Recent Advances in Resource Utilization of Huangshui from Baijiu Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Huangshui Main Property and Its Resource Value
2.1. Huangshui Main Components and Property
2.2. Huangshui Resource Value
2.2.1. Some Microbial Resources
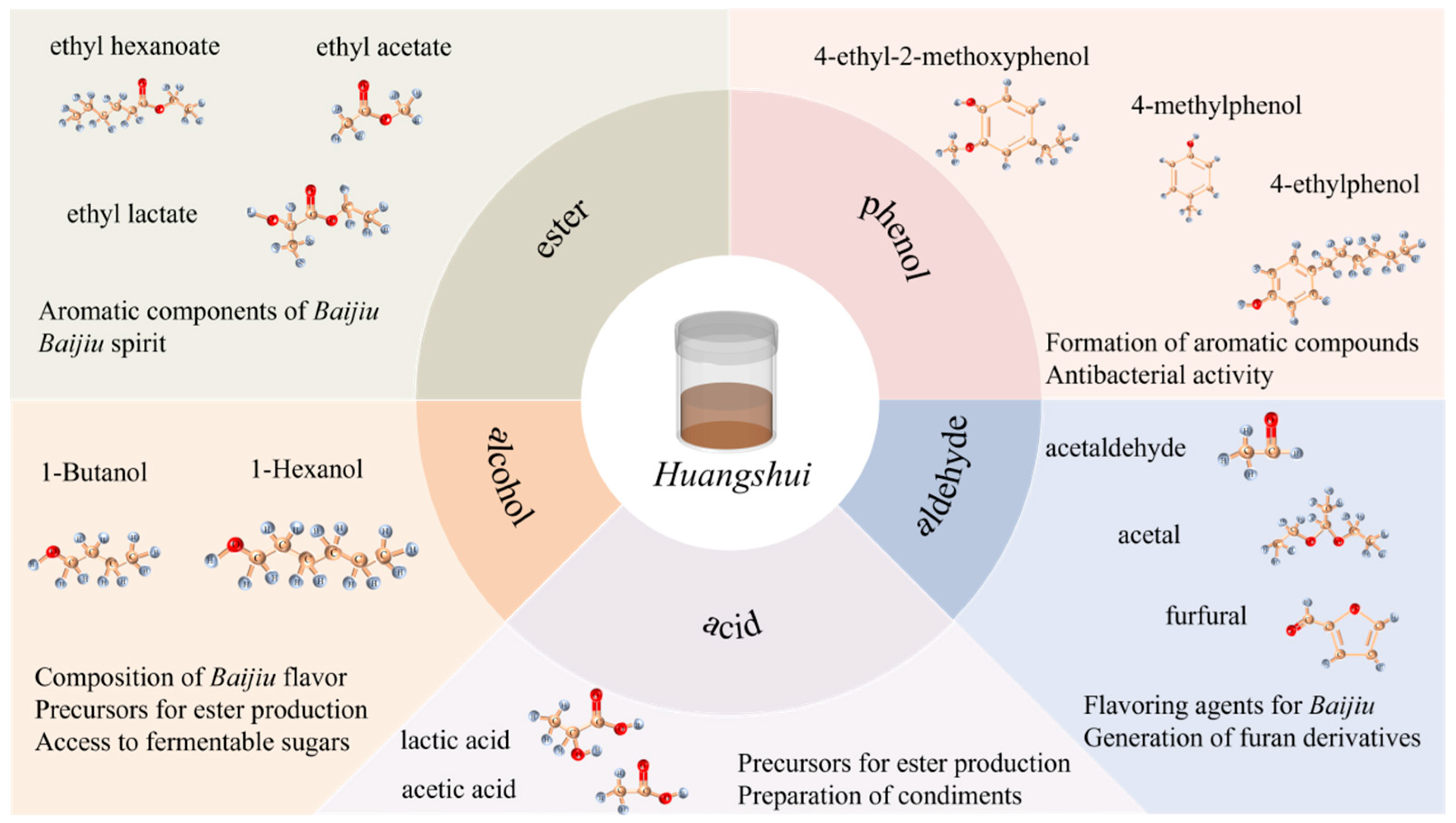
2.2.2. Flavor Substances
3. Huangshui Utilization Approaches and Techniques
3.1. Exploration and Utilization of Functional Microbes
3.2. Baijiu Blending
3.3. Organic Acids
3.4. Polysaccharides
3.5. Proteins and Amino Acids
3.6. Aldehydes, Flavonoids, Ketones and Phenols
3.7. Full Utilization of Huangshui in Different Fields
4. Future Challenges and Prospects
4.1. Challenges
4.2. Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, C.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Z.M.; Chai, L.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, S.T.; Shen, C.H.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Daqu microbiota exhibits species-specific and periodic succession features in Chinese baijiu fermentation process. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.H.; Sun, B.G.; Zhao, M.M.; Huang, M.Q.; Wu, J.H.; Li, H.H.; Sun, X.T. Integrated distilled spent grain with husk utilization: Current situation, trend, and design. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2023, 179, 113275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xie, F.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.H.; Du, L.Q.; Wei, Y.X.; Zhou, J.; He, G.Q. Correlation between microbial diversity and flavor metabolism in Huangshui: A by-product of solid-state fermentation Baijiu. Lwt 2023, 181, 114767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.M.; Sun, Y.T.; Huang, X.N.; Ye, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, X.X.; Zheng, X.W.; Han, B.Z. Unraveling the microbial compositions, metabolic functions, and antibacterial properties of Huangshui, a byproduct of Baijiu fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Zhao, C.Q.; Luo, H.B. Diversity and Function of Microbial Community in Chinese Strong-Flavor Baijiu Ecosystem: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.Q.; Yang, H.M.; Zeng, L.L.; Hu, H.; Hu, C. Production and characterization of bacterial cellulose obtained by Gluconacetobacter xylinus utilizing the by-products from Baijiu production. Bioproc. Biosyst. 2020, 43, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Liu, S.P.; Huang, C.H.; Ge, X.Y.; Xi, B.D.; Mao, J. Chinese Baijiu distiller’s grains resourcing: Current progress and future prospects. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2022, 176, 105900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Chang, R.; Zhou, Z.L.; Ren, Q.X.; Sheng, C.H.; Lan, Y.; Cao, X.N.; Mao, J. Conversion of Baijiu distillers’ grains to functional peptides: Process optimization and antioxidant activity evaluation. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 108, 105722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.Y.; Li, M.; Wei, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Hao, W.J.; Sun, W.Z.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, M.Q. RNA-seq based elucidation of mechanism underlying the protective effect of Huangshui polysaccharide on intestinal barrier injury in Caco-2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.S.; Sun, J.Y.; Chandrapala, J.; Majzoobi, M.; Brennan, C.; Zeng, X.A.; Sun, B.G. Current situation, trend, and prospects of research on functional components from by-products of baijiu production: A review. Food Res. Int. 2024, 180, 114032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.Y.; Xu, Y.B.; Lu, C.S.; Hou, W.E.; Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Du, Q.P. Microbial contamination control mechanism in lipid production using distillery wastewater and oleaginous yeast—Antimicrobial compounds in wastewater as a double-edged sword. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 291, 112672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Liao, Q.J.; Chen, P.P.; Zhao, D.; Huo, J.Y.; An, M.Z.; Li, Y.H.; Wu, J.H.; Xu, Z.M.; Sun, B.G.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and methylene blue adsorption of multiple-responsive hydrogels loaded with Huangshui polysaccharides, polyvinyl alcohol, and sodium carboxyl methyl cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Kong, B.; Wang, H.; Cai, L.Y.; Zhang, R.J.; Cai, F.J.; Zhu, Z.J.; Cao, J.H.; Xu, J. Production of butanol from distillers’ grain waste by a new aerotolerant strain of Clostridium beijerinckii LY-5. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Z.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.X. Effect of Pit Mud on Bacterial Community and Aroma Components in Yellow Water and Their Changes during the Fermentation of Chinese Strong-Flavor Liquor. Foods 2020, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Chandar, B.; Parani, M. Use of succinic & oxalic acid in reducing the dosage of colistin against New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 bacteria. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 147, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.X.; Zhao, D.R.; Sun, B.G. Research Progress on the Profile of Trace Components in Baijiu. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1666–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Eweys, A.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Darwesh, O.M.; Zhang, H.B.; Xiao, X. Fermentation Affects the Antioxidant Activity of Plant-Based Food Material through the Release and Production of Bioactive Components. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, M.Q.; Zhao, M.M.; Sun, W.Z.; Sun, X.T.; Zheng, F.P. Structural characterization and immuno-stimulating activities of a novel polysaccharide from Huangshui, a byproduct of Chinese Baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Kong, X.Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Ai-lati, A.; Ji, Z.W.; Mao, J. Baijiu vinasse as a new source of bioactive peptides with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.Y.; Cheng, K.; Zhao, D.; Yang, G.R.; Qiao, Z.W.; Qiu, S.Q.; Yu, X.J.; Liu, H.Q.; Li, T.; Feng, H.J.; et al. Bacillus aquiftavi sp. nov., isolated from yellow water of strongly flavored Chinese baijiu. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3406–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Sun, M.X.; Hou, P.; Wang, W.Y.; Shen, X.K.; Zhang, L.X.; Han, S.N.; Pan, C.M. Analysis of microbial community structure and volatile compounds in pit mud used for manufacturing Taorong-type Baijiu based on high-throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.T.; Cheng, K.C.; Lai, C.N.; Lai, Y.J. Isolation and identification of aroma producing strain with esterification capacity from yellow water. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e211356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.L.; Du, H.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y. Illuminating Anaerobic Microbial Community and Cooccurrence Patterns across a Quality Gradient in Chinese Liquor Fermentation Pit Muds. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2016, 82, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.S.; Yang, J.G.; Zhang, K.Z.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhao, X.X.; Su, C.; Cao, X.Z. Lactic acid bacteria in the brewing of traditional Daqu liquor. J. Inst. Brew. 2020, 126, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murindangabo, Y.T.; Kopecky, M.; Perná, K.; Nguyen, T.G.; Konvalina, P.; Kavková, M. Prominent use of lactic acid bacteria in soil-plant systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Ye, G.B.; Zhang, K.Z. Diversity, Function, and Application of Clostridium in Chinese Strong Flavor Baijiu Ecosystem: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvaux, M.; Guedon, E.; Petitdemange, H. Cellulose Catabolism by Clostridium cellulolyticum Growing in Batch Culture on Defined Medium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, D.; Morita, M.; Sasaki, K.; Watanabe, A.; Ohmura, N. Acceleration of cellulose degradation and shift of product via methanogenic co-culture of a cellulolytic bacterium with a hydrogenotrophic methanogen. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.X.; Ju, X.; Liangzhi, L.Z.; Hu, C.Y.; Yan, L.S.; Wu, T.Y.; Fu, J.L.; Qin, M. Improved in situ saccharification of cellulose pretreated by dimethyl sulfoxide/ionic liquid using cellulase from a newly isolated Paenibacillus sp LLZ1. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.B.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Chinese Liquor Fermentation: Identification of Key Flavor-Producing Lactobacillus spp. by Quantitative Profiling with Indigenous Internal Standards. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2020, 86, e00456–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y. Comparison on aroma compounds in Chinese soy sauce and strong aroma type liquors by gas chromatography-olfactometry, chemical quantitative and odor activity values analysis. J. Food Sci. 2014, 239, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Li, A.J.; Liang, C.C.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y. Domination of pit mud microbes in the formation of diverse flavour compounds during Chinese strong aroma-type Baijiu fermentation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 137, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Song, Z.; Xu, Y. Ethyl Carbamate Formation Regulated by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Nonconventional Yeasts in Solid-State Fermentation of Chinese Moutai-Flavor Liquor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 66, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Yang, D.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Cao, W.T. A novel thermostable cellulase-producing Bacillus licheniformis A5 acts synergistically with Bacillus subtilis B2 to improve degradation of Chinese distillers’ grains. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Lu, Z.M.; Chai, L.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.T.; Shen, C.H.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Cooperation within the microbial consortia of fermented grains and pit mud drives organic acid synthesis in strong-flavor Baijiu production. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Yang, F.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.; Cao, N.; Ni, D.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Construction of Chinese baijiu compound database using text mining and its application in assisting compound identification of liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry data. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wu, C.D.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.Q. Selection and application of potential whole-cell enzymes in the esterification of Huangshui, a by-product formed during Chinese liquor-making. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldhe, A.; Kumari, S.; Ramanna, L.; Ramsundar, P.; Singh, P.; Rawat, I.; Bux, F. Prospects, recent advancements and challenges of different wastewater streams for microalgal cultivation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D. Novel minor lipase from Rhizopus chinensis during solid-state fermentation: Biochemical characterization and its esterification potential for ester synthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Shan, T. Effects of oils and oil-related substrates on the synthetic activity of membrane-bound lipase from Rhizopus chinensis and optimization of the lipase fermentation media. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 41, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.B.; Liu, H.; Zhen, D.; Fang, S.L. Research on the esterification property of esterase produced by Monascus sp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 5166–5172. [Google Scholar]
