Integrated Process Combining High-Temperature Fermentation and Extractive Ethanol Removal via CO2 Stripping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment
2.2. Influence of High Temperature in the Ethanol Removal by CO2 Stripping
2.3. Ethanol Stripping Process: Ethanol and Water Removal Model
2.4. Microorganism and Culture Media
2.5. Evaluation of the Temperature Tolerance of Yeasts
2.6. Conventional and Extractive Ethanol Fermentation at High Temperature
2.7. Analytical Methods
2.8. Mathematical Modeling of Batch Ethanol Fermentations
2.8.1. Conventional Ethanol Fermentation
2.8.2. Kinetic Parameter Estimation Procedure
2.8.3. Extractive Ethanol Fermentation with Ethanol Removal by CO2 Stripping
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Hight Temperature on Ethanol Removal by CO2 Stripping
3.2. Experimental Design: Statistical Analysis and Mathematical Modeling
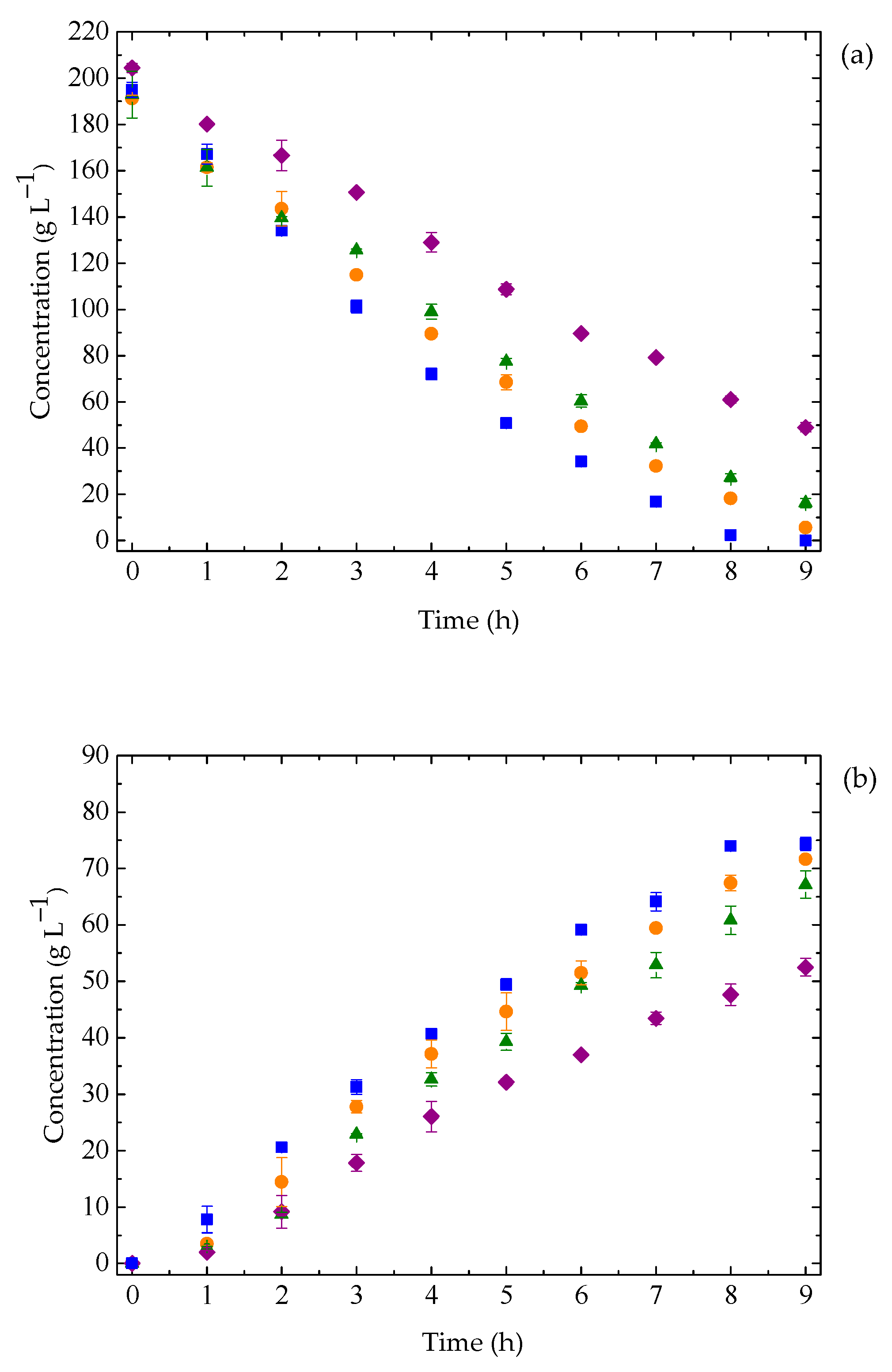
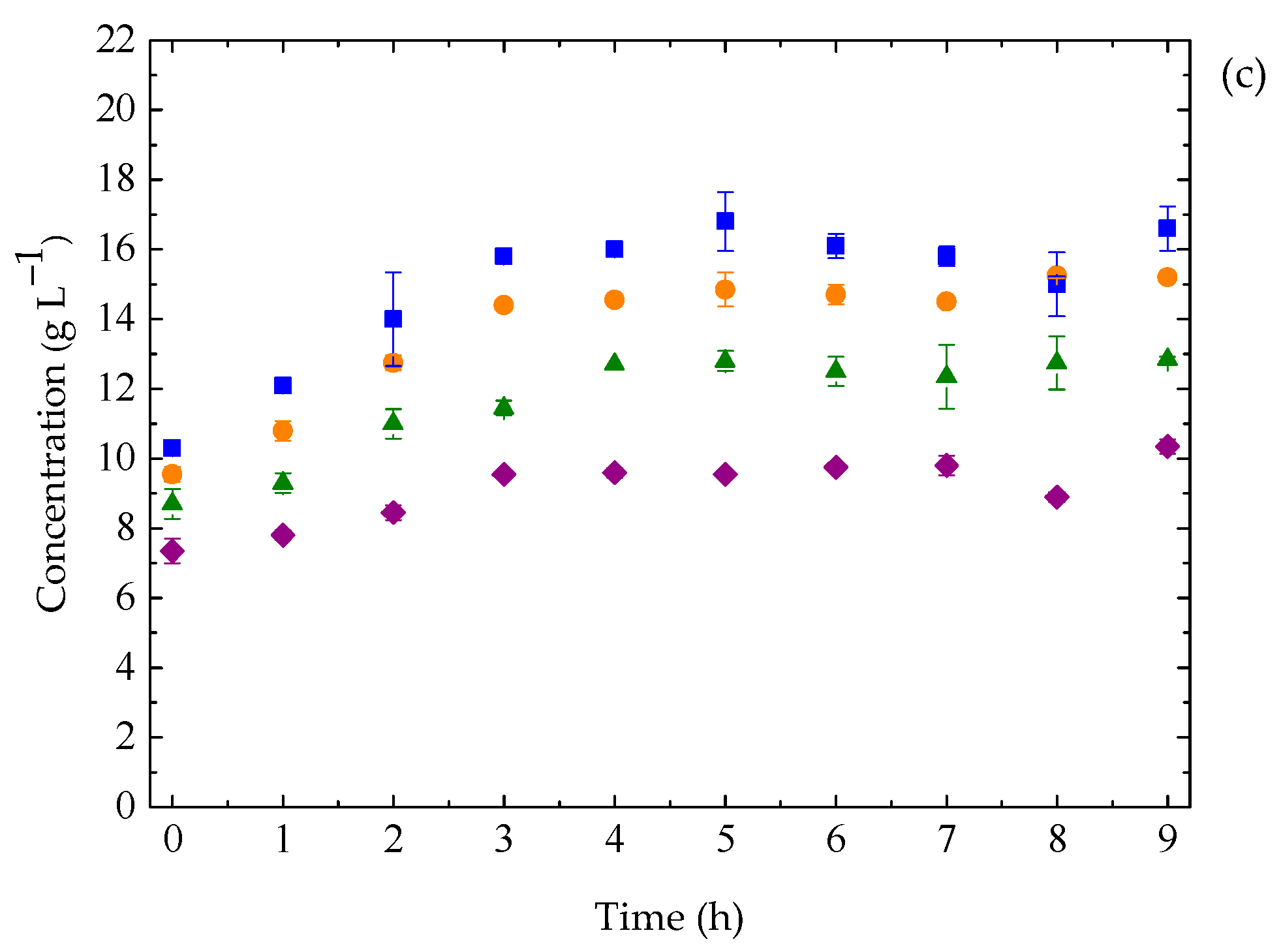
3.3. Ethanol Fermentation by K. marxianus: Effect of Temperature
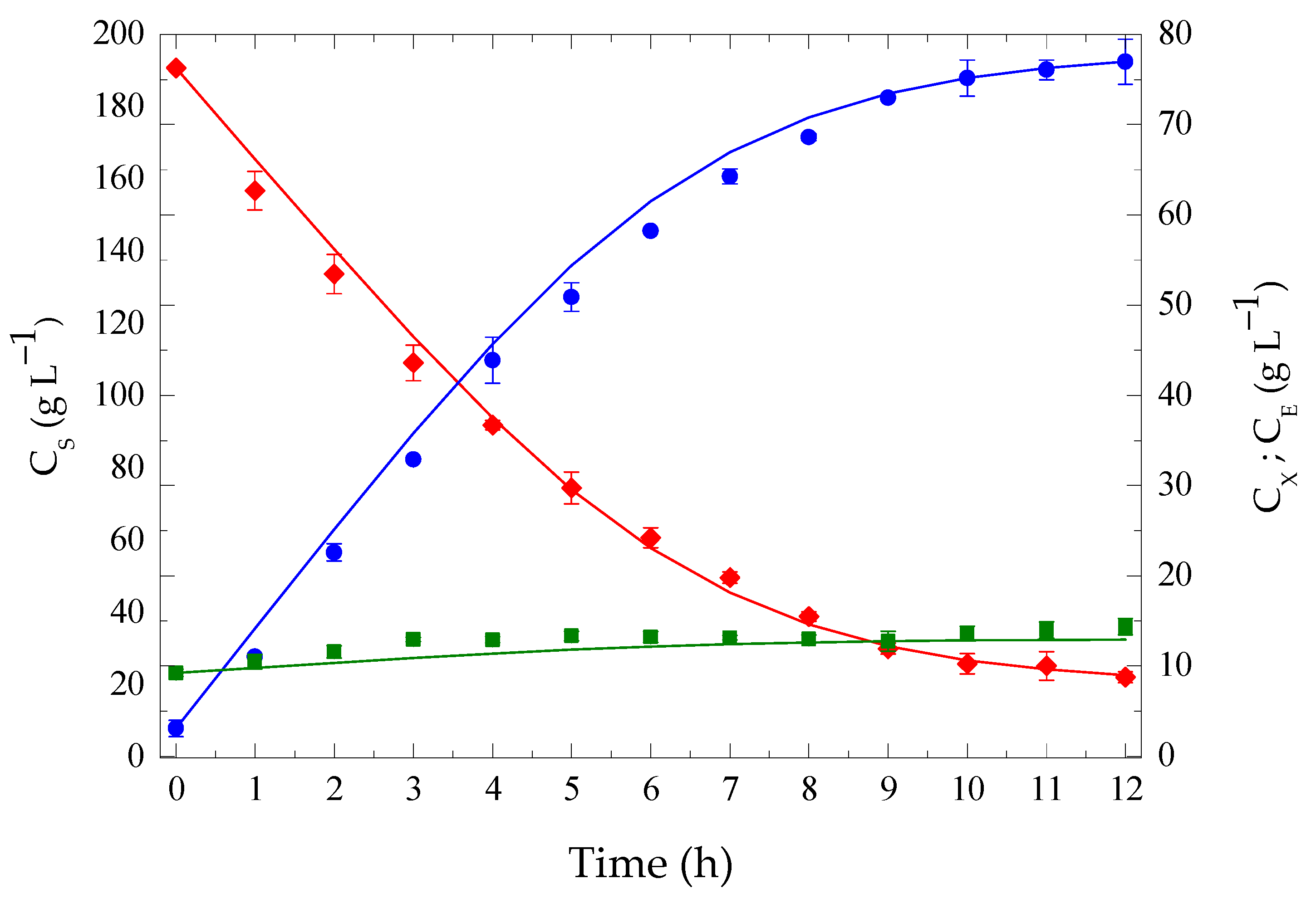
3.4. Conventional Batch Fermentation at High Temperature: Model Fitting
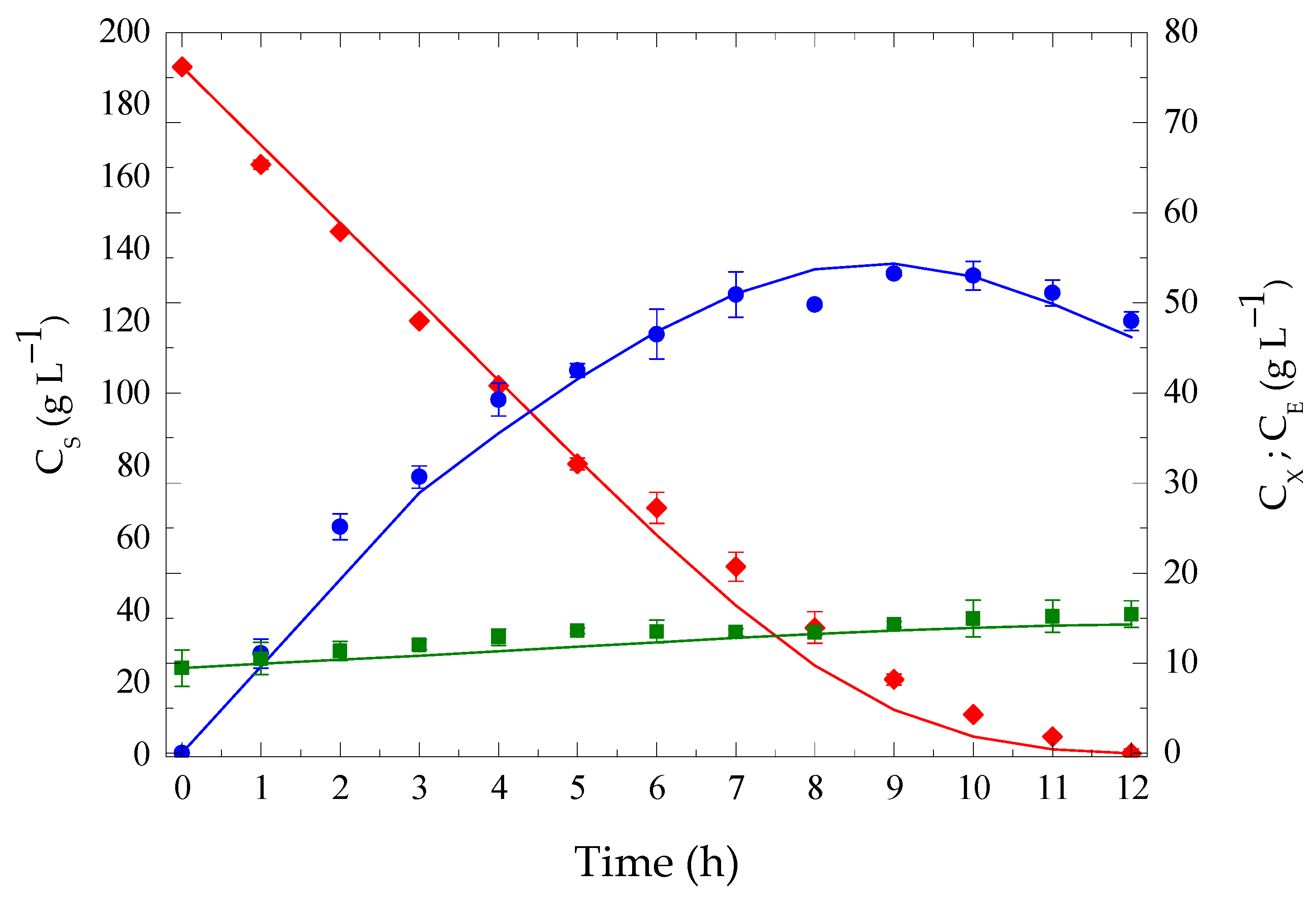
3.5. Extractive Batch Ethanol Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Valladares-Diestra, K.K.; Bittencourt, G.A.; Zevallos Torres, L.A.; Vieira, S.; Karp, S.G.; Sydney, E.B.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Thomaz Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Beyond sugar and ethanol: The future of sugarcane biorefineries in Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Scapini, T.; Rempel, A.; Abaide, E.R.; Camargo, A.F.; Nazari, M.T.; Tadioto, V.; Bonatto, C.; Tres, M.V.; Zabot, G.L.; et al. Challenges and opportunities for third-generation ethanol production: A critical review. Eng. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, J.V., Jr.; Gombert, A.K. Towards high-temperature fuel ethanol production using Kluyveromyces marxianus: On the search for plug-in strains for the Brazilian sugarcane-based biorefinery. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.L.; Paulillo, S.C.d.L.; Godoy, A.; Cherubin, R.A.; Lorenzi, M.S.; Giometti, F.H.C.; Bernardino, C.D.; de Amorim Neto, H.B.; de Amorim, H.V. Ethanol production in Brazil: A bridge between science and industry. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.H.; Lemos, D.A.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Badino, A.C.; Silva, R.G.; Soneno, J.L.S. Bioethanol Production Using Mixtures of Sorghum Juice and Sugarcane Molasses: Experimental Data and Kinetic Modeling. Sugar Tech 2024, 26, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.G.; Veloso, I.I.K.; Ribeiro, M.P.A.; Badino, A.C.; Cruz, A.J.G. Thermal analysis of extractive fed-batch ethanol fermentation with CO2 stripping: Modeling and simulation. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 182, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentou, H.; Abidin, Z.Z.; Yunus, R.; Biak, D.R.A.; Korelskiy, D. Overview of Alternative Ethanol Removal Techniques for Enhancing Bioethanol Recovery from Fermentation Broth. Processes 2019, 7, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.P.; Silva, C.R.; Martins, T.B.; Pereira, R.D.; Esperança, M.N.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Badino, A.C. Heat transfer evaluation for conventional and extractive ethanol fermentations: Saving cooling water. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 304, 127063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, L.; Basso, T.; Rocha, S. Ethanol production in Brazil: The industrial process and its impact on yeast fermentation. Biofuel Prod.-Recent Dev. Prospect. 2011, 1530, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Godoy, A.; Amorim, H.V.; Lopex, M.L.; Oliveira, A.J. Continuous and batch fermentation processes: Advantages and disadvantages of these processes in the Brazilian ethanol production. Int. Sugar J. 2008, 110, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Wheals, A.E.; Basso, L.C.; Alves, D.M.G.; Amorim, H.V. Fuel ethanol after 25 years. Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, H.V.; Lopes, M.L.; de Castro Oliveira, J.V.; Buckeridge, M.S.; Goldman, G.H. Scientific challenges of bioethanol production in Brazil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, I.M.; Nigam, P.; Singh, D.; Marchant, R.; McHale, A.P. Review: Ethanol production at elevated temperatures and alcohol concentrations: Part I—Yeasts in general. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 14, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino de Souza, J.; Dias do Prado, C.; Eleutherio, E.C.A.; Bonatto, D.; Malavazi, I.; Ferreira da Cunha, A. Improvement of Brazilian bioethanol production—Challenges and perspectives on the identification and genetic modification of new strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeasts isolated during ethanol process. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.D.; Mandrujano, G.P.L.; Souza, J.P.; Sgobbi, F.B.; Novaes, H.R.; da Silva, J.P.M.O.; Alves, M.H.R.; Eliodório, K.P.; Cunha, G.C.G.; Giudici, R.; et al. Physiological characterization of a new thermotolerant yeast strain isolated during Brazilian ethanol production, and its application in high-temperature fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Dheeran, P.; Singh, S.P.; Mishra, I.M.; Adhikari, D.K. Cooling System Economy in Ethanol Production Using Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces Sp. IIPE453. Am. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiadpum, A.; Limtong, S.; Phisalaphong, M. High-temperature ethanol fermentation by immobilized coculture of Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuanpeng, S.; Thanonkeo, S.; Yamada, M.; Thanonkeo, P. Ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice at high temperatures using a newly isolated thermotolerant yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae DBKKU Y-53. Energies 2016, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, S.; Flynn, O.; Hack, C.J.; Marchant, R. Fermentation of molasses using a thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus IMB3: Simplex optimisation of media supplements. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 46, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, W.R.; Fadil, M.; Nigam, P.; Banat, I.M. Isolation of thermotolerant ethanologenic yeasts and use of selected strains in industrial scale fermentation in an Egyptian distillery. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 68, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limtong, S.; Sringiew, C.; Yongmanitchai, W. Production of fuel ethanol at high temperature from sugar cane juice by a newly isolated Kluyveromyces marxianus. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3367–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.-W.; Liang, J.-J.; Qin, X.-J.; Wang, J.-R.; Feng, J.-X.; Huang, R.-B. Multiple induced mutagenesis for improvement of ethanol production by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dheeran, P.; Singh, S.P.; Mishra, I.M.; Adhikari, D.K. Kinetic studies of ethanol fermentation using Kluyveromyces sp. IIPE453. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radecka, D.; Mukherjee, V.; Mateo, R.Q.; Stojiljkovic, M.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M. Looking beyond Saccharomyces: The potential of non-conventional yeast species for desirable traits in bioethanol fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015, 15, fov053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonklang, S.; Abdel-Banat, B.M.A.; Cha-aim, K.; Moonjai, N.; Hoshida, H.; Limtong, S.; Yamada, M.; Akada, R. High-temperature ethanol fermentation and transformation with linear DNA in the thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus DMKU3-1042. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7514–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.-H.; Geng, Q. Simultaneous Fermentation and Separation in the Ethanol and ABE Fermentation. Sep. Purif. Rev. 1992, 21, 127–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhao, J.; Yang, S.-T.; Wei, D. Fed-batch fermentation for n-butanol production from cassava bagasse hydrolysate in a fibrous bed bioreactor with continuous gas stripping. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonego, J.L.S.; Lemos, D.A.; Rodriguez, G.Y.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Badino, A.C. Extractive Batch Fermentation with CO2 Stripping for Ethanol Production in a Bubble Column Bioreactor: Experimental and Modeling. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7552–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonego, J.L.S.; Lemos, D.A.; Pinto, C.E.M.