Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Carbon Dots: A Hybrid Approach with Levofloxacin, Curcumin, and Tea Polyphenols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
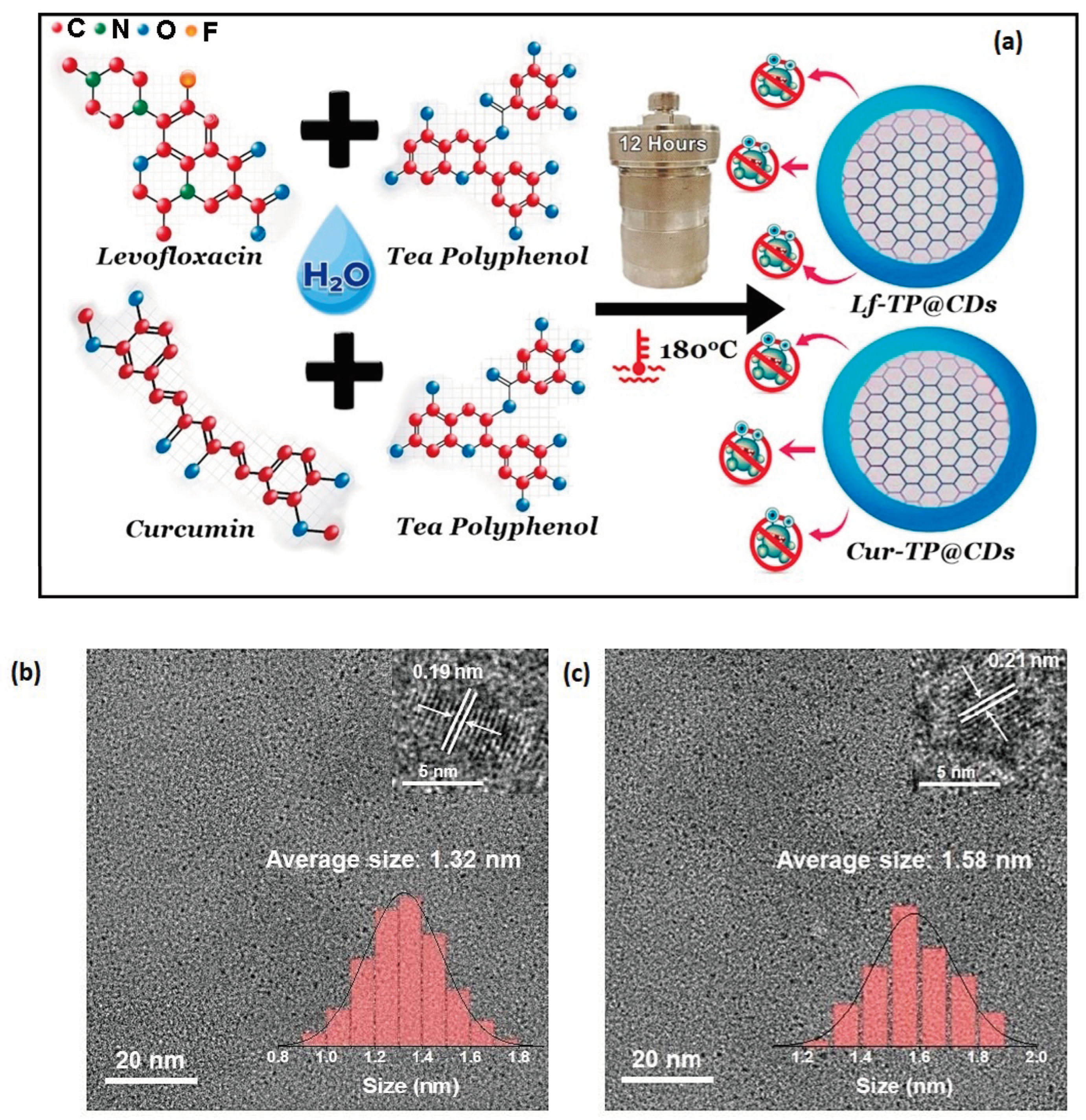
2.2.1. Synthesis of Cur-TP@CDs and Lf-TP@CDs
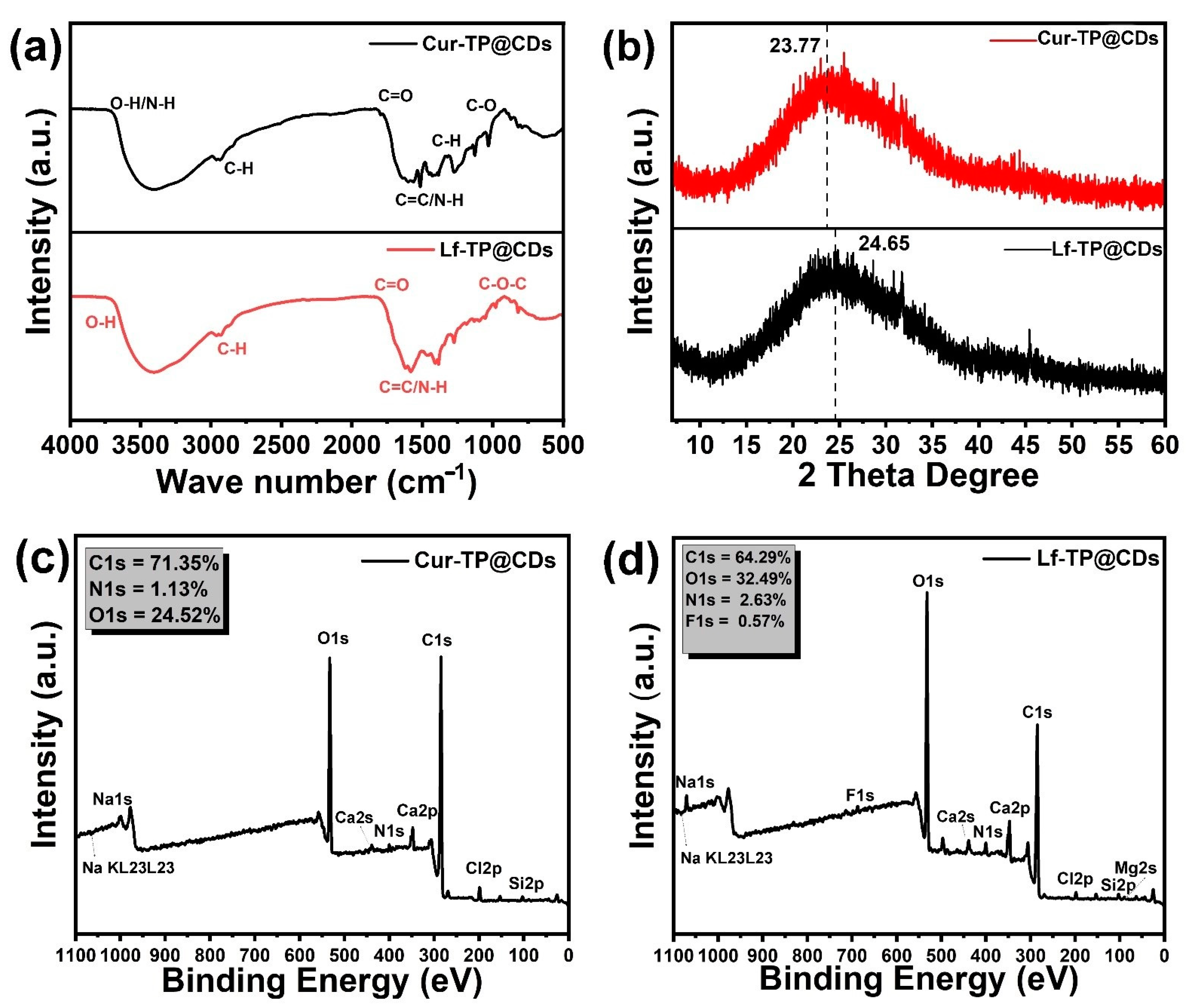
2.2.2. Characterization
2.2.3. Bacterial Culture Preparation
2.2.4. Broth Dilution Method
2.2.5. Disc Diffusion Method
2.2.6. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
2.2.7. Live and Dead Bacteria Assay
2.2.8. Morphology Study of Bacteria by SEM
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Lf-TP@CDs and Cur-TP@CDs
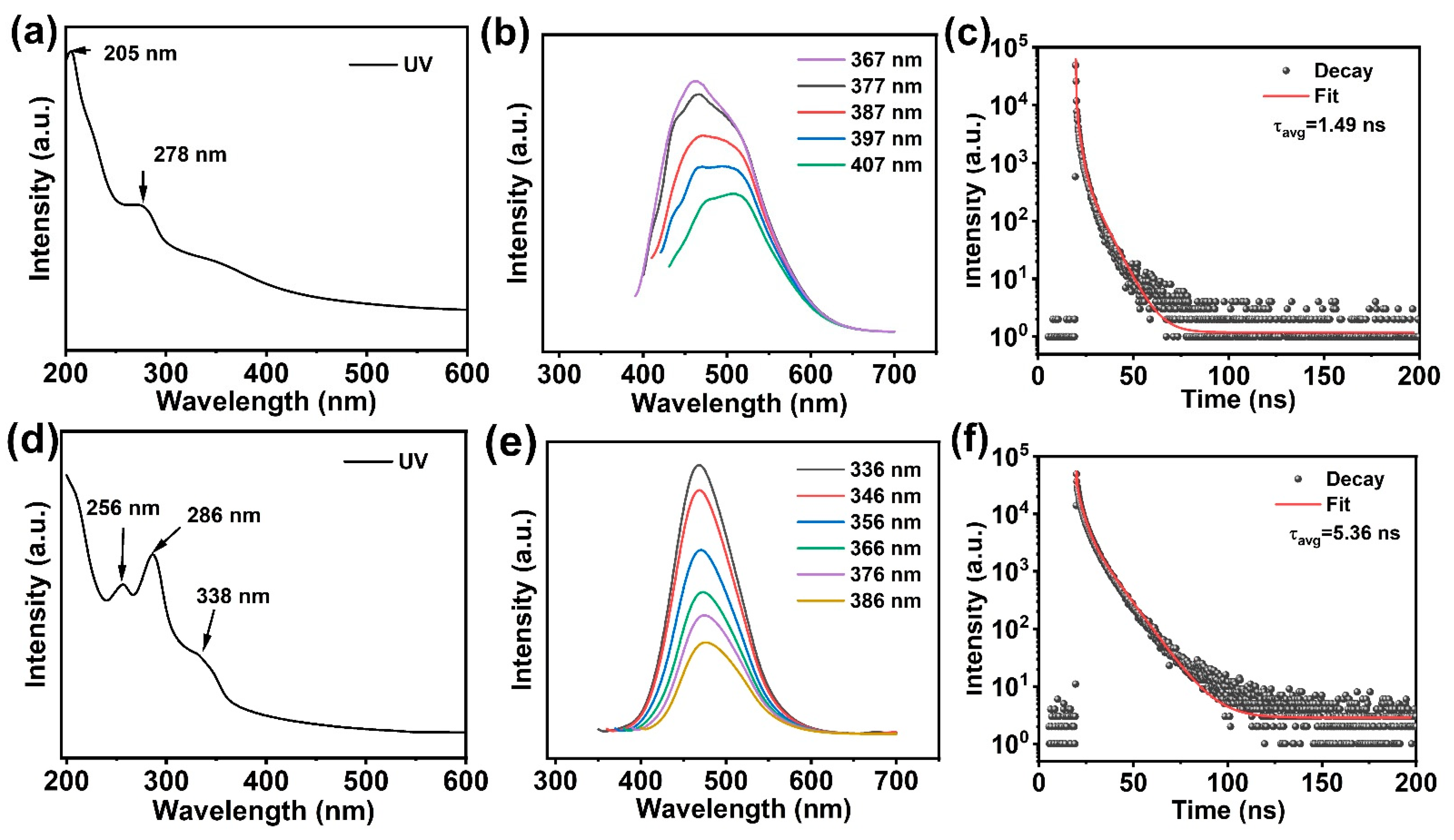
3.2. Optical Properties of Cur-TP@CDs and Lf-TP@CDs
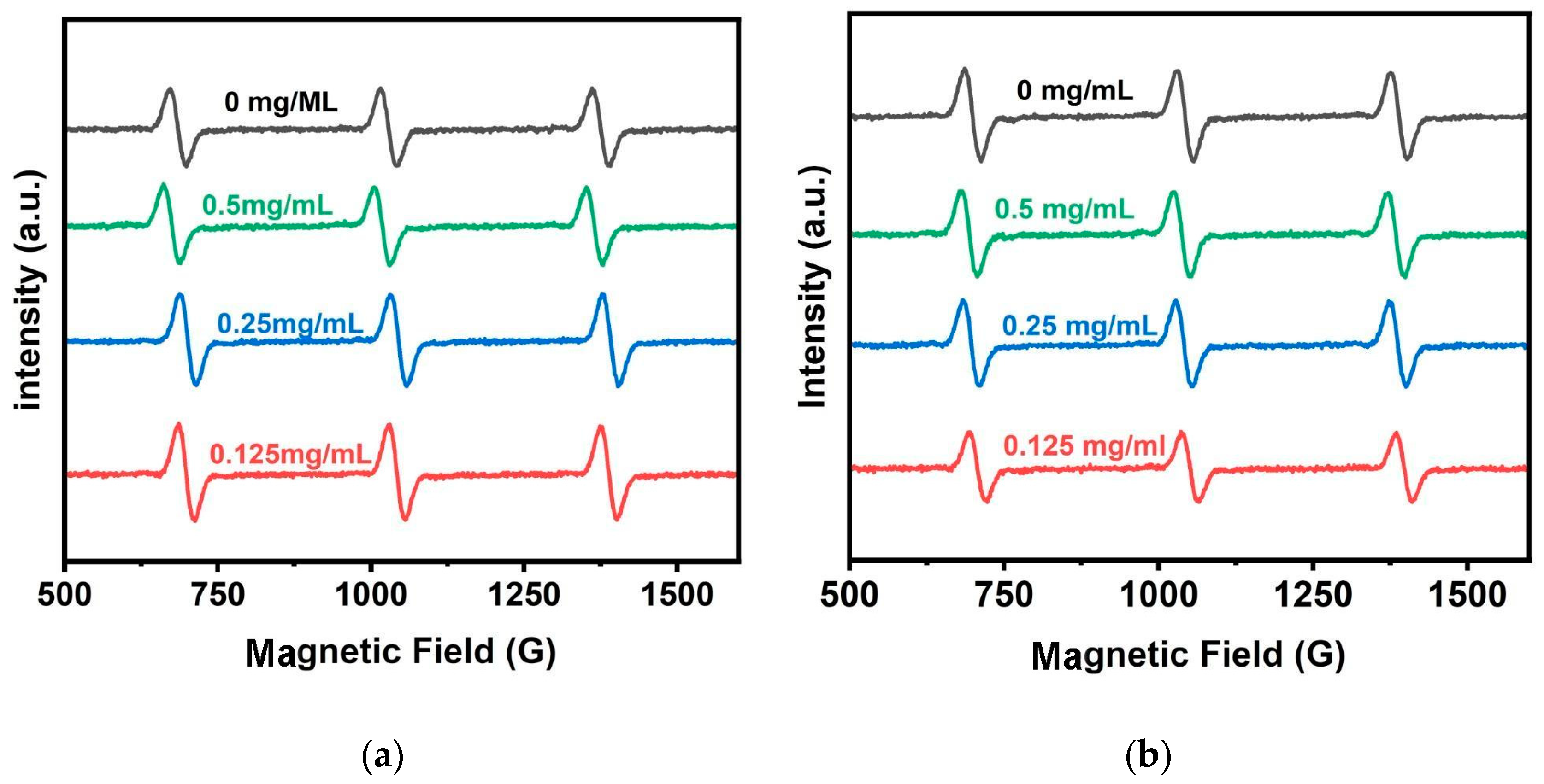
3.3. ROS Production of Cur-TP@CDs and Lf-TP@CDs
3.4. Antibacterial Mechanism of Cur-TP@CDs and Lf-TP@CDs
3.4.1. Broth Dilution Assay
3.4.2. Disc Diffusion Assay
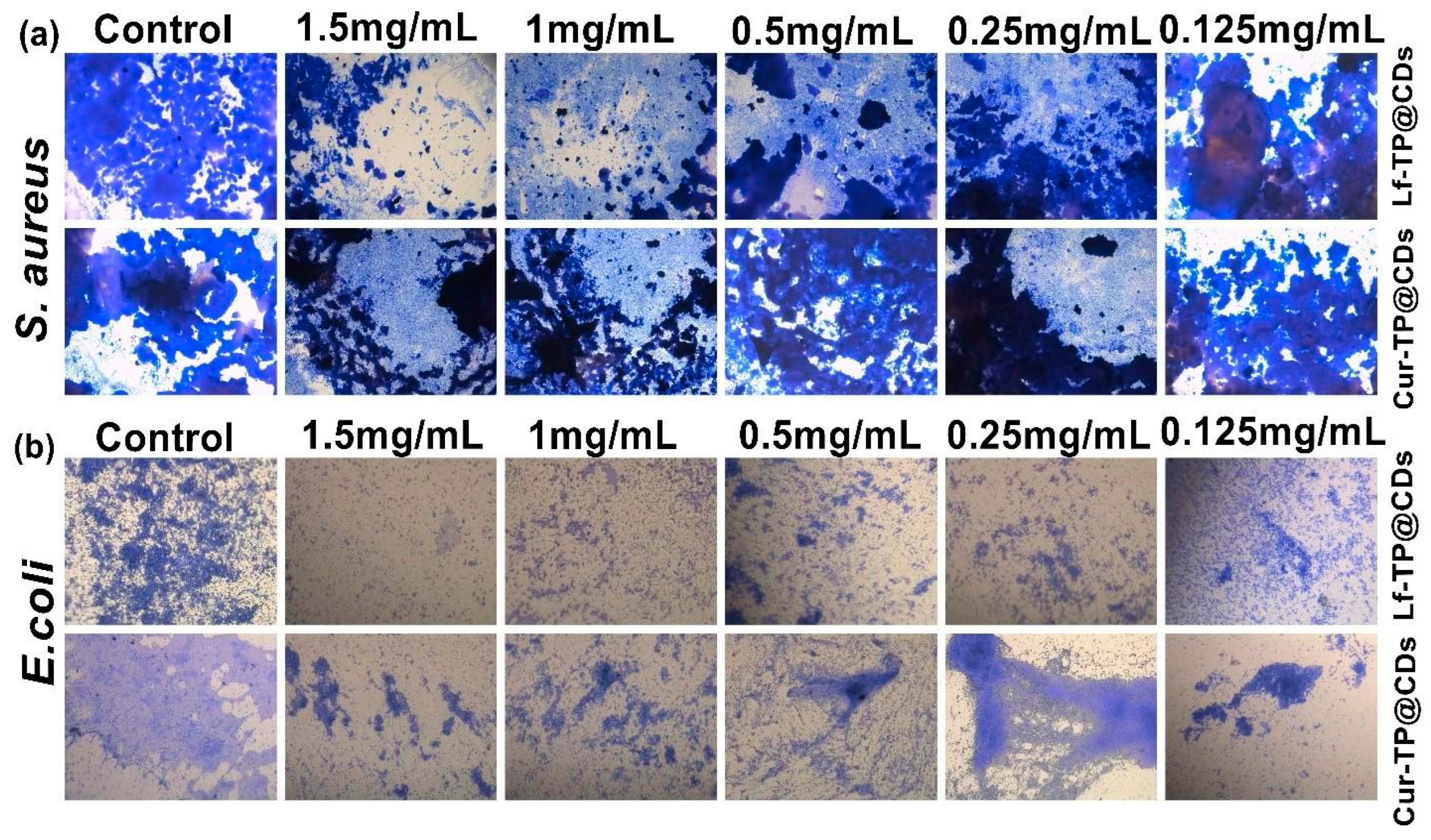
3.4.3. Biofilm Inhibition Evaluation
3.4.4. Live and Dead Bacterial Staining
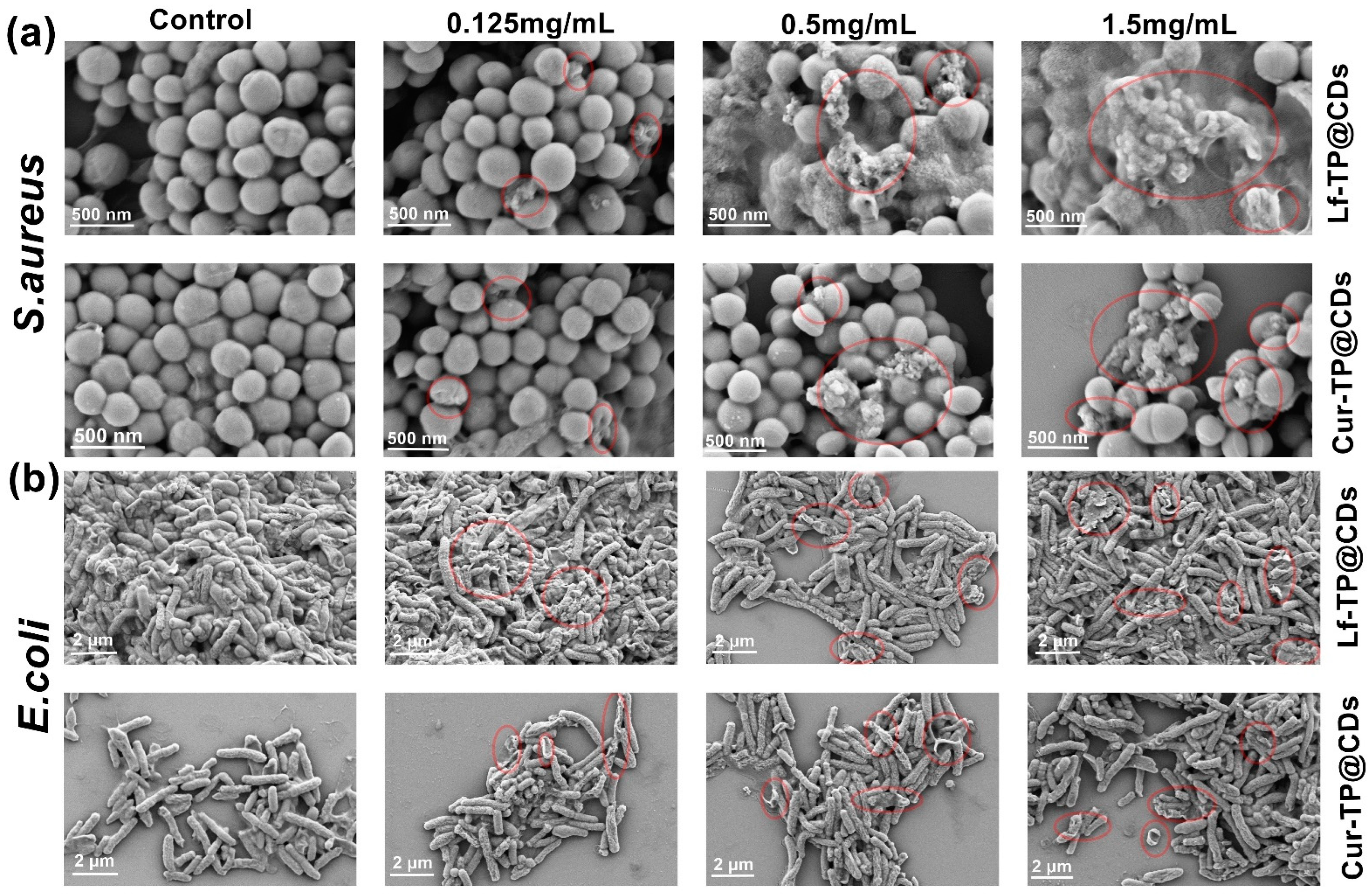
3.4.5. SEM Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial antibiotic resistance: The most critical pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, C.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J.; Ren, Y. Carbon quantum dots derived from different carbon sources for antibacterial applications. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deusenbery, C.; Wang, Y.; Shukla, A. Recent innovations in bacterial infection detection and treatment. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 695–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Wang, P.; Cong, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, L. Preparation of ciprofloxacin-based carbon dots with high antibacterial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Saini, A.K.; Kumar, N.; Tejwan, N.; Singh, T.A.; Thakur, V.K.; Das, J. Methods of preparation of metal-doped and hybrid tungsten oxide nanoparticles for anticancer, antibacterial, and biosensing applications. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcu, E.; Bastan, F.E.; Guney, M.; Avcu, Y.Y.; Rehman, M.A.U.; Boccaccini, A.R. Biodegradable polymer matrix composites containing graphene-related materials for antibacterial applications: A critical review. Acta Biomater. 2022, 151, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon dots for killing microorganisms: An update since 2019. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.-H.; Gao, G.; Chen, X.; Jia, H.-R.; Li, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon dot-based platform for simultaneous bacterial distinguishment and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32170–32181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lu, F.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Degradable carbon dots from cigarette smoking with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities against drug-resistant bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kuang, W.; Shi, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Shi, Q.; Tan, S. Carbon quantum dot-decorated TiO2 for fast and sustainable antibacterial properties under visible-light. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, W. Water-solvable carbon dots derived from curcumin and citric acid with enhanced broad-spectrum antibacterial and antibiofilm activity. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shu, W.; Lei, B.; Zhang, H. Antibacterial activity and synergistic mechanism of carbon dots against Gram-positive and-negative bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 6937–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-N.; Yang, Y.-J.; Huang, L.-X.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.-R.; Lin, L.-Q.; Lei, Y.; Liu, A.-L. Levofloxacin-based carbon dots to enhance antibacterial activities and combat antibiotic resistance. Carbon 2022, 186, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. RNA-Targeting Carbon Dots for Live-Cell Imaging of Granule Dynamics. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2210776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadaqat, M.H.; Mohabati Mobarez, A.; Nikkhah, M. Curcumin Carbon Dots Inhibit Biofilm Formation and Expression of esp and gelE Genes of Enterococcus faecium. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 173, 105860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, E.; Helal, M.; El Nemr, A. Curcumin Loaded onto Folic Acid Carbon Dots as a Potent Drug Delivery System for Antibacterial and Anticancer Applications. J. Cluster Sci. 2024, 35, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, H.; Li, Z.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. Carbon dots derived from tea polyphenols as photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, S.