The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward ncRNA Precision
(This article belongs to the Section Long Non-Coding RNA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Long Non-Coding RNAs (LncRNAs)
1.2. LncRNAs and, in Particular, LINC RNA Worth Studying
1.3. Review Methodology
1.4. Review Aim
2. Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs (LincRNAs) and Their Involvement in Cancer
2.1. In Silico Databases Search (accessed on 22 November 2022 and Revised on 31 March 2023)
2.1.1. According to the Database by Ghent University LNCipedia
2.1.2. Pseudogenes-Derived LncRNAs (a Hot Area for Research; A Research Gap to Tackle)
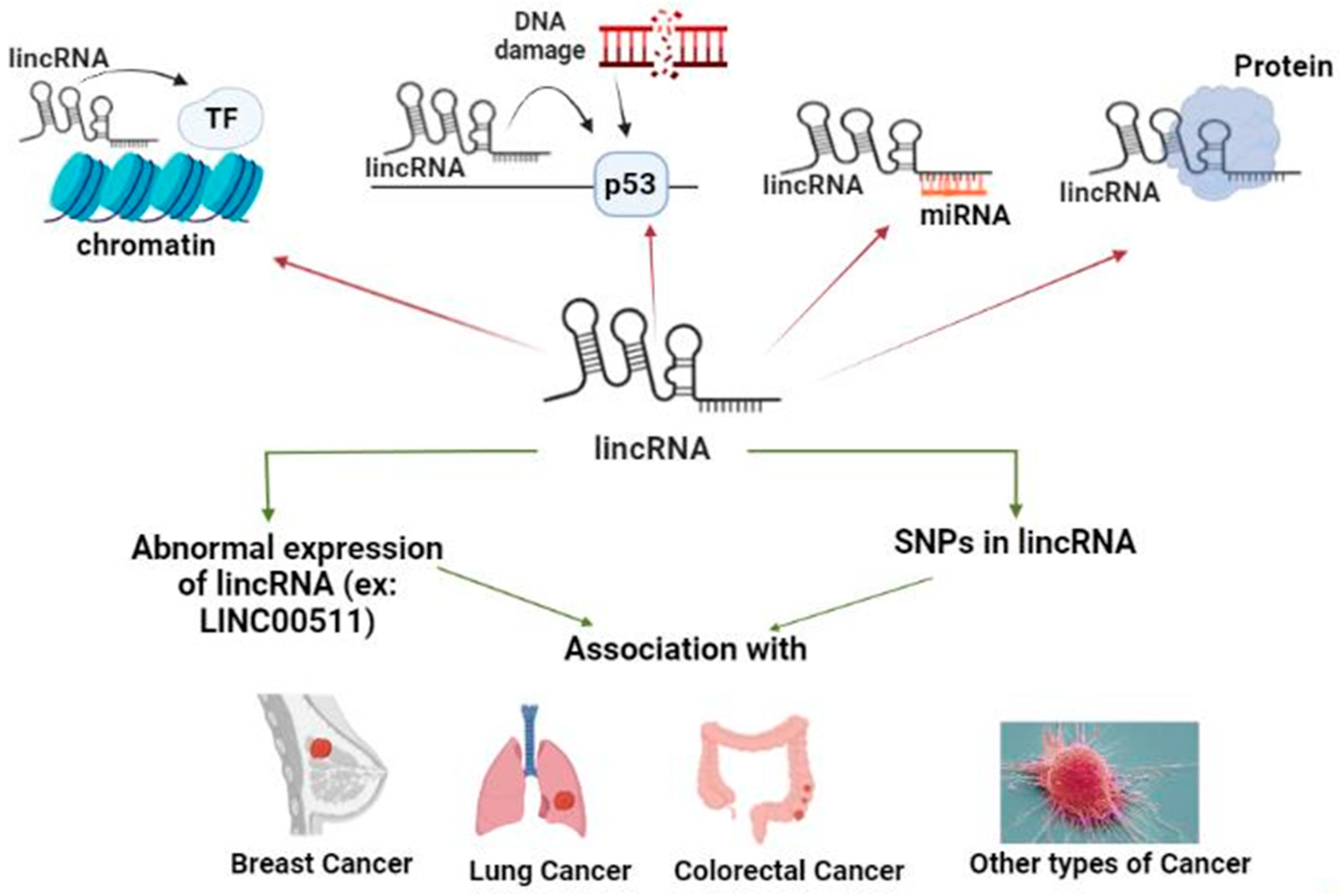
2.2. What Are LincRNAs?
2.2.1. LincRNA Role in Chromatin Remodeling
2.2.2. LincRNA Role in DNA Damage Repair (DDR)
2.2.3. LincRNA Role as a Competitive Endogenous RNA (ceRNA)
2.2.4. LincRNAs Role as Protein Scaffold (PS)
2.3. LincRNAs in Different Types of Cancer
2.3.1. LincRNAs List in Different Types of Cancer, Their Role and Mechanism(s) of Action (Table 2)
| Cancer Type | LincRNA | Expression | Sponging miR- | Mechanism of Action [Ref.] | Role in Cancer | Approach of the Study | Type of Samples Used in the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | MALAT-1 | Upregulated | 204, 143, 195, 490, 216b, 146-5p | Promoting disease progression [45] | Oncogene | Knockdown of MALAT-1 | Human blood samples |
| GBM | LINC00657 | Downregulated | 190a-3p | Regulation of PTEN expression [46] | Tumor suppressor | Overexpression of LINC00657 | Human GBM tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and GBM cell lines U-87 MG, LN-18, U-118 MG vs. astrocyte HA1800 |
| LINC00707 | Upregulated | 613 | Promotes progression, migration and invasion of glioma cells [47] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00707 | Human Glioma tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and glioma cell lines U87, U251, SHG-44, A172, T98G vs. normal astrocyte cell lines NHA, human embryonic kidney cell line HEK-293 | |
| TSCC | LINC00152 | Upregulated | 193b-3p | PI3K signaling pathway activation and downstream AKT enhancing cell cycle progression, tumor migration, invasion [48] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00152 | Human TSCC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and cell lines SCC-9, CAL-27 |
| Prostate | LINC00662 | Upregulated | 34a | Promotes cancer progression [49] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00662 | Human Prostate cancer tissues vs normal tissues and prostate cancer cells DU145, 22RV1, PC-3, and LNCaP vs. normal prostate epithelial cells WPMY-1 |
| CC | LINC00657 | Downregulated | 20a-5p | Upregulation of RUNX3 that targets DR5 leading to activation of NK cells [50] | Tumor suppressor | Overexpression of LINC00657 | Human CC tissues vs normal tissues and CC cell lines SiHa, HeLa, C33A, Caski vs. normal cervical squamous cell line Ect1/E6E7 |
| Colon CSCs | LINC01567 | Upregulated | 9 | CCND2 modulation and AQP3 regulation CREB/cAMP–PKA and proliferation and tumorigenesis regulation of colon CSCs [51] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC01567 | Human Colon cancer tissues vs. normal tissues |
| GC | LINC00473 | Upregulated | 16-5p | Modulating CCND2 expression, Promoting progression of GC and migration [52] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00473 | Human GC tissues vs. normal tissues and GC cell lines BGC823, AGS, MKN-45, NCI-N87, SGC7901 vs GES-1 and female BALB/c-nude mice for implantation |
| LINC00355 | Upregulated | - | Regulating Wnt/β-catenin, promoting progression and inhibition of apoptosis [53] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00355 | Human GC tissues vs normal tissues and GC cell lines BGC-823, MGC-803, AGS, SGC-7901 vs normal gastric epithelial cells GES-1 | |
| LINC01555 | Upregulated | - | Interacting with Notch signalling pathway for progression of GC [54,55] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC01555 | Human GC tissues vs para-carcinoma tissues and GC cell lines MGC803, MKN45, BSG823, SGC7901, vs normal human gastric mucosal epithelial cell GES-l | |
| LSCC | HOTAIR | Upregulated | - | Promoting PTEN methylation, progression, invasiveness, resistance to apoptosis [56] | Oncogene | Knockdown of HOTAIR | Human LSCC tissues vs adjacent normal tissues and and mice BALB/c for implantation |
| Lung adenocarcinoma | LINC00673 | Upregulated | - | Activation of Wnt/B-catenin for progression of the disease [57,58] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00673 | Human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines HCC827, NCI-H1650, A549, NCI-H596, NCI-H1975, NCI-H1299, SK-LU-1, NCI-H358, NCI-H2009, HCC4006, NCI-H2030, PC9, and nude mice for implantation |
| Various cancer types | MALAT-1 | Upregulated | - | Interaction with Serine/Arginine splicing factors, changing distribution to nuclear speckle domains, promoting progression of the disease [59] | Oncogene | Knockdown of MALAT-1 | Human HeLa cells |
| Neuro-blastoma | MIAT | Upregulated | - | Modulation of MYCN and PHOX2B driver genes leading to progression of the disease [60] | Oncogene | Knockdown of MIAT | RNA sequencing data analysis |
| BC | Linc-ROR | Upregulated | 205, 145 | EMT induction and promoting metastasis [61] | Oncogene | Knockdown of Linc-ROR | Human BC tissues vs adjacent normal tissues and MCF10A, MDA-MB-231, BT549, BT474, MDA-MB-436, MDA-MB-435, HEK 293 and immunodeficient nude mice for implantation |
| LincRNA-BC2 | Upregulated | - | Interacting with BRCA1 and BRCA2 [62] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LincRNA-BC2 | Human BC tissues vs adjacent normal tissues | |
| TNBC | LINC00299 | Hyper-methylated | - | Hypermethylation [63] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00299 | Human blood samples |
| BC | LINC00641 | Downregulated | 194-5p | Inhibition of cell growth, invasion, migration [64] | Tumor suppressor | Overexpression of LINC00641 | Human BC tissues vs adjacent normal tissues and BCAP-37, MDA-MB-453, UACC-812, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 vs normal breast epithelial cell line MCF-10A |
| TNBC | LINC00993 | Downregulated | - | Generating G0/G1 arrest and regulation of p21 and p53 genes [65] | Tumor suppressor | Overexpression of LINC00993 | Human BC cell lines MDA-MB-231, BT-549 and female BALB/c nude mice for implantation |
| BC | LINC00885 | Upregulated | - | EGFR, EREG, FOXM1 and TP53 activation, progression of early stage BC [66] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00885 | Human BC cell lines MCF10 DCIS.COM, MDA-MB-231, MCF7, T47D vs normal breast epithelial cell lines MCF10A, 184A1 |
| Linc-APOC1P1-3 | Upregulated | - | Binding tubulin to decrease α-tubulin acetylation and inactivate caspase-3, BC progression, prevention of BC cells apoptosis [67] | Oncogene | Knockdown of Linc-APOC1P1-3 | Human BC tissues vs normal tissues | |
| Linc-HOTAIR | Upregulated | - | Interaction with PRC2 and Promoting BC metastasis [68] | Oncogene | Knockdown of Linc-HOTAIR | Human BC tissues vs normal tissues, human cell lines MDA-MB-231, SK-BR-3, MCF-10A, MCF-7, HCC1954, T47D, MDA-MB-453, H16N2 and nude mice for implantation | |
| LINC00657 | Upregulated | 590-3p | GOLPH3 upregulation leading to invasion, migration, proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis of BC cells [69] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00657 | Human BC tissues vs adjacent normal tissues and human BC cell lines MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, T47D, BT-549 vs normal breast epithelial cell line MCF-10A | |
| LINC00511 | Upregulated | 185-3p | - [42] | Oncogenic | Knockdown of LINC00511 | Human blood samples | |
| LINC00460 | Upregulated | 320a | MAL2 upregulation and promoting cancer cell proliferation and migration [70] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00460 | MDA-MB-231, BT-549 cells | |
| LINC00922 | Upregulated | - | Promoting NKD2 methylation, promoting tumorigenesis, invasion, metastasis and regulation EMT [71] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC00922 | Human BC tissues vs adjacent normal tissues and human MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, SK-BR3, MCF10A | |
| CRC | LINC01088 | Upregulated | 548b-5p and 548c-5p | G3BP1 expression upregulation, enhancing CRC progression [72] | Oncogene | Knockdown of LINC01088 | Human CRC tissues vs para-cancerous tissues, human CRC cell lines, colonic epithelial cells, and mice for implantation |
2.3.2. LincRNAs List in Breast Cancer (BC)
3. LINC00511 and Its Contribution in Different Cancer Types
3.1. LINC00511 In Silico Info (Accessed on 25 November 2022 and Revised on 31 March 2023)
3.2. LINC00511 in Cancer
3.2.1. LINC00511 Role in Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
3.2.2. LINC00511 Role in Lung Cancer
3.2.3. LINC00511 Role in Cervical Cancer (CC)
3.2.4. LINC00511 Role in Gastric Cancer (GC)
3.2.5. LINC00511 Role in Pancreatic Cancer (PC)
3.2.6. LINC00511 Role in Hepatocellular Cancer (HCC)
3.2.7. LINC00511 Role in Glioblastoma (GBM)
3.2.8. LINC00511 Role in Osteosarcoma (OS)
3.2.9. LINC00511 Role in Different Types of Breast Cancer (BC)
4. LncRNAs SNPs in Different Cancer Types and Their Mechanism of Action
4.1. LncRNAs SNPs List in Breast Cancer, Their Role and Mechanism of Action (Table 4)
| LncRNA List | SNPs List | Mechanism of Action [Ref.] | Role in BC | Type of Samples Used in the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDKN2B-AS1; ANRIL | rs310965215 | Sponging miR-4440 [117] | Cells’ altered ability to proliferate, invade, migrate | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| rs1333045, rs1333048, rs4977574, and rs10757278 | - [120] | Increased risk | ||
| MALAT1 | rs7927113 | - [121] | Association with BC susceptibility; AG, AG + GG | |
| rs619586 | - [121] | Protects against | ||
| rs3200401 | - [121] | Reduces risk | ||
| GAS5 | rs145204276 | Increasing promoter activity, binding TF specificity protein 1, raise GAS5 [123] | Inhibition of BC development | |
