Stable Carbon Dots from Microwave-Heated Carbon Nanoparticles Generating Organic Radicals for In Situ Additions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurement
2.3. NEC-CDots
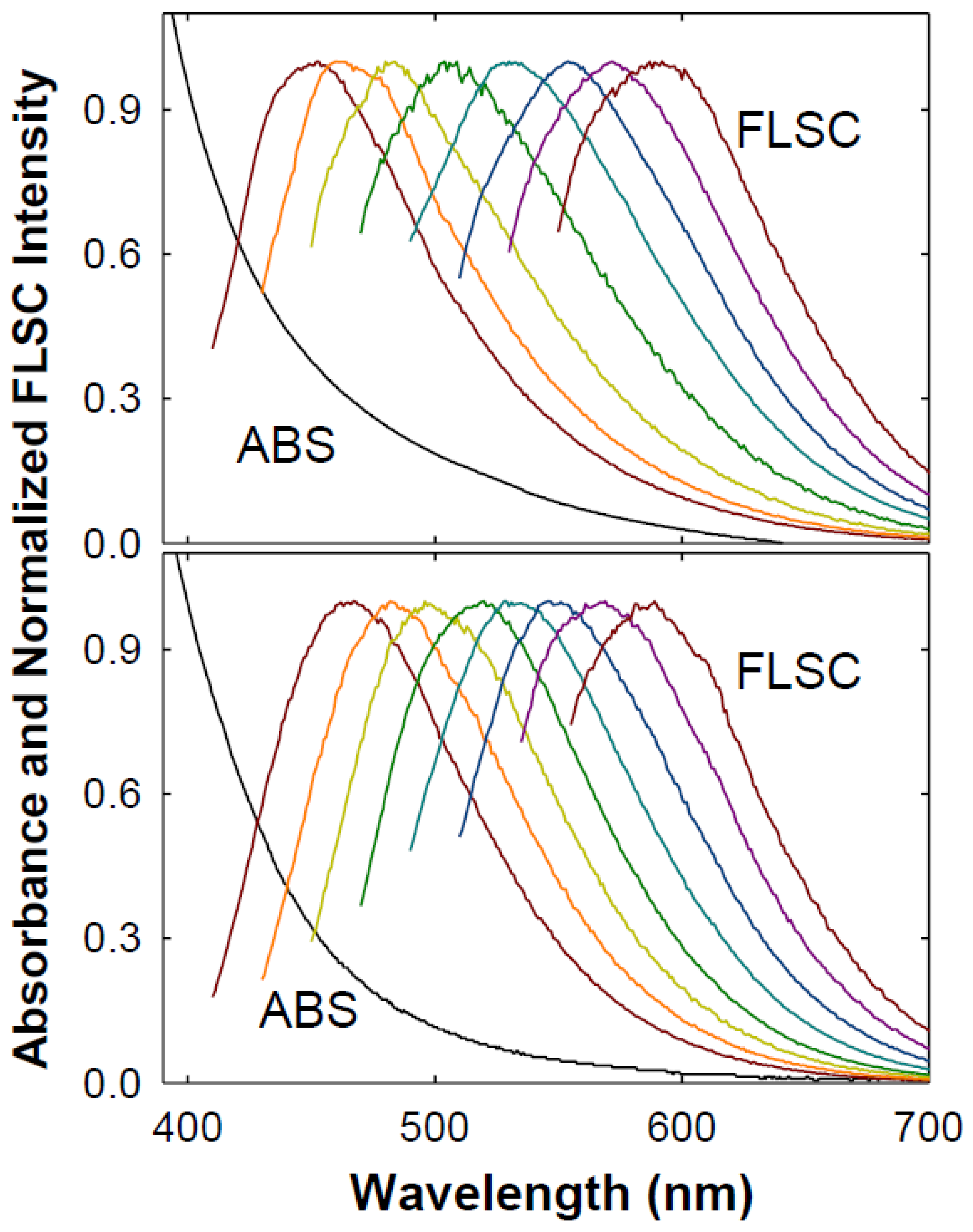
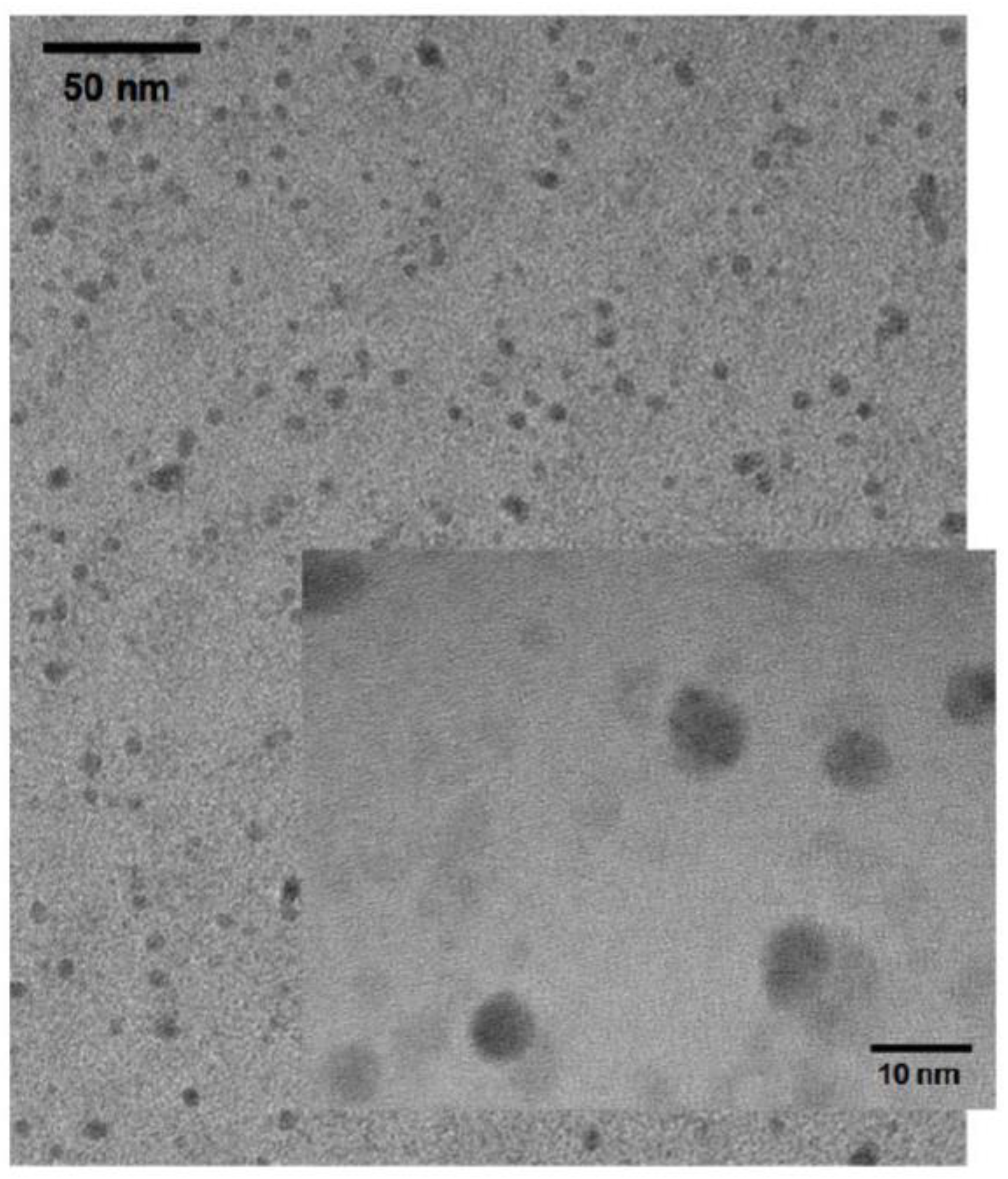
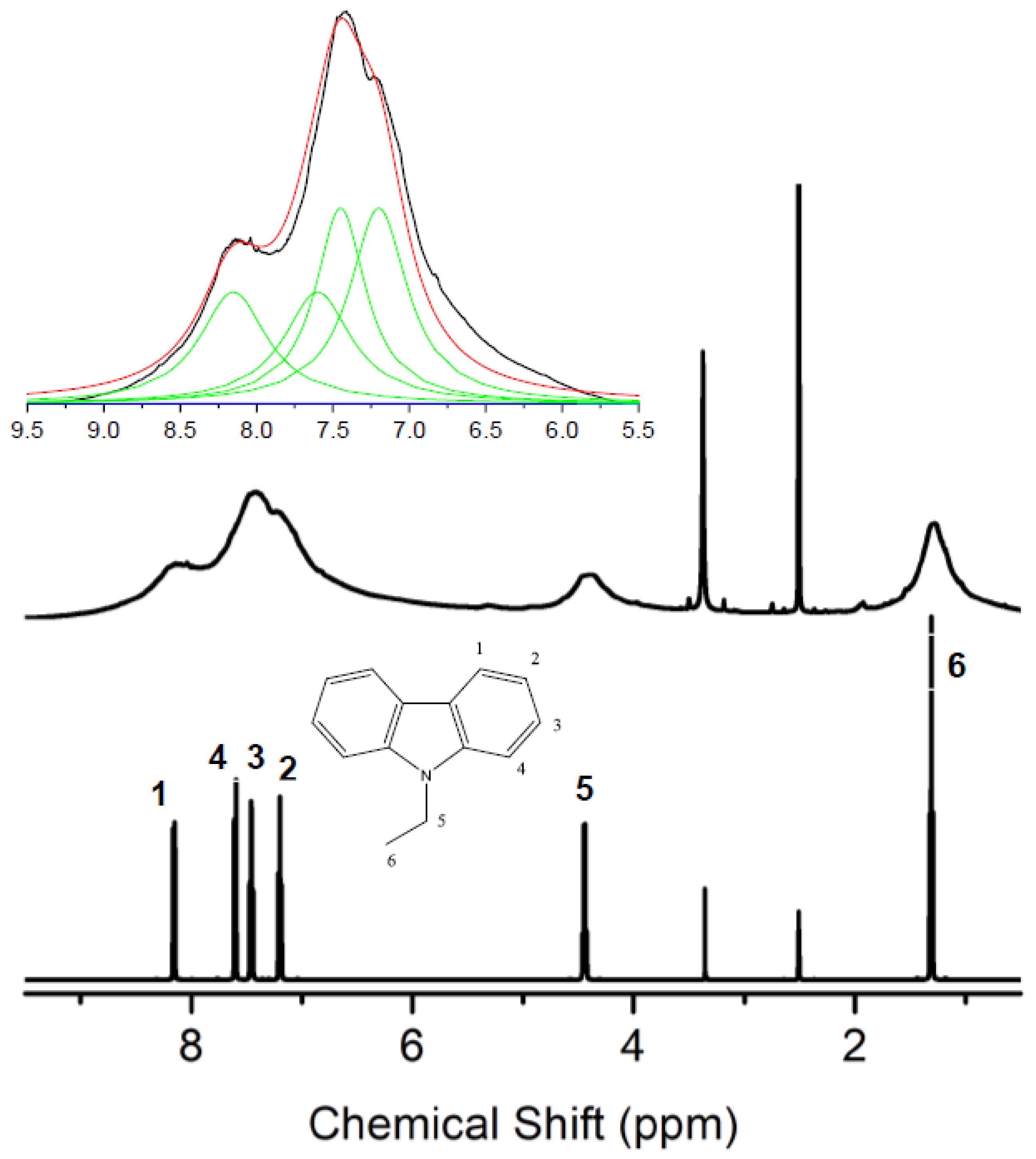
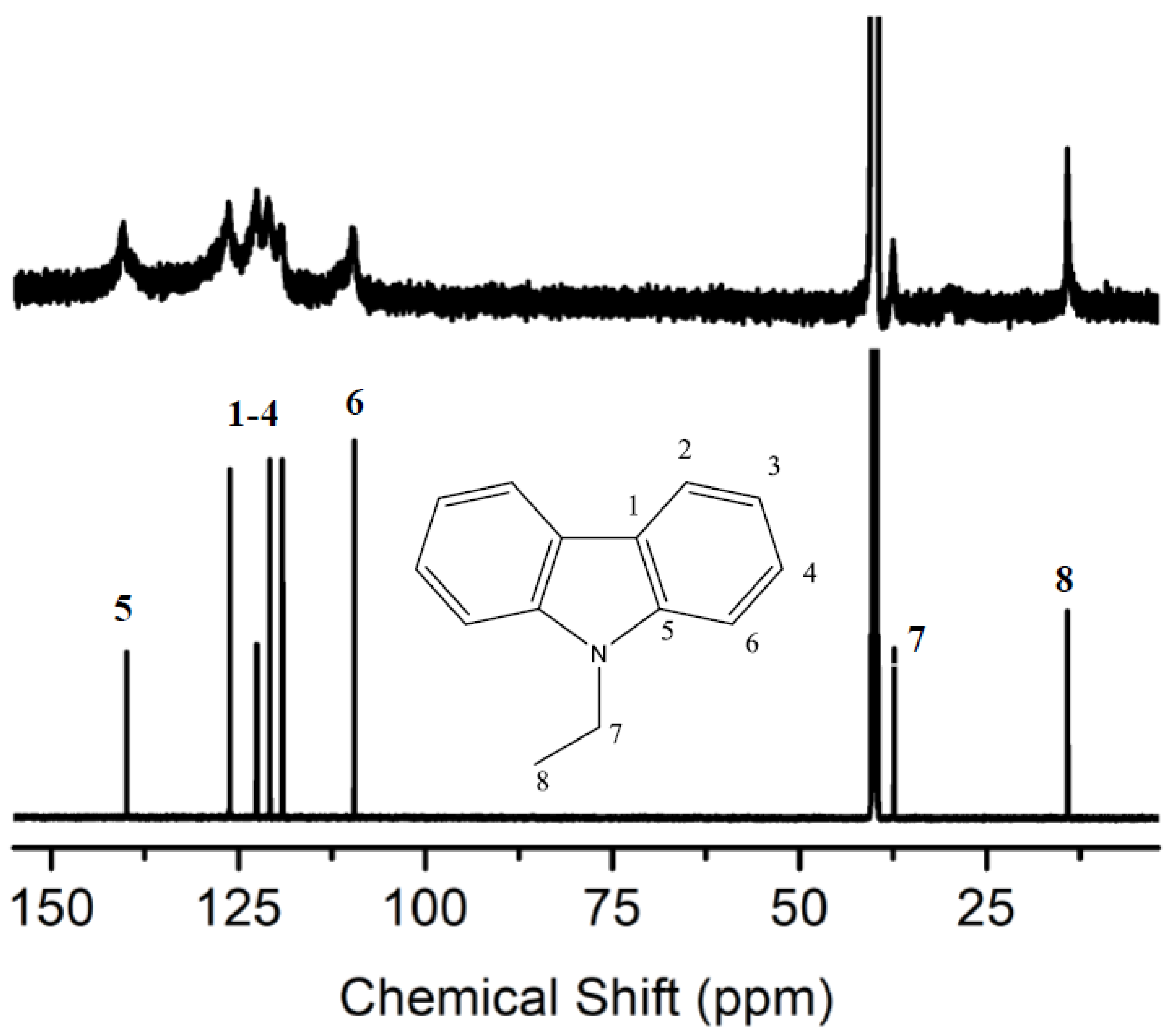
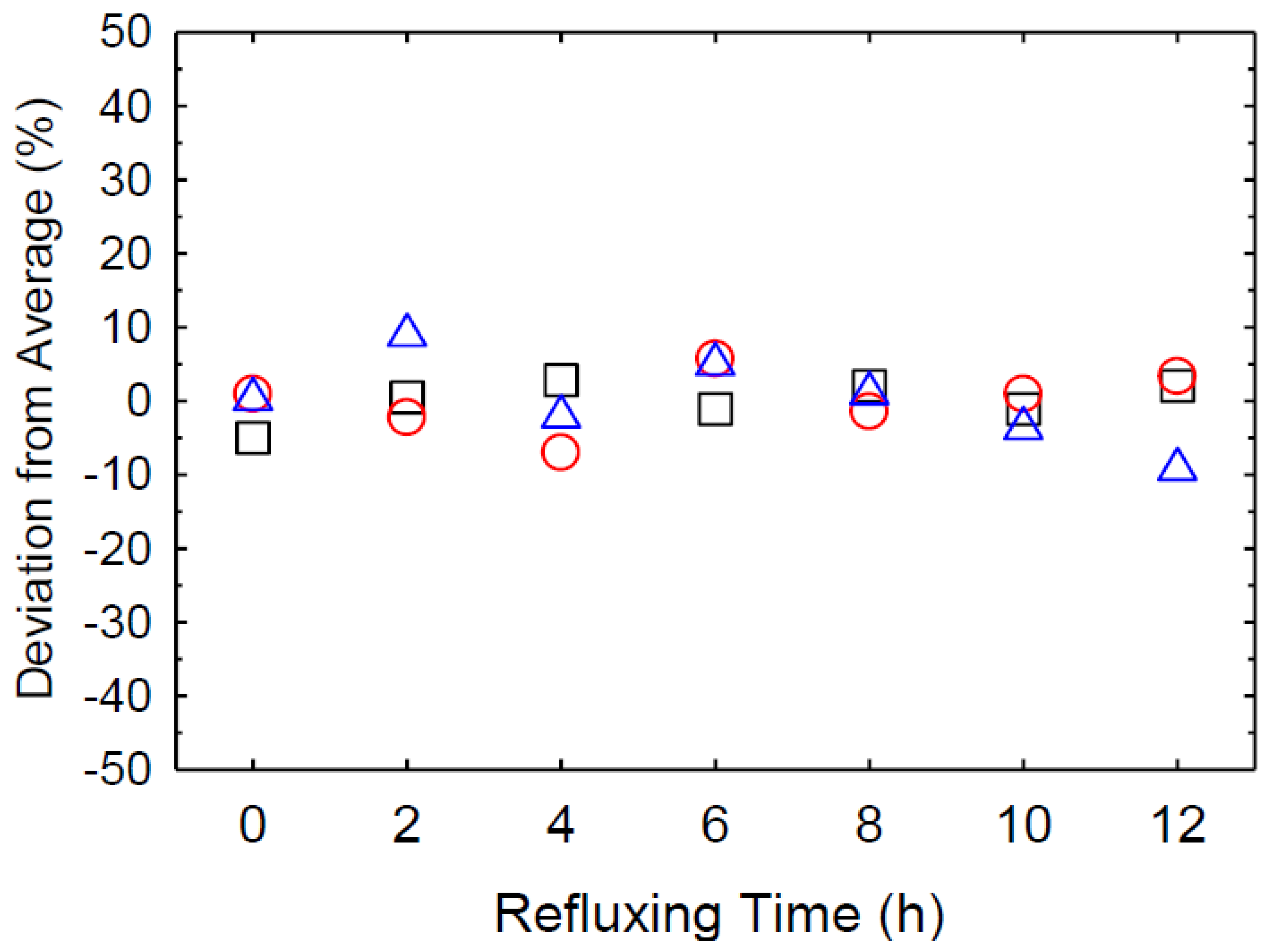
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-Sized Carbon Particles for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-P. Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles. U.S. Patent 7,829,772 B2, 9 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots—Exploring Carbon at Zero-Dimension; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.; Huang, Q.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Truly Fluorescent Excitation-Dependent Carbon Dots and Their Applications in Multicolor Cellular Imaging and Multidimensional Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7782–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Toward High-Efficient Red Emissive Carbon Dots: Facile Preparation, Unique Properties, and Applications as Multifunctional Theranostic Agents. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8659–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, Z.; Huang, P. Intense Multi-State Visible Absorption and Full-Color Luminescence of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Blue-Light-Excitable Solid-State-Lighting. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9027–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Ji, W.; Jing, P.; Han, D.; Liu, L.; Zeng, H.; Shen, D. Toward Efficient Orange Emissive Carbon Nanodots through Conjugated sp2-Domain Controlling and Surface Charges Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3516–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.