Silica Precursor Effect on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Cobalt Incorportated MCM-41 Catalysts and Their Performance towards Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Silica Characterization
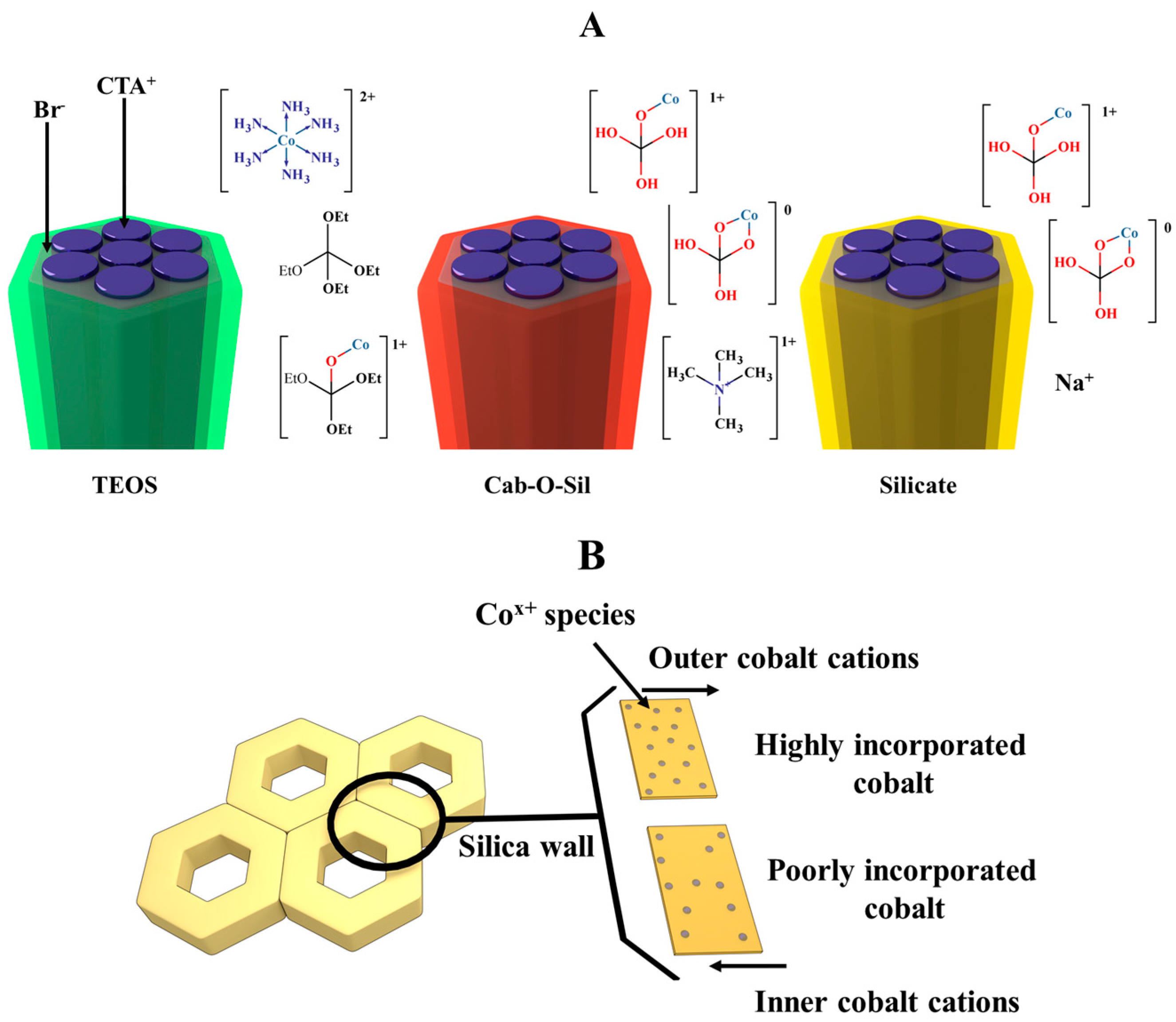
2.2. Catalysts Characterization
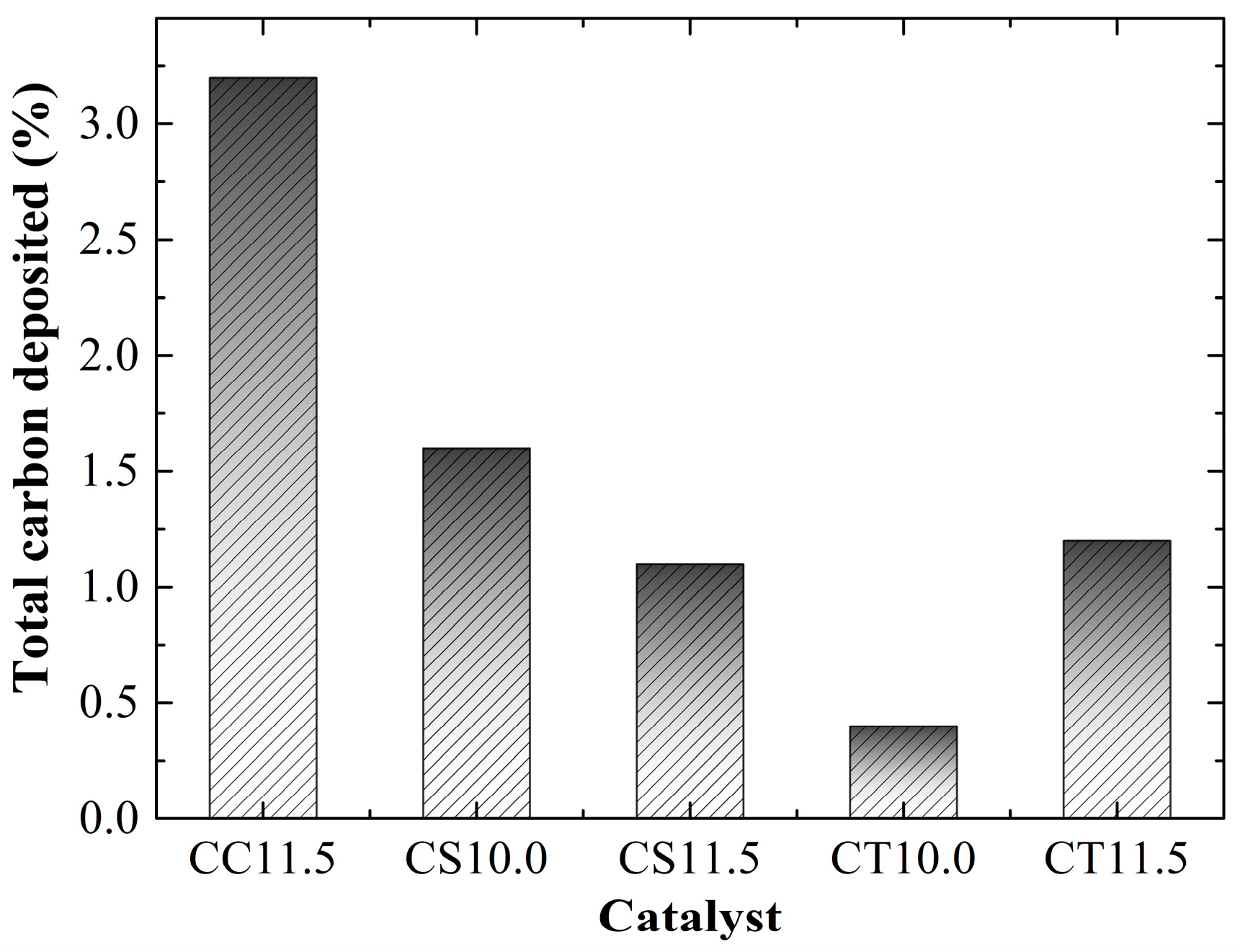
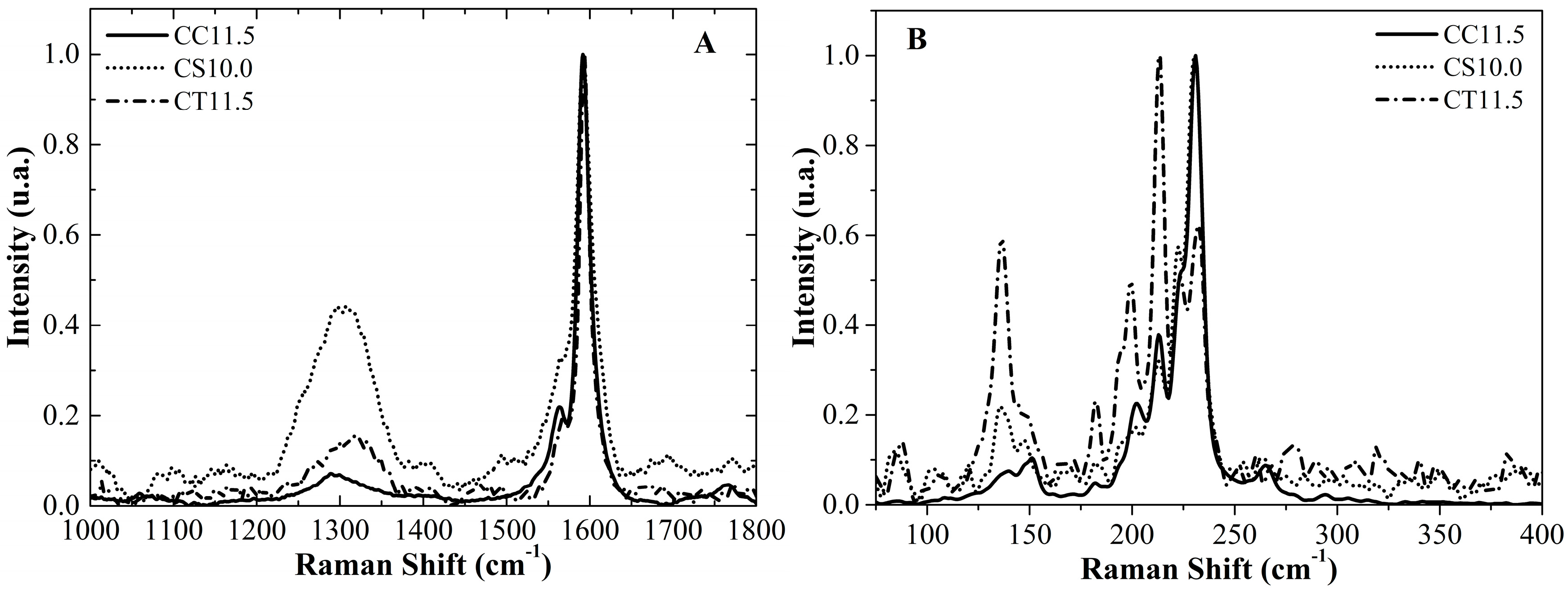
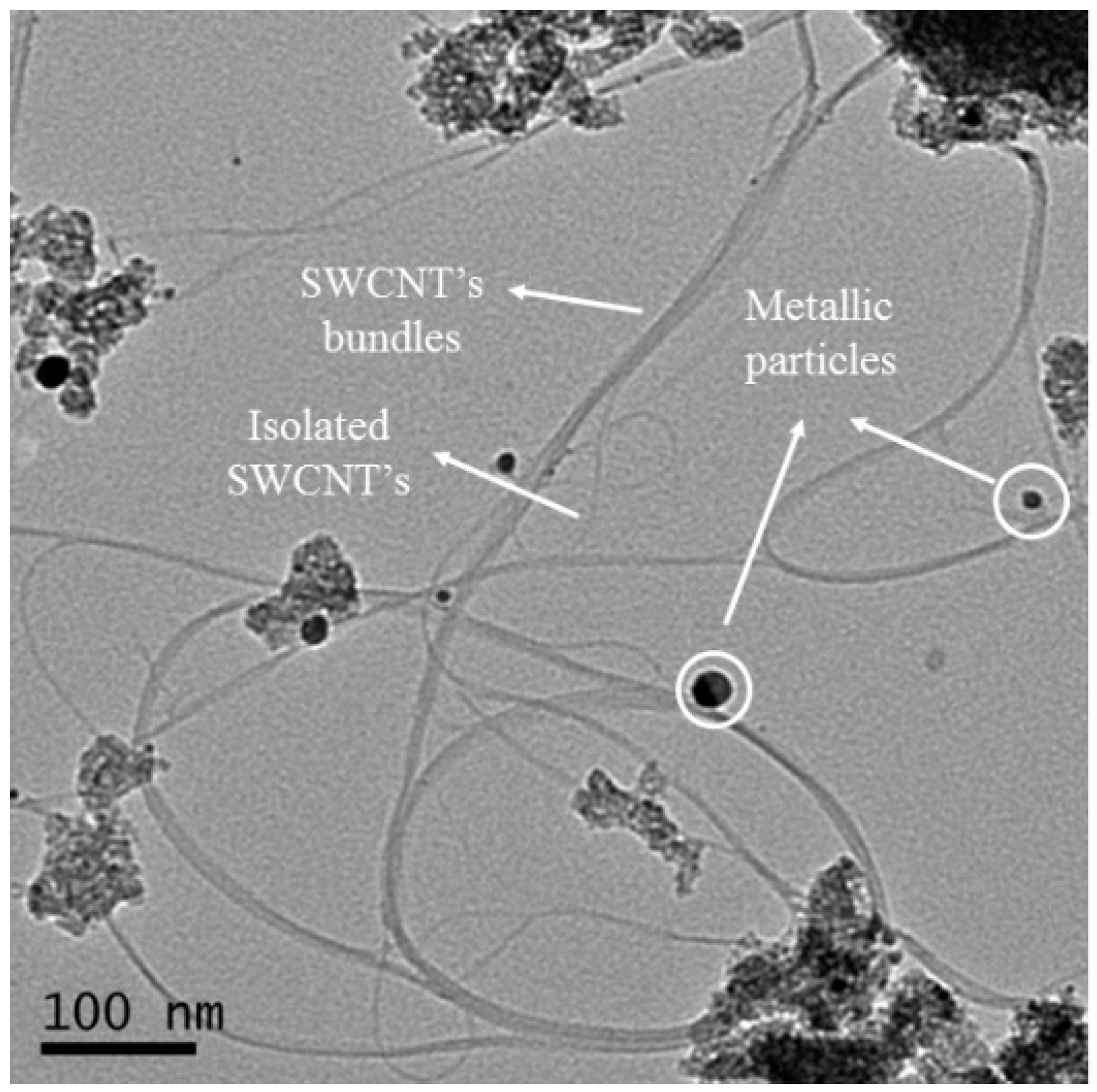
2.3. Catalyst Performance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Co-MCM-41 Synthesis Using Colloidal Silica Cab-O-Sil as the Precursor (CC11.5)
3.2. Co-MCM-41 Synthesis Using Sodium Silicate as the Precursor
3.3. Co-MCM-41 Synthesis Using TEOS as the Precursor
3.4. MCM-41 Silica Synthesis
3.5. Catalytic Performance Evaluation
3.6. Characterization of the Co-MCM-41 Catalysts
3.7. CCVD Deposited Products Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donohue, M.; Aranovich, G. Classification of Gibbs adsorption isotherms. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 76–77, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cao, K.; Yang, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Highly dispersed nickel loaded on mesoporous silica: One-spot synthesis strategy and high performance as catalysts for methane reforming with carbon dioxide. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Kosugi, Y. Highly Selective Conversion of Ethene to Propene and Butenes on Nickel Ion-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Catalysts Highly Selective Conversion of Ethene to Propene and Butenes on Nickel Ion-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Catalysts. Society 