| CASC15 | rs7740084, rs1928168 | - [122] | Reduce risk | |
| rs9393266 | - [124] | Correlated to risk | ||
| HOTAIR | rs920778 | Interaction with reproductive factors [125] | Elevation of risk | |
| MIR2052HG | rs34841297 | Regulation of miR-4456 expression [126] | Increased susceptibility | |
| LINC00520 | rs8012083 | - [128] | Increased TNBC susceptibility | |
| AQP4-AS1 | rs527616 | - [129] | Increased susceptibility | DNA extracted from human blood samples and BC tissues vs. normal tissues |
| SOX2OT | rs9839776 | Influencing SOX2OT expression [130] | Increases risk and related to onset | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| H19 | rs3741219, rs217727, rs2839698 | - [128] | Increased risk | |
| rs3741216 | - [131] | Decreased risk | ||
| SRA | rs10463297 | Affecting SRA mRNA expression [132] | Increased risk | |
| LINC00511 | rs11657109, rs17780195, rs9906859 | - [133] | Protection | |
| Linc-ROR | rs4801078 | Interplay with reproductive factors [134] | Increased risk |
4.2. LncRNAs SNPs List in Lung Cancer, Their Role and Mechanism of Action (Table 5)
| LncRNA List | SNPs List | Mechanism of Action [Ref.] | Role in Lung Cancer | Type of Samples Used in the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEAT1 | rs2239895 | - [135] | Increased carcinoma risk | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| CCAT1 | rs1948915 | - [136] | Decreased cancer in females’ | |
| LOC105369301 | rs219741 | - [137] | Elevated risk | |
| LINC01833 | rs498238 | - [137] | Elevated risk | |
| lnc-NDUFS6-5:5 | rs16901995 | - [137] | Reduced risk | |
| AC008392.1 | rs7248320 | - [138] | Reduced risk in GG genotype | |
| HOTAIR | rs4759314 | - [139] | Increases cancer risk | |
| rs12826786 | - [137] | “CT” and “CT + TT” decreases risk | ||
| HOTAIR | rs920778 and rs1899663 | - [140] | Increased susceptibility | |
| GAS5 | rs145204276 | - [141] | Aiding in tumor stage, distal metastases, LN metastasis prediction, in EGFR wild type patients | |
| PRNCR1 | rs1456315 | Affecting lncRNA secondary structure and target miRNAs [143] | Increased risk in patients with T allele | |
| CCAT2 | rs6983267 | Affecting the secondary structure of lncRNA and target of miRNAs [143] | Increased risk of lung cancer in patients with G allele | |
| MALAT1 | rs3200401 | MALAT1’s structural properties alterationand cancer genes expression [144] | Increased susceptibility | |
| HOXA11-AS | rs17427875 | Associating with TFs [145] | (T allele) increases risk | |
| rs11564004 | - [143] | (G allele) play a protective role | ||
| H19 | rs217727 | - [146] | Elevated risk in A/A homozygous | |
| LOC146880 | rs140618127 | miR-539-5p alternative binding site, ENO1 phosphorylation, PI3K/Akt activation [147] | Decreased risk | Human NSCLC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human NSCLC cell lines A549, PC9 vs. human lung epithelial BEAS-2B cells |
4.3. LncRNAs SNPs List in Colorectal Cancer (CRC), Their Role and Mechanism of Action (Table 6)
| LncRNA List | SNPs List | Mechanism of Action [Ref.] | Role in CRC | Type of Samples Used in the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MALAT1 | rs619586, rs664589, rs1194338 | Affecting binding of TFs [146] | Associated with risk | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| CCAT1 | rs67085638 | - [149] | Increases risk | |
| rs7013433 | - [147] | Related to CRC late clinical stage | ||
| RP11-108K3.2 | rs2470151 | - [150] | Decreased risk with CT/TT genotype | |
| LINC-ROR | rs1942347 | - [151] | Associated with large tumor size and mortality | Extracted DNA from FFPE tissue samples |
| H19 | rs2839698, rs4930101, rs11042170, rs27359703 | rs2839698 change activity of promotor and H19 function [152,153] | Increased risk | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| HOTTIP | rs1859168 | Regulates lncRNA gene expression [154,155] | Increased susceptibility | |
| rs3807598, rs2067087, rs17427960 | Affect TFBSs [154,155] | |||
| GAS5 | rs55829688 | Reduced GAS5 expression by altering TF YY1′s affinity to GAS5 [154] | Increased risk | |
| PCAT1 | rs2632159 | - [155] | Increased risk | |
| PUNISHER “AGAP2-AS1” | rs12318065 | Modify regulatory motifs; MRG1, Sin3Ak-20_disc6, HOXA9_1, affect TFs binding POL2, ZNF263, and STAT1 [156] | Elevated risk, tumor relapse and short survival time | Extracted DNA from FFPE tissue samples |
| MAGI2-AS3 | rs7783388 | Influencing binding ability of GR to lncRNA promoter [157] | Increased risk | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| SNHG16 | rs7353 | Influencing lncRNA expression [158] | Suppresses susceptibility | |
| rs8038, rs15278 | Increased risk | |||
| CCSlnc362 “RP11-362K14.5” | rs1317082 | Binding miR-4658 and impairing lncRNA expression [159] | Protection | Human CRC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human CRC cell lines HCT116, DLD-1, SW480, LOVO, HT29, RKO vs. the immortalized human colorectal epithelial cell line FHC |
| PTCSC3 | rs944289 | - [163] | Decreased risk | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| PRNCR1 | rs1456315 | - [164] | Increased risk | |
| MEG3 | rs7158663 | - [165] | Increased risk | |
| LAMC2-1:1 | rs2147578 | Losing miR-128-3p binding [164] | Increased risk | |
| HOTAIR | rs7958904 | - [165] | Associated with mortality and incidence | |
| UCA1 | rs12982687 | Affecting UCA1’s binding to miR-873-5p and HIF-1 signaling [166] | Progression of smoking-triggered CRC | |
| HULC | rs7763881 | Correlated with expression of HULC [167] | Genetic indicator for CRC | |
| TINCR | rs2288947 | Affected motifs; Nanog_disc3, CTCF_disc9, Rad21_disc10, SP1_disc3, and SMC3_disc3 [168] | Allele G associated with decreased risk | |
| rs8105637 | TCF12 and PITX2 expression linked to carcinogenesis [168] | Allele A associated with increased risk |
4.4. LncRNAs SNPs List in Pancreatic Cancer, Their Role and Mechanism of Action (Table 7)
| LncRNA List | SNPs List | Mechanism of Action [Ref.] | Role in Pancreatic Cancer | Type of Samples Used in the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANRIL | rs1537373 | Affecting TF binding and regulating CDKN2B expression [171] | Increased susceptibility | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
| rs1412832 | CDKN2A, p16 exhibit harmful somatic, germline mutations and dysregulation [172] | Increased risk | ||
| HOTAIR | rs4759314 | - [173] | Increased susceptibility | |
| rs200349340 | Interfering with binding of miR-29a [173] | |||
| lnc-SMC2-1 | rs7046076 | Interfering with binding to miR-1256 [174] | Increased risk | |
| LINC00673 | rs11655237 | Binding site for miR-1231 and limits PTPN11 degradation [176] | Increased risk | Extracted DNA from human PDAC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues |
| HOTTIP | rs1859168 | - [177] | Decreased susceptibility | Extracted DNA from human blood samples |
4.5. LncRNAs SNPs List in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Their Role and Mechanism of Action (Table 8)
| LncRNA List | SNPs List | Mechanism of Action [Ref.] | Role in HCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| HOTAIR | rs7958904 | Binding miR-615-3p [176] | Linked to incidence and prognosis |
| PVT1 | rs3931282, rs1134492, rs10589312 | Bind miR-205-5p, 34b-5p, 183-3p, 31-5p [176] | |
| EGFR-AS1 | rs84557 | Binding miR-33b-5p [176] | |
| HOTTIP | rs2067087, rs17501292, rs17427960 | Regulation of certain motifs [177] | Increased susceptibility |
| MALAT1 | rs4102217 | ||
| H19 | rs2839698 | - [178] | Prediction of risk and prognosis |
| LINC00673 | rs9914618 | - [179] | Increased susceptibility and LN metastasis |
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEBP1 | AE Binding Protein 1 |
| AGAP2-AS1 | AGAP2 Antisense RNA 1 |
| ANRIL | Antisense non-coding RNA in the INK4 locus |
| APE1 | Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 |
| AQP3 | Aquaporin 3 |
| AQP4-AS1 | AQP4 Antisense RNA 1 |
| AS | Antisense |
| Bax | Bcl-2 Associated X-protein |
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| Bcl 2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BRCA1 | Breast Cancer antigen 1 |
| BRCA2 | Breast Cancer antigen 2 |
| CASC15 | Cancer Susceptibility 15 |
| CC | Cervical cancer |
| CCAT1 | Colon Cancer Associated Transcript 1 |
| CCAT2 | Colon Cancer Associated Transcript 2 |
| CCND2 | Cyclin D2 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A |
| CDKN2B | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B |
| CDKN2B-AS1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense RNA 1 |
| ceRNA | competitive endogenous RNA |
| chr6 | chromosome 6 |
| CRC | Colorectal Cancer |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| CSCs | Cancer Stem Cells |
| CTCF | CCCTC-binding factor |
| DDR | DNA Damage Repeat |
| DRAM1 | DNA Damage Regulated Autophagy Modulator 1 |
| DSB | Double Strand Break |
| E2F1 | E2F Transcription Factor 1 |
| E2F2 | E2F Transcription Factor 2 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EGFR-AS1 | Epidermal growth factor receptor-Antisense RNA 1 |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| ENO1 | Enolase 1 |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| EREG | Epiregulin |
| EYA1 | Eyes absent homolog 1 |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded |
| FOXM1 | Forkhead box M1 |
| G3BP1 | G3BP Stress Granule Assembly Factor 1 |
| GACAT2 | Gastric Cancer Associated Transcript 2 |
| GAS5 | Growth Arrest Specific 5 |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| GC | Gastric Cancer |
| GCNT3 | Glucosaminyl (N-acetyl) transferase 3 |
| GOLPH3 | Golgi Phosphoprotein 3 |
| GR | Glucocorticoid Receptor |
| GWAS | Genome Wide Association Studies |
| HC | Hepatic Cancer |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus |
| HER-2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| hg38 | ID used for Genome Reference Consortium Human Reference 38 |
| HIF-1 | Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 |
| HNF4 | Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 |
| hnRNP-K | heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-K |
