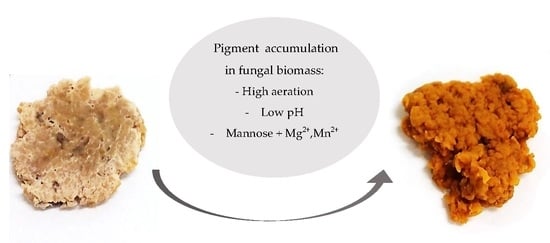
Pigment Production by the Edible Filamentous Fungus Neurospora Intermedia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strain
2.2. Submerged Cultivation in Shake-Flasks
2.3. Bubble Column Bioreactor
2.4. Extraction and Estimation of Neurospora Intermedia Orange Pigment
2.5. Analytical Methods
Thin-Layer Chromatography
3. Results
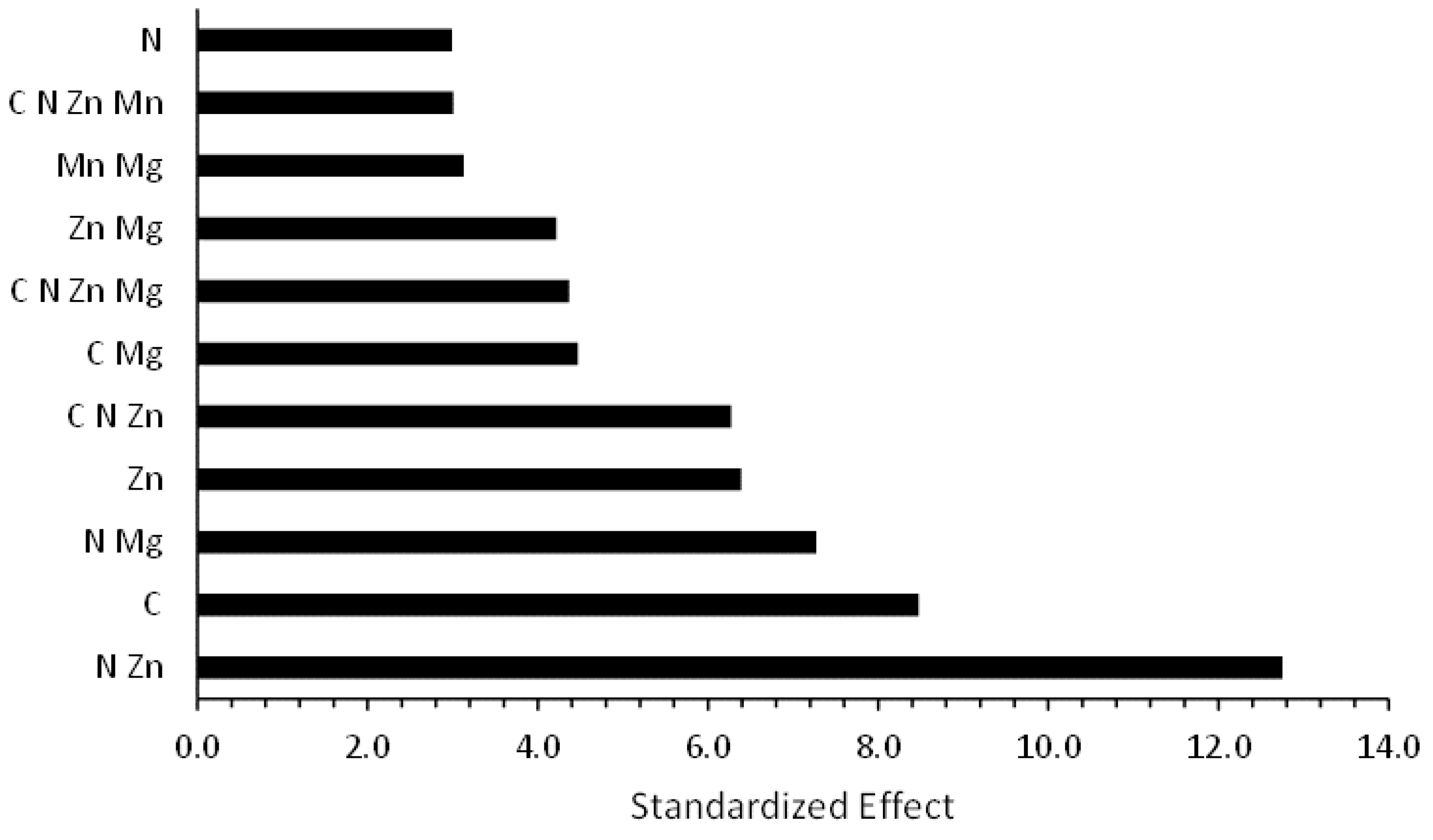
3.1. Effect from Factors on Pigmentation from Full Factorial Design
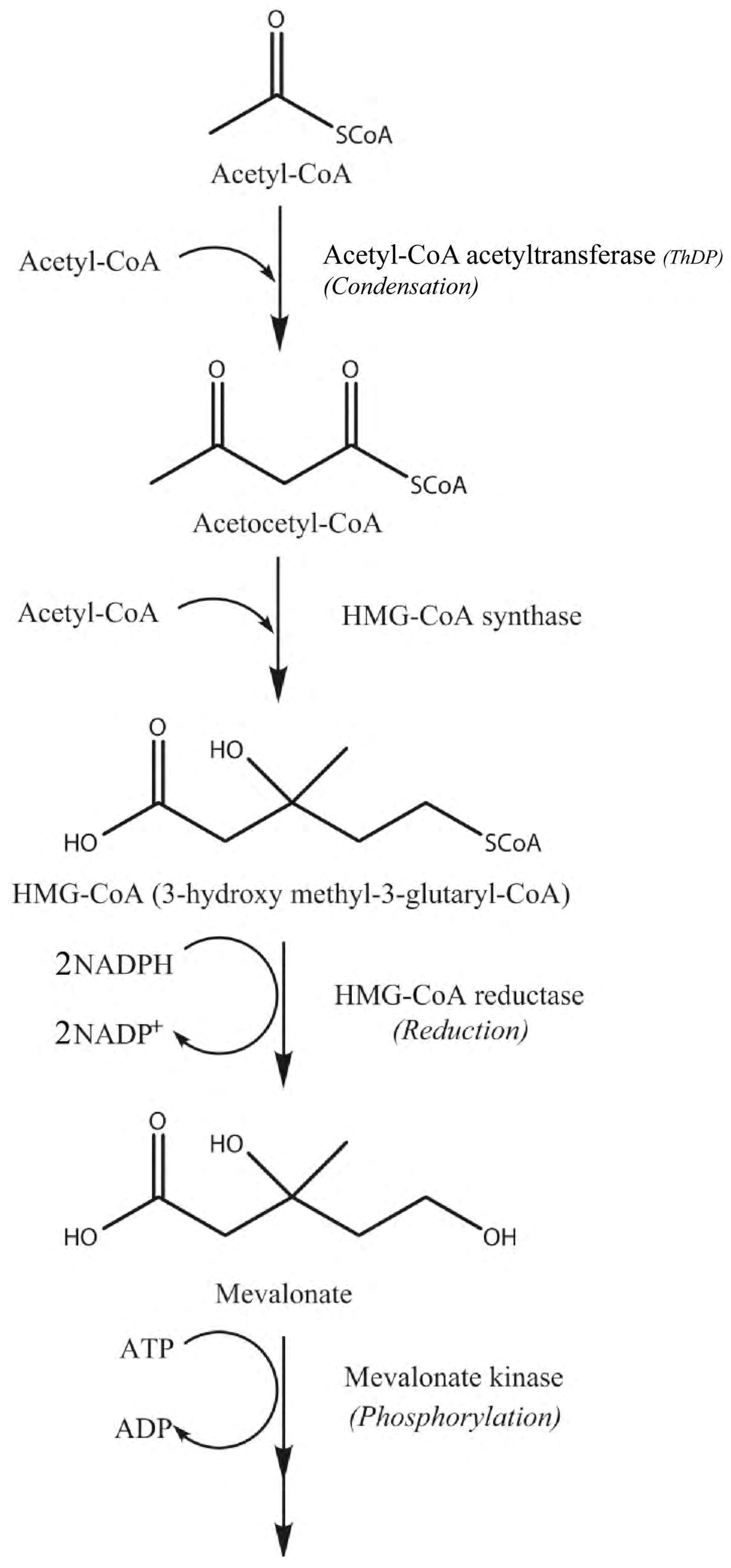
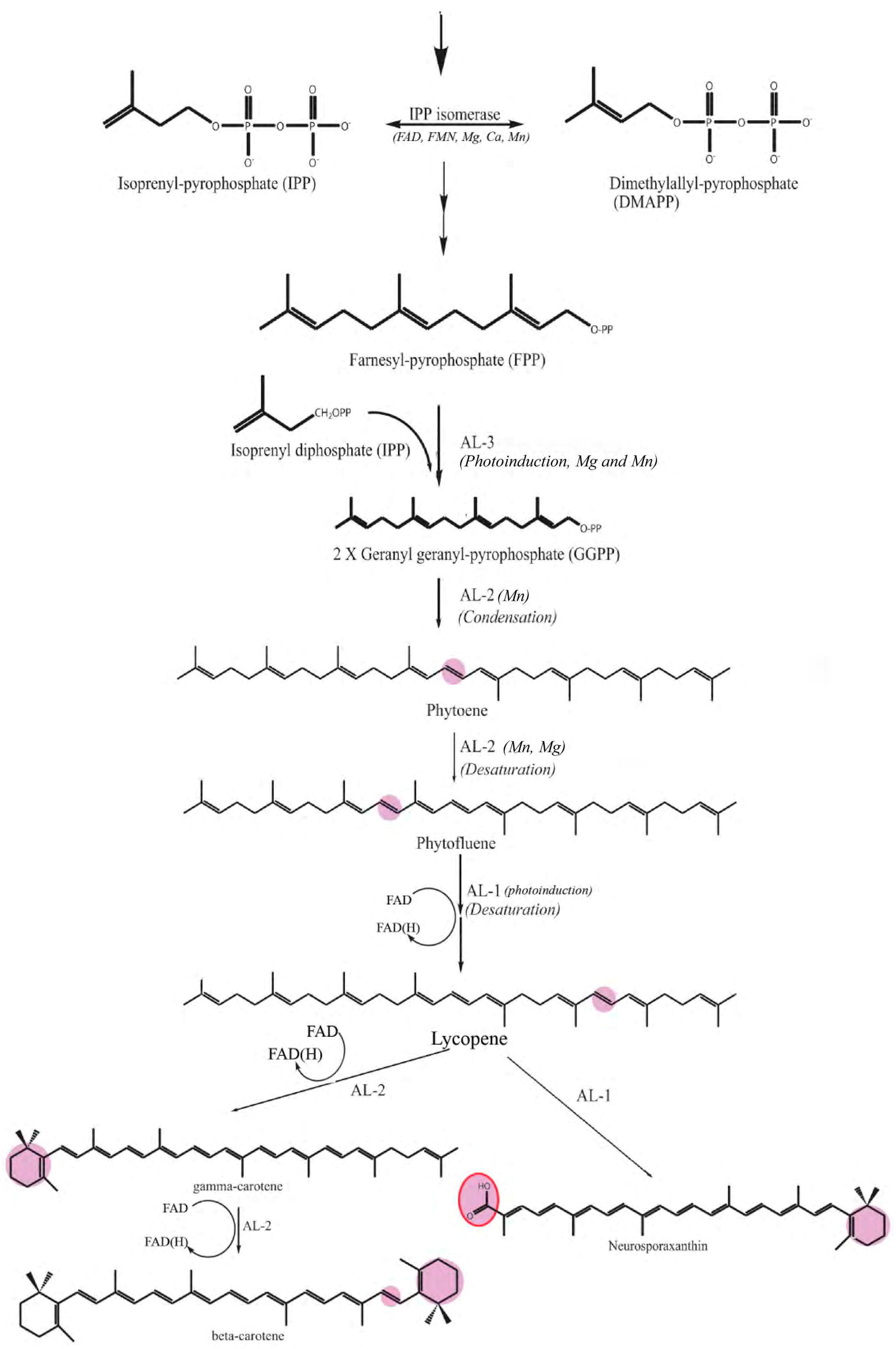
3.2. Effect of Carbon Source
3.3. Effect of Addition of Trace Metals
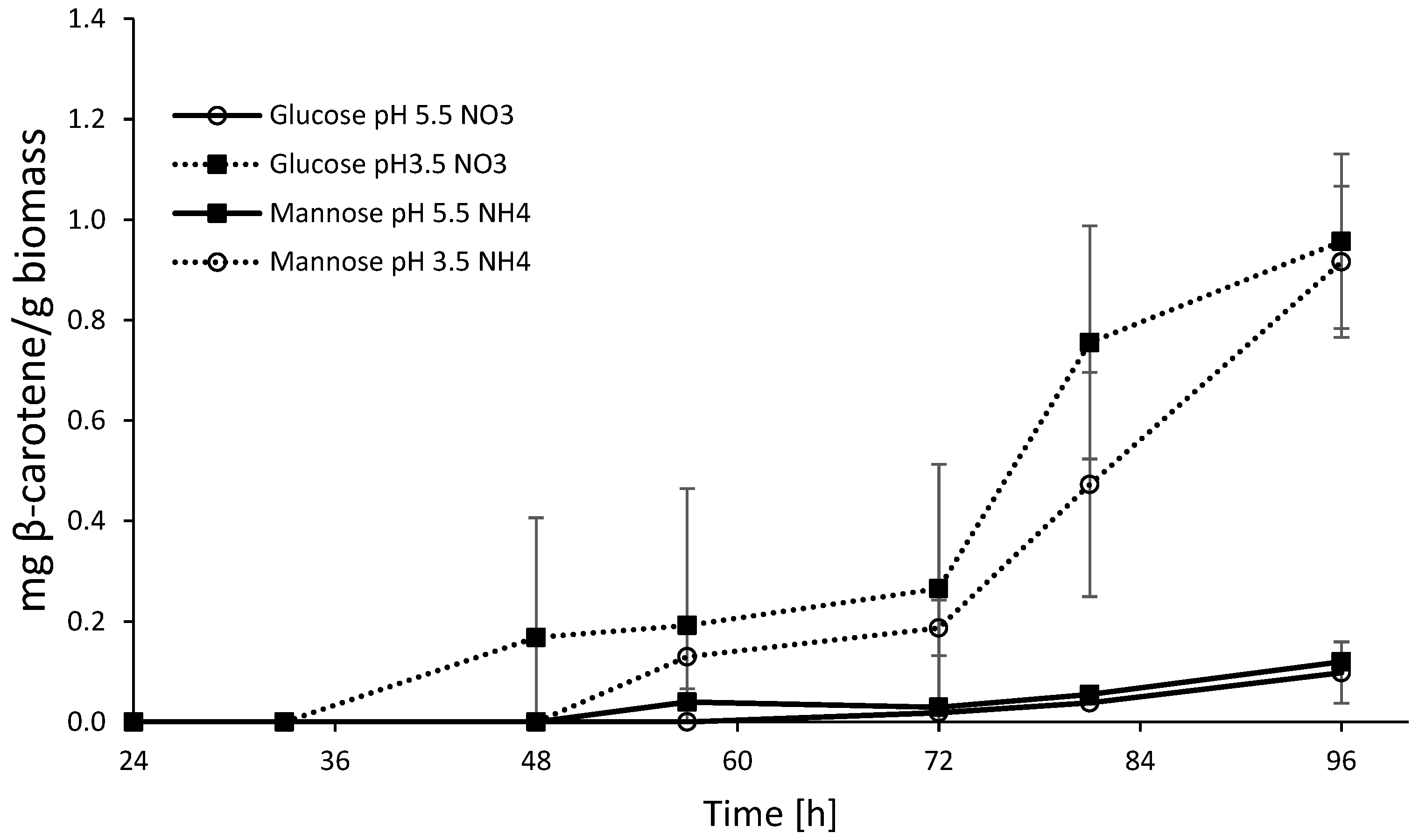
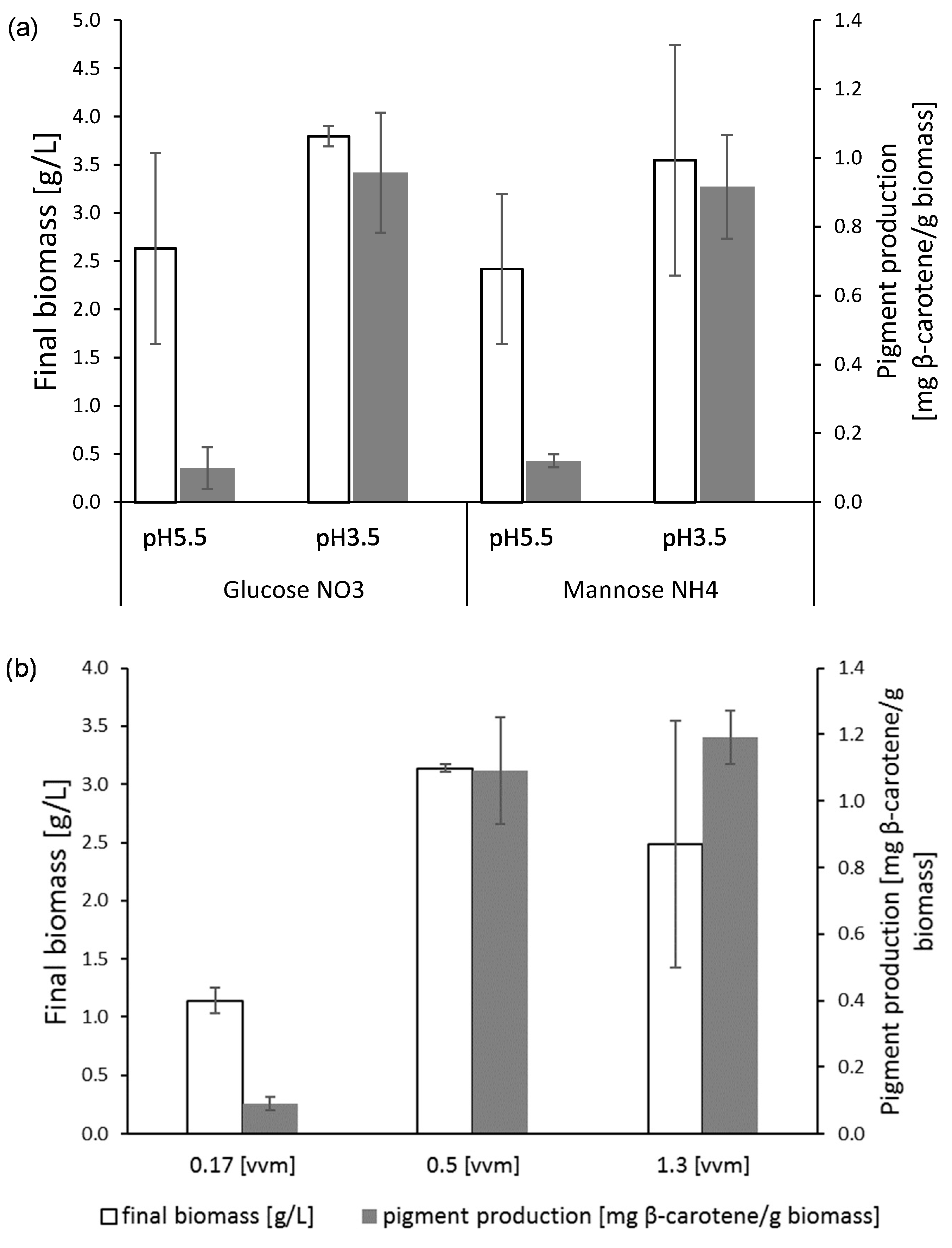
3.4. Effect of Nitrogen Source vs. pH
3.4.1. Nitrogen Source
3.4.2. Effect of pH
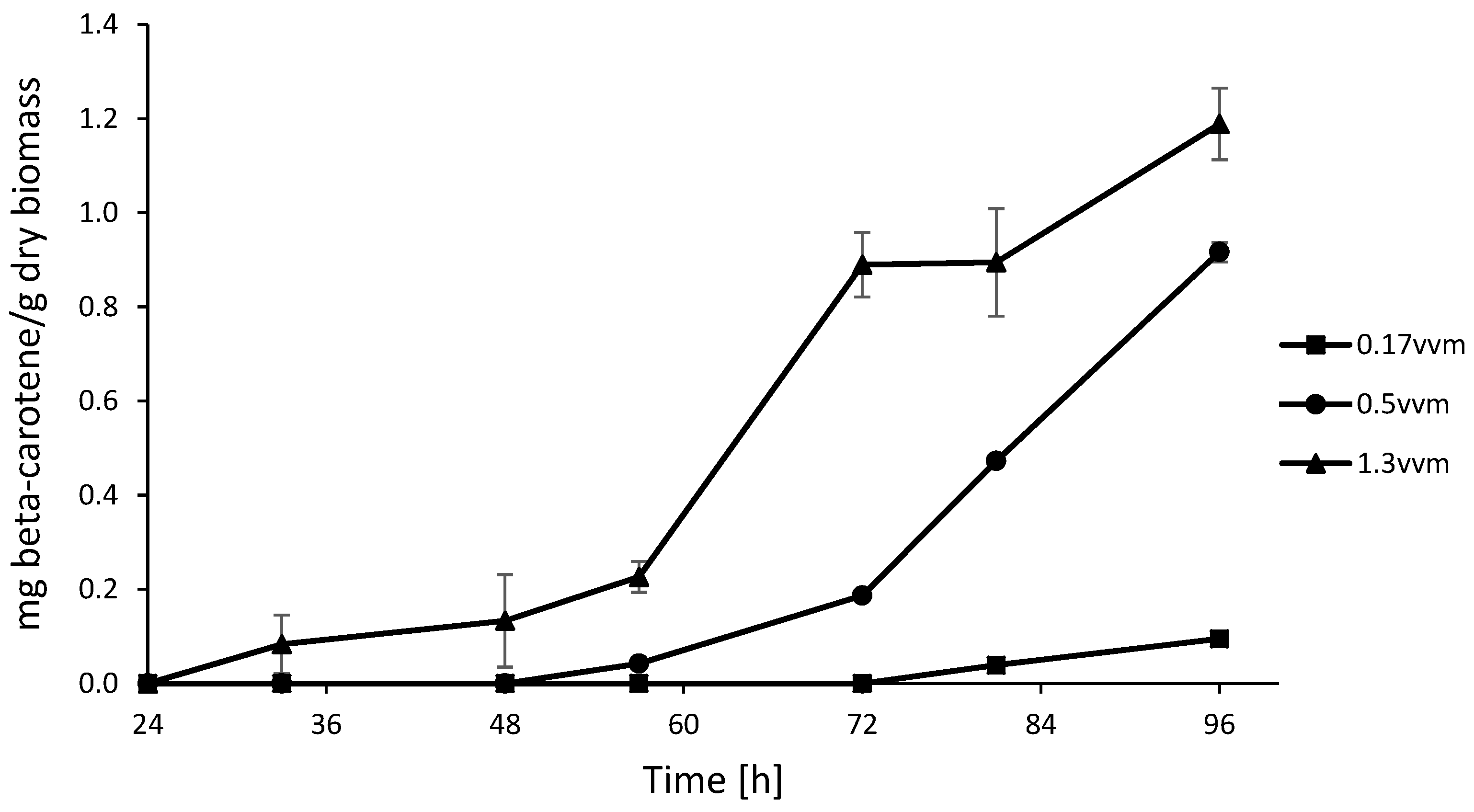
3.5. Aeration
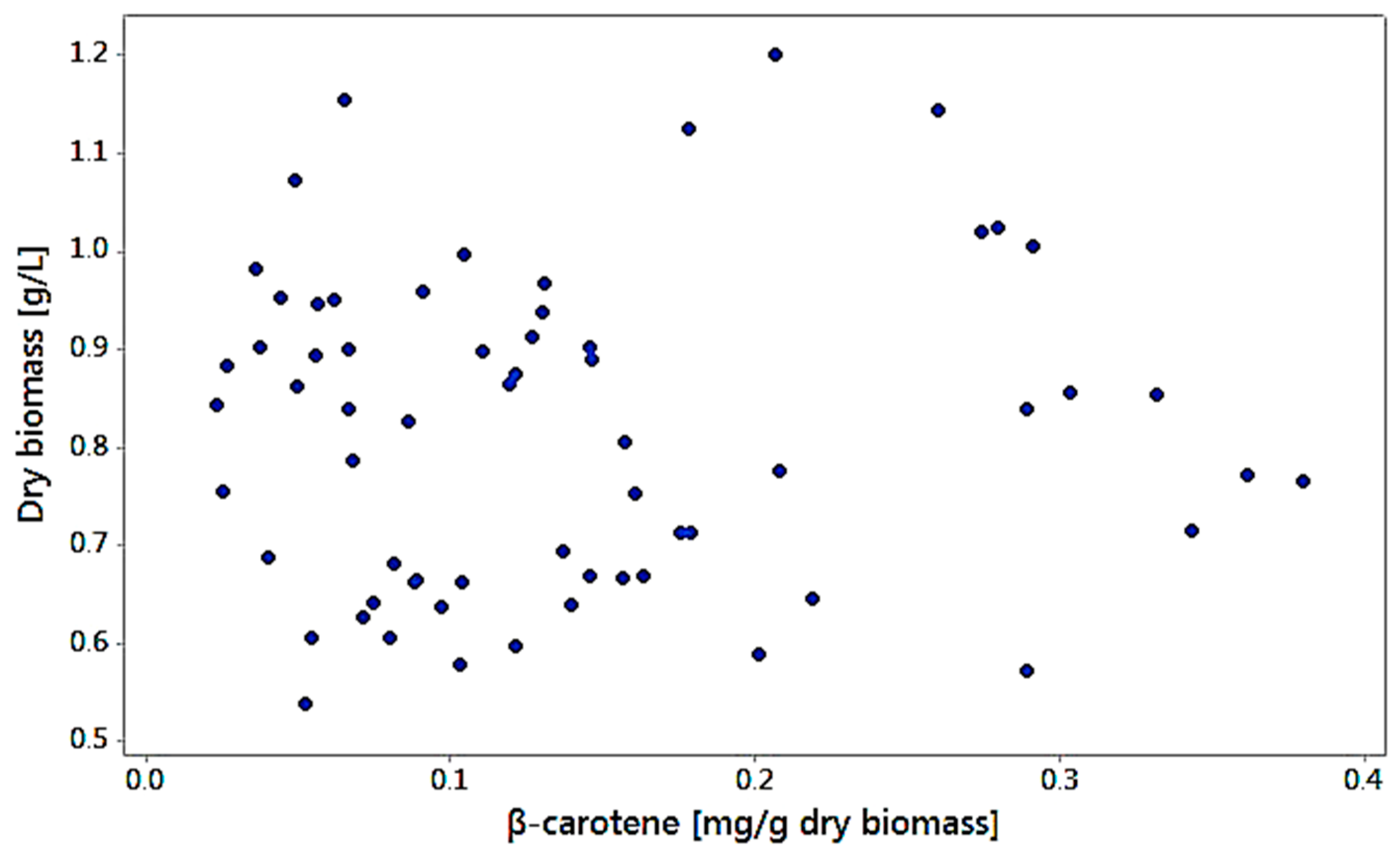
3.6. Biomass Production Related to Carotenoid Production
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gusdinar, T.; Singgih, M.; Priatni, S.; Sukmawati, A.; Suciati, T. Enkapsulasi dan stabilitas pigmen karotenoid dari Neurospora intermedia n-1 (encapsulation and the stability of carotenoids from Neurospora intermedia n-1). J. Mns. Lingkung. 2014, 18, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Holme, I. Sir william henry perkin: A review of his life, work and legacy. Coloration Technol. 2006, 122, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A.Y.; Alnaeeli, M.; Park, J.K. Production control and characterization of antibacterial carotenoids from the yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa ay-01. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.A.E.; Zaccarim, B.R.; de Lencastre Novaes, L.C.; Jozala, A.F.; Dos Santos, C.A.; Teixeira, M.F.S.; Santos-Ebinuma, V.C. Natural colorants from filamentous fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.K.; Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Carotenoids from fruits and vegetables: Chemistry, analysis, occurrence, bioavailability and biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Almanza, A.; Montanez, J.C.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Martínez-Ávila, C.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Aguilar, C.N. Rhodotorula glutinis as source of pigments and metabolites for food industry. Food Biosci. 2014, 5, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, B.; Archer, D.; Giavasis, I.; Harvey, L. Microbial Production of Food Ingredients, Enzymes and Nutraceuticals; Elsevier Science: Burlington, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Singgih, M.; Andriatna, W.; Damayanti, S.; Priatni, S. Carotenogenesis study of neurospora intermedia n-1 in liquid substrate fermentation. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 842–847. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa Souza, P.N.; Grigoletto, T.L.B.; de Moraes, L.A.B.; Abreu, L.M.; Guimarães, L.H.S.; Santos, C.; Galvão, L.R.; Cardoso, P.G. Production and chemical characterization of pigments in filamentous fungi. Microbiology 2016, 162, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nout, M.J.R.; Aidoo, K.E. Asian fungal fermented food. In Industrial applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 29–58. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, D.D.; Davis, R.H. Evidence for safety of neurospora species for academic and commersial uses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5107–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, A.M. Ramesh Life-history of neurospora intermedia in a sugar cane field. J. Biosci. 