Abstract
Economic development increases and brings about issues such as the secure supply of food in a sustainable way. Phytases are enzymes catalyzing phytate hydrolysis to release phosphorus in an inorganic form. Animal feeds could be supplemented with bacterial phytases to increase their phosphorus and micronutrients bioavailability. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the purification and characterization of an alkalophilic phytase from Cobetia marina. The purified newly isolated phytase from the halophilic Cobetia marina strain 439 appears to be appropriate for use as an additive in food and feed processing. Its molecular weight was determined to be 43 kDa by gel filtration and 40 kDa by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The purified enzyme had maximum activity at pH 8.0 and 45 °C, while at 70 °C, it was 80% and about 50% at 80 °C for 40 min, showing its thermostability. Enzyme activity was retained at a broad pH range from 6.5 to 9.0. The half-life of the phytase of 15 min at pH 10 and 30 min at pH 4.0 was registered. The enzyme was proven to be with high substrate specificity. In addition, the purified phytase showed strong proteolytic tolerance against trypsin and pepsin. The pH profile, its thermostability, and proteolytic tolerance of the studied phytase as a halophilic bacterial product determine it as a unique candidate for application in agriculture, food, and feed industries.
1. Introduction
Phytase enzymes (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolase, EC 3.1.3.8) are a subgroup of phosphatases catalyzing the release of phosphate from phytic acid (phytate or myo-inositol hexakisphosphate), and this form of phosphorus is mainly found in cereal grains, legumes, and oilseeds. This organic form of phosphorus represents 60–90% of the total phosphorus content [1,2]. Phytate is the most widely distributed form of phosphorus in soil [3]. Phosphorus is essential for plants in their various basic processes such as photosynthesis, flowering, giving fruits, and maturation. However, plants cannot directly utilize the phytate present in the soil. The phytate in soil favors plant phosphorus nutrition, as phosphate ester (C-O-P), phosphoanhydride (P-O-P), or phosphonate (C-P) have to be first dephosphorylated via phytase-mediated hydrolysis [3,4]. The presence of phytate in plant food material may appear as an anti-nutritional factor causing mineral deficiency in non-ruminants [5]. This action of phytate can be diminished by the support of phytase to improve the degradation of amino acids, trace minerals, and phosphorus excretion into the environment. This is the cause of eutrophication in the surface waters and subsequently algal blooms [6]. Phytases were suggested as an animal feed additive with the purpose of increasing the plant content nutritional quality in the feed of simple-stomached animals by releasing phosphate [7]. Low or even no phytase activity was found in fish, chicken, and other monogastric animals’ digestive tracts [8,9]. Therefore, phosphorus availability from granular feeds lessened to 15–20% of its content in the feed. In the meantime, the utilization degree of associated minerals was reduced by 9–26%. Phytic phosphorus remains and moves unchanged along the digestive tract to be excreted with manure. The manure, in turn, may be applied as an organic fertilizer. Soil contamination and the appearance of insoluble phosphates in groundwater and underground water are connected with high levels of unassimilable phosphorus in fertilizers [10]. The addition of phytase to animal feed is seen as a way of increasing phosphates and other minerals’ bioavailability, but at the same time it is seen as an opportunity to reduce the level of phosphate pollution in intensive animal husbandry areas, as inorganic phosphate does not need to be added to animal feed. As a result, the fecal excretion of phosphate by simple-stomached animals can be reduced by up to 50% [11].
The complete hydrolysis of phytate yields one molecule of inositol and six molecules of inorganic phosphate. Meanwhile, partial hydrolysis leads to the release of myo-inositol intermediates, namely mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, and pentaphosphates in addition to inorganic phosphate. Phytases are widely classified into three types depending on the initiation site of the dephosphorylation of the phytate, namely 3-phytases, 4/6-phytases, and 5-phytases. 3-Phytases (EC 3.1.3.8) initiate the hydrolysis of phytate at the third phosphate group, 6-phytases (EC 3.1.3.26) initiate the hydrolysis of phytate at the sixth phosphate group, whereas 5-phytases (EC 3.1.3.72) initiate phytate hydrolysis at the fifth phosphate group [12]. Considering their pH optimum, phytases can be divided into alkaline and acid phytases. Fungi, most bacteria, and plants can produce acid phytases, while a small number of bacteria and plants secrete neutral or alkaline phytases [13]. In view of their catalytic mechanism, phytases are primarily divided into four categories—histidine acid phosphatases, cysteine phytases, purple acid phosphatases, and β-propeller phytases [14]. Phytases are abundantly found in nature. Microbial sources, including bacteria, fungi, and yeasts, are the most significant ones for phytase production. The most important phytase-producing microorganisms include the following: Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus terreus, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus caespitosus, Aspergillus nidulans, Thermomyces lanuginosus, Penicillium simplicissimum, Penicillium lycii, Pichia anomala, Candida krusei, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella terrigena, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella aerogenes, Pantoea agglomerans, Citrobacter braakii, Pseudomonas syringae, Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Phytases are also obtained from plants like rye, oat, barley, maize, and soybean [15]. Both plant and microbial phytases play a significant role in phytate solubilization. Phytases of microbial origin are the most appropriate to be applied in the commercial biotechnological production of enzymes thanks to their strong catalytic properties and simplicity of enzyme production. Phytases from several species of bacteria, yeast, and fungi have already been characterized [16,17,18]. However, the commercial production recently focalizes on the soil fungus Aspergillus [11]. On the other hand, bacterial phytases possess some other biological properties, such as phytate specificity and activity in a broad pH range from neutral to alkaline. The resistance to proteolysis and high catalytic efficiency are of particular importance. Recently, phytases have attracted considerable attention from both scientists working in the field of nutrition and environmental protection as well as from entrepreneurs with a focus on other different biotechnological applications. Some of them are in food and feed industries as well as in the production of myo-inositol phosphates with their role in phosphorous storage in plants. No less important feature is their possible use in the semi synthesis of peroxidase, in the paper and pulp industries, and as a soil amendment and plant growth promoter [1,19]. Apart from the commercial values in the feed and food industries, phytases have potential biotechnological applications in various other fields, such as ecology, agriculture, and aquaculture [20]. The market is currently broadening for phytase applications in numerous sectors like functional food, thus creating the need for the enzyme and search of further commercial development. A single phytase does not exist that could meet the diverse needs for all applications in commerce and the environment. Therefore, there is a growing demand for screening bacteria or other microorganisms for novel and efficient phytases. Only a restricted number of reports exist on mesophilic bacterial phytases, and the knowledge of phytases from extremophilic bacteria is limited. Halophilic bacteria are a source of a variety of extremozymes called halozymes. Their unique structural, chemical, and physiological properties allow them to effectively act under extreme conditions where mesophilic enzymes lose their activity. They are unusually adapted to high temperature, pH, salt, and heavy metal concentrations. Halophilic enzymes are distinguished in classes: hydrolases, oxidoreductases, transferases, and lyases that are well known for their industrial and biotechnological usefulness. Effective halozyme producers belong to different genera of halophilic microorganisms, including Halobacillus, Haloferax, Halobacterium, Marinococcus, Natronococcus, and Acinetobacter. The protein structure determines the biocatalytic potential of halozymes. Except for their use in the textile, agriculture, food, detergent, pulp, and paper industries, they also contribute to the bioremediation of xenobiotics. Halophilic and halotolerant microorganisms have proven to be capable of synthesizing extremozymes as a sustainable tool for bioeconomy development [21].
Halozymes remain active under conditions typically encountered in the industrial processes that usually lead to protein precipitation and denaturation, such as extreme values of pH, temperature, and salt and organic solvent concentrations. In the field of animal nutrition, wastewater treatment, and food production, industrial extremozymes are urgently sought after. Halophiles have important biotechnological advantages like the reduced risk of contamination during cultivation, low nutritional requirements, and the ability to utilize a wide range of substances such as carbon and energy sources. Therefore, much attention is paid to finding new halophilic sources of phytases and characterizing them in detail. Compared to mesophilic enzymes, halophilic and halotolerant enzymes exhibit their activity in a wide range of salt levels and are applicable in industrial processes that demand it, not hindering enzymatic transformations. These salt-adapted enzymes are characterized by an excess of acidic amino acids situated on the surface of the protein molecule and a general decrease in the abundance of hydrophobic amino acids [22]. The halophiles possess features such as reduced risk in contamination during cultivation, minimal nutritional requirements, and the ability to use a broad range of substances as their only carbon and energy sources [23].
The main disadvantage in extremophilic exploration is a low biomass and correspondingly lower enzyme levels achieved in comparison to their mesophilic counterparts. However, the selection of an appropriate producer or adaptation of specific cultivation conditions could significantly improve enzyme production [24].
Many halophilic strains of the genus Cobetia have been reported as a source of biomolecules and activities interesting for biotechnological applications. The genomic analysis of these strains proved their unique potential in the biosynthesis of biosurfactants, aromatic hydrocarbon and alginate degradation, inorganic carbon fixation, polyhydroxy-alkanoates’ synthesis, and surface colonization [25,26].
The aim of the present study was to isolate, purify, and characterize a novel phytase from the halophilic bacterium Cobetia marina strain 439, seeking to achieve high enzymatic activity at physiological temperatures and a broad pH range and high substrate specificity with a potential application in the agriculture, food, and feed industries.
2. Materials and Methods
All reagents and chemicals used in this study were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA) unless otherwise stated.
2.1. Screening of Phytase-Producing Bacteria
Twenty-two strains of moderately halophilic bacteria were previously isolated from salterns, situated in the cities of Pomorie and Burgas bay of Burgas, Bulgaria, and screened for phytase activity [27]. Screening was conveyed on solid phytase screening medium (PSM) according to Palla et al. [28]. PSM contained (w/v) 1.5% glucose, 1.0% sodium phytate, 0.2% CaCl2, 0.5% (NH4)2SO4, 0.05% KCl, 0.05% MgSO4, 0.001% FeSO4, 0.001% MnSO4, 10% NaCl, and 3% agar (pH 7.2). After incubation for 72 h at 35 °C, a specific two-step staining of the medium with 2% CoCl2 and subsequent soaking with a solution of 6.25% (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O and 0.42% NH4VO3 (1:1) were applied [29]. A total of 12 bacterial strains showed sodium phytate hydrolysis, which was recognized by the clear halo surrounding them. After a quantitative assay on PSM broth, Cobetia marina strain 439 had the highest phytase production compared to the other 12 halophilic bacterial strains tested), and for this reason, it was selected for further study.