| HOTAIR | HOX transcript antisense RNA |
| HOTTIP | HOXA transcript at the distal tip |
| HOXA9 | Homeobox protein Hox-A9 |
| HOXA11-AS | HOXA11 Antisense RNA |
| HPV | Human papillomavirus |
| HULC | Highly upregulated in liver cancer |
| IL-24 | Interleukin 24 |
| KDM2A | Lysine-specific demethylase 2A |
| KLF2 | KLF transcription factor 2 |
| LATS2 | Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 2 |
| LINC00511 | Long intergenic non coding RNA 00511 |
| LINC-PINT | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA, P53 Induced Transcript |
| lincRNAs | Long intergenic non-coding RNAs |
| lincRNA-BC2 | Long intergenic non-coding RNA-Breast Cancer 2 |
| Linc-ROR | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA, Regulator Of Reprogramming |
| LN | Lymph Node |
| LncRNA | Long non coding RNA |
| lnc-SMC2-1 | Long non coding RNA structural maintenance of chromosomes 2 |
| LSCC | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| LSD1 | Lysine-specific demethylase 1 |
| MAEL | Maelstrom Spermatogenic Transposon Silencer |
| MAGI2-AS3 | MAGI2 Antisense RNA 3 |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| MEG3 | Maternally Expressed 3 |
| MIR2052HG | MIR2052 Host Gene |
| miR | Micro-RNA |
| miRNA | Micro-RNA |
| MMP13 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 13 |
| MRG1 | Melanocyte-specific gene-related gene 1 |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| MRP1 | Multidrug resistance protein 1 |
| NEAT1 | Nuclear Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 |
| NFIA | Nuclear Factor 1 A |
| NFIX | Nuclear factor 1/X gene |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| NKD2 | Naked cuticle homolog 2 |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| OS | Osteosarcoma |
| PC | Pancreatic Cancer |
| PCAT-1 | Prostate Cancer Associated Transcript-1 |
| PRC2 | Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 |
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| PDK4 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoamide kinase isozyme 4 |
| PHOX2B | Paired-like homeobox 2b |
| PITX2 | Paired Like Homeodomain 2 |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase M2 |
| PLD1 | Phospholipase D1 |
| Pol ll | RNA Polymerase ll |
| PR | Progesterone Receptor |
| PRNCR1 | Prostate Cancer Associated Non-Coding RNA 1 |
| PS | Protein Scafold |
| PTPN11 | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-receptor type 11 |
| PTCSC3 | Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Susceptibility Candidate 3 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| PVT1 | Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 |
| RPIseq | RNA-Protein Interaction Prediction |
| RNA | Ribo Nucleic Acid |
| RUNX3 | RUNX Family Transcription Factor 3 |
| RXRA | retinoic X receptor alpha |
| SDGs #3 | Sustainable Development Goals; goal 3 |
| SMC3 | Structural Maintenance Of Chromosomes 3 |
| smORFs | Small Open Reading Frames |
| SNHG16 | Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 16 |
| SNPs | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| SOX2OT | SOX2 overlapping transcript |
| SOX4 | SRY-box transcription factor 4 |
| SP1 | Specificity protein 1 |
| SR | Serine/Arginine |
| SRA | Steroid Receptor RNA Activator |
| ST5 | Suppression of tumorigenicity 5 |
| STXBP4 | Syntaxin Binding Protein 4 |
| STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| TADA1 | Transcriptional Adaptor 1 |
| TASs | Trait-associated SNPs |
| TCF12 | Transcription Factor 12 |
| TCNR | Tumor cell necrosis rate |
| TFs | Transcription factors |
| TFBSs | Transcription Factor Binding Sites |
| TGFA | Transforming growth factor alpha |
| TINCR | Terminal differentiation-induced non-coding RNA |
| TNBC | Triple Negative Breast Cancer |
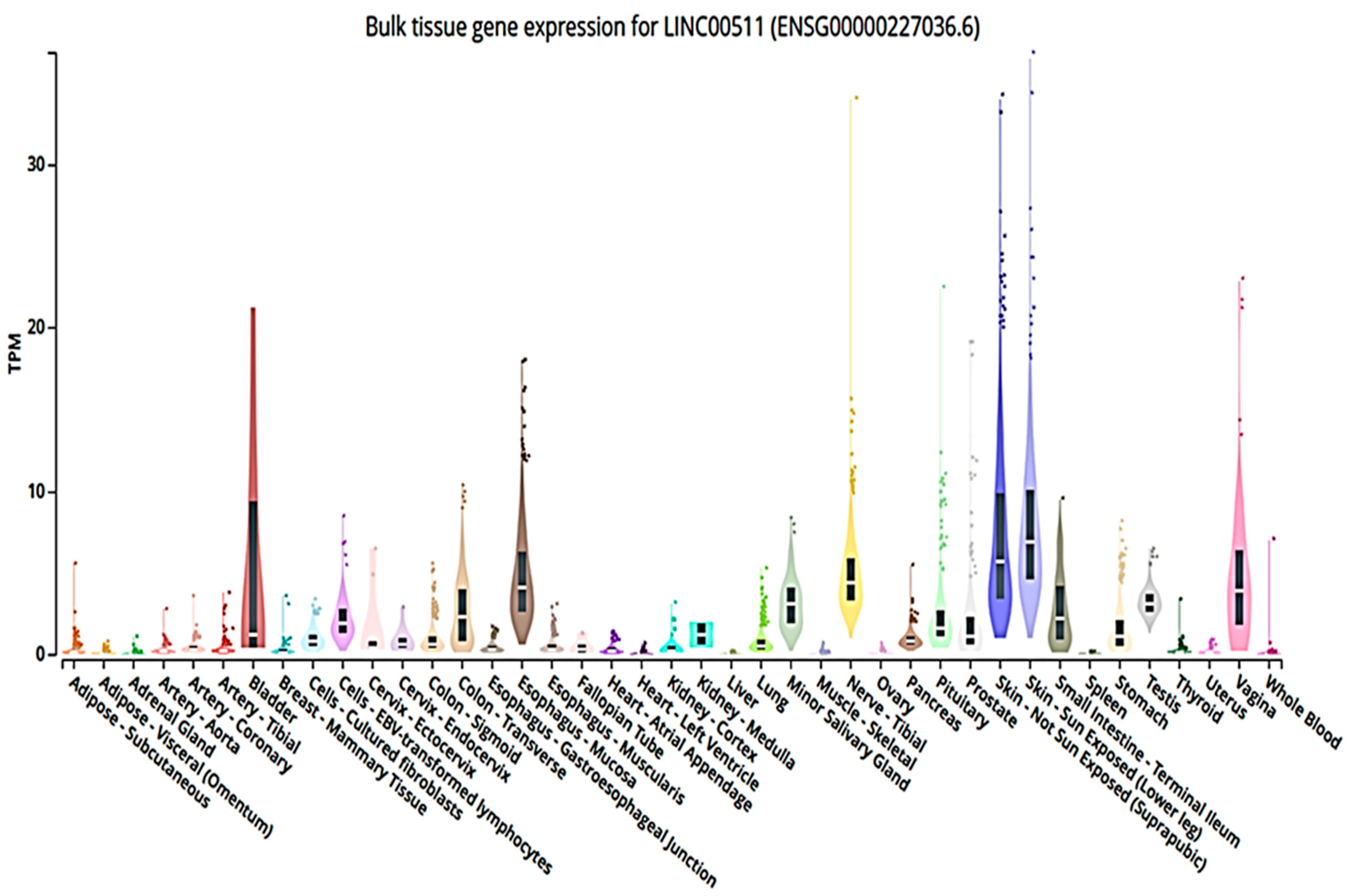
| TPM | Transcripts per million |
| TSCC | Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| UCA1 | Urothelial cancer associated 1 |
| VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| VLDLR-AS1 | VLDLR Antisense RNA 1 |
| Wnt | Wingless-INT |
| Wnt10A | Wnt Family Member 10A |
| Xist | X-inactive specific transcript |
| YB1 | Y box binding protein 1 |
| YY1 | Yin Yang 1 |
| ZEB1 | Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 |
| ZNF263 | Zinc Finger Protein 263 |
References
- Xiu, B.; Chi, Y.; Liu, L.; Chi, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Si, J.; Li, L.; Xue, J.; et al. LINC02273 drives breast cancer metastasis by epigenetically increasing AGR2 transcription. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, F.; Chen, W.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, T.; Mo, L. An autophagy-related long non-coding RNA signature for glioma. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, G.; Spector, D.L. MALAT1 long non-coding RNA and breast cancer. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fullwood, M.J. Roles, Functions, and Mechanisms of Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, H. Gene regulation of mammalian long non-coding RNA. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheikh, N.M.; Abulsoud, A.I.; Fawzy, A.; Wasfey, E.F.; Hamdy, N.M. LncRNA NNT-AS1/hsa-miR-485–5p/HSP90 axis in-silico and clinical prospect correlated-to histologic grades-based CRC stratification: A step toward ncRNA Precision. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 247, 154570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznaourova, M.; Schmerer, N.; Schmeck, B.; Schulte, L.N. Disease-Causing Mutations and Rearrangements in Long Non-coding RNA Gene Loci. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 527484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R. What Are Long Noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs)? Goldlab. 2023. Available online: https://www.gold-lab.org/why-lncrnas (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Sun, M.; Gadad, S.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kraus, W.L. Discovery, Annotation, and Functional Analysis of Long Noncoding RNAs Controlling Cell-Cycle Gene Expression and Proliferation in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, K.; Yu, R.; Zhou, B.; Huang, P.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. From “Dark Matter” to “Star”: Insight Into the Regulation Mechanisms of Plant Functional Long Non-Coding RNAs. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 650926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, M.M.; Johnson, A.M. Exploring the mechanisms behind long noncoding RNAs and cancer. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2018, 3, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitiyiming, Y.; Ye, L.; Yang, T.; Yu, W.; Naranmandura, H. Linear and Circular Long Non-Coding RNAs in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: From Pathogenesis to Classification and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska, J.; Kolenda, T.; Poter, P.; Sobocińska, J.; Guglas, K.; Stasiak, M.; Bliźniak, R.; Teresiak, A.; Lamperska, K. Long intergenic non-coding rnas in HNSCC: From “junk dna” to important prognostic factor. Cancers 2021, 13, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shan, G. The physiological function of long-noncoding RNAs. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, M.; Gkretsi, V. LincRNAs and snoRNAs in Breast Cancer Cell Metastasis: The Unknown Players. Cancers 2022, 14, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volders, P.J.; Anckaert, J.; Verheggen, K.; Nuytens, J.; Martens, L.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J. Lncipedia 5: Towards a reference set of human long non-coding rnas. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D135–D139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Lin, L.; Chen, B.; Dai, J. L1 elements, processed pseudogenes and retrogenes in mammalian genomes. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.; Ding, B.; Fu, P. Pseudogene-Derived lncRNAs and Their miRNA Sponging Mechanism in Human Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, R.L.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.; Jones, T.E.M.; Tweedie, S.; Haim-Vilmovsky, L.; Bruford, E.A. Genenames.org: The HGNC resources in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1003–D1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, R.L.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.; Jones, T.E.M.; Tweedie, S.; Haim-Vilmovsky, L.B.E. Symbol Report for LINC00265-2P. HUGO Gene Nomencl. Comm. 2023. Available online: https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:38523 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Seal, R.L.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.; Jones, T.E.M.; Tweedie, S.; Haim-Vilmovsky, L.B.E. Symbol Report for LINC00265-3P. HUGO Gene Nomencl. Comm. 2023. Available online: https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:38536 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Seal, R.L.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.; Jones, T.E.M.; Tweedie, S.; Haim-Vilmovsky, L.B.E. Symbol Report for LINC00268-2P. HUGO Gene Nomencl. Comm. 2023. Available online: https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:37771 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Seal, R.L.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.; Jones, T.E.M.; Tweedie, S.; Haim-Vilmovsky, L.B.E. Symbol Report for LINC00328-2P. HUGO Gene Nomencl. Comm. 2023. Available online: https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:42027 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The Diversity of Long Noncoding RNAs and Their Generation. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, M.J.; Vaughn, I.W.; McManus, M.T. Pervasive Transcription of the Human Genome Produces Thousands of Previously Unidentified Long Intergenic Noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, J.D.; Wei, Y.; Khavari, P.A. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changizian, M.; Nourisanami, F.; Hajpoor, V.; Parvaresh, M.; Bahri, Z.; Motovali-Bashi, M. LINC00467: A key oncogenic long non-coding RNA. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 536, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutenberg-Schoenberg, M.; Sexton, A.N.; Simon, M.D. The Properties of Long Noncoding RNAs That Regulate Chromatin. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2016, 17, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Yang, Y.W.; Liu, B.; Sanyal, A.; Corces-Zimmerman, R.; Chen, Y.; Lajoie, B.R.; Protacio, A.; Flynn, R.A.; Gupta, R.A.; et al. A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature 2011, 472, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, E.; Erman, B. Long noncoding RNA (lincRNA), a new paradigm in gene expression control. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2017, 17, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongtrakoongate, P.; Riddick, G.; Fucharoen, S.; Felsenfeld, G. Association of the Long Non-coding RNA Steroid Receptor RNA Activator (SRA) with TrxG and PRC2 Complexes. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirinejad, R.; Rezaei, M.; Shirvani-Farsani, Z. An update on long intergenic noncoding RNA p21: A regulatory molecule with various significant functions in cancer. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Xu, M.; Mo, Y.-Y. Role of the lncRNA-p53 regulatory network in cancer. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh, N.M.; Abulsoud, A.I.; Wasfey, E.F.; Hamdy, N.M. Insights on the potential oncogenic impact of long non-coding RNA nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase antisense RNA 1 in different cancer types; integrating pathway(s) and clinical outcome(s) association. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 240, 154183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannan, W.J.; Pederson, D.S. Mechanisms and Consequences of Double-Strand DNA Break Formation in Chromatin. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianatpour, A.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. The Role of Long Non Coding RNAs in the Repair of DNA Double Strand Breaks. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thapar, R. Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair by non-coding RNAs. Molecules 2018, 23, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, E.A.; Fridman, M.V.; Moscovtsev, A.A.; Filippova, E.A.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Kushlinskii, N.E. Lncrnas in ovarian cancer progression, metastasis, and main pathways: Cerna and alternative mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ai, S.; Cheng, L. The lncrna linc00691functions as a cerna for miRNA-1256 to suppress osteosarcoma by regulating the expression of ST5. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 13171–13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Sanad, E.F.; Elshimy, R.A.A.; Hamdy, N.M. Competitive Endogenous Role of the LINC00511/miR-185-3p Axis and miR-301a-3p From Liquid Biopsy as Molecular Markers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 749753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitale, R.C.; Tsai, M.C.; Chang, H.Y. RNA templating the epigenome: Long noncoding RNAs as molecular scaffolds. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Srikantan, S.; Yang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; De, S.; Huarte, M.; Zhan, M.; Becker, K.G.; Gorospe, M. LincRNA-p21 suppresses target mRNA translation. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraih, E.A.; Ellawindy, A.; Fala, S.Y.; Al Ageeli, E.; Gouda, N.S.; Fawzy, M.S.; Hosny, S. Oncogenic long noncoding RNA MALAT1 and HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Song, S.; Yang, H.; Han, F.; Liu, F.; Hu, Y. Long intergenic non-coding LINC00657 regulates tumorigenesis of glioblastoma by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-190a-3p. Aging 2019, 11, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hu, K. The Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA 00707 Sponges MicroRNA-613 (miR-613) to Promote Proliferation and Invasion of Gliomas. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Rui, B.; Cao, Y.; Gong, X.; Li, H. Long non–coding RNA LINC00152 acts as a sponge of miRNA–193b–3p to promote tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Qiao, Y.-H.; Song, R.-J. Long noncoding RNA LINC00662 functions as miRNA sponge to promote the prostate cancer tumorigenesis through targeting miR-34a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3688–3698. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Zhou, M.; Lv, H.; Mao, X.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Li, L.; Xing, H. Long noncoding RNA LINC00657 inhibits cervical cancer development by sponging miR-20a-5p and targeting RUNX3. Cancer Lett. 2021, 498, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Mi, L.; Dong, J.; Zou, J. Long intergenic non-protein-coding RNA 1567 (LINC01567) acts as a “sponge” against microRNA-93 in regulating the proliferation and tumorigenesis of human colon cancer stem cells. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Sun, M.; Bai, R.; Lu, D.; Di, S.; Ma, T.; Zou, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00473 promotes proliferation and migration of gastric cancer via the miR-16-5p/CCND2 axis and by regulating AQP3. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, P.-B.; Sun, X.-M.; Yao, J. LINC00355 inhibits apoptosis and promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8377–8383. [Google Scholar]
- Emam, O.; Wasfey, E.F.; Hamdy, N.M. Notch-associated lncRNAs profiling circuiting epigenetic modification in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, Z. Linc01555 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric carcinoma cells by interacting with Notch signaling pathway. J. Buon 2020, 25, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Feng, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, M. Long intergenic noncoding RNA HOTAIR is overexpressed and regulates PTEN methylation in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El Fattah, Y.K.; Abulsoud, A.I.; AbdelHamid, S.G.; Hamdy, N.M. Interactome battling of lncRNA CCDC144NL-AS1: Its role in the emergence and ferocity of cancer and beyond. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zhu, T.; Wu, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Cai, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, M.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00673-v4 promotes aggressiveness of lung adenocarcinoma via activating WNT/β-catenin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14019–14028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; et al. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombaut, D.; Chiu, H.S.; Decaesteker, B.; Everaert, C.; Yigit, N.; Peltier, A.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Bartenhagen, C.; Fischer, M.; Roberts, S.; et al. Integrative analysis identifies lincRNAs up- and downstream of neuroblastoma driver genes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Yao, R.; Ma, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Lu, J. LincRNA-ROR induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and contributes to breast cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhu, L.; Ji, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Gan, S.; Zhao, M.; Yang, H. Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs (LincRNAs) Identified by RNA-Seq in Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, J.L.; Huang, G.; Manoochehri, M.; Mesa, K.G.; Schick, M.; Silos, R.G.; Ko, Y.D.; Brüning, T.; Brauch, H.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Long intergenic noncoding RNA 299 methylation in peripheral blood is a biomarker for triple-negative breast cancer. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Lv, M.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, S. Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00641 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by sponging miR-194-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 2668–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Jian, L.; Tao, K.; Chen, C.; Yu, H.; Liu, S. Novel Breast-Specific Long Non-coding RNA LINC00993 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, M.C.; Canzoneri, R.; Gurruchaga, A.; Lee, J.; Tatineni, P.; Kil, H.; Lacunza, E.; Aldaz, C.M. Linc00885 a novel oncogenic long non-coding rna associated with early stage breast cancer progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.H.; Wang, J.G.; Li, L.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; Ren, K.H.; Jin, Y.T.; Lv, L.; Yu, J.G.; Yang, J.Y.; Lu, Q.; et al. Long intergenic non-coding RNA APOC1P1-3 inhibits apoptosis by decreasing α-tubulin acetylation in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.; Qu, F.; Yang, W.; Chen, N. Effect of LINC00657 on apoptosis of breast cancer cells by regulating mir-590-3p. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 4561–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Shi, T.; Wang, Q. LINC00460 Facilitates Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Ferroptosis in Breast Cancer Through the miR-320a/MAL2 Axis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231164359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, T.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Wu, G.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. LINC00922 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasive and migratory capacities in breast cancer through promoting NKD2 methylation. Cell. Signal. 2021, 77, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pan, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Gao, T.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, S. Upregulated LINC01088 facilitates malignant phenotypes and immune escape of colorectal cancer by regulating microRNAs/G3BP1/PD-L1 axis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 1965–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Baran, J.; Cros, A.; Guberman, J.M.; Haider, S.; Hsu, J.; Liang, Y.; Rivkin, E.; Wang, J.; Whitty, B.; et al. International cancer genome consortium data portal-a one-stop shop for cancer genomics data. Database 2011, 2011, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LINC00511. Int. Cancer Genome Consort. 