1996, 21, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.; Lennartsson, P.R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Production of ethanol and biomass from thin stillage using food-grade zygomycetes and ascomycetes filamentous fungi. Energies 2014, 7, 3872–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapari, S.A.; Thrane, U.; Meyer, A.S. Fungal polyketide azaphilone pigments as future natural food colorants? Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gmoser, R.; Ferreira, J.A.; Lennartsson, P.R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Filamentous ascomycetes fungi as a source of natural pigments. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2017, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sues, A.; Millati, R.; Edebo, L.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Ethanol production from hexoses, pentoses, and dilute-acid hydrolyzate by mucor indicus. FEMS Yeast Res. 2005, 5, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, B.-B.; Liu, X.-D.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Xu, G.-R.; Cheung, P.C.K. Enhanced production of natural yellow pigments from monascus purpureus by liquid culture: The relationship between fermentation conditions and mycelial morphology. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varzakakou, M.; Roukas, T.; Kotzekidou, P.; Giamoustaris, A. Effect of non-ionic surfactants and beta-ionone on the morphology of blakeslea trispora and carotenoids production from cheese whey in submerged aerobic growth: A statistical approach. Food Biotechnol. 2010, 24, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, A.; Pérez, C.; Montañéz, J.C.; Martínez, G.; Aguilar, C.N. Red pigment production by penicillium purpurogenum gh2 is influenced by ph and temperature. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2011, 12, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandmann, G. Photoregulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in mutants of Neurospora crassa: Activities of enzymes involved in the synthesis and conversion of phytoene. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 1993, 48, 570–574. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Du, X.; Li, P.; Liang, B.; Cheng, X.; Du, L.; Huang, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Complete genome sequence and transcriptomics analyses reveal pigment biosynthesis and regulatory mechanisms in an industrial strain, Monascus purpureus yy-1. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.; Zheng, H.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Optimization of β-glucuronidase activity from Lactobacillus delbrueckii Rh2 and its use for biotransformation of baicalin and wogonoside. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S. Finding and producing probiotic glycosylases for the biocatalysis of ginsenosides: A mini review. Molecules 2016, 21, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcoleta, A.; Niklitschek, M.; Wozniak, A.; Lozano, C.; Alcaíno, J.; Baeza, M.; Cifuentes, V. Glucose and ethanol-dependent transcriptional regulation of the astaxanthin biosynthesis pathway in Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolland, F.; Winderickx, J.; Thevelein, J.M. Glucose-sensing and-signalling mechanisms in yeast. FEMS Yeast Res. 2002, 2, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaíno, J.; Bravo, N.; Córdova, P.; Marcoleta, A.E.; Contreras, G.; Barahona, S.; Sepúlveda, D.; Fernández-Lobato, M.; Baeza, M.; Cifuentes, V. The involvement of mig1 from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous in catabolic repression: An active mechanism contributing to the regulation of carotenoid production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, P. Environmental and cultural stimulants in the production of carotenoids from microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 63, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, R.; Kritchevsky, D. Advances in Lipid Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- An, G.-H.; Chang, K.-W.; Johnson, E.-A. Effect of oxygen radicals and aeration on carotenogenesis and growth of phaffia rhodozyma (Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Clastre, M.; Bantignies, B.; Feron, G.; Soler, E.; Ambid, C. Purification and characterization of geranyl diphosphate synthase from vitis vinifera l. Cv muscat de frontignan cell cultures. Plant Physiol. 1993, 102, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium. Uniprot: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45, D158–D169. [Google Scholar]
- Mitzka-Schnabel, U. Carotenogenic enzymes from neurospora. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.T.; McHan, F. Some effects of zinc on the utilization of carbon sources by Monascus purpureus. Mycologia 1975, 67, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, F.M.; Brooks, J.; Chisti, Y. Optimal c: N ratio for the production of red pigments by Monascus ruber. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carels, M.; Shepherd, D. The effect of different nitrogen sources on pigment production and sporulation of Monascus species in submerged, shaken culture. Can. J. Microbiol. 