Functions of Circular RNA in Human Diseases and Illnesses
Abstract
1. Introduction
Circular RNA (circRNA) and Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA)
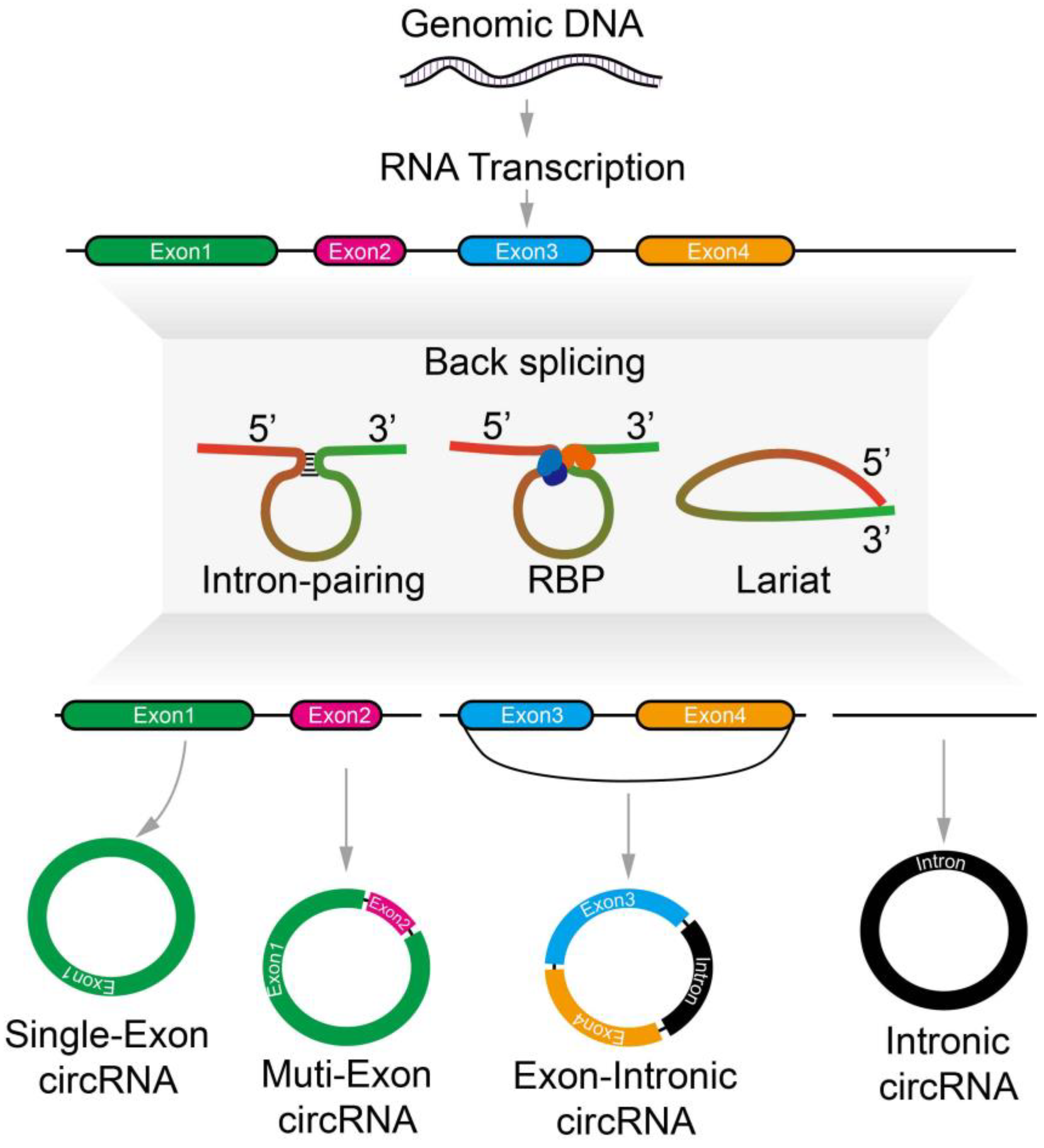
2. Metabolism of Circular RNA
Biogenesis, Localization, Modification, and Regulation of CircRNAs
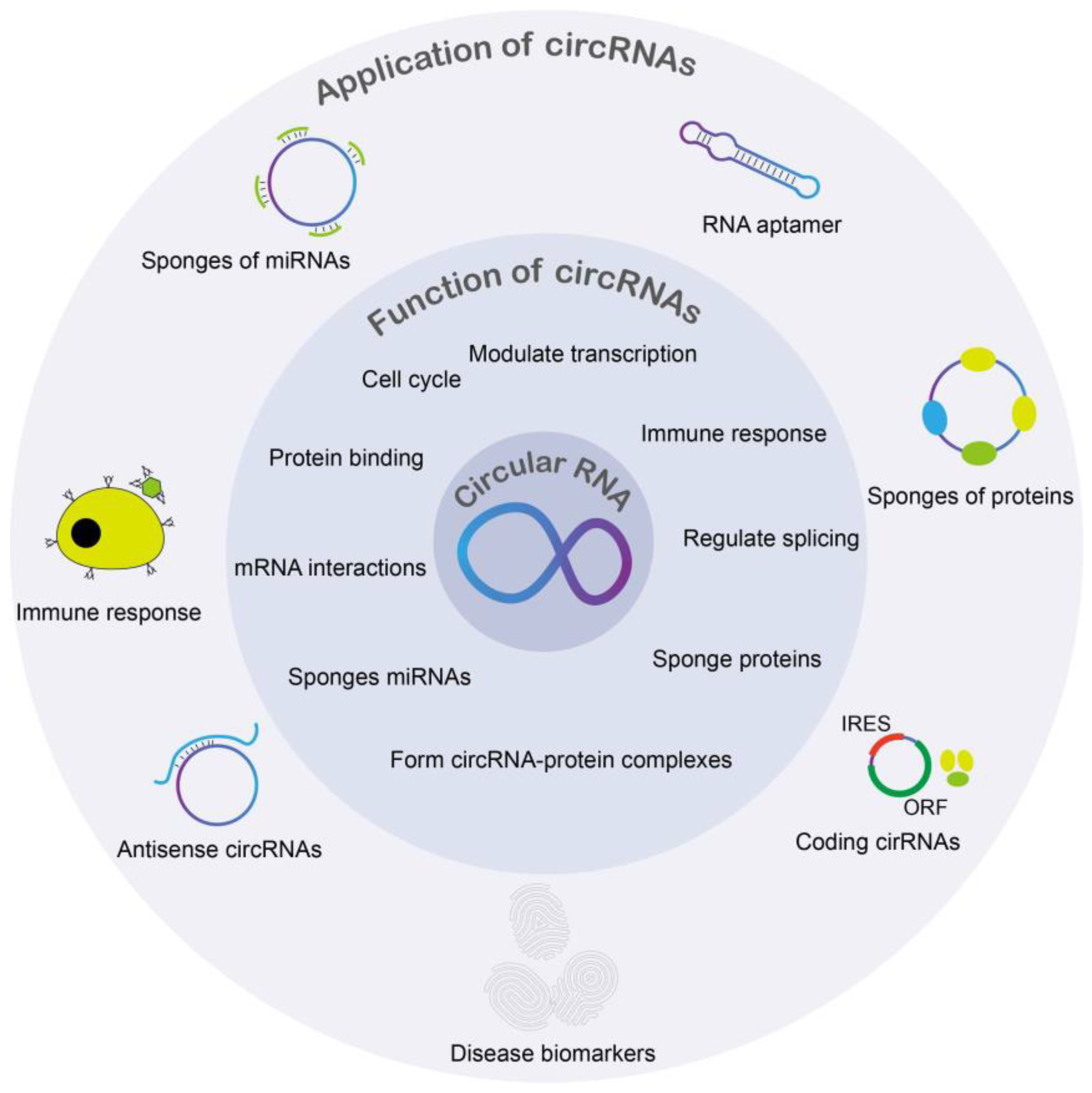
3. Functions of Circular RNA
3.1. Cell Proliferation and CircRNAs
3.2. CircRNAs Functioning as miRNA Sponges
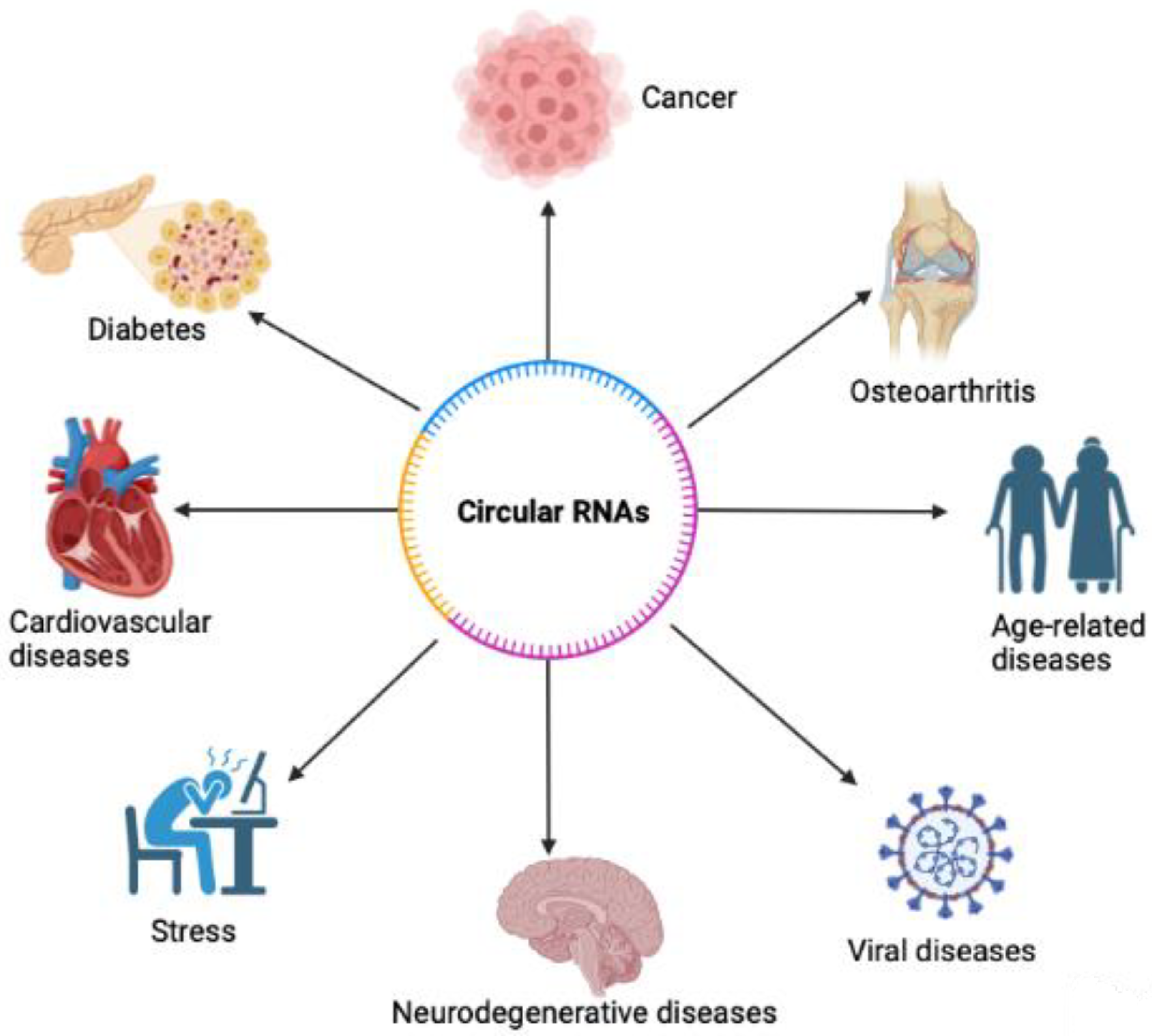
3.3. Role in Diagnosis of Diseases: Cancer
3.4. Immune Response and CircRNAs
3.5. Proteins and CircRNA
3.6. CircRNAs in Transcription and Splicing Regulation
3.7. Role in Diagnosis of Diseases: Neurological Diseases
3.8. Role in Diagnosis in Diseases: Autoimmune Diseases
4. Circular RNA’s Role in Pathogenic Infection
4.1. CircRNAs in Viral Infections
4.2. CircRNAs in Bacterial Infection
4.3. Cellular Circular RNA during Virus Infection
4.3.1. CircRNA in Respiratory Syncytial Virus
4.3.2. CircRNAs in Herpes Simplex Virus 1
4.3.3. CircRNAs in Coxsackievirus Group B Infection
4.4. Viral Circular RNA (DNA/RNA Virus)
4.4.1. CircRNA in Epstein–Barr Virus
4.4.2. CircRNAs in Kaposi Sarcoma Virus (KSHV)
4.4.3. CircRNA in Human Papillomaviruses (HPV)
4.4.4. CircRNA in Coronavirus
5. Characteristics of Viral Circular RNA
5.1. Breakpoint Motif of HCMV CircRNAs
5.2. Length Distribution, Exon Numbers, and Strand Preference
6. Functions of Cellular/Viral Circular RNA
6.1. Biological Effects Caused by Protein Binding
6.2. Platforms/Sponges for Proteins
6.3. CircRNA Expression Abundance
6.4. Competing with Linear mRNAs
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Zhou, H.; Cruz-Cosme, R.; Liu, M.; Xu, J.; Niu, X.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals abundant and diverse circRNAs of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV origin. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Chen, L.L. Circular RNAs: Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2016–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Lu, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, X.; Wu, A.; Jiang, T.; et al. Identification and characterization of circRNAs encoded by MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Brief Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.T.; Coca-Prados, M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 1979, 280, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.L.; Bao, Y.; Yee, M.C.; Barrett, S.P.; Hogan, G.J.; Olsen, M.N.; Dinneny, J.R.; Brown, P.O.; Salzman, J. Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.O.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Kuo, H.C. The emerging roles and functions of circular RNAs and their generation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, L.P.; Hu, C.D.; Kong, D.M.; Zhou, Z.C.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.H.; Fei, F.M.; Shen, Y.Y. CircZFR promotes pancreatic cancer progression through a novel circRNA-miRNA-mRNA pathway and stabilizing epithelial-mesenchymal transition protein. Cell Signal. 2023, 107, 110661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Lyu, L.; Huang, T.; Zheng, F.X.; Yuan, J.D.; Zhang, C.H.; Jiang, G.S. The long non-coding RNA SNHG1 promotes bladder cancer progression by interacting with miR-143-3p and EZH2. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11858–11873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Agarwal, V.; Guo, H.; Bartel, D.P. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnerio, J.; Bezzi, M.; Jeong, J.C.; Paffenholz, S.V.; Berry, K.; Naldini, M.M.; Lo-Coco, F.; Tay, Y.; Beck, A.H.; Pandolfi, P.P. Oncogenic Role of Fusion-circRNAs Derived from Cancer-Associated Chromosomal Translocations. Cell 2016, 165, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Chan, T.M.; Lin, X.; Kim, Y.; Wong, D.T.; Xiao, X. The landscape of microRNA, Piwi-interacting RNA, and circular RNA in human saliva. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. The emerging functions and roles of circular RNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Li, X.J.; Jian, D.D.; Hao, P.Y.; Rao, L.X.; Li, M.W. Hsa_circ_0054633 in peripheral blood can be used as a diagnostic biomarker of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta. Diabetol. 2017, 54, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Li, C.; Tan, C.L.; Liu, X.B. Circular RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human diseases. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.B.; Du, D.; Huang, G.X.; Chen, A.M.; Zhu, L. Circular RNA Atp9b, a competing endogenous RNA, regulates the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting miR-138-5p. Gene 2018, 646, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.Y.; Lin, P.R.; Wang, J.R.; Yu, H.Y.; Lv, T.T.; Sun, L.; Du, G.H. Circular RNAs: Promising Molecular Biomarkers of Human Aging-Related Diseases via Functioning as an miRNA Sponge. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 18, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Ding, W.; Sun, T.; Tariq, M.A.; Xu, T.; Li, P.F.; Wang, J.X. Biogenesis of circular RNAs and their roles in cardiovascular development and pathology. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.W.; Leung, A.K.L. CircRNAs: A regulator of cellular stress. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. 2017, 52, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.S.; Hur, K.; Cho, H.S.; Ban, H.S. Epigenetic Associations between lncRNA/circRNA and miRNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.J.; Zhou, H.C.; Feng, Z.Y.; Xu, Z.H.; Tang, Y.; Li, P.Y.; Wu, M.H. CircRNA: Functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Garcia, L.; Lopez-Royo, T.; Calvo, A.C.; Toivonen, J.M.; de la Torre, M.; Moreno-Martinez, L.; Molina, N.; Aparicio, P.; Zaragoza, P.; Manzano, R.; et al. Competing Endogenous RNA Networks as Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.H.; Sun, H. Biogenesis, cellular effects, and biomarker value of circHIPK3. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNA genes. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, BS1-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zuo, X.; Deng, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Ji, A. Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 97, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and Functions of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, E.A.; Fridman, M.V.; Moscovtsev, A.A.; Filippova, E.A.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Kushlinskii, N.E. LncRNAs in Ovarian Cancer Progression, Metastasis, and Main Pathways: ceRNA and Alternative Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, I.M.; Emanueli, C. Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2017, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, A.; Maruyama, M.; Suzuki, H. MicroRNA and long non-coding RNA in neuropathic pain. Pain Res. 2019, 34, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, K.K.; Zeidler, M.; Kress, M. Non-coding RNAs–Expression patterns and mechanistic aspects in neuropathic pain models. Acta Physiol. 2019, 227, NS20190099. [Google Scholar]