-S.; Zhong, N.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Xiong, H.-M. Highly Efficient Red-Emitting Carbon Dots with Gram-Scale Yield for Bioimaging. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12635–12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lei, B.; Zhuang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Solid-State Carbon Dots with Red Fluorescence and Efficient Construction of Dual-Fluorescence Morphologies. Small 2017, 13, 1700075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoçak, B.B.; Liang, J.; Kavadiya, S.; Berezin, M.Y.; Biswas, P.; Ravi, N. Optimizing the Synthesis of Red-Emissive Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Use in Bioimaging. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 3682–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Shao, J.; Chi, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, G. Polyamine-Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots for Chemical Sensing. Carbon 2012, 50, 2810–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.; Bai, T.; Li, W.; Dai, L.; Liu, W. Highly Luminescent Carbon Nanodots by Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7955–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Ge, L.; Hou, X.; Ren, X.; Yang, L.; Bunker, C.E.; Overton, C.M.; Ping, W.; Sun, Y.-P. Evaluation of Commercial “Carbon Quantum Dots” Sample on Origins of Red Absorption and Emission Features. C 2019, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Ge, L.; Yang, L.; Patel, A.K.; Morgan, S.O.; Sun, Y.-P. On the Myth of “Red/Near-IR Carbon Quantum Dots” from Thermal Processing of Specific Colorless Organic Precursors. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4186–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Overton, C.M.; Hewitt, B.; Sun, Y.-P. Chemical Reactions in Thermal Carbonization Processing of Citric Acid-Urea Mixtures. Gen. Chem. 2021, 7, 210011. [Google Scholar]
- Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Dallas, P.; Giannelis, E.P. Formation Mechanism of Carbogenic Nanoparticles with Dual Photoluminescence Emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Schneider, J.; Ushakova, E.V.; Rogach, A.L. Influence of Molecular Fluorophores on the Research Field of Chemically Synthesized Carbon Dots. Nano Today 2018, 23, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Sharma, A.; Ghoshal, S.; Jain, S.; Hazra, M.K.; Nandi, C.K. Small Molecular Organic Nanocrystals Resemble Carbon Nanodots in Terms of Their Properties. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinterberger, V.; Damm, C.; Haines, P.; Guldi, D.M.; Peukert, W. Purification and Structural Elucidation of Carbon Dots by Column Chromatography. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8464–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, B.; Bogo, A.; Amato, F.; Ragazzon, G.; Prato, M. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Reveals Molecular Species in Carbon Nanodot Samples Disclosing Flaws. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Al Awak, M.M.; Tang, Y.; Twara, F.K.; Qian, H.J.; Sun, Y.-P. Modified Facile Synthesis for Quantitatively Fluorescent Carbon Dots. Carbon 2017, 122, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Pan, N.; Jin, J.; Wang, P.; LeCroy, G.E.; Liang, W.; Yang, L.; Teisl, L.R.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.-P. Systematic Comparison of Carbon Dots from Different Preparations—Consistent Optical Properties and Photoinduced Redox Characteristics in Visible Spectrum and Structural and Mechanistic Implications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 21667–21676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Fu, Y.; Bunker, C.E.; Hou, X.; Yang, L.; Msellek, H.; Zaharias, M.; Darby, J.P.