Optimization of Anaerobic Co-Digestion Parameters for Vinegar Residue and Cattle Manure via Orthogonal Experimental Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock and Inoculum
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Index Determination Method
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
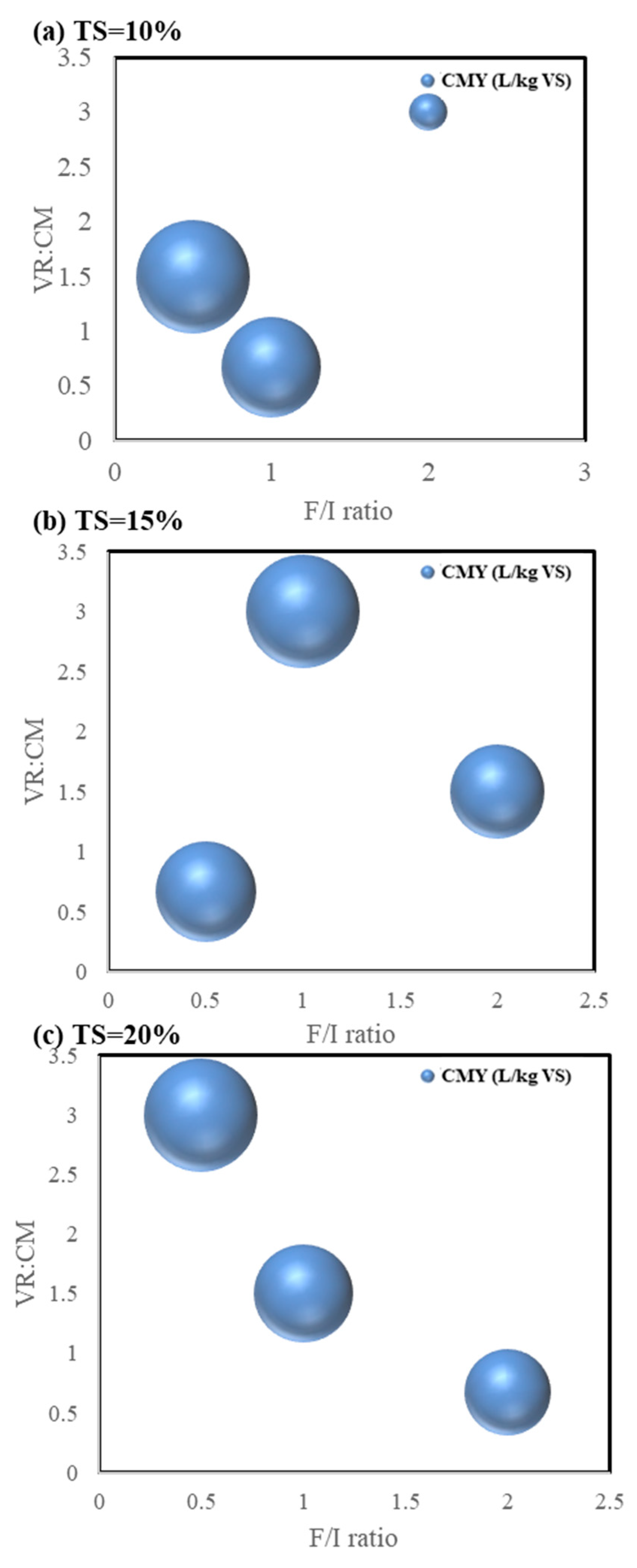
3.1. Methane Yield
3.1.1. Orthogonal Test Results
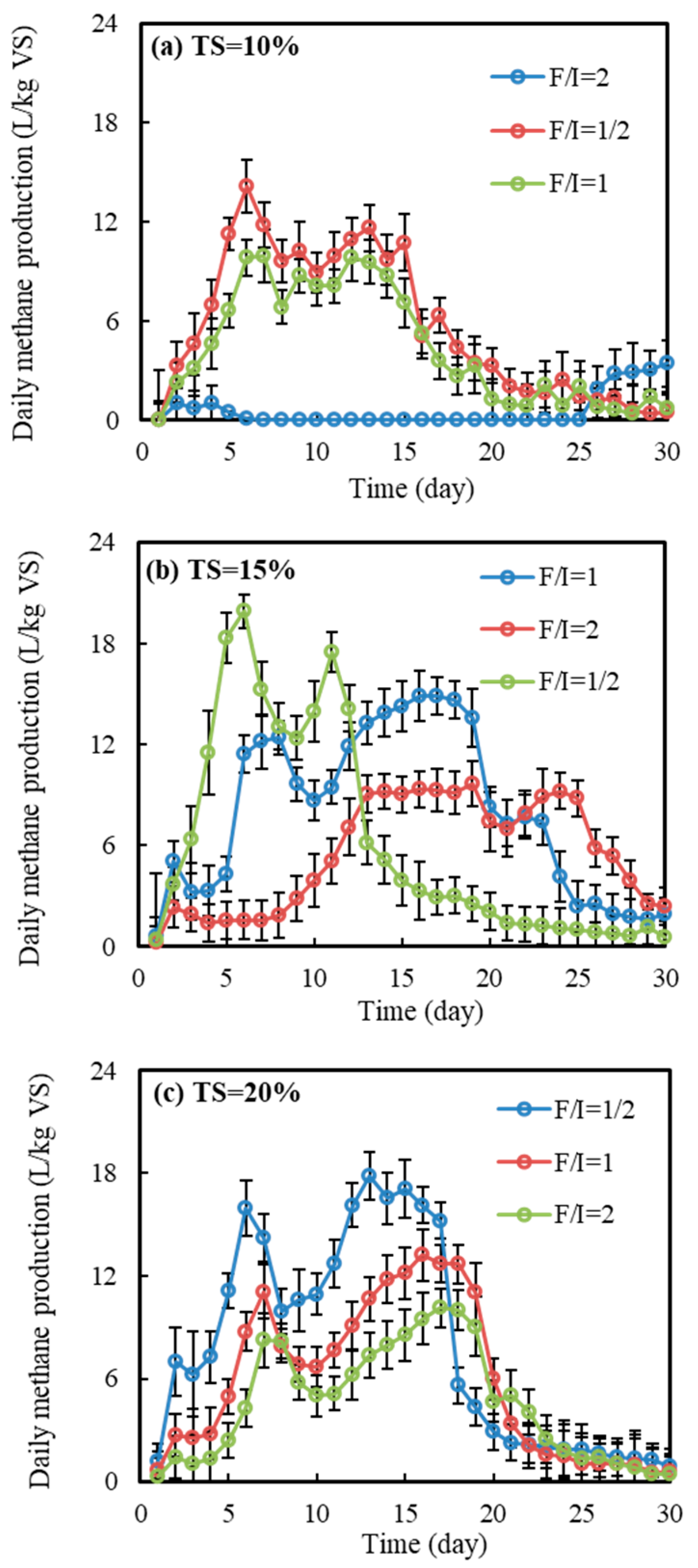
3.1.2. Dynamic Changes in Daily Methane Yield
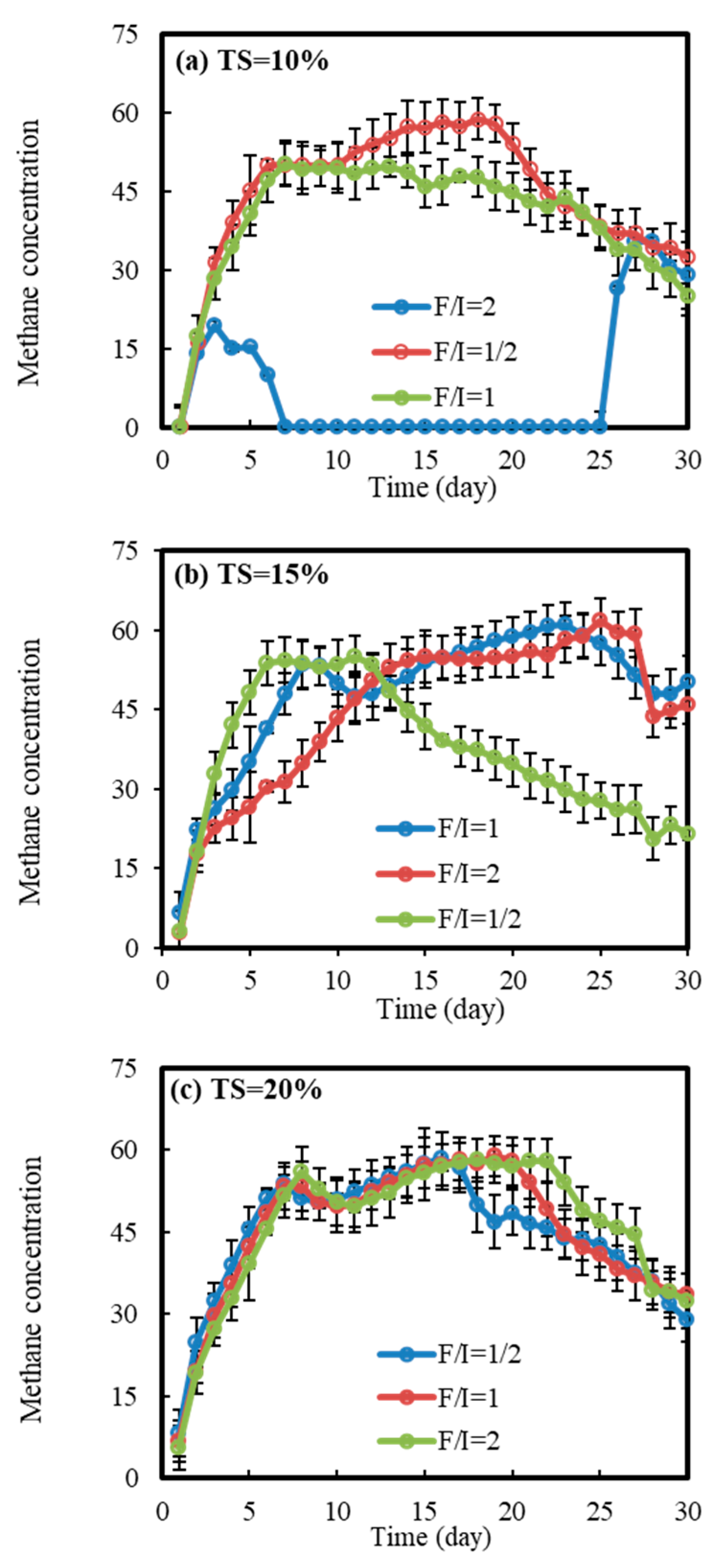
3.1.3. Dynamic Changes in Methane Concentration
3.1.4. Cumulative Methane Yield
3.2. Physical and Chemical Indicators
3.2.1. pH and VFAs Variation
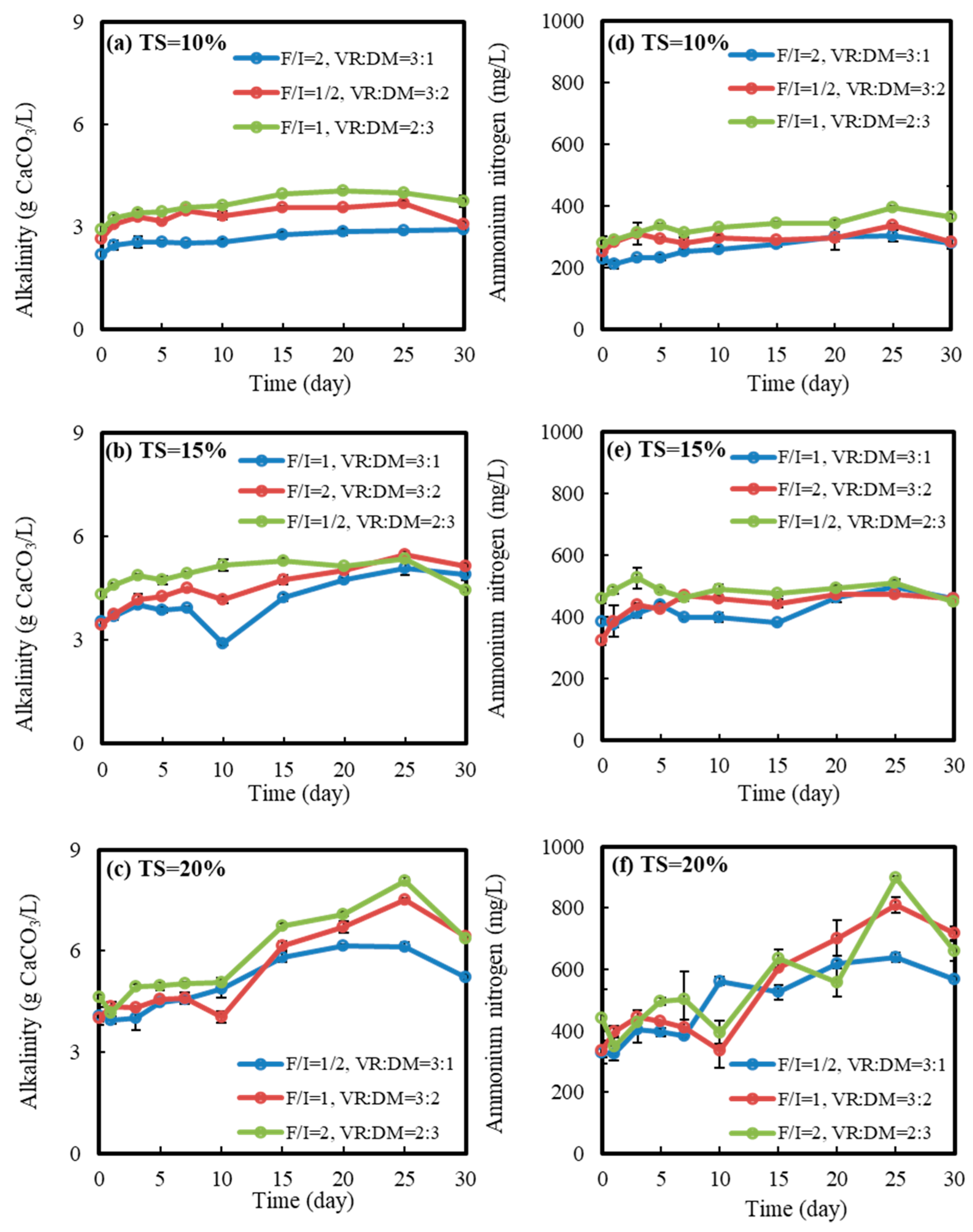
3.2.2. Alkalinity and Ammonium Nitrogen Variation
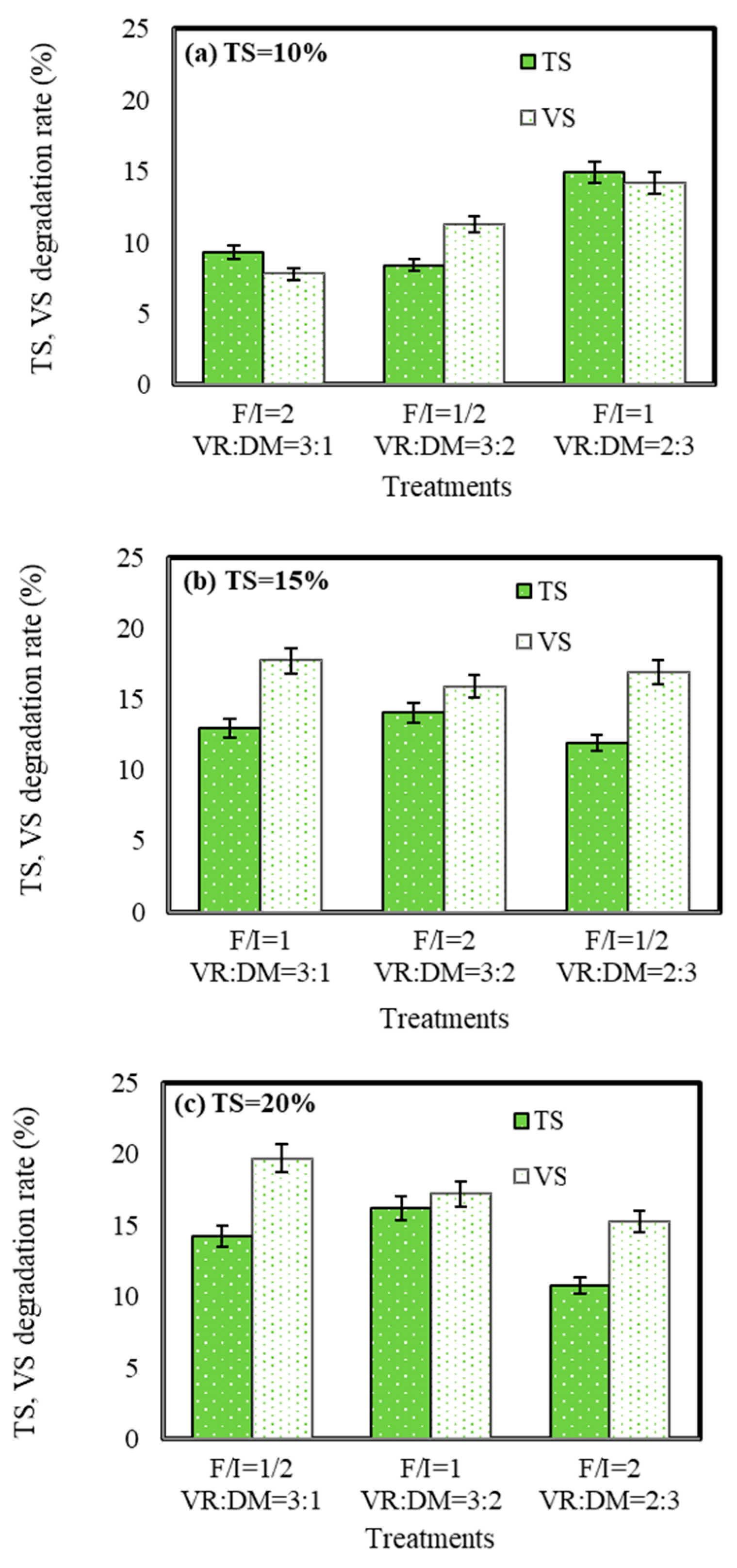
3.3. Degradation of TS and VS
3.4. Nutrient Characteristics of Liquid Digestate
3.4.1. Nutrient Composition of Liquid Digestate
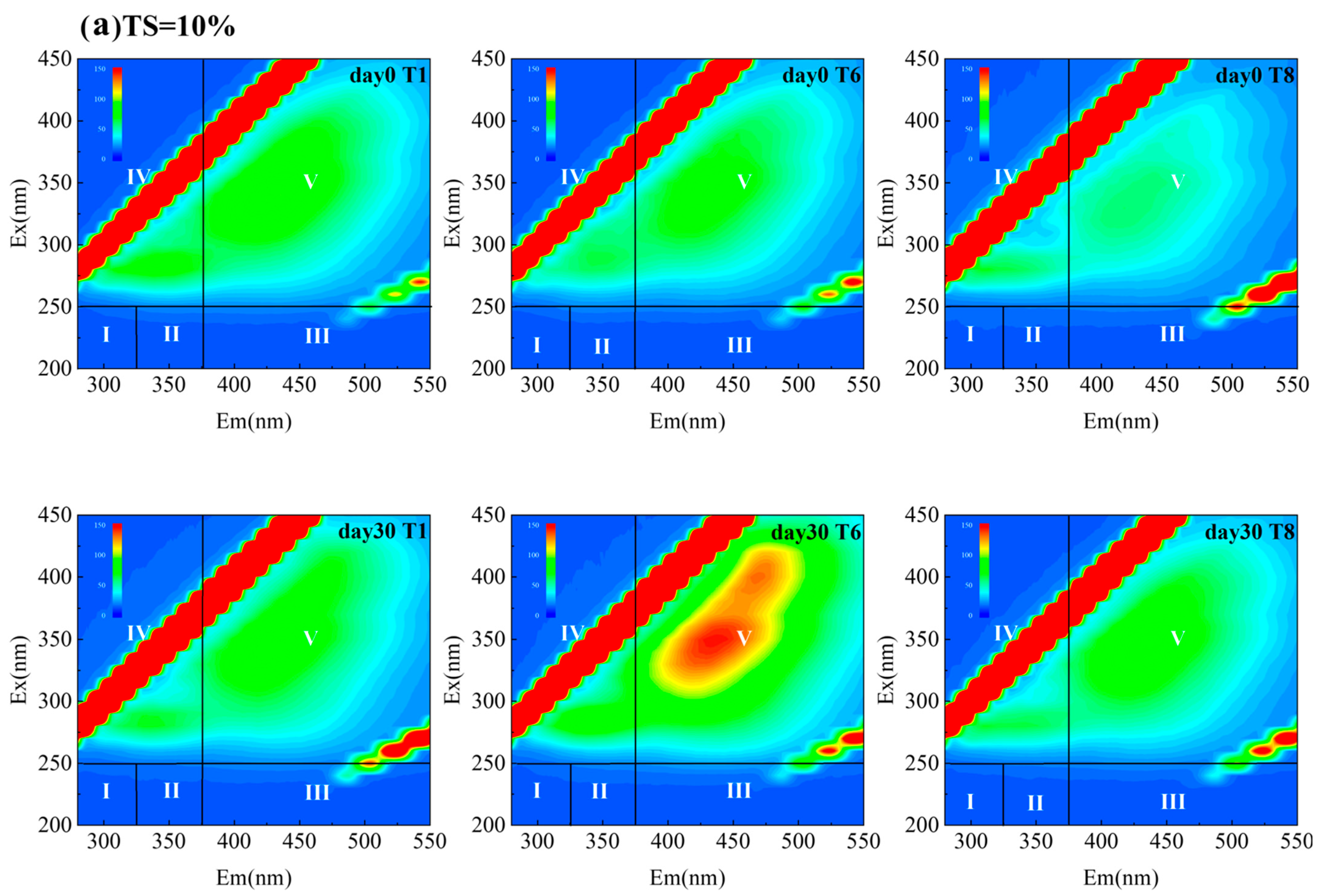
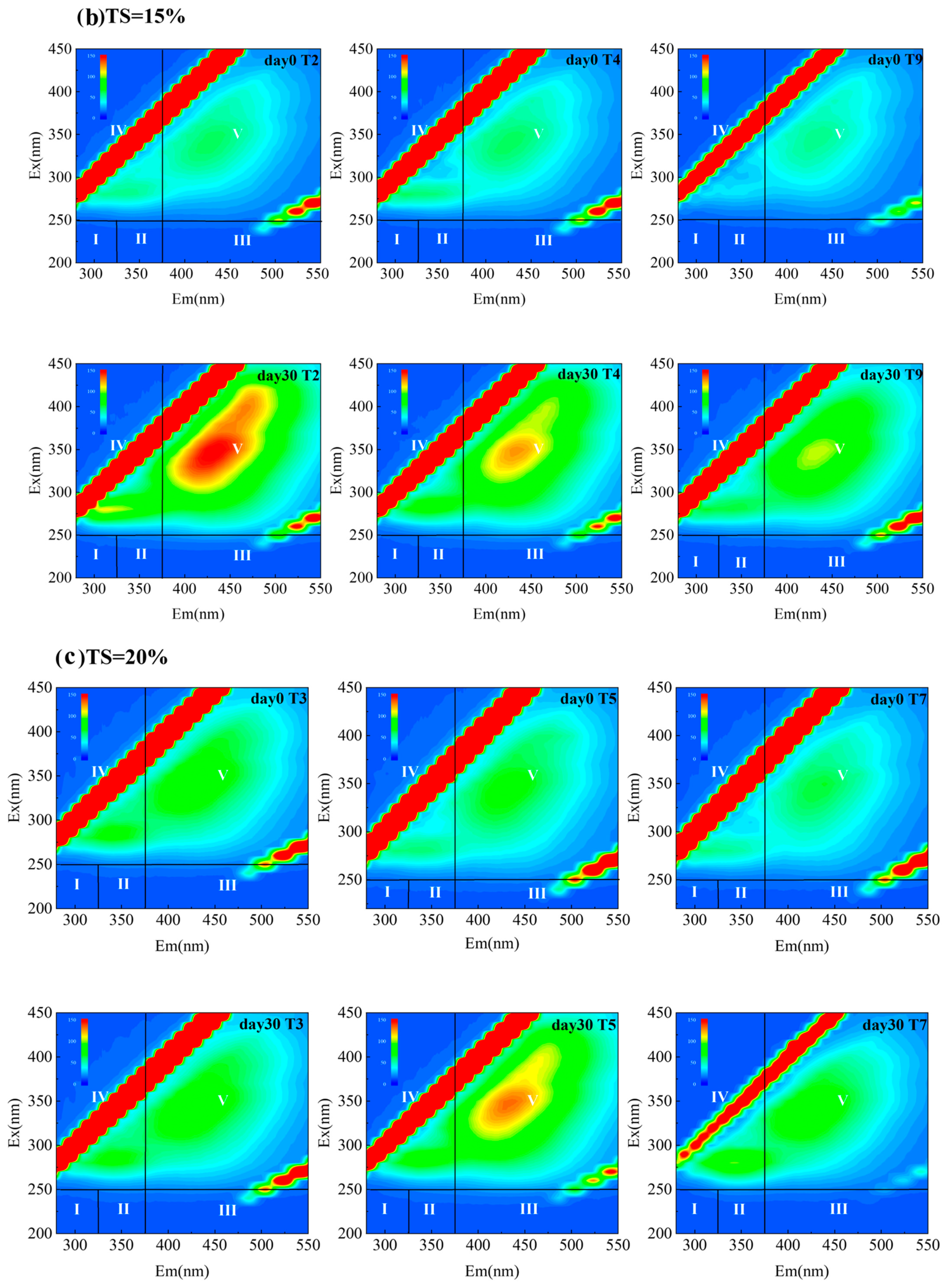
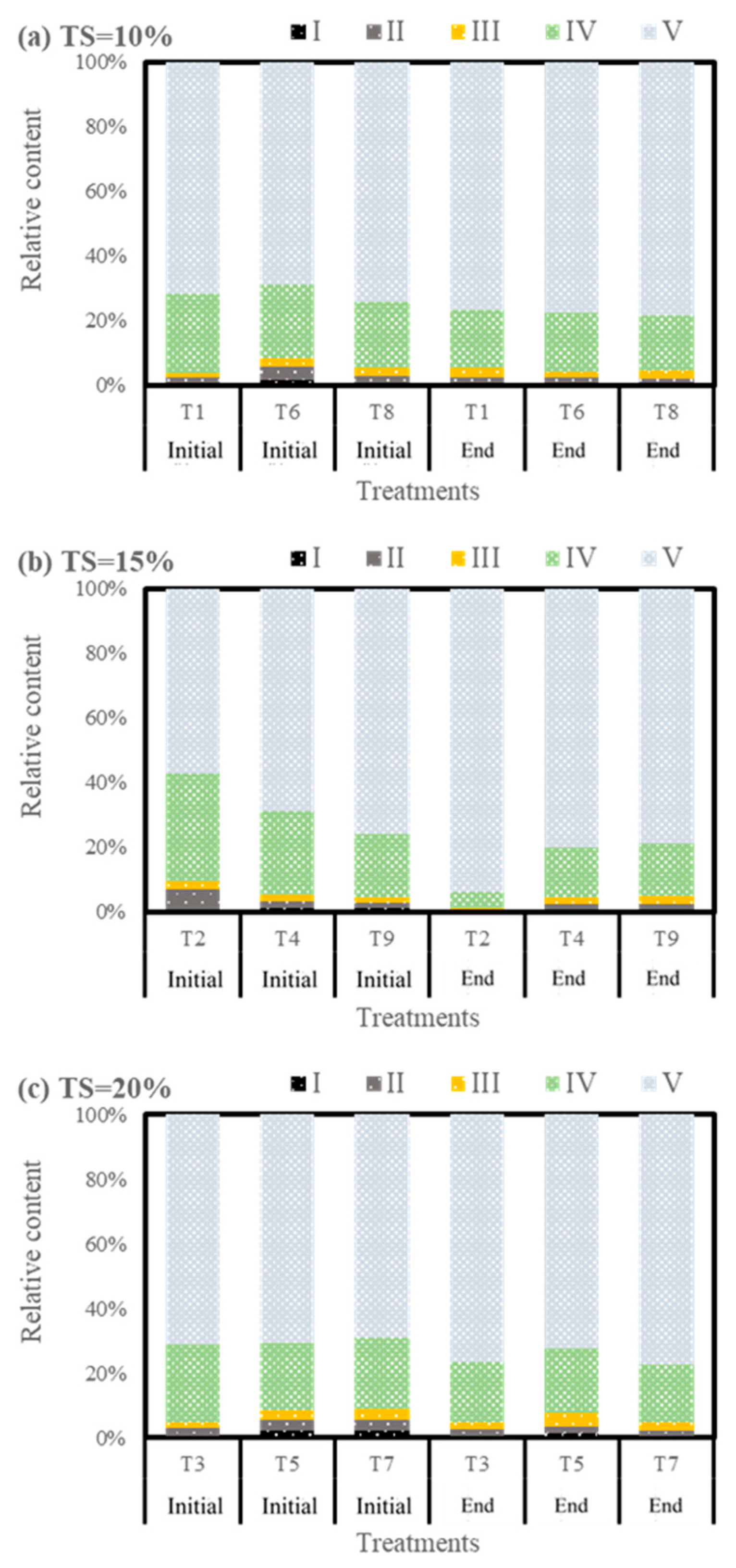
3.4.2. Humification Characteristics
3.5. Nutrient Characteristics of Solid Digestate
3.5.1. Solid Digestate Nutrient Composition
3.5.2. Humification Characteristics of Solid Digestate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-substrate Ratio | 3.03 | 2 | 102.92 | 0.010 |
| F/I ratio | 0.29 | 2 | 9.75 | 0.093 |
| Total Solids | 13.22 | 2 | 449.64 | 0.002 |
| Error | 0.03 | 2 | - | - |
| Factor | N | P | K | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| K1 | 2547.40 | 2779.5 | 1798.55 | 2852.35 | 33.82 | 49.87 | 68.24 | 53.77 | 3293.11 | 4427.53 | 2536.57 | 4086.96 |
| K2 | 2815.55 | 3088.15 | 2631.50 | 2848.95 | 96.40 | 46.35 | 31.17 | 90.85 | 3907.34 | 3967.28 | 3874.49 | 4112.16 |
| K3 | 3079.6 | 2574.91 | 4012.50 | 2741.25 | 55.83 | 89.83 | 86.64 | 41.43 | 5088.66 | 3894.30 | 5878.05 | 4089.99 |
| k1 | 849.13 | 926.50 | 599.52 | 950.78 | 11.27 | 16.62 | 22.75 | 17.92 | 1097.70 | 1475.84 | 845.52 | 1362.32 |
| k2 | 938.52 | 1029.38 | 877.17 | 949.65 | 32.13 | 15.45 | 10.39 | 30.28 | 1302.45 | 1322.43 | 1291.50 | 1370.72 |
| k3 | 1026.53 | 858.30 | 1337.50 | 913.75 | 18.61 | 29.94 | 28.88 | 13.81 | 1696.22 | 1298.10 | 1959.35 | 1363.33 |
| R | 177.40 | 171.08 | 737.98 | 37.03 | 20.86 | 13.32 | 18.49 | 16.47 | 598.62 | 177.75 | 1113.83 | 8.40 |
| Influencing Order | C > A > B > D | A > C > D > B | C > A > B > D | |||||||||
| Source of Variation | N | P | K | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | df | F | p * | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * | |
| Co-substrate Ratio | 47,207.07 | 2 | 17.74 | 0.053 | 671.85 | 2 | 1.52 | 0.396 | 555,202.94 | 2 | 4401.43 | 0.000 |
| F/I ratio | 44,505.73 | 2 | 116.72 | 0.056 | 388.86 | 2 | 0.88 | 0.531 | 55,722.13 | 2 | 441.74 | 0.002 |
| Total Solids | 833,615.70 | 2 | 313.21 | 0.003 | 532.19 | 2 | 1.21 | 0.453 | 18,885,529.54 | 2 | 14,947.72 | 0.000 |
| Error | 2661.56 | 2 | - | - | 441.06 | 2 | - | - | 126.14 | 2 | - | - |
| Treatment | Co-Substrate Ratio (A) | F/I Ratio (B) | Total Solids (%) (C) | Error (D) | Seed GI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 3:1 | 2:1 | 10 | 1 | 166 |
| T2 | 3:1 | 1:1 | 15 | 2 | 88 |
| T3 | 3:1 | 1:2 | 20 | 3 | 136 |
| T4 | 3:2 | 2:1 | 15 | 3 | 124 |
| T5 | 3:2 | 1:1 | 20 | 1 | 100 |
| T6 | 3:2 | 1:2 | 10 | 2 | 137 |
| T7 | 2:3 | 2:1 | 20 | 2 | 139 |
| T8 | 2:3 | 1:1 | 10 | 3 | 160 |
| T9 | 2:3 | 1:2 | 15 | 1 | 133 |
| K1 | 390 | 429 | 463 | 399 | - |
| K2 | 361 | 348 | 345 | 364 | - |
| K3 | 432 | 406 | 375 | 420 | - |
| k1 | 130 | 143 | 154 | 133 | - |
| k2 | 120 | 116 | 115 | 121 | - |
| k3 | 144 | 135 | 125 | 140 | - |
| R | 14 | 27 | 39 | 19 | - |
| Influencing order | C > B > D > A | ||||
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-substrate Ratio | 849.56 | 2 | 1.59 | 0.386 |
| F/I ratio | 1161.56 | 2 | 2.18 | 0.315 |
| Total Solids | 2507.56 | 2 | 4.70 | 0.175 |
| Error | 533.56 | 2 | - | - |
| Treatment | Co-Substrate Ratio (A) | F/I Ratio (B) | Total Solids (%) (C) | Error (D) | N + P2O5 + K2O (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 3:1 | 2:1 | 10 | 1 | 22.31 |
| T2 | 3:1 | 1:1 | 15 | 2 | 25.00 |
| T3 | 3:1 | 1:2 | 20 | 3 | 27.68 |
| T4 | 3:2 | 2:1 | 15 | 3 | 25.11 |
| T5 | 3:2 | 1:1 | 20 | 1 | 26.36 |
| T6 | 3:2 | 1:2 | 10 | 2 | 29.11 |
| T7 | 2:3 | 2:1 | 20 | 2 | 32.82 |
| T8 | 2:3 | 1:1 | 10 | 3 | 30.94 |
| T9 | 2:3 | 1:2 | 15 | 1 | 30.27 |
| K1 | 75.00 | 80.24 | 82.38 | 78.93 | - |
| K2 | 80.60 | 82.31 | 80.38 | 86.96 | - |
| K3 | 94.03 | 87.08 | 86.86 | 83.73 | - |
| k1 | 25.00 | 26.75 | 27.46 | 26.331 | - |
| k2 | 26.87 | 27.44 | 26.79 | 28.99 | - |
| k3 | 31.34 | 29.03 | 28.95 | 27.91 | - |
| R | 6.34 | 2.28 | 2.16 | 2.68 | - |
| Influencing Order | A > D > B > C | ||||
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-substrate Ratio | 63.85 | 2 | 5.92 | 0.144 |
| F/I ratio | 8.16 | 2 | 0.76 | 0.569 |
| Total Solids | 7.36 | 2 | 0.68 | 0.595 |
| Error | 10.78 | 2 | - | - |
| Element | N | P | K | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| K1 | 836.45 | 839.66 | 861.98 | 833.01 | 11,709.73 | 11,919.04 | 12,762.96 | 12,116.43 | 25,377.71 | 27,776.89 | 27,995.40 | 26,943.66 |