2007, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, M.; Pirovano, C.; Ravasio, N.; Lázaro, B.; Fraile, J.M.; Mayoral, J.A.; Coq, B.; Galarneau, A.; Lazaro, B.; Fraile, J.M.; Mayoral, J.A.; et al. The use of H2O2 over titanium-grafted mesoporous silica catalysts: A step further towards sustainable epoxidation. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Bhaumik, A. Soft templating strategies for the synthesis of mesoporous materials: Inorganic, organic-inorganic hybrid and purely organic solids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 189–190, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katok, K.V.; Tertykh, V.A.; Brichka, S.Y.; Prikhod’ko, G.P. Pyrolytic synthesis of carbon nanostructures on Ni, Co, Fe/MCM-41 catalysts. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 96, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ciuparu, D.; Yang, Y.; Lim, S.; Wang, C.; Haller, G.L.; Pfefferle, L.D. Single-wall carbon nanotube synthesis by CO disproportionation on nickel-incorporated MCM-41. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, S476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.-P.; Zein, S.H.S.; Mohamed, A.R. Preparation of carbon nanotubes over cobalt-containing catalysts via catalytic decomposition of methane. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferle, L.; Haller, G.; Chen, Y.; Ciuparu, D.; Lim, S.; Yang, Y.H. Mechanism study on cobalt cluster size control in Co-MCM-41 during single wall carbon nanotubes synthesis by Co disproportionation. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 229, 15565–15571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoican Loebick, C.; Abanulo, D.; Majewska, M.; Haller, G.L.; Pfefferle, L.D. Effect of reaction temperature in the selective synthesis of single wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT) on a bimetallic CoCr-MCM-41 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 374, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizokawa, T.; Tjeng, L.H.; Steeneken, P.G.; Brookes, N.B.; Tsukada, I.; Yamamoto, T.; Uchinokura, K.; Burnus, T.; Hu, Z.; Hsieh, H.H.; et al. Relationship between the Structure/Composition of Co–Mo Catalysts and Their Ability to Produce Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by CO Disproportionation. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 108, 16201–16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couteau, E.; Hernadi, K.; Seo, J.W.; Thiên-Nga, L.; Mikó, C.; Gaál, R.; Forró, L. CVD synthesis of high-purity multiwalled carbon nanotubes using CaCO3 catalyst support for large-scale production. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 378, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, M.; Cheng, R.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Mo, Y. Effect of hydroxyl radical on the structure of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Synth. Met. 2005, 155, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpranot, J.; Kaewkun, S.; Praserthdam, P.; Goodwin, J.G. Effect of cobalt precursors on the dispersion of cobalt on MCM-41. Catal. Lett. 2003, 91, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigney, A.; Coquay, P.; Flahaut, E.; Vandenberghe, R.E.; De Grave, E.; Laurent, C. A Study of the Formation of Single- and Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by a CVD Method. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 9699–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuparu, D.; Chen, Y.; Lim, S.; Haller, G.L.; Pfefferle, L. Uniform-diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes catalytically grown in cobalt-incorporated MCM-41. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ciuparu, D.; Lim, S.; Yang, Y.; Haller, G.L.; Pfefferle, L. Synthesis of uniform diameter single-wall carbon nanotubes in Co-MCM-41: Effects of the catalyst prereduction and nanotube growth temperatures. J. Catal. 2004, 225, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, L.F.; Echeverri, M.; López, B.L. Reinforcement of polyamide 6 with nanoparticles. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 258, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Ryoo, R.; Ko, C.H. Determination of Pore Size and Pore Wall Structure of MCM-41 by Using Nitrogen Adsorption, Transmission Electron Microscopy, and X-ray Diffraction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amama, P.B.; Lim, S.; Ciuparu, D.; Pfefferle, L.; Haller, G.L. Hydrothermal synthesis of MCM-41 using different ratios of colloidal and soluble silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 81, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghampson, I.T.; Newman, C.; Kong, L.; Pier, E.; Hurley, K.D.; Pollock, R.A.; Walsh, B.R.; Goundie, B.; Wright, J.; Wheeler, M.C.; et al. Effects of pore diameter on particle size, phase, and