- Kruis, A.J.; Bohnenkamp, A.C.; Patinios, C.; van Nuland, Y.M.; Levisson, M.; Mars, A.E.; van den Berg, C.; Kengen, S.W.M.; Weusthuis, R.A. Microbial production of short and medium chain esters: Enzymes, pathways, and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhu, P.Y.; Mei, Z.L.; Zhou, X.N.; Yu, H. Potential use of ultrasound to promote fermentation, maturation, and properties of fermented foods: A review. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhao, Z.G.; Li, X.T.; Sun, B.G. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Zhao, M.M.; Sun, W.Z.; Sun, J.Y.; Li, H.H.; Huang, M.Q. Immunomodulatory activity of a novel polysaccharide extracted from Huangshui on THP-1 cells through NO production and increased IL-6 and TNF-α expression. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, A.I.; Yokouchi, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Kondo, K. Extraction of succinic acid by aqueous two-phase system using alcohols/salts and ionic liquids/salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 155, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.Y.; Chai, L.J.; Zhong, X.Z.; Lu, Z.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Wu, L.H.; Wang, S.T.; Shen, C.H.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Comparative Genomics Unveils the Habitat Adaptation and Metabolic Profiles of Clostridium in an Artificial Ecosystem for Liquor Production. mSystems 2022, 7, e00297–00222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlin, B.V.; Muthuvel, S.; Govidasamy, P.; Villavan, M.; Alagawany, M.; Ragab Farag, M.; Dhama, K.; Gopi, M. Role of acidifiers in livestock nutrition and health: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.M.; Foo, H.L.; Loh, T.C.; Lim, E.T.C.; Mutalib, N.E.A. Comparative Studies of Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activities, and Organic Acids Compositions of Postbiotics Produced by Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains Isolated From Malaysian Foods. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 602280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezirci, E.; Taspinar-Demir, H.; Turanli-Yildiz, B.; Erdem, A.; Alemdar, F.; Türker, M. Propionic acid production via two-step sequential repeated batch fermentations on whey and flour. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 192, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, Y.W.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, S.W. Antimicrobial Activities of Acetic Acid, Citric Acid and Lactic Acid against Shigella Species. J. Food Saf. 2013, 33, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’aertrycke, J.B.D.; Morlot, J.; Robeyns, K.; Filinchuk, Y.; Leyssens, T. Exploring the solid-state phases and thermodynamics of calcium L-lactate. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Sit, N. Extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials using combination of various novel methods: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.Y.; Wu, Z.Y.; Sun, W.Z.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, M.Q.; Wang, B.W.; Sun, B.G. Protective Effects of Natural Polysaccharides on Intestinal Barrier Injury: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 711–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.L.; Chen, F.; Yang, W.J.; Huang, H.L. Preparation, deproteinization and comparison of bioactive polysaccharides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Belwal, T.; Devkota, H.P.; Li, L.; Luo, Z.S. Trends of utilizing mushroom polysaccharides (MPs) as potent nutraceutical components in food and medicine: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 94–110. [Google Scholar]
- Do, M.H.; Seo, Y.S.; Park, H.Y. Polysaccharides: Bowel health and gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 61, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himashree, P.; Sengar, A.S.; Sunil, C.K. Food thickening agents: Sources, chemistry, properties and applications—A review. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 100468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xing, M.; Kang, Q.; Sun, J.; Zeng, X.; Gao, W.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, A. Pulse electric field assisted process for extraction of Jiuzao glutelin extract and its physicochemical properties and biological activities investigation. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 123304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.Y.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhao, H.; Sun, W.Z.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, M.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Sun, B.G. Structure-activity relationship of antioxidant polysaccharides from Huangshui based on the HPLC fingerprint combined with chemometrics methods. LWT-Food Sci. 2022, 159, 113201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.B.; Nam, T.G.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Seo, D.W.; Yoo, M. Quantification of 21 free amino acids in traditional and nontraditional soybean pastes. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 3569–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, B.; Baghaei-Yazdi, N.; Bahmaie, M.; Abhari, F.M. The role of plant-derived natural antioxidants in reduction of oxidative stress. Biofactors 2022, 48, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Y.; Jannat, S.; Rahman, M.M. Ginsenoside derivatives inhibit advanced glycation end-product formation and glucose-fructose mediated protein glycation in vitro via a specific structure-activity relationship. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 111, 104844. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Luo, Q.Y.; Nie, R.X.; Yang, X.P.; Tang, Z.Z.; Chen, H. Potential implications of polyphenols on aging considering oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy, and gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2175–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.L.; Gu, X.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, L.J.; Pei, J.Z. Performance and mechanism of lignin and quercetin as bio-based anti-aging agents for asphalt binder: A combined experimental and ab initio study. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Wang, H.; Han, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Cheng, R.X.; Hu, F.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, R.J.; Cai, F.J. Co-production of biobutanol and biomethane from distillers’ grain waste by an integrated process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2024, 99, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.L.; Du, R.; Peng, Y.Z. Achieving partial denitrification using carbon sources in domestic wastewater with waste-activated sludge as inoculum. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 283, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.H.; Xu, C.J.; Zuo, Y.P.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.Q.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.J.; Yan, D.; Liang, T. Analysis of water quality indexes and their relationships with vegetation using self-organizing map and geographically and temporally weighted regression. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, J.J.; Gonzalez, J.M. Tannic acid reduces recovery of water-soluble carbon and nitrogen from soil and affects the composition of Bradford-reactive soil protein. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamad, L.; Miskimins, J. Minimizing calcium lactate precipitation via the addition of gluconate ions for matrix acidizing with lactic acid. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2022, 218, 110995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, W.Y.; Chew, K.W.; Le, C.F.; Lam, S.S.; Chee, C.S.C.; Ooi, M.S.L.; Show, P.L. Sustainable utilization of biowaste compost for renewable energy and soil amendments. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Lei, L.Y.; Shen, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Ruan, R.G.; Cui, X. A co-ensiling strategy of food wastes: Peanut shell as an additive to distillers’ grains to improve efficiency of energy conversion. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Kong, B.; Feng, J.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.J.; Cai, F.J.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, Z.J.; Cao, J.H.; Xu, J. A novel strategy for comprehensive utilization of distillers’ grain waste towards energy and resource recovery. Process Biochem. 2022, 113, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodbeygi, Y.; Askari, M.; Salehi, E.; Kheirieh, S. A review on hybrid membrane-adsorption systems for intensified water and wastewater treatment: Process configurations, separation targets, and materials applied. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
