Obtention and Characterization of GO/Epoxy and GO-GPTMS/Epoxy Nanocompounds with Different Oxidation Degrees and Ultrasound Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Pretreatment of GO
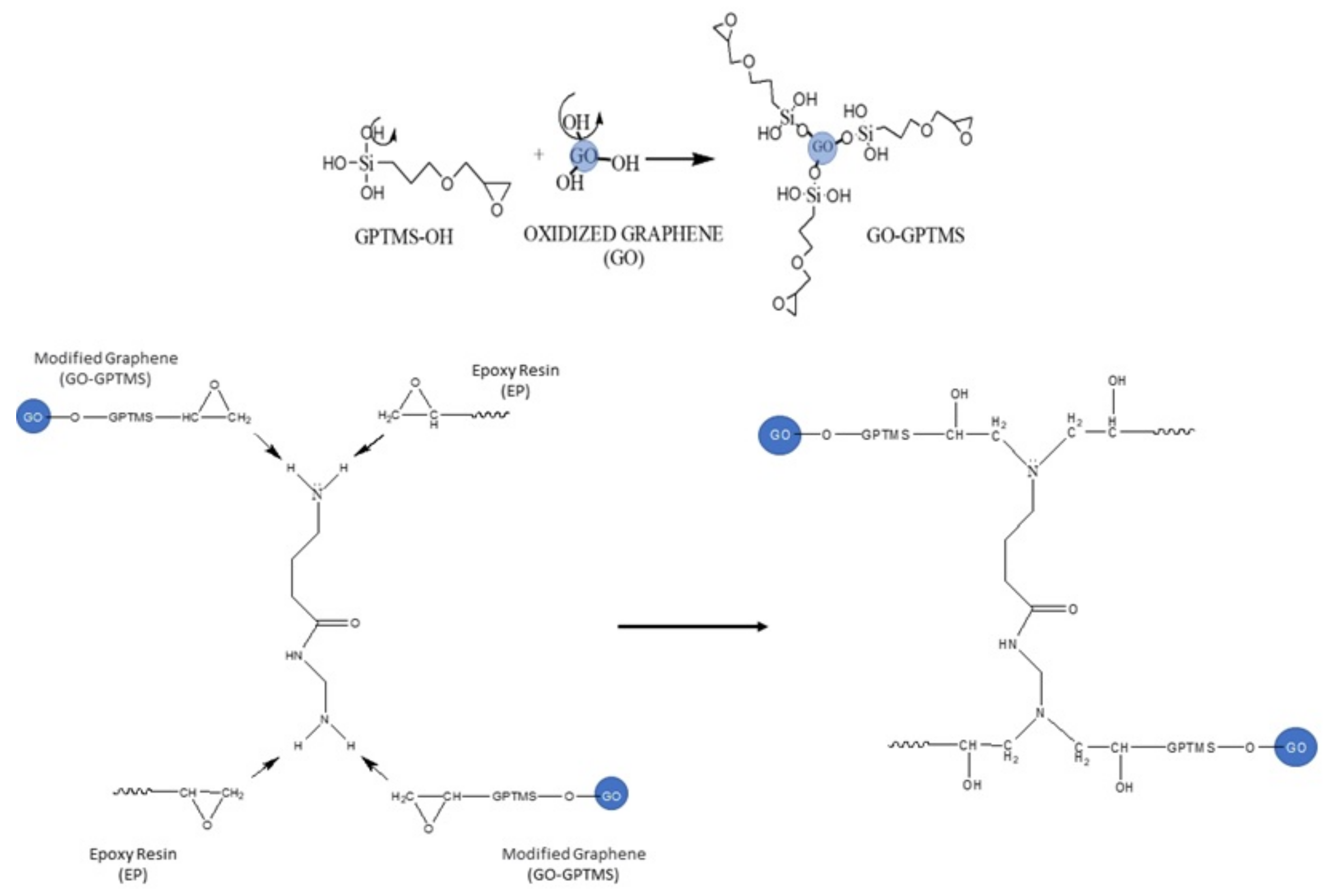
2.2.2. Functionalization of GO Using Silane (GPTMS)
2.2.3. Preparation of GO/Epoxy and GO-GPTMS/Epoxy Nanocompounds
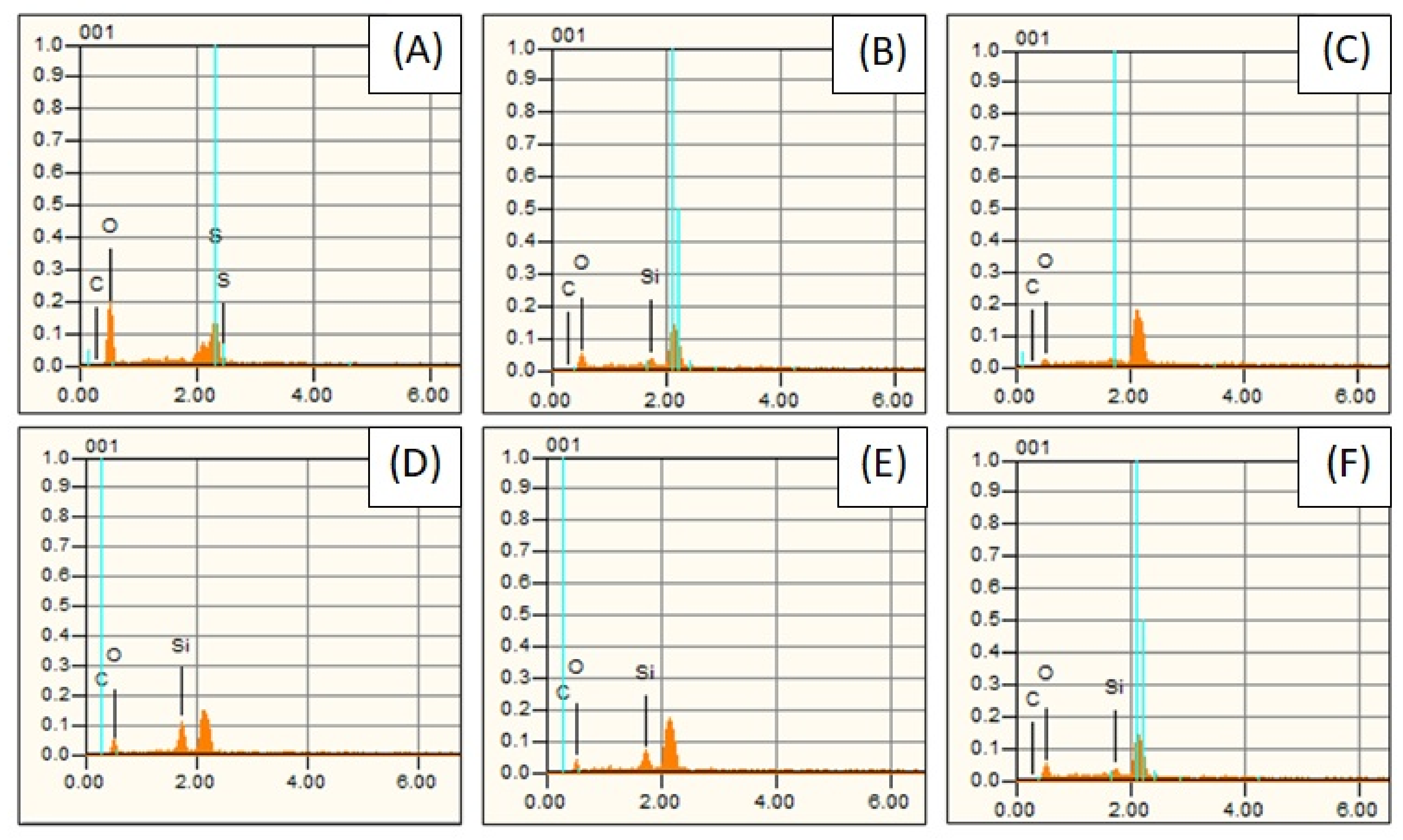
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
2.3.3. Optical Microscopy