| K2 | 802.74 | 806.81 | 802.80 | 800.75 | 12,224.04 | 12,263.40 | 12,134.84 | 13,328.81 | 27,681.13 | 28,487.95 | 27,660.39 | 29,744.36 |
| K3 | 805.81 | 798.53 | 780.22 | 811.24 | 14,154.99 | 13,906.32 | 13,190.97 | 12,643.53 | 32,446.43 | 29,240.44 | 29,849.49 | 28,817.25 |
| k1 | 278.82 | 279.89 | 287.33 | 277.67 | 3903.24 | 3973.01 | 4254.32 | 4038.81 | 8459.24 | 9258.96 | 9331.80 | 8981.22 |
| k2 | 267.58 | 268.94 | 267.60 | 266.92 | 4074.68 | 4087.80 | 4044.95 | 4442.94 | 9227.04 | 9495.98 | 9220.13 | 9914.79 |
| k3 | 268.60 | 266.18 | 260.07 | 270.41 | 4718.33 | 4635.44 | 4396.99 | 4214.51 | 10,815.48 | 9746.81 | 9949.83 | 9605.75 |
| R | 10.21 | 13.71 | 27.25 | 10.75 | 8621.57 | 662.43 | 352.05 | 404.12 | 2356.24 | 487.85 | 729.70 | 933.57 |
| Influencing Order | C > B > D > A | A > B > D > C | A > D > C > B | |||||||||
| Source of Variation | N | P | K | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | df | F | p * | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * | |
| Co-substrate Ratio | 231.62 | 2 | 1.28 | 0.438 | 1,108,032.40 | 2 | 4.50 | 0.182 | 8,664,509.00 | 2 | 6.39 | 0.135 |
| F/I ratio | 315.48 | 2 | 1.75 | 0.364 | 751,899.82 | 2 | 3.05 | 0.247 | 357,091.79 | 2 | 0.26 | 0.792 |
| Total Solids | 1188.54 | 2 | 6.58 | 0.132 | 188,129.73 | 2 | 0.76 | 0.567 | 926,893.36 | 2 | 0.68 | 0.594 |
| Error | 180.52 | 2 | - | - | 246,363.73 | 2 | - | - | 1,357,096.39 | 2 | - | - |
| Factor | HA | FA | HA/FA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| K1 | 119.26 | 101.70 | 91.85 | 90.81 | 52.11 | 65.39 | 77.30 | 65.37 | 7.26 | 4.52 | 3.41 | 4.07 |
| K2 | 131.25 | 128.71 | 134.25 | 142.50 | 73.28 | 65.26 | 60.92 | 67.33 | 5.45 | 6.87 | 7.29 | 7.18 |
| K3 | 111.34 | 131.44 | 135.74 | 128.54 | 77.89 | 72.63 | 65.07 | 70.58 | 4.35 | 5.67 | 6.37 | 5.81 |
| k1 | 39.75 | 33.90 | 30.62 | 30.27 | 17.37 | 21.80 | 25.77 | 21.79 | 2.42 | 1.51 | 1.14 | 1.36 |
| k2 | 43.75 | 42.90 | 44.75 | 47.50 | 24.43 | 21.75 | 20.31 | 22.44 | 1.82 | 2.29 | 2.43 | 2.39 |
| k3 | 37.11 | 43.81 | 45.25 | 42.85 | 25.96 | 24.21 | 21.69 | 23.53 | 1.45 | 1.89 | 2.12 | 1.94 |
| R | 6.64 | 9.91 | 14.63 | 12.58 | 8.59 | 2.45 | 5.46 | 1.74 | 0.97 | 0.78 | 1.29 | 1.04 |
| Influencing Order | C > D > B > A | A > C > B > D | C > D > B > A | |||||||||
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-substrate Ratio | 1.44 | 2 | 0.89 | 0.531 |
| F/I ratio | 0.92 | 2 | 0.57 | 0.639 |
| Total Solids | 2.76 | 2 | 1.69 | 0.372 |
| Error | 1.63 | 2 | - | - |
References
