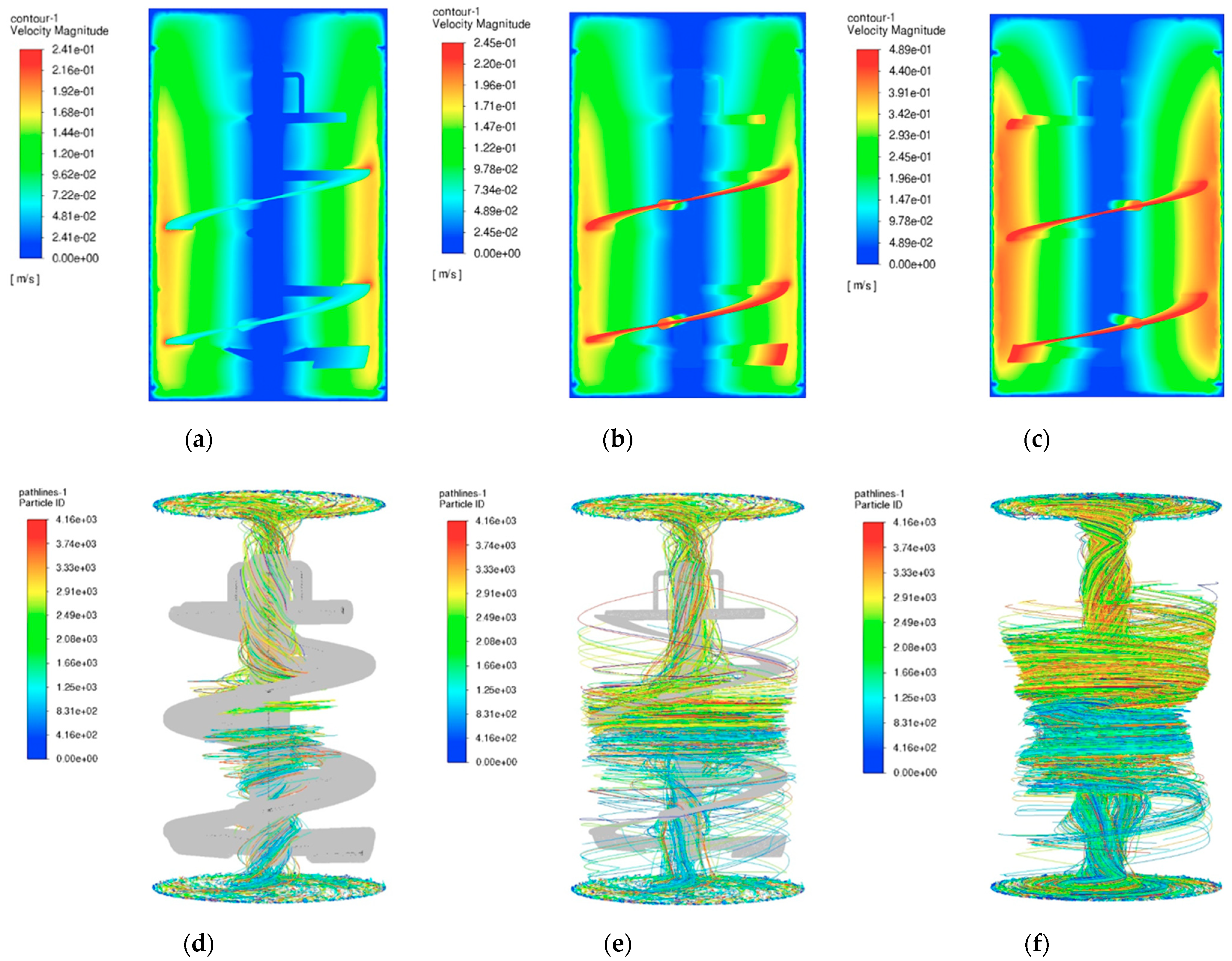
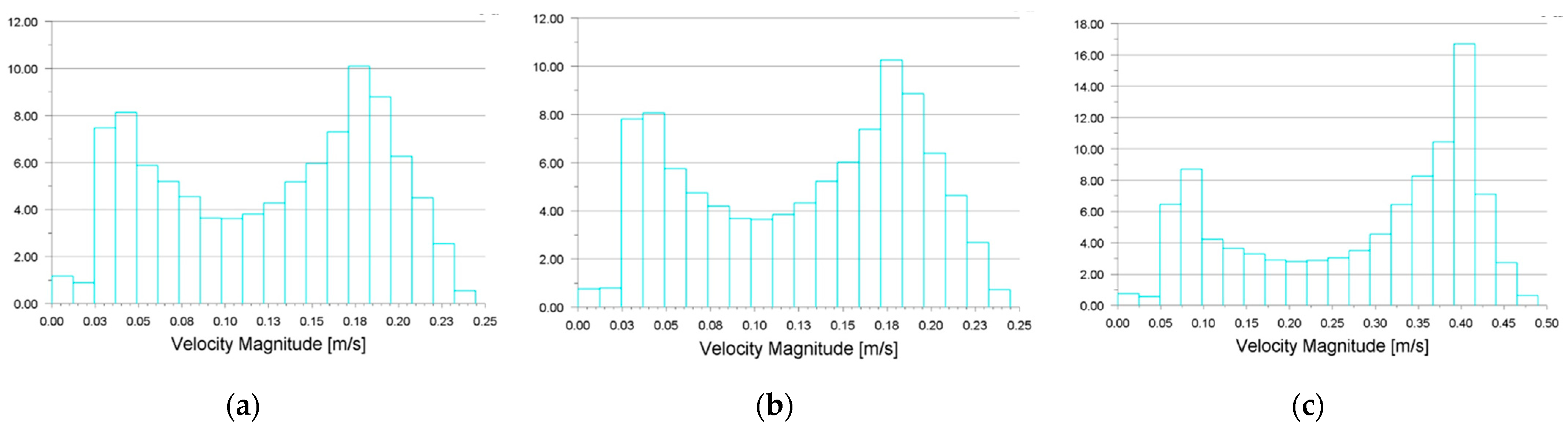
4. Numerical Simulation of Digester Hydrodynamics
5. Effect of Geometrical Characteristics on Flow Patterns and Mixing Efficiency
6. Practical Implication of This Study
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dieter Deublein, A.S. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, A.; Di Capua, F.; Esposito, G.; Pirozzi, F. Long-term biogas desulfurization under different microaerobic conditions in full-scale thermophilic digesters co-digesting high-solid sewage sludge. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 142, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfner-sixt, K.; Amon, T. Monitoring of Agricultural Biogas Plants in Austria—Mixing Technology and Specific Values of Essential Process Parameters. In Proceedings of the 15th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, Berlin, Germany, 7–11 May 2007; Volume 711, p. 17181728. [Google Scholar]
- Gerardi, M.H. The Microbiology of Anaerobic Digesters; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Buta, S.; Zoltán, S.; Zoltán, S. State of the art on mixing in an anaerobic digester: A review. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. CFD simulation of gas and non-Newtonian fluid two-phase flow in anaerobic digesters. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3861–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, U.; Viccione, G.; Coppola, S.; Landi, A.; Meda, A.; Gualtieri, C. Analysis of anaerobic digester mixing: Comparison of long shafted paddle mixing vs gas mixing. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tay, J.H. The essential role of hydrodynamics shear force in the formation of biofilm and granular sludge. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1635–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.A.; Garcia, M.L.; Veskivar, M.; Karim, K.; Al-Dahhan, M.H.; Angenent, L.T. Effect of shear on performance and microbial ecology of continuously stirred anaerobic digesters treating animal manure. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 100, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, J.; Poncin, S.; Li, H.Z. Effect of hydrodynamic shear on biogas production and granule characteristics in a continuous stirred tank reactor. Process. Biochem. 2016, 51, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, J.; Grüssing, F.; Nägele, H.; Oechsner, H. Cutting the Electric Power Consumption of Biogas Plants: The Impact of New Technologies. Landtechnik 2013, 68, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Szamosi, Z.; Siménfalvi, Z. Hydrodynamic factors in an anaerobic digester. Publ. MultiScience 2018, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebranchu, A.; Delaunay, S.; Marchal, P.; Blanchard, F.; Pacaud, S.; Fick, M.; Olmos, E. Impact of shear stress and impeller design on the production of biogas in anaerobic digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Fino, D.; Mancini, G.; Ruggeri, B. Mixing in digesters used to treat high viscosity substrates: The case of olive oil production wastes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trad, Z.; Vial, C.; Fontaine, J.P.; Larroche, C. Mixing and liquid-to-gas mass transfer under digester operating conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 170, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, V. Mixing V1: Theory And Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 0323154727. [Google Scholar]
- Aranowski, R.; Hupka, J.; Jungnickel, C. Changes in rheological properties during anaerobic digestion of activated sludge. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2010, 44, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hreiz, R.; Adouani, N.; Fünfschilling, D.; Marchal, P.; Pons, M.N. Rheological characterization of raw and anaerobically digested cow slurry. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 119, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Capua, F.; Spasiano, D.; Giordano, A.; Adani, F.; Fratino, U.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Capua, F.; Adani, F.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G.; Giordano, A. Air side-stream ammonia stripping in a thin film evaporator coupled to high-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Process performance and interactions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Tian, L.; Yuan, H.; Pang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zou, D.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Improving the mixing performances of rice straw anaerobic digestion for higher biogas production by computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivard, C.J.; Kay, B.D.; Kerbaugh, D.H.; Nagle, N.J.; Himmel, M.E. Horsepower requirements for high-solids anaerobic digestion. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1995, 51–52, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiraftabi, M.; Khiadani, M.; Mohammed, H.A. Chemical Engineering & Processing: Process Intensification Performance of a dual helical ribbon impeller in a two-phase (gas-liquid) stirred tank reactor. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2020, 148, 107811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, E.; Wirth, R.; Maróti, G.; Bagi, Z.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, K.L. Biogas production from protein-rich biomass: Fed-batch anaerobic fermentation of casein and of pig blood and associated changes in microbial community composition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B. CFD investigation of turbulence models for mechanical agitation of non-Newtonian fluids in anaerobic digesters. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B. Large eddy simulation of mechanical mixing in anaerobic digesters. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadrezaei, R.; Zareei, S.; Behroozi-Khazaei, N. Improving the performance of mechanical stirring in biogas plant by computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2017, 19, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Manea, E.; Robescu, D. Simulation of mechanical mixing in anaerobic digesters. UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. D Mech. Eng. 2012, 74, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X. Rheological properties of municipal sewage sludge: Dependency on solid concnetration and temperature. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, B.; Yin, Y.; Li, X. Calculation of Metzner Constant for Double Helical Ribbon Impeller by Computational Fluid Dynamic Method. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 16, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.C.; Pearce, M.E.J. Effects of mixing on anaerobic treatment of potato-processing wastewater. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1991, 18, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Chauliac, D.; Pullammanappallil, P. Comparison of non-agitated and agitated batch, thermophilic anaerobic digestion of sugarbeet tailings. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Cabrol, L.; Ruiz-Filippi, G.; Pullammanappallil, P. Microbial ecology in anaerobic digestion at agitated and non-agitated conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, X.; Cuetos, M.J.; Cara, J.; Morán, A.; García, A.I. Anaerobic co-digestion of primary sludge and the fruit and vegetable fraction of the municipal solid wastes. Conditions for mixing and evaluation of the organic loading rate. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanimeh, S.A.; Al-Sanioura, D.N.; Saikaly, P.E.; El-Fadel, M. Correlation between system performance and bacterial composition under varied mixing intensity in thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 206, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astals, S.; Nolla-Ardèvol, V.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and crude glycerol at mesophilic conditions: Biogas and digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavilin, V. Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Material: Multidimensional Modeling of Continuous-Flow Reactor With Non-Uniform Influent Concentration Distributions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, M.; Ahring, B.K. Ahring Anaerobic treatment of fish meal process waste-water in a UASB reactor at high pH. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 36, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parag, R.; Gogatea Anthony, A.C.M.; Beenackersb, A.B.P. Multiple-impeller systems with a special emphasis on bioreactors: A critical review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2000, 6, 109–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Yuan, H.; Pang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zou, D.; Zhu, B.; Ma, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Performances of anaerobic co-digestion of fruit & vegetable waste (FVW) and food waste (FW): Single-phase vs. two-phase. Bioresource Technol. 