2.3.4. Mechanical Tension Testing
3. Results
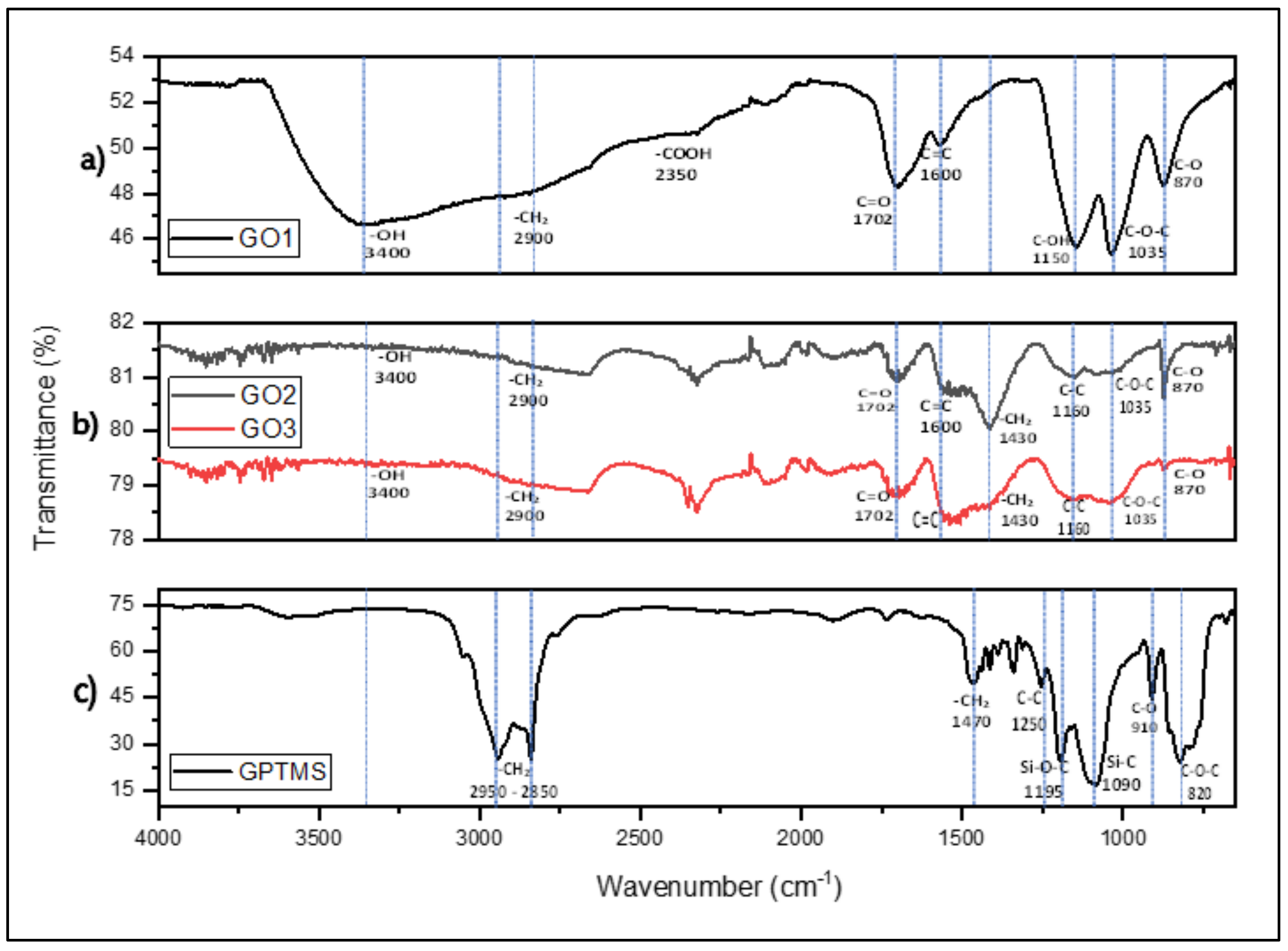
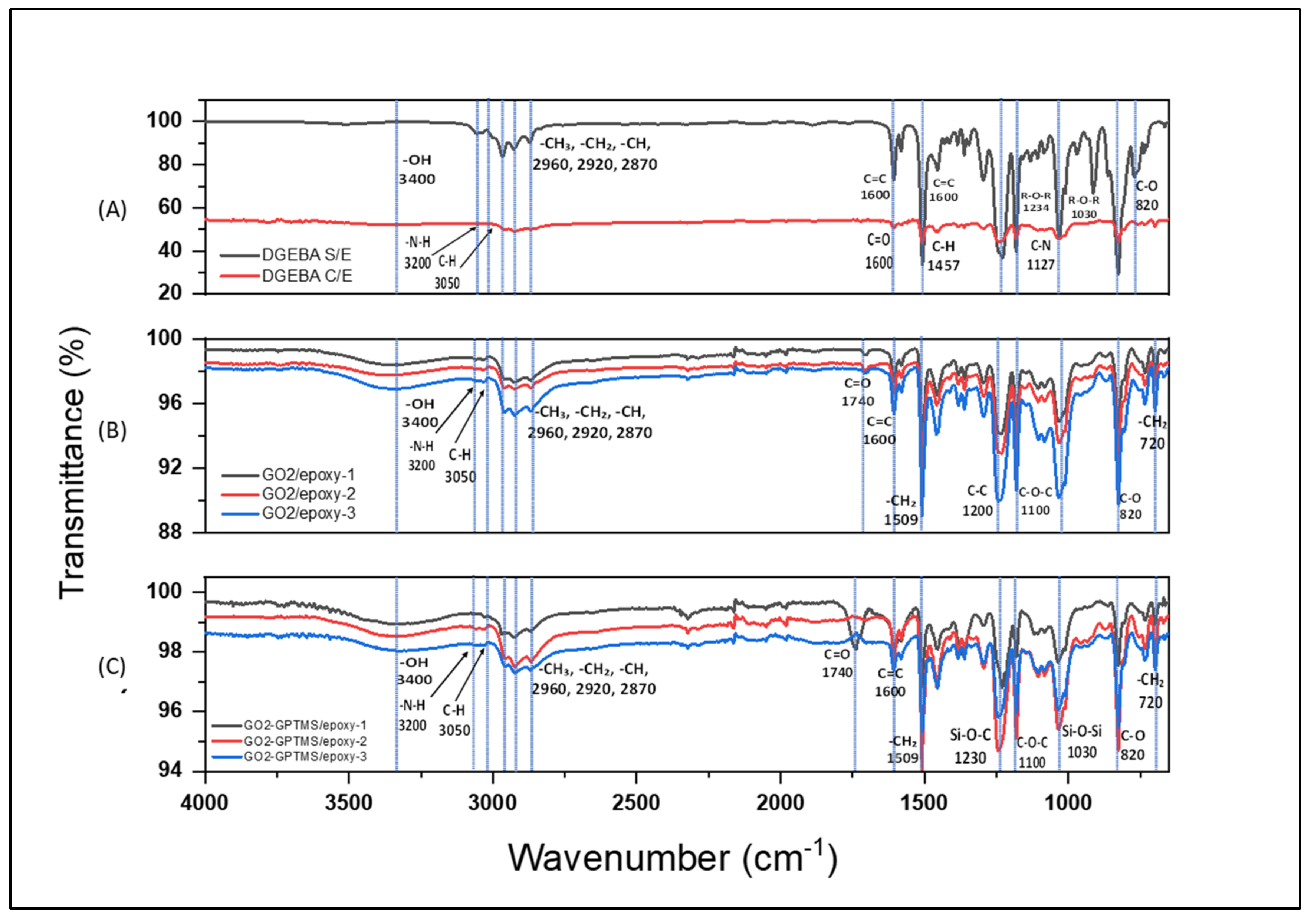
3.1. Characterization of GO, GO-GPTMS, and Nanocompounds by FTIR Spectroscopy
- The bands were measured using originPro, (integration option) to obtain the areas of each selected peak or signal.
- A polynomial baseline was drawn from the raw spectra.
- The resulting spectrum was multiplied by −1, and the origin was set to y = 0 to obtain positive bands.
