Preparation and Properties of C/C-(TiZrHfNbTa)C Composites via Inorganic Salt Precursor Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Composites
2.2. Mechanical and Ablation Tests
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
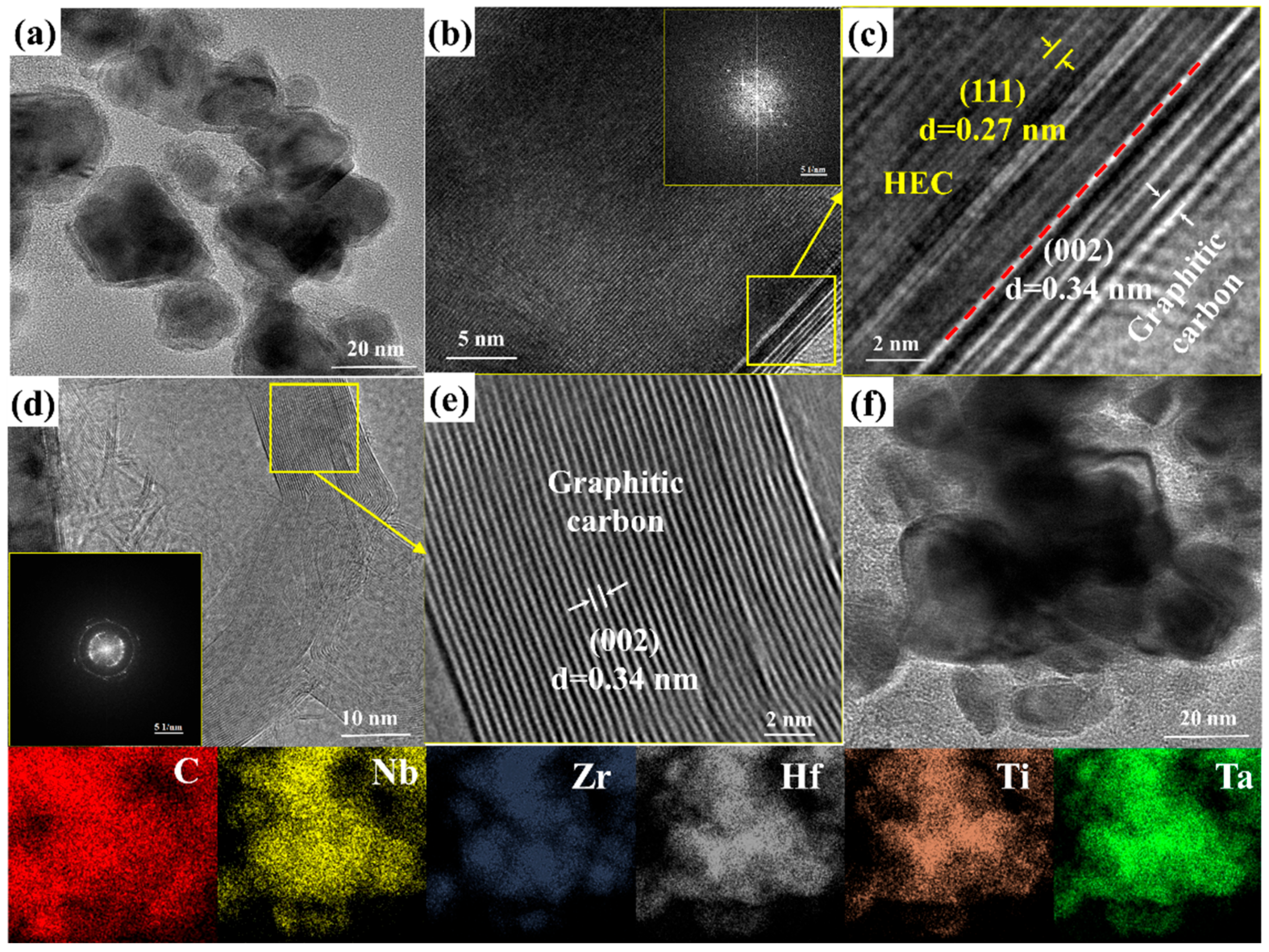
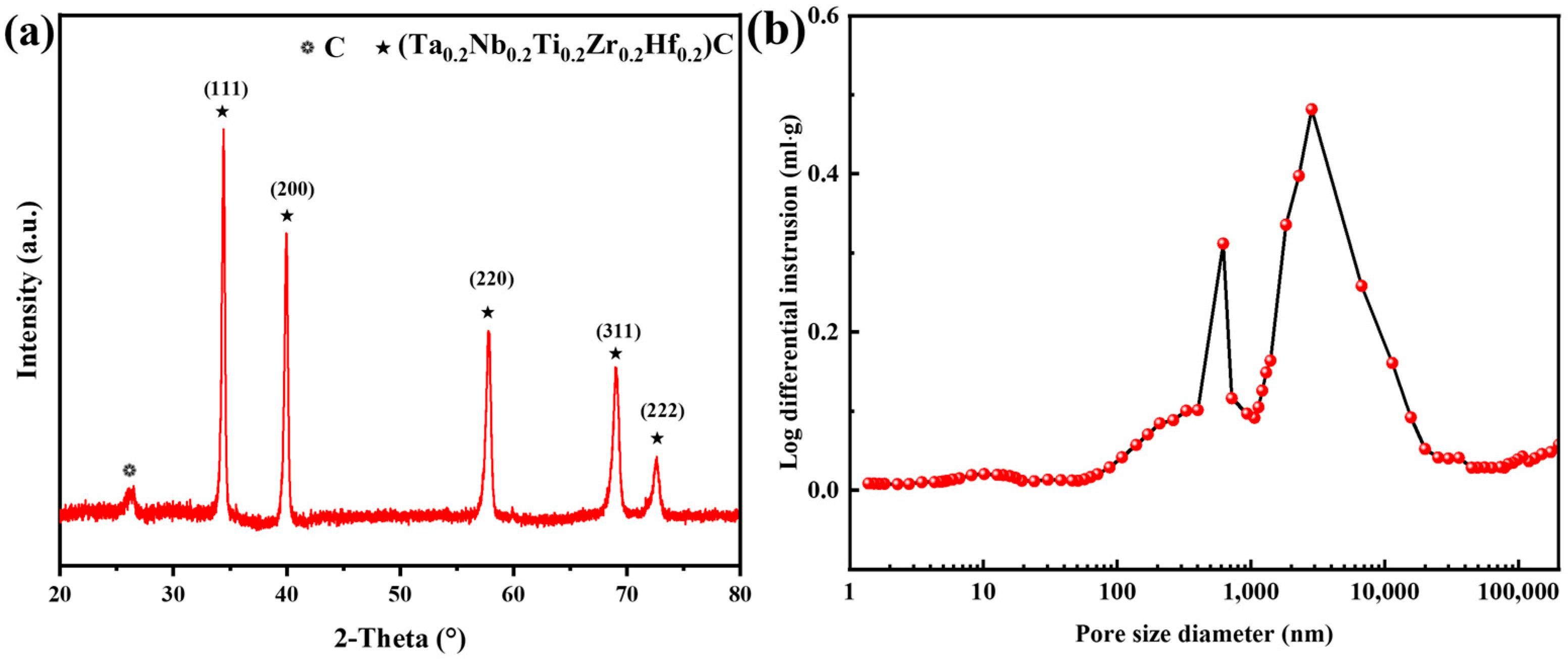
3.1. Synthesis of HEC Powder
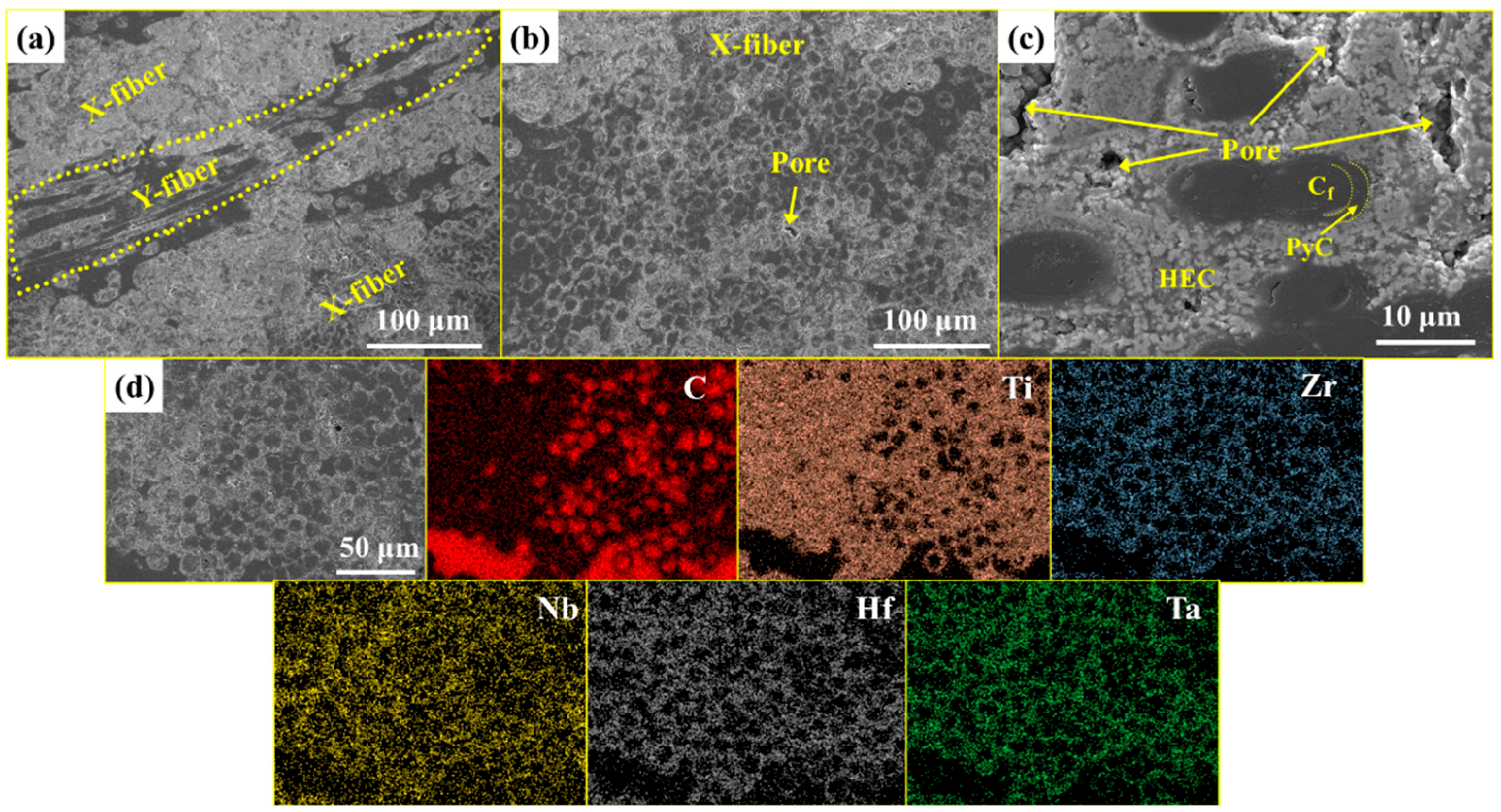
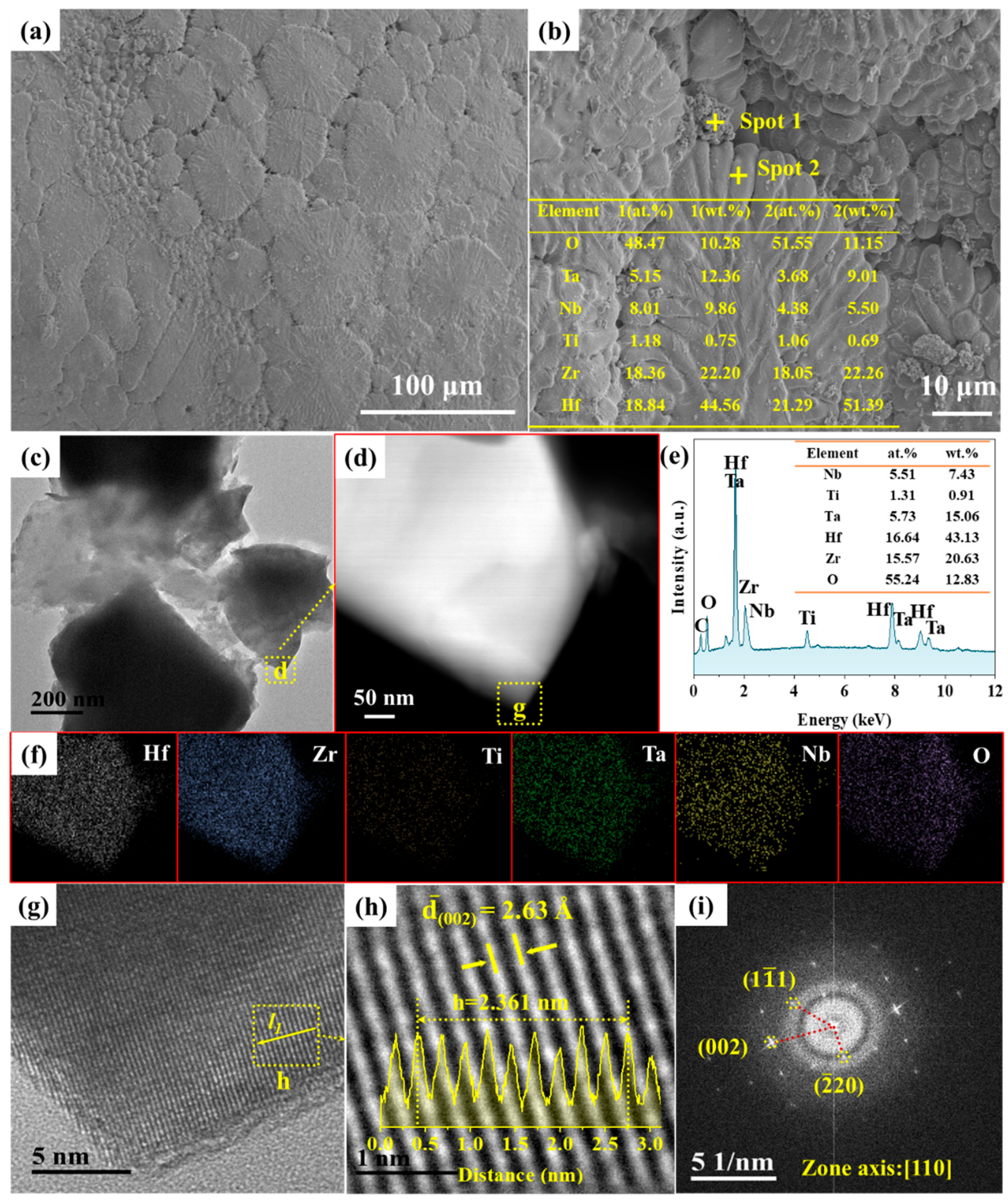
3.2. Phase Composition and Microstructure of C/C-HEC Composites
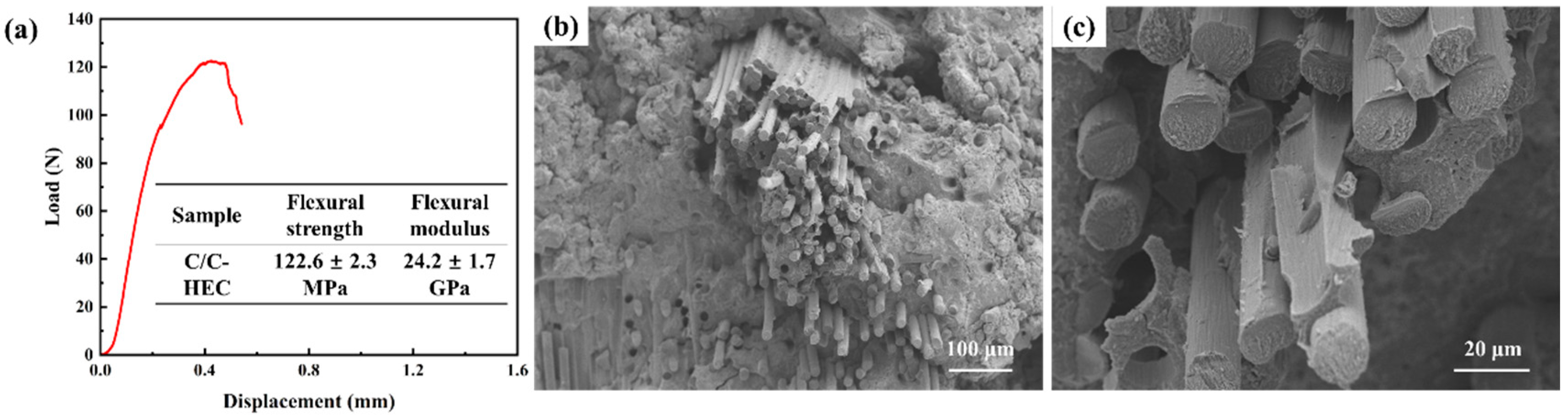
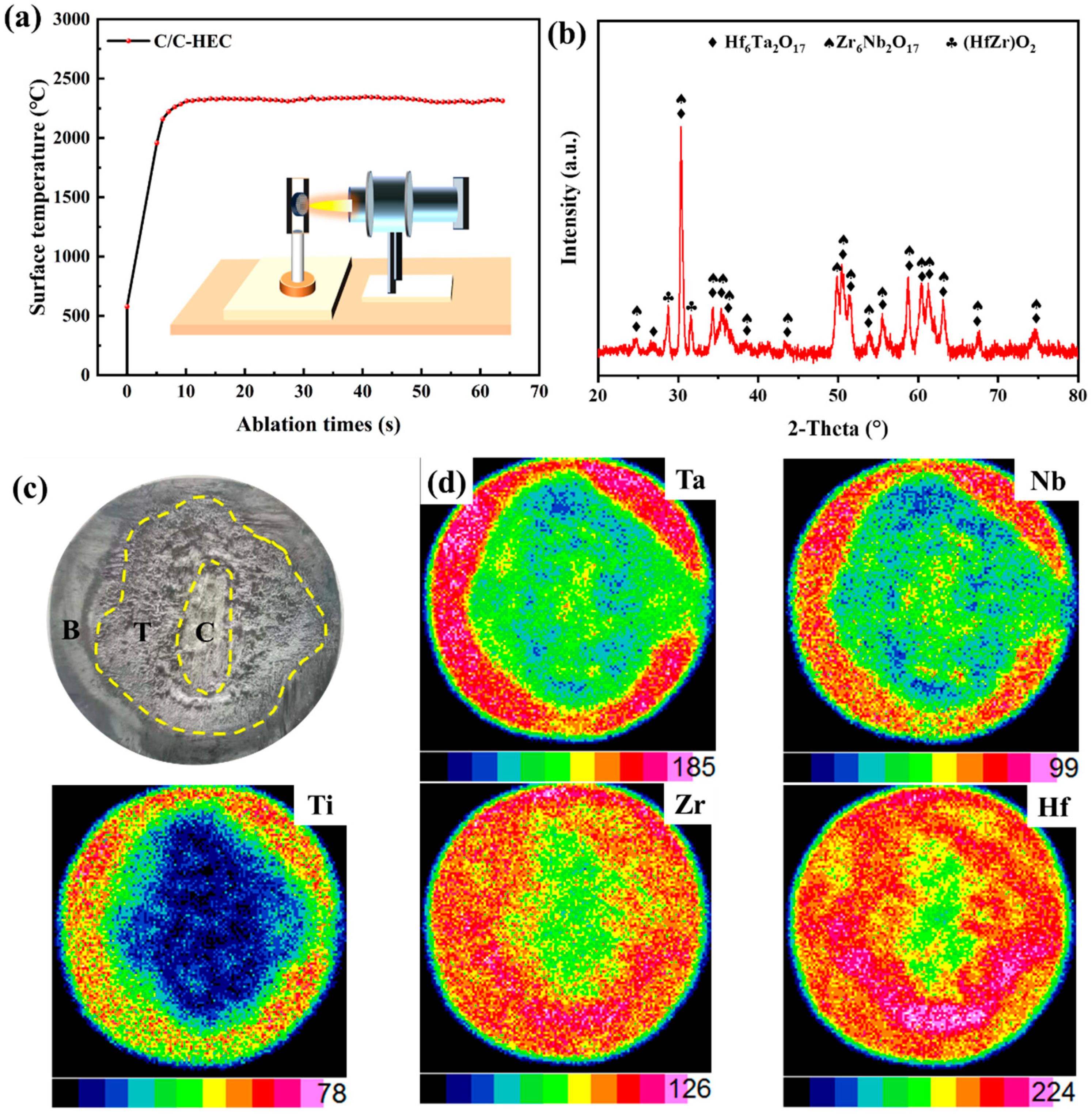
3.3. Mechanical and Ablation Properties of C/C-HEC Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ouyang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Huang, J.; Li, H. Effects of ZrC/SiC ratios on mechanical and ablation behavior of C/C–ZrC–SiC composites prepared by carbothermal reaction of hydrothermal co-deposited oxides. Corros. Sci. 2020, 163, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, Q.; Wang, C.; Lu, J. Effects of precursor feeding rate on the microstructure and ablation resistance of gradient C/C ZrC SiC composites prepared by chemical liquid-vapor deposition. Vacuum 2019, 164, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Ni, D.; Chen, B.; Lu, J.; Cai, F.; Qin, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Dong, S. Ablation behavior and mechanisms of 3D-Cf/Ta0. 