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Jia, X.; et al. Orange-red to NIR emissive carbon dots for antimicrobial, bioimaging and bacteria diagnosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathap, N.; Balla, P.; Shivakumar, M.S.; Periyasami, G.; Karuppiah, P.; Ramasamy, K.; Venkatesan, S. Prosopis juliflora hydrothermal synthesis of high fluorescent carbon dots and its antibacterial and bioimaging applications. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dop, R.A.; Neill, D.R.; Hasell, T. Sulfur-polymer nanoparticles: Preparation and antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 20822–20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazou, T.P.; Chaintoutis, S.C. Comparison of disk diffusion and broth microdilution methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Campylobacter isolates of meat origin. J. Microbiol. Methods 2023, 204, 106649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaure, A.; Houdkova, M.; Antih, J.; Urbanova, K.; Doskocil, I.; Naik, M.L.; Patel, K.S.; Kokoska, L. Validation of Broth Macrodilution Volatilization Method for Testing of Essential Oils in Liquid and Vapor Phase: Chemical Composition, Cytotoxicity, and Antibacterial Effect of Indian Medicinal Plants against Pneumonia-Causing Pathogens. Molecules 2023, 28, 4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhou, C.; Benouda, H.; Bellaouchi, R.; Merzouki, M.; Fraj, E.; Harit, T.; Challioui, A.; Asehraou, A.; Touzani, R.; Ozdemir, I. Synthesis of novel tetrazolic derivatives and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1278, 134913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Hassan, K.T.; Hassan, O.M. Assessment of antimicrobial activity of chitosan/silver nanoparticles hydrogel and cryogel microspheres. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, E.; Coşkun, M.K.; Çobanoğlu, Ş.; Aslan, M.H.; Yazıcı, A. Effects of four antibiotics on Pseudomonas aeruginosa motility, biofilm formation, and biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance genes expression. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 106, 115931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Cao, C.; Ming, T.; Cao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Gan, N. Simultaneous and rapid screening of live and dead E. coli O157 with three signal outputs: An all-in-one biosensor using phage-apoferritin@ CuO2 signal tags on MXenes-modified electrode platform. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisada, A.; Matsumoto, E.; Hirano, R.; Konomi, M.; Bou Khalil, J.Y.; Raoult, D.; Ominami, Y. Detection of antimicrobial impact on gram-negative bacterial cell envelope based on single-cell imaging by scanning electron microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lv, X.; Qian, J.; Li, H.; Qian, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Lin, W.; Wang, H. Graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots embedded in carbon nanosheets for near-infrared imaging-guided combined photo-chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13304–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Guo, L.; Niu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P. Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3113–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, R.; Kaur, G. A novel facile synthesis of carbon dots-silver nanocomposite (CDs–Ag NCs) as potent antibacterial agent. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 5751–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinelnik, A.D.; Rybin, M.V.; Gets, D.S.; Khubezhov, S.A.; Zelenkov, L.E.; Makarov, S.V.; Shishkin, I.I. Ultra-broadband photoluminescent carbon dots synthesized by laser-induced thermal shock. Laser Photon. Rev. 2023, 17, 2200295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, M.; Liang, Q.; Wu, X.; Abbas, K.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Q.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. Single-atom manganese anchored on carbon dots for promoting mitochondrial targeting and photodynamic effect in cancer treatment. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 6679–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Abbas, K.; Huang, X.; Zhang, R.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. F, N-Doped carbon dots as efficient type I photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Li, P.; Meng, H.; Yan, H.; Huang, X.; Cui, H.; Su, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots/curcumin nanocomposite for combined photodynamic/photothermal dual-mode antibacterial therapy. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 39, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Li, G.; Lei, J.; Liu, M.; Jin, Y.; Li, B. One-step and one-precursor hydrothermal synthesis of carbon dots with superior antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7095–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Lv, C.; Liang, J.; Zhong, X.