turnover frequency in mesoporous silica supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 388, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegtlin, A.C.; Matijasic, A.; Patarin, J.; Sauerland, C.; Grillet, Y.; Huve, L. Room-temperature synthesis of silicate mesoporous MCM-41-type materials: Influence of the synthesis pH on the porosity of the materials obtained. Microporous Mater. 1997, 10, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, M.; Unger, K.K.; Matsumoto, A.; Tsutsumi, K. Novel pathways for the preparation of mesoporous MCM-41 materials: Control of porosity and morphology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrlstad, T.; Glomm, W.R.; Rønning, M.; Dathe, H.; Lercher, J.A.; Stcker, M.; Sjblom, J.; Vrålstad, T.; Sjo, J. Spectroscopic Characterization of Cobalt-Containing Mesoporous Materials Spectroscopic Characterization of Cobalt-Containing Mesoporous Materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 4, 5386–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, J.E.; Resasco, D.E. Loss of single-walled carbon nanotubes selectivity by disruption of the Co-Mo interaction in the catalyst. J. Catal. 2004, 221, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Yang, Y.; Ciuparu, D.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Pfefferle, L.; Haller, G.L. The effect of synthesis solution pH on the physicochemical properties of Co substituted MCM-41. Top. Catal. 2005, 34, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Ciuparu, D.; Pfefferle, L.; Haller, G.L. Evidence for anchoring and partial occlusion of metallic clusters on the pore walls of MCM-41 and effect on the stability of the metallic clusters. Catal. Today 2007, 123, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, T.; Epron, F. Characterization methods of carbon nanotubes: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2005, 119, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Ciuparu, D.; Pak, C.; Dobek, F.; Chen, Y.; Harding, D.; Pfefferle, L.; Haller, G. Synthesis and Characterization of Highly Ordered Co−MCM-41 for Production of Aligned Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWNT). J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 11048–11056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Ciuparu, D.; Yang, Y.; Du, G.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Haller, G.L. Improved synthesis of highly ordered Co-MCM-41. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 101, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Ciupani, D.; Chen, Y.; Pfefferle, L.; Haller, G.L. Effect of Co-MCM-41 conversion to cobalt silicate for catalytic growth of single wall carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 20095–20101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

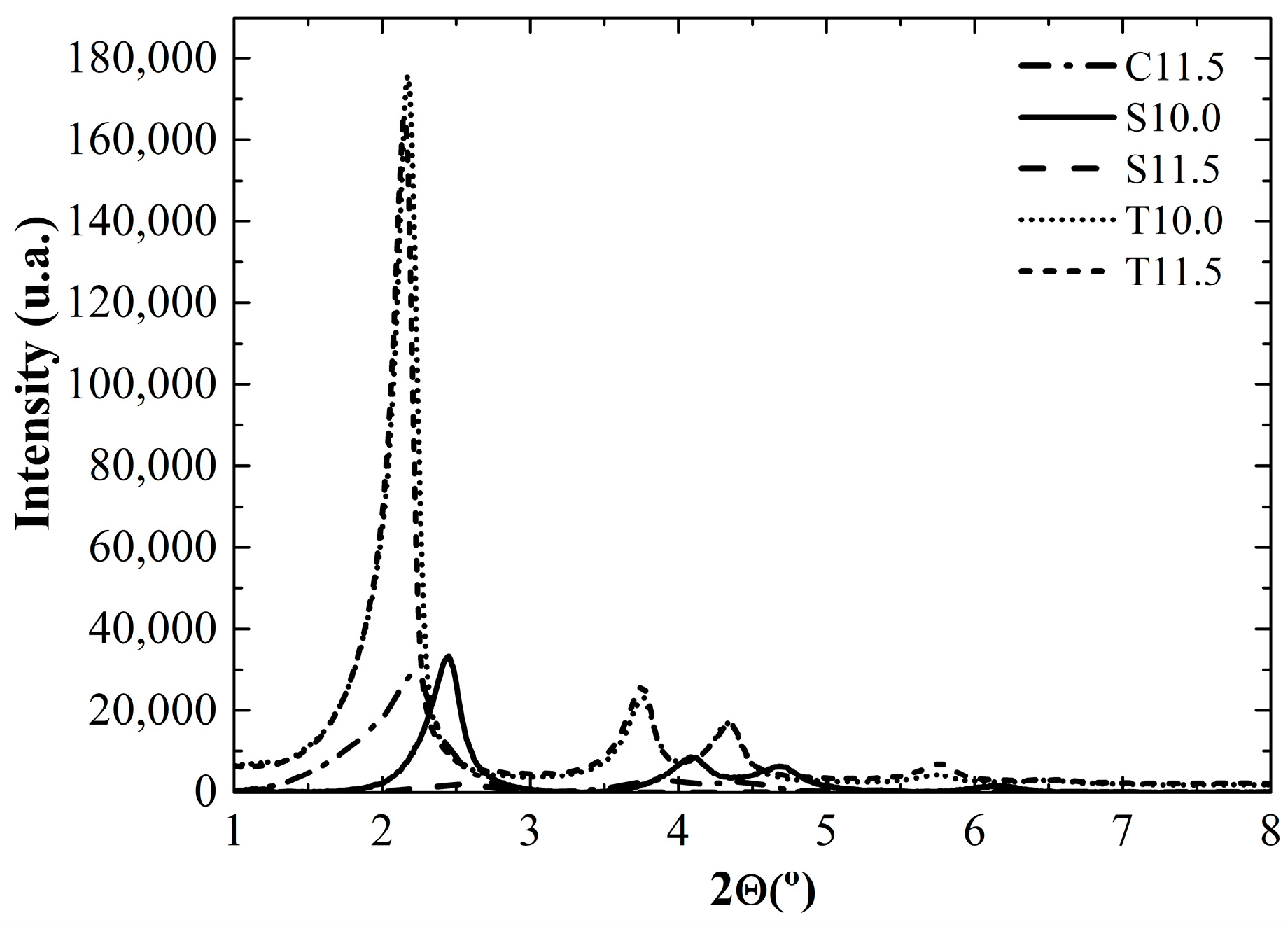

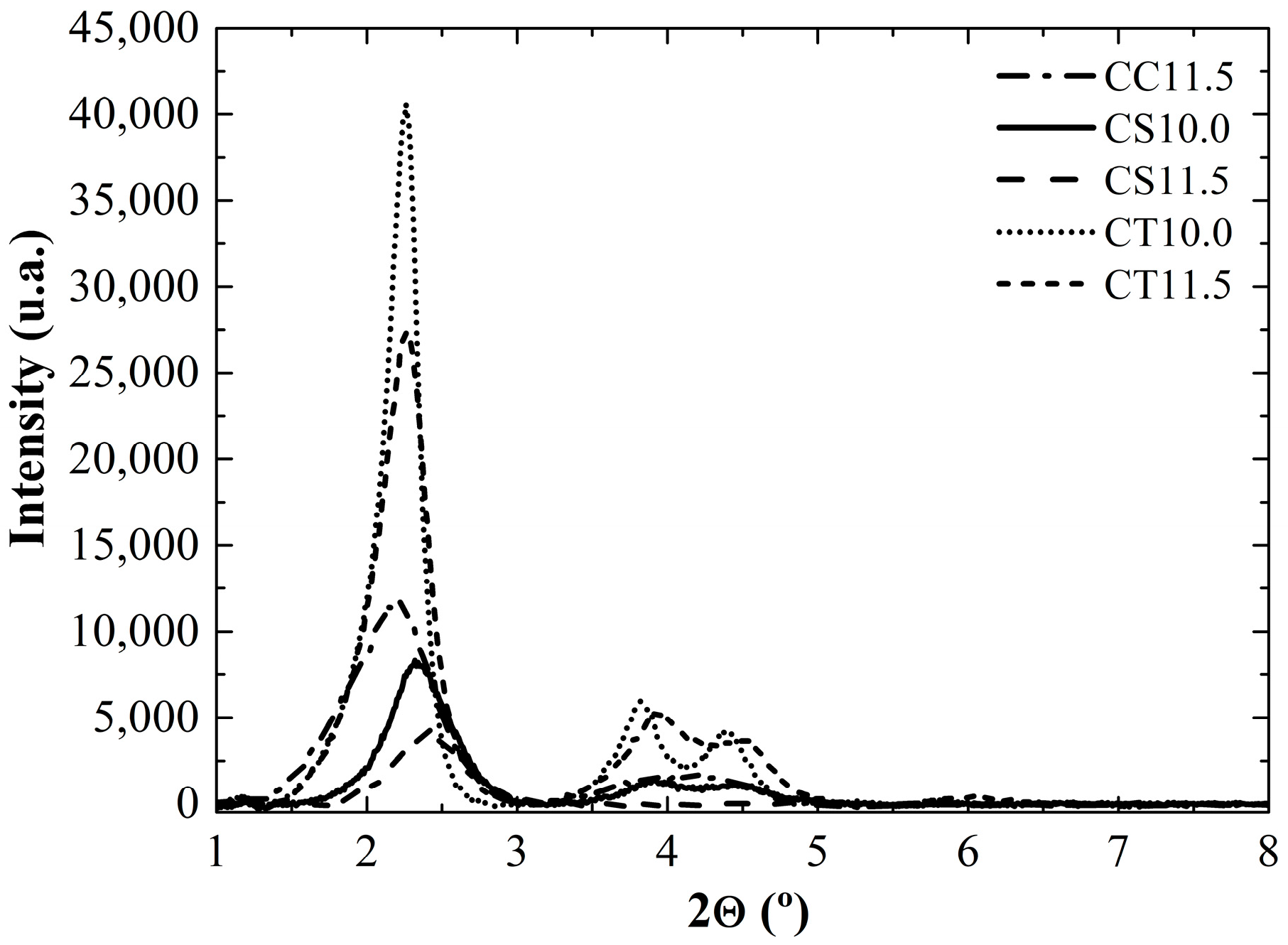
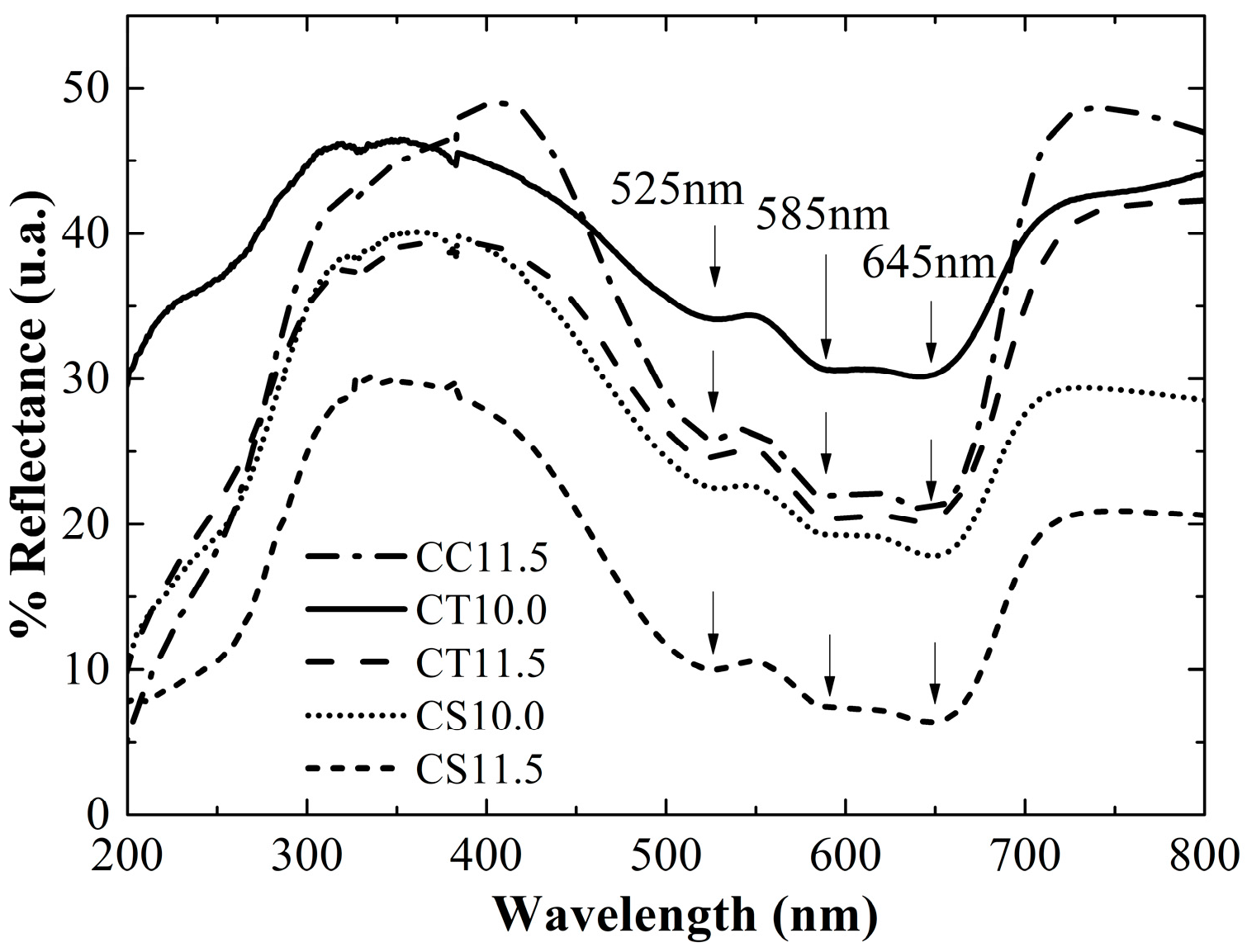

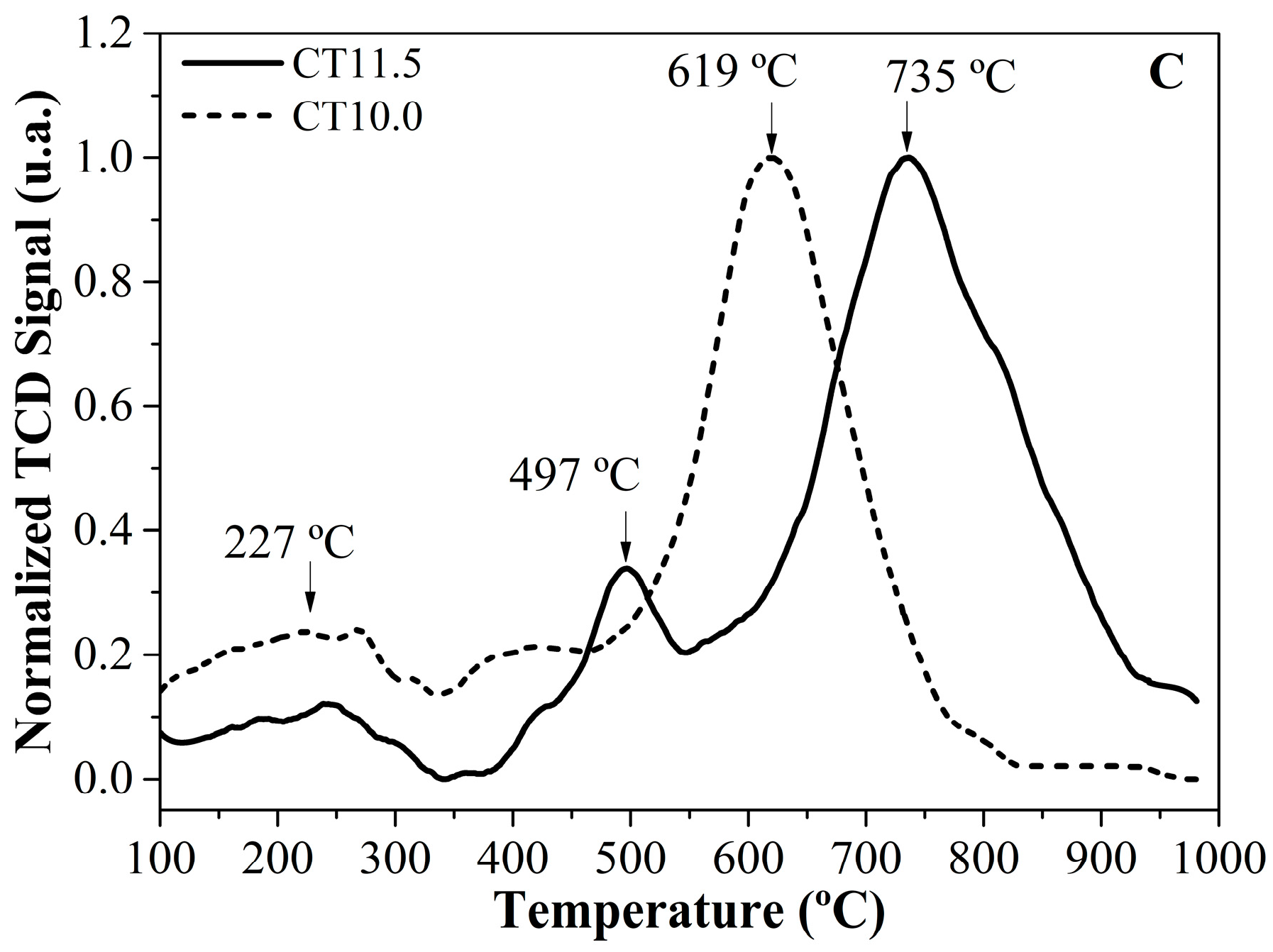

| Silica | SA (m2g−1) | Dp (nm) | DP FWMH (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C11.5 | 1239.6 | 2.3 | 0.48 |
| S10.0 | 1080.2 | 2.5 | 0.25 |
| T10.0 | 902.3 | 2.6 | 0.16 |
| T11.5 | 899.6 | 2.5 | 0.16 |