- Guan, B.; Zhao, J.; Cai, M.; Lin, H.; Yao, L.; Sun, L. Analysis of volatile organic compounds from chinese vinegar substrate during solid-state fermentation using a colorimetric sensor array. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9383–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, W.; Morales, M.L.; García-Parrilla, M.C.; Troncoso, A.M. Wine vinegar: Technology, authenticity and quality evaluation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y. A review of the current state and future prospects in resource recovery of chinese cereal vinegar residue. Foods 2022, 11, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, L.; Zhang, R.; He, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. anaerobic digestion performance of vinegar residue in continuously stirred tank reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, H. Effect of the organic loading rates increase on process stability and microbial community composition during the anaerobic digestion of fresh vinegar residue. Waste Biomass Valor 2021, 12, 5505–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatut, R.A.; Angenent, L.T.; Scott, N.R. Biochemical methane potential and biodegradability of complex organic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Thakur, N.; Salama, E.-S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Xing, X.; Yue, J.; Song, Z.; Nan, L.; Yujun, S.; et al. Potential Applications of protein-rich waste: Progress in energy management and material recovery. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 182, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samadder, S.R. Performance evaluation of anaerobic digestion technology for energy recovery from organic fraction of municipal solid waste: A Review. Energy 2020, 197, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadianroshanfekr, M.; Pazoki, M.; Pejman, M.B.; Ghasemzadeh, R.; Pazoki, A. kinetic modeling and optimization of biogas production from food waste and cow manure co-digestion. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Krooneman, J.; Euverink, G.J.W. Strategies to boost anaerobic digestion performance of cow manure: Laboratory achievements and their full-scale application potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, P.; Karrabi, M.; Danesh, S. Anaerobic co-digestion of poultry slaughterhouse wastes with sewage sludge in batch-mode bioreactors (Effect of inoculum-substrate ratio and total solids). Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 107, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Okopi, S.I.