- Starke, S.; Jost, I.; Rossbach, O.; Schneider, T.; Schreiner, S.; Hung, L.H.; Bindereif, A. Exon circularization requires canonical splice signals. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Tatomer, D.C.; Luo, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L.; Cherry, S.; Wilusz, J.E. The Output of Protein-Coding Genes Shifts to Circular RNAs When the Pre-mRNA Processing Machinery Is Limiting. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Cai, Z.R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.S.; Ju, H.Q.; Xu, R.H. Circular RNA: Metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, J.M.; Cho, K.R.; Fearon, E.R.; Kern, S.E.; Ruppert, J.M.; Oliner, J.D.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Scrambled exons. Cell 1991, 64, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, Q.F.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.W.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Coordinated circRNA Biogenesis and Function with NF90/NF110 in Viral Infection. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 214–227.e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, T.; Avsar Ilik, I.; Maticzka, D.; Bhardwaj, V.; Pessoa Rodrigues, C.; Mittler, G.; Manke, T.; Backofen, R.; Akhtar, A. DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome. Nature 2017, 544, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, R.; Rahimi, K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Mayeda, A. Biosynthesis of Circular RNA ciRS-7/CDR1as Is Mediated by Mammalian-wide Interspersed Repeats. iScience 2020, 23, 101345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.O.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glazar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.H.; Ha, H.; Lee, Y.; Boo, S.H.; Kwon, D.H.; Song, H.K.; Kim, Y.K. Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage of m(6)A-Containing RNAs by RNase P/MRP Complex. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 494–507.e498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmayr-Heyda, A.; Reiner, A.T.; Auer, K.; Sukhbaatar, N.; Aust, S.; Bachleitner-Hofmann, T.; Mesteri, I.; Grunt, T.W.; Zeillinger, R.; Pils, D. Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation--exemplified with colorectal and ovarian cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Li, X.; Nan, F.; Jiang, S.; Gao, X.; Guo, S.K.; Xue, W.; Cui, Y.; Dong, K.; Ding, H.; et al. Structure and Degradation of Circular RNAs Regulate PKR Activation in Innate Immunity. Cell 2019, 177, 865–880.e821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs Co-Precipitate with Extracellular Vesicles: A Possible Mechanism for circRNA Clearance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Xiao, M.S.; Li, Z.; Shan, G.; Huang, C. Defining an evolutionarily conserved role of GW182 in circular RNA degradation. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Xie, Y.; Yu, T.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z.; Woolsey, R.J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. m(6)A-dependent biogenesis of circular RNAs in male germ cells. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Timoteo, G.; Dattilo, D.; Centron-Broco, A.; Colantoni, A.; Guarnacci, M.; Rossi, F.; Incarnato, D.; Oliviero, S.; Fatica, A.; Morlando, M.; et al. Modulation of circRNA Metabolism by m(6)A Modification. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.T.; Chen, J.N.; Gong, L.P.; Bi, Y.H.; Liang, J.; Zhou, L.; He, D.; Shao, C.K. Identification of virus-encoded circular RNA. Virology 2019, 529, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.X.; Chen, X.; Xia, L.P.; Zhang, J.X.; Pan, Z.Z.; Ma, X.D.; Han, K.; Chen, J.W.; Judde, J.G.; Deas, O.; et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Du, W.W.; Wu, N.; Yang, W.; Awan, F.M.; Fang, L.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. A circular RNA promotes tumorigenesis by inducing c-myc nuclear translocation. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Long, H.; Zheng, Q.; Bo, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, B. Circular RNA circRHOT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by initiation of NR2F6 expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; et al. Exosomal circRNAs: Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Chao, J.; Yao, H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 187, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Liu, C.; Liu, B.H.; Chen, X.; Dong, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, J.J.; et al. Circular Noncoding RNA HIPK3 Mediates Retinal Vascular Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2017, 136, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Gong, X.; Sun, L.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, B.; Zhu, L. The Circular RNA Cdr1as Act as an Oncogene in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Targeting miR-7 Expression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; Li, J.; Jia, R.; Pan, Y.; Liang, H. CircNT5E Acts as a Sponge of miR-422a to Promote Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4812–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.; Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Xu, T.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; He, B.; Wang, S. CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, H. Circular RNA WDR77 target FGF-2 to regulate vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration by sponging miR-124. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, Y.; Sun, G.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Xiao, R.; Xu, Z. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0064559 affects tumor cell growth and progression of colorectal cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.S.; Neilson, J.R.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA sponges: Competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Pan, F.; Mao, X.D.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.J. Biological functions of circular RNAs and their roles in occurrence of reproduction and gynecological diseases. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.F.; Saetrom, P. Circular RNAs are depleted of polymorphisms at microRNA binding sites. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanniford, D.; Ulloa-Morales, A.; Karz, A.; Berzoti-Coelho, M.G.; Moubarak, R.S.; Sanchez-Sendra, B.; Kloetgen, A.; Davalos, V.; Imig, J.; Wu, P.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of CDR1as Drives IGF2BP3-Mediated Melanoma Invasion and Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 55–70.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Hao, Y.; Lin, K.; Lyu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Zou, D.; Jiang, X.; Wang, R.; Jin, D.; et al. Circular RNA CDR1as disrupts the p53/MDM2 complex to inhibit Gliomagenesis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel, B.; Swain, A.; Nicolis, S.; Hacker, A.; Walter, M.; Koopman, P.; Goodfellow, P.; Lovell-Badge, R. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell 1993, 73, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J. circRNA_0084043 promote malignant melanoma progression via miR-153-3p/Snail axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, C.; Hu, Q.; Fu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, A.; Marks, J.R.; et al. CircIRAK3 sponges miR-3607 to facilitate breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 430, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Li, T.C.; Wu, Y.Y.; Yeh, C.H.; Chiang, W.; Chuang, C.Y.; Kuo, H.C. The circular RNA circBIRC6 participates in the molecular circuitry controlling human pluripotency. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Chang, C.; Wang, X.; Yeh, S. ERbeta-Mediated Alteration of circATP2B1 and miR-204-3p Signaling Promotes Invasion of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2550–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Hou, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J. Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging miR-424-5p and regulating LATS1 expression. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Xue, J.; Shi, M.; Chen, C.; Luo, F.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, B.; Sun, Q.; Yang, Q.; et al. Circ008913, via miR-889 regulation of DAB2IP/ZEB1, is involved in the arsenite-induced acquisition of CSC-like properties by human keratinocytes in carcinogenesis. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Zhao, X.S.; Zhao, H.Y.; Suzuki, T.; Wen, J.K. A Novel Regulatory Mechanism of Smooth Muscle alpha-Actin Expression by NRG-1/circACTA2/miR-548f-5p Axis. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduci, L.; Ferraiuolo, M.; Sacconi, A.; Ganci, F.; Vitale, J.; Colombo, T.; Paci, P.; Strano, S.; Macino, G.; Rajewsky, N.; et al. The oncogenic role of circPVT1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated through the mutant p53/YAP/TEAD transcription-competent complex. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Liu, H.; Cai, Z.; Dong, W.; Jiang, N.; Yang, M.; Huang, J.; Lin, T. Circ-BPTF promotes bladder cancer progression and recurrence through the miR-31-5p/RAB27A axis. Aging 2018, 10, 1964–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Chang, N.; Yen, L.; Sun, H.S.; Tsai, S.J. Noncoding Effects of Circular RNA CCDC66 Promote Colon Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Bao, W.; Li, S.; Liang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C. Circular RNA circMAN2B2 facilitates lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion via miR-1275/FOXK1 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, W.; Jiang, C. Overexpressing circular RNA hsa_circ_0002052 impairs osteosarcoma progression via inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by regulating miR-1205/APC2 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Lv, M.; Chen, J. Screening differential circular RNA expression profiles reveals the regulatory role of circTCF25-miR-103a-3p/miR-107-CDK6 pathway in bladder carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Li, Q.; Chen, L. CircZFR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulating miR-3619-5p/CTNNB1 axis and activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 661, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Shu, R.; Wang, F.; Chen, C.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, H. Circular RNA-ZFR Inhibited Cell Proliferation and Promoted Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer by Sponging miR-130a/miR-107 and Modulating PTEN. Cancer Res. Treat 2018, 50, 1396–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Pan, L.; Tao, D.; Li, R. Circular RNA circZFR contributes to papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation and invasion by sponging miR-1261 and facilitating C8orf4 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S. Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_103809 promotes lung cancer progression via facilitating ZNF121-dependent MYC expression by sequestering miR-4302. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.M.; Zhang, M.; Huang, L.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhu, J.N.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Q.X.; Zheng, X.L.; Yang, M.; et al. CircRNA_000203 enhances the expression of fibrosis-associated genes by derepressing targets of miR-26b-5p, Col1a2 and CTGF, in cardiac fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Su, X.; Hou, J.; Gu, Y.; Qian, C.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, M.; et al. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; Peng, E.; Qiu, X.; Lyu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. circFBLIM1 act as a ceRNA to promote hepatocellular cancer progression by sponging miR-346. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.C.; Ke, S.; Meng, F.K.; Lu, J.; Zou, X.J.; He, Z.G.; Wang, W.F.; Fang, M.H. CiRS-7 promotes growth and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of miR-7/HOXB13. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, W. Circular RNA CDR1as regulates osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via the miR-7/GDF5/SMAD and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwecka, M.; Glazar, P.; Hernandez-Miranda, L.R.; Memczak, S.; Wolf, S.A.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Filipchyk, A.; Klironomos, F.; Cerda Jara, C.A.; Fenske, P.; et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 2017, 357, eaam8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, S.; Li, W.; Yu, P. The circular RNA Cdr1as, via miR-7 and its targets, regulates insulin transcription and secretion in islet cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, X.; Yuan, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Yang, H.; Li, P.; et al. CircRNA-Cdr1as Exerts Anti-Oncogenic Functions in Bladder Cancer by Sponging MicroRNA-135a. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.H.; Li, R.; Su, Y.M.; Xiao, J.; Pan, M.; Cai, X.X.; Ji, X.P. The Circular RNA Cdr1as Promotes Myocardial Infarction by Mediating the Regulation of miR-7a on Its Target Genes Expression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Wei, Y. Overexpressed CDR1as functions as an oncogene to promote the tumor progression via miR-7 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 3979–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, M.; Meng, L.; Sang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ding, P.; Ju, Y.; Liu, F.; Gu, L.; Lian, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Circular RNA ciRS-7 accelerates ESCC progression through acting as a miR-876-5p sponge to enhance MAGE-A family expression. Cancer Lett. 2018, 426, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, L.; Sobel, J.; Rodriguez-Trejo, A.; Guay, C.; Lee, K.; Veno, M.T.; Kjems, J.; Laybutt, D.R.; Regazzi, R. Circular RNAs as novel regulators of beta-cell functions in normal and disease conditions. Mol. Metab. 2018, 9, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, J. circHIPK3 regulates cell proliferation and migration by sponging miR-124 and regulating AQP3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, D.; Yannian, L.; Yitian, C.; Dinghao, G.; Xin, Z.; Wu, J. Circular RNA HIPK3 promotes gallbladder cancer cell growth by sponging microRNA-124. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, F.; Xiao, X.; Xie, F.; Tao, D.; Huang, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Zeng, F.; et al. CircHIPK3 sponges miR-558 to suppress heparanase expression in bladder cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 1646–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Long, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, W. CircRNA8924 Promotes Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Competitively Binding to MiR-518d-5p /519-5p Family and Modulating the Expression of CBX8. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X. Circular RNA circITGA7 inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the Ras pathway and upregulating transcription of its host gene ITGA7. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, M.D.; Li, C.P.; Shan, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, B.; Li, X.M.; Yao, J.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Silencing of Circular RNA-ZNF609 Ameliorates Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2863–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, C.; Shan, K.; Liu, B.H.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhou, R.M.; Dong, R.; Yan, B.; Sun, X.H. Circular RNA-ZNF609 regulates retinal neurodegeneration by acting as miR-615 sponge. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3408–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C. A Zfp609 circular RNA regulates myoblast differentiation by sponging miR-194-5p. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.R.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharya, M.; Saha, A.; Lee, S.S.; Chakraborty, C. Recent progress of circular RNAs in different types of human cancer: Technological landscape, clinical opportunities and challenges (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraldsdottir, S.; Einarsdottir, H.M.; Smaradottir, A.; Gunnlaugsson, A.; Halfdanarson, T.R. Colorectal cancer–Review. Laeknabladid 2014, 100, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Grady, W.M. Colorectal cancer molecular biology moves into clinical practice. Gut 2011, 60, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, J.N.; Cieslik, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shukla, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Engelke, C.G.; Cao, X.; et al. The Landscape of Circular RNA in Cancer. Cell 2019, 176, 869–881.e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.C.; Chen, Y.G. Circular RNAs in Immune Response and Viral Infection. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolet, B.P.; Engels, S.; Aglialoro, F.; van den Akker, E.; von Lindern, M.; Wolkers, M.C. Circular RNA expression in human hematopoietic cells is widespread and cell-type specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 8168–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Pei, X.L.; Yang, D.L.; Han, M.Z. Deregulated Expression of Circular RNAs Is Associated with Immune Evasion and Leukemia Relapse after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Genes 2022, 13, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.M.; Xiang, B.; Zhang, Z.X.; Li, Y.P.; Shi, Q.L.; Li, M.J.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.H.; Lu, P.; Liu, F.; et al. The Regulatory Network and Role of the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA Network in the Progression and the Immune Response of Wilms Tumor Based on RNA-Seq. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 849941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Morikawa, S.; Nakashima, M.; Yoshikawa, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Suga, N.; Tsuji, A.; Matsuda, S. CircRNAs and RNA-Binding Proteins Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cancers or Central Nervous System Disorders. Noncoding RNA 2023, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Das, A.; Panda, A.C. Antisense Oligo Pulldown of Circular RNA for Downstream Analysis. Biol. Protoc. 2021, 11, e4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Xue, J.; Wu, R.; Meng, H.; Li, R.; Mo, Z.; Zhai, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Lai, G.; et al. CREBZF mRNA nanoparticles suppress breast cancer progression through a positive feedback loop boosted by circPAPD4. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumani, P.K. AGO-RBP crosstalk on target mRNAs: Implications in miRNA-guided gene silencing and cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 21, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Rong, J.; Yu, Y. Circular RNA circ0005276 promotes the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells by interacting with FUS to transcriptionally activate XIAP. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, M.E.; Oksanen, M.; Lejerkrans, S.; Mastropasqua, F.; Gorospe, M.; Tammimies, K. Circular RNAs arising from synaptic host genes during human neuronal differentiation are modulated by SFPQ RNA-binding protein. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Bian, X.; Wu, C.; Hua, J.; Chang, S.; Yu, T.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; et al. CircURI1 interacts with hnRNPM to inhibit metastasis by modulating alternative splicing in gastric cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2012881118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, V.M.; Hugouvieux, V.; Nayak, A.; Conos, S.A.; Capovilla, G.; Cildir, G.; Jourdain, A.; Tergaonkar, V.; Schmid, M.; Zubieta, C.; et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, V.M.; Gabryelska, M.; Toubia, J.; Kirk, K.; Gantley, L.; Powell, J.A.; Cildir, G.; Marri, S.; Liu, R.; Stringer, B.W.; et al. Circular RNAs drive oncogenic chromosomal translocations within the MLL recombinome in leukemia. Cancer Cell 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Gao, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, W.; Yuan, X.; Yin, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, K.; et al. CircRNA inhibits DNA damage repair by interacting with host gene. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Haroutounian, S.; Kamerman, P.; Baron, R.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Bouhassira, D.; Cruccu, G.; Freeman, R.; Hansson, P.; Nurmikko, T.; et al. Neuropathic pain: An updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain 2016, 157, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebl, A.; Neiss, A.; Spannheimer, A.; Reitberger, U.; Wieseler, B.; Stammer, H.; Goertz, A. Complications, co-morbidity, and blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Germany—Results from the CODE-2 study. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2002, 110, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xiong, Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, C.; Fan, Y. Identification of the Spinal Expression Profile of Non-coding RNAs Involved in Neuropathic Pain Following Spared Nerve Injury by Sequence Analysis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zou, Y.; Shao, T.; Wang, O. CircRNA circHIPK3 serves as a prognostic marker to promote glioma progression by regulating miR-654/IGF2BP3 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, M.; Fan, F.; Yu, M.; Gao, C.; Lu, Y.; Luo, Y. Circular RNA HIPK3 regulates human lens epithelial cells proliferation and apoptosis by targeting the miR-193a/CRYAA axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, T.; Bao, Z.; Li, Y.; Bu, W. Intrathecal circHIPK3 shRNA alleviates neuropathic pain in diabetic rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Vlatkovic, I.; Babic, A.; Will, T.; Epstein, I.; Tushev, G.; Akbalik, G.; Wang, M.; Glock, C.; Quedenau, C.; et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junn, E.; Lee, K.W.; Jeong, B.S.; Chan, T.W.; Im, J.Y.; Mouradian, M.M. Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13052–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.C.; Chae, Y.J.; Kabaria, S.; Chaudhuri, A.D.; Jain, M.R.; Li, H.; Mouradian, M.M.; Junn, E. MicroRNA-7 protects against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced cell death by targeting RelA. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 12725–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatro, E.T.; Risbrough, V.; Soontornniyomkij, B.; Young, J.; Shumaker-Armstrong, S.; Jeste, D.V.; Achim, C.L. Short-term recognition memory correlates with regional CNS expression of microRNA-138 in mice. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 21, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, J.; Ansaloni, S.; Schilling, M.; Liu, T.; Radke, J.; Jaedicke, M.; Schjeide, B.M.; Mashychev, A.; Tegeler, C.; Radbruch, H.; et al. MicroRNA-138 is a potential regulator of memory performance in humans. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Chen, Y. Roles of Circular RNAs in Neurologic Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonskaya, I.; Shekoyan, A.R.; Hebron, M.L.; Desforges, N.; Algarzae, N.K.; Moussa, C.E. Diminished parkin solubility and co-localization with intraneuronal amyloid-beta are associated with autophagic defects in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 33, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L. Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.J.; Gao, J.P.; Li, J.; Han, J.W.; Xu, Q.; Hu, W.L.; Pan, T.M.; Cheng, Y.L.; Yu, Z.Y.; Ni, C.; et al. Follow-up study identifies two novel susceptibility loci PRKCB and 8p11.21 for systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Yu, X.; Huang, J.; Dai, Y. Circular RNA expression profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients, based on microarray chip technology. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8029–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardamone, G.; Paraboschi, E.M.; Rimoldi, V.; Duga, S.; Solda, G.; Asselta, R. The Characterization of GSDMB Splicing and Backsplicing Profiles Identifies Novel Isoforms and a Circular RNA That Are Dysregulated in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, O.G.; Mahmoud, R.H.; Abdelaleem, O.O.; Ibrahem, E.G.; Mohamed, A.A.; Zaki, O.M.; Abdelghaffar, N.K.; Ahmed, T.I.; Hemeda, N.F.; Ahmed, N.A.; et al. LncRNAs, MALAT1 and lnc-DC as potential biomarkers for multiple sclerosis diagnosis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardamone, G.; Paraboschi, E.M.; Soldà, G.; Cantoni, C.; Supino, D.; Piccio, L.; Duga, S.; Asselta, R. Not only cancer: The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 affects the repertoire of alternatively spliced transcripts and circular RNAs in multiple sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lee, E.E.; Kim, J.; Yang, R.; Chamseddin, B.; Ni, C.; Gusho, E.; Xie, Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Buszczak, M.; et al. Transforming activity of an oncoprotein-encoding circular RNA from human papillomavirus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.J.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhao, W.; Tao, S.S.; Li, B.Z.; Xu, S.Z.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wu, J.; Leng, R.X.; et al. Circular RNA expression profile and potential function of hsa_circ_0045272 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 2018, 155, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.J.; Liu, J.; Qin, J. miR-138 suppressed the progression of osteoarthritis mainly through targeting p65. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shi, W. The down-regulation of hsa_circ_0012919, the sponge for miR-125a-3p, contributes to DNA methylation of CD11a and CD70 in CD4(+) T cells of systemic lupus erythematous. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shi, W. CircIBTK inhibits DNA demethylation and activation of AKT signaling pathway via miR-29b in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macintyre, A.N.; Finlay, D.; Preston, G.; Sinclair, L.V.; Waugh, C.M.; Tamas, P.; Feijoo, C.; Okkenhaug, K.; Cantrell, D.A. Protein kinase B controls transcriptional programs that direct cytotoxic T cell fate but is dispensable for T cell metabolism. Immunity 2011, 34, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, K.; Lai, W.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Chu, S.; Wang, H.; Kang, C.; Qiu, Y. Comprehensive circular RNA profiles in plasma reveals that circular RNAs can be used as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 480, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Kukia, N.; Abbasi, A. New insights on circular RNAs and their potential applications as biomarkers, therapeutic agents, and preventive vaccines in viral infections: With a glance at SARS-CoV-2. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 29, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, T.; Wang, W.; Xi, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Yang, A.; Wang, T. Circular RNAs in immune responses and immune diseases. Theranostics 2019, 9, 588–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shuai, M.; Xia, Y. Knockdown of EBV-encoded circRNA circRPMS1 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis through sponging multiple miRNAs. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.C.; Li, X.; Chen, L.J.; Fan, J.H.; Lai, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J. Differential expression profile of hepatic circular RNAs in chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.Y.; Huang, Z.L.; Xu, Y.H.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Z.Y.; Huang, X.Y. Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals the regulatory role of the circRNA-100338/miR-141-3p pathway in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiss, G.K.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Birditt, B.; Dahl, T.; Dowidar, N.; Dunaway, D.L.; Fell, H.P.; Ferree, S.; George, R.D.; Grogan, T.; et al. Direct multiplexed measurement of gene expression with color-coded probe pairs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Aljabbari, A.; Lokras, A.; Foged, C.; Thakur, A. Opportunities and Challenges in the Delivery of mRNA-based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legnini, I.; Di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M.; et al. Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA that Can Be Translated and Functions in Myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.T.; Mahiny, A.J.; Vlatkovic, I. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: Platforms and current developments. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1850–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Yi, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, F.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tian, F.; et al. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Cell 2022, 185, 1728–1744.e1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Anderson, D.G. Engineering circular RNA for potent and stable translation in eukaryotic cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Dain, L.; Mei, L.; Zhu, G. Circular RNA: An emerging frontier in RNA therapeutic targets, RNA therapeutics, and mRNA vaccines. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Parker-Hale, F.C.; Huang, Y.; Bisaria, N.; Anderson, D.G. RNA Circularization Diminishes Immunogenicity and Can Extend Translation Duration In Vivo. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Guo, S.K.; Nan, F.; Xu, Y.F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. RNA circles with minimized immunogenicity as potent PKR inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 420–434.e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, D.; Jin, X.; Luo, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Xi, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Blood circRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16483–16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Circ-ATP5H Induces Hepatitis B Virus Replication and Expression by Regulating miR-138-5p/TNFAIP3 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11031–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Shinagawa, K.; Castellino, F.J.; Schorey, J.S. Exosomes released from macrophages infected with intracellular pathogens stimulate a proinflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 3234–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Shi, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, J.; Xie, X.; Bai, Y.; et al. Potential Diagnostic Power of Blood Circular RNA Expression in Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis. EBioMedicine 2018, 27, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, B.; Yang, B.; Fu, J.; Liu, L.; Amjad, N.; Cai, A.; Tan, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Circular RNA Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Infected with Meningitic Escherichia coli. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Niu, M.; Hao, Z.; Liu, M.; Tong, C.; Zhao, X. Selective packaged circular RNAs in milk extracellular vesicles during Staphylococcus aureus infection may have potential against bacterial infection. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, C.; Sridhar, D. Who pays for cooperation in global health? A comparative analysis of WHO, the World Bank, the Global Fund to Fight HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, and Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance. Lancet 2017, 390, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.G.; Zhang, J.A.; Luo, H.L.; Liu, G.B.; Lu, Y.B.; Ge, N.H.; Zheng, B.Y.; Li, R.X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; et al. The circular RNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Hsa_circ_0005836 as a new diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target of active pulmonary tuberculosis. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 90, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiao, J.; Yi, Z. Signature of circular RNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with active tuberculosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W.; Hu, X.; Gan, J. Identification and comparison of novel circular RNAs with associated co-expression and competing endogenous RNA networks in pulmonary tuberculosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113571–113582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Pan, J.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Z.; Liang, M.; Xia, S.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, X.; Peng, T.; Zhou, X.; et al. The Cellular and Viral circRNAome Induced by Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. mBio 2021, 12, e0307521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Schweitzer, J.W.; Justice, N.A. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, M.S.; Djakovic, L.; Kluge, M.; Hennig, T.; Whisnant, A.W.; Backes, S.; Dolken, L.; Friedel, C.C. HSV-1 and influenza infection induce linear and circular splicing of the long NEAT1 isoform. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Wilson, D.W. HSV-1 Cytoplasmic Envelopment and Egress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, A.D.; Frenkel, N. Herpes simplex virus-infected cells contain a function(s) that destabilizes both host and viral mRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1926–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiflett, L.A.; Read, G.S. mRNA decay during herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections: Mutations that affect translation of an mRNA influence the sites at which it is cleaved by the HSV virion host shutoff (Vhs) protein. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemson, C.M.; Hutchinson, J.N.; Sara, S.A.; Ensminger, A.W.; Fox, A.H.; Chess, A.; Lawrence, J.B. An architectural role for a nuclear noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA is essential for the structure of paraspeckles. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, C.S.; Fox, A.H. Paraspeckles: Nuclear bodies built on long noncoding RNA. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, F.; Kapeller, A.; Pichler, M.; Klec, C. The Implications of the Long Non-Coding RNA NEAT1 in Non-Cancerous Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, N.; Kyriakopoulos, C. Group B Coxsackie Virus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Shin, H.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Jeon, E.S.; Lim, B.K. Protein Kinase B2 (PKB2/AKT2) Is Essential for Host Protection in CVB3-Induced Acute Viral Myocarditis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Lin, L.; Wu, S.; Guo, Z.; Wang, T.; Qin, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhong, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. MiR-10a* up-regulates coxsackievirus B3 biosynthesis by targeting the 3D-coding sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 3760–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Y.; Chaulagain, A.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Yi, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, S.; et al. MiR-146a down-regulates inflammatory response by targeting TLR3 and TRAF6 in Coxsackievirus B infection. RNA 2020, 26, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Shen, H. The circRNA circSIAE Inhibits Replication of Coxsackie Virus B3 by Targeting miR-331-3p and Thousand and One Amino-Acid Kinase 2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 779919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, A.; Qin, Y.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yue, E.; Ding, X.; et al. A Novel Circular RNA Mediates Pyroptosis of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Functioning as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Lin, L.; Yang, S.