2023. Available online: https://dcc.icgc.org/genes/ENSG00000227036 (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Agbana, Y.L.; Abi, M.E.; Ni, Y.; Xiong, G.; Chen, J.; Yun, F.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; et al. LINC00511 as a prognostic biomarker for human cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanski, C.R.; White, N.M.; Dang, H.X.; Silva-Fisher, J.M.; Rauck, C.E.; Cicka, D.; Maher, C.A. Pan-cancer transcriptome analysis reveals long noncoding RNAs with conserved function. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Cao, J.; Chen, Z.; He, Z. The role of long intergenic noncoding RNA 00511 in malignant tumors: A meta-analysis, database validation and review. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Xia, C.; Xu, Y. HIF-1α induced lncRNA LINC00511 accelerates the colorectal cancer proliferation through positive feedback loop. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Qi, P.; Jiang, W. Prognostic significance of long intergenic non-protein-coding RNA 511expression in malignant tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2015, 99, e23054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Z.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00511 contributes to breast cancer tumourigenesis and stemness by inducing the miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, F.; Han, Y.; Xue, H.; Sun, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, Z. LINC00511-dependent inhibition of IL-24 contributes to the oncogenic role of HNF4α in colorectal cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G338–G350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Xu, R. Lncrna linc00511 acts as an oncogene in colorectal cancer via sponging mir-29c-3p to upregulate nfia. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 13413–13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Han, G.; Xu, N.; Ye, J.; Wang, R. Long non-coding RNA LINC00511 facilitates colon cancer development through regulating microRNA-625-5p to target WEE1. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.Y.; Zhang, S.R.; Wang, L.H.; Wu, W.D.; Zhao, H. LINC00511 promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer through downregulating LATS2 and KLF2 by binding to EZH2 and LSD1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8377–8390. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.C.; Li, S.J.; Li, G.; Hua, R.X.; Zhou, X.H.; Li, D.J. Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA 00511 Acts as an Oncogene in Non–small-cell Lung Cancer by Binding to EZH2 and Suppressing p57. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhang, F. LncRNA LINC00511 plays an oncogenic role in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating PKM2 expression via sponging miR-625-5p. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Hu, X. LINC00511 enhances LUAD malignancy by upregulating GCNT3 via miR-195-5p. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Mu, X. Long non-coding RNA LINC00511 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting miR-625-5p/GSPT1. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 5159–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. LINC00511 promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and migration via inhibiting miR-150-5p and activating TADA1. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L. Promotion of cell autophagy and apoptosis in cervical cancer by inhibition of long noncoding RNA LINC00511 via transcription factor RXRA-regulated PLD1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6592–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao BDi Xu, P.; Zhong, Y.; Ding, W.W.; Meng, Q.Z. LINC00511 knockdown prevents cervical cancer cell proliferation and reduces resistance to paclitaxel. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Kong, F.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J. Long non-coding rna linc00511 accelerates proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer through targeting mir-324-5p/dram1 axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 10245–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, T. LINC00511 promotes cervical cancer progression by regulating the miR-497-5p/MAPK1 axis. Apoptosis 2022, 27, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Mao, X.; Luo, F.; Wang, J. LINC00511 promotes gastric cancer progression by regulating SOX4 and epigenetically repressing PTEN to activate PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 9112–9127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, K.; Chen, E. LINC00511 promotes proliferation and invasion by sponging miR-515-5p in gastric cancer. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Han, X.Q.; Liu, Y.N.; Wang, M.C.; Zhang, H.X.; Gu, Y.F.; Leng, X.G. LINC00511 promotes gastric cancer cell growth by acting as a ceRNA. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, B. LINC00511 accelerated the process of gastric cancer by targeting miR-625-5p/NFIX axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Bi, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; et al. Linc00511 acts as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate VEGFA expression through sponging hsa-miR-29b-3p in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.P.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.X. Increased long noncoding RNA LINC00511 is correlated with poor prognosis and contributes to cell proliferation and metastasis by modulating miR-424 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3291–3301. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.Y.; Wei, H.Y.; Li, K.M.; Wang RBen Xu, X.Q.; Feng, R. LINC00511 as a ceRNA promotes cell malignant behaviors and correlates with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients by modulating miR-195/EYA1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Cui, H.; Lei, T.; Li, S.; Mai, E.; Jia, F. Linc00511 indicates a poor prognosis of liver hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 9367–9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Huang, M.; Wei, S.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Jin, H.; Li, B.; et al. LINC00511 drives invasive behavior in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating exosome secretion and invadopodia formation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Tu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Bao, Z.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Pan, M.; Ji, J. LINC00511 contributes to glioblastoma tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via LINC00511/miR-524-5p/YB1/ZEB1 positive feedback loop. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tao, B.; Li, L.; Liu, P.; Xia, K.; Zhong, C. LINC00511 knockdown suppresses glioma cell malignant progression through miR-15a-5p/AEBP1 axis. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 173, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tian, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, K. LINC00511 facilitates Temozolomide resistance of glioblastoma cells via sponging miR-126-5p and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, H.; Li, H. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 511 promotes the progression of osteosarcoma cells through sponging microRNA 618 to upregulate the expression of maelstrom. Aging 2019, 11, 5351–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Gu, H.; Xia, J.; Yin, X. LINC00511 Promotes Osteosarcoma Tumorigenesis and Invasiveness through the miR-185-3p/E2F1 Axis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1974506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xian, W. LncRNA Linc00511 promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration through sponging miR-765. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 7248–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Qi, K.; Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Long intergenic non-coding RNA 511 correlates with improved prognosis, and hinders osteosarcoma progression both in vitro and in vivo. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.H.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Li, S.; Hong, X. Long non-coding RNA LINC00511/miR-150/MMP13 axis promotes breast cancer proliferation, migration and invasion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 165957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Niu, Z.; Liu, J.; Qian, C. Upregulation of LINC00511 expression by DNA hypomethylation promotes the progression of breast cancer. Gland Surg. 2021, 10, 1418–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Kong, D.; Chen, Q.; Ping, Y.; Pang, D. Oncogenic long noncoding RNA landscape in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sui, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Pang, D. The transcriptional landscape of lncRNAs reveals the oncogenic function of LINC00511 in ER-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yu, W. LINC00511 knockdown enhances paclitaxel cytotoxicity in breast cancer via regulating miR-29c/CDK6 axis. Life Sci. 2019, 228, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, A.M.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y. Long noncoding RNA LINC00511 involves in breast cancer recurrence and radioresistance by regulating STXBP4 expression via miR-185. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7457–7468. [Google Scholar]