2013, 144, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindall, R.; Bridgeman, J.; Carliell-Marquet, C. Velocity gradient as a tool to characterise the link between mixing and biogas production in anaerobic waste digesters. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 2800–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, H.K.; Greenfield, P.F.; Pullammanappallil, P.C. Effect of mixing on biomethanation of cattle-manure slurry. Environ. Technol. 2002, 23, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.-F.; Ren, N.-Q.; Guo, W.-Q. CFD optimization of continuous stirred-tank (CSTR) reactor for biohydrogen production. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7005–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmer, A.; Naegele, H.J.; Sondermann, J. How efficient are agitators in biogas digesters? Determination of the efficiency of submersible motor mixers and incline agitators by measuring nutrient distribution in full-scale agricultural biogas digesters. Energies 2013, 6, 6255–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Szamosi, Z.; Siménfalvi, Z. Impact of mixing intensity and duration on biogas production in an anaerobic digester: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrew, G. Hashimoto Effect of mixing duration and vacuum on methane production rate from beef cattle waste. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1982, 24, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Hughes, W. Optimisation of Methane Production from Anaerobically Digested Cow Slurry Using Mixing Regime and Hydraulic Retention Time. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, K.; Hoffmann, R.; Klasson, T.; Al-Dahhan, M.H. Anaerobic digestion of animal waste: Waste strength versus impact of mixing. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
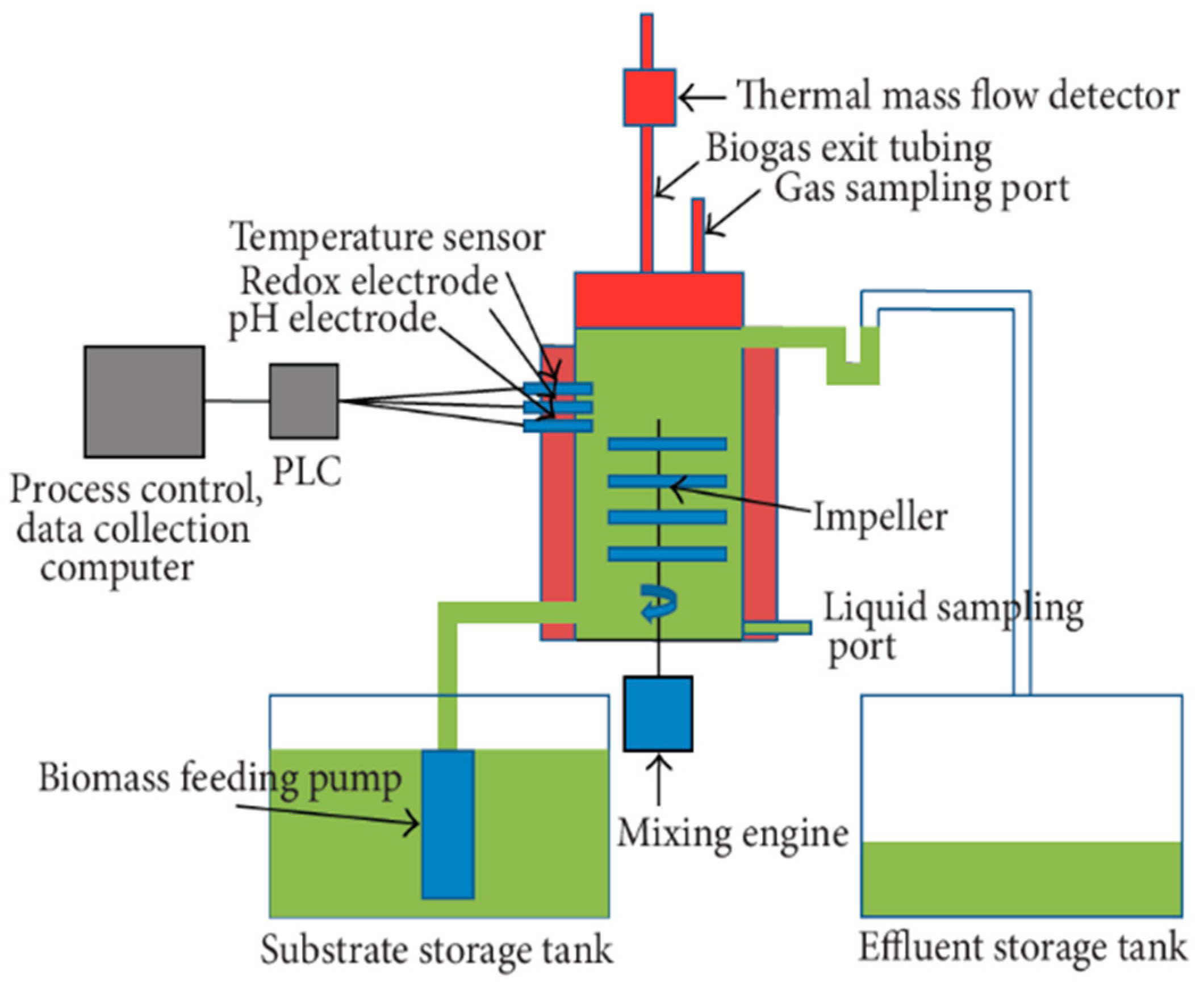




| Parameter. | Dimensions (mm) |
|---|---|
| Diameter of tank (D) | 260 |
| Height of liquid (H) | 232 |
| Diameter of impeller (d) | 150 |
| Height of blade (h) | 15 |
| Length of blade (l) | 20 |
| Off bottom clearance (C1) | 50 |
| Inter impeller spacing (C2) | 88 |
| C1/d | 0.9 |
| C2/d | 1.2 |
| Parameter | Value Range |
|---|---|
| TS (%) | 4.28 |
| SS (g L−1) | 57.8 ± 10.0 |
| Total carbon (%) | 46.2 |
| TVS (g L−1) | 87.6 ± 3.4 |
| COD (g L−1) | 141 ± 6.4 |
| VFA (g L−1) | 4.15 ± 1.38 |
| pH | 8.6 |
| ρ (kg m−3) | 1068 |
| HRT (d) | 15 |
| Temperature (°C) | (Pa sn) | n | y (s−1) | η (Pa s) | ρ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37 | 0.19 | 0.56 | 0.237 | 0.01–0.03 | 1000.78 |
| n (rpm) | Mixing Regime | Shear Rate [ (s−1)] | Shear Stress [τ (Pa)] | BPR (L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5 min/h | 5.6 | 5.14 | 43.5 |