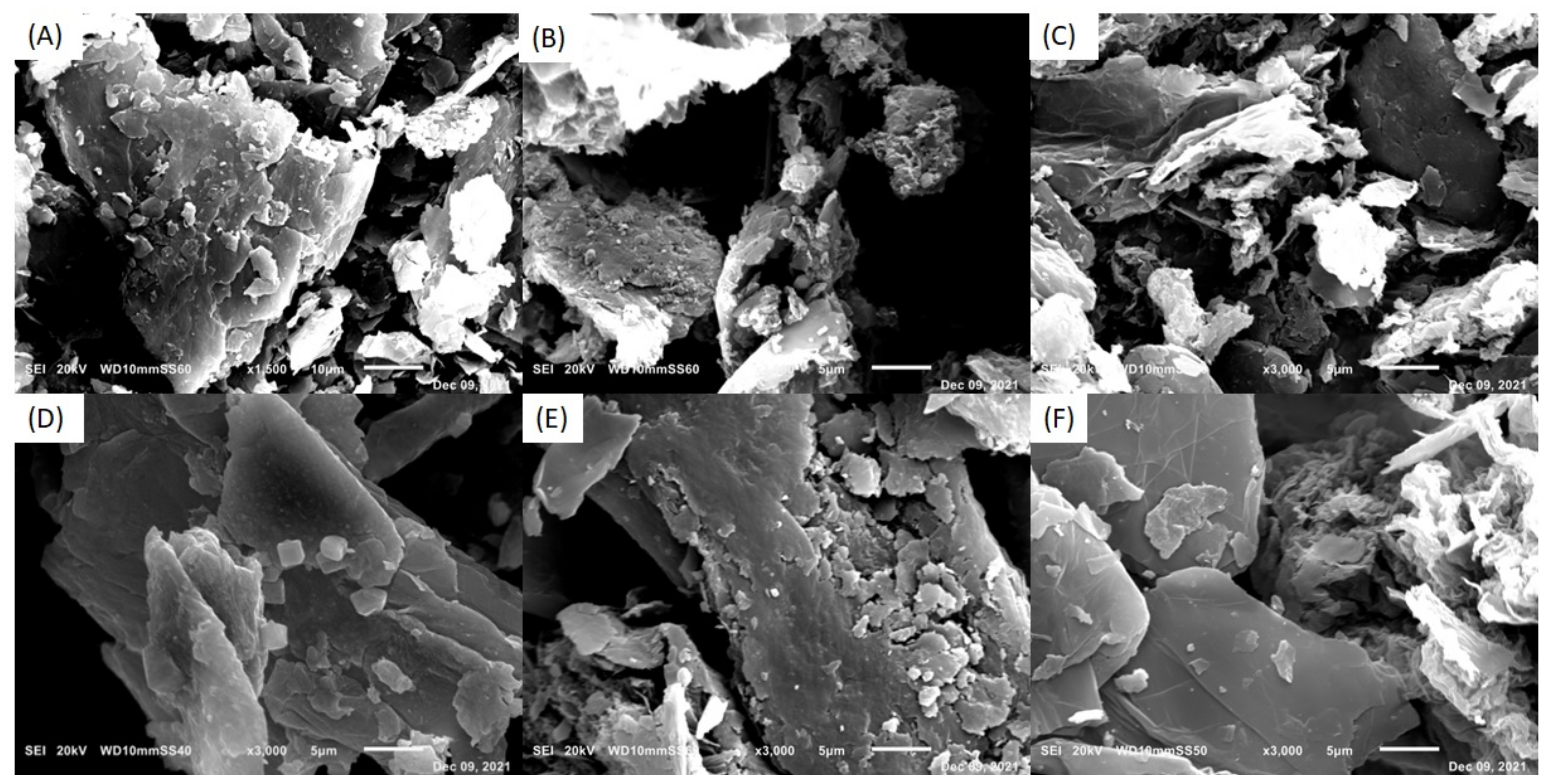
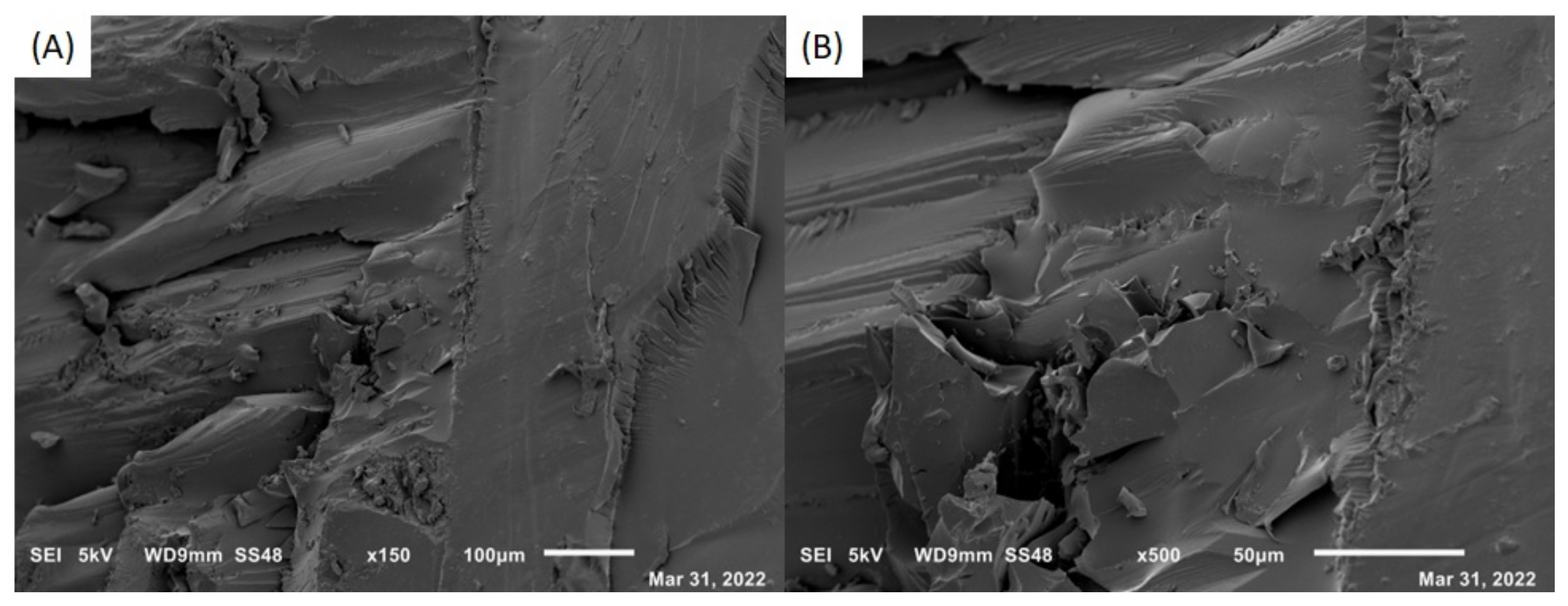
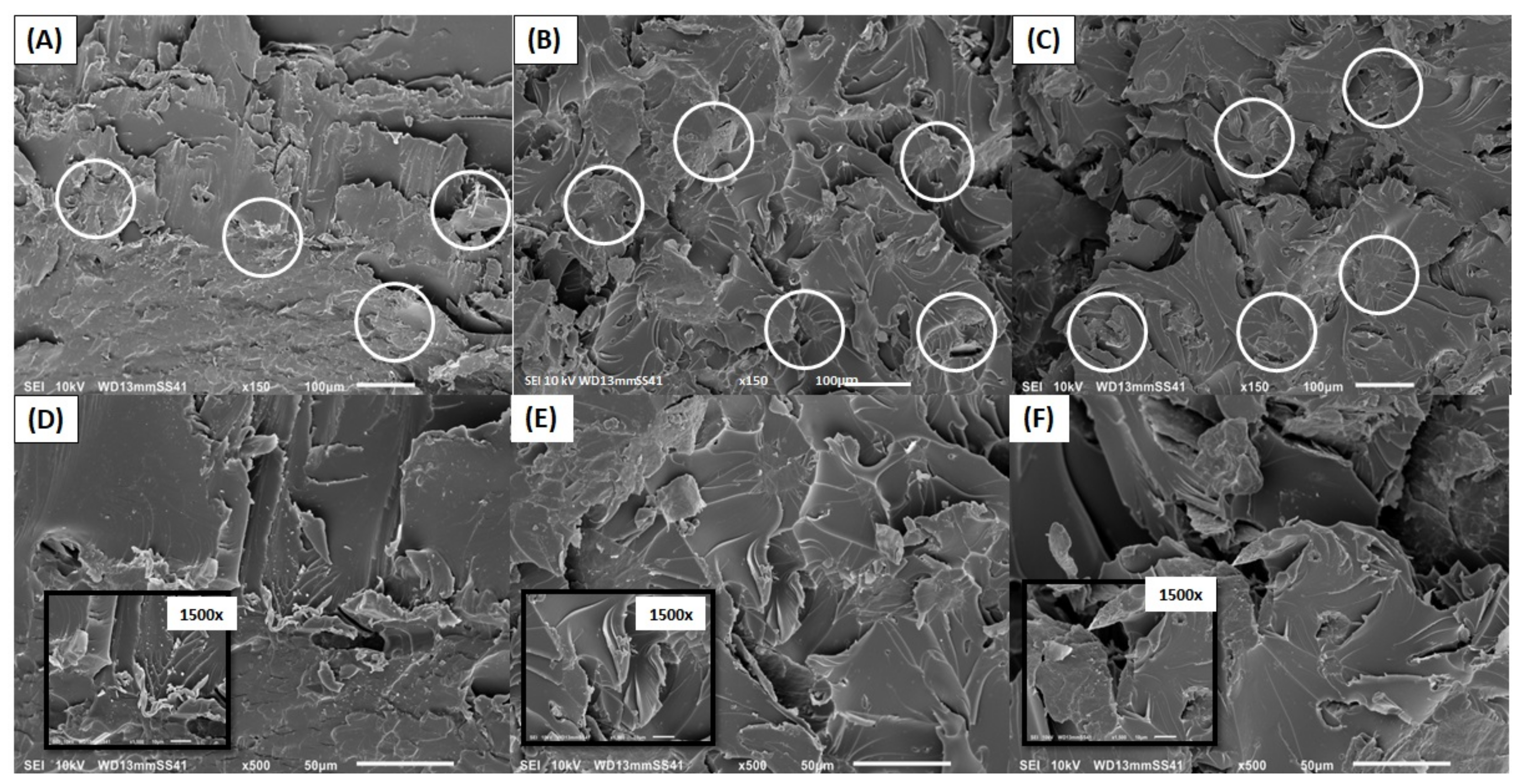
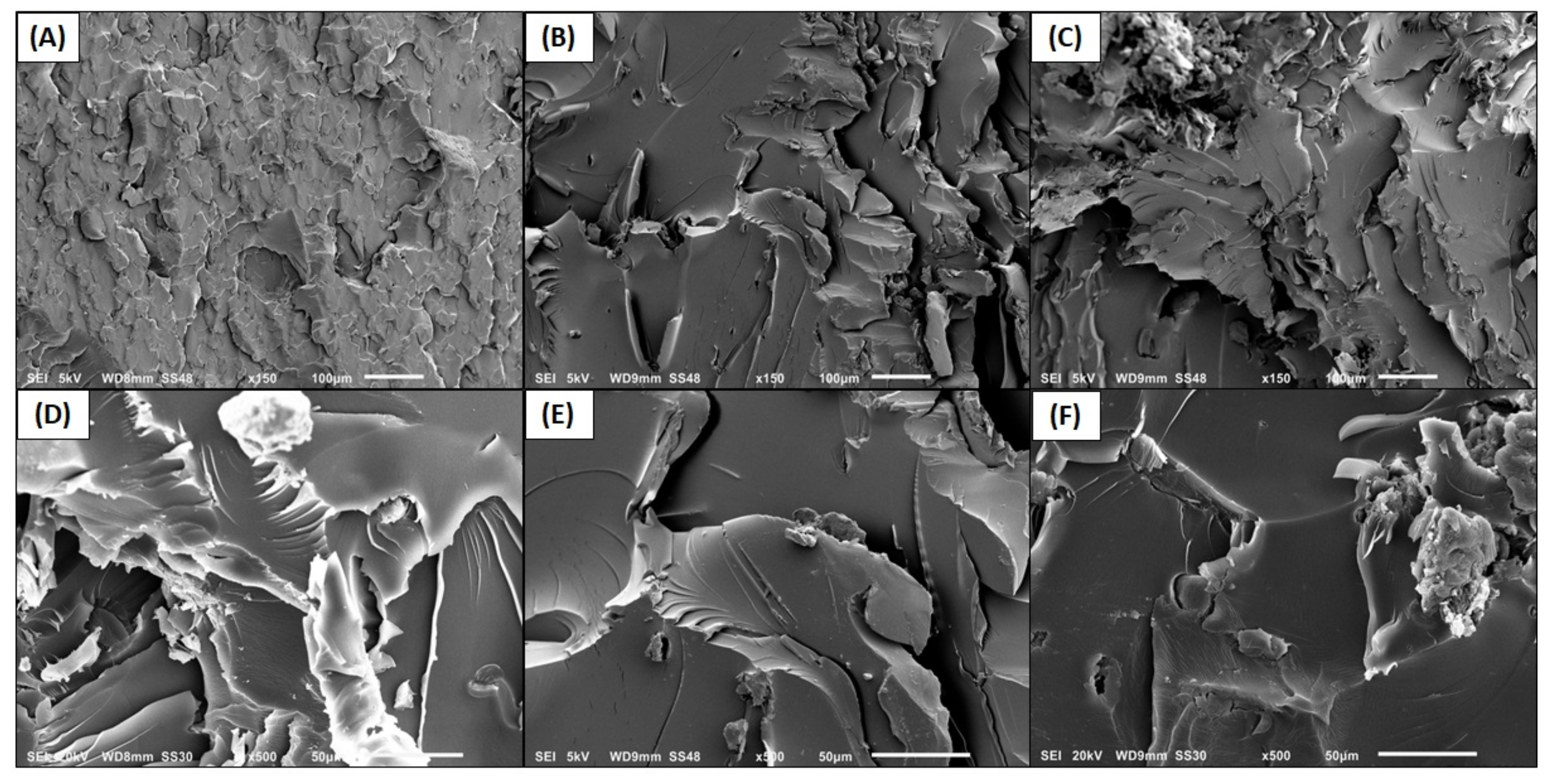
3.2. Morphological Characterization
3.2.1. Characterization of Silane-GPTMS Functionalized GOs and GOs by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM/EDS)
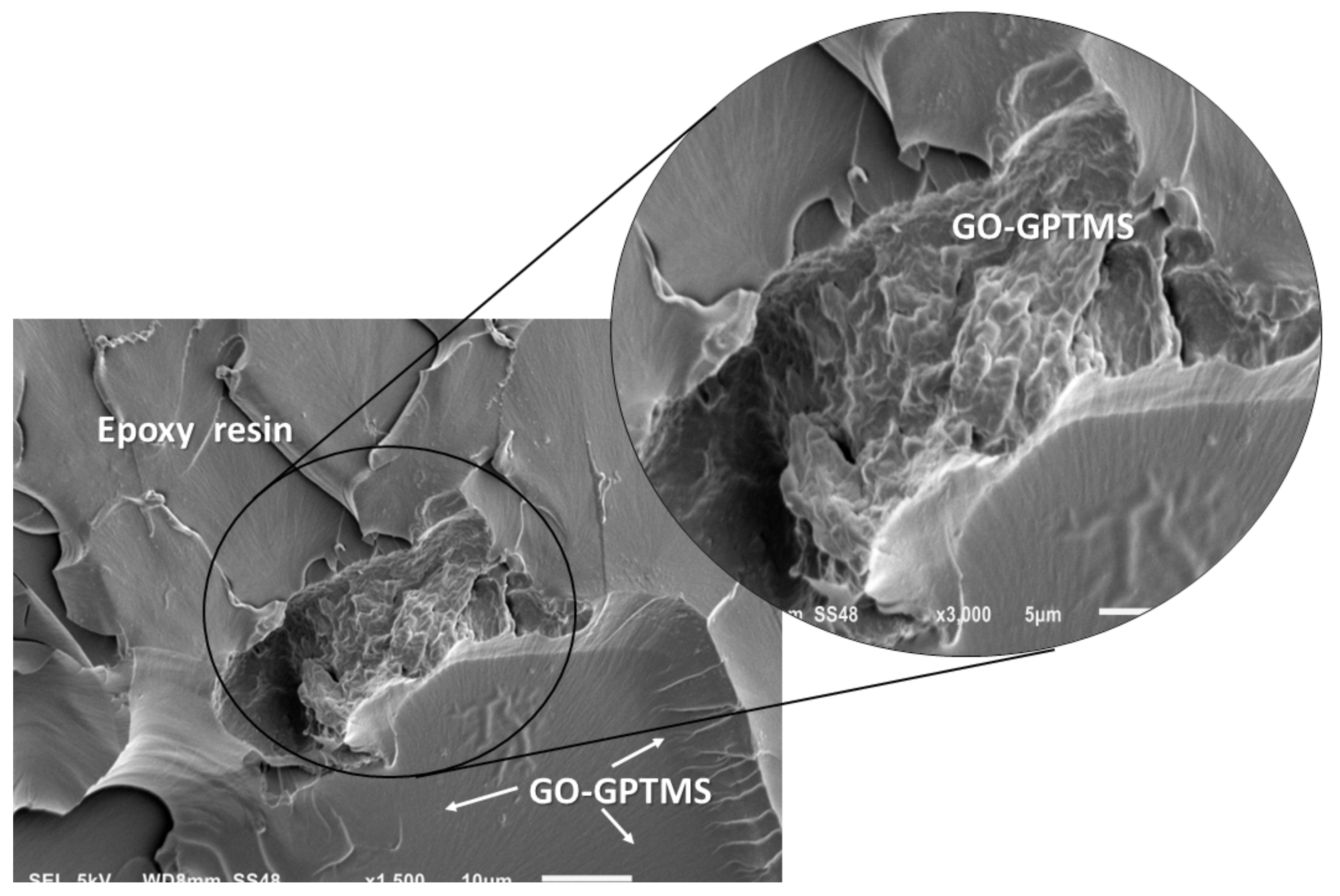
3.2.2. Interface and Microstructure of Nanocompounds
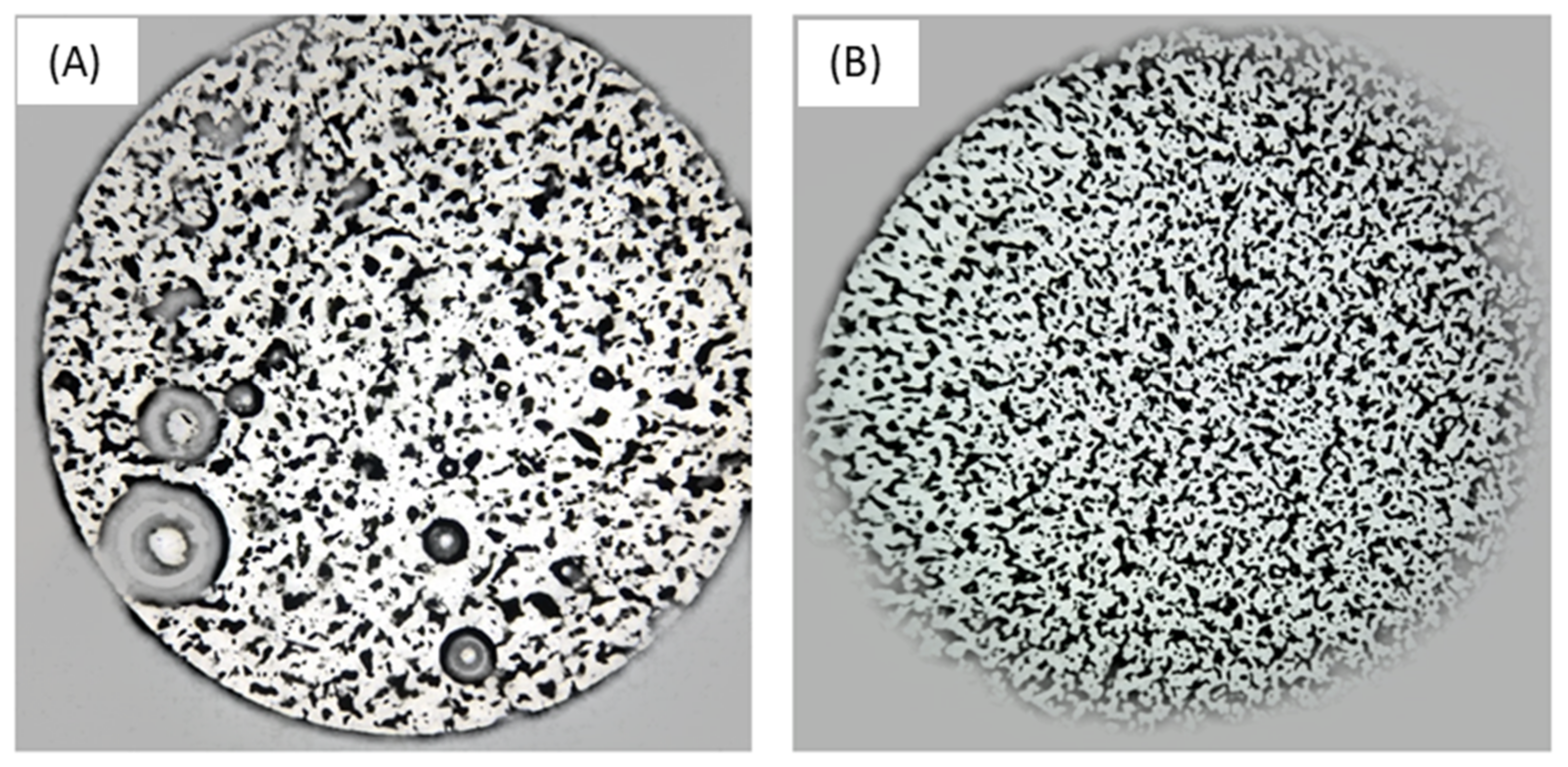
3.3. Characterization of GO/Epoxy and GO-GPTMS/Epoxy Nanocompounds by Optical Microscopy
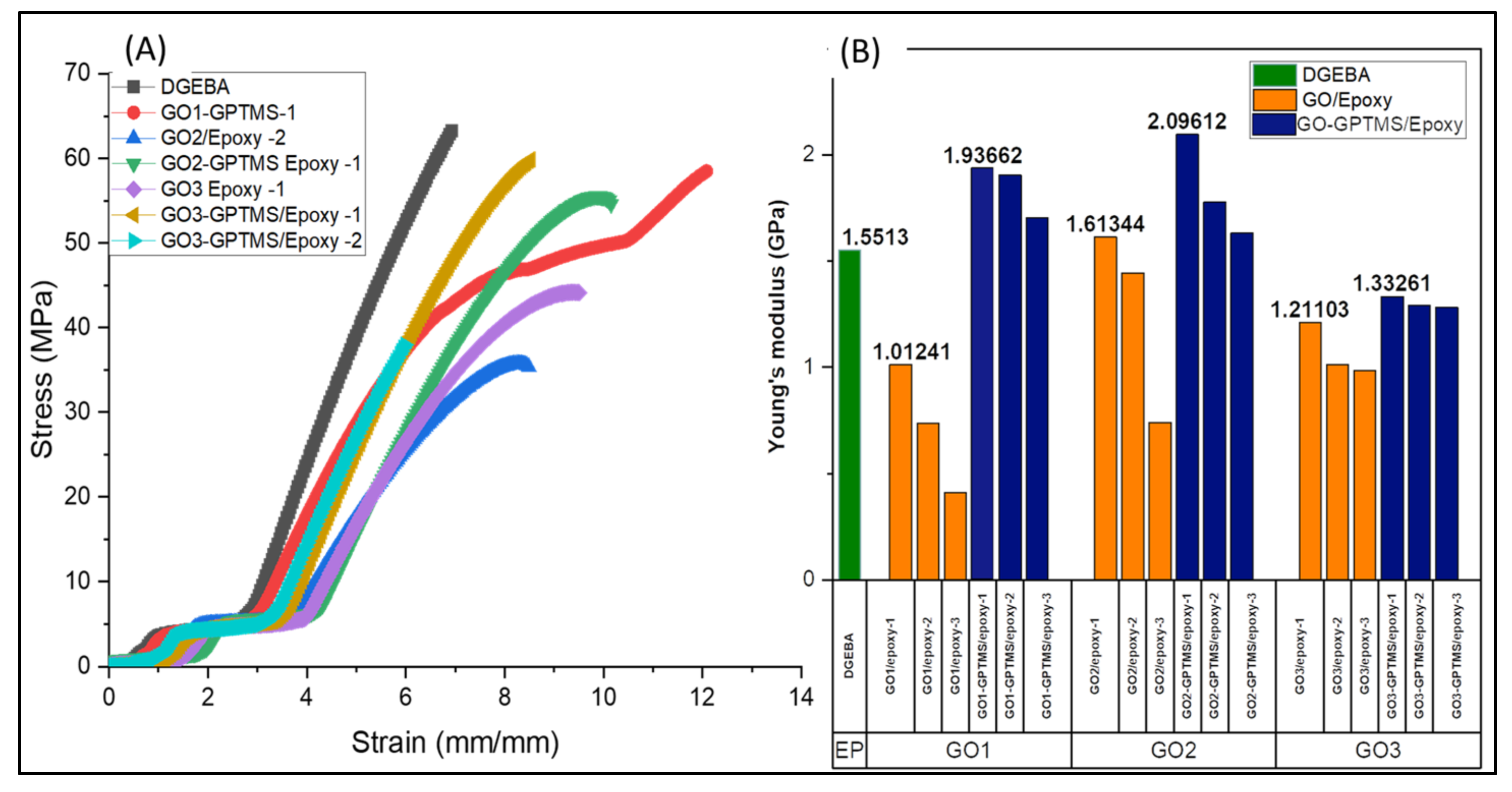
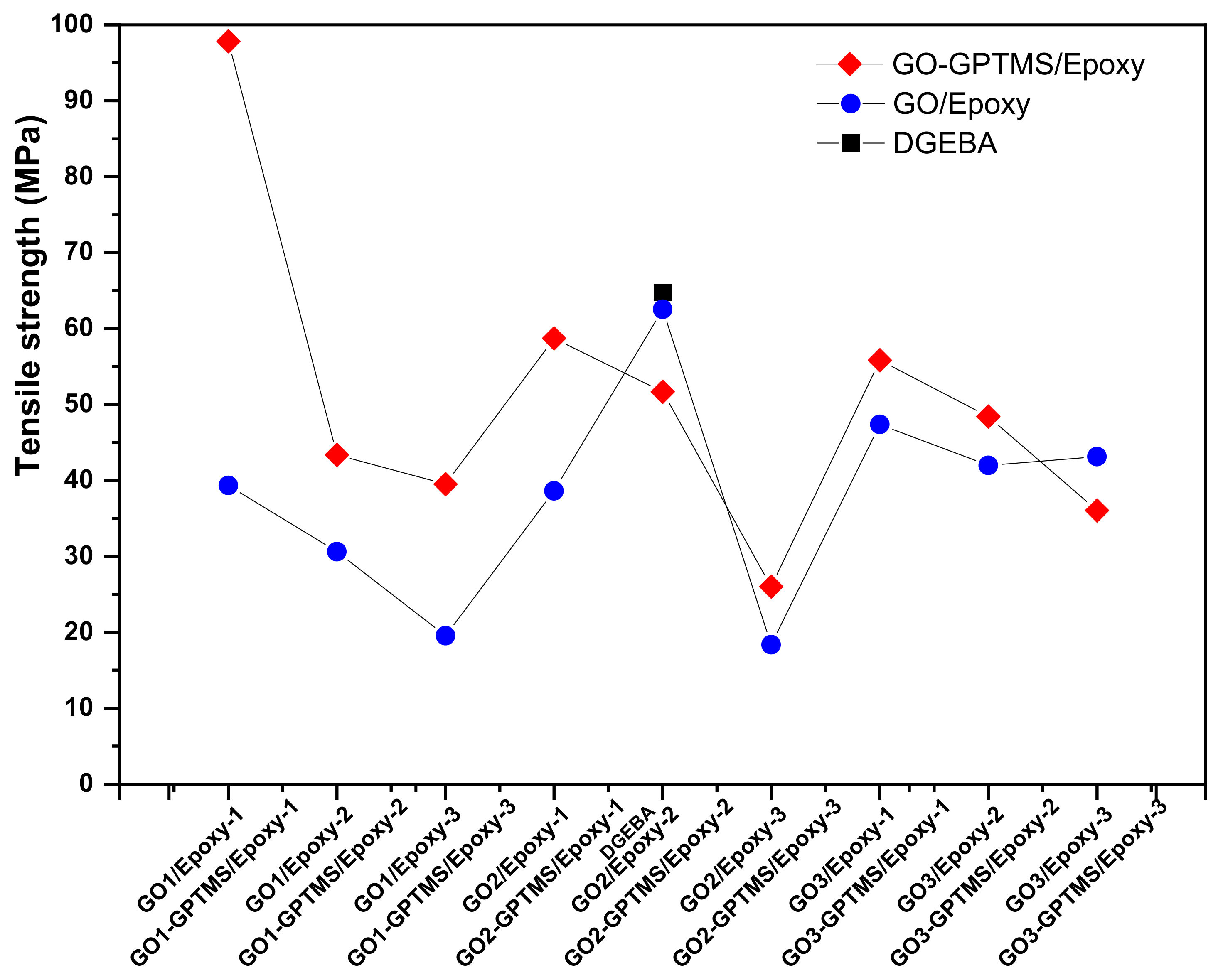
3.4. Mechanical Characterization of Nanocompounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braun, T.; Schubert, A.; Zsindely, S. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology on the Balance. Scientometrics 1997, 38, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Onyebueke, L.; Abatan, A. Characterizing and Modeling Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposites-Review and Evaluation. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2010, 9, 275–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, E.; Attar, M.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Investigation of corrosion protection properties of an epoxy nanocomposite loaded with polysiloxane surface modified nanosilica particles on the steel substrate. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 78, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Rasouli, S.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Askari, A. Electrochemical investigation of the properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticle as a corrosion inhibitive pigment for modifying corrosion resistance of the epoxy coating. Corros. Sci. 2014, 88, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Li, X.; Park, S. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Ma, C.; Park, S. Thermal and mechanical interfacial properties of epoxy composites based on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 8517–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, F.; Han, E. Protection of epoxy coatings containing polyaniline modified ultra-short glass fibers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Kahrizsangi, A.; Neshati, J.; Shariatpanahi, H.; Akbarinezhad, E. Improving the UV degradation resistance of epoxy coatings using modified carbon black nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 85, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Deng, X.; Shen, W.; Jia, M. Preparation and characterization of the spherical nanosized cellulose by the enzymatic hydrolysis of pulp fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, C.; Yang, S.; Song, X.; Wang, S.; Li, K. Enzyme-assisted