Cobetia marina strain 439 was isolated from lye collected from Burgas salterns (33% salinity). Its phylogenetic affiliation was determined by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, and the nucleotide sequence has been deposited in EMBL under nucleotide accession no. LN849908 [27].
The ability of the Cobetia marina strain 439 for sodium phytate degradation was also proven by its growth in liquid PSM containing 1.0% (w/v) sodium phytate as a sole source of phosphorus. The strain was cultivated at 35 °C for 72 h in flasks and its growth was monitored by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (OD600nm). Then, the liquid cultures underwent centrifugation at 10,000× g for 20 min, and the phytase activity of the cell-free supernatant of the strain was measured as described below.
2.2. Phytase Assay and Protein Determination
The phytase activity was determined by incubating 0.1 mL of enzyme solution with 0.9 mL of 0.5% sodium phytate in 0.1 M Tris–HCl buffer, containing 10% NaCl, (pH 8.0). The enzyme reaction was carried out at 45 °C for 20 min, followed by stopping the reaction by the introduction of 0.75 mL of 5% trichloroacetic acid. The released phosphate was measured at 700 nm after the addition of 1.5 mL of color reagent, which was freshly prepared just before the assay by mixing four volumes of 2.5% ammonium molybdate solution in 5.5% sulfuric acid and one volume of 2.5% ferrous sulfate water solution. One unit of phytase activity was defined as 1 μmol of phosphate liberated per minute under the assay condition. A control reaction was carried out with the lack of an enzyme. A standard curve (using 0.5–10 μg/mL KH2PO4) was prepared by treating standard phosphate solutions without phytase present under the same conditions [29]. The total protein content was calculated by the Lowry assay with bovine serum albumin as a standard (concentration range of 0–1000 µg/mL). The absorbance at 540 nm was monitored [30]. After establishing the concentration of protein in different enzyme samples, their specific activity was evaluated.
2.3. Partial Purification of Phytase
All purification steps were performed at room temperature with 0.1 M Tris–HCl buffer, pH 8.0, containing 10% NaCl. The purification of the phytase was sequentially carried out by ultrafiltration using Amicon™ stirred cell, DEAE-Sepharose anion-exchange column chromatography, and Sephadex G-75 size-exclusion column chromatography using the ÄKTAprime plus system (Amersham, Biosciences, Uppsala, Sweden).
A fresh culture cell-free supernatant was subjected to ultrafiltration and concentrated (1/20 of the original volume) using 10 kDa cellulose membrane (Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany). After ultrafiltration, the enzyme solution was loaded on a DEAE–Sepharose column (1.6 × 40 cm) and fractions were eluted at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The proteins were eluted by a linear gradient of 0–0.5 M NaCl. The phytase activity was found in the fraction eluted with 0.2 M NaCl. By measuring the absorbance at 280 nm, the presence of proteins in the collected fractions was revealed. The phytase-containing fractions were pooled and the subject of further purification by size-exclusion chromatography. The sample (1.0 mL) was loaded to a glass column packed with Sephadex G-75 (1.6 × 40 cm). Phytase active fractions were combined and then stored at 4 °C until further investigation.
2.4. Molecular Weight Determination
Gel filtration was applied to determine the native molecular weight on a Sephadex G-100 column using standard proteins in a concentration of 1 mg/mL with different Mw (150–14 kDa). The purified phytase enzyme was added to the column separately. The elution took place under the same conditions. The flow rate through the column was 0.4 mL/min. The elution volume was compared with the volumes of standard proteins, following Whitaker’s method [31].
The degree of purity and molecular weight were examined by SDS-PAGE in 10% resolving and 5% stacking gel, respectively, each containing 0.1% SDS by the method depicted by Laemmli [32] using Bio-Rad electrophoresis apparatus (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). A constant voltage of 80 V was used to run the gel. Molecular markers 10–170 kDa (Fisher BioReagents, Waltham, MA, USA) were taken as standard. Gels were stained with 0.1% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 in methanol/acetic acid/dH2O (in a ratio of 5:4:1) for 1.5 h and discolored by washing with methanol/acetic acid/dH2O (in a ratio of 5:4:1) several times.
2.5. Zymogram Assay
The zymogram was carried out according to Bae et al. [29] to detect the presence of active phytase. The previously obtained gels (SDS–PAGE) were immersed in 1% Triton X-100 for 1 h at 25 °C and then transferred to a 0.1 M Tris–HCl buffer with pH 8.0, containing 10% NaCl and maintained for 1 h at 35 °C. The phytase activity was detected by incubating the gels in the same buffer containing 0.5% (w/v) sodium phytate for 16 h. Activity bands were visualized through immersion of the gels in a 2% (w/v) aqueous cobalt chloride solution for 5 min at 25 °C. Then, this solution was replaced with a mixture, containing equal volumes of 6.25% (w/v) aqueous ammonium molybdate solution and 0.42% (w/v) ammonium vanadate solution, freshly prepared. The phytase activity was assessed by the formation of the clear zone against an opaque background.
2.6. Characterization of Phytase Activity
For phytase activity characterization, purified phytase was used. All tests were performed in triplicate.
The activity of the enzyme was assayed at different concentrations of NaCl (0%, 3%, 5%, 7%, 10%, and 15%).
To determine the effect of substrate concentration during enzyme–substrate reaction, varying concentrations of sodium phytate (0.3%, 0.5%, 0.7%, and 1.0%) were prepared, and then the enzyme activity was tested.
The optimum reaction time was determined as the reaction mixture was incubated for different time intervals (5, 10, 20, 30, and 40 min) under optimized temperature and pH values.
The optimum temperature for the enzyme activity was evaluated by incubating the reaction mixture at pH 8.0 and different temperature ranges between 30 °C and 70 °C. The activity was expressed as a percent relative activity with respect to the 100% maximum activity.
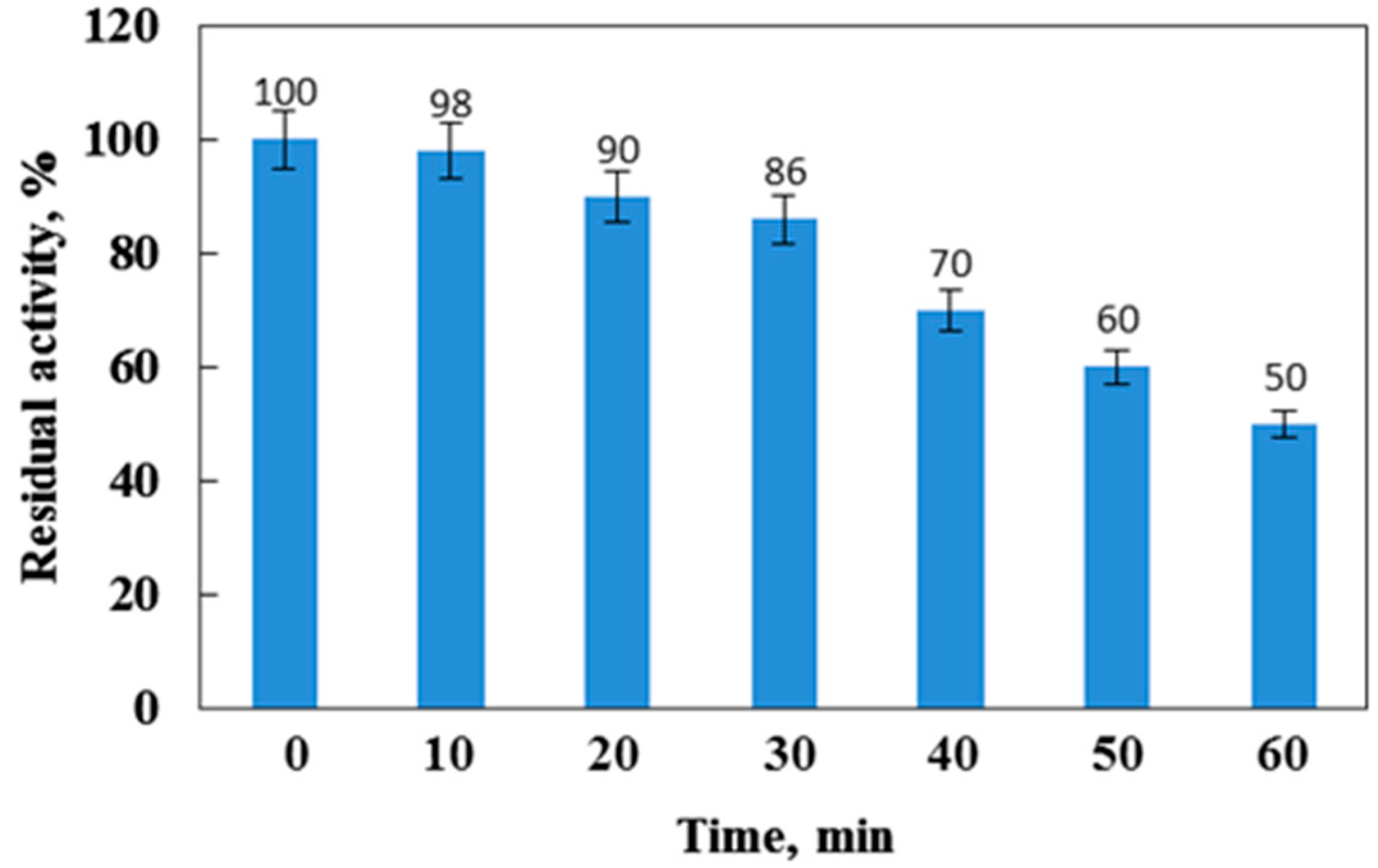
In order to study its thermostability, the enzyme was exposed to various elevated temperatures (50 °C, 60 °C, 70 °C, 80 °C) for varying time intervals (0–60 min). Then, the phytase activity was estimated under standard reaction conditions. Control treatments were performed without incubation at different temperatures for various time intervals for comparison in each assay under the standard conditions of the enzyme activity assay. The percentage residual enzyme activity was calculated by comparing it with the non-incubated enzyme, considered as the 100% control.