| Silica | Dp (nm) | FWMH (nm) | 2Θ (°) | d100 (nm) | a0 (nm) | Wt (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11.5 | 2.3 | 0.48 | 2.22 | 3.97 | 4.58 | 2.3 |
| S10.0 | 2.51 | 0.25 | 2.45 | 3.6 | 4.16 | 1.7 |
| T10.0 | 2.58 | 0.16 | 2.17 | 4.06 | 4.69 | 2.1 |
| T11.5 | 2.49 | 0.16 | 2.15 | 4.10 | 4.74 | 2.2 |
| Catalyst | Catalyst SA (m2g−1) | ∆SA (m2g−1) | Silica Dp (nm) | Catalyst Dp (nm) | Co (%) # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC11.5 | 1024.4 | 215.2 | 2.29 | 2.51 | 2.02 |
| CS10.0 | 957.1 | 123.1 | 2.49 | 2.46 | 1.66 |
| CS11.5 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.90 |
| CT10.0 | 810.9 | 91.4 | 2.55 | 2.41 | 1.99 |
| CT11.5 | 990.2 | -90.6 | 2.45 | 2.39 | 2.18 |
| Radial Breathing Mode (RBM) Peaks of the SWNCT Deposited on CC11.5 | ||||
| Peak Number | Raman Shift (cm−1) | Tube Diameter (nm) | Peak Area (cm−1. Intensity) | Population (%) |
| 1 | 138.76 | 1.8 | 1.82 | 7.6 |
| 2 | 150.67 | 1.7 | 0.82 | 3.4 |
| 3 | 201.87 | 1.2 | 3.06 | 12.8 |
| 4 | 212.87 | 1.2 | 2.53 | 10.6 |
| 5 | 223.10 | 1.1 | 3.22 | 13.4 |
| 6 | 231.00 | 1.1 | 11.45 | 47.7 |
| 7 | 265.01 | 0.9 | 1.08 | 4.5 |
| RBM peaks of the SWNCT deposited on CS10.0 | ||||
| Peak number | Raman shift (cm−1) | Tube diameter (nm) | Peak area (cm−1. Intensity) | Population (%) |
| 1 | 136.86 | 1.8 | 2.10 | 9.9 |
| 2 | 147.39 | 1.7 | 0.69 | 3.2 |
| 3 | 199.39 | 1.2 | 1.48 | 7.0 |
| 4 | 212.05 | 1.2 | 2.14 | 10.0 |
| 5 | 222.00 | 1.1 | 2.96 | 13.9 |
| 6 | 230.53 | 1.1 | 11.90 | 56.0 |
| RBM peaks of the SWNCT deposited on CT11.5 | ||||
| Peak number | Raman shift (cm−1) | Tube diameter (nm) | Peak area (cm−1. Intensity) | Population (%) |