8Hf0. 2C-SiC composite at temperatures up to 2500 °C. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Cheng, L.; Fan, X.; Shi, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L. Effect of interlayer on the ablation properties of laminated HfC–SiC ceramics under oxyacetylene torch. Corros. Sci. 2015, 93, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binner, J.; Porter, M.; Baker, B.; Zou, J.; Venkatachalam, V.; Diaz, V.R.; D’ANgio, A.; Ramanujam, P.; Zhang, T.; Murthy, T.S.R.C. Selection, processing, properties and applications of ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composites, UHTCMCs—A review. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 65, 389–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Binner, J.G.P.; Vaidhyanathan, B.; Heaton, A.C.J.; Brown, P.M. Heat flux mapping of oxyacetylene flames and their use to characterise Cf-HfB2composites. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2016, 115, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Venugopal, S.; Binner, J.; Vaidhyanathan, B.; Heaton, A.; Brown, P. UHTC–carbon fibre composites: Preparation, oxya-cetylene torch testing and characterization. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, S.; Edalati, P.; Fuji, M.; Edalati, K. High-entropy ceramics: Review of principles, production and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 146, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Li, C.; Ouyang, H.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Bao, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhong, X. A facile fine-grain strategy to fabricate (Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2Hf0.2Zr0.2)C-SiC ceramics with enhanced strength and toughness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 929, 148125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiang, H.; Dai, F.-Z.; Liu, J.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y. High porosity and low thermal conductivity high entropy (Zr0.2Hf0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, E.; Csanádi, T.; Grasso, S.; Dusza, J.; Reece, M. Processing and Properties of High-Entropy Ultra-High Temperature Car-bides. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Yun, X.; Huang, Z. Toughening in low-dimensional nanomaterials high-entropy ceramic nanocomposite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 231, 109586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, F.; Li, T.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y. Superior synergistic oxidation resistance of medium-entropy carbide ceramic powders rather than multi-phase carbide ceramic powders. J. Adv. Ceram. 