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots Versus Nano-Carbon/Organic Hybrids—Dramatically Different Behaviors in Fluorescence Sensing of Metal Cations with Structural and Mechanistic Implications. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 2316–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Quimby, J.L.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon “Quantum” Dots for Bioapplications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, A.F.; Wang, P.; Cao, E.Y.; Ge, L.; Tang, Y.; Ferguson, I.S.; Abu Sweilem, F.S.; Petta, L.; Cannon, W.; Yang, L.; et al. Carbon Dots versus Nano-Carbon/Organic Hybrids—Divergence between Optical Properties and Photoinduced Antimicrobial Activities. C 2022, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Yang, S.-T.; Lu, F.; Meziani, M.J.; Tian, L.; Sun, K.W.; Bloodgood, M.A.; Sun, Y.-P. Bandgap-Like Strong Fluorescence in Functionalized Carbon Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5310–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCroy, G.E.; Sonkar, S.K.; Yang, F.; Veca, L.M.; Wang, P.; Tackett, K.N.; Yu, J.-J.; Vasile, E.; Qian, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Toward Structurally Defined Carbon Dots as Ultracompact Fluorescent Probes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4522–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; LeCroy, G.E.; Wang, P.; Liang, W.; Chen, J.; Fernando, K.S.; Bunker, C.E.; Qian, H.; Sun, Y.-P. Functionalization of Carbon Nanoparticles and Defunctionalization—Toward Structural and Mechanistic Elucidation of Carbon “Quantum” Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 25604–25611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ren, X.; LeCroy, G.E.; Song, J.; Wang, P.; Beckerle, L.; Bunker, C.E.; Xiong, Q.; Sun, Y.