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Badino, A.C. Extractive Fed-Batch Ethanol Fermentation with CO2 Stripping in a Bubble Column Bioreactor: Experiment and Modeling. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, E.; Larsson, C.; Lidén, G.; Niklasson, C.; Gustafsson, L. Continuous estimation of product concentration with calorimetry and gas analysis during anaerobic fermentations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 394, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, E.C.; Costa, A.C.; Atala, D.I.P.; Maugeri, F.; Maciel, M.R.W.; Filho, R.M. Evaluation of optimization techniques for parameter estimation: Application to ethanol fermentation considering the effect of temperature. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1682–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.B.; Motoki, M.; Matsumura, M.; Kataoka, H. Simultaneous ethanol fermentation and stripping process coupled with rectification. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1989, 68, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.R.; Esperança, M.N.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Moura, L.F.; Badino, A.C. Stripping of ethanol with CO2 in bubble columns: Effects of operating conditions and modeling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 102, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.I.; Iemma, A.F. Experimental Design and Process Optimization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeji, T.C.; Karcher, P.M.; Qureshi, N.; Blaschek, H.P. Improving performance of a gas stripping-based recovery system to remove butanol from Clostridium beijerinckii fermentation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 27, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vrije, T.; Budde, M.; van der Wal, H.; Claassen, P.A.; López-Contreras, A.M. “In situ” removal of isopropanol, butanol and ethanol from fermentation broth by gas stripping. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, K.N.; Blackburn, J.W. The stripping of organic chemicals in biological treatment processes. Environ. Prog. 1984, 3, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.F. A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1968, 10, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. The Monod equation: A revisit and a generalization to product inhibition situations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1980, 22, 1671–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenfeld, M.; Kerpes, R.; Becker, T. Understanding the Impact of Industrial Stress Conditions on Replicative Aging in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Fungal Biol. 2021, 2, 665490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Run | Independent Variables | Response Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | kE (h−1) | kW (h−1) | |
| 1 | −1 (1.61) | −1 (36.1) | −1 (37.1) | 0.084 | 0.0024 |
| 2 | +1 (3.39) | −1 (36.1) | −1 (37.1) | 0.106 | 0.0028 |
| 3 | −1 (1.61) | +1 (53.9) | −1 (37.1) | 0.084 | 0.0037 |
| 4 | +1 (3.39) | +1 (53.9) | −1 (37.1) | 0.083 | 0.0035 |
| 5 | −1 (1.61) | −1 (36.1) | +1 (43.0) | 0.076 | 0.0022 |
| 6 | +1 (3.39) | −1 (36.1) | +1 (43.0) | 0.129 | 0.0032 |
| 7 | −1 (1.61) | +1 (53.9) | +1 (43.0) | 0.085 | 0.0035 |
| 8 | +1 (3.39) | +1 (53.9) | +1 (43.0) | 0.155 | 0.0054 |
| 9 | −1.68 (1.0) | 0 (45.0) | 0 (40.0) | 0.044 | 0.0017 |
| 10 | +1.68 (4.0) | 0 (45.0) | 0 (40.0) | 0.147 | 0.0044 |
| 11 | 0 (2.5) | −1.68 (30.0) | 0 (40.0) | 0.081 | 0.0019 |
| 12 | 0 (2.5) | +1.68 (60.0) | 0 (40.0) | 0.091 | 0.0044 |
| 13 | 0 (2.5) | 0 (45.0) | −1.68 (35.0) | 0.064 | 0.0024 |
| 14 | 0 (2.5) | 0 (45.0) | +1.68 (45.0) | 0.118 | 0.004 |
| 15 | 0 (2.5) | 0 (45.0) | 0 (40.0) | 0.128 | 0.0042 |
| 16 | 0 (2.5) | 0 (45.0) | 0 (40.0) | 0.123 | 0.0039 |
| 17 | 0 (2.5) | 0 (45.0) | 0 (40.0) | 0.119 | 0.0037 |
| Parameter | Temperature (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 38 | 40 | 42 | 44 | |
| YX/S (gx gs−1) | 0.032 ± 0.0031 a | 0.030 ± 0.0002 a | 0.023 ± 0.0004 ab | 0.019 ± 0.0041 b |
| YE/S (gE gs−1) | 0.38 ± 0.003 a | 0.39 ± 0.004 a | 0.38 ± 0.01 a | 0.34 ± 0.02 b |
| PV (gE L−1 h−1) | 8.26 ± 0.13 a | 7.96 ± 0.40 ab | 7.46 ± 0.30 b | 5.83 ± 0.20 c |
| µmax (h−1) | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.14 ± 0.003 a | 0.097 ± 0.001 a | 0.087 ± 0.001 a |
| Yield Coefficient | Value * |
|---|---|