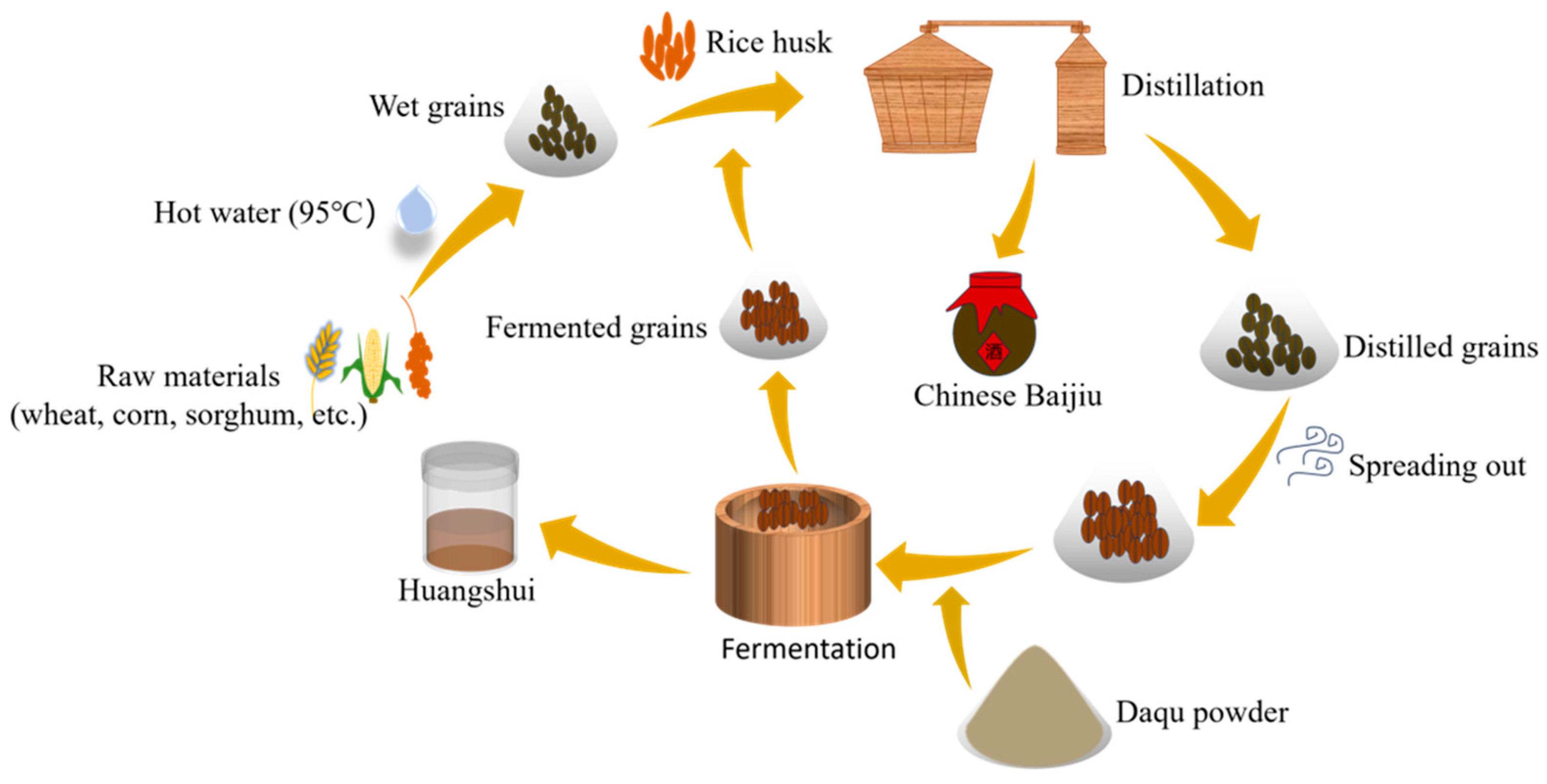
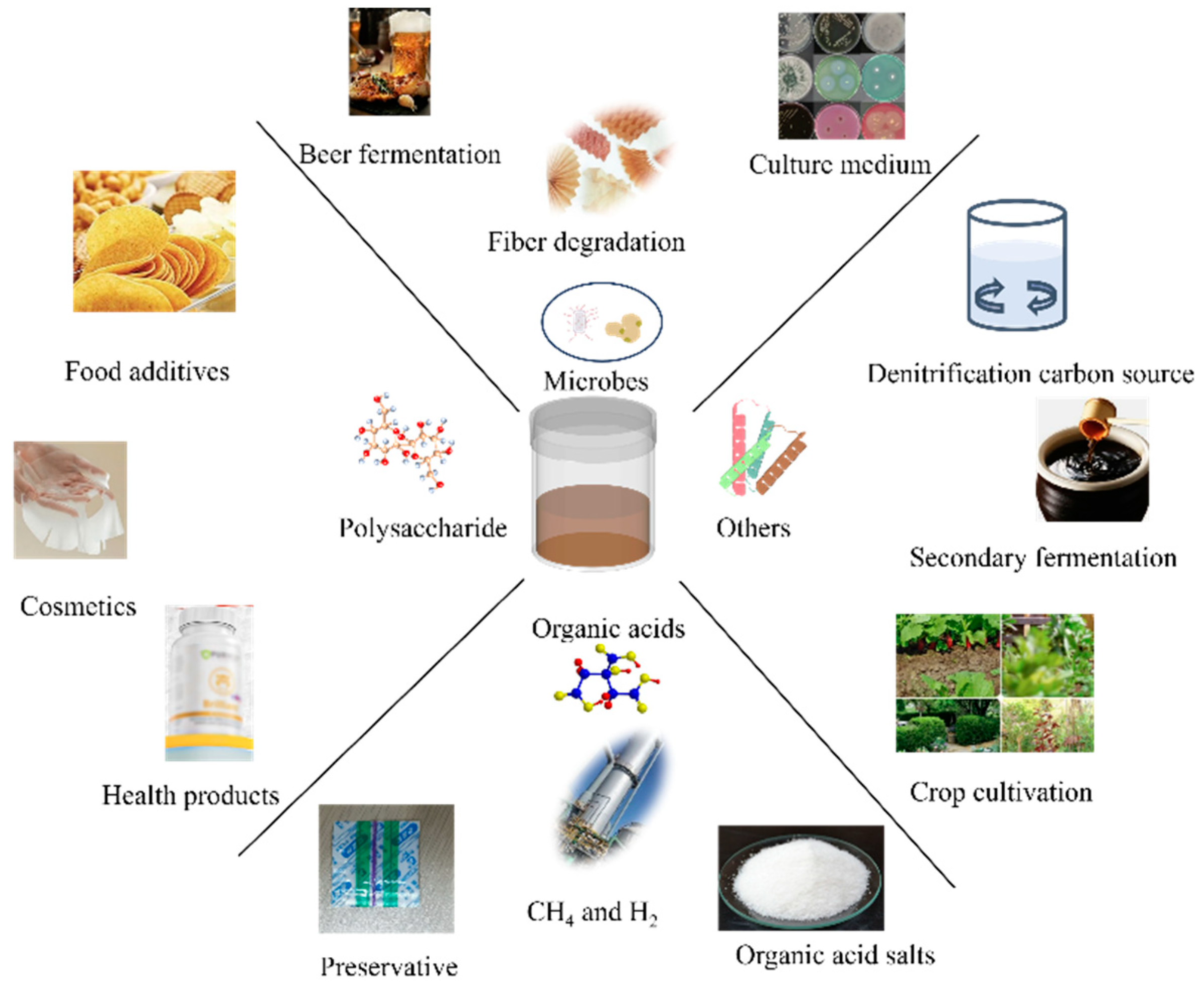

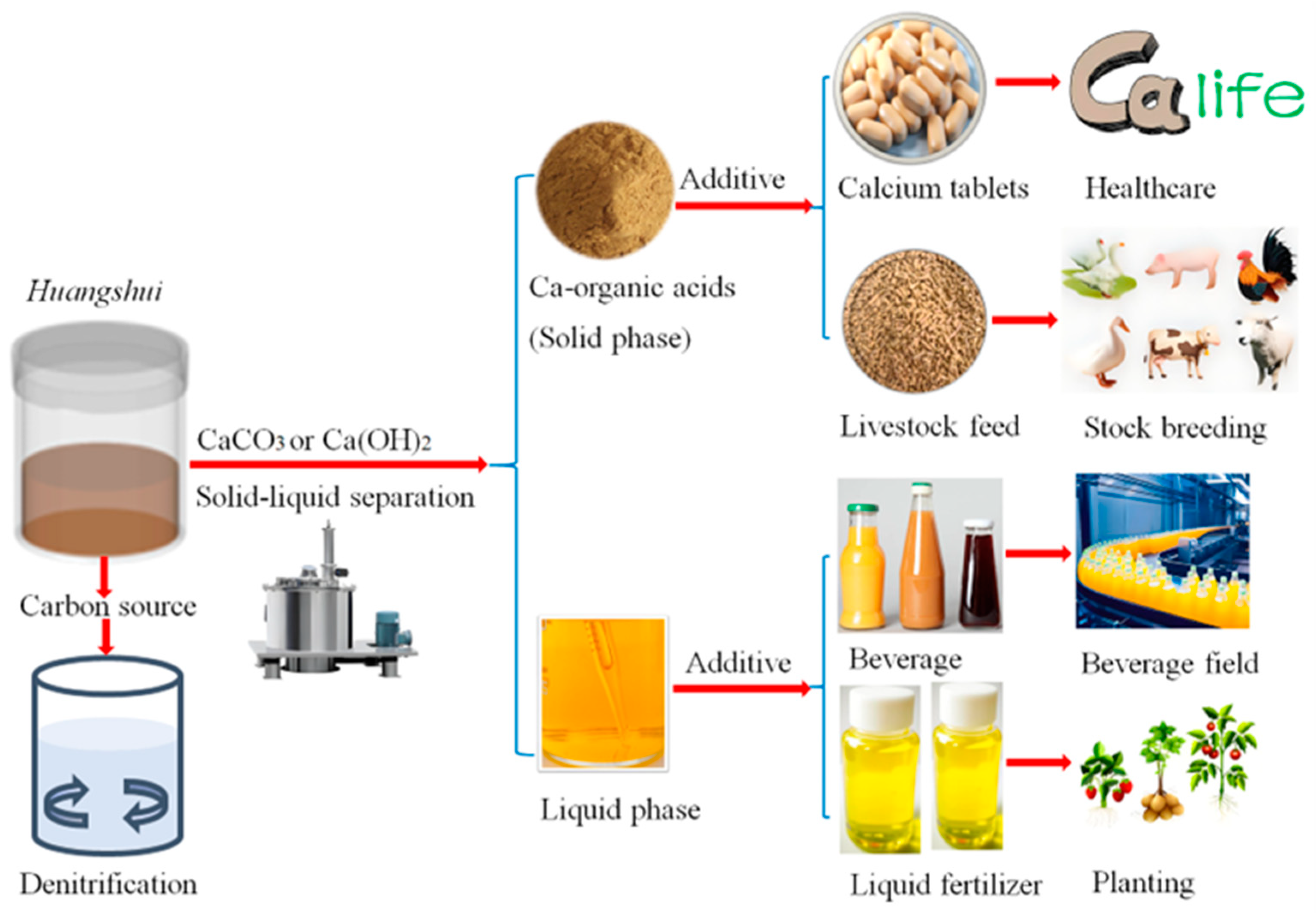
| Index | Content | Index | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3.15–3.77 | Lactic acid (mg/100 mL) | 3688.08–4863.51 |
| Acidity (mmol/100 g) | 35.13–44.93 | Succinic acid (mg/100 mL) | 73.21–388.07 |
| Starch content (%) | 1.41–3.71 | Malic acid (mg/100 mL) | 247.53–382.34 |
| Alcohol content (% vol) | 3.13–5.37 | Acetic acid (mg/100 mL) | 270.51–416.45 |
| Reducing sugar (%) | 0.28–0.86 | Citric acid (mg/100 mL) | 59.25–95.44 |
| Ester (%) | 0.13–0.27 | Tartaric acid (mg/100 mL) | 47.93–70.64 |
| Tannin and pigment (%) | 0.12–0.27 | CODCr (mg/L) | 25,000–85,300 |
| Glycerol (mg/100 mL) | 537.09–627.36 | BOD5 (mg/L) | 25,000–30,000 |
| Bacterial Strain | Results and Applications | References |
|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis, Candida utilis | They could use to ferment distillers’ grains for feed production, raising the total amino acid by 17.74%. | [2] |
| Lactic acid bacteria | The bacteria could use starch and reducing sugars in Huangshui to produce lactic acid. | [4] |
| Acid tolerant yeast Strain | The strain showed high acetic acid tolerance and grew normally at 12 g/L acetic acid. | [13] |
| Lactic acid bacteria | They could convert lactic acid into ethanol. | [24] |
| Lactobacillus | The Lactobacillus screened from Huangshui could improve flavor and eliminate ethyl carbamate. | [30] |
| Lactic acid bacteria | They could competitively degrade arginine with yeasts cooperation. | [33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J. Recent Advances in Resource Utilization of Huangshui from Baijiu Production. Fermentation 2024, 10, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10060310
Zhang X, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Wang R, Zhang J. Recent Advances in Resource Utilization of Huangshui from Baijiu Production. Fermentation. 2024; 10(6):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10060310
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoying, Huiwen Zhang, Zhengyi Zhang, Ruixi Wang, and Jishi Zhang. 2024. "Recent Advances in Resource Utilization of Huangshui from Baijiu Production" Fermentation 10, no. 6: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10060310
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, R., & Zhang, J. (2024). Recent Advances in Resource Utilization of Huangshui from Baijiu Production. Fermentation, 10(6), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10060310