mechanical grinding for cellulose nanofibers from bagasse: Energy consumption and nanofiber characteristics. Cellulose 2018, 25, 7065–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Tung, V.; Kaner, R. Honeycomb Carbon: A Review of Graphene. Chem. Rev. 2009, 110, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sun, H.; Li, H.; Peng, H. Developing Polymer Composite Materials: Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene? Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5153–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Dai, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, D.; Zeng, L.; Jiang, N. Enhanced thermal and electrical properties of epoxy composites reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets. Polym. Compos. 2014, 36, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Zhu, H. Structure and Properties of Graphene. In Graphene; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Le, Q.; Kim, C.; Kim, S. Use of silane-functionalized graphene oxide in organic photovoltaic cells and organic light-emitting diodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 9369–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Bae, J.; Kim, T.; Chang, S.; Kim, S. Using silane-functionalized graphene oxides for enhancing the interfacial bonding strength of carbon/epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 75, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Feng, H.; Li, J. Graphene Oxide: Preparation, Functionalization, and Electrochemical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6027–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yin, Z.; Wu, S.; Qi, X.; He, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Q.; Boey, F.; Zhang, H. Graphene-Based Materials: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, and Applications. Small 2011, 7, 1876–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Song, M. An investigation of the mechanism of graphene toughening epoxy. Carbon 2013, 65, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zou, H.; Chen, Y.; Liang, M. Effect of graphene oxide with different exfoliation levels on the mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 6033–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.-C.; Wan, Y.-J.; Yan, D.; Pei, Y.-B.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.-B.; Wu, L.-B.; Jiang, J.-X.; Lai, G.-Q. The effect of graphene dispersion on the mechanical properties of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2013, 60, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zong, P.; Chen, L.; Dong, X.; Shang, D.; Yu, W.; Shi, L.; Deng, W. A Facile Approach to Covalently Functionalized Graphene Nanosheet Hybrids and Polymer Nanocomposites. Chemnanomat 2016, 2, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Wei, H.; Zhu, J. Ultrasound enhanced radical graft polymerization of starch and butyl acrylate. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 90, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria Tafoya, J.; Doszczeczko, S.; Titirici, M.; Jorge Sobrido, A. Enhancement of the electrocatalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction of boron-doped reduced graphene oxide via ultrasonic treatment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 5462–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzadeh, B.; Niroumandrad, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Mahdavian, M.; Moghadam, M. Enhancement of barrier and corrosion protection performance of an epoxy coating through wet transfer of amino functionalized graphene oxide. Corros. Sci. 2016, 103, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, T.; Liu, G. Liquid-phase exfoliated fluorographene as a two dimensional coating filler for enhanced corrosion protection performance. Corros. Sci. 2016, 103, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.-J.; Tang, L.-C.; Gong, L.-X.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.-B.; Wu, L.-B.; Jiang, J.-X.; Lai, G.-Q. Grafting of epoxy chains onto graphene oxide for epoxy composites with improved mechanical and thermal properties. Carbon 2014, 69, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Vaezi, M.; Rashidi, A.; Bagherzadeh, M. Distinctive roles of silane coupling agents on the corrosion inhibition performance of graphene oxide in epoxy coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 111, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xing, W.; Zhang, P.; Song, L.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y. Covalent functionalization of graphene with organosilane and its use as a reinforcement in epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Young, R.J.; Deng, L.; Yang, F.; Hao, L.; Jiao, W.; Liu, W. Control of the functionality of graphene oxide for its application in epoxy nanocomposites. Polymer 2013, 54, 6437–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Xiong, L. Corrosion protection of AA2024-T3 by sol-gel film modified with graphene oxide. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 725, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryonis, O.; Harrell, T.M.; Andritsch, T.; Vaughan, A.S.; Lewin, P.L. Solvent Mixing and Its Effect on Epoxy Resin Filled with Graphene Oxide. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Dielectrics (ICD), Budapest, Hungary, 1–5 July 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Liu, P.; Peng, Z. Space charge characteristics of graphene oxide/epoxy resin nanocomposites under polarity reversal voltage. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Conference on the Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials (ICPADM), Xi’an, China, 20–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Zuo, S.; Luo, S.; Yao, C.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Mao, H.; Li, Z. Preparation of polyaniline/graphene composites with excellent anti-corrosion properties and their application in waterborne polyurethane anticorrosive coatings. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 95965–95972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Contreras, J.; Caballero-Briones, F. Graphene oxide powders with different oxidation degree, prepared by synthesis variations of the Hummers method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 153, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Weng, M.; Huang, S. Preparation and Characterization of pH Sensitive Chitosan/3-Glycidyloxypropyl Trimethoxysilane (GPTMS) Hydrogels by Sol-Gel Method. Polymers 2020, 12, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, T.; Pan, Y.; Liu, G. Inhibited corrosion-promotion activity of graphene encapsulated in nanosized silicon oxide. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 16843–16848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louafi, Y.; Ladjouzi, M.; Taibi, K. Dissolved carbon dioxide effect on the behavior of carbon steel in a simulated solution at different temperatures and immersion times. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 14, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Rashidi, A.; Vaezi, M.; Bagherzadeh, M. Excellent corrosion protection performance of epoxy composite coatings filled with amino-silane functionalized graphene oxide. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 317, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, Y.; Baeck, S.; Shim, S. Effect of surface treatment of graphene nanoplatelets for improvement of thermal and electrical properties of epoxy composites. Carbon Lett. 2015, 16, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, T.; Berkesi, O.; Forgó, P.; Josepovits, K.; Sanakis, Y.; Petridis, D.; Dékány, I. Evolution of Surface Functional Groups in a Series of Progressively Oxidized Graphite Oxides. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, G. Inhibiting the Corrosion-Promotion Activity of Graphene. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Su, S.; Kasner, M.; Shah, P.; Patel, K.; Madarang, C. Formation of highly stable dispersions of silane-functionalized reduced graphene oxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 501, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Nie, X. A simple and novel method to design flexible and transparent epoxy resin with tunable mechanical properties. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical Properties of Graphene-Epoxy Nanocomposites—A Review. Polymers 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; He, C.; Wen, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, X.; Mai, Y. Improving thermal and flame retardant properties of epoxy resin by functionalized graphene containing phosphorous, nitrogen and silicon elements. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 103, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmer, C.M.; Zvokel, C.; Vick, A.; Bowden, N.B. Bowden Separation of saturated fatty acids and fatty acid methyl esters with epoxy nanofiltration membranes. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5562655632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Lv, Y. Uniaxial Tensile Creep Behavior of Epoxy-Based Polymer Using Molecular Simulation. Polymers 2021, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
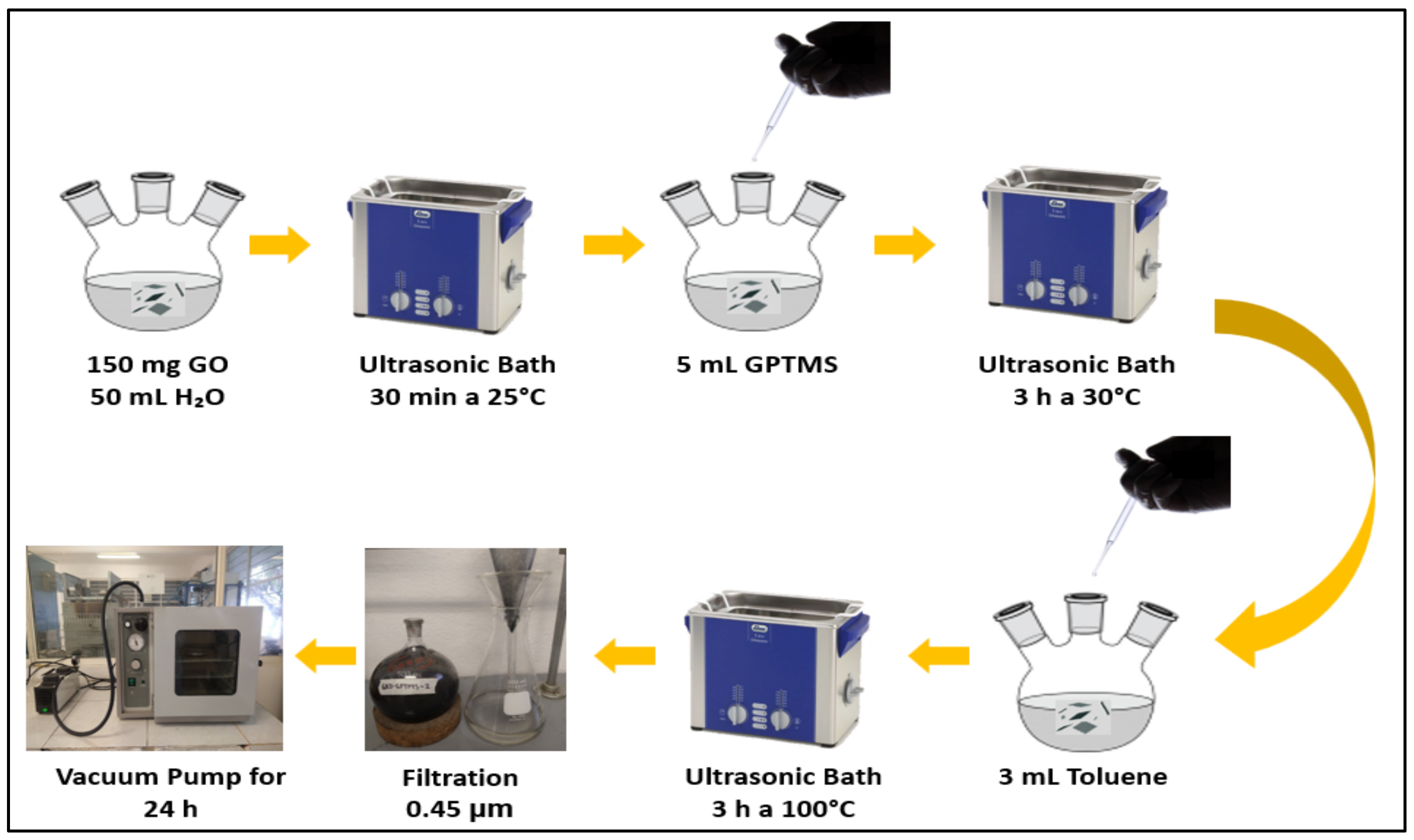
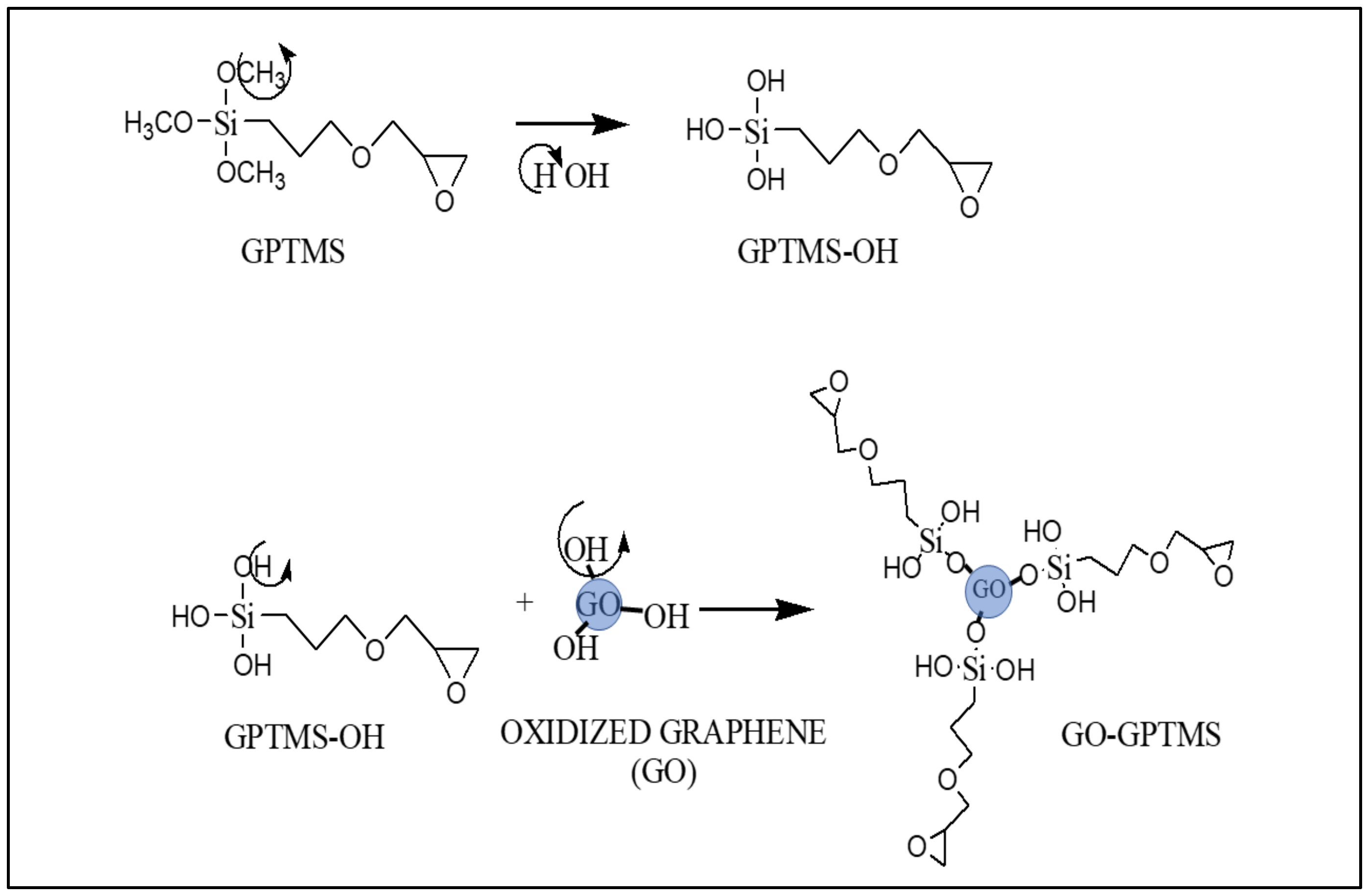


| Sample | %wt GO | Acetone | Epoxy Resin (EP) | Catalyst |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 mg | 0.6 mL | 3.960 g | 1.980 g |
| 2 | 120 mg | 1.2 mL | 3.918 g | 1.962 g |
| 3 | 180 mg | 1.8 mL | 3.882 g | 1.938 g |
| Material | Sample | |
|---|---|---|
| GO/Epoxy | GO-GPTMS/Epoxy | |
| EP | DGEBA | DGEBA |
| GO1/Epoxy-1 | GO1-GPTMS/Epoxy-1 | |
| GO1 | GO1/Epoxy-2 | GO1-GPTMS/Epoxy-2 |
| GO1/Epoxy-3 | GO1-GPTMS/Epoxy-3 | |
| GO2 | GO2/Epoxy-1 | GO2-GPTMS/Epoxy-1 |
| GO2/Epoxy-2 | GO2-GPTMS/Epoxy-2 | |
| GO2/Epoxy-3 | GO2-GPTMS/Epoxy-3 | |
| GO3 | GO3/Epoxy-1 | GO3-GPTMS/Epoxy-1 |
| GO3/Epoxy-2 | GO3-GPTMS/Epoxy-2 | |
| GO3/Epoxy-3 | GO3-GPTMS/Epoxy-3 | |
| GOs | -OH | -CH2 | -COOH | C=O | C=C | C-OH | C-CH2 | C-C | C-O-C | C-O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO1 | 84,319.7 | 5128.66 | 4912.41 | 13,917.2 | 12,355.6 | 9571.69 | - | - | 7374.74 | 11,531.9 |
| GO2 | 40,603.72 | 9028.46 | - | 11,700.27 | 10,756.05 | - | 15,674.61 | 12,592.19 | 19,341.69 | 6832.46 |
| GO3 | 31,760.92 | 14,156.32 | - | 11,304.44 | 11,802.26 | - | 16,037.42 | 12,706.46 | 16,115.51 | 4287.52 |
| Sample | -OH | -CH2 | C=O | C=C | C-C | Si-O-C | C-O-C | Si-O-Si | C-O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO1-GPTMS | 45,787.94 | 12,791.81 | 13,293.09 | 24,618.71 | 10,334.75 | 7311.22 | 4338.98 | 6312.62 | 10,332.37 |
| GO2-GPTMS | 44,145.55 | 11,314.32 | 11,794.27 | 25,673.36 | 9081.82 | 7038.82 | 4217.75 | 5586.69 | 9992.90 |
| GO3-GPTMS | 30,844.95 | 10,996.61 | 7151.31 | 25,175.67 | 8201.3 | 6050.94 | 3834.42 | 4962.36 | 8772.26 |
