Mechanistic Evaluation of Pb(II) Adsorption on Magnetic Activated Carbon/Fe3O4 Composites: Influence of Hydrothermal and Ultrasonic Synthesis Routes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Activated Carbon
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
2.3. Synthesis of AC/Fe3O4 Composites
2.3.1. Ultrasonication-Assisted Synthesis of us-AC/Fe3O4 Composite
2.3.2. Hydrothermal Synthesis of h-AC/Fe3O4 Composite
2.4. Adsorption Performance Test
2.5. Determination of the Point of Zero Charge
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Activated carbon |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| BC | Biochar |
| BJH | Barrett–Joyner–Halenda method |
| C | Carbon |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| ES | Eggshell/starch |
| SEM | Field-emission scanning electron microscopy |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| HAP | Hydroxyapatite |
| JCPDS | Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards |
| NC | Nanoclay |
| PANi | Polyaniline |
| PZC | The point of zero charge |
| SCCM | Standard Cubic Centimeter per Minute |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- World Health Organization. Arsenic. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Ng, J.C.; Wang, J.; Shraim, A. A Global Health Problem Caused by Arsenic from Natural Sources. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Lead Poisoning and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lead-poisoning-and-health (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Bjørklund, G.; Chirumbolo, S.; Dadar, M.; Pivina, L.; Lindh, U.; Butnariu, M.; Aaseth, J. Mercury Exposure and Its Effects on Fertility and Pregnancy Outcome. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, W.; Bashir, H. Managing the Unintended Consequences of Radical Sustainability Innovations: The Case of Cat-astrophic Failure of Leaded Gasoline Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, J.M.; Andreu, C.M.; Merino, S.; Herrero, M.A.; Vázquez, E.; Sánchez-Migallón, A.M.; Castañeda, G. Few-Layer Graphene-Hybrid Sulfonate Hydrogels for High-Efficient Adsorption of Heavy Metal (Pb2+, Ni2+, Cd2+) in Water Treatment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 292, 117934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taharia, M.; Dey, D.; Das, K.; Sukul, U.; Chen, J.-S.; Banerjee, P.; Dey, G.; Sharma, R.K.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y. Microbial Induced Carbonate Precipitation for Remediation of Heavy Metals, Ions and Radioactive Elements: A Comprehensive Exploration of Prospective Applications in Water and Soil Treatment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Patel, A.R.; Pandey, A.; Hait, M.; Patra, G.K. Assessment of Heavy Metal Ion Toxicity in Wastewater: A Com-prehensive Review. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2025, 585, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, H.; Kanjariya, P.; Ballal, S.; Panigrahi, R.; Ariffin, I.A.; Tantawi, D.; Abosaoda, M.K.; Nathiya, D.; Jayabalan, K.; Chauhan, A.S. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Magnetic Nanocomposites for the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1345, 143019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.-H.; Xiao, L.-P.; Wang, Q.; Fu, X.; Xu, Q.; He, H.; Qin, C.; Zheng, M.; Sánchez, J.; Sun, R.-C. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Wastewater and Reuse as a Hydrogenolysis Catalyst: Multistage Application of Lignin-Based Adsorbent. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 228, 120919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, K.; Thankachan, D.; Shakya, K.; Mehrotra, N.; Nimish, C.S.; Verma, V. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions (Pb2+, Cu2+, Cr3+, and Cd2+) from Multimetal Simulated Wastewater Using 3-Aminopropyl Triethoxysilane Grafted Agar Porous Cryogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, Q.; Yu, W. The Improvement of Heavy Metals Removal by Wood Membrane in Drinking Water Treatment: Comparison with Polymer Membrane and Associated Mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, A.; Bharath, G.; Patah, M.F.A.; AlMohamadi, H.; Banat, F.