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Deng, F.; Yue, X.; Ren, L.; Fei, Y.; et al. Circular RNA circ_0076631 promotes coxsackievirus B3 infection through modulating viral translation by sponging miR-214-3p. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 975223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerleider, N.; Concha, M.; Lin, Z.; Roberts, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Baddoo, M.; Moss, W.N.; Yu, Y.; Seddon, M.; et al. The Epstein Barr virus circRNAome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundhoff, A.; Sullivan, C.S. Virus-encoded microRNAs. Virology 2011, 411, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.S. High conservation of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNAs implies important function. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, V.; Parks, T.; Bagni, R.; Wang, C.D.; Samols, M.A.; Hu, J.; Wyvil, K.M.; Aleman, K.; Little, R.F.; Yarchoan, R.; et al. Conservation of virally encoded microRNAs in Kaposi sarcoma—Associated herpesvirus in primary effusion lymphoma cell lines and in patients with Kaposi sarcoma or multicentric Castleman disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, T.; Gao, S.; Koparde, V.N.; Gonzalez, M.; Spouge, J.L.; Serquina, A.P.; Lurain, K.; Ramaswami, R.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; et al. Discovery of Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus-encoded circular RNAs and a human antiviral circular RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12805–12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toptan, T.; Abere, B.; Nalesnik, M.A.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Ranganathan, S.; Lee, N.; Shair, K.H.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Circular DNA tumor viruses make circular RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8737–E8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesut, E.; Dukic, A.; Lulic, L.; Skelin, J.; Simic, I.; Milutin Gasperov, N.; Tomaic, V.; Sabol, I.; Grce, M. Human Papillomaviruses-Associated Cancers: An Update of Current Knowledge. Viruses 2021, 13, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowy, D.R.; Schiller, J.T. Reducing HPV-associated cancer globally. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, M.; Jaijyan, D.; Cruz-Cosme, R.; Ramasamy, S.; Subbian, S.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Niu, X.; et al. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV encode circular RNAs of spliceosome-independent origin. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3203–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, D.; Palermo, C.I.; Barbagallo, C.; Battaglia, R.; Caponnetto, A.; Spina, V.; Ragusa, M.; Di Pietro, C.; Scalia, G.; Purrello, M. Competing endogenous RNA network mediated by circ_3205 in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, Y.M.; Sacar Demirci, M.D. Circular RNA-MicroRNA-MRNA interaction predictions in SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2021, 18, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Singh, P.; Dohare, R.; Jha, R.; Ali Syed, M. Unravelling host-pathogen interactions: ceRNA network in SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). Gene 2020, 762, 145057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, W. Virus entry into host, establishment of infection, spread in host, mechanisms of tissue damage. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Mocarski, E., Moore, P.S., Roizman, B., Whitley, R., Yamanishi, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, A.C.; De, S.; Grammatikakis, I.; Munk, R.; Yang, X.; Piao, Y.; Dudekula, D.B.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. High-purity circular RNA isolation method (RPAD) reveals vast collection of intronic circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ji, P.; Chen, S.; Hou, L.; Zhao, F. Reconstruction of full-length circular RNAs enables isoform-level quantification. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Cao, D.; Jaijyan, D.K.; Enescu, N.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, W.; et al. Circular RNAs Represent a Novel Class of Human Cytomegalovirus Transcripts. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, S.H.; Eason, A.B.; Bigi, R.; Kim, Y.; Kang, S.; Tan, K.; Seltzer, T.A.; Venkataramanan, R.; An, H.; Dittmer, D.P. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency Locus Renders B Cells Hyperresponsive to Secondary Infections. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01138-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Yong, T.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, B.B. Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-Protein Interaction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, R.J.A.; Tong, S.; Mok, B.W.; Liu, J.; He, S.; Zong, J.; Chen, Y.; Tsao, S.W.; Lung, M.L.; Chen, H. Epstein-Barr Virus BART Long Non-coding RNAs Function as Epigenetic Modulators in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Zou, Q.; Lin, C. CRBPDL: Identification of circRNA-RBP interaction sites using an ensemble neural network approach. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; Munk, R.; Grammatikakis, I.; Dudekula, D.B.; De, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Su, L.; Luo, J. Circular RNA-MTO1 suppresses breast cancer cell viability and reverses monastrol resistance through regulating the TRAF4/Eg5 axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.K.; Foster, F.S.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, B.B. Foxo3 circular RNA promotes cardiac senescence by modulating multiple factors associated with stress and senescence responses. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Fang, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, N.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, Z.; Yang, B.B. Induction of tumor apoptosis through a circular RNA enhancing Foxo3 activity. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Du, W.W.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Awan, F.M.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Yee, A.; et al. A Circular RNA Binds to and Activates AKT Phosphorylation and Nuclear Localization Reducing Apoptosis and Enhancing Cardiac Repair. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3842–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, D.; Caponnetto, A.; Cirnigliaro, M.; Brex, D.; Barbagallo, C.; D’Angeli, F.; Morrone, A.; Caltabiano, R.; Barbagallo, G.M.; Ragusa, M.; et al. CircSMARCA5 Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Regulating a Molecular Axis Involving Splicing Factors SRSF1/SRSF3/PTB. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, Z.; Fang, L.; Lyu, J.; Li, F.; Peng, C.; Krylov, S.N.; et al. A circular RNA circ-DNMT1 enhances breast cancer progression by activating autophagy. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5829–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdt, L.M.; Stahringer, A.; Sass, K.; Pichler, G.; Kulak, N.A.; Wilfert, W.; Kohlmaier, A.; Herbst, A.; Northoff, B.H.; Nicolaou, A.; et al. Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jiang, R.