| 30 | 5 min/h | 17.4 | 9.54 | 45.2 |
| 67 | 5 min/h | 39 | 14.99 | 52.5 |
| Batch 1 (10 RPM) (Period 15–30 Days) | Batch 2 (30 RPM) (Period 31–48 Days) | Batch 3 (67 RPM) (Period 48–64 Days) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermenters | F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F3 |
| Total biogas production | 45.1 | 44.2 | 43.5 | 48.6 | 42.6 | 45.2 | 51.5 | 48.6 | 52.5 |
| VFAs (g/L) | 7.3 | 6.1 | 5.8 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 4.9 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| pH | 7.4 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.0 |
| NH4+-N (g/L) | 0.95 | 0.93 | 1.15 | 0.78 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.59 |
| FAS/TOC ratio | 0.35 | 0.69 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.41 |
| Data Set | p Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | F1 | F2 | F3 | 0.66454 |
| 30 | F2 | F3 | F3 | 0.561287 |
| 67 | F1 | F3 | F3 | 0.084101 |
| F1 | 10 | 30 | 0.0032712 | |
| 30 | 67 | 1.0968 × 10−12 | ||
| 10 | 67 | 6.65976 × 10−26 | ||
| F2 | 10 | 30 | 0.00138614 | |
| 30 | 67 | 7.69224 × 10−10 | ||
| 10 | 67 | 0.001386142 | ||
| F3 | 10 | 30 | 0.01789452 | |
| 30 | 67 | 2.47333 × 10−12 | ||
| 10 | 67 | 2.49809 × 10−18 | ||
| Rpm | Torque (Nm) | Maximum Velocity (m s−1) | Average Velocity (m s−1) | Dead Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3.9 × 10−6 | 0.5 | 0.28 | 18% |
| 30 | 3.9 × 10−6 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 17% |
| 67 | 1.33 × 10−5 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, B.; Kovács, K.L.; Bagi, Z.; Nyári, J.; Szepesi, G.L.; Petrik, M.; Siménfalvi, Z.; Szamosi, Z. Enhancing Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion by Optimization of Mixing Regimes Using Helical Ribbon Impeller. Fermentation 2021, 7, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040251
Singh B, Kovács KL, Bagi Z, Nyári J, Szepesi GL, Petrik M, Siménfalvi Z, Szamosi Z. Enhancing Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion by Optimization of Mixing Regimes Using Helical Ribbon Impeller. Fermentation. 2021; 7(4):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040251
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Buta, Kornél L. Kovács, Zoltán Bagi, József Nyári, Gábor L. Szepesi, Máté Petrik, Zoltán Siménfalvi, and Zoltán Szamosi. 2021. "Enhancing Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion by Optimization of Mixing Regimes Using Helical Ribbon Impeller" Fermentation 7, no. 4: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040251
APA StyleSingh, B., Kovács, K. L., Bagi, Z., Nyári, J., Szepesi, G. L., Petrik, M., Siménfalvi, Z., & Szamosi, Z. (2021). Enhancing Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion by Optimization of Mixing Regimes Using Helical Ribbon Impeller. Fermentation, 7(4), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040251