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Incorporation of Transition Met-al-Oxide on 3D Porous Carbon Network for Electrochemical Water Desalination and Heavy-Metals Removal. Electrochim. Acta 2025, 528, 146337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandehali, S.; Moghadassi, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Parvizian, F.; Ghanbari, D.; Rahimizadeh, R.; Ebrahimi, A.A. Smart Ion Exchange Membrane with High Impact in Heavy Metals Separation Prepared by Electrospinning Process with Ultra-sensitive Responsiveness for Water Treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 205, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Napoli, I.E.; Zanetti, E.M.; Fragomeni, G.; Giuzio, E.; Audenino, A.L.; Catapano, G. Transport Modeling of Convec-tion-Enhanced Hollow Fiber Membrane Bioreactors for Therapeutic Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Peng, Y.; Yang, W. Modification Strategies for Metal-Organic Frameworks Targeting at Membrane-Based Gas Separations. Green. Chem. Eng. 2021, 2, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Moehring, N.K.; Idrobo, J.C.; Ivanov, I.N.; Kidambi, P.R. Scalable Synthesis of Nanoporous Atomically Thin Graphene Membranes for Dialysis and Molecular Separations via Facile Isopropanol-Assisted Hot Lamination. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2825–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Mamrol, N.; Yang, X.; Gao, C.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Metal-Organic Framework Based Mem-branes for Selective Separation of Target Ions. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 634, 119407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhol, P.; Yadav, S.; Altaee, A.; Saxena, M.; Misra, P.K.; Samal, A.K. Graphene-Based Membranes for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 3274–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarighat, M.A.; Barghandan, F.; Hashemifard, S.A.; Abdi, G. Development and Characterization of PAN/GO-Tyrosine Hollow Fiber Membranes for Enhanced Heavy Metal Adsorption and SPME-Spectrophotometric Detection. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 3721–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.-X.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Xu, Z.-L.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Gao, P.; Xu, S.-J. Thin-Film Nanocomposite NF Membrane with GO on Macroporous Hollow Fiber Ceramic Substrate for Efficient Heavy Metals Removal. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Tang, D.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Q. Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polyacrylonitrile-Chitosan Electro-Spun Nanofibrous Membrane as Recyclable Adsorbent with Selective Heavy Metal Removal and Antibacterial Fouling in Water Treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, H.A.; Sebak, M.A.; Aladim, A.K.; Shahat, M.A. Innovative Experimental and Theoretical Strategies for Sustain-able Heavy Metal Ion Removal Using chitosan@TiO2 Composites Functionalized with Nanostructured Metal Oxides. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 431, 127814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somyanonthanakun, W.; Ahmed, R.; Krongtong, V.; Thongmee, S. Studies on the Adsorption of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions Using Sugarcane Bagasse-Based Modified Activated Carbon with Nitric Acid: Kinetic, Isotherm and Desorption. Chem. Phys. Impact 2023, 6, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Nghiem, X.S.; Le Minh, T.; Vu, A.-T. Preparation of Functional Materials Based on Activated Carbon from Bagasse and Its Application in Pb2+ Adsorption in an Aqueous Environment. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 113158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarinejad, Z.; Rahmanian, O.; Heidari, M. Production of KOH-Activated Carbon from Date Press Cake: Effect of the Activating Agent on Its Properties and Pb(II) Adsorption Potential. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 165, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıntıg, E.; Altundag, H.; Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A. Effective Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions Using Magnetic Loaded Activated Carbon as Novel Adsorbent. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 122, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, N.; Mi, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z. Enhanced Dyes Adsorption from Wastewater via Fe3O4 Nano-particles Functionalized Activated Carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, S.G.; Abulyazied, D.E.; Ahmed, S.M. Application of Polyaniline/Activated Carbon Nanocomposites De-rived from Different Agriculture Wastes for the Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Media. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 170, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Jiang, J.; Hu, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, S. Removal of Pb(Ⅱ) from Aqueous Solution by Hydroxyapatite/Carbon Composite: Preparation and Adsorption Behavior. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, B.Y.; Alswat, A.A.; Ali, S.L.; Al-Odaini, N.A.; Alshorifi, F.T. Facile Synthesis of NiO–CuO/Activated Carbon Nanocomposites for Use in the Removal of Lead and Cadmium Ions from Water. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 47183–47191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojoudi, F.; Hamidian, A.H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. Synthesis and Evaluation of Activated Carbon/Nanoclay/Thiolated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Lead(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by Magnetic Activated Carbon and Its Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, N.; Parvini, M.; Niavarani, Z. High Surface Area and Mesoporous Graphene/Activated Carbon Composite for Adsorption of Pb(II) from Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, Y.G.; Anwar, D.; Safitri, H.; Surya, I.; Sudibyo, S.; Yuliansyah, A.T.; Murti Petrus, H.T.B. Functionalized Magnetite-Biochar with Live and Dead Bacteria for Adsorption-Biosorption of Highly Toxic Metals: Cd, Hg, and Pb. Next Mater. 2025, 6, 100487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyangadze, M.; Chikuruwo, N.H.M.; Narsaiah, T.B.; Chakra, C.S.; Radhakumari, M.; Danha, G. Enhancing Adsorp-tion Capacity of Nano-Adsorbents via Surface Modification: A Review. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 31, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiya, N.P.; Mahlangu, T.P.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Review on Advancing Heavy Metals Removal: The Use of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Microalgae-Based Adsorbents. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2025, 11, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.I.A.; Ahmad, W.; Anwar, M.; Shah, R.; Khan, J.A.; Shah, N.S.; Al-Anazi, A.; Han, C. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4-Based Nanocomposites: A Review. Appl. Catal. O Open 2025, 203, 207049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudravarapu, K.; Yarramuthi, V.; Munagapati, V.S.; Gutha, Y.; Wen, J.-C.; Prasad, C.; Pilla, V.A.R.; Gumma, L.; Won, J.S.; Choi, H.Y. Recent Progresses in the Development of Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Supported Cellulose-Based Composites: A Review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 182, 115588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolluru, S.S.; Agarwal, S.; Sireesha, S.; Sreedhar, I.; Kale, S.R. Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using Nano-materials-Process and Engineering Aspects. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 150, 323–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, G.T.; Gok, X.Y.; Yong, W.F. Adsorption of Pollutants in Wastewater via Biosorbents, Nanoparticles and Magnetic Biosorbents: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Bhavani Lakshmi, M.; Das, T.K.; Ghosh, M. Spinel Ferrites in the Photocatalytic and Adsorptive Remediation of Dyes and Heavy Metals: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 71, 107259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y. Pb(II) Sorption by Biochar Derived from Cinnamomum Camphora and Its Improvement with Ultrasound-Assisted Alkali Activation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 556, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Sheng, D.; Sun, K.; Si, Y.; Azeem, M.; Abbas, A.; Bilal, M. Remediation of Heavy Metals Polluted Environment Using Fe-Based Nanoparticles: Mechanisms, Influencing Factors, and Environmental Implications. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Kwon, S.; Lee, J.; Koo, J.; Seo, Y.-S. Instantaneous Integration of Magnetite Nanoparticles on Graphene Oxide Assisted by Ultrasound for Efficient Heavy Metal Ion Retrieval. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 64, 104962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.-X.; Yang, J.; Yoon, K.-B. Biochars and Modified-Biochars for Toxic-Metal/Metalloid Ions Sorption in Various Mixed Solution Systems: A Review on Kinetic and Isotherm Models. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raturi, S.; Kumari, S.; András, K.; Khargotra, R.; Sebestyén, V.; Singh, T. Advancements of Nanotechnological Strategies as Conventional Approach for Heavy Metal Removal from Industrial Wastewater: Start-of-the-Art Review. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 9, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeleuov, M.; Seidl, C.; Temirgaliyeva, T.; Taurbekov, A.; Prikhodko, N.; Lesbayev, B.; Sultanov, F.; Daulbayev, C.; Ku-mekov, S. Modified Activated Graphene-Based Carbon Electrodes from Rice Husk for Supercapacitor Applications. Energies 2020, 13, 4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansurov, Z.; Smagulova, G.; Kaidar, B.; Imash, A.; Lesbayev, A. PAN—Composite Electrospun-Fibers Decorated with Magnetite Nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, I.R.; Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Ahmed, A. Removal of Lead Ions (Pb2+) from Water and Wastewater: A Review on the Low-Cost Adsorbents. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wei, Q.; Wei, D.; Yan, T.; Yan, L.; Hu, L.; Du, B. Rapid Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Branched Polyethylenimine Enhanced Magnetic Carboxymethyl Chitosan Optimized with Response Surface Method-ology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, L. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Tolerance Strains to Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Wastewater. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32156–32162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maliky, E.A.; Gzar, H.A.; Al-Azawy, M.G. Determination of Point of Zero Charge (PZC) of Concrete Particles Ad-sorbents. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1184, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, N.R.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Kusuma, H.S.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Faizal, A.N.M. Advances in Chromium Removal Using Biomass-derived Activated Carbon: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Env. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2025, 44, e14598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyatnyk, I.; Yakupova, I. Impact of Chemical and Physical Treatments on the Structural and Surface Properties of Activated Carbon and Hydrochar. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 2500–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Banerjee, S.; Kar, K.K. Characteristics of Activated Carbon. In Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansūrov, Z.A. (Ed.) Carbon Nanomaterials in Biomedicine and the Environment; Jenny Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, B.K.; Kumar, A. Study of Graphitic Crystalline Structure in Highly Porous Activated Carbons Derived from Rice Husk Biomass. Chem. Pap. 2025, 79, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwanya, A.C.; Musheghyan-Avetisyan, A.; György, E.; Pérez Del Pino, Á. Fabrication of Asymmetric Supercapacitors by Laser Processing of Activated Carbon-Based Electrodes Produced from Rice Husk Waste. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 54, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Bazrafshan, A.A.; Jannesar, R. Comparative Study on Ultrasonic Assisted Ad-sorption of Dyes from Single System onto Fe3O4 Magnetite Nanoparticles Loaded on Activated Carbon: Experimental Design Methodology. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2017, 34, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, H.; Lin, H.; Liang, J. Preparation and Characterization of Fe3O4 Particles with Novel Nanosheets Morphology and Magnetochromatic Property by a Modified Solvothermal Method. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurien, U.; Hu, Z.; Lee, H.; Dastoor, A.P.; Ariya, P.A. Radiation Enhanced Uptake of Hg0(g) on Iron (Oxyhydr)Oxide Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 45010–45021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, B.; Wang, D.; Botte, G.G. Carbon-Coated Fe3O4 Nanospindles as Solid Electrolyte Interface for Improving Graphite Anodes in Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2020, 50, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariani, P.L.; Faizal, M.; Ridwan; Marsi; Setiabudidaya, D. Removal of Procion Red MX-5B from Songket’s Industrial Wastewater in South Sumatra Indonesia Using Activated Carbon-Fe3O4 Composite. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrebola, J.C.; Caballero, A.; Hernán, L.; Morales, J. Graphitized Carbons of Variable Morphology and Crystallinity: A Comparative Study of Their Performance in Lithium Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, A986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Zeng, S.; Feng, W.; Zhu, L.; Tan, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H. Facile Synthesis and Enhanced Microwave Absorption Properties of Fe-Fe3C@C Composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 14573–14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdisattar, A.; Yerdauletov, M.; Yeleuov, M.; Napolskiy, F.; Merkulov, A.; Rudnykh, A.; Nazarov, K.; Kenessarin, M.; Zhomartova, A.; Krivchenko, V. The Impact of Biowaste Composition and Activated Carbon Structure on the Electro-chemical Performance of Supercapacitors. Molecules 2024, 29, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Miao, C.; Liu, H.; Feng, L.; Yang, X.; Guo, H. A Hydrothermal Synthesis of Fe3O4@C Hybrid Nanoparticle and Magnetic Adsorptive Performance to Remove Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Liang, X. Model Construction of Micro-Pores in Shale: A Case Study of Silurian Longmaxi Formation Shale in Dianqianbei Area, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.-J.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis of Activated Carbon Derived from Rice Husks for Improving Hydrogen Storage Capacity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, B.; Shang, H.; Zhang, P.