- Minotti, L.; Agnoletto, C.; Baldassari, F.; Corrà, F.; Volinia, S. SNPs and somatic mutation on long non-coding RNA: New frontier in the cancer studies? High-Throughput 2018, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wu, L.-X.; Tan, L.; Shang, F.-F.; Zhou, H.-H. Significance of Single-Nucleotide Variants in Long Intergenic Non-protein Coding RNAs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, S. Effect of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on the structure of long noncoding RNAs and their interaction with RNA Binding Proteins. bioRxiv 2022, 2022, 501647. Available online: http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2022/07/28/2022.07.26.501647.abstract (accessed on 8 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Chong, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zou, Y.; Song, C. Association study of SNPs in LncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 with breast cancer susceptibility in Chinese Han population. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 143, 106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, E.; Latifi-Navid, S.; Latifi-Navid, H. LncRNA polymorphisms and breast cancer risk. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 229, 153729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Luo, C.; Guo, Q.; Cao, J.; Yang, Q.; Dong, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Song, C. Association analyses of genetic variants in long non-coding RNA MALAT1 with breast cancer susceptibility and mRNA expression of MALAT1 in Chinese Han population. Gene 2018, 642, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Dai, X.; Yeung, S.C.J.; He, X. The role of long non-coding RNA GAS5 in cancers. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, K. A Genetic Variant of rs145204276 in the Promoter Region of Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2019, 19, e415–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, R.; Guo, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B.; Pang, J.; Cao, W. CASC15 Polymorphisms are Correlated with Breast Cancer Susceptibility in Chinese Han Women. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, e518–e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Cao, J.; Song, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, K.; Dai, L. Polymorphisms in lncRNA HOTAIR and susceptibility to breast cancer in a Chinese population. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, Q.; Chong, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zou, Y.; Xu, L.; Song, C. Polymorphisms in lncRNA MIR2052HG and susceptibility to breast cancer in Chinese population. Aging 2021, 13, 24360–24378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Niu, M.; Cui, J.J.; Xiang, C.X.; Sang, J.W.; Wen, S.X.; Wang, B.Q. Expression and clinical significance of long non-coding RNA LINC00520 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 32, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Xu, L.; Peng, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chong, F.; Song, M.; Dai, L.; Song, C. Characterization of lncRNA LINC00520 and functional polymorphisms associated with breast cancer susceptibility in Chinese Han population. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 2252–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, R.D.; Mathias, C.; Reiter, G.A.K.; de Lima, R.S.; Kuroda, F.; de Andrade Urban, C.; de Souza, R.L.R.; Gradia, D.F.; Ribeiro, E.M.S.F.; Cavalli, I.J.; et al. Association between snp rs527616 in lncrna aqp4-as1 and susceptibility to breast cancer in a southern brazilian population. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2021, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yu, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, L.; Sun, K.; Zhu, B.; Xu, M.; Liu, J. Correlations between lncRNA-SOX2OT polymorphism and susceptibility to breast cancer in a Chinese population. Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzarei, S.; Hashemi, M.; Sattarifard, H.; Hashemi, S.M.; Bahari, G. Genetic polymorphisms in long noncoding RNA H19 are associated with breast cancer susceptibility in Iranian population. Meta Gene 2017, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, K.; Peng, R.; Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, P.; Song, C. Genetic variants in lncRNA SRA and risk of breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22486–22496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, F.F.; Cao, J.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, Q.Y.; Song, M.M.; Jiang, X.R.; Wang, K.J.; Xu, L.P.; Song, C.H. The Association between LINC00511 Variants and Breast Cancer Susceptibility among the Han Chinese Population. J. Nutr. Oncol. 2020, 5, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Cao, J.; Peng, R.; Guo, Q.; Ye, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Song, C. Functional Variants in Linc-ROR are Associated with mRNA Expression of Linc-ROR and Breast Cancer Susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Lv, X.; Yang, Z.; Gao, M.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, B.; et al. LncRNA NEAT1 polymorphisms and lung cancer susceptibility in a Chinese Northeast Han Population: A case-control study. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Z. Polymorphisms in lncRNA CCAT1 on the susceptibility of lung cancer in a Chinese northeast population: A case–control study. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Feng, N.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, F.; Qian, Y.; Gao, M.; Yu, H.; Zhou, B.; Qian, B. SNPs in LncRNA genes are associated with non-small cell lung cancer in a Chinese population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Cui, Z.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhou, B.; Yin, Z. Polymorphism in lncRNA AC008392.1 and its interaction with smoking on the risk of lung cancer in a Chinese population. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Lv, X.; Gao, M.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Li, N.; et al. Genetic variants in LncRNA HOTAIR are associated with lung cancer susceptibility in a Chinese Han population in China: A case-control study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5209–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.W.; Zhang, H.B.; Gong, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W.T.; Liu, H.Y.; Chen, J. HOTAIR lncRNA SNPs rs920778 and rs1899663 are associated with smoking, male gender, and squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese lung cancer population. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.H.; Wu, Y.L.; Tsao, T.C.Y.; Huang, Y.W.; Lin, J.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, S.F. Impact of LncRNA GAS5 Genetic Variants and the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Phenotypes on the Clinicopathological Characteristics of Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, A.; Banerjee, A.; Basu, K.; Pal, D.K.; Ghosh, A. PRNCR1: A long non-coding RNA with a pivotal oncogenic role in cancer. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.L.; Yao, J.J.; Xie, Z.Z.; Huang, Y.J.; Xiao, S. Lncrna prncr1 rs1456315 and ccat2 rs6983267 polymorphisms on 8q24 associated with lung cancer. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.; Tong, W.; He, R.; Cui, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, B.; Yin, Z. MALAT1 Polymorphisms and Lung Cancer Susceptibility in a Chinese Northeast Han Population. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, H.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhou, B.; Yin, Z. The polymorphisms of lncRNA HOXA11-AS and the risk of lung cancer in Northeastern Chinese population. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, B.; Bai, L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, Y. Association between H19 SNP rs217727 and lung cancer risk in a Chinese population: A case control study. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Feng, N.; Zhu, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhou, B.; Yu, H.; Zheng, M.; et al. A SNP-mediated lncRNA (LOC146880) and microRNA (miR-539-5p) interaction and its potential impact on the NSCLC risk. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Yan, G.; Yu, S.; Li, F.; Su, Z.; Hou, X.; Xiao, J.; Tian, T. Associations of MALAT1 and its functional single nucleotide polymorphisms with cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 236, 153988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jing, F.; Ding, Y.; He, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, C. Long noncoding RNA CCAT1 polymorphisms are associated with the risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer Genet. 2018, 222, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Jin, M.; Ye, D.; Li, Y.; Jing, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, K. Polymorphisms of a novel long non-coding RNA RP11-108K3.2 with colorectal cancer susceptibility and their effects on its expression. Int. J. Biol. Mark. 2020, 35, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, A.A.M.; Mokhtar, S.H.; Ahmedah, H.T.; Almars, A.I.; Toraih, E.A.; Ibrahiem, A.T.; Fawzy, M.S.; Salem, M.A. Prognostic Value of LINC-ROR (rs1942347) Variant in Patients with Colon Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hua, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, H.; Du, M.; Zhu, L.; Chu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. Association of genetic variants in lncRNA H19 with risk of colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25470–25477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; et al. Functional polymorphisms of the lncRNA H19 promoter region contribute to the cancer risk and clinical outcomes in advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Xu, Q.; Sun, L.; Wen, J.; Fang, X.; Xing, C.; Yuan, Y. Four novel polymorphisms in long non-coding RNA HOTTIP are associated with the risk and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Shaker, O.G.; Ezzat, E.M.; Gaber, S.N.; Hassan, E.A.; Abdelwahed, M.Y.; AbdelHafez, M.N.; Khalil, M.A.F.; Abouelseoud, S. Association between rs1859168/HOTTIP Expression Level and Colorectal Cancer and Adenomatous Polyposis Risk in Egyptians. J. Interface Cytokine Res. 2020, 40, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, R. Association between polymorphism in the promoter region of lncRNA GAS5 and the risk of colorectal cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Huang, Z.; Wu, L.N.; Wu, R.; Ding, H.X.; Wang, B.G. LncRNA-PCAT1 rs2632159 polymorphism could be a biomarker for colorectal cancer susceptibility. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.; Alshammari, E.M.; Mokhtar, S.H.; Alshanwani, A.R.; Toraih, E.A.; Ibrahiem, A.T.; Fawzy, M.S.; Maher, S.A. PUNISHER rs12318065 C>A transversion: A putative somatic driver mutation for poor prognosis in colon cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20220465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Chen, R. MAGI2-AS3 rs7783388 polymorphism contributes to colorectal cancer risk through altering the binding affinity of the transcription factor GR to the MAGI2-AS3 promoter. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.; Gu, X. Correlation between lncRNA SNHG16 gene polymorphism and its interaction with environmental factors and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. Medicine 2020, 99, e23372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yan, T.; Wang, Z.; Su, H.; Zhu, X.; Tian, X.; Fang, J.; Chen, H.; Hong, J. Variant of SNP rs1317082 at CCSlnc362 (RP11-362K14.5) creates a binding site for miR-4658 and diminishes the susceptibility to CRC. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, G.; Yang, P.; Zhang, G. LncRNA PTCSC3 is upregulated in osteoporosis and negatively regulates osteoblast apoptosis. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Tian, G.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, R.; Peng, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhang, S.; Xi, Y. Association between long noncoding RNA rs944289 and rs7990916 polymorphisms and the risk of colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMutairi, M.; Parine, N.R.; Shaik, J.P.; Aldhaian, S.; Azzam, N.A.; Aljebreen, A.M.; Alharbi, O.; Almadi, M.A.; Al-Balbeesi, A.O.; Alanazi, M. Association between polymorphisms in PRNCR1 and risk of colorectal cancer in the Saudi population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhuang, S.; Hu, Y.; Xi, L.; Deng, L.; Sheng, H.; Shen, W. Associations between polymorphisms of long non-coding RNA MEG3 and risk of colorectal cancer in Chinese. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19054–19059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Tian, J.; Lou, J.; Ke, J.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A functional polymorphism in lnc-LAMC2-1:1 confers risk of colorectal cancer by affecting miRNA binding. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.O.; Jun, H.H.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Ryu, C.S.; Kim, S.; Oh, D.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, N.K. Genetic Variants of HOTAIR Associated With Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility and Mortality. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Yang, G.; Peng, S.; Mi, W.; Yin, X.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. SNP rs12982687 affects binding capacity of lncRNA UCA1 with miR-873-5p: Involvement in smoking-triggered colorectal cancer progression. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, O.G.; Senousy, M.A.; Elbaz, E.M. Association of rs6983267 at 8q24, HULC rs7763881 polymorphisms and serum lncRNAs CCAT2 and HULC with colorectal cancer in Egyptian patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Tong, S.; Ding, Y.; Deng, W.; Song, D.; Xiao, K. Genetic variation of long non-coding RNA TINCR contribute to the susceptibility and progression of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33536–33543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, J.; Shen, N.; Li, J.; Lou, J.; Ke, J.; Yang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Gong, J.; et al. A functional variant rs1537373 in 9p21.3 region is associated with pancreatic cancer risk. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaccherini, M.; Farinella, R.; Gentiluomo, M.; Mohelnikova-Duchonova, B.; Kauffmann, E.F.; Palmeri, M.; Uzunoglu, F.; Soucek, P.; Petrauskas, D.; Cavestro, G.M.; et al. Association between a polymorphic variant in the CDKN2B-AS1/ANRIL gene and pancreatic cancer risk. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Xu, L.; Ni, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M.; Shen, L. Functional polymorphisms in LncRNA HOTAIR contribute to susceptibility of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, C.; Gentiluomo, M.; Gajdán, L.; Cavestro, G.M.; Kreivenaite, E.; Di Franco, G.; Sperti, C.; Giaccherini, M.; Petrone, M.C.; Tavano, F.; et al. Genome-wide scan of long noncoding RNA single nucleotide polymorphisms and pancreatic cancer susceptibility. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Ning, S.; Wan, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Pang, D. LINC00673 is activated by YY1 and promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells via the miR-515-5p/MARK4/Hippo signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; Tan, W.; Yu, D.; Du, Z.; Chang, J.; Wei, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Che, X.; et al. Pancreatic cancer risk variant in LINC00673 creates a miR-1231 binding site and interferes with PTPN11 degradation. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Qiao, O.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Jin, H.; Li, Z.; Yan Jin, Y. rs1859168 A>C polymorphism regulates HOTTIP expression and reduces risk of pancreatic cancer in a Chinese population. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; Wang, X.; Ji, G.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Jia, X.; Xu, L.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. The effect of SNPs in lncRNA as ceRNA on the risk and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.G.; Xu, Q.; Lv, Z.; Fang, X.X.; Ding, H.X.; Wen, J.; Yuan, Y. Association of twelve polymorphisms in three onco-lncRNa genes with hepatocellular cancer risk and prognosis: A case-control study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2482–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.H.; Ma, S.N.; Wu, R.; Cai, W.S. The association of polymorphisms in lncRNA-H19 with hepatocellular cancer risk and prognosis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Lee, H.L.; Shih, P.C.; Chen, L.H.; Tang, C.H.; Chang, L.C.; Wang, H.L.; Yang, S.F.; Chien, M.H. Genetic Polymorphisms of lncRNA LINC00673 as Predictors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression in an Elderly Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, S.S.; Hamdy, N.M. SOCS1 and pattern recognition receptors: TLR9 and RIG-I.; novel haplotype associations in Egyptian fibrotic/cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 4. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mesallamy, H.O.; Rashed, W.M.; Hamdy, N.M.; Hamdy, N. High-dose methotrexate in Egyptian pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: The impact of ABCG2 C421A genetic polymorphism on plasma levels, what is next? J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboouf, M.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Amin, A.I.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Genotype screening of APLN rs3115757 variant in Egyptian women population reveals an association with obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 109, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.M.; Hamdy, N.M.; Hegab, H.M.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Expression of thioredoxin-1 (TXN) and its relation with oxidative DNA damage and treatment outcome in adult AML and ALL: A comparative study. Hematology 2016, 21, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Gibriel, A.A.; ELMesallamy, H.O. Investigation of the relationship between CTLA4 and the tumor suppressor RASSF1A and the possible mediating role of STAT4 in a cohort of Egyptian patients infected with hepatitis C virus with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Derany, M.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Al-Ansari, N.L.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Integrative role of vitamin D related and Interleukin-28B genes polymorphism in predicting treatment outcomes of Chronic Hepatitis, C. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aziz, M.K.A.; Dawoud, A.; Kiriacos, C.J.; Fahmy, S.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Youness, R.A. Decoding hepatocarcinogenesis from a noncoding RNAs perspective. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 1982–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Sanad, E.F.; Hamdy, N.M. MicroRNAs’ role in the environment-related non-communicable diseases and link to multidrug resistance, regulation, or alteration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 36984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| LncRNA Transcripts ID | Gene ID | Chromosome Location (hg38) | Strand |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnc-DAAM2-9:1 to 10 | lnc-DAAM2-9 | chr6 | + |
| VLDLR-AS1:8 to 10 | VLDLR-AS1 | chr9 | − |
| LINC01228:1 | LINC01228 | chr16 | − |
| LINC00951:1 to 6 | LINC00951 | chr6 | − |
| LINC-ROR:1 to 5 | LINC-ROR | chr18 | − |
| LINC-PINT:11 to 81 | LINC-PINT | chr7 | − |
| GACAT2:2 | GACAT2 | chr18 | − |
| Cancer Type | Expression | Sponged miR- | Mechanism of Action [Ref.] | Role in Cancer | Type of Samples Used in the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRC | Upregulated | 153-5p | HIF-1 activates LINC00511, targeting HIF-1’s 3-UTR and +ve feedback loop [78] | Oncogene | Human CRC tissues vs. paired adjacent non-tumor and CRC cell lines HT29, LOVO, SW620, SW480 vs. normal colon epithelial FHC cell line and athymic BALB/c nude mice for implantation |
| - | HNF4 promotes LINC00511 transcription, interaction with EZH2/IL-24 expression downregulation [81] | Human CRC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and CRC cell lines HCT116, HT-29, LoVo, SW480, SW620, immortalized human colonic mucosal epithelial cell line NCM460, and female athymic BALB/c mice for implantation | |||