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Zhao, A.; Li, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, X. Molecular engineering of efficient singlet oxygen generators with near-infrared AIE features for mitochondrial targeted photodynamic therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli Yaraki, M.; Wu, M.; Middha, E.; Wu, W.; Daqiqeh Rezaei, S.; Liu, B.; Tan, Y.N. Gold nanostars-AIE theranostic nanodots with enhanced fluorescence and photosensitization towards effective image-guided photodynamic therapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Yu, F.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Ma, M.; Li, Z.; Tedesco, A.C.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Q.; Bi, H. Photo-activated autophagy-associated tumour cell death by lysosome impairment based on manganese-doped graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 2466–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Huang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Tian, J.; Yu, Q. Meticulously designed carbon dots as photo-triggered RNA-destroyer for evoking pyroptosis. Bioconjug. Chem. 2023, 34, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.J.; Dods, K.; Hammer, K.A. Development and validation of a new microplate assay that utilises optical density to quantify the antibacterial activity of honeys including Jarrah, Marri and Manuka. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauba, A.; Rahman, K.M. Evaluation of antibiotic resistance mechanisms in gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmehbad, N.Y.; Mohamed, N.A.; Abd El-Ghany, N.A.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M. Reinforcement of the antimicrobial activity and biofilm inhibition of novel chitosan-based hydrogels utilizing zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 246, 125582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Fan, J.; Wan, Y.; Li, J.; Pi, F. Enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of carbon-dots nanozymes modulated with P-doping. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, K.; Zhu, H.; Qin, W.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Bi, H. Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Carbon Dots: A Hybrid Approach with Levofloxacin, Curcumin, and Tea Polyphenols. C 2024, 10, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10030084
Abbas K, Zhu H, Qin W, Wang M, Li Z, Bi H. Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Carbon Dots: A Hybrid Approach with Levofloxacin, Curcumin, and Tea Polyphenols. C. 2024; 10(3):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10030084
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Khurram, Haimei Zhu, Weixia Qin, Meiyan Wang, Zijian Li, and Hong Bi. 2024. "Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Carbon Dots: A Hybrid Approach with Levofloxacin, Curcumin, and Tea Polyphenols" C 10, no. 3: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10030084
APA StyleAbbas, K., Zhu, H., Qin, W., Wang, M., Li, Z., & Bi, H. (2024). Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Carbon Dots: A Hybrid Approach with Levofloxacin, Curcumin, and Tea Polyphenols. C, 10(3), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10030084