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Deng, S. Ultramicroporous Carbon Granules with Narrow Pore Size Distribution for Efficient CH4 Separation from Coal-bed Gases. AIChE J. 2021, 67, e17281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Zhang, R.; Rong, R.; Wu, P.; Chen, S.; Ao, J.; An, L.; Fu, Y.; Xie, H. Adsorption Characteristics of Heavy Metals Pb2+ and Zn2+ by Magnetic Biochar Obtained from Modified AMD Sludge. Toxics 2023, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofomaja, A.E.; Naidoo, E.B.; Modise, S.J. Kinetic and Pseudo-Second-Order Modeling of Lead Biosorption onto Pine Cone Powder. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 2562–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-L.; Lo, A.-Y.; Liu, J.-H.; Dai, Y.-M. Optimized Adsorptive Desulfurization Using Waste Tire-Derived Carbon. C 2025, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.A.S. Equilibrium and Kinetics Investigations for Adsorption of Aqueous Lead Ions Using Olive Stone Waste. J. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 26, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.; Azizian, S.; Douven, S. Implications of Apparent Pseudo-Second-Order Adsorption Kinetics onto Cellulosic Materials: A Review. BioRes 2019, 14, 7582–7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Qiang, Z.; Chang, J.-H.; Ben, W.; Qu, J. Synthesis of Carbon-Coated Magnetic Nanocomposite (Fe3O4@C) and Its Application for Sulfonamide Antibiotics Removal from Water. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizzadeh, S.E.; Bariki, S.G.; Movahedirad, S. Magnetic Orange Leaf Biochar for Favipiravir Removal from Wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektaş, T.E.; Uğurluoğlu, B.K.; Tan, B. Phosphate Removal by Ion Exchange in Batch Mode. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, N.F.; Barbosa, C.M.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.M.; Duarte, M.M. Removal of Naphthenic Acids Using Activated Charcoal: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Characteristics of Elovich Equation Used for the Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics in Dye-Chitosan Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nworie, F.S.; Nwabue, F.I.; Oti, W.; Mbam, E.; Nwali, B.U. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using activated rice husk biochar: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and error analysis. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2019, 64, 4365–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V. Modeling of Batch Sorber System: Kinetic, Mechanistic, and Thermodynamic Modeling. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3173–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumanjit; Rani, S.; Mahajan, R.K. Equilibrium, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Parameters for Adsorptive Removal of Dye Basic Blue 9 by Ground Nut Shells and Eichhornia. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S1464–S1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, N.; Selimi, T.; Mele, A.; Thaçi, V.; Halili, J.; Berisha, A.; Sadiku, M. Theoretical, Equilibrium, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Investigations of Methylene Blue Adsorption onto Lignite Coal. Molecules 2022, 27, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjelloun, M.; Miyah, Y.; Akdemir Evrendilek, G.; Zerrouq, F.; Lairini, S. Recent Advances in Adsorption Kinetic Models: Their Application to Dye Types. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.A.W.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Desorption Studies of Basic Dye on Activated Carbon Derived from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyun, T.S.; Mseer, A.H. Comparison of the Experimental Results with the Langmuir and Freundlich Models for Copper Removal on Limestone Adsorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, S.; Abu-Khamsin, S.A.; Kamal, M.S.; Patil, S. Surfactant Adsorption Isotherms: A Review. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32342–32348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmari, T.A.; Gallon, R.; Schwaab, M.; Barbosa-Coutinho, E.; Severo, J.B.; Pinto, J.C. Statistical Analysis of Linear and Non-Linear Regression for the Estimation of Adsorption Isotherm Parameters. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 433–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imla Syafiqah, M.S.; Yussof, H.W. Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamic Studies on the Adsorption of Mercury (Ii) Ion from Aqueous Solution Using Modified Palm Oil Fuel Ash. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 21690–21697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.A.A.; Puteh, M.H.; Khamidun, M.H.; Fulazzaky, M.A.; Abdullah, N.H.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Ahmad, N.; Lazim, Z.M.; Nuid, M. Interpretation of Isotherm Models for Adsorption of Ammonium onto Granular Activated Carbon. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 11, 9227–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, H.K.; Joseph, M.; O’Carroll, D.M. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Cadmium Ion Removal by Adsorption onto Nano Zerovalent Iron Particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheeta, M.A.; Goher, M.E.; Abd El-Moghny, M.G.; El-Deab, M.S. Efficient Elimination of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Magnetic Fe3O4-Nanoparticles/Activated Carbon Derived from Agricultural Waste. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 258, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaithianathan, R.; Anitha, P.; Ramachandran, A.; Sudha, R. A Green Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanocomposites Loaded Castor Seed Shell Carbon for Lead(II) Removal from Water: Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 280, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Hamadi, A.; Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Ramavandi, B. Decontamination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from Aqueous Solution Using a Magnetic Nanocomposite of Eggshell/Starch/Fe3O4. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiullah, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Khan, M.A.; Zheng, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, X. Fabrication of Fe3O4/Biochar Composites for Ef-fective Lead (II) Removal. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2025, 236, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanayake, A.G.; Todd, O.A.; Crowley, M.; Ricchetti, L.; Pittman, C.U.; Anderson, R.; Mohan, D.; Mlsna, T. Lead and Cadmium Remediation Using Magnetized and Nonmagnetized Biochar from Douglas Fir. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, K.K.; Jafari, D. Activated Carbon/Alginate/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposite as a Superior Functional Material for Removal of Lead from Aqueous Media. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 19025–19043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
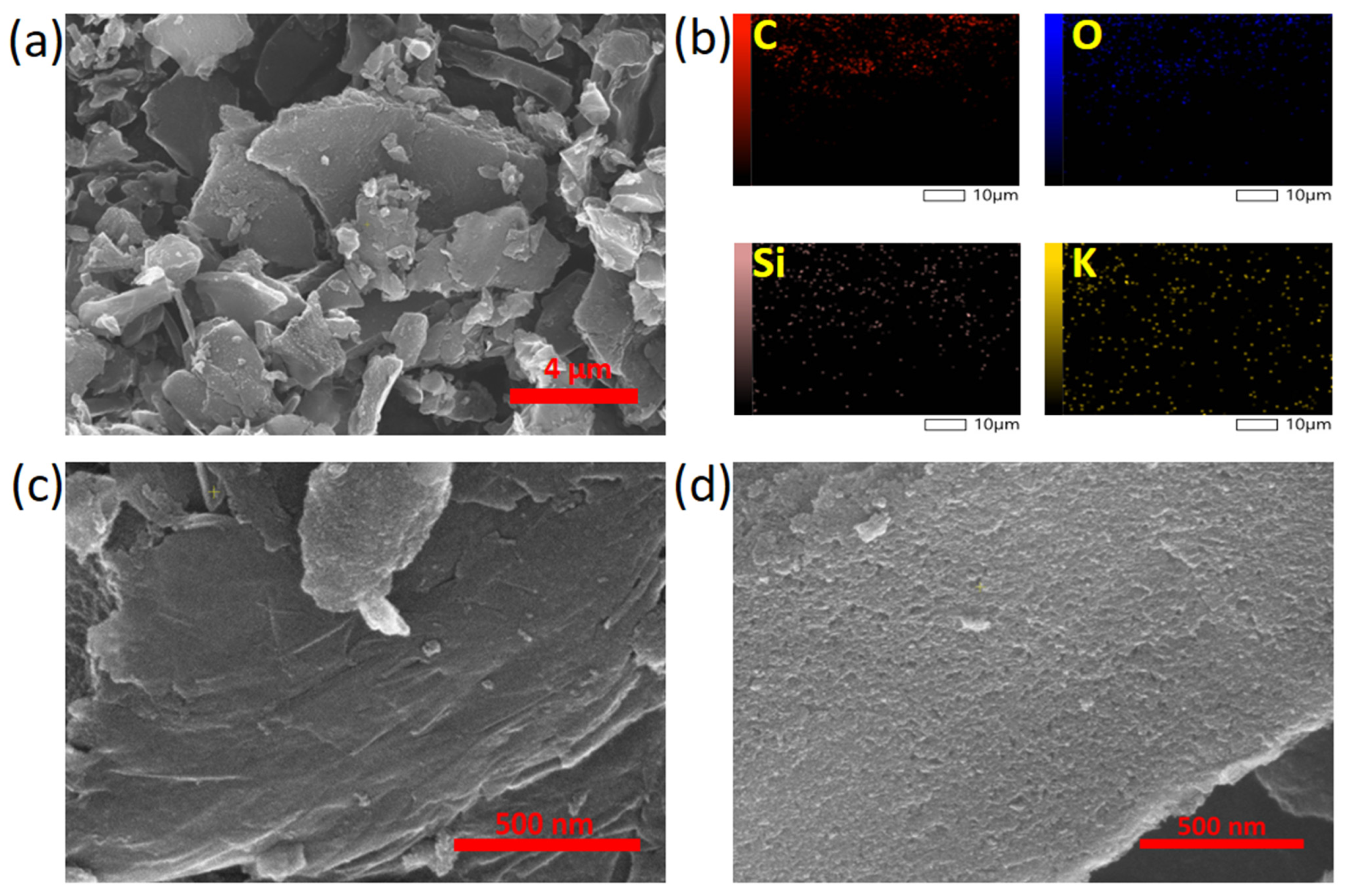
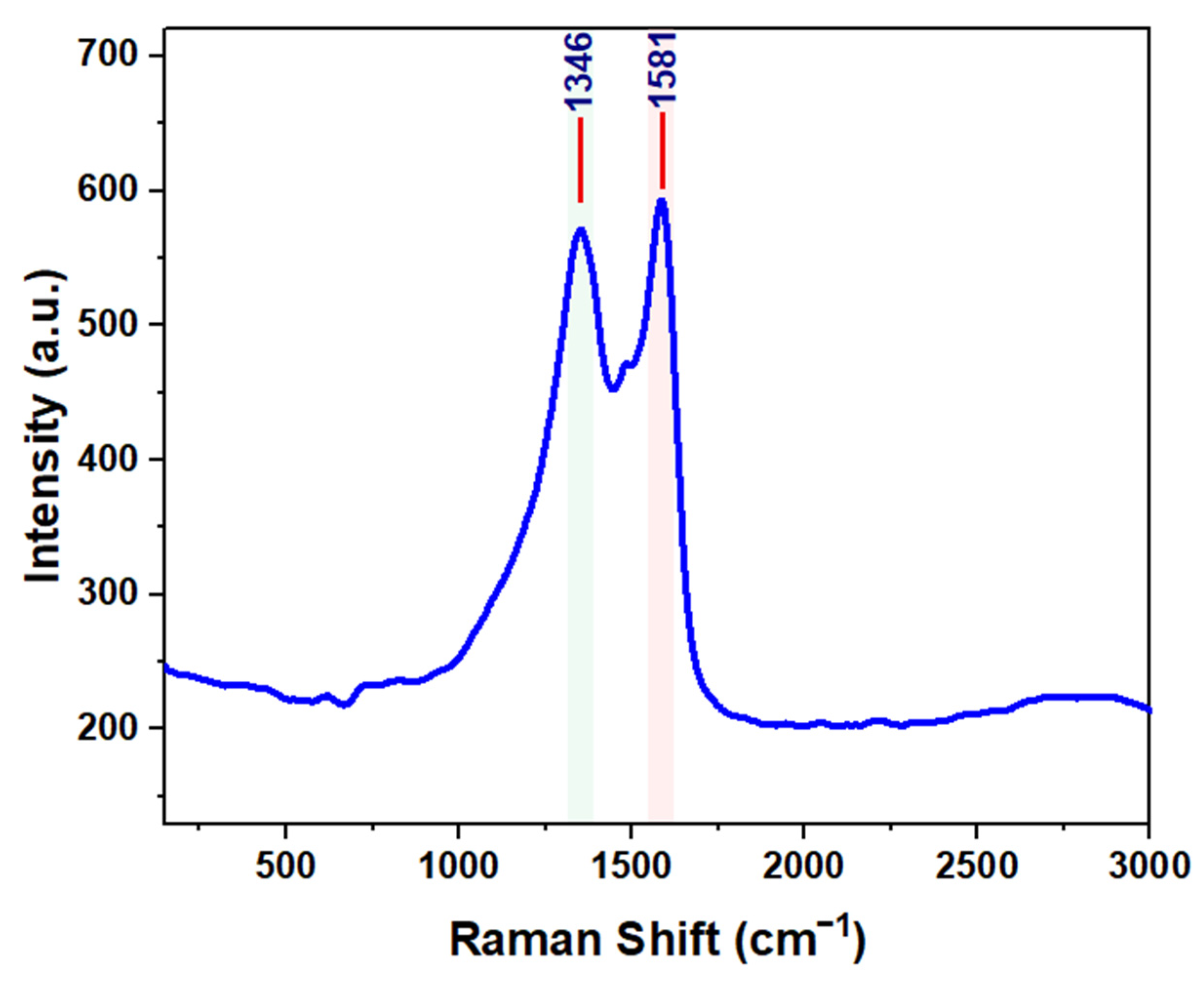


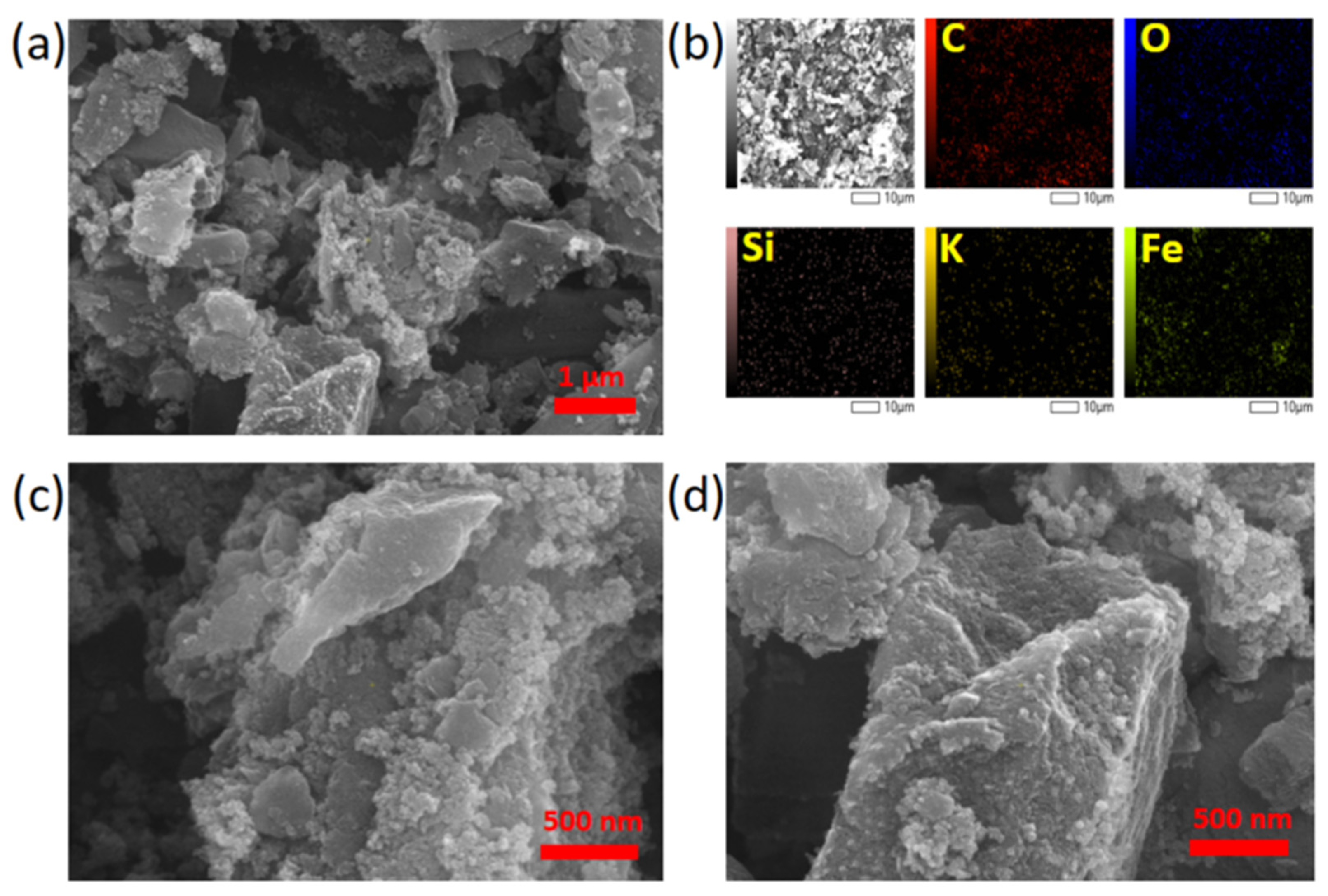
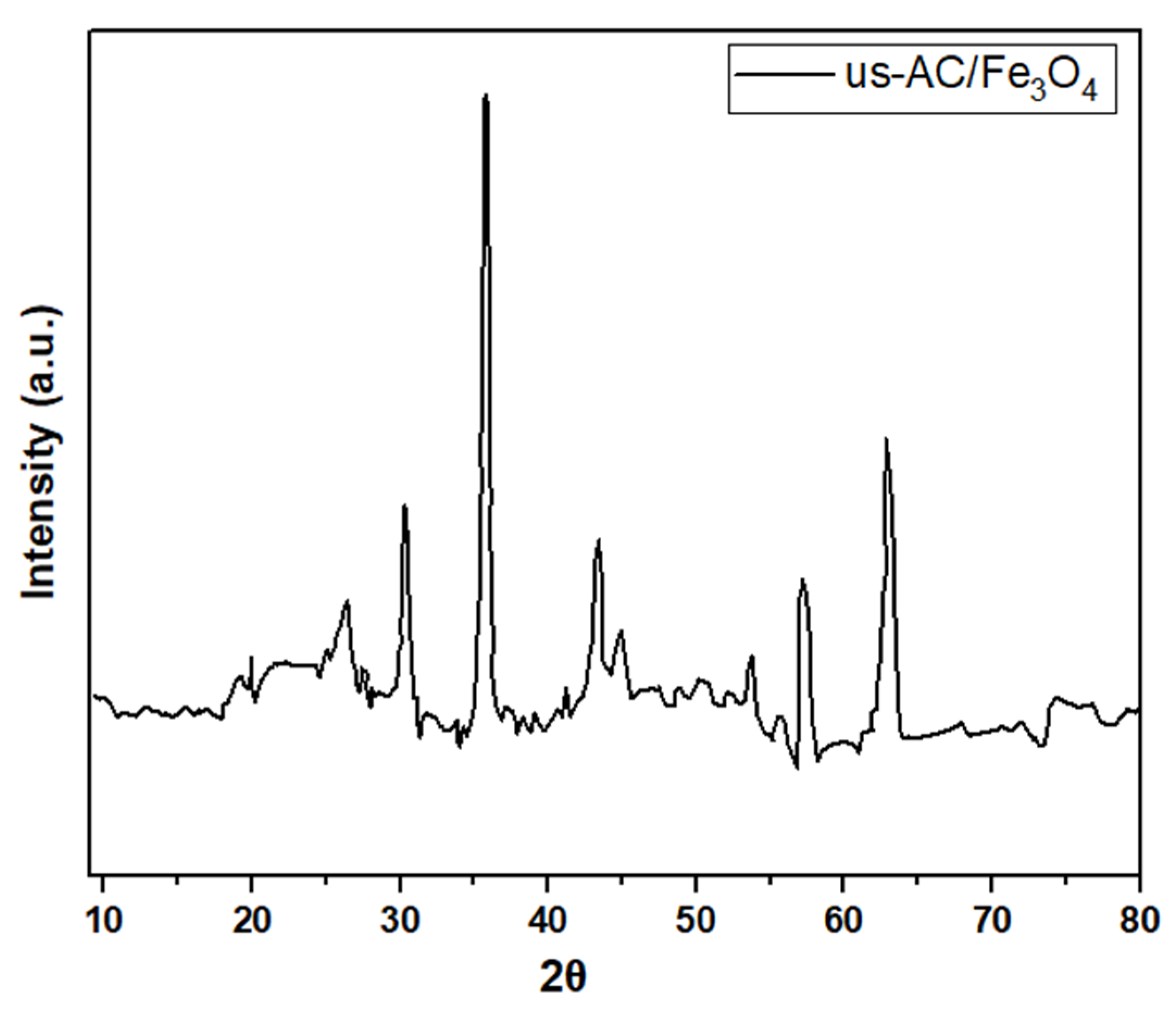
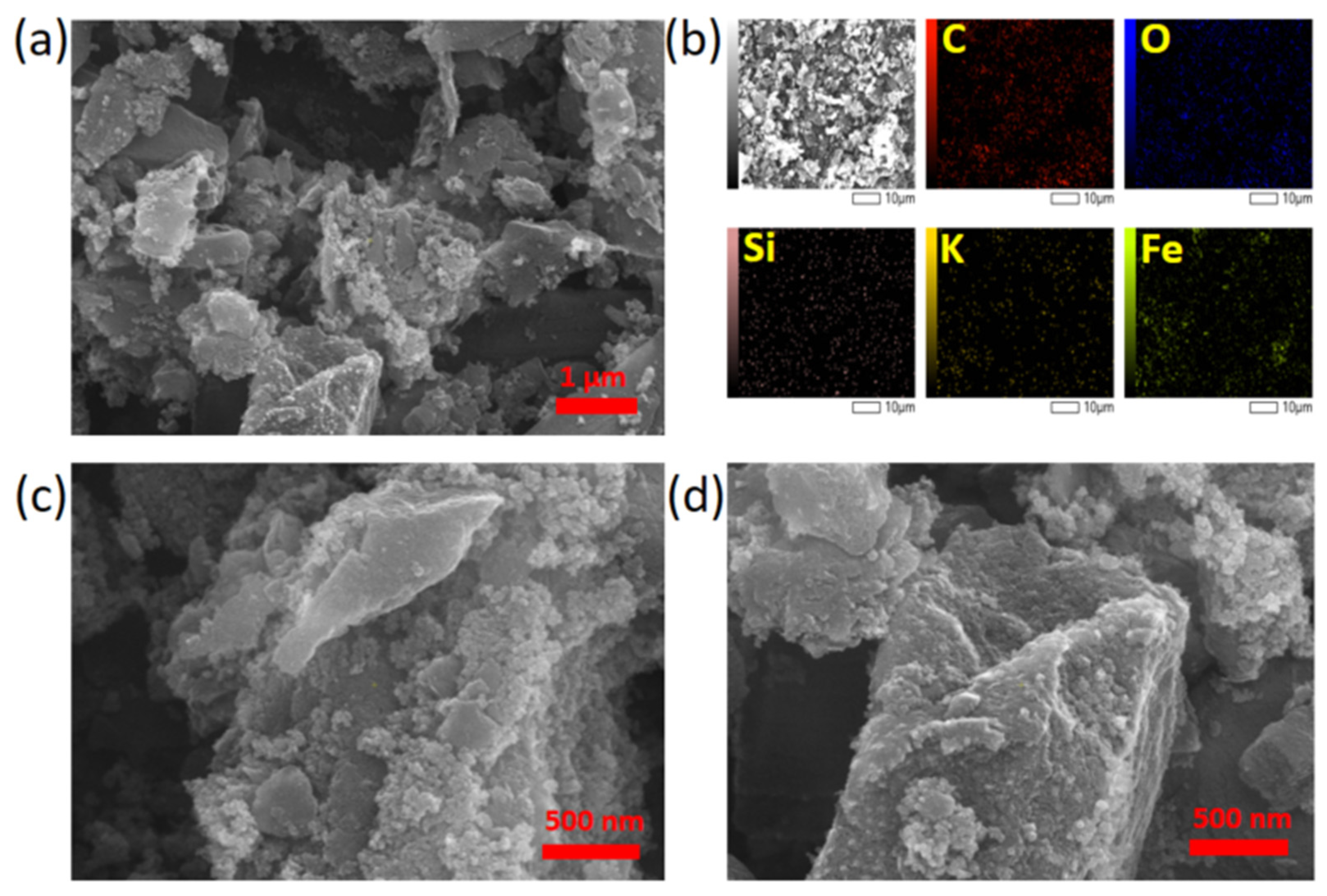
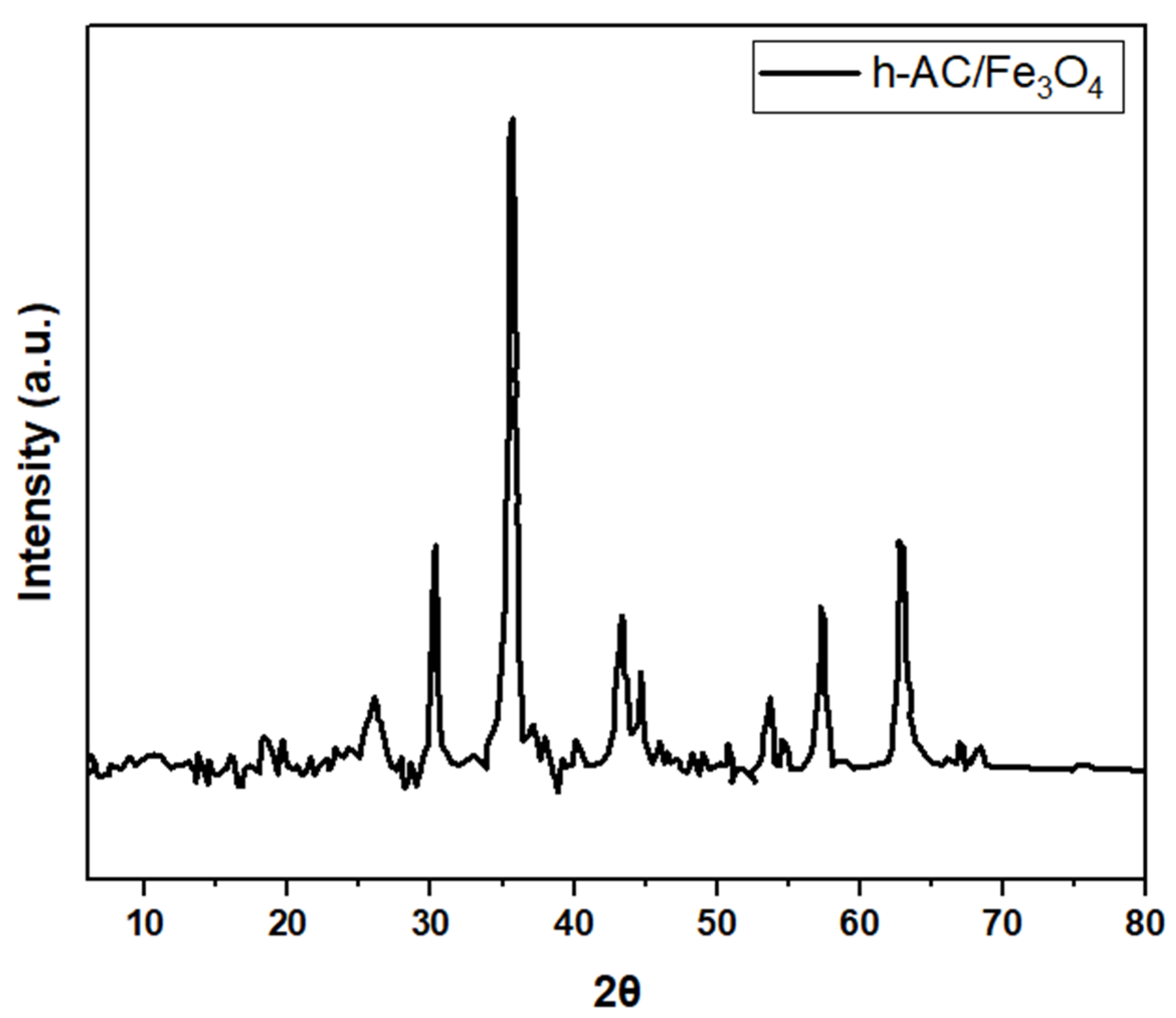
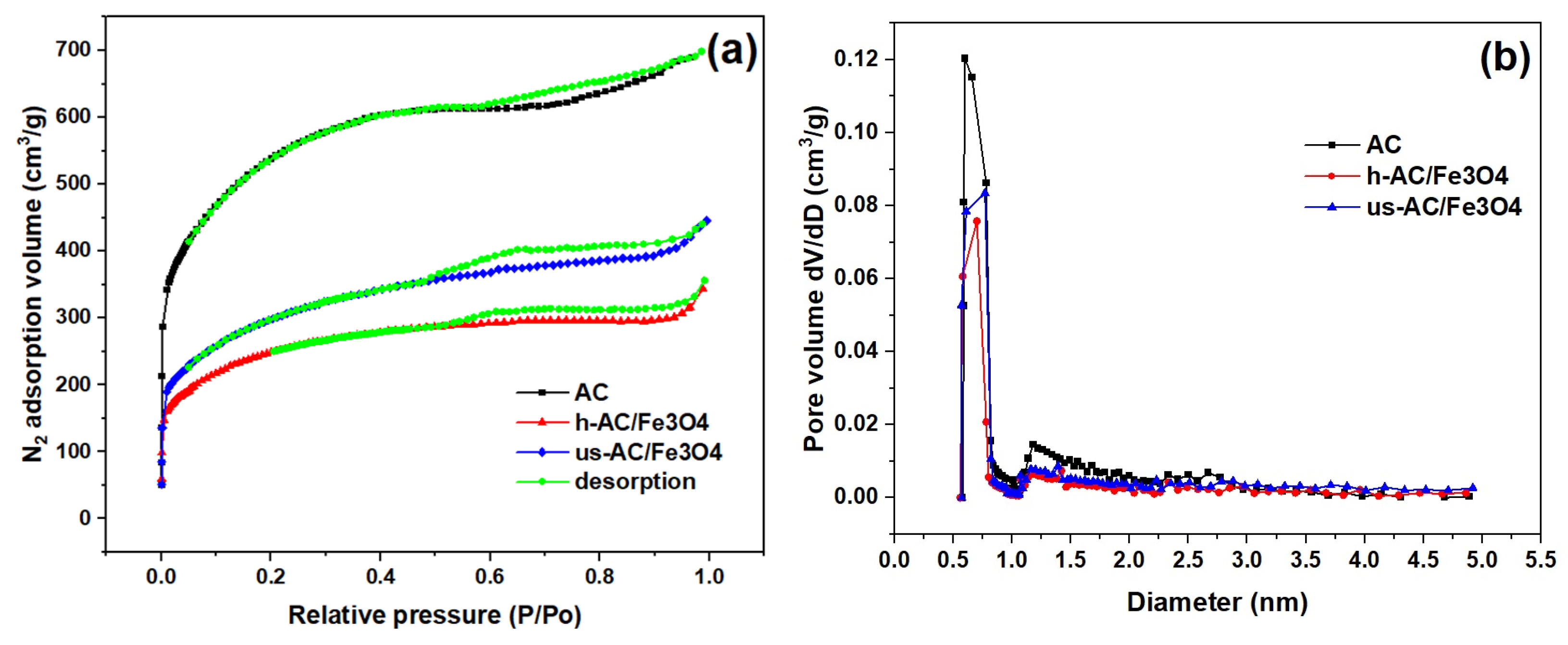
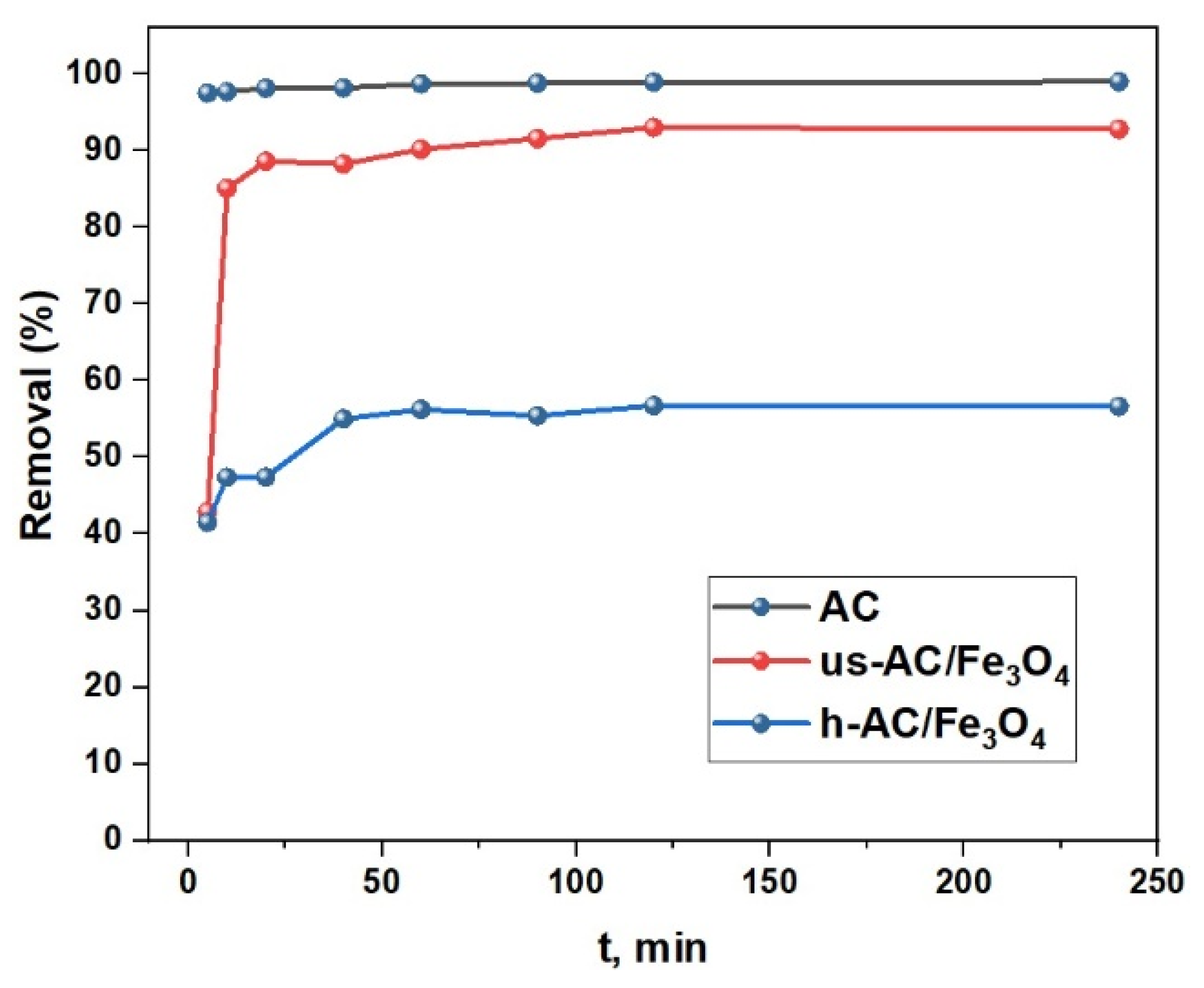


| Composite Sorbent | AC Precursor | Component Synthesis Method | Composite Synthesis Approach | Pollutant | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC/PANi | Waste biomass from fruit skins and pits | PANi—Polymerization | Polymerization | Pb (II) | 6.81 | [29] |
| AC/HAP | Commercial product | HAP—Co-precipitation | Co-precipitation | Pb (II) | 401.58 | [30] |
| AC/NiO−CuO | Arabo-khata leaves | NiO, CuO—Commercial product | Ultrasonic treatment | Pb (II) | 182.78 | [31] |
| AC/NC/GO | Sugar beet | Nanoclay—Carbonization, graphene oxide—Hummers’ method | Mixing | Pb (II) | 208 | [32] |
| AC | Rapeseed straw | - | Hydrothermal method | Pb (II) | 253.2 | [33] |
| AC/GO | Glucose | GO—Chemical exfoliation, Hummers’ method | Ultrasonic treatment | Pb(II) | 217 | [34] |
