Bioleaching Process of Sewage Sludge and Anaerobically Digested Sludge via Indigenous Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria to Improve Dewaterability and Reduce Heavy Metal Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Indigenous Inoculum for Bioleaching
2.2. Bioleaching Experiment
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
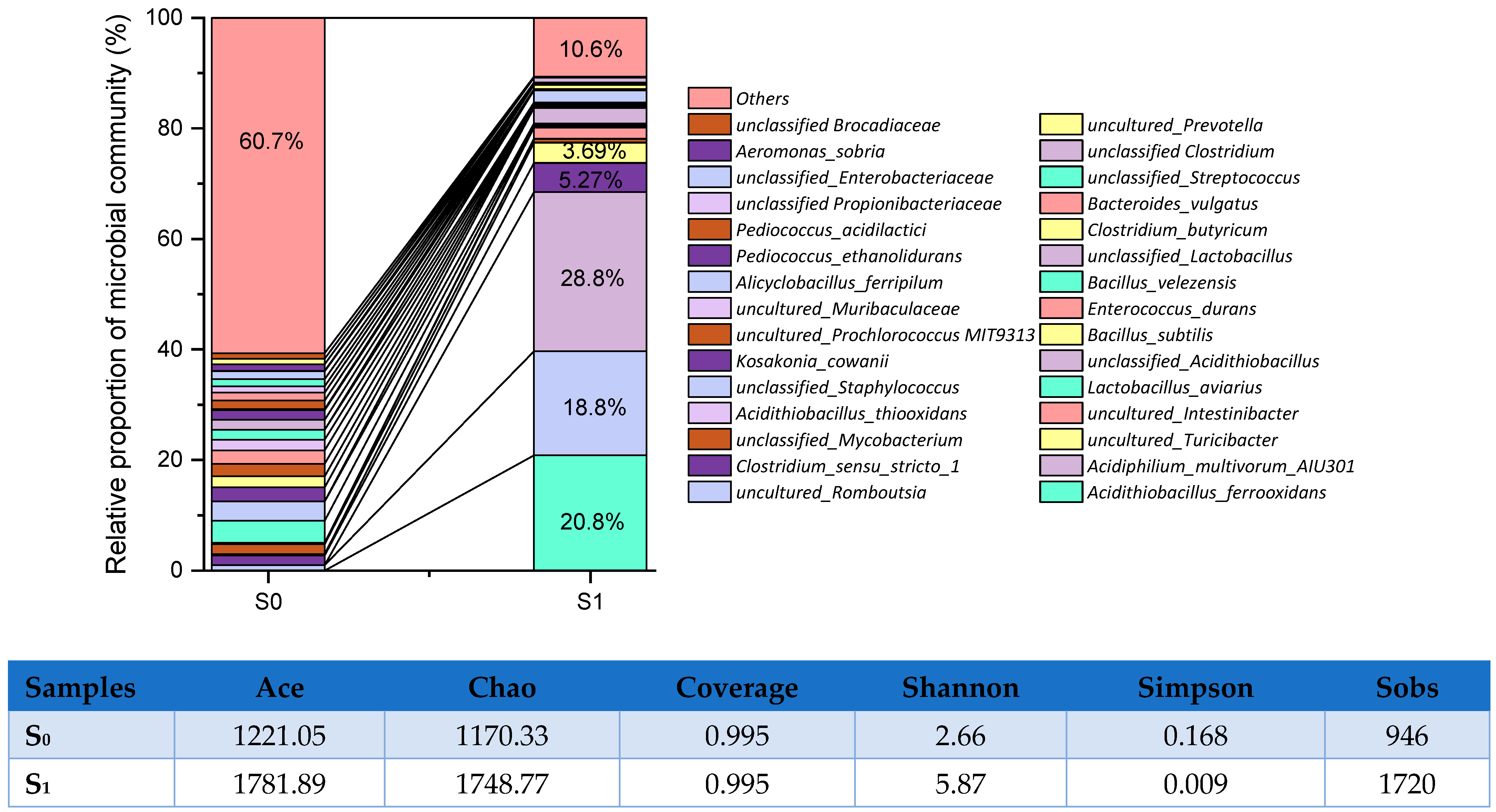
3.1. Microbial Community in Bioleaching Culture
3.2. pH and ORP Changes During Bioleaching Treatment
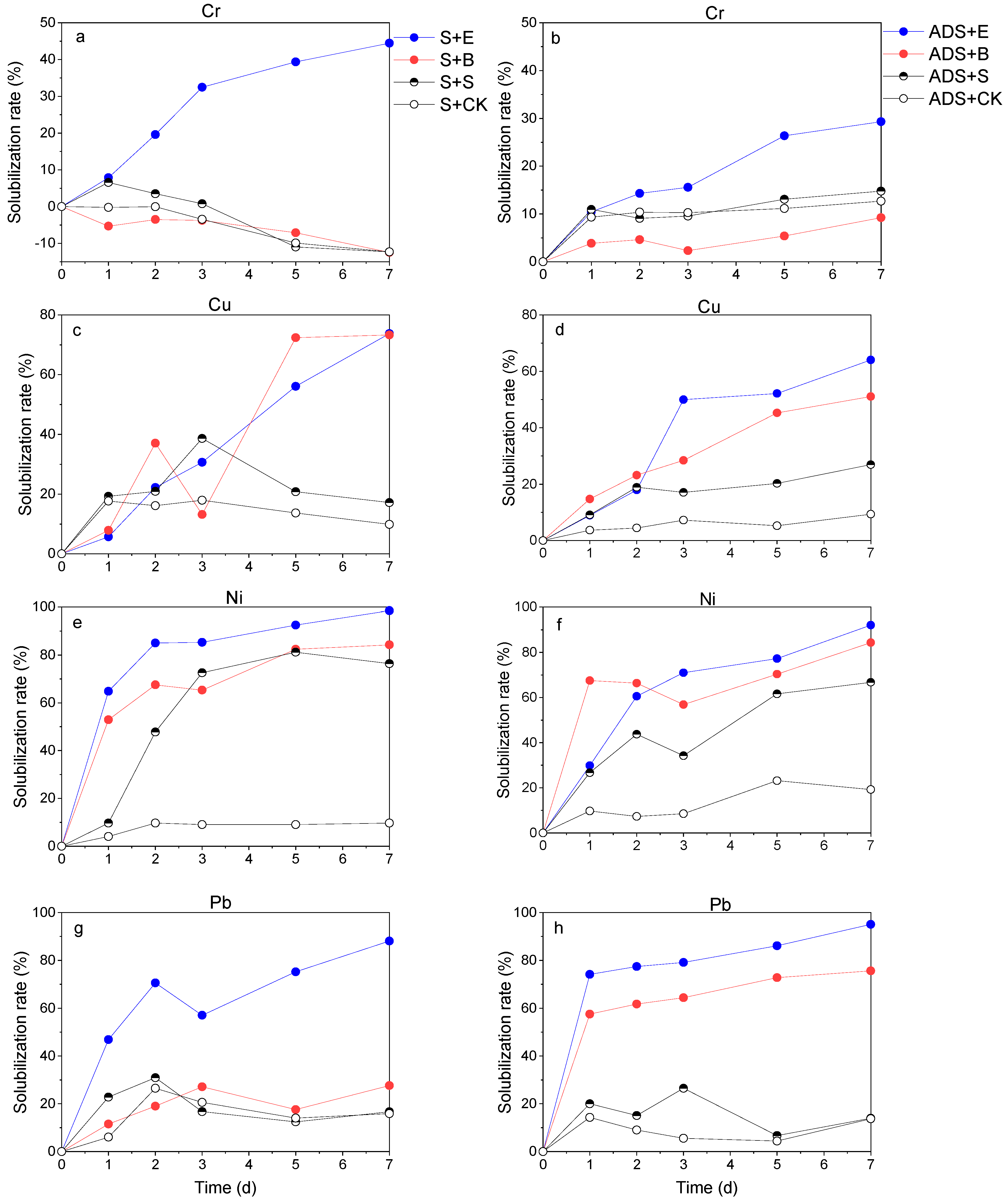
3.3. Heavy Metal Solubilization During Bioleaching Treatment
3.3.1. Differentiated Removal Rates for Cr/Cu and Ni/Pb in Bioleaching Process
3.3.2. Comparative Removal Rates for Different Test Groups
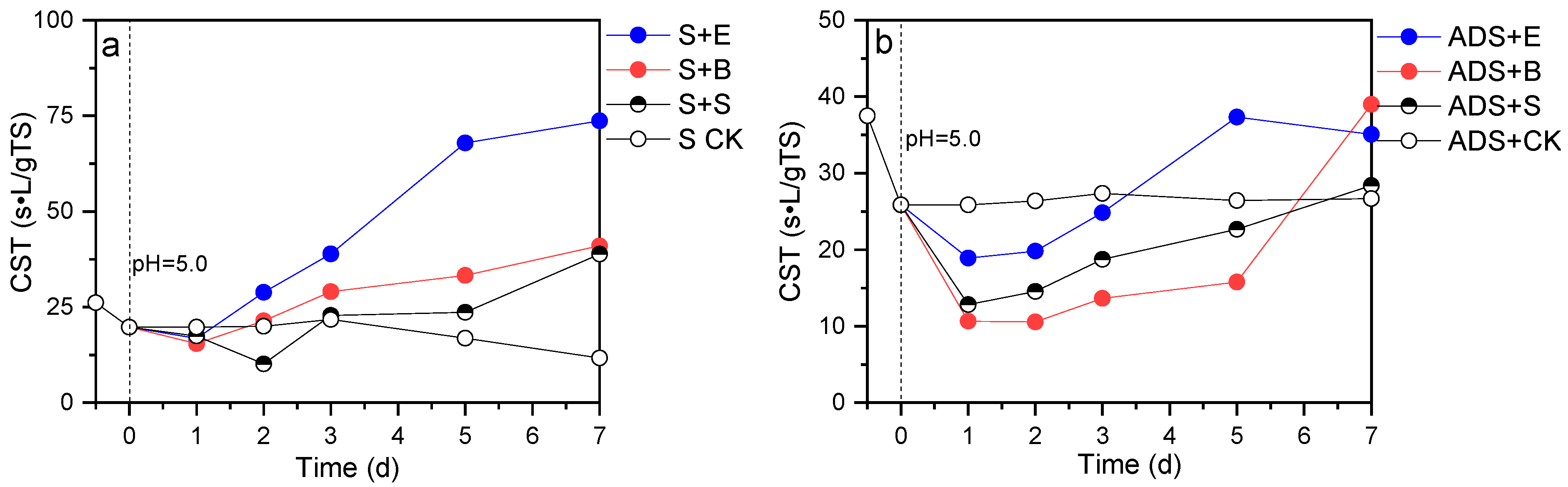
3.4. Changes in Sludge Dewaterability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Cui, M.; Wong, J.W.C. Effects of different thermal pretreatments on the biodegradability and bioaccessibility of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2019, 94, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Xu, S.Y. Post-treatment of food waste digestate towards land application: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.W.C.; Zhou, J.; Kurade, M.B.; Murugesan, K. Influence of ferrous ions on extracellular polymeric substances content and sludge dewaterability during bioleaching. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, Q.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Q. Effects of total solids content on performance of sludge mesophilic anaerobic digestion and dewaterability of digested sludge. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, F.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z. Physical conditioning methods for sludge deep dewatering: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, K.; Ravindran, B.; Selvam, A.; Kurade, M.B.; Yu, S.-M.; Wong, J.W.C. Enhanced dewaterability of anaerobically digested sewage sludge using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans culture as sludge conditioner. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, T.; Cho, J.; Hur, J. Improved dewaterability of anaerobically digested sludge and compositional changes in extracellular polymeric substances by indigenous persulfate activation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ni, G.; Xia, J.; Song, Y.; Hu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, M. Bioleaching of toxic metals from anaerobically digested sludge without external chemical addition. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Wang, D. Improvement of sludge dewaterability and removal of sludge-borne metals by bioleaching at optimum pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, B.; Fang, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, L. Enhancing sludge dewatering efficiency through bioleaching facilitated by increasing reactive oxygen species. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, R.; Najafi-Vosough, R.; Shabanloo, A.; Torkshavand, Z.; Mahmoudi, M.M.; Abasi, M.A. Removing heavy metals and improving the dewaterability of sewage sludge with the bioleaching process by Thiobacillus Ferrooxidans bacteria. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khidr, R.; Qurbani, K.; Muhammed, V.; Salim, S.; Abdulla, S.; Wsw, H. Synergistic effects of indigenous bacterial consortia on heavy metal tolerance and reduction. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanyan, A.; Vyrides, I. Acidophilic bioleaching at high dissolved organic compounds: Inhibition and strategies to counteract this. Miner. Eng. 2019, 143, 105943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Zhou, L.X. Enhanced Cr bioleaching efficiency from tannery sludge with coinoculation of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans TS6 and Brettanomyces B65 in an air-lift reactor. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.S.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, I.S.; Choi, H.M. Effect of solids concentration on bacterial leaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.Y.; Wong, J.W.C. Identification of inhibitory substances affecting bioleaching of heavy metals from anaerobically digested sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2934–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.X.; Li, P.J.; Zheng, L.; Fan, S.X.; Verhozina, V.A. Effects of dissolved low molecular weight organic acids on oxidation of ferrous iron by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B. Importance of microbial ecology in the development of new mineral technologies. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, L. Heterotrophic microorganism Rhodotorula mucilaginosa R30 improves tannery sludge bioleaching through elevating dissolved CO2 and extracellular polymeric substances levels in bioleach solution as well as scavenging toxic DOM to Acidithiobacillus species. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5423–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, D.Z.; Zhou, L.X. Enhancement of sludge dewaterability by sequential inoculation of filamentous fungus Mucor circinelloides ZG-3 and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans LX5. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jiang, M.; Hsieh, L.; Cai, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, Q.; Shen, C.; Hu, B.; Lou, L. Feasibility of bioleaching of heavy metals from sediment with indigenous bacteria using agricultural sulfur soil conditioners. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, L.; Qiao, Z.; He, P. Comparative facilitation of activated carbon and goethite on methanogenesis from volatile fatty acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossop, K.F.; Davidson, C.M. Comparison of original and modified BCR sequential extraction procedures for the fractionation of copper, iron, lead, manganese and zinc in soils and sediments. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 478, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G.; Yuan, L.; Feng, Y. Correlations between microbial community and C:N:P stoichiometry during the anaerobic digestion process. Energy 2019, 174, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Dastidar, M.G.; Sreekrishnan, T.R. Bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 4284-2018; Control Standards of Pollutants in Sludge for Agricultural Use. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, D.S.; Stabnikova, O.; Tay, J.H. Evaluation of electrokinetic removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 124, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, D.; Liao, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, W. Bioleaching of heavy metals from pig manure with indigenous sulfur-oxidizing bacteria: Effects of sulfur concentration. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.B.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, Y.G.; Li, X.M. Effect of polyhydroxyalkanoates on dark fermentative hydrogen production from waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2015, 73, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M. Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.W.C.; Xiang, L.; Gu, X.Y.; Zhou, L.X. Bioleaching of heavy metals from anaerobically digested sewage sludge using FeS2 as an energy source. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R.D.; Couillard, D.; Tran, F. Heavy metals removal from anaerobically digested sludge by chemical and microbiological methods. Environ. Pollut. 1988, 50, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, S.; Yuan, H.; Tao, H.; Xu, S.; Gu, L. Advanced application of tea residue extracts rich in polyphenols for enhancing sludge dewaterability: Unraveling the role of pH regulation. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.G.; Yang, H.Z.; Gu, G.W. Effect of acid and surfactant treatment on activated sludge dewatering and settling. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.-H.; He, P.-J.; Shao, L.-M. Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) fractions from excess sludges and their effects on bioflocculability. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3193–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezawada, J.; Hoang, N.V.; More, T.T.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, N.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by Serratia sp.1 using wastewater sludge as raw material and flocculation activity of the EPS produced. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Sheng, G.P.; Luo, H.W.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, S.J.; Xu, J.; Zeng, R.J.; Wu, J.G.; Yu, H.Q. Contribution of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the sludge aggregation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4355–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, K.; Ravindran, B.; Selvam, A.; Kurade, M.B.; Yu, S.M.; Wong, J.W. Fate of extracellular polymeric substances of anaerobically digested sewage sludge during pre-dewatering conditioning with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 217, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffrath, S.F.; Carissimi, E.; Schner, J.C.; Ferrari, K.F.; Etchepare, R.G. Understanding the interplay of sludge characteristics and dewatering in water treatment plants: A review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2024, 13, 794–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrylin, J.; Kaliappan, S.; Adish Kumar, S.; Yeom, I.T.; Rajesh, B.J. Effect of extracellular polymeric substances on sludge reduction potential of Bacillus licheniformis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 10, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.U.; Kumar, S.A.; Kaliappan, S.; Yeom, I.T.; Banu, J.R. Low temperature thermo-chemical pretreatment of dairy waste activated sludge for anaerobic digestion process. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.E.; Banu, J.R.; Kaliappan, S.; Yeom, I.-T.; Adish Kumar, S. Effects of side-stream, low temperature phosphorus recovery on the performance of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic systems integrated with sludge pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.F.; Hu, H.; Wang, H.J.; Bai, Y.N.; Shen, X.F.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, R.J. Comprehensive investigation of the relationship between organic content and waste activated sludge dewaterability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Y. Pivotal role of intracellular oxidation by HOCl in simultaneously removing antibiotic resistance genes and enhancing dewaterability during conditioning of sewage sludge using Fe2+/Ca (ClO)2. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, W.; Tang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, L. Enhancing sludge dewaterability in sequential bioleaching: Degradation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) by filamentous fungus Mucor sp. ZG-3 and the influence of energy source. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameters | SS | ADS |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.24 ± 0.55 | 8.08 ± 0.36 |
| TS (%) | 2.31 ± 0.20 | 4.20 ± 0.14 |
| VS (%) | 1.33 ± 0.08 | 2.10 ± 0.10 |
| SCOD (mg/L) | 110.0 ± 4.67 | 1656.7 ± 22.11 |
| Ni (mg/kg TS) | 147.8 ± 3.26 | 50.5 ± 1.94 |
| Pb (mg/kg TS) | 76.4 ± 2.11 | 52.5 ± 2.34 |
| Cu (mg/kg TS) | 431.9 ± 14.84 | 786.3 ± 24.13 |
| Cr (mg/kg TS) | 363.1 ± 19.51 | 196.8 ± 9.41 |
| CST | Coef. | St. Err. | t-Value | p-Value | 95% Conf. | Interval | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −85.047 | 24.672 | −3.45 | 0.001 | −134.433 | −35.662 | *** |
| ORP | −1.304 | 0.414 | −3.15 | 0.003 | −2.134 | −0.475 | *** |
| sCOD | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.74 | 0.465 | −0.01 | 0.021 | |
| EPS-slime | −0.402 | 0.575 | −0.7 | 0.487 | −1.554 | 0.749 | |
| EPS-LB | 0 | ||||||
| EPS-TB | −3.44 | 1.219 | −2.82 | 0.007 | −5.88 | −1 | *** |
| EPS-slime-polysaccharide | 3.791 | 1.729 | 2.19 | 0.032 | 0.329 | 7.252 | ** |
| EPS-slime-protein | 0 | ||||||
| EPS-LB-polysaccharide | −4.533 | 1.405 | −3.23 | 0.002 | −7.345 | −1.721 | *** |
| EPS-LB-protein | −1.089 | 0.961 | −1.13 | 0.262 | −3.014 | 0.835 | |
| EPS-TB-polysaccharide | 21.283 | 4.924 | 4.32 | 0 | 11.427 | 31.138 | *** |
| EPS-TB-protein | 0 | ||||||
| EPS-slime-protein/polysaccharide | 1.072 | 10.454 | 0.1 | 0.919 | −19.854 | 21.998 | |
| EPS-LB-protein/polysaccharide | 5.732 | 4.371 | 1.31 | 0.195 | −3.018 | 14.482 | |
| EPS-TB-protein/polysaccharide | 0.024 | 2.921 | 0.01 | 0.994 | −5.824 | 5.871 | |
| Total-EPS | 0.423 | 0.905 | 0.47 | 0.642 | −1.389 | 2.235 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, R.; Zhu, X.; Liu, H. Bioleaching Process of Sewage Sludge and Anaerobically Digested Sludge via Indigenous Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria to Improve Dewaterability and Reduce Heavy Metal Content. Fermentation 2025, 11, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060321
Xu S, Jiang Y, Zou R, Zhu X, Liu H. Bioleaching Process of Sewage Sludge and Anaerobically Digested Sludge via Indigenous Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria to Improve Dewaterability and Reduce Heavy Metal Content. Fermentation. 2025; 11(6):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060321
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Suyun, Yuze Jiang, Ruixiang Zou, Xuefeng Zhu, and Hongbo Liu. 2025. "Bioleaching Process of Sewage Sludge and Anaerobically Digested Sludge via Indigenous Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria to Improve Dewaterability and Reduce Heavy Metal Content" Fermentation 11, no. 6: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060321
APA StyleXu, S., Jiang, Y., Zou, R., Zhu, X., & Liu, H. (2025). Bioleaching Process of Sewage Sludge and Anaerobically Digested Sludge via Indigenous Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria to Improve Dewaterability and Reduce Heavy Metal Content. Fermentation, 11(6), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060321