The optimum pH for enzyme activity was determined by using the following buffers (0.1 M) containing 10% NaCl: citrate buffer (pH 4.0–4.5), succinate buffer (pH 5.0–6.5), Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0–8.5), and glycine–NaOH buffer (pH 9.0–9.5). The activity was expressed as a percent relative activity with respect to the maximum activity (100%).
The pH stability of the enzyme was determined by measuring the residual enzyme activity after incubation in the corresponding buffer at 45 °C for various times (0–60 min). The phytase activity after incubation was determined under standard reaction conditions. The percentage residual enzyme activity was calculated by comparison with the non-incubated enzyme, considered as the 100% control.
The substrate specificity of the pure phytase enzyme was determined in the presence of the following phosphate-containing substrates at a concentration of 0.5% in 0.1 M Tris–HCl buffer with 10% NaCl: sodium phytate, glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-diphosphate, adenosine diphosphate (ADP), p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The enzyme reaction was conveyed at 45 °C and pH 8.0.
The kinetic parameters of the phytase were determined by measuring the rate of phytate hydrolysis at various substrate concentrations, ranging from 2.0 to 37 mM in the standard reaction mixture (at 45 °C and 0.1 M Tris–HCl buffer with 10% NaCl, pH 8.0). The Michaelis–Menten constant (Km) and maximum velocity (Vmax) values were calculated from the Lineweaver–Burk plot using Microsoft Excel software.
Separately investigated was the effect of metal ions on the enzyme activity. It was implemented with the addition of chloride salts of Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Ca2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Hg2+, and Fe2+ directly to the standard reaction mixture in a final concentration of 1 mM, 5 mM, and 10 mM. The enzyme activity determined in the absence of metal ions was defined as 100%. To investigate the influence of some chemicals on the enzyme activity, SDS, Triton X-100, Tween 20, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) were separately introduced to the standard reaction mixture in final concentrations of 1, 5, and 10%. The percentage residual activities were shown after comparing it with the standard assay mixture without a chemical.
The proteolytic tolerance of the enzyme was evaluated as described by Dokuzparmak et al. [16]. The phytase resistance against trypsin and chymotrypsin was determined as the purified enzyme with a final concentration of 0.1 mg/mL and incubated with protease mix with a final concentration of 0.1 mg/mL. Trypsin–chymotrypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, Protease Type VIII bacterial from Bacillus licheniformis) in 0.1 M Tris–HCl buffer with 10% NaCl, pH 8.0 at a ratio of 1:1 (w/w) for 30, 60, and 90 min at 45 °C was used. The residual phytase activity was determined applying the standard phytase assay. The percentage residual activities were revealed compared with a standard assay mixture without protease.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The experiments and analyses were performed in triplicate, and the data expressed represent the mean values with the standard error of the mean (±SEM) of the three independent investigations. The statistical analysis was performed using MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEL 2020 software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening of Phytase Secretion
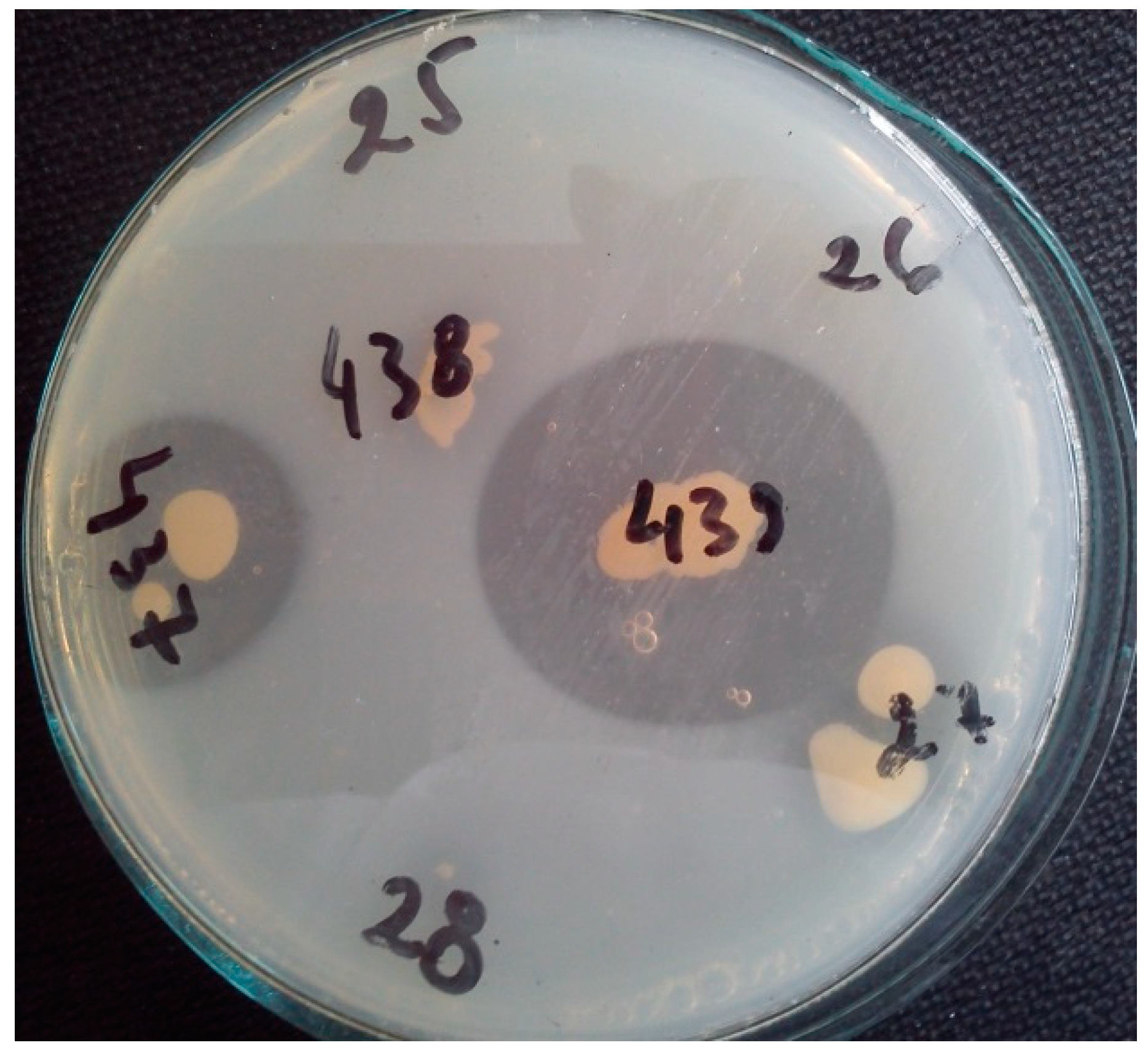
The Cobetia marina strain 439 secreted alkaline phytase when it was grown on phytase screening medium. The strain produced a 2.30 cm zone around the colony after 72 h (Figure 1).
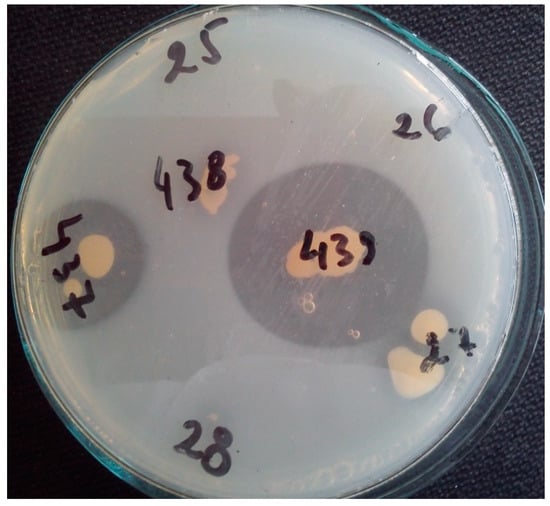
Figure 1.
Visualization of Cobetia marina strain 439 and Cobetia marina strain 437 clear zones (2.3 cm and 1.8 cm, respectively) as a result of sodium phytate hydrolysis. The remaining numbers of the other tested strains show lack of growth and clear zones on phytase screening medium.
