The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Gene (CFTR) Is under Post-Transcriptional Control of microRNAs: Analysis of the Effects of agomiRNAs Mimicking miR-145-5p, miR-101-3p, and miR-335-5p
Abstract
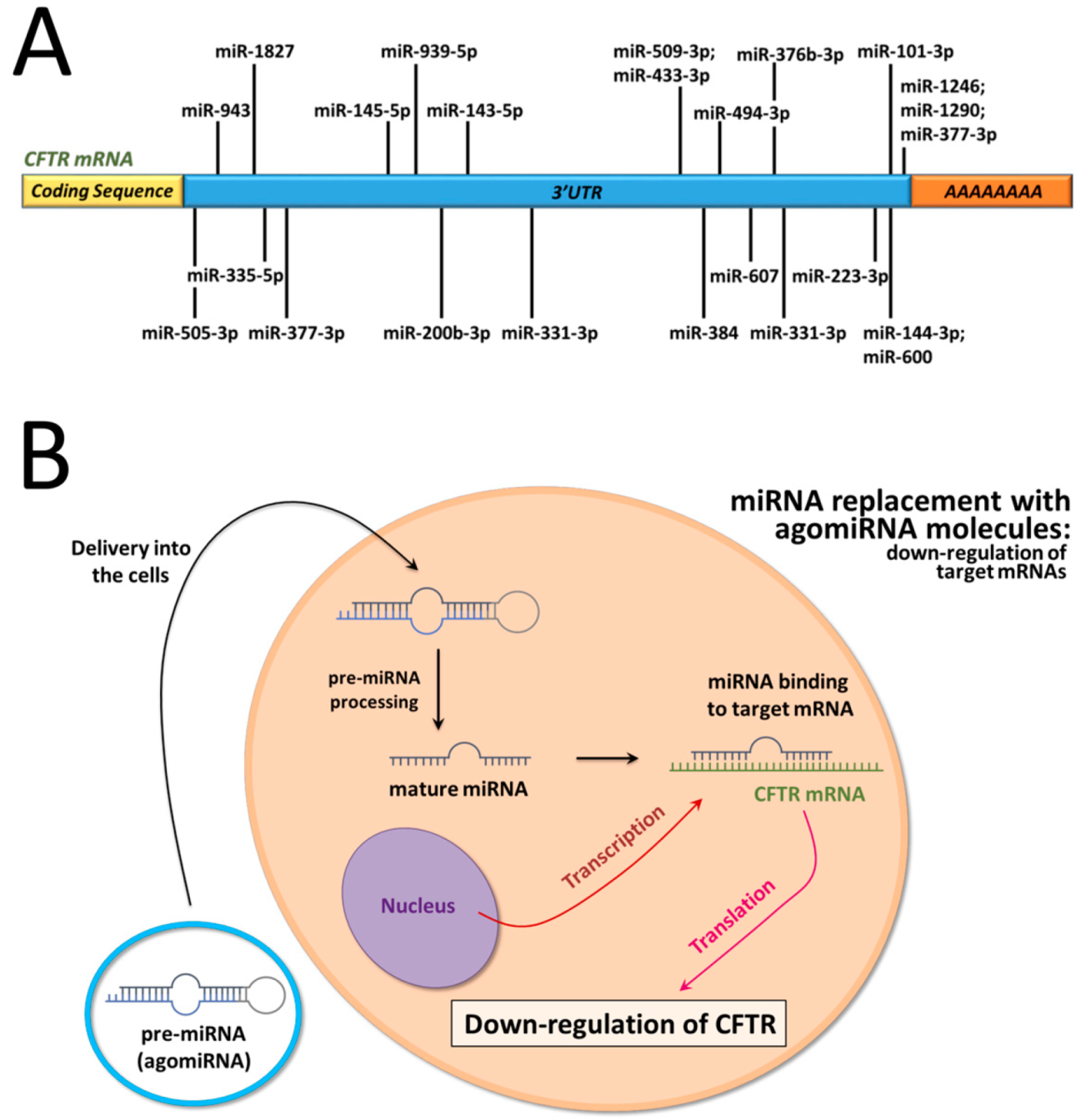
1. Introduction
2. Results