| 1 | 136.34 | 1.9 | 6.59 | 22.2 |
| 2 | 148.66 | 1.7 | 0.97 | 3.3 |
| 3 | 182.19 | 1.4 | 0.76 | 2.6 |
| 4 | 193.68 | 1.3 | 0.99 | 3.3 |
| 5 | 199.24 | 1.2 | 3.53 | 11.9 |
| 6 | 213.13 | 1.2 | 8.10 | 27.3 |
| 7 | 223.75 | 1.1 | 2.96 | 10.0 |
| 8 | 232.00 | 1.1 | 5.79 | 19.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez Rodríguez, F.; Giraldo, L.F.; Lopez, B.L. Silica Precursor Effect on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Cobalt Incorportated MCM-41 Catalysts and Their Performance towards Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes. C 2018, 4, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010016
Ramírez Rodríguez F, Giraldo LF, Lopez BL. Silica Precursor Effect on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Cobalt Incorportated MCM-41 Catalysts and Their Performance towards Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes. C. 2018; 4(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez Rodríguez, Frank, Luis Fernando Giraldo, and Betty Lucy Lopez. 2018. "Silica Precursor Effect on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Cobalt Incorportated MCM-41 Catalysts and Their Performance towards Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes" C 4, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010016
APA StyleRamírez Rodríguez, F., Giraldo, L. F., & Lopez, B. L. (2018). Silica Precursor Effect on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Cobalt Incorportated MCM-41 Catalysts and Their Performance towards Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes. C, 4(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010016