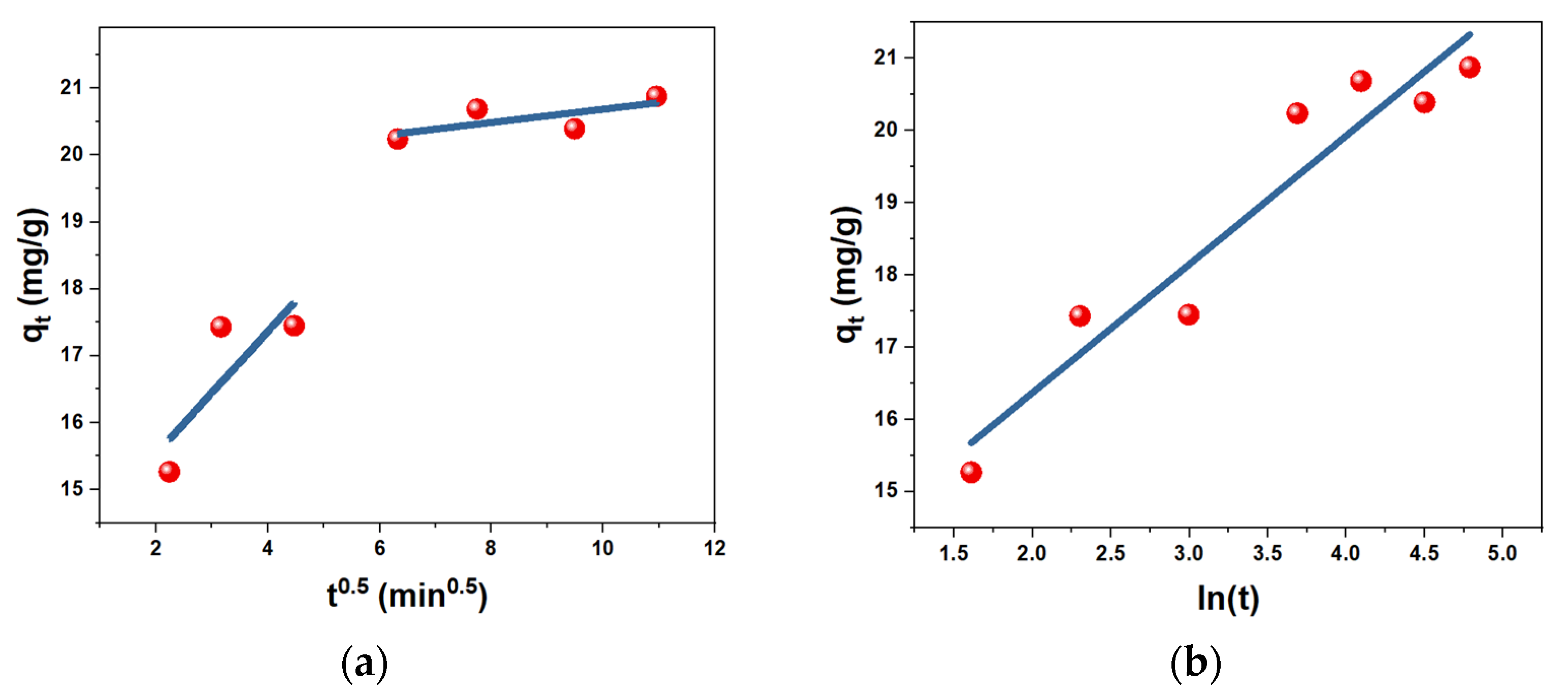
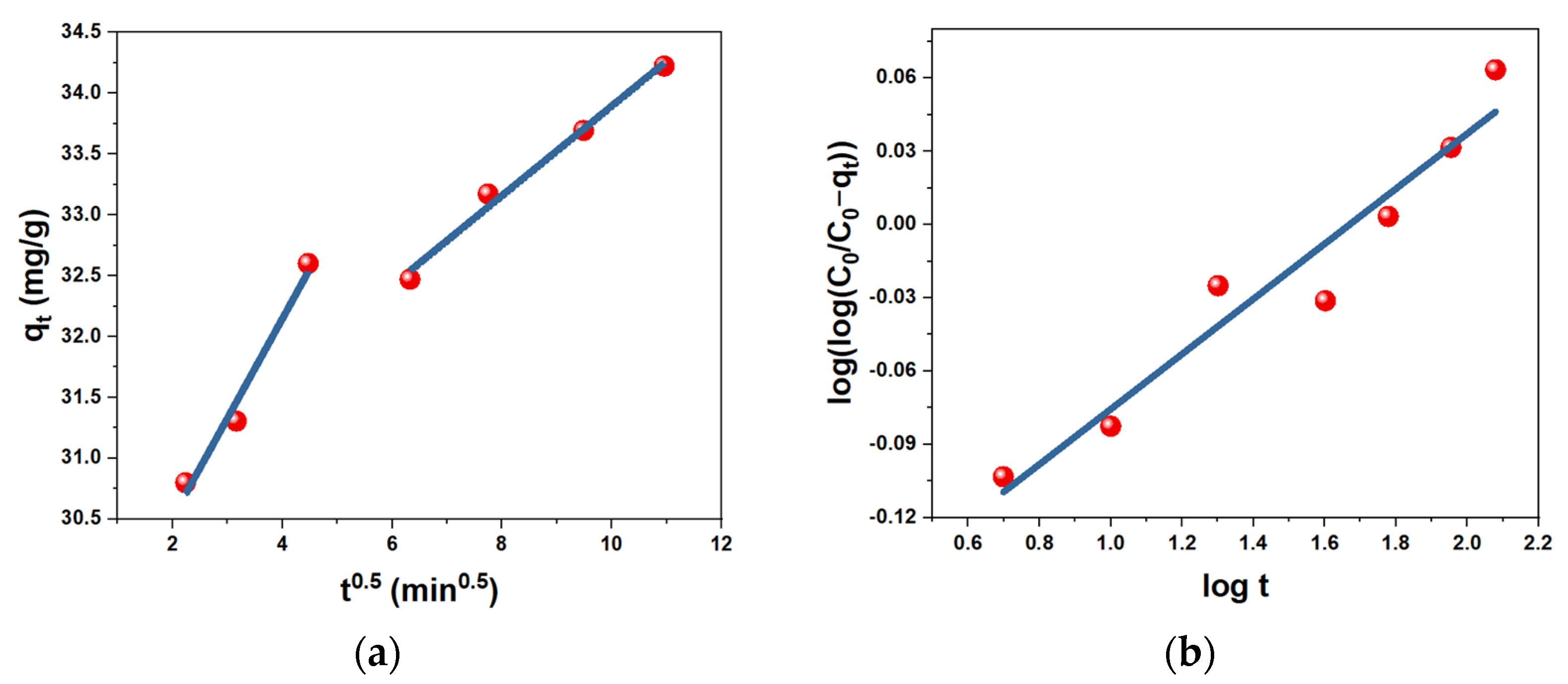
| Sorbent | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | R2 | k2 (g·min·mg−1) | R2 | |
| AC | 0.0001 | 0.8649 | 0.0632 | 0.9999 |
| h-AC/Fe3O4 | 0.0065 | 0.7282 | 0.1082 | 0.9994 |
| us-AC/Fe3O4 | 0.0021 | 0.8892 | 0.0671 | 0.9997 |
| Sorbent | Weber-Morris | Boyd | Bangham | Elovich | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kid1 mg/(g/min) | R2 Step 1 | kid2 mg/(g/min) | R2 Step 2 | kB, min−1 | R2 | α | k, mg/g·min−α | R2 | α (mg g−1 min−1) | β (g mg−1) | R2 | |
| AC | 0.0648 | 0.8302 | 0.0266 | 0.9982 | 0.0002 | 0.8649 | 0.0681 | 1.413 | 0.937 | ~3.24 × 1030 | 2.0016 | 0.9113 |
| h-AC/Fe3O4 | 0.9125 | 0.6664 | 0.0996 | 0.4905 | 0.0066 | 0.7283 | 0.1407 | 440.19 | 0.9138 | 58.01 | 0.1883 | 0.9306 |
| us-AC/Fe3O4 | 0.8182 | 0.9781 | 0.3687 | 0.9898 | 0.0022 | 0.8893 | 0.1128 | 74.43 | 0.9389 | 52.238 | 0.3355 | 0.9215 |
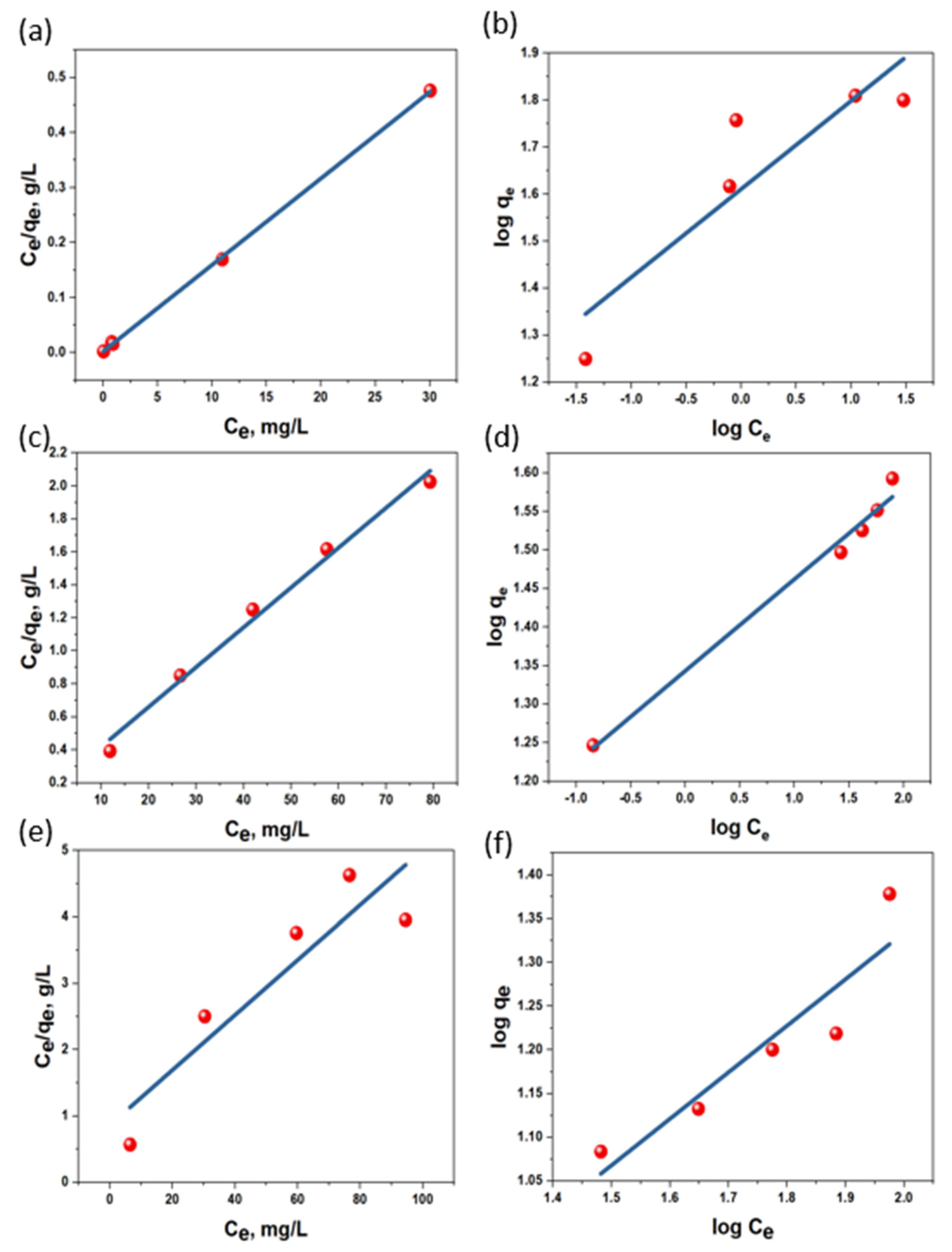
| Sorbent | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax, mg/g | KL, L/mg | R2 | n | KF, mg/g·(L/mg)1/n | R2 | |
| AC | 63.6943 | 7.1364 | 0.9997 | 5.3333 | 40.8413 | 0.8117 |
| h-AC/Fe3O4 | 24.1546 | 0.0478 | 0.8373 | 1.8783 | 1.8569 | 0.8568 |
| us-AC/Fe3O4 | 41.3223 | 0.1367 | 0.9899 | 8.4104 | 22.0445 | 0.9873 |
| Composite Sorbent | Support Material | Component Synthesis Method | Composite Synthesis Approach | Pollutant | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC/Fe3O4 | Rice straw | - | In situ co-precipitation | Pb(II) | 33 | [95] |
| AC/Fe3O4(2) | Rice straw | - | In situ co-precipitation | Pb(II) | 68 | |
| AC/Fe3O4 | Castor seed shell | Fe3O4—Co-precipitation | Conventional co-precipitation | Pb(II) | 122 | [96] |
| ES/Fe3O4 | Eggshell + starch | Fe3O4—Co-precipitation | Ultrasonic-assisted | Pb(II) | 57.14 | [97] |
| BC/Fe3O4 | Tangerine peel | Fe3O4—Co-precipitation | Co-precipitation on biochar | Pb(II) | 125.23 | [98] |
| BC/Fe3O4 | Waste wood | - | In situ precipitation on biochar | Pb(II) | 40.7 | [99] |
| C/Fe3O4 | Pinewood + feedstocks | - | Pyrolysis + magnetic precipitation | Pb(II) | ~30 | |
| C/Fe3O4 | Switchgrass | - | Pyrolysis + magnetic precipitation | Pb(II) | ~30 | |
| AC/Fe3O4 | Commercial AC | - | Co-precipitation with alginate | Pb(II) | 36.764 | [100] |
| AC/Fe3O4 | Rice husks | Fe3O4—Co-precipitation | Hydrothermal-assisted | Pb(II) | 23.89 | This work |
| AC/Fe3O4 | Rice husks | Fe3O4—Co-precipitation | Ultrasonic-assisted | Pb(II) | 39.15 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smagulova, G.; Imash, A.; Baltabay, A.; Keneshbekova, A.; Abdisattar, A.; Kazhdanbekov, R.; Lesbayev, A.; Mansurov, Z. Mechanistic Evaluation of Pb(II) Adsorption on Magnetic Activated Carbon/Fe3O4 Composites: Influence of Hydrothermal and Ultrasonic Synthesis Routes. C 2025, 11, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11040083
Smagulova G, Imash A, Baltabay A, Keneshbekova A, Abdisattar A, Kazhdanbekov R, Lesbayev A, Mansurov Z. Mechanistic Evaluation of Pb(II) Adsorption on Magnetic Activated Carbon/Fe3O4 Composites: Influence of Hydrothermal and Ultrasonic Synthesis Routes. C. 2025; 11(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmagulova, Gaukhar, Aigerim Imash, Akniyet Baltabay, Aruzhan Keneshbekova, Alisher Abdisattar, Ramazan Kazhdanbekov, Aidos Lesbayev, and Zulkhair Mansurov. 2025. "Mechanistic Evaluation of Pb(II) Adsorption on Magnetic Activated Carbon/Fe3O4 Composites: Influence of Hydrothermal and Ultrasonic Synthesis Routes" C 11, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11040083
APA StyleSmagulova, G., Imash, A., Baltabay, A., Keneshbekova, A., Abdisattar, A., Kazhdanbekov, R., Lesbayev, A., & Mansurov, Z. (2025). Mechanistic Evaluation of Pb(II) Adsorption on Magnetic Activated Carbon/Fe3O4 Composites: Influence of Hydrothermal and Ultrasonic Synthesis Routes. C, 11(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11040083