2024, 13, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wen, Q.; Lun, H. Elucidating the role of preferential oxidation during ablation: Insights on the design and optimization of multicomponent ultra-high temperature ceramics. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 1956–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Yin, J.; Reece, M.J. Ablation behaviour of (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high entropy carbide ceramic at temperatures above 2100 °C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 113, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Zeng, Y.; Xiong, X. High-temperature ablation behavior and failure mechanism of (Hf0.25Zr0.25Ti0.25Ta0.25)C high-entropy carbide in wide temperature range. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 44, 6815–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced anti-ablation performance of carbon/carbon composites modified with ZrC-SiC. Vacuum 2018, 156, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Ni, D.; Chen, B.; Zou, X.; Liao, C.; Gao, L.; He, P.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, S. Efficient fabrication and properties of 2D Cf/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C-SiC high-entropy ceramic matrix composites via slurry infiltration lamination combined with precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 7403–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, T.; Meng, J. Effect of HfC-SiC transition layer on the ablation resistance of SiC/HfC-SiC/HfC mul-ti-layer coating for C/C composites. Vacuum 2019, 169, 108886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Hu, P.; Dong, S.; Feng, J.; Xun, L.; Zhang, X. Influence of hydrothermal carbon coating on the properties of CF/ZrB2/SiBCN prepared by slurry injection. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Ni, D.; Bao, W.; Chen, B.; Lu, J.; Zou, X.; Qin, Y.; Dong, S. Ablation behavior and mechanisms of Cf/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C–SiC high-entropy ceramic matrix composites. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 2022, 243, 110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, N.; Dong, X.; Yuan, F.; He, R. Low temperature fabrication of Cf/BNi/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2) C-SiCm high entropy ceramic matrix composite by slurry coating and laminating combined with precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hu, J.; Fang, W.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bai, S. A novel strategy for rapid fabrication of continuous carbon fiber reinforced (TiZrHfNbTa)C high-entropy ceramic composites: High-entropy alloy in-situ reactive melt infiltration. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, C.; Ouyang, H.; Gao, R.; Shen, T.; Li, Y. Synthesis of HfC nanowires on carbon fibers by a novel catalyst-assisted pyrolysis using HfCl4 as precursor. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 24901–24906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, R.; Ouyang, H.; Shen, T.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y. Hierarchical porous (Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2) C high-entropy ceramics prepared by a self-foaming method for thermal insulation. J. Adv. Ceram. 2024, 13, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhou, X.; Tao, B.; Wu, H.; Huang, S. Crystal structure and enhanced microwave dielectric properties of the Ce2[Zr1−x(Al1/2Ta1/2)x]3(MoO4)9 ceramics at microwave frequency. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Wen, T.; Huang, K.; Wang, C.Z.; Chu, Y. First-principles study, fabrication, and characterization of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 4344–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Luo, X.; Weng, Y.; Fang, C.; Huang, Q. Formation mechanism of (Ti, Zr, Hf) C medium-entropy carbide derived from polymer precursors and its modification on the ablative mechanism of C/C-SiC composites. Corros. Sci. 2024, 230, 111935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Ren, K.; Wang, Y. Oxyacetylene ablation of (Hf0.2Ti0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2)C at 1350−2050 °C. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| C/C-HEC | 2.22 | 18.2 |
| Sample | Mass Ablation Ratio (mg·s−1) | Line Ablation Ratio (mm·s−1) |
|---|---|---|
| C/C-HEC | 0.67 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Shen, T.; Liu, J.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Bao, L. Preparation and Properties of C/C-(TiZrHfNbTa)C Composites via Inorganic Salt Precursor Method. C 2025, 11, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030041
Ouyang H, Liu J, Li C, Shen T, Liu J, He M, Li Y, Bao L. Preparation and Properties of C/C-(TiZrHfNbTa)C Composites via Inorganic Salt Precursor Method. C. 2025; 11(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Haibo, Jiyong Liu, Cuiyan Li, Tianzhan Shen, Jiaqi Liu, Mengyao He, Yanlei Li, and Leer Bao. 2025. "Preparation and Properties of C/C-(TiZrHfNbTa)C Composites via Inorganic Salt Precursor Method" C 11, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030041
APA StyleOuyang, H., Liu, J., Li, C., Shen, T., Liu, J., He, M., Li, Y., & Bao, L. (2025). Preparation and Properties of C/C-(TiZrHfNbTa)C Composites via Inorganic Salt Precursor Method. C, 11(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030041