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Meng, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, C. Multi-criteria assessment of food waste and waste paper anaerobic co-digestion: Effects of inoculation ratio, total solids content, and feedstock composition. Renew. Energy 2022, 194, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Meng, S.; Chen, G.; Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Co-digestion of garden waste, food waste, and tofu residue: Effects of mixing ratio on methane production and microbial community structure. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, T.; Amon, B.; Kryvoruchko, V.; Zollitsch, W.; Mayer, K.; Gruber, L. Biogas production from maize and dairy cattle manure—Influence of biomass composition on the methane yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, S.; Shah, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, X.; Li, G. Reactor performance and energy analysis of solid state anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure with corn stover and tomato residues. Waste Manag. 2018, 73, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Ammar, M.; Zou, D.; Korai, R.M.; Li, X. An insight into the anaerobic co-digestion of municipal solid waste and food waste: Influence of co-substrate mixture ratio and substrate to inoculum ratio on biogas production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Li, Y. Effects of total ammonia nitrogen concentration on solid-state anaerobic digestion of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Stiverson, J.A.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y. Effects of microbial and non-microbial factors of liquid anaerobic digestion effluent as inoculum on solid-state anaerobic digestion of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 157, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellera, F.-M.; Gidarakos, E. Effect of substrate to inoculum ratio and inoculum type on the biochemical methane potential of solid agroindustrial waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3217–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demichelis, F.; Tommasi, T.; Deorsola, F.A.; Marchisio, D.; Fino, D. Effect of inoculum origin and substrate-inoculum ratio to enhance the anaerobic digestion of organic fraction municipal solid waste (OFMSW). J. Clean Prod. 2022, 351, 131539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Wei, L.; Shi, G.; Zhang, M. Effects of inoculums ratio and urea concentration on biochemical methane of rural domestic waste with anaerobic digestion. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2017, 34, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin, A.M.; Liebetrau, J.; Proeter, J.; Kleinsteuber, S. Microbial community structure and dynamics during anaerobic digestion of various agricultural waste materials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 5161–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudi, K.; Alvarez-Gallego, C.J.; Romero-Garcia, L.I. Influence of total solids concentration on the anaerobic co-digestion of sugar beet by-products and livestock manures. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhen, X.F.; Dong, H.Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y. Comparison of methanogenesis between sunflower and corn stalks mixed with pig manure at different temperatures. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkarahman, A.R.; Cysneiros, D.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Karatzas, K.-A.G. Anaerobic digestion of whey permeate: Impact of feedstock ratio and organic loading rate in batch and semi-continuous systems. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Alves, M.; Bolzonella, D.; Borzacconi, L.; Campos, J.L.; Guwy, A.J.; Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Jenicek, P.; van Lier, J.B. Defining the biomethane potential (BMP) of solid organic wastes and energy crops: A proposed protocol for batch assays. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Xi, B.; Sun, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, C.; He, X.; Li, M.; Yang, T.; Wang, P.; et al. Biogas production improvement and C/N control by natural clinoptilolite addition into anaerobic co-digestion of Phragmites australis, feces and kitchen waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 180, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Pan, L.; Zhu, X.; Xie, S.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhu, G.; Angelidaki, I. Treatment of digestate residues for energy recovery and biochar production: From lab to pilot-scale verification. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 265, 121852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, J.C.; Escudié, R.; Bernet, N.; Delgenes, J.P.; Steyer, J.P.; Dumas, C. Dynamic effect of total solid content, low substrate/inoculum ratio and particle size on solid-state anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusín, J.; Kašáková, K.; Chamrádová, K.; Staněk, B.; Obroučka, K. High-and low-solids anaerobic digestion in laboratory model fermenter made from silage bags. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 15, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Li, Z.; Hou, S.; Feng, R.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Guo, H. The influence of total solid and inoculum ratio on Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 878, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Peng, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Mironov, V.; Zhang, S. Deeper insights into the effects of substrate to inoculum ratio selection on the relationship of kinetic parameters, microbial communities, and key metabolic pathways during the anaerobic digestion of food waste. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Chuenchart, W.; Surendra, K.C.; Sung, S.; Raskin, L.; Khanal, S.K. Anaerobic co-digestion of various organic wastes: Kinetic modeling and synergistic impact evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.; Li, Y. Solid state anaerobic co-digestion of yard waste and food waste for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 127, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Vinegar Residue | Cattle Manure | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3.91 ± 0.04 | 8.42 ± 0.09 | 9.01 ± 0.06 |
| Volatile fatty acids (g/L) a | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| Alkalinity (g CaCO3/L) a | ND c | 7.72 ± 0.32 | 5.34 ± 0.04 |
| Ammonium nitrogen (g/L) a | 0.40 ± 0.01 | 2.62 ± 0.03 | 2.31 ± 0.09 |
| Sodium ions (g/L) a | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 0.30 ± 0.04 |
| Total solids (TS, %) a | 27.81 ± 0.03 | 22.11 ± 0.02 | 18.01 ± 0.03 |
| Volatile solids (VS) (%) a | 24.51 ± 0.19 | 17.32 ± 0.05 | 12.62 ± 0.02 |
| VS/TS (%) a | 88.81 ± 0.18 | 78.43 ± 0.13 | 70.22 ± 0.23 |
| Total carbon (%) b | 45.01 ± 0.20 | 33.61 ± 0.11 | 37.31 ± 0.23 |
| Total nitrogen (%) b | 1.91 ± 0.07 | 1.61 ± 0.12 | 1.41 ± 0.18 |
| C/N ratio | 24.33 ± 0.09 | 20.83 ± 0.05 | 27.42 ± 0.07 |
| Cellulose (%) b | 28.42 ± 0.08 | 35.61 ± 0.05 | 32.22 ± 0.02 |
| Hemicellulose (%) b | 12.22 ± 0.02 | 13.51 ± 0.04 | 11.03 ± 0.05 |
| Lignin (%) b | 18.32 ± 0.14 | 9.41 ± 0.02 | 21.74 ± 0.07 |
| Treatment | Co-Substrate Ratio (A) | F/I Ratio (B) | TS (%) (C) | Error (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 3:1 | 2:1 | 10 | 1 |
| T2 | 1:1 | 15 | 2 | |
| T3 | 1:2 | 20 | 3 | |
| T4 | 3:2 | 2:1 | 15 | 3 |
| T5 | 1:1 | 20 | 1 | |
| T6 | 1:2 | 10 | 2 | |
| T7 | 2:3 | 2:1 | 20 | 2 |
| T8 | 1:1 | 10 | 3 | |
| T9 | 1:2 | 15 | 1 |
| Treatment | Co-Substrate Ratio (A) | F/I Ratio (B) | Total Solids (%) (C) | Error (D) | Cumulative Methane Yield (L/kg VS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 3:1 | 2:1 | 10 | 1 | 17.55 |
| T2 | 3:1 | 1:1 | 15 | 2 | 238.73 |
| T3 | 3:1 | 1:2 | 20 | 3 | 235.62 |
| T4 | 3:2 | 2:1 | 15 | 3 | 165.30 |
| T5 | 3:2 | 1:1 | 20 | 1 | 175.62 |
| T6 | 3:2 | 1:2 | 10 | 2 | 168.44 |
| T7 | 2:3 | 2:1 | 20 | 2 | 135.08 |
| T8 | 2:3 | 1:1 | 10 | 3 | 130.49 |
| T9 | 2:3 | 1:2 | 15 | 1 | 185.51 |
| K1 | 491.90 | 317.93 | 316.48 | 378.68 | - |
| K2 | 509.36 | 544.84 | 589.54 | 542.25 | - |
| K3 | 451.08 | 589.57 | 546.32 | 531.41 | - |
| k1 | 163.97 | 105.98 | 105.49 | 126.23 | - |
| k2 | 169.79 | 181.61 | 196.51 | 180.75 | - |
| k3 | 150.36 | 196.52 | 182.11 | 177.14 | - |
| R | 58.28 | 271.64 | 273.06 | 163.57 | - |
| Influencing Order | C > B > D > A | ||||
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | df | F | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-substrate Ratio | 596.41 | 2 | 0.11 | 0.903 |
| F/I Ratio | 14,141.91 | 2 | 2.54 | 0.283 |
| Total Solids | 14,361.79 | 2 | 2.58 | 0.280 |
| Error | 5577.68 | 2 | - | - |
| Treatment | Co-Substrate Ratio (A) | F/I Ratio (B) | Total Solids (%) (C) | Error (D) | N + P2O5 + K2O (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 3:1 | 2:1 | 10 | 1 | 1.96 |
| T2 | 3:1 | 1:1 | 15 | 2 | 2.90 |
| T3 | 3:1 | 1:2 | 20 | 3 | 4.40 |
| T4 | 3:2 | 2:1 | 15 | 3 | 3.56 |
| T5 | 3:2 | 1:1 | 20 | 1 | 5.17 |
| T6 | 3:2 | 1:2 | 10 | 2 | 2.13 |
| T7 | 2:3 | 2:1 | 20 | 2 | 6.38 |
| T8 | 2:3 | 1:1 | 10 | 3 | 3.03 |
| T9 | 2:3 | 1:2 | 15 | 1 | 4.07 |
| K1 | 9.20 | 11.73 | 7.01 | 11.13 | - |
| K2 | 10.82 | 11.12 | 10.44 | 11.25 | - |
| K3 | 13.37 | 10.54 | 15.91 | 11.00 | - |
| k1 | 3.07 | 3.91 | 2.34 | 3.71 | - |
| k2 | 3.61 | 3.71 | 3.48 | 3.75 | - |
| k3 | 4.46 | 3.51 | 5.31 | 3.67 | - |
| R | 1.39 | 0.40 | 2.97 | 0.08 | - |
| Influencing Order | C > A > B > D | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J.; Han, T.; Tian, P.; Li, G.; Li, Y. Optimization of Anaerobic Co-Digestion Parameters for Vinegar Residue and Cattle Manure via Orthogonal Experimental Design. Fermentation 2025, 11, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090493
Lu Y, Huang G, Zhang J, Han T, Tian P, Li G, Li Y. Optimization of Anaerobic Co-Digestion Parameters for Vinegar Residue and Cattle Manure via Orthogonal Experimental Design. Fermentation. 2025; 11(9):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090493
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yuan, Gaoyuan Huang, Jiaxing Zhang, Tingting Han, Peiyu Tian, Guoxue Li, and Yangyang Li. 2025. "Optimization of Anaerobic Co-Digestion Parameters for Vinegar Residue and Cattle Manure via Orthogonal Experimental Design" Fermentation 11, no. 9: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090493
APA StyleLu, Y., Huang, G., Zhang, J., Han, T., Tian, P., Li, G., & Li, Y. (2025). Optimization of Anaerobic Co-Digestion Parameters for Vinegar Residue and Cattle Manure via Orthogonal Experimental Design. Fermentation, 11(9), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090493