| Sample | Stress (MPa) | Young Module (GPa) | Strain Max (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DGEBA | 64.778 ± 2.02 | 1.551 ± 0.52 | 9.860 ± 0.72 |
| GO1/Epoxy-1 | 39.332 ± 1.33 | 1.012 ± 0.46 | 10.573 ± 0.39 |
| GO1/Epoxy-2 | 30.603 ± 1.35 | 0.736 ± 0.18 | 10.340 ± 0.16 |
| GO1/Epoxy-3 | 19.550 ± 1.35 | 0.409 ± 0.33 | 10.870 ± 0.78 |
| GO1-GPTMS/Epoxy-1 | 87.836 ± 1.17 | 1.936 ± 0.27 | 13.195 ± 0.89 |
| GO1-GPTMS/Epoxy-2 | 63.358 ± 1.61 | 1.905 ± 0.51 | 10.415 ± 0.65 |
| GO1-GPTMS/Epoxy-3 | 59.524 ± 1.36 | 1.704 ± 0.92 | 10.567 ± 0.42 |
| GO2/Epoxy-1 | 38.623 ± 1.78 | 1.613 ± 0.63 | 10.917 ± 0.83 |
| GO2/Epoxy-2 | 62.528 ± 1.53 | 1.443 ± 0.32 | 9.763 ± 0.52 |
| GO2/Epoxy-3 | 18.357 ± 1.23 | 0.740 ± 0.05 | 9.041 ± 0.20 |
| GO2-GPTMS/Epoxy-1 | 98.713 ± 1.23 | 2.096 ± 0.19 | 14.90 ± 0.19 |
| GO2-GPTMS/Epoxy-2 | 51.688 ± 1.25 | 1.777 ± 0.33 | 10.530 ± 0.51 |
| GO2-GPTMS/Epoxy-3 | 46.017 ± 1.78 | 1.631 ± 0.33 | 10.899 ± 0.97 |
| GO3/Epoxy-1 | 47.363 ± 2.65 | 1.211 ± 0.61 | 9.381 ± 0.42 |
| GO3/Epoxy-2 | 41.970 ± 2.03 | 1.010 ± 0.39 | 8.353 ± 0.67 |
| GO3/Epoxy-3 | 33.145 ± 2.85 | 0.984 ± 0.19 | 8.138 ± 0.45 |
| GO3-GPTMS/Epoxy-1 | 55.836 ± 1.12 | 1.332 ± 0.52 | 9.446 ± 0.66 |
| GO3-GPTMS/Epoxy-2 | 52.417 ± 1.79 | 1.291 ± 0.17 | 9.765 ± 0.35 |
| GO3-GPTMS/Epoxy-3 | 46.038 ± 1.45 | 1.281 ± 0.49 | 9.736 ± 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salgado-Delgado, A.M.; González-Mondragón, E.G.; Hernández-Pérez, R.; Salgado-Delgado, R.; Santana-Camilo, J.A.; Olarte-Paredes, A. Obtention and Characterization of GO/Epoxy and GO-GPTMS/Epoxy Nanocompounds with Different Oxidation Degrees and Ultrasound Methods. C 2023, 9, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010028
Salgado-Delgado AM, González-Mondragón EG, Hernández-Pérez R, Salgado-Delgado R, Santana-Camilo JA, Olarte-Paredes A. Obtention and Characterization of GO/Epoxy and GO-GPTMS/Epoxy Nanocompounds with Different Oxidation Degrees and Ultrasound Methods. C. 2023; 9(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalgado-Delgado, Areli Marlen, Elizabeth Grissel González-Mondragón, Ricardo Hernández-Pérez, René Salgado-Delgado, José Alfonso Santana-Camilo, and Alfredo Olarte-Paredes. 2023. "Obtention and Characterization of GO/Epoxy and GO-GPTMS/Epoxy Nanocompounds with Different Oxidation Degrees and Ultrasound Methods" C 9, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010028
APA StyleSalgado-Delgado, A. M., González-Mondragón, E. G., Hernández-Pérez, R., Salgado-Delgado, R., Santana-Camilo, J. A., & Olarte-Paredes, A. (2023). Obtention and Characterization of GO/Epoxy and GO-GPTMS/Epoxy Nanocompounds with Different Oxidation Degrees and Ultrasound Methods. C, 9(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010028