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, H.; Chao, J. circRNA Mediates Silica-Induced Macrophage Activation Via HECTD1/ZC3H12A-Dependent Ubiquitination. Theranostics 2018, 8, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Wang, S.; Ye, B.; Du, Y.; Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Qu, Y.; Fan, Z. A Circular RNA Protects Dormant Hematopoietic Stem Cells from DNA Sensor cGAS-Mediated Exhaustion. Immunity 2018, 48, 688–701.e687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongvaux, A.; Jackson, R.; Harman, C.C.; Li, T.; West, A.P.; de Zoete, M.R.; Wu, Y.; Yordy, B.; Lakhani, S.A.; Kuan, C.Y.; et al. Apoptotic caspases prevent the induction of type I interferons by mitochondrial DNA. Cell 2014, 159, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Legnini, I.; Megiorni, F.; Colantoni, A.; Santini, T.; Morlando, M.; Di Timoteo, G.; Dattilo, D.; Dominici, C.; Bozzoni, I. Circ-ZNF609 regulates G1-S progression in rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3843–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Beltran, M.; Damizia, M.; Grelloni, C.; Colantoni, A.; Setti, A.; Di Timoteo, G.; Dattilo, D.; Centron-Broco, A.; Nicoletti, C.; et al. Circular RNA ZNF609/CKAP5 mRNA interaction regulates microtubule dynamics and tumorigenicity. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 75–89.e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Guo, W. CircZNF609 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through regulating HRAS via miR-338-3p. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. Function and clinical significance of circRNAs in solid tumors. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.Z.; Cao, S.M.; Lei, Y.N.; Liu, C.X.; Guo, S.K.; Shan, L.; et al. Screening for functional circular RNAs using the CRISPR-Cas13 system. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsipatis, D.; Grammatikakis, I.; Driscoll, R.K.; Yang, X.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Harris, S.C.; Yang, J.H.; Herman, A.B.; Chang, M.W.; Munk, R.; et al. AUF1 ligand circPCNX reduces cell proliferation by competing with p21 mRNA to increase p21 production. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 1631–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Circular RNA | Functions | Targets | Interactions with Protein | Cell Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circRNA_0084043 | Stimulates cancer progression | SNAIL | miR-153-3p | melanoma | [76] |
| circIRAK3 | Promotes migration/invasion | FOXC1 | miR-3607 | Breast cancer cells | [77] |
| circBIRC6 | Maintains pluripotency | SOX2, NANOG, OCT4 | miR-145, -34a | hESCs, iPSCs | [78] |
| circATP2B1 | Stimulates invasion | FN1 | miR-204-3p | CCRCC | [79] |
| circLARP4 | Prevents proliferation/invasion | LATS1 | miR-424-5p | Gastric cancer | [80] |
| circADAT1 (circRNA_008913) | Decreases carcinogenesis | DAB2IP | miR-889 | HaCaT | [81] |
| circACTA2 | VSMC contraction | SMA | miR-548f-5p | HASMC | [82] |
| circPVT1 | Stimulates proliferation | Aurka, mKi67, Bub1 | miR-497-5p | HNSCC | [83] |
| Hsa_circ_0000799 (circBPTF) | Stimulates cancer progression | RAB27A | miR-31-5p | Bladder cancer | [84] |
| circCCDC66 | Stimulates cancer progression | MYC, EZH2, DNMT3B | miR-93, -185, -33b | CRC | [85] |
| circNASP | Stimulates cancer progression | FOXF1 | miR-1253 | Osteosarcoma | [86] |
| Hsa_circ_0002052 | Prevents cancer progression | APC2 | miR-1205 | Osteosarcoma | [87] |
| circTCF25 | Stimulates cancer progression | CDK6 | miR-107, -103a-30 | Bladder carcinoma | [88] |
| circZFR | Stimulates cancer progression; prevents cancer progression | a) PTEN b) ZNF121 c) C8orf4 d) CTNNB1 | a) miR-107, -130a b) miR-4302 c) miR-1261 d) miR-3619-5p | a) Gastric Cancer b) PTC c) Lung cancer d) HCC | [89,90,91,92] |
| circMYO9A (circRNA_000203) | Stimulates fibrosis | Col3a1, Col1a2, CTGF, SMA | miR-26b-5p | Cardiac fibroblast | [93] |
| circMTO1 | Prevents cancer progression | HCC | miR-9 | P21 | [94] |
| circFBLIM1 | Stimulates cancer progression | FBLIM1 | miR-346 | HCC | [95] |
| CDR1as | Myocardial infarction; Neural development; anti-oncogenic; stimulates proliferation/metastasis; osteoblastic differentiation insulin secretion; | a) MAGE-A b) HOXB13 c) EGFR CCNE1, PIK3CD, d) GDF5 e) P21 f) PARP, SP1 g) Pax6, Myrip h) Fox | a) miR-876-5p b) miR-7 c) miR-7 d) miR-7 e) miR-135a, -7 f) miR-7 g) miR-7 h) miR-67, -7 | a) ESCC b) Islet cells c) NSCLC d) PDLSC e) Bladder cancer f) Cardiomyocytes g) ESCC h) Neural Tissue | [64,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104] |
| circNT5E | Stimulates cancer progression | PIK3CA, NT5E | miR-422a | Glioblastoma | [65] |
| circHIPK | Stimulates proliferation/ migration; prevents cancer from progressing; β-cell function | a) AQP3 b) HPSE c) CDK6, ROCK1, d) FZD4, VEGF-C WNT2, e) Mtpn Slc2a2, Akt1, f) FAK, EGFR, IGF1R g) IL6R, DLX2 | a) miR-124 b) miR-558 c) miR-124 d) miR-30a-30 e) miR-124-3p, -338-3p f) miR-7 g) miR-193a, -584, -29b, -654-193a, -124, -379, -152, -338, 29a | Cancer tissues | [63,66,105,106,107,108,109] |
| circWDR77 | Stimulates proliferation | FGF2 | miR-124 | VSMC | [67] |
| circC1orf116 (circRNA_8924) | Stimulates cancer progression | CBX8 | miR-519-5p, -518d-5p | Cervica tumor cells | [110] |
| circITGA7 | Prevents proliferation/metastasis | NF1 | miR-370-3p | CRC | [111] |
| circZNF609 | Myoblast differentiation Retinal vascular dysfunction; neurodegeneration | a) MEF2A b) METRN c) BCLAF1 | a) miR-615 b) miR-194-5p c) miR-615 | a) Vascular endothelial b) RGC c) C2C12 | [112,113,114] |
| SRY | Determines sex | miR-138 | Testis | [16] |
| Circular RNA | Cell Type | Interactions with Protein | Functions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| circPABPN1 | HeLa | HuR | Inhibits PABPN1 translation | [220] |
| circMTO1 | Breast Cancer Cells | TRAF4 | Suppresses proliferation | [221] |
| circFOXO3 | Heart Tissues, Non-Cancer Cells | P53, P21, ID-1, FAK, MDM2, HIF1α, CDK2, E2F1 | Induces apoptosis Inhibits cell cycle progression Cardiac senescence | [110,222,223] |
| circAMOTL1 | Cardiomyocytes | AKT1, PDK1 | Supports cell survival | [224] |
| circSMARCA5 | Glioblastoma | SRSF1 | Suppressor of tumor | [225] |
| circDNMT1 | Breast Cancer Cells | Auf1, P53 | Promotes proliferation | [226] |
| circANRIL | Vascular Tissues | PES1 | rRNA maturation | [227] |
| circHECTD1 | Macrophage | ZC3H12A | Activation of macrophage | [228] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, A.; Jaijyan, D.K.; Yang, S.; Zeng, M.; Pei, S.; Zhu, H. Functions of Circular RNA in Human Diseases and Illnesses. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040038
Gu A, Jaijyan DK, Yang S, Zeng M, Pei S, Zhu H. Functions of Circular RNA in Human Diseases and Illnesses. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Alison, Dabbu Kumar Jaijyan, Shaomin Yang, Mulan Zeng, Shaokai Pei, and Hua Zhu. 2023. "Functions of Circular RNA in Human Diseases and Illnesses" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040038
APA StyleGu, A., Jaijyan, D. K., Yang, S., Zeng, M., Pei, S., & Zhu, H. (2023). Functions of Circular RNA in Human Diseases and Illnesses. Non-Coding RNA, 9(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040038