| 29c-3p | Upregulation of NFIA [82] | Human CRC tissues vs. normal tissues and CRC cell lines HT-29, HCT8, HCE8693, SW620 vs. normal cell line NCM460 | |||
| 625-5p | Enhancing WEE1 protein [83] | Human CC tissues vs. normal tissues and human CC cells SW480, SW620, HCT16, HT29 vs. normal cell line NCM460 and male nude mice for implantation | |||
| Lung | Upregulated | - | Binding to LSD1 and EZH2 inhibiting LATS2 and KLF2 genes [84] | Oncogene | Human NSCLC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human lung cancer cell lines A549, PC9 and H460 vs. normal human bronchial epithelial cell line BEAS-2B |
| - | Binding EZH2 and silencing p57 expression [85] | Human NSCLC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human NSCLC cell lines A549, SK-MES-1, H1299, 95D, H460, H520, H1975, H157, SK-LU-1, SPC-A-1 vs. normal human bronchial epithelial cell line 16HBE | |||
| 625-5p | Regulation of PKM2 expression [86] | Human lung adenocarcinoma tissues vs. adjacent normal lung tissues and human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines H1299and A549 vs. human pulmonary epithelial cells BEAS-2B | |||
| 195-5p | Upregulation of GCNT3 [87] | Human lung adenocarcinoma tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human lung adenocarcinoma cells A549, Calu-3, DV-90, PC-9 vs. human bronchial epithelial cells BEAS-2B | |||
| 625-5p | Targeting GSPT leading to progression and invasion of lung cancer cells [88] | Human NSCLC tissues vs. normal tissues and NSCLC cell lines A549, NCIH1299, NCIH1650, NCIH1975, NCIH460 vs. human bronchial epithelial cell line 16HBE | |||
| 150-5p | Activating TADA1 leading to progression and migration of lung cancer [89] | Human lung squamous cell carcinoma cell lines SK-MES-1, H226 vs. the human bronchial epidermal cells 16-HBE and TCGA database for LINC00511 expression in lung squamous cell carcinoma tissues | |||
| CC | Upregulated | - | Upregulating PLD1 expression, through the transcription factor RXRA leading to progression of the disease [90] | Oncogene | Human CC tissues vs. paracancerous tissues and human CC cells SiHa, CaSki, C33A, ME180, HeLa vs. normal cervical epithelial cells NCECs and mixed gender BALA/C nude mice for implantation |
| - | LINC00511 inhibition results in lowering cell viability, inducing apoptosis, regulating Bcl-2, Bax, metalloproteinases 2 and 9, MRP1, P-glycoprotein and cleaved caspase-3, increasing Paclitaxel sensitivity and decreasing proliferation [91] | Human CC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human CC cell line HeLa | |||
| 324-5p | Regulation of DRAM1 axis leading to CC progression and invasion of CC cells [92] | Human CC tissues vs. paracancerous tissues and human CC cell lines SiHa, CaSki; HPV-positive vs. C33A; HPV-negative, normal cervical epithelial cells HUCEC, HEK 293T | |||
| 497-5p | Regulation of MAPK1 axis leading to progression of the disease [93] | Human CC tissues vs. para-cancerous tissues and human CC cell lines SiHa, HeLa, C4-1, HT-3 vs. normal cervical epithelial cell line End1/E6E7 | |||
| GC | Upregulated | 195-5p | Elevation of SOX4 and EZH2 and repression of PTEN to activate P13/AKT resulting in GC tumorigenesis and stemness [94] | Oncogene | Human GC cell lines AGS, HGC-27, ACP01, SNU-1 vs. normal oesophageal epithelial cell line Het-1A and Male BALB/C nude mice for implantation |
| 515-p | MAPK signaling pathway leading to GC cells’ invasion and progression of the disease [95] | Human GC tissues vs. normal gastric tissues and human GC cell lines AGS, SGC7901, BGC823, MKN45, MGC803 vs. gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 and BALB/c nude mice for implantation | |||
| 124-3p | Regulation of PDK4 resulting in progression of the disease [96] | Human GC cell lines MKN-45, BGC-823, HGC-27, MGC-803 vs. normal gastric epithelial cells GES-1 | |||
| 625-5p | Targeting NFIX resulting in progression of the disease [97] | Human GC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human GC cells HGC27, BGC823, MGC803, SGC7901 vs. gastric mucosa epithelial cell GES1 and nude mice for implantation | |||
| PDAC | Upregulated | 29b-3p | Upregulation of VEGFA leading to PDAC stemness [98] | Oncogene | Human pancreatic cancer tissues vs. adjacent normal pancreatic tissues and human pancreatic cancer cell lines PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, Capan-2, SW1990, ASPC-1, BxPC-3, immortalized human pancreatic ductal epithelial cell line HPDE6 and nude mice for implantation |
| HCC | Upregulated | 424 | Promoting progression and metastasis of HCC [99] | Oncogene | Human HCC tissues vs. normal tissues and human HCC cell lines Hep3B, HepG2, SMMC-7721, MHCC97H, Huh7, HCCLM3 vs. normal liver cells LO2 |
| 195 | Correlating with EYA1 and promoting HCC progression [100] | Human HCC cell lines SMCC7721, HepG2, Huh7, Hep3B vs. normal hepatocytes L-02 and TCGA database for LINC00511/miR-195/EYA1 expression levels in HCC tissues | |||
| 29c | [101] | Human HCC tissues vs. paracancerous tissues and human HCC cell lines MHCC-97H, Huh7, HCC-LM3, Hep3B, MHCC-97L, Huh6 vs. normal hepatocytes LO2 | |||
| - | Affecting exosome secretion and invadopodia formation leading to progression of HCC [102] | Human HCC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human cell lines Huh7, Hep3B and female BALB/c nude mice for implantation | |||
| GBM | Upregulated | 524-5p | Indirectly controlling YB1 and boosting ZEB1, forming + feedback loop leading to migration and invasion of GBM cells [103] | Oncogene | Human GBM tissues vs. normal brain tissues and human GBM cell lines U87, LN229, U251, A172 vs. normal human astrocyte line NHA, HEK 293T and male BALB/c nude mice for implantation |
| 15a-5p | LINC00511 knockdown and targeting miR-15a-5p/AEBP1 axis result in prevention of GBM [104] | Human GBM tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human GBM cell lines T98 G, A172, LN229, U-87MG, U-251MG vs. normal human astrocytes HEB, NHA | |||
| 126-5p | Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and Temozolomide resistance [105] | Human GBM tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human GBM cell lines U87, A172, U138, U251, U373, LN-18, T98G, HEK293T and female BALB/C nude mice for implantation | |||
| OS | Upregulated | 618 | Boosting MAEL expression and promoting progression of the disease [106] | Oncogene | Human OS tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human OS cell lines MG-63, HOS, Saos-2 and 143B vs. osteoblast cell line hFOB 1.19 and male BALB/c nude mice for implantation |
| 185-3p | Regulation of E2F1 expression leading to progression and invasiveness of OS [107] | Human OS tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human OS cell lines SW1353, U2OS | |||
| 765 | Promoting APE1 and progression of OS [108] | Human OS tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human OS cell lines MG-63, Saos-2, U2OS, HOS vs. normal osteoblast cell line NHOst | |||
| Downregulated | - | Inhibition of proliferation and increasing apoptosis of OS cells and tumor cell necrosis rate (TCNR) [109] | Tumor suppressor | Human OS tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human OS cell lines MG-63, U-2OS, Saos-2, and HOS vs. hFOB1.19, 293T cells and male BALB/c-nude mice for implantation | |
| BC | Upregulated | 150 | Regulation of MMP-13 and inducing BC cell migration [110] | Oncogene | Human BC tissues vs. normal breast tissues and MDA-MB-231 cell line vs. MCF-7 cells |
| - | DNA hypomethylation induce LINC00511; Wnt10A, E2F2, TGFA, MET upregulation [111] | Human BC tissues vs. normal tissues and MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, T47D, MDA-MB-468, MCF-10a | |||
| 185-3p | targeting E2F1 protein to bind Nanog promotor region activation [80] | Human BC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and human BC cell lines MDA-MB-468, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-453 and MCF-7 vs. MCF-10A and male null mice for implantation | |||
| 185-3p | Increasing BC cells expression, transcription control of downstream genes [42] | Human blood samples | |||
| - | [112] | Human BC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and BC cell lines MDA-MB-453, MCF-7, UACC812, T47D | |||
| - | Accelerating G1/S transition, apoptosis suppression and enhancement of -ve ER BC cell growth [113] | MCF7, UACC-812, MDA-MB-231, T47D and pathogen-free female athymic BALB/c mice for implantation | |||
| 29c | LINC00511 downregulation enhances Paclitaxel cytotoxicity by regulating miR-29c/CDK6 axis [114] | Human BC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, Hs-578T, T47D, immortalized breast epithelial cell line MCF-10A | |||
| 185 | Regulating STXBP4 expression and promoting BC recurrence and radio-resistance [115] | Human BC tissues vs. adjacent normal tissues and MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-436, MDA-MB-361, MCF-7, in addition to breast epithelial cell MCF-10A and nude mice for implantation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eldash, S.; Sanad, E.F.; Nada, D.; Hamdy, N.M. The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward ncRNA Precision. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9050058
Eldash S, Sanad EF, Nada D, Hamdy NM. The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward ncRNA Precision. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(5):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9050058
Chicago/Turabian StyleEldash, Shorouk, Eman F. Sanad, Dina Nada, and Nadia M. Hamdy. 2023. "The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward ncRNA Precision" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 5: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9050058
APA StyleEldash, S., Sanad, E. F., Nada, D., & Hamdy, N. M. (2023). The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward ncRNA Precision. Non-Coding RNA, 9(5), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9050058