-P. Zero-Dimensional Carbon Allotropes—Carbon Nanoparticles versus Fullerenes in Functionalization by Electronic Polymers for Different Optical and Redox Properties. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5685–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Cao, L.; Liang, W.; Wang, P.; Bunker, C.E.; Yang, L.; Teisl, L.R.; Sun, Y.-P. Photoexcited State Properties of Poly (9-vinylcarbazole)-Functionalized Carbon Dots in Solution versus in Nanocomposite Films: Implications for Solid-State Optoelectronic Devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, P.; Bunker, C.E.; Coleman, M.; Teisl, L.R.; Cao, L.; Sun, Y.-P. A New Approach in Functionalization of Carbon Nanoparticles for Optoelectronically Relevant Carbon Dots and Beyond. Carbon 2019, 141, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhou, J.; Yao, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Wei, B.; Tan, R.; Li, Z. Multi-Shell Hollow Porous Carbon Nanoparticles with Excellent Microwave Absorption Properties. Carbon 2021, 172, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, B.L. Microwave Synthesis: Chemistry at the Speed of Light; CEM Publishing: Matthews, NC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, A.A.; Hutcheon, R.; Zhang, Z. Dielectric Properties of Quinoline, 4,6-Dimethyldibenzothiophene and Hexadecane as Model Compounds in the Upgrading of LCO. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Fernando, K.S.; LeCroy, G.E.; Maimaiti, H.; Harruff-Miller, B.A.; Lewis, W.K.; Bunker, C.E.; Hou, Z.-L.; Sun, Y.-P. Enhanced Fluorescence Properties of Carbon Dots in Polymer Films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 6967–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, H.; Kuwata, K.; Honma, H. Novel Interactions of Radical-Ion Pairs: Cidep Studies of Photoionization and Photooxidation Reactions. Res. Chem. Intermed. 