Bioactive Peptides Derived from Whey Proteins for Health and Functional Beverages
Abstract
1. Introduction
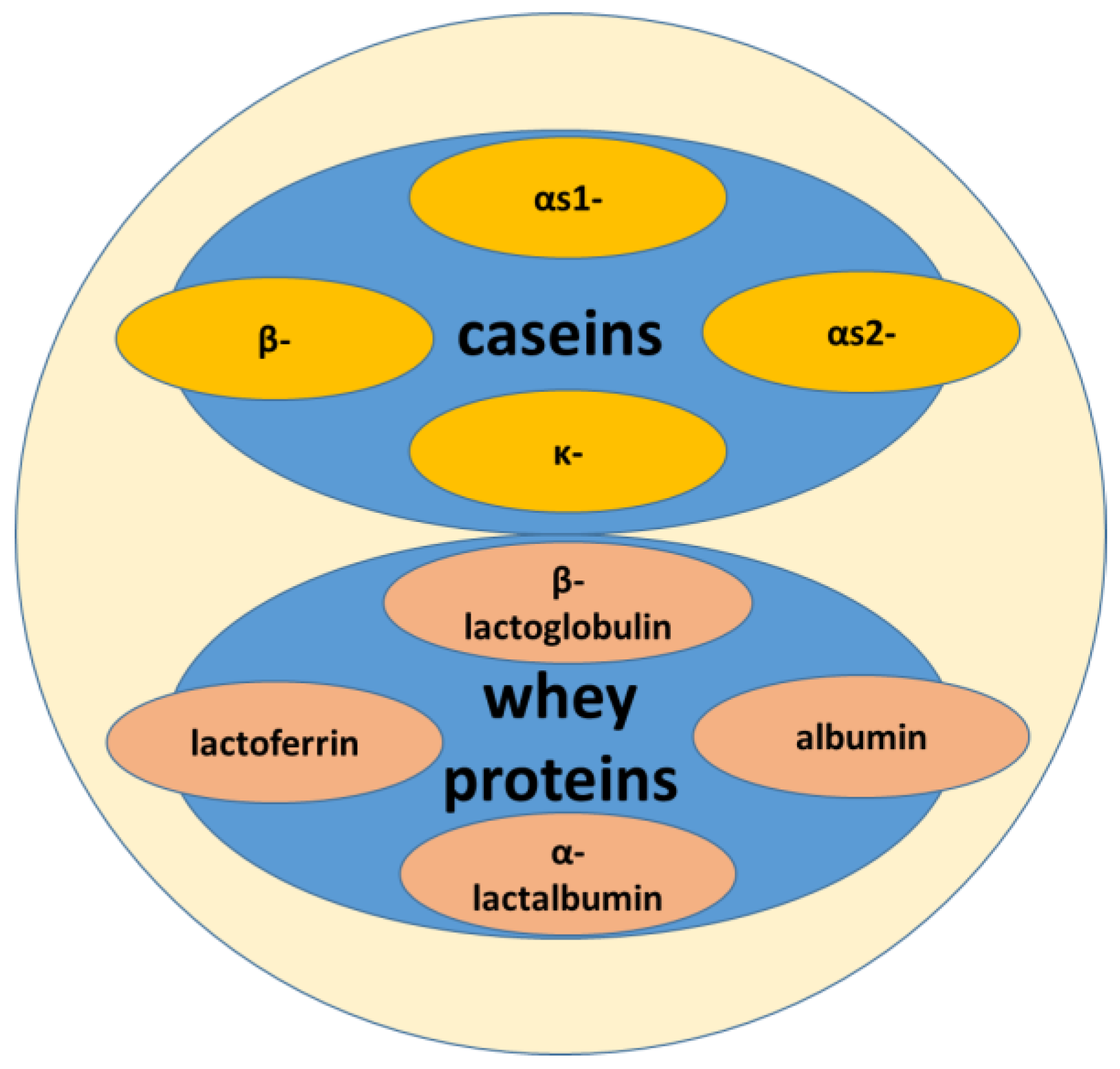
2. Milk and Whey
2.1. Milk
2.2. Whey
3. Peptides
3.1. Relevance of Peptide Preparations
3.2. Antimicrobial Peptides
3.3. Bioactive Peptides and Health
3.4. Whey Protein Peptides
4. Proteolytic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria
5. Whey-Based Drinks
6. Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- León-López, A.; Pérez-Marroquín, X.A.; Estrada-Fernández, A.G.; Campos-Lozada, G.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Milk whey hydrolysates as high value-added natural polymers: Functional properties and applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Wei, J.; Hao, L.; Shan, Q.; Li, H.; Gao, D.; Jin, Y.; Sun, P. Bioactive proteins and their physiological functions in milk. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Shan, Q.; Wei, J.; Ma, F.; Sun, P. Lactoferrin: Major physiological functions and applications. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minj, S.; Anand, S. Whey proteins and its derivatives: Bioactivity, functionality, and current applications. Dairy 2020, 1, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: Current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Kamal, M.M.; Rahman, M.H.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Haque, M.A.; Saha, K.K.; Rahman, M.A. Functional dairy products as a source of bioactive peptides and probiotics: Current trends and future prospectives. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, I.S.; Evdokimov, I.A.; Abakumova, E.A. Biotechnological bases of a functional drink based on whey. Mod. Sci. Innov. 2023, 1, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Nam, M.S. Bioactive peptides in milk and dairy products: A Review. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.T.; Bule, M.; Ullah, R.; Nadeem, M.; Asif, S.; Niaz, K. The antioxidant components of milk and their role in processing, ripening, and storage: Functional food. Vet. World 2019, 12, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.T.; Ross, R.P.; Bolton, D.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: Meat and fish. Nutrients 2011, 3, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Luchian, T.; Park, Y. New antimicrobial peptide kills drug-resistant pathogens without detectable resistance. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 15616–15634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, R.A.; Poppitt, S. Milk protein for improved metabolic health: A review of the evidence. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, S.K. Antioxidants capacity of milk, probiotics and postbiotics: A review. FSNT 2024, 9, 000327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, S.Y.; Khlgatian, S.V.; Emel’yanova, O.Y.; Pishulina, L.A.; Berzhets, V.M. Current data about milk caseins. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 48, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, E.S.; Christensen, B. Milk osteopontin and human health. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldrá, F.; Reig, M.; Aristoy, M.C.; Mora, L. Generation of bioactive peptides during food processing. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán-Rodríguez, F.; Gómez-Ruizy, L.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.; Alatorre-Santamaría, S.; García-Garibay, M.; Cruz-Guerrero, W.A. Iron binding and antithrombotic peptides released during the fermentation of milk by Lactobacillus casei shirota. Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2019, 18, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Liang, N.; Rathish, H.; Kim, B.J.; Lueangsakulthai, J.; Koh, J.; Qu, Y.; Schulz, H.J.; Dallas, D.C. Bioactive milk peptides: An updated comprehensive overview and database. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 28, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintieri, L.; Fanelli, F.; Monaci, L.; Fusco, V. Milk and its derivatives as sources of components and microorganisms with health-promoting properties: Probiotics and bioactive peptides. Foods 2024, 13, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive peptides derived from human milk proteins-mechanisms of action. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudkiewicz, M.; Berlowska, J.; Kregiel, D. Acid whey as a medium for cultivation of conventional and non-conventional yeasts. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2016, 80, 75–82. Available online: http://www.bfs.p.lodz.pl (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Chizhayeva, A.; Oleinikova, Y.; Saubenova, M.; Sadanov, A.; Amangeldi, A.; Aitzhanova, A.; Yelubaeva, M.; Alybaeva, A. Impact of probiotics and their metabolites in enhancement the functional properties of whey-based beverages. AIMS Agric. Food 2020, 5, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Oliveira, M.B.P.; Mafra, I. Bovine milk allergens: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Han, S.; He, H. Lactoferrin alleviates inflammation and regulates gut microbiota composition in H5N1-infected mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trybek, G.; Metlerski, M.; Szumilas, K.; Aniko-Włodarczyk, M.; Preuss, O. The biological properties of lactoferrin. Cent. Eur. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2016, 15, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abad, I.; Vignard, J.; Bouchenot, C.; Graikini, D.; Grasa, L.; Pérez, M.D.; Mirey, G.; Sánchez, L. Dairy by-products and lactoferrin exert antioxidant and antigenotoxic activity on intestinal and hepatic cells. Foods 2023, 12, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchik, P.; Zuber, T.; Zuber, A.; Moraru, C.I. Short communication: Composition of coproduct streams from dairy processing: Acid whey and milk permeate. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3978–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera Rodriguez, F.; Fernández-Martinez, A.; Muro Urista, C. Whey: Types, Composition and Health Implications, 1st ed.; Benitez, R., Ortero, G., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bylund, G. Dairy Processing Handbook, 3rd. ed.; Tetra Pak Processing Systems AB: Lund, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zotta, T.; Solieri, L.; Iacumin, L.; Picozzi, C.; Gullo, M. Valorization of cheese whey using microbial fermentations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2749–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.; Athira, S.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, R.; Sarkar, P. Bioactive peptides from whey proteins. In Whey Proteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Mendoza, D.; Kosmerl, E.; Krentz, A.; Zhang, L.; Badiger, S.; Miyagusuku-Cruzado, G.; Mayta-Apaza, A.; Giusti, M.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; García-Cano, I. Invited review: Acid whey trends and health benefits. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballatore, M.B.; del Rosario Bettiol, M.; Braber, N.L.V.; Aminahuel, C.A.; Rossi, Y.E.; Petroselli, G.; Erra-Balsells, R.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Montenegro, M.A. Antioxidant and cytoprotective effect of peptides produced by hydrolysis of whey protein concentrate with trypsin. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullius, A.; Goettert, M.I.; de Souza, C.F.V. Whey protein hydrolysates as a source of bioactive peptides for functional foods—Biotechnological facilitation of industrial scale-up. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaver, E.H.; Kempka, A.P. Potential of milk-derived bioactive peptides as antidiabetic, antihypertensive, and xanthine oxidase inhibitors: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis and updated review. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 1829–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavinson, V.K.; Popovich, I.G.; Linkova, N.S.; Mironova, E.S.; Ilina, A.R. Peptide regulation of gene expression: A systematic review. Molecules 2021, 26, 7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldrá, F.; Gallego, M.; Reig, M.; Aristoy, M.C.; Mora, L. Bioactive peptides generated in the processing of dry-cured ham. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Enhancing bioactive peptide release and identification using targeted enzymatic hydrolysis of milk proteins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3407–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansinhbhai, C.H.; Sakure, A.; Maurya, R.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Das, S.; Hati, S. Significance of whey protein hydrolysate on anti-oxidative, ACE-inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities and release of peptides with biofunctionality: An in vitro and in silico approach. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 2629–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haj Mustafa, M.; Soleimanian-Zad, S.; Albukhaty, S. Whey protein concentrate hydrolyzed by microbial protease: Process optimization and evaluation of its dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitory activity. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 15, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.A.; Ghosh, B.C. Production of whey protein hydrolyzates and its incorporation into milk. FPPN 2021, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, Y.A.A.H.; Rosa, J.C.; Cabral, H. Peptides with antioxidant properties identified from casein, whey, and egg albumin hydrolysates generated by two novel fungal proteases. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Pourahmad, R.; Taheri, S.; Eyvazzadeh, O. Isolation and purification of bioactive peptides from yogurt whey: Application as a natural preservative in a model food system. JFPP 2021, 45, e16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, S.; Belton, O.; Fitzgerald, D.J. Milk-derived bioactive peptides and their health promoting effects: A potential role in atherosclerosis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 83, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendse, L.B.; Danser, A.H.J.; Poglitsch, M.; Touyz, R.M. Novel therapeutic approaches targeting the renin-angiotensin system and associated peptides in hypertension and heart failure. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 539–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.J. Food proteins as a source of bioactive peptides with diverse functions. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 49–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; Mudgil, P.; Palakkott, A.; Iratni, R.; Gan, C.Y.; Maqsoo, S.; Ayoub, M.A. Molecular basis of the anti-diabetic properties of camel milk through profiling of its bioactive peptides on dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) and insulin receptor activity. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttenthaler, M.; King, G.F.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggag, Y.A.; Donia, A.A.; Osman, M.A.; El-Gizawy, S.A. Peptides as drug candidates: Limitations and recent development perspectives. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Bin, Y.; Xia, J. PrMFTP: Multi-functional therapeutic peptides prediction based on multi-head self attention mechanism and class weight optimization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Yan, Z.B.; Meng, Y.M.; Hong, X.Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.; Cheng, X.R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.P.; Mohapatra, S.; Misra, S.; Sahu, P.S. Milk derived bioactive peptides and their impact on human health—A review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, I.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Hayat, S.; Aslam, B.; Sarfraz, M.H.; Yaseen, H.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Shah, A.A.; Khurshid, M. Prospects of antimicrobial peptides as an alternative to chemical preservatives for food safety. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 45, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.A.T.; Mantovani, H.C.; Jain, S. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria and their potential in the preservation of fruit products. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansi, M.S.; Iram, D.; Vij, S.; Kapila, S.; Meena, S. In vitro biosafety and bioactivity assessment of the goat milk protein derived hydrolysates peptides. J. Food Saf. 2023, 43, e13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A. Physicochemical and sequence determinants of antiviral peptides. Biol. Futur. 2023, 74, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Kumar, H.; Alghamdi, W.; Kateb, F.A.; Alarfaj, F.K. Recent advances in machine learning-based models for prediction of antiviral peptides. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 4033–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefin, N.; Herrera-Belén, L.; Farias, J.G.; Beltrán, J.F. Review and perspective on bioinformatics tools using machine learning and deep learning for predicting antiviral peptides. Mol. Divers. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnepolsky, B.; Grigolava, M.; Gabrielian, A.; Rosenthal, A.; Hurt, D.; Tartakovsky, M.; Pirtskhalava, M. Analysis, modeling, and target-specific predictions of linear peptides inhibiting virus entry. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 46218–46226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Raza, A.; Zou, Q. Deepstacked-AVPs: Predicting antiviral peptides using tri-segment evolutionary profile and word embedding based multi-perspective features with deep stacking model. BMC Bioinform. 2024, 25, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pei, H.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Zou, Q.; Lv, Z. FEOpti-ACVP: Identification of novel anti-coronavirus peptide sequences based on feature engineering and optimization. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xiang, C.; Huang, J. ACP-Dnnel: Anti-coronavirus peptides’ prediction based on deep neural network ensemble learning. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 1121–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfi, R.; Kahaki, F.A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Montazersaheb, S.; Eyvazi, S.; Babaeipour, V.; Tarhriz, V. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): Roles, functions and mechanism of action. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Doull, F.; Rutherfurd, K.J.; Cross, M. Immunoregulatory peptides in bovine milk. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, S111–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Technological options for the production of health-promoting proteins and peptides derived from milk and colostrum. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matar, C.; LeBlanc, J.G.; Martin, L.; Perdigon, G. Active peptides released in fermented milk: Role and functions. In Handbook of Fermented Functional Foods; Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals Series; Farnworth, E.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 177–201. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Chen, K.; Yu, Y.; Le, N.Q.K.; Chua, M.C.H. Prediction of anticancer peptides based on an ensemble model of deep learning and machine learning using ordinal positional encoding. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbac630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J. MA-PEP: A novel anticancer peptide prediction framework with multimodal feature fusion based on attention mechanism. Prot. Sci. 2024, 33, e4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, H. ACPPfel: Explainable deep ensemble learning for anticancer peptides prediction based on feature optimization. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1352504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Hayat, M.; Tahir, M.; Khan, S.; Alarfaj, F.K. cACP-DeepGram: Classification of anticancer peptides via deep neural network and skip-gram-based word embedding model. Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 131, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanea, M.; Dukyil, A.S.; Afnan; Riaz, B.; Alebeisat, F.; Islam, M.; Habib, S. To assist oncologists: An efficient machine learning-based approach for anti-cancer peptides classification. Sensors 2022, 22, 4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakaya, O.; Kilimci, Z.H. An efficient consolidation of word embedding and deep learning techniques for classifying anticancer peptides: FastText+ BiLSTM. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, O.; Yousef, A.; Jumani, T.A.; Armghan, A. Response score-based protein structure analysis for cancer prediction aided by the Internet of Things. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W. (Ed.) Bioactive components of goat milk. In Bioactive Components in Milk and Dairy Products; Wiley-Blackwell Publishers: Ames, IA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 43–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, L.; Shah, N.P. Release and identification of angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides as influenced by ripening temperatures and probiotic adjuncts in Cheddar cheeses. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopada, K.; Basaiawmoit, B.; Sakure, A.A.; Maurya, R.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Solanki, D.; Singh, B.P.; Padhi, S.; Rai, A.K.; et al. Purification and characterization of novel antihypertensive and antioxidative peptides from whey protein fermentate: In Vitro, In Silico, and Molecular Interactions Studies. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2023, 42, 598–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.; Huang, J.; Bao, C.; Meng, J.; Chen, H.; Cao, J. Effect of different proteases on the degree of hydrolysis and angiotensin i-converting enzyme-inhibitory activity in goat and cow milk. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkçi, N.; Akdeniz, V.; Akalın, A.S. Probiotic whey-based beverages from cow, sheep and goat milk: Antioxidant activity, culture viability, amino acid contents. Foods 2023, 12, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, H.; Tokas, J.; Malik, A.; Sangwan, S.; Baloda, S.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Bhuker, A.; Singh, P.; Yashveer, S.; et al. Identification and detection of bioactive peptides in milk and dairy products: Remarks about agro-foods. Molecules 2020, 25, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, U.; Álvarez, F.; Rodriguez, R.; Cuenca, A.; Jurado, T. Review: Production and functionality of active peptides from milk. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2011, 17, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Márquez-Hernández, R.I.; Hernández-Castellano, L.E. Bioactive peptides from milk: Animal determinants and their implications in human health. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S.; Huma, N.; Butt, M.S.; Aleem, M.; Abbas, M. Therapeutic potential of dairy bioactive peptides: A contemporary perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.N.; Tang, S.H.; He, Q.; Hu, J.X.; Zheng, J. In vitro antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of fermented milk with different culture combinations. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.S.; Santos, M.L.; Abreu, J.P.; Rocha, R.S.; Esmerino, E.A.; Freitas, M.Q.; Mársico, E.T.; Campelo, P.H.; Pimentel, T.C.; Cristina Silva, M.; et al. Probiotic fermented whey-milk beverages: Effect of different probiotic strains on the physicochemical characteristics, biological activity, and bioactive peptides. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, J.; Arslan, A.A.; Fedorova, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Kucukcetin, A.; Pischetsrieder, M. Peptide profiling of bovine kefir reveals 236 unique peptides released from caseins during its production by starter culture or kefir grains. J. Proteom. 2015, 117, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Lv, J.; Gong, J.Y.; Xiao, G.N.; Zhu, R.Y.; Li, L.; Qiu, J.N. Secondary structures and their effects on antioxidant capacity of antioxidant peptides in yogurt. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, E.I.; Bogdanova, E.V.; Koshevarova, I.B. Nutritional evaluation of whey protein hydrolysate: Chemical composition, peptide profile, and osmolarity. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e110721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Kumar, H.; Kumar, N.; Ranvir, S.; Jana, A.; Buttar, H.S.; Telessy, I.G.; Awuchi, C.G.; Okpala, C.O.R.; Korzeniowska, M.; et al. Whey proteins processing and emergent derivatives: An insight perspective from constituents, bioactivities, functionalities to therapeutic applications. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, J.K.; Sharma, P.K. Mini review on antimicrobial peptides, sources, mechanism and recent applications. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarini, M. Bioactive peptides in milk: From encrypted sequences to nutraceutical aspects. Beverages 2017, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iukalo, A.V.; Datsyshyn, K.Y.; Yukalo, V.G. Bioactive peptides of the cow milk whey proteins (Bos taurus). Biotechnol. Acta 2013, 6, 49–61. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Ul Ain, Q.; Schulz, C.; Pircher, J. Role of antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in thrombosis and thromboinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1151926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, P.; Li, X.; Zou, X.; Wang, K.; Yao, L.; Sun, Z.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Tan, Y. Antihypertensive effects of whey protein hydrolysate involve reshaping the gut microbiome in spontaneously hypertension rats. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 13, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, S.; Makhlouf, C.; Nacer, N.E.; Halima, B.; Faiza, A.; Kahina, H.; Wahiba, F.; Afaf, K.; Rabah, K.; Saoudi, Z. Whey proteins as multifunctional food materials: Recent advancements in hydrolysis, separation, and peptidomimetic approaches. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Rosales, L.B.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; García-Garibay, J.M.; Gómez-Ruíz, L.C.; Contreras-López, E.; Guzmán-Rodríguez, F.; González-Olivares, L.G. Bioactive peptides of whey: Obtaining, activity, mechanism of action, and further applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10351–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkerroum, N. Antimicrobial peptides generated from milk proteins: A survey and prospects for application in the food industry. A review. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, M.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yamauchi, K.; Teraguchi, S.; Hayasawa, H. Bovine lactoferrin and lactoferricin derived from milk: Production and applications. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touch, V.; Hayakawa, S.; Saitoh, K. Relationships between conformational changes and antimicrobial activity of lysozyme upon reduction of its disulfide bonds. Food Chem. 2004, 84, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, C.; Izzo, L.; Ritieni, A.; Mañes, J.; Meca, G. Antifungal and antimycotoxigenic activity of hydrolyzed goat whey on Penicillium spp: An application as biopreservation agent in pita bread. LWT 2020, 118, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théolier, J.; Hammami, R.; Labelle, P.; Fliss, I.; Jean, J. Isolation and identification of antimicrobial peptides derived by peptic cleavage of whey protein isolate. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafaa, N.; Elbarbary, H.A.; Ibrahim, E.M.A.; Mohamed, H.A.; Jenssen, H. Effect of enzyme type and hydrolysis time on antibacterial and antioxidant activity of whey protein hydrolysates. Iraqi J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 53, 1340–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheroufi, A.; Brassesco, M.E.; Campos, D.A.; Mouzai, A.; Boughellouta, H.; Pintado, M.E. Whey protein-derived peptides: The impact of chicken pepsin hydrolysis upon whey proteins concentrate on their biological and technological properties. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 134, 105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, J.; Fernández-Fernández, A.M.; Tironi, V.; Bollati-Fogolín, M.; Añón, M.C.; Medrano-Fernández, A. Identification and characterization of antioxidant peptides obtained from the bioaccessible fraction of α-lactalbumin hydrolysate. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 4479–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, L.; Cakir-Kiefer, C.; N’Negue, M.A.; Gaillard, J.L.; Girardet, J.M.; Miclo, L. Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from bovine α-lactalbumin. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, W.S.; Ibrahim, E.A.; Elbarbary, H.A.; Mohamed, H.A.; Jenssen, H. Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of sheep whey protein hydrolysates and their fractions. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.L.; Hussain, N.; Ujiroghene, O.J.; Pang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Lu, J.; Lv, J.P. Generation and characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from trypsin-hydrolyzed α-lactalbumin-rich whey proteins. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, I.M.; Li-Chan, E.C. Isolation and characterization of peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity from pepsin-treated bovine whey. Peptides 2014, 54, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otte, J.; Shalaby, S.M.; Zakora, M.; Nielsen, M.S. Fractionation and identification of ACE-inhibitory peptides from α-lactalbumin and β-casein produced by thermolysin-catalysed hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakır, B.; Okuyan, B.; Şener, G.; Tunali-Akbay, T. Investigation of beta-lactoglobulin derived bioactive peptides against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): In silico analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 891, 173781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gong, H.; Zou, Y.; Mao, X. Antihyperuricemic activity and inhibition mechanism of xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptides derived from whey protein by virtual screening. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, T.G.; Contreras, M.M.; Amorim, M.; Martín-Álvarez, P.J.; Pintado, M.E.; Recio, I.; Malcata, F.X. Optimisation, by response surface methodology, of degree of hydrolysis and antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities of whey protein hydrolysates obtained with cardoon extract. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.; Sevilla, M.Á.; Montero, M.J.; Carrón, R.; Malcata, F.X. Acute effect of whey peptides upon blood pressure of hypertensive rats, and relationship with their angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villadóniga, C.; Cantera, A.M.B. New ACE-inhibitory peptides derived from α-lactalbumin produced by hydrolysis with Bromelia antiacantha peptidases. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 101258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospitti, A.; Cancelarich, L.N.; Perrando, J.; Natalucci, C.L.; Pardo, M.F. Balansain R, a new proteolytic preparation for the production of antioxidant peptides from bovine whey. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2015, 34, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Mora-Cortes, W.G.; Leandro-Roldan, M.M.; González-Velázquez, D.A.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; Ramírez-Suarez, J.C.; Vallejo-Córdoba, B. Production of whey protein hydrolysates with angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory activity using three new sources of plant proteases. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.F.; Kise, F.; Rosso, A.M.; Parisi, M.G. Potential antioxidant peptides produced from whey hydrolysis with an immobilized aspartic protease from Salpichroa origanifolia fruits. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helal, A.; Nasuti, C.; Sola, L.; Sassi, G.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Solieri, L. Impact of spontaneous fermentation and inoculum with natural whey starter on peptidomic profile and biological activities of cheese whey: A comparative study. Fermentation 2023, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescuma, M.; Hébert, E.M.; Mozzi, F.; Valdez, G.F.D. Hydrolysis of whey proteins by Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus grown in a chemically defined medium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamme, V.; Sannier, F.; Piot, J.M.; Bordenave-Juchereau, S. Goat whey fermentation by Kluyveromyces marxianus and Lactobacillus rhamnosus release tryptophan and tryptophan-lactokinin from a cryptic zone of alpha-lactalbumin. J. Dairy Res. 2009, 76, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamme, V.; Sannier, F.; Piot, J.M.; Didelot, S.; Bordenave-Juchereau, S. Crude goat whey fermentation by Kluyveromyces marxianus and Lactobacillus rhamnosus: Contribution to proteolysis and ACE inhibitory activity. J. Dairy Res. 2009, 76, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babij, K.; Dąbrowska, A.; Szołtysik, M.; Pokora, M.; Zambrowicz, A.; Kupczyński, R.; Chrzanowska, J. Zastosowanie enzymatycznej hydrolizy białek serwatkowych do otrzymywania peptydów o aktywności przeciwutleniającej. Przemysł Chem. 2014, 93, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Messaoui, H.; Roudj, S.; Karam, N. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of bovine whey proteins hydrolysed with selected lactobacillus strains. Food Environ. Saf. J. 2020, 19. Available online: http://fens.usv.ro/index.php/FENS/article/view/703 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Solieri, L.; Valentini, M.; Cattivelli, A.; Sola, L.; Helal, A.; Martini, S.; Tagliazucchi, D. Fermentation of whey protein concentrate by Streptococcus thermophilus strains releases peptides with biological activities. Process Biochem. 2022, 121, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirkhan, F.; Mirdamadi, S.; Mirzaei, M.; Akbari-adergani, B.; Nasoohi, N. The role of lactic acid bacteria in production of bioactive peptides in fermented milk with antioxidant and antidiabetic properties. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 4727–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, G.; Comerford, K.B. Dairy foods and dairy proteins in the management of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of the clinical evidence. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveschot, C.; Cudennec, B.; Coutte, F.; Flahaut, C.; Fremont, M.; Drider, D.; Dhulster, P. Production of bioactive peptides by Lactobacillus species: From gene to application. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, E.F.T.; Barbosa, M.A.P.; de Figueirêdo Marinho, T.A.; Lima, G.C.; dos Santos, W.L.; Espindola, M.T.A.; Soares, L.B.F.; Gomes, J.E.G.; Moreira, K.A. Ten years of research on bioactive peptides in Brazil: A scientometric analysis. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e131022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Pobiega, K.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M. Characteristics of the proteolytic enzymes produced by lactic acid bacteria. Molecules 2021, 26, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescuma, M.; Hébert, E.M.; Mozzi, F.; de Valdez, G.F. Functional fermented whey-based beverage using lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirilov, N.; Petkova, T.; Atanasova, J.; Danova, S.; Iliev, I.; Popov, Y.; Haertle, T.; Ivanova, I.V. Proteolytic activity in lactic acid bacteria from Iraq, Armenia and Bulgaria. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2009, 23 (Suppl S1), 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satılmış, M.K.; Öztürk, H.İ.; Demirci, T.; Denktaş, B.; Akın, N. Revealing the proteolytic characteristics of Lactobacillus, lacticaseibacillus, and Lactiplantibacillus isolates by in vitro and in situ perspectives. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Robles-Porchas, G.R.; González-Velázquez, D.A.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; García-Sifuentes, C.O.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Córdoba, B. Cheese Whey Fermentation by Its Native Microbiota: Proteolysis and Bioactive Peptides Release with ACE-Inhibitory Activity. Fermentation 2020, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.F.; Høie, M.H.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Marcatili, P.; Hansen, E.B. Comparative Structure Analysis of the Multi-Domain, Cell Envelope Proteases of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas-Ortega, M.G.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Martinez-Hernandez, J.L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Nevarez-Moorillon, G.V. Production of bioactive peptides from lactic acid bacteria: A sustainable approach for healthier foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alu′datt, M.H.; Al-U′datt, D.G.F.; Alhamad, M.N.; Tranchant, C.C.; Rababah, T.; Gammoh, S.; Althnaibat, R.M.; Daradkeh, M.G.; Kubow, S. Characterization and biological properties of peptides isolated from dried fermented cow milk products by RP-HPLC: Amino acid composition, antioxidant, antihypertensive, and antidiabetic properties. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 3046–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Guo, T.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, D.X.A.; Zhang, S. Isolation and identification of novel casein-derived bioactive peptides and potential functions in fermented casein with Lactobacillus helveticus. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, R.J.S.; Sato, H.H. Biologically active peptides: Processes for their generation, purification and identification and applications as natural additives in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Food Res. Int. 2015, 74, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypczak, K.; Gustaw, W.; Fornal, E.; Kononiuk, A.; Michalak-Majewska, M.; Radzki, W.; Waśko, A. Functional and technological potential of whey protein isolate in production of milk beverages fermented by new strains of Lactobacillus helveticus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievore, P.; Simões, D.R.; Silva, K.M.; Drunkler, N.L.; Barana, A.C.; Nogueira, A.; Demiate, I.M. Chemical characterisation and application of acid whey in fermented milk. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skryplonek, K.; Jasińska, M. Fermented probiotic beverages based on acid whey. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. 2015, 14, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skryplonek, K.; Dmytrów, I.; Mituniewicz-Małek, A. Probiotic fermented beverages based on acid whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7773–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, M. Value Added Products Utilizing Acid Whey: Development of a Fruit Yogurt Beverage and a Sports Drink. Master’s Thesis, Department of Food Science, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oleinikova, Y.; Alybayeva, A.; Daugaliyeva, S.; Alimzhanova, M.; Ashimuly, K.; Yermekbay, Z.; Khadzhibayeva, I.; Saubenova, M. Development of an antagonistic active beverage based on a starter including Acetobacter and assessment of its volatile profile. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 148, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.M.; Nobre, M.S.C.; Cavalcanti, M.T.; Olbrich Dos Santos, K.M.; Salles, H.O.; Alonso Buriti, F.C. Proteolysis of reconstituted goat whey fermented by Streptococcus thermophilus in co-culture with commercial probiotic Lactobacillus strains. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareb, O.; Aïder, M. Whey and its derivatives for probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and functional foods: A critical review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 348–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleinikova, Y.; Amangeldi, A.; Yelubaeva, M.; Alybaeva, A.; Sadanov, A.; Saubenova, M.; Chizhaeva, A.; Aitzhanova, A.; Berzhanova, R. Immobilization of dairy starter on wheat bran enhance viability under acid and bile stress. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barukčić, I.; Lisak Jakopović, K.; Božanić, R. Valorisation of whey and buttermilk for production of functional beverages—An overview of current possibilities. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos Reis, S.; Mendes, G.D.R.L.; Mesquita, B.M.A.D.C.; Lima, W.J.N.; Pinheiro, C.A.F.D.; Ruas, F.A.O.; Santos, G.L.M.; Brandi, I.V. Development of milk drink with whey fermented and acceptability by children and adolescents. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2847–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Fidan, H.; Ozogul, F.; Rocha, J.M. Industrial and health applications of lactic acid bacteria and their metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jain, A.K.; Ghosh, M. Industrial whey utilization as a medium supplement for biphasic growth and bacteriocin production by probiotic Lactobacillus casei LA-1. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2012, 4, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabo, S.S.; Converti, A.; Ichiwaki, S.; Oliveira, R.P.S. Bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum ST16Pa in supplemented whey powder formulations. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitzhanova, A.; Oleinikova, Y.; Mounier, J.; Hymery, N.; Leyva Salas, M.; Amangeldi, A.; Saubenova, M.; Alimzhanova, M.; Ashimuly, K.; Sadanov, A. Dairy associations for the targeted control of opportunistic Candida. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandelli, A.; Daroit, D.J.; Corrêa, A.P.F. Whey as a source of peptides with remarkable biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeth, H.C.; Bansal, N. Whey Proteins: From Milk to Medicine; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; p. 746. [Google Scholar]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Keskin Ulug, S.; Hong, H.; Wu, J. Regulatory requirements of bioactive peptides (protein hydrolysates) from food proteins. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 58, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchinin, A.G.; Bolshakova, E.I.; Barkovskaya, I.A. Bioinformatic modeling (in silico) of obtaining bioactive peptides from the protein matrix of various types of milk whey. Fermentation 2023, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Beverly, R.L.; Qu, Y.; Dallas, D.C. Milk bioactive peptide database: A comprehensive database of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides and novel visualization. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.F.; Marnotes, N.G.; Rubio, O.D.; Garcia, A.C.; Pereira, C.D. Dairy by-products: A review on the valorization of whey and second cheese whey. Foods 2021, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krunic, T.; Rakin, M.; Bulatovic, M.; Zaric, D. Chapter 9—The contribution of bioactive peptides of whey to quality of food products. In Food Processing for Increased Quality and Consumption, Handbook of Food Bioengineering; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 251–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, F.; Masood, S. How nutrition can help to fight against COVID-19 pandemic. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, S121–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, A.; Sharma, S.; Kant, A.; Sevda, S.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Garlapati, V.K. Functional foods as a formulation ingredients in beverages: Technological advancements and constraints. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 11055–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saubenova, M.; Oleinikova, Y.; Rapoport, A.; Maksimovich, S.; Yermekbay, Z.; Khamedova, E. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Whey Proteins for Health and Functional Beverages. Fermentation 2024, 10, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10070359
Saubenova M, Oleinikova Y, Rapoport A, Maksimovich S, Yermekbay Z, Khamedova E. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Whey Proteins for Health and Functional Beverages. Fermentation. 2024; 10(7):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10070359
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaubenova, Margarita, Yelena Oleinikova, Alexander Rapoport, Sviatoslav Maksimovich, Zhanerke Yermekbay, and Elana Khamedova. 2024. "Bioactive Peptides Derived from Whey Proteins for Health and Functional Beverages" Fermentation 10, no. 7: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10070359
APA StyleSaubenova, M., Oleinikova, Y., Rapoport, A., Maksimovich, S., Yermekbay, Z., & Khamedova, E. (2024). Bioactive Peptides Derived from Whey Proteins for Health and Functional Beverages. Fermentation, 10(7), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10070359