3.2. Cultivation of Cobetia marina Strain 439
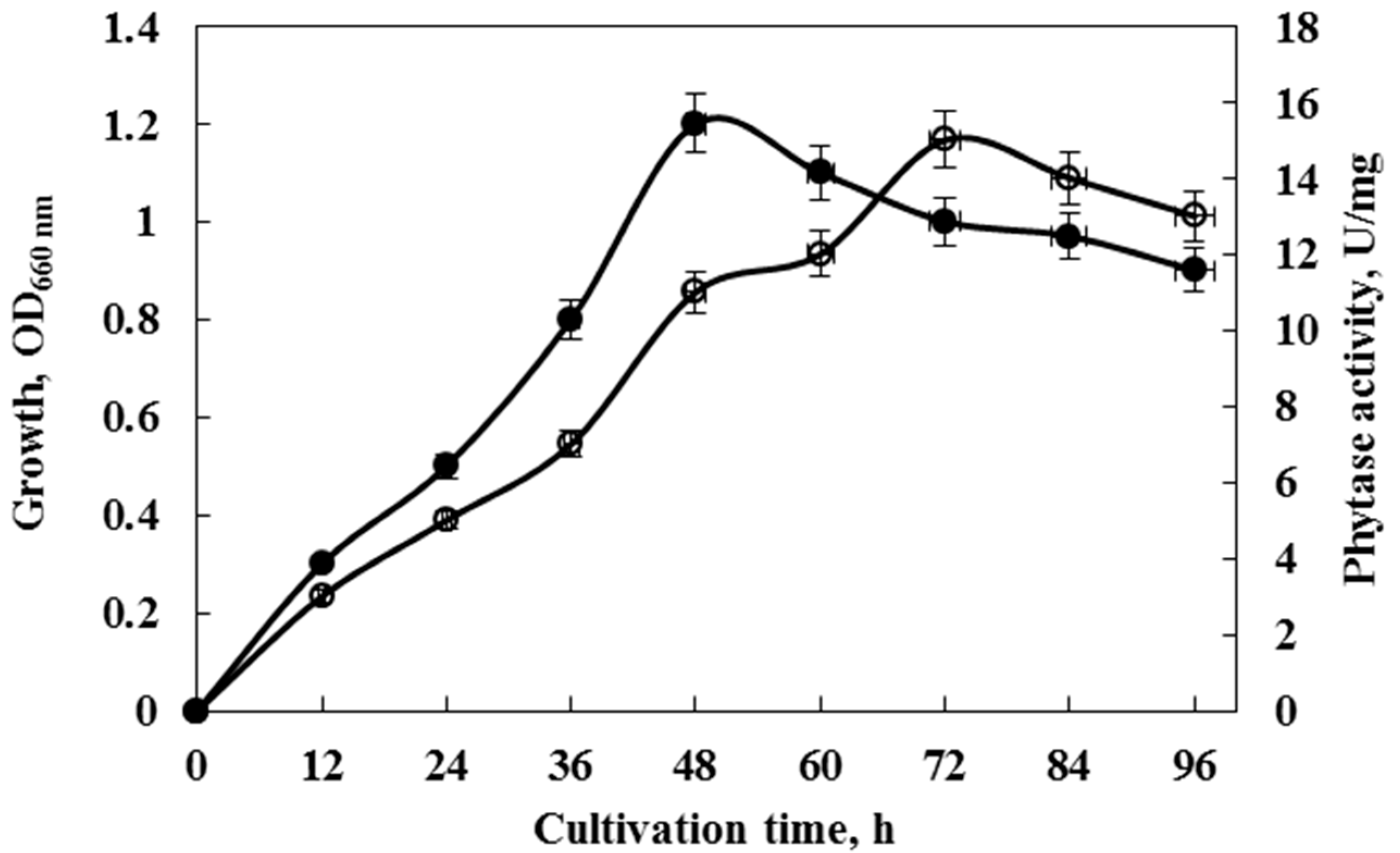
Cultivation for phytase production was carried out aerobically at 35 °C in the PSM for 96 h with no addition of phosphate salts. The activity increased significantly after the cells had reached the stationary phase (Figure 2). The maximum activity of the enzyme was recorded at 72 h of cultivation. Since the enzyme synthesis is initiated as soon as growth rates begin to decline, we speculate that either nutrient or energy limitations during the stationary phase may underlie phytase induction. This induction in the stationary phase suggests that phytase is not needed during balanced growth and may be synthesized in response to some nutrient or other limitations. The same correlation was observed in the cultivation of phytase-producing Bacillus sp. KHU-10 [33]. In contrast, in a bacterium isolated from Malaysian wastewater, remarkable phytase activity was detected during all growth phases, and the activity was not significantly increased once the cells reached the stationary phase. This phytase is therefore a constitutive enzyme and unlike the phytase produced by Cobetia marina strain 439, and its synthesis is not induced by nutrient or energy limitation [34].

Figure 2.
Growth (-●-) and phytase activity (-◌-) of Cobetia marina strain 439 cultivated on PSM, containing 1.0% (w/v) sodium phytate and 10% NaCl. Initial pH = 7.2. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
3.3. Purification of Phytase
The supernatant obtained by centrifugation of the culture broth at 10,000× g for 20 min was used as an enzyme source. The purification of the phytase was consecutively performed by ultrafiltration, DEAE-Sepharose anion-exchange column chromatography, and Sephadex G-75 size-exclusion column chromatography. The purification results are presented in Table 1. The phytase activity was eluted as a single sharp activity peak from each column used. The phytase was purified 17-fold from the culture broth with 35% yield. The enzyme exhibited an activity of 260 U/mg. Phytase enzymes were purified from Bacillus sp. DS11 [35], Bacillus sp. KHU-10 [33], and Bacillus subtilis P6 [36] with specific activities of 20, 36, and 104.39 U/mg, respectively.

Table 1.
Purification steps of the phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439.
3.4. Molecular Weight Determination and Zymogram Analysis
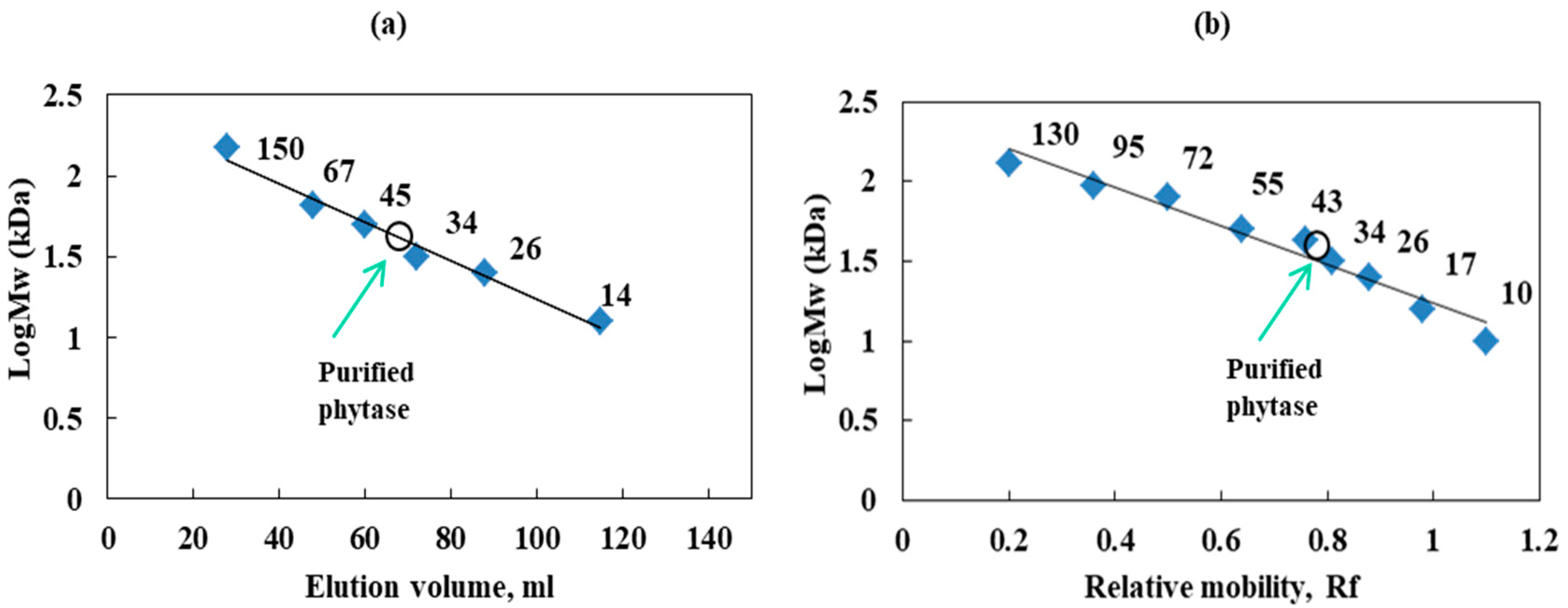
The molecular mass and homogeneity of the purified enzyme were evaluated by gel filtration and SDS-PAGE (Figure 3a,b). The molecular weight of the purified phytase estimated by SDS-PAGE was 40 kDa, and the molecular mass of the native enzyme was determined to be 43 kDa on calibrated Sephadex G-100 gel chromatography.
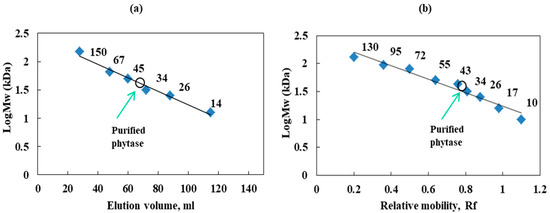
Figure 3.
Determination of the molecular weight of purified phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 (a)—standard curve of elution volume plotted against the logMw of known protein standards; (b)—standard curve of Rf (band spacing/dye front spacing) was plotted vs. logMw of the known protein standard markers—filled squares (Fisher BioReagents, Waltham, MA, USA); unfilled circles—purified enzyme.
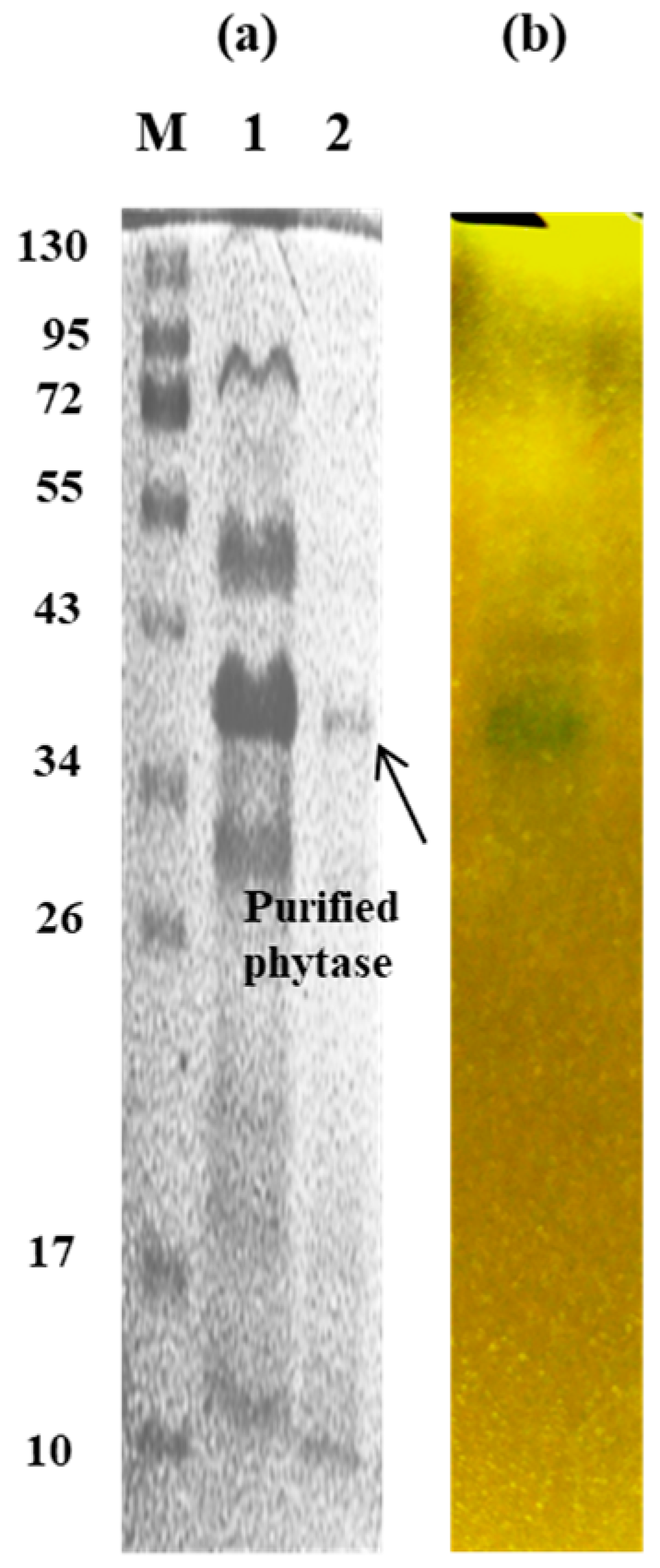
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions showed only one single protein band after Coomassie staining of the gels (Figure 4a). The band corresponding to phytase activity was visualized by the use of zymogram, stained according to Bae et al. [29] (Figure 4b). Zymogram analysis of the enzyme was also performed, and its homogeneity was confirmed.

Figure 4.
(a)—SDS-PAGE gel and M—standard protein markers (Fisher BioReagents): 1—crude enzyme; 2—purified enzyme; (b)—zymogram analysis of phytase activity of purified enzyme.
The molecular masses of different phytases are quite variable and are within the range of 32–330 kDa. The higher molecular weight of fungal and yeast phytases is attributed to the glycosylation of these enzymes [12]. For instance, Aspergillus phytases had larger molecular masses—214 kDa for Aspergillus terrus [37], 85–100 kDa for A. ficuum [38], and 630 kDa for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CY strain [39]. The molecular masses of the bacterial phytases purified from Klebsiella pneumoniae 9-3B [40], Bacillus sp. DS11 [35], and Bacillus sp. KHU-10 [33] were found to be 45, 44, and 46 kDa, respectively, similarly to that of Cobetia marina strain 439 phytase (43 kDa) in our study. In contrast, a molecular mass of 106.04 kDa was established for Geobacillus sp. TF16 [16].
3.5. Characterization of Purified Phytase
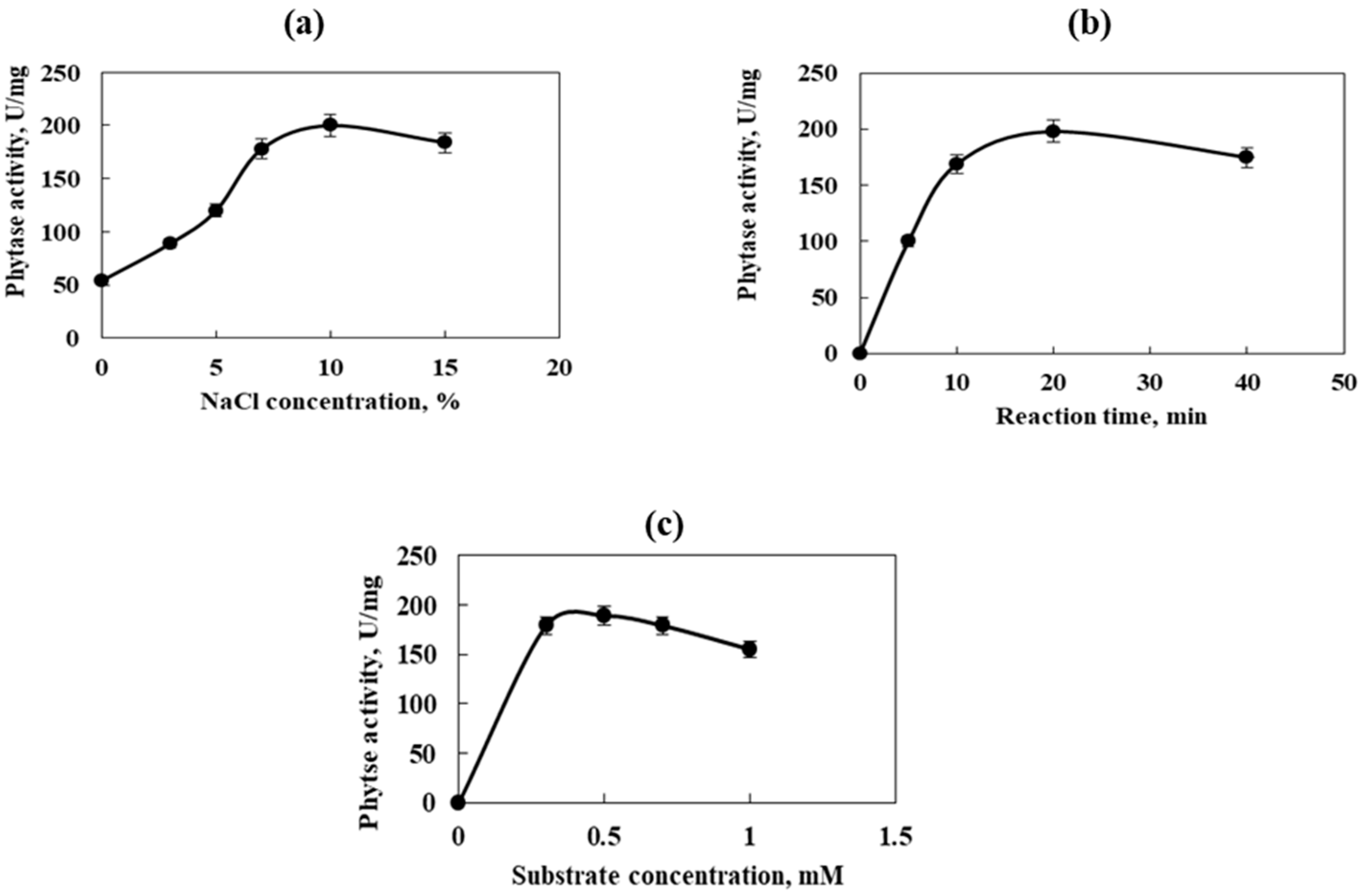
The effect of different enzyme reaction factors on the activity of the purified phytase is shown in Figure 5. The enzyme–substrate reaction was conducted at pH 7.5 and a temperature of 35 °C. The maximum enzyme activity was recorded in the presence of 10% NaCl, 1% sodium phytate, and 30 min incubation time (200 U/mg, Figure 5a). It was performed after 20 min of enzyme–substrate reaction time with 1% sodium phytate and 10% NaCl (198 U/mg, Figure 5b) and sodium phytate as a substrate in a concentration of 0.5%, 30 min incubation time, and 10% NaCl (189 U/mg, Figure 5c).
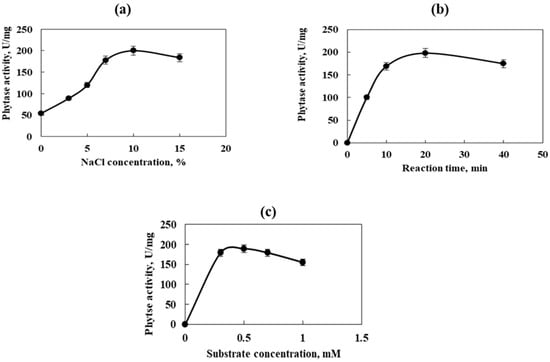
Figure 5.
Effect of different enzyme reaction factors on the activity of the purified phytase. (a)—NaCl concentration; (b)—reaction time; (c)—substrate concentration. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
The results show the halophilic nature of phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439, which is a prerequisite for the resistance of this enzyme to various extreme conditions. It should be noted that halozymes preserve their activity in the presence of organic solvents, extreme pH and temperature values, and salt concentrations. That is why their utilization in some industrial processes is adequate without any protein precipitation and denaturation [41].
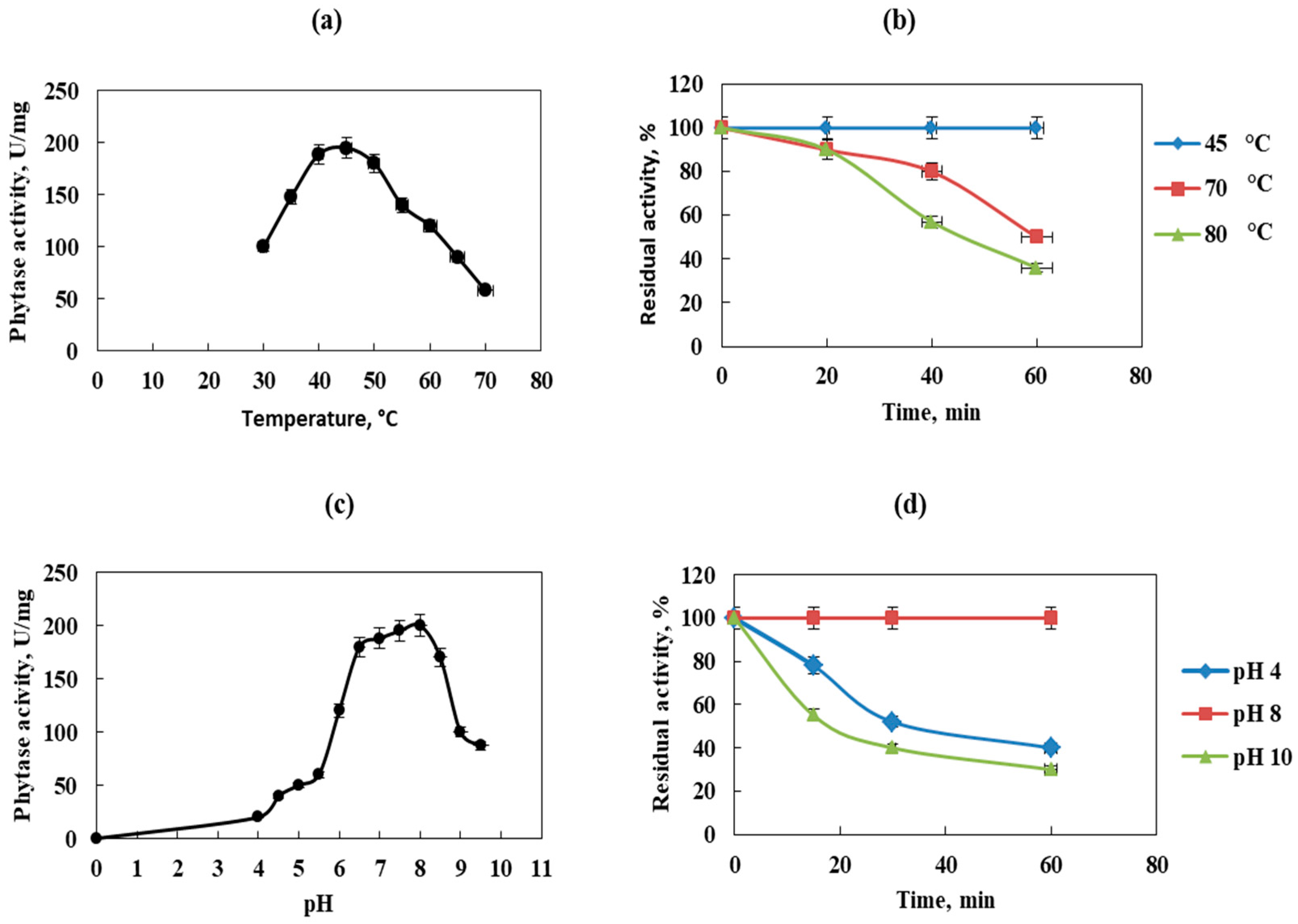
The enzymatic activity of the purified phytase is shown in Figure 6. The optimum temperatures of phytase for most microorganisms fall into the range between 30 °C and 70 °C. The activity of the phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 increased when the temperature was elevated from 30 to 50 °C and reached a maximal value at 45 °C and pH 8.0 (Figure 6a). Afterwards, it decreased rapidly as the temperature increased up to 55 °C. Similarly, the optimum temperature for the phytase activity in L. sanfranciscensis [42], G. stearothermophilus DM12 [43], and Bacillus subtilis P6 [36] was reported at 45 °C, 50 °C, and 40 °C, respectively. High optimum temperatures for phytase activity have been established in bacteria such as Bacillus sp. DS11 (70 °C) [35], Geobacillus sp. TF16 (85 °C) [16], and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (70 °C) [44]. When concerning yeasts, Pichia anomala showed maximum phytase activity at 60 °C and Arxula adeninivorans [45] and Candida krusei at 40 °C [44]. The phytase of Aspergillus terreus and Aspergillus caespitosus exhibited optimum temperatures at 70 °C and 80 °C, but Aspergillus oryzae exhibited optimum temperature at 50 °C [44]. Figure 6b represents the thermostability profile of the purified enzyme incubated for different time periods at various temperatures and pH 8.0. The phytase retained its activity at about 90% when incubated at 80 °C for 20 min and has a half-life of 40 min at the same temperature. The phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 showed strong thermal stability observed at 4, 35, and 45 °C, with the enzyme retaining about 90% of its activity for 12 h. The thermal stability of the phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 proved to be higher than this observed in phytases of Bacillus nealsonii ZJ0702 (40% at 80 °C for 30 min) [46], L. sanfranciscensis CB1 (70% at 70 °C for 30 min) [42], and Bacillus megaterium EBD 9-1 (20% at 70 °C for 40 min) [47]. Compared to the commercially available phytases from A. niger and P. lycii, the purified enzyme from Cobetia marina strain 439 exhibited higher thermal stability. The enzymes from A. niger kept only 40% and the phytase from P. lycii, and this was completely inactivated after 15 s at 70 °C [34]. The thermal stability of phytases is important for animal feed preparation and processing as these enzymes can be normally incorporated into the grains for feed pelleting by treatment for a few seconds at 80–85 °C [12]. In addition, the thermal stability of the studied enzyme at 4 °C elucidates an important advantage of easily applicable storage conditions. The obtained results suggest that Cobetia marina strain 439 phytase remains stable both at high and low temperatures, and this feature makes it very attractive for animal feed applications.

Figure 6.
Effect of temperature and pH on the activity and stability of purified phytase. (a)—temperature profile; (b)—thermostability of phytase; (c)—effect of pH on phytase activity; (d)—pH stability profile. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
The effect of pH on phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 was examined at various pH values in the range of 4.0–9.5 at 45 °C (Figure 6c). The results demonstrated that the enzyme was more active at pH 6.5 to 8.5, with an optimum activity at pH 7.5–8.0. The relative activities of the enzyme at pH 6.0, 8.0, and 9.0 were found to be 60%, 100%, and 50%, respectively. Similarly, the phytase from Bacillus sp. KHU-10 showed high activity at a relatively broad pH range between pH 6.5 and 8.5 [33]. Phytases from several Bacillus sp. showed maximum activity around neutral and slightly alkaline conditions (pH 6.0–8.0). Such data are reported for phytase from Bacillus megaterium EBD 9-1. Its enzyme was the most active in a pH range of 5.0–8.0 [47]. The highest activity of the phytase from Bacillus nealsonii ZJ0702 was observed at pH 7.5 [46]. Some other bacterial phytases purified from K. pneumoniae 9-3B [39], L. sanfranciscensis CB1 [42], and G. stearothermophilus strain DM12 [43] were found to have optimum pH values of 4.0, 4.0, and 4.5, respectively. However, fungal phytases from A. niger, A. oryzae, and P. lycii exhibited maximum activities at a pH of 2.2–5.0, 5.5, and 5.5, respectively [16].
The pH stability of the purified phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 was determined after enzyme incubation for 10, 30, and 60 min in buffers with pH values of 4.0, 8.0, and 10.0 at 45 °C. Figure 6d shows that after 30 min of incubation, the enzyme retained about 52% of its initial activity at pH 4.0 and has about 40% residual activity at pH 10.0. The pH stability profile of B. nealsonii ZJ0702 phytase demonstrated that the enzyme lost almost all of its original activity after 30 min of incubation at pH 4.0 and 40% of its original activity after 30 min of incubation at pH 6.0 [46]. The phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 showed optimal activity at pH 7.5–8.0, indicating that it is neutral and slightly alkaline and should be suitable for use in some aquaculture species whose digestive system pH is neutral. Many studies show that neutral phytases as an additive to carp feed had a better effect on growth and phosphorus utilization in crucian carp (Carassius auratus) than acid phytases [48].
The substrate specificity of the pure phytase enzyme from Cobetia marina strain 439 was determined in the presence of the following phosphate-containing substrates: sodium phytate, glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-diphosphate, adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP). The Cobetia marina strain 439 phytase was able to hydrolyze only phytate as a substrate. The purified enzyme (Table 2) did not significantly hydrolyze all other compounds tested. Similar data have been reported for the phytase from Bacillus subtilis P6; the highest activity was recorded with sodium phytate as the substrate, but there was negligible activity for the other phosphorus-containing substrates [36]. These results imply that Cobetia marina strain 439 phytase is specific for inositol polyphosphate. Bacillus sp. DS11 [35] and Bacillus sp. KHU-10 [33] phytases showed high activity for phytate but no activity on the other phosphorylated compounds. On the other hand, Geobacillus sp. TF16 phytase had a broad specific activity for phosphorylated compounds [16].

Table 2.
Substrate specificity of the purified phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439. Each experiment was performed at least in triplicate.