1993, 19, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, M.; Maeda, K.; Murai, H. Delayed Fluorescence Detected Magnetic Resonance Study on the Spin Dynamics of the Transient Radical-Ion Pair Formed in the Photolysis of Carbazole in 2-Propanol. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 302, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.P.; Wang, T.; Sandanayaka, A.S.; Araki, Y.; Ito, O. Photoinduced Charge Separation and Charge Recombination in [60]Fullerene-Ethylcarbazole and [60]Fullerene-Triphenylamines in Polar Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 4713–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panich, A.M. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Nanodiamond Surface Modification. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 79, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, L. Spectral Line Shapes: Gaussian and Lorentzian Functions in Magnetic Resonance. J. Chem. Educ. 1967, 44, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, J.E.; Guo, Z.; Carroll, D.L.; Sun, Y.-P. Strong Luminescence of Solubilized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; i Zubiri, M.R.; Vigolo, B.; Dossot, M.; Fort, Y.; Ehrhardt, J.J.; McRae, E. Efficient Microwave-Assisted Radical Functionalization of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. Carbon 2007, 45, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Li, R.K.Y. A Facile, Green, and Tunable Method to Functionalize Carbon Nanotubes with Water-Soluble Azo Initiators by One-Step Free Radical Addition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3286–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Liang, W.; Seilkop, A.; Monica Veca, L.; Sun, Y.-P.; Bunker, C.E. Carbon Dots for Energy Conversion Applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 220903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhou, B.; Martin, R.B.; Henbest, K.B.; Harruff, B.A.; Riggs, J.E.; Guo, Z.-X.; Allard, L.F.; Sun, Y.-P. Visible Luminescence of Carbon Nanotubes and Dependence on Functionalization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 14779–14782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Bunker, C.E.; Meziani, M.J.; Lu, F.; Guliants, E.A.; Sun, Y.-P. Fluorescence Decoration of Defects in Carbon Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 20941–20946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, J.B. Photophysics of Aromatic Molecules; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, W.; Singh, B.; Cao, E.Y.; Bunker, C.E.; Cannon, W.; Petta, L.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Cao, L.; Scorzari, A.; et al. Stable Carbon Dots from Microwave-Heated Carbon Nanoparticles Generating Organic Radicals for In Situ Additions. C 2023, 9, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010005
Liang W, Singh B, Cao EY, Bunker CE, Cannon W, Petta L, Wang P, Yang L, Cao L, Scorzari A, et al. Stable Carbon Dots from Microwave-Heated Carbon Nanoparticles Generating Organic Radicals for In Situ Additions. C. 2023; 9(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Weixiong, Buta Singh, Elton Y. Cao, Christopher E. Bunker, William Cannon, Lauren Petta, Ping Wang, Liju Yang, Li Cao, Annalise Scorzari, and et al. 2023. "Stable Carbon Dots from Microwave-Heated Carbon Nanoparticles Generating Organic Radicals for In Situ Additions" C 9, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010005
APA StyleLiang, W., Singh, B., Cao, E. Y., Bunker, C. E., Cannon, W., Petta, L., Wang, P., Yang, L., Cao, L., Scorzari, A., & Sun, Y.-P. (2023). Stable Carbon Dots from Microwave-Heated Carbon Nanoparticles Generating Organic Radicals for In Situ Additions. C, 9(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9010005







