Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for Xylitol Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Media, and Cultural Condition
2.2. DNA Manipulation Techniques
2.3. SDS-PAGE and Protein Expression
2.4. Batch Fermentation in Shake Flasks
2.5. Analytical Procedures
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
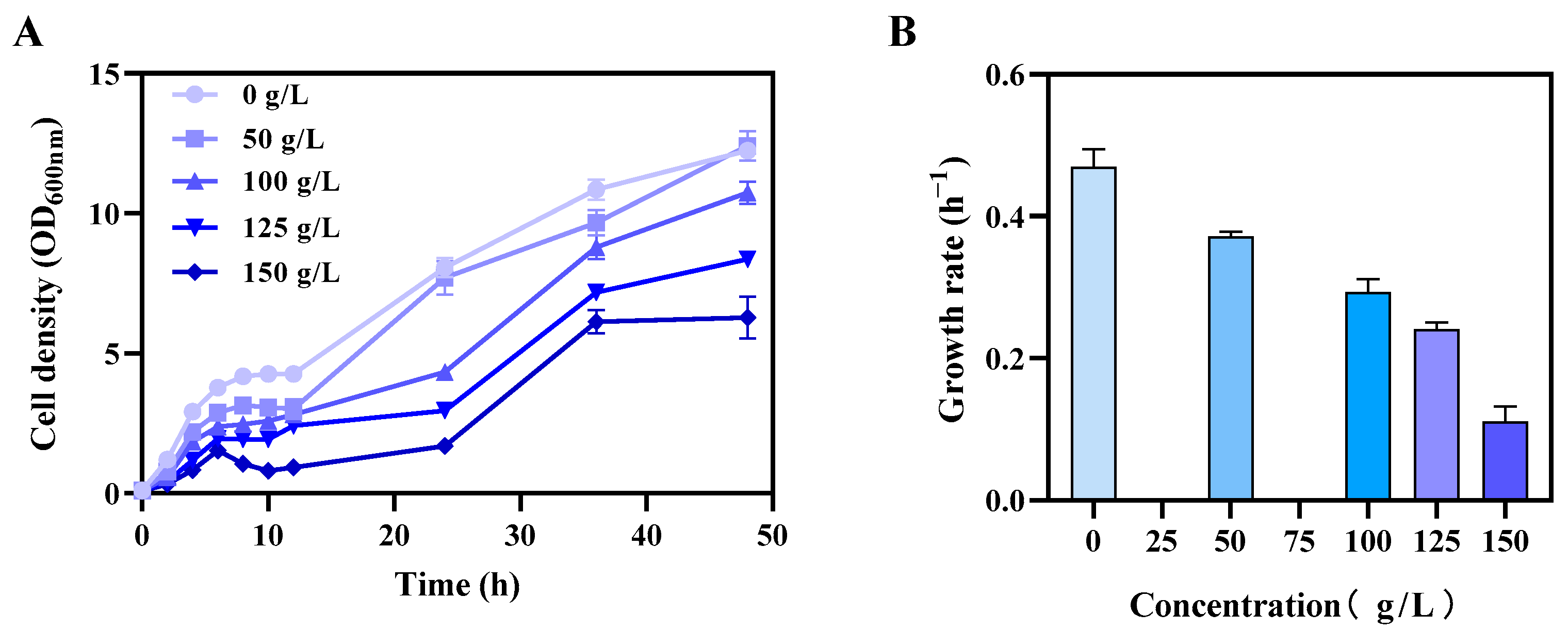
3.1. Investigation of Xylitol Toxicity to E. coli
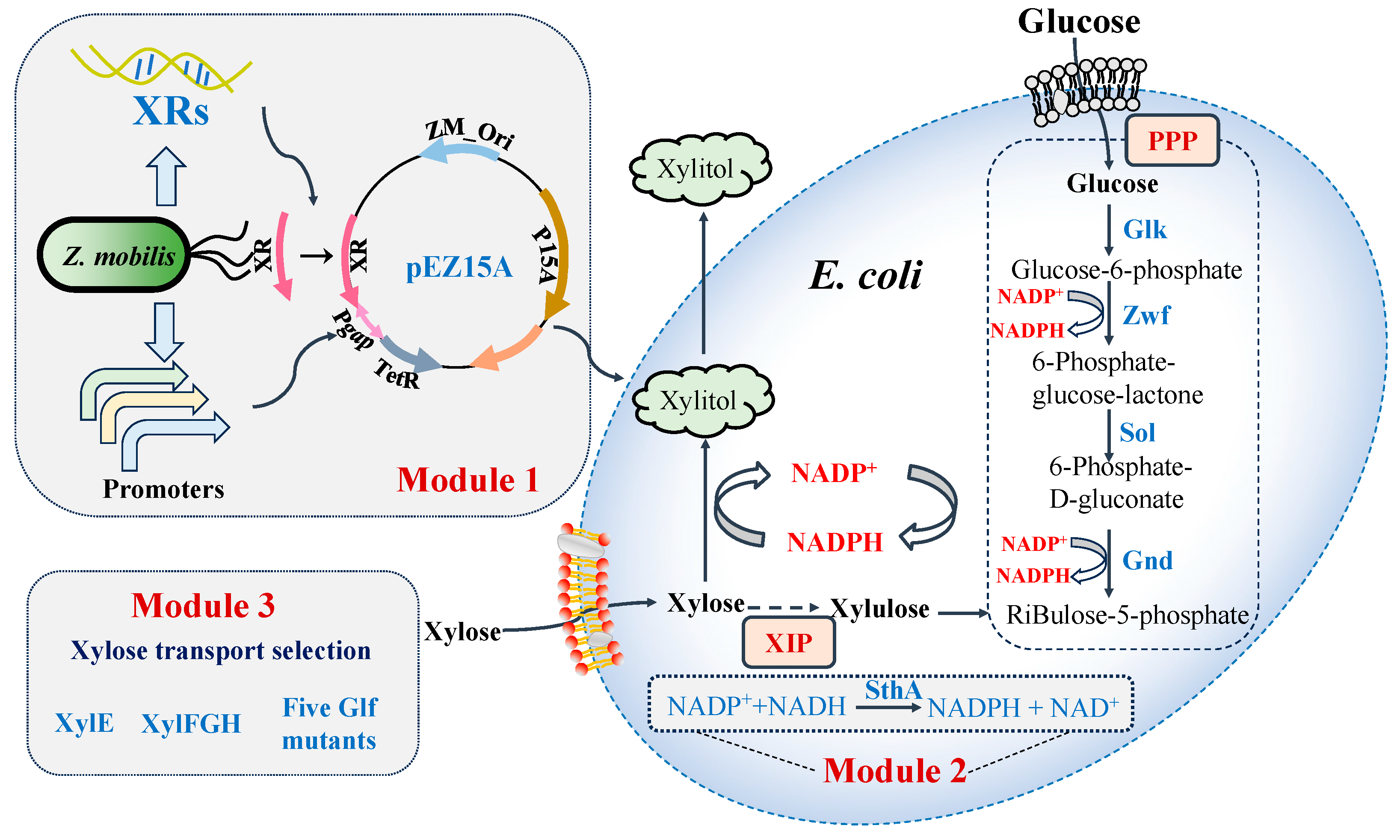
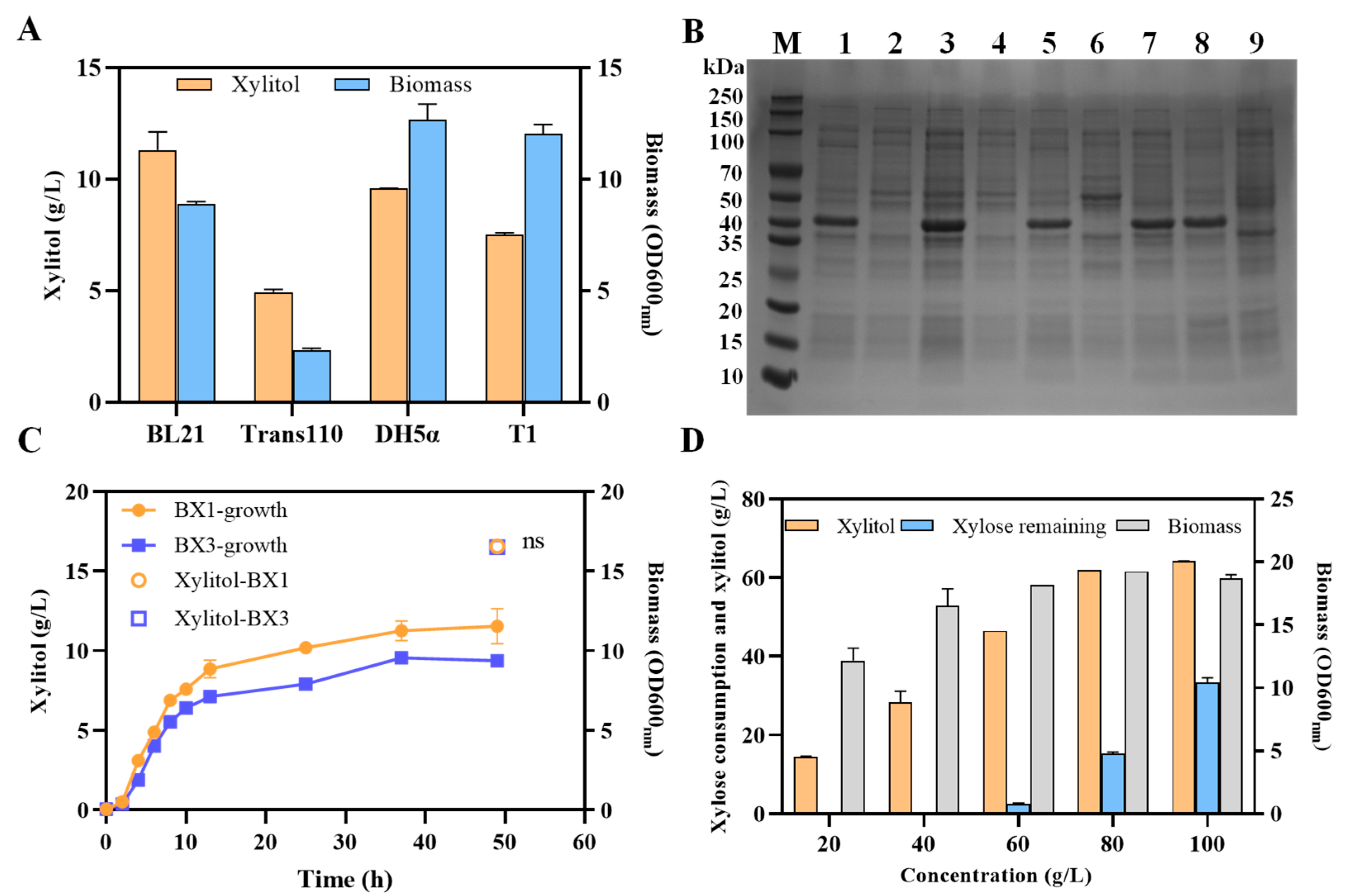
3.2. Selection and Comparison of Xylose Reductases from Different Microorganisms for Efficient Xylitol Producers of E. coli
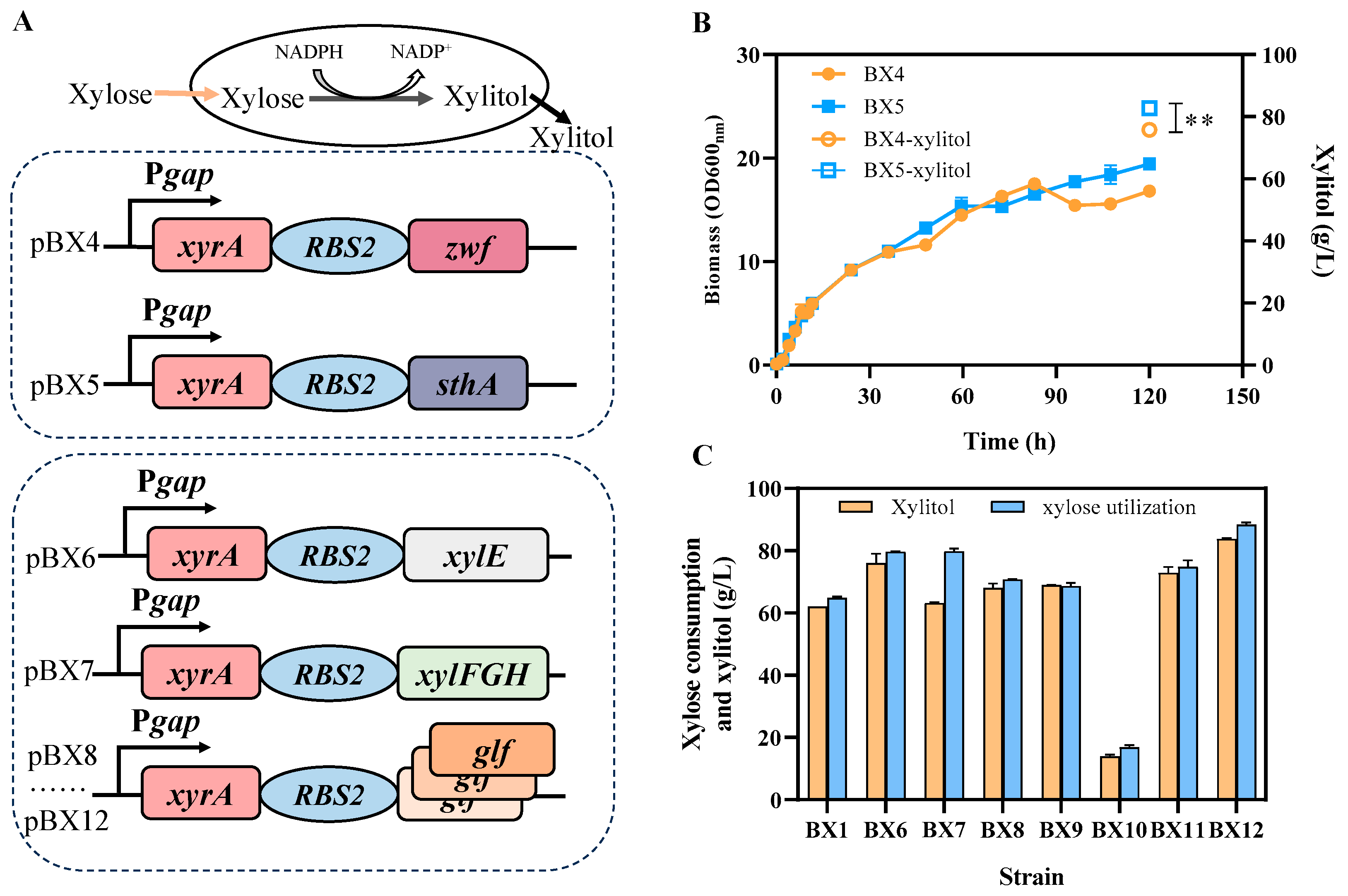
3.3. Improvement of Xylitol Production by Enhancing NADPH Supply and Xylose Transport
3.4. Effect of Oxygen to Xylitol Production
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.B.; Chuang, C.Y.; Liao, J.F. Effects of xylitol in chewing gum on dental plaque and Streptococcus mutans. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajó, J.C.; Domínguez, H.; Domínguez, J. Biotechnological production of xylitol. Part 1: Interest of xylitol and fundamentals of its biosynthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 65, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais Junior, W.G.; Pacheco, T.F.; Trichez, D.; Almeida, J.R.M.; Gonçalves, S.B. Xylitol production on sugarcane biomass hydrolysate by newly identified Candida tropicalis JA2 strain. Yeast 2019, 36, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werpy, T.; Petersen, G. Top Value Added Chemicals from Biomass: Volume I–Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Sugars and Synthesis Gas; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2004; 76p. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, B.C.; Kennedy, G.J. Optimization of xylitol production from xylose by a novel arabitol limited co-producing Barnettozyma populi NRRL Y-12728. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 51, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswar Rao, L.; Goli, J.K.; Gentela, J.; Koti, S. Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to xylitol: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 213, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Mulay, S. A review on different modes and methods for yielding a pentose sugar: Xylitol. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.-I.; Suzuki, T.; Kawai, K.; Horitsu, H.; Takamizawa, K. Purification, characterization and structure analysis of NADPH-dependent d-xylose reductases from Candida tropicalis. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1995, 79, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallezot, P. Metal Catalysts for the Conversion of Biomass to Chemicals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, V.; Bhatt, A.; Mehta, S.; Sharma, V.; Rathour, R.; Verdhan, S. Xylitol production by Pseudomonas gessardii VXlt-16 from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate and cost analysis. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, G.; Lin, J.; Yang, L.; Lian, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ye, L.; et al. XylR overexpression in Escherichia coli alleviated transcriptional repression by arabinose and enhanced xylitol bioproduction from xylose mother liquor. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 6624–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelhausen, E.; Kuzmanova, S. Microbial conversion of d-xylose to xylitol. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1998, 86, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Bura, R.; Doty, S.L. Genetic analysis of D-xylose metabolism by endophytic yeast strains of Rhodotorula graminis and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2011, 34, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.J.; Ha, S.J.; Rin Kim, S.; Lee, W.H.; Galazka, J.M.; Cate, J.H.; Jin, Y.S. Enhanced xylitol production through simultaneous co-utilization of cellobiose and xylose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 2013, 15, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Shin, H.S.; Rogers, P.L. Xylitol production from a mutant strain of Candida tropicalis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Tu, S.; Lin, J.; Yang, L.; Shen, H.; Wu, M. Combination of the CRP mutation and ptsG deletion in Escherichia coli to efficiently synthesize xylitol from corncob hydrolysates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, K.S.; Wendisch, V.F.; Nampoothiri, K.M. Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for xylitol production from lignocellulosic pentose sugars. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 230, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povelainen, M.; Miasnikov, A.N. Production of xylitol by metabolically engineered strains of Bacillus subtilis. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 128, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, I.d.A.; Sene, L.; da Cunha, M.A.A.; Felipe, M.d.G.d.A. Short-term adaptation strategy improved xylitol production by Candida guilliermondii on sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic hydrolysate. BioEnergy Res. 2022, 15, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirimand, G.; Sasaki, K.; Inokuma, K.; Bamba, T.; Hasunuma, T.; Kondo, A. Cell surface engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae combined with membrane separation technology for xylitol production from rice straw hydrolysate. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3477–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Mukherjee, M.; Goswami, G.; Das, D. Adaptive laboratory evolution induced novel mutations in Zymomonas mobilis ATCC ZW658: A potential platform for co-utilization of glucose and xylose. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 47, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.S.; Kim, D.M.; Yoon, B.H.; Bai, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, I.C. Enhancement of xylitol production by attenuation of intracellular xylitol dehydrogenase activity in Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Qiu, C.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Bao, X. Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the efficient co-utilization of glucose and xylose. FEMS Yeast Res. 2017, 17, fox034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Hu, M.; He, Q.; Du, J.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; et al. Development and characterization of efficient xylose utilization strains of Zymomonas mobilis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, J.B.; Jang, S.W.; Ha, S.J. Enhanced xylitol production by mutant Kluyveromyces marxianus 36907-FMEL1 due to improved xylose reductase activity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. Stepwise metabolic engineering of Candida tropicalis for efficient xylitol production from xylose mother liquor. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Yang, L. Efficient production of xylitol from hemicellulosic hydrolysate using engineered Escherichia coli. Metab. Eng. 2015, 31, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.-Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Efficient biosynthesis of xylitol from xylose by coexpression of xylose reductase and glucose dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.T.; Soares, P.O.; Romaní, A.; Thevelein, J.M.; Domingues, L. Xylose fermentation efficiency of industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast with separate or combined xylose reductase/xylitol dehydrogenase and xylose isomerase pathways. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Branco, R.; Chandel, A.K.; Silva, S.S.d. Enzymatic production of xylitol: Current status and future perspectives. In D-Xylitol: Fermentative Production, Application and Commercialization; da Silva, S.S., Chandel, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for L-alanine production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 49, kuab057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lama, S.; Kim, J.R.; Park, S.H. Production of 1,3-propanediol from glucose by recombinant Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2018, 23, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Causey, T.B.; Hasona, A.; Shanmugam, K.T.; Ingram, L.O. Production of optically pure D-lactic acid in mineral salts medium by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli W3110. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tan, Z.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X. Metabolic evolution of two reducing equivalent-conserving pathways for high-yield succinate production in Escherichia coli. Metab. Eng. 2014, 24, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, H.; Haselbeck, R.; Niu, W.; Pujol-Baxley, C.; Burgard, A.; Boldt, J.; Khandurina, J.; Trawick, J.D.; Osterhout, R.E.; Stephen, R.; et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for direct production of 1,4-butanediol. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; He, Q.; Geng, B.; Yang, S. Microbial cell factories in the bioeconomy era: From discovery to creation. Biodes. Res. 2024, 6, 0052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Li, M.; Yang, S. Cysteine supplementation enhanced inhibitor tolerance of Zymomonas mobilis for economic lignocellulosic bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Li, R.; Shen, W.; Ma, X.; Ma, L.; Yi, L.; Yang, S.; et al. Characterization and repurposing of the endogenous type I-F CRISPR-Cas system of Zymomonas mobilis for genome engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 11461–11475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Shen, W.; Yan, X.; He, Q.; Cai, D.; Chen, S.; Wei, H.; Knoshaug, E.P.; Zhang, M.; Himmel, M.E.; et al. Metabolic engineering of Zymomonas mobilis for anaerobic isobutanol production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, W.; Zhan, Y.; Gao, J.; Wu, B.; He, M.; et al. Development and characterization of acidic-pH-tolerant mutants of Zymomonas mobilis through adaptation and next-generation sequencing-based genome resequencing and RNA-Seq. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Chen, R.R. Discovery and characterization of a xylose reductase from Zymomonas mobilis ZM4. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, I.d.A.; Jofre, F.M.; Queiroz, S.d.S.; Lacerda, T.M.; Felipe, M.d.G.d.A. Relation of xylitol formation and lignocellulose degradation in yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3143–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, S.S.; Raiker, V.A.; Rewanwar, S.; Kotwal, P.; Kumar, A.; Padmanabhan, S. Enhanced fluorescent properties of an OmpT site deleted mutant of green fluorescent protein. Microb. Cell Fact. 2010, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Du, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, N.; Mei, M.; Xiong, Z.; Tang, K.; et al. Determination of Nucleotide Sequences within Promoter Regions Affecting Promoter Compatibility between Zymomonas mobilis and Escherichia coli. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 2811–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.X.; Yan, X.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.W.; Bai, F.W.; He, Q.N.; Yang, S.H. Metabolic engineering of Zymomonas mobilis for continuous co-production of bioethanol and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB). Green Chem. 2022, 24, 2588–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Bao, J. Enhancement of furan aldehydes conversion in Zymomonas mobilis by elevating dehydrogenase activity and cofactor regeneration. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, K.L.; Rao, C.V. Expression of a xylose-specific transporter improves ethanol production by metabolically engineered Zymomonas mobilis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6897–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekshmi Sundar, M.S.; Madhavan Nampoothiri, K. An overview of the metabolically engineered strains and innovative processes used for the value addition of biomass derived xylose to xylitol and xylonic acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, R.; Candeliere, F.; Moreno-Garcia, J.; Mauricio, J.C.; Rossi, M.; Raimondi, S.; Amaretti, A. Fermentative processes for the upcycling of xylose to xylitol by immobilized cells of Pichia fermentans WC1507. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1339093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plasmid | Description | Source |
| pEZ15A | Shuttle vector contains Z. mobilis origin and E. coli origin p15A, SpR | Lab stock |
| pX1 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX2 | pEZ15A carrying gra1 genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX3 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA genes driven by strong promoter Pgap-6M, SpR | This work |
| pX4 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, zwf genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX5 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, sthA genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX6 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, xylE genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX7 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, xylFGH genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX8 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, glfRD5 genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX9 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, glf1028T genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX10 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, glfA18T genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX11 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, glfV275F genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX12 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, glfL445I genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| pX13 | pEZ15A carrying xyrA, sthA, glfL445I genes driven by strong promoter Pgap, SpR | This work |
| Strain | Description | Source |
| E. coli DH5α | E. coli strain for plasmid construction | Lab stock |
| E. coli T1 | E. coli strain for plasmid construction | Lab stock |
| E. coli Trans 110 | E. coli strain for plasmid demethylation | Lab stock |
| E. coli BL21 | E. coli BL21 strain for xylitol production | Lab stock |
| Z. mobilis ZM4 | Z. mobilis wild-type strain | Lab stock |
| BX1 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX1 | This work |
| BX2 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX2 | This work |
| BX3 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX3 | This work |
| BX4 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX4 | This work |
| BX5 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX5 | This work |
| BX6 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX6 | This work |
| BX7 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX7 | This work |
| BX8 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX8 | This work |
| BX9 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX9 | This work |
| BX10 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX10 | This work |
| BX11 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX11 | This work |
| BX12 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX12 | This work |
| BX13 | E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain containing pX13 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; He, Z.; Yan, X.; Yang, S. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for Xylitol Production. Fermentation 2025, 11, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030131
Li J, Zhang L, Li C, He Z, Yan X, Yang S. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for Xylitol Production. Fermentation. 2025; 11(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiapeng, Lei Zhang, Changzheng Li, Zhaoqing He, Xiongying Yan, and Shihui Yang. 2025. "Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for Xylitol Production" Fermentation 11, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030131
APA StyleLi, J., Zhang, L., Li, C., He, Z., Yan, X., & Yang, S. (2025). Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for Xylitol Production. Fermentation, 11(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030131