1977, 23, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuraini, S.; Latif, S.A. Improving the quality of tapioca by product through fermentation by Neurospora crassa to produce $ carotene rich feed. Pak. J. Nutr. 2009, 8, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Ortiz, R.; Limón, M.C.; Avalos, J. Regulation of carotenogenesis and secondary metabolism by nitrogen in wild-type Fusarium fujikuroi and carotenoid-overproducing mutants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.H. Chemical requirements for growth. In Fungal Physiology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 133. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, S.; Rutz, B.; Rodríguez-Sanoja, R. Microbial production of carotenoids. In Microbial Production of Food Ingredients, Enzymes and Nutraceuticals; McNeil, B., Archer, D., Giavasis, I., Harvey, L., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Burlington, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 194–223. [Google Scholar]
- Velmurugan, P.; Lee, Y.H.; Nanthakumar, K.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Dufossé, L.; Mapari, S.A.S.; Oh, B.T. Water-soluble red pigments from Isaria farinosa and structural characterization of the main colored component. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Niu, Y.; Duan, C.; Su, H.; Yan, G. A ph control strategy for increased β-carotene production during batch fermentation by recombinant industrial wine yeast. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Ju, J.Y. Morphological change and enhanced pigment production of Monascus when cocultured with Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Aspergillus oryzae. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998, 59, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaj, H.; Blanc, P.; Groussac, E.; Uribelarrea, J.-L.; Goma, G.; Loubiere, P. Kinetic analysis of red pigment and citrinin production by Monascus ruber as a function of organic acid accumulation. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2000, 27, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Jung, J.; Hyung, W.; Haam, S.; Shin, C. Enhancement of monascus pigment production by the culture of Monascus sp. J101 at low temperature. Biotechnol. Progress 2006, 22, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Carbon Source (100 mM) | Nitrogen Source (4 mM) | ZnCl2 (mM) | MgCl2 (mM) | MnCl2 (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Ammonium chloride | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Mannose | Sodium nitrate | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nitrogen Source (4 mM) | Zn2+ (mM) | Mn2+ (mM) | Mg2+ (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+ | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| NO3− | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| NH4+ | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| NH4+ | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| NH4+ | 10 | 10 | 0 |
| NO3− | 10 | 10 | 0 |
| NO3− | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| NH4+ | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| NO3− | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| NO3− | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| NH4+ | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NO3− | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NO3− | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| NO3− | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| NH4+ | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| NH4+ | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| Term | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Constant | 34.61 | 0.000 |
| Carbon | 8.47 | 0.000 |
| Nitrogen | 2.99 | 0.005 |
| Zn | −6.39 | 0.000 |
| Carbon × Mg | 4.47 | 0.000 |
| Nitrogen × Zn | 12.75 | 0.000 |
| Nitrogen × Mg | 7.27 | 0.000 |
| Zn × Mg | 4.22 | 0.000 |
| Mn × Mg | 3.13 | 0.004 |
| Carbon × Nitrogen × Zn | 6.27 | 0.000 |
| Carbon × Nitrogen × Zn × Mn | 3.01 | 0.005 |
| Carbon × Nitrogen × Zn × Mg | 4.37 | 0.000 |
| S | R-sq | R-sq(adj) |
| 0.0322918 | 93.86% | 87.92% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gmoser, R.; Ferreira, J.A.; Lundin, M.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Lennartsson, P.R. Pigment Production by the Edible Filamentous Fungus Neurospora Intermedia. Fermentation 2018, 4, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4010011
Gmoser R, Ferreira JA, Lundin M, Taherzadeh MJ, Lennartsson PR. Pigment Production by the Edible Filamentous Fungus Neurospora Intermedia. Fermentation. 2018; 4(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleGmoser, Rebecca, Jorge A. Ferreira, Magnus Lundin, Mohammad J. Taherzadeh, and Patrik R. Lennartsson. 2018. "Pigment Production by the Edible Filamentous Fungus Neurospora Intermedia" Fermentation 4, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4010011
APA StyleGmoser, R., Ferreira, J. A., Lundin, M., Taherzadeh, M. J., & Lennartsson, P. R. (2018). Pigment Production by the Edible Filamentous Fungus Neurospora Intermedia. Fermentation, 4(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4010011