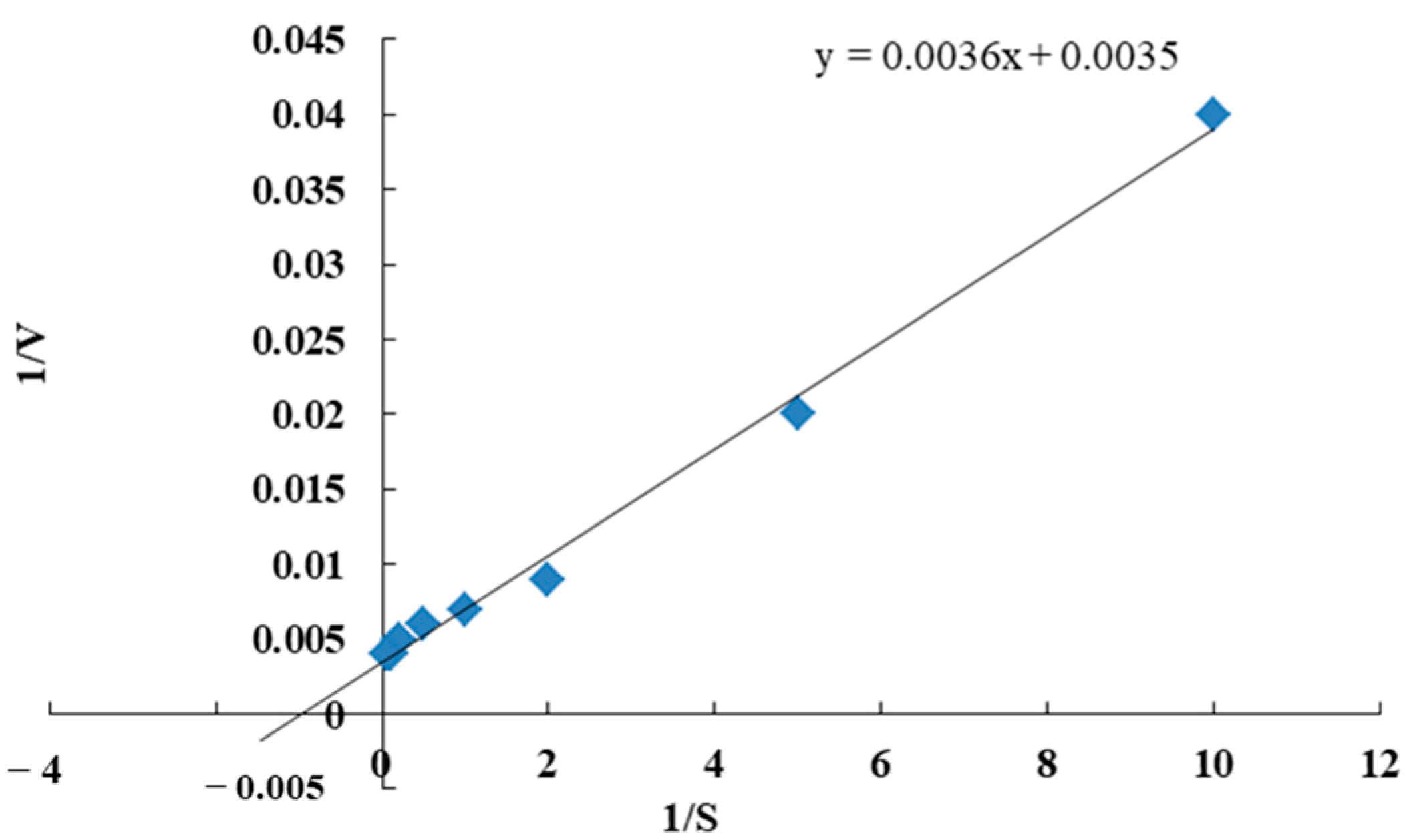
The kinetic parameters of the phytase were determined at various substrate concentrations. Km and Vmax values of Cobetia marina strain 439 phytase were calculated from the Lineweaver–Burk plot to be 0.96 mM and 260 U/mg protein, respectively (Figure 7). Km represents the enzyme affinity for a specific substrate. A small Km is evidence that the enzyme reaches saturation with a small amount of substrate, while a big Km demonstrates the requirement of higher substrate amounts to reach the maximum reaction velocity. Vmax represents the maximum velocity of enzymatic reactions when the binding site is saturated with substrate [16]. The Km values of phytases are reported to fall in the range from 0.08 to 10 mM. The Km values of phytases in the presence of sodium phytate as the substrate were reported to be 0.04, 0.55, 0.1, 0.03, 0.177, and 1.31 mM for K. pneumoniae 9-3B [40], Bacillus sp. DS11 [35], C. krusei [49], G. stearothermophilus DM12 [43], and Geobacillus sp. TF16 [16], respectively.

Figure 7.
Lineweaver–Burk plot for the determination of Km and Vmax of Cobetia marina strain 439 phytase toward Na-phytate as a substrate at 45 °C. The intercept on the y-axis corresponds to 1/Vmax, while the intercept of the x-axis corresponds to 1/Km. The data are presented as their mean values from three replicates.
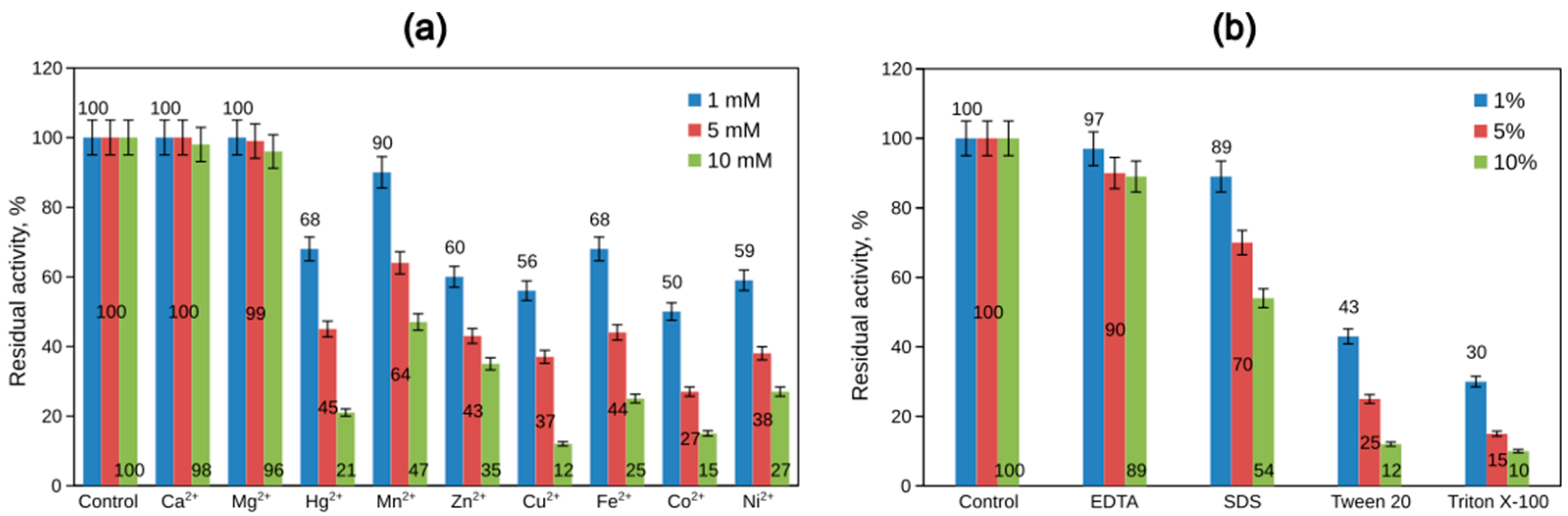
Concerning the catalytic activity, 75% of all known enzymes require metal ions [50]. Different bacterial phytases differ in their requirement for metal ions for enzyme activity. Most of the phytate-degrading enzymes characterized so far are significantly inhibited by EDTA, Zn2+, Cd2+, Ba2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Al3+, and SDS [47]. Many other phytases, however, are not metalloenzymes. The most potent inhibitors of these phytases are Cu2+, Zn2+, fluoride, molybdate, vanadate, and phosphate ions [33]. The effect of Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Ca2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Hg2+, and Fe2+ on the phytase activity of Cobetia marina strain 439 was tested at 1, 5, and 10 mM final concentrations of each ion in the reaction mixture. Our results showed that Cu2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Fe2+ ions greatly inhibited the enzyme, and at a metal concentration of 1 mM, the residual activity was 56%, 50%, 59%, and 68%, respectively (Figure 8). The metal ions Ca2+ and Mg2+ did not remarkably affect the phytase activity. The enzyme was almost completely inhibited in the presence of 10% Triton X-100 and Tween 20, and its residual activity after treatment with 10% SDS was 54%, whereas EDTA did not show any inhibitory effect, indicating that the purified enzyme might not be a metalloenzyme. Generally, the inhibitory effect of the metal ions could be attributed to the strong chelating property of the substrate, which results in a metal–phytate complex that effectively reduces the availability of the phytate for the enzyme.

Figure 8.
Effect of some metal ions (a) and of some chemical compounds (b) on the phytase activity. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
The nutritional value of phytases has led scientific investigations worldwide towards the study of their resistance to the action of proteolytic enzymes. The stomach and intestine are the main functional sites of supplemental phytases. Such enzymes that possess high resistance to pepsin and trypsin can be assessed as promising candidates for the purpose of the effective application of nutritional supplements. Various bacterial phytases have been proven to be resistant to these proteolytic enzymes. The purified phytase from B. subtilis P6 retained 90% of its activity after incubation with pepsin and trypsin, revealing tolerance to a high proteolytic environment [36]. For Geobacillus sp. TF16, approximately 80% and 60% of phytase activity was retained after incubation in a protease solution for 30 min and 60 min, respectively [16]. The trypsin resistance activity of the three commercial phytases from A. niger, A. oryzae, and E. coli was determined as 10, 84, and 79% after 20 min of incubation, respectively [51]. Our results showed that approximately 86% and 50% of phytase activity remained after incubation in the protease solution for 30 min and 60 min, respectively (Figure 9). These results can, therefore, suggest that Cobetia marina strain 439 phytase is more stable than A. niger, A. oryzae, and E. coli phytases.

Figure 9.
Residual activity of the purified phytase after treating with trypsin–chymotrypsin at 1:1 (w/w) of protease/phytase ratio. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
4. Conclusions
A novel phytase from Cobetia marina strain 439 was purified and characterized. The enzyme showed optimal activity at neutral to slightly alkaline pH, strong thermal stability, high substrate specificity for sodium phytate, and good resistance towards proteolytic enzymes. Optimum pH in the alkaline range (7.5–8.0) is very close to the physiological pH of poultry and of fish guts. The newly isolated phytase could therefore be used as an additive in poultry and fish feed to effectively increase the bioavailability and utilization of phosphorus, leading to improved growth by enhancing the digestibility of minerals and diminishing the excretion of nutrients. These unique properties could make this novel alkalophilic phytase an attractive beneficial enzyme for the feed and food processing industries where the hydrolysis of phytic acid and phytates is required. Advancements in scientific research in microbial phytases may promote new insights into their purification, characterization, mass production, and application as beneficial environmentally friendly enzymes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.B. and L.K.; methodology, K.B. and N.K.; validation, N.A.; investigation, K.B., N.A. and N.K.; data curation, I.B.; writing—original draft preparation, I.B.; writing—review and editing, L.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jain, J.; Sapna; Singh, B. Characteristics and Biotechnological Applications of Bacterial Phytases. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgessa, O.E.; Koyamo, R.; Dinka, H.; Tefese, K.; Gemeda, M.T. Review on Desirable Microbial Phytases as a Poultry Feed Additive: Their Sources, Production, Enzymatic Evaluation, Market Size, and Regulation. Int. J. Microbiol. 2024, 1, 9400374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwanuddin, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, P.; Naik, B.; Mishra, S.; Chauhan, M.; Saris, P.E.J.; Verma, A.; Kumar, V. Insight into Phytase-Producing Microorganisms for Phytate Solubilization and Soil Sustainability. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-López, A.M.; Delgado, A.; Plassard, C. Kinetics of phytate adsorption and response of phosphorus forms initially present in alkaline soils. Geoderma 2024, 443, 116800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudaki, H.; Aria, N.; Moravej, R.; Rezaei Yazdi, M.; Emami-Karvani, Z.; Hamblin, M.R. Microbial phytases: Properties and applications in the food industry. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloot, A.P.M.; Kalschne, D.L.; Amaral, J.A.S.; Baraldi, I.J.; Canan, C. A review of phytic acid sources, obtention, and applications. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersjant-Li, Y.; Awati, A.; Schulze, H.; Partridge, G. Phytase in non-ruminant animal nutrition: A critical review on phytase activities in the gastrointestinal tract and influencing factors. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 878–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selle, P.H.; Ravindran, V. Microbial phytase in poultry nutrition. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 135, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K. Significance of phytic acid and supplemental phytase in chicken nutrition: A review. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2008, 64, 553–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametzyanova, A.D.; Akhmetova, A.I.; Sharipova, M.R. Microorganisms as Phytase Producers. Microbiology 2012, 81, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konietzny, U.; Greiner, R. Bacterial Phytase: Potential Application, in Vivo Function and Regulation of Its Synthesis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2004, 35, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.E.C.S.; Rao, K.V.; Reddy, T.P.; Reddy, V.D. Molecular Characterization, Physicochemical Properties, Known and Potential Applications of Phytases: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2009, 29, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Yong, X.; Zhao, Z.; Dolce, V.; Li, Y.; Curcio, R. Research Status of Bacillus Phytase. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwanuddin, S.; Kumar, V.; Naik, B.; Singh, P.; Mishra, S.; Rustagi, S.; Kumar, V. Microbial Phytase: Their Sources, Production, and Role in the Enhancement of Nutritional Aspects of Food and Feed Additives. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esakkiraj, P.; Sandoval, G.; Sankaralingam, S.; Immanuel, G.; Palavesam, A. Preliminary Optimization of Solid-State Phytase Production by Moderately Halophilic Pseudomonas AP-MSU 2 Isolated from Fish Intestine. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuzparmak, E.; Sirin, Y.; Cakmak, U.; Saglam Ertunga, N. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Phytase from the Thermophilic Geobacillus Sp. TF16. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, A.; Satyanarayana, T. Purification and Characterization of a Thermostable and Acid-Stable Phytase from Pichia anomala. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, D.M.; Lawal, O.T.; Enujiugha, V.N. Purification and Characterization of Phytase from Aspergillus Fumigatus Isolated from African Giant Snail (Achatina Fulica). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Anoopkumar, A.N.; Tarafdar, A.; Madhavan, A.; Binoop, M.; Lakshmi, N.M.; Arun, K.B.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Sirohi, R.; et al. Microbial Engineering for the Production and Application of Phytases to the Treatment of the Toxic Pollutants: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, M.; Martínez, O.; Maruyama, F.; Marschner, P.; De La Luz Mora, M. Current and Future Biotechnological Applications of Bacterial Phytases and Phytase-Producing Bacteria. Microbes Environ. 2008, 23, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, H.G.; Wardah, Z.H.; Prajapati, V.; Raol, G. Halozymes: Sources, catalytic mechanisms, and potential applications in industries. In Extremozymes and Their Industrial Application; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruginescu, R.; Gomoiu, I.; Popescu, O.; Cojoc, R.; Neagu, S.; Lucaci, I.; Enache, M. Bioprospecting for novel halophilic and halotolerant sources of hydrolytic enzymes in brackish, saline and hypersaline lakes of Romania. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathakrishnan, D.; Gopalan, A.K. Isolation and characterization of halophilic isolates from Indian salterns and their screening for production of hydrolytic enzymes. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyadzhieva, I.; Radchenkova, N.; Atanasova, N.; Poli, A.; Finore, I.; Kambourova, M. Isolation and characterization of a thermostable pectinase by Anoxybacillus gonensis strain 357. CR Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2021, 74, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.; Balabanova, L.; Otstavnykh, N.; Zhukova, N.; Detkova, E.; Seitkalieva, A.; Bystritskaya, E.; Noskova, Y.; Tekutyeva, L.; Isaeva, M. In-Depth Genome Characterization and Pan-Genome Analysis of Strain KMM 296, a Producer of Highly Active Alkaline Phosphatase; Proposal for the Reclassification of Cobetia litoralis and Cobetia pacifica as the Later Heterotypic Synonyms of Cobetia Amphilec. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balabanova, L.A.; Golotin, V.A.; Kovalchuk, S.N.; Babii, A.V.; Shevchenko, L.S.; Son, O.M.; Rasskazov, V.A. The genome of the marine bacterium Cobetia marina KMM 296 isolated from the mussel Crenomytilus grayanus (Dunker, 1853). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2016, 42, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyadzhieva, I.; Tomova, I.; Radchenkova, N.; Kambourova, M.; Poli, A.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E. Diversity of Heterotrophic Halophilic Bacteria Isolated from Coastal Solar Salterns, Bulgaria and Their Ability to Synthesize Bioactive Molecules with Biotechnological Impact. Microbiol. 2018, 87, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, M.; Cristani, C.; Giovannetti, M.; Agnolucci, M. Identification and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeasts of PDO Tuscan Bread Sourdough by Culture Dependent and Independent Methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 250, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.D.; Yanke, L.J.; Cheng, K.J.; Selinger, L.B. A Novel Staining Method for Detecting Phytase Activity. J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 39, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.R. Determination of Molecular Weights of Proteins by Gel Filtration of Sephadex. Anal. Chem. 1963, 35, 1950–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.M.; Suh, H.J.; Kim, J.M. Purification and Properties of Extracellular Phytase from Bacillus Sp. KHU-10. J. Protein Chem. 2001, 20, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, R.; Farouk, A.E. Purification and Characterization of a Bacterial Phytase Whose Properties Make It Exceptionally Useful as a Feed Supplement. Protein J. 2007, 26, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.O.; Kim, H.K.; Bae, K.S.; Yu, J.H.; Oh, T.K. Purification and Properties of a Thermostable Phytase from Bacillus Sp. DS11. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1998, 22, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, S.; Husain, I.; Sharma, A. Purification and Characterization of Phytase from Bacillus subtilis P6: Evaluation for Probiotic Potential for Possible Application in Animal Feed. Food Front. 2022, 3, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Minoda, Y.; Yamamoto, S. Phytase from Aspergillus terreus Part I. Production, Purification and Some General Properties of the Enzyme. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1968, 32, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, D.M. Production of Extracellular Phytase from Aspergillus ficuum on Starch Media. Biotechnol. Lett. 1987, 9, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, M.J.; Seo, S.W.; Kim, D.C.; Oh, N.S. Purification and Biochemical Properties of an Extracellular Acid Phytase Produced by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CY Strain. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobin-Mopera, L.; Ohtani, M.; Sekiguchi, S.; Sone, T.; Abe, A.; Tanaka, M.; Meevootisom, V.; Asano, K. Purification and Characterization of Phytase from Klebsiella pneumoniae 9-3B. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Choudhury, B.; Navani, N.K. Production and Characterization of an Organic Solvent Activated Protease from Haloalkaliphilic Bacterium Halobiforma Sp. Strain BNMIITR. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Gallo, G.; Corbo, M.R.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Faccia, M.; Giovine, M.; Gobbetti, M. Phytase Activity in Sourdough Lactic Acid Bacteria: Purification and Characterization of a Phytase from Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis CB1. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 87, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhamfar, M.; Badoei-dalfard, A.; Khaleghi, M.; Hassanshahian, M. Purification and Characterization of an Acidic, Thermophilic Phytase from a Newly Isolated Geobacillus stearothermophilus Strain DM12. Prog. Biol. Sci. 2015, 5, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.M.H.; Quick, J.S.; Kaya, R.; Grandgirard, J.; Poinsot, D.; Krespi, L.; Nénon, J.P.; Cortesero, A.M.; Islam, A.U.; Chhabra, A.K.; et al. Evaluation of Spring Wheat Genotypes for Heat Tolerance Using Cell Membrane Thermostability. Crop Pasture Sci. 2017, 2, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, K.; Fukuhara, H.; Nakamura, Y. Phytase of the Yeast Arxula adeninivorans. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 21, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Chen, Y. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Neutral and Heat-Tolerant Phytase from a Newly Isolated Strain Bacillus nealsonii ZJ0702. BMC Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkan, E.; Sevgi, T.; Akcakoca, D.; Ersoy, F. Bacillus megaterium EBD 9-1 Suşundan Yeni Bir Fitazın Kısmen Saflaştırılması, Karakterizasyonu ve Buğday Kepeğini Parçalama Çalışmaları. Turk. J. Biochem. 2017, 42, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.X.; Dai, B.Y.; Qian, L.C. Effects of Neutral Phytase on Growth Performance and Phosphorus Utilization in Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus). J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2017, 18, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.S.; Fan, S.D.; Zhang, L.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Ohta, Y. Purification and Properties of a Phytase from Candida krusei WZ-001. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2002, 94, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, Y.; Şenol Kotan, M.; Dikbaş, N.; Beydemir, Ş. Phytase from Weissella halotolerans: Purification, Partial Characterisation and the Effect of Some Metals. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Dong, X.F.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.X.; Tong, J.M. Purification, Characterization, and Cloning of a Novel Phytase with Low PH Optimum and Strong Proteolysis Resistance from Aspergillus Ficuum NTG-23. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4125–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).