| YX/S (gX gS−1) | 0.022 ± 0.003 |
| YE/S (gE gS−1) | 0.44 ± 0.02 |
| Parameter | Value * |
| μmax (h−1) | 0.177 ± 0.014 |
| KS (g L−1) | 33.45 ± 5.8 |
| KIS (g L−1) | 94.60 ± 3.2 |
| CEmax (g L−1) | 77.93 ± 0.60 |
| n (-) | 0.62 ± 0.12 |
| Variable | Unit | Fermentation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFHT | EFHT1 | EFHT2 | EFHT3 | ||
| CS0 | g L−1 | 190.70 | 193.82 | 192.12 | 190.53 |
| CSf | g L−1 | 22.14 | 0.96 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Maximum CE in the broth | g L−1 | 76.89 | 66.44 | 62.12 | 53.26 |
| Final CE in the fermentation broth | g L−1 | 76.89 | 64.87 | 57.48 | 47.98 |
| Total CEf at the end of fermentation | g L−1 | 76.89 | 84.86 1 | 84.48 1 | 83.83 1 |
| Ethanol volumetric productivity (PE) | g L−1 h−1 | 6.41 2 | 7.10 2 | 7.04 2 | 6.99 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sonego, J.L.S.; de Moraes, J.M.; de Vargas, N.S.; da Cunha, A.F.; da Silva Cruz, R.G.; Cruz, A.J.G.; Badino, A.C. Integrated Process Combining High-Temperature Fermentation and Extractive Ethanol Removal via CO2 Stripping. Fermentation 2025, 11, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11050270
Sonego JLS, de Moraes JM, de Vargas NS, da Cunha AF, da Silva Cruz RG, Cruz AJG, Badino AC. Integrated Process Combining High-Temperature Fermentation and Extractive Ethanol Removal via CO2 Stripping. Fermentation. 2025; 11(5):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11050270
Chicago/Turabian StyleSonego, Jorge Luíz Silveira, Jaqueline Machado de Moraes, Nayana Simon de Vargas, Anderson Ferreira da Cunha, Rosineide Gomes da Silva Cruz, Antonio José Gonçalves Cruz, and Alberto Colli Badino. 2025. "Integrated Process Combining High-Temperature Fermentation and Extractive Ethanol Removal via CO2 Stripping" Fermentation 11, no. 5: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11050270
APA StyleSonego, J. L. S., de Moraes, J. M., de Vargas, N. S., da Cunha, A. F., da Silva Cruz, R. G., Cruz, A. J. G., & Badino, A. C. (2025). Integrated Process Combining High-Temperature Fermentation and Extractive Ethanol Removal via CO2 Stripping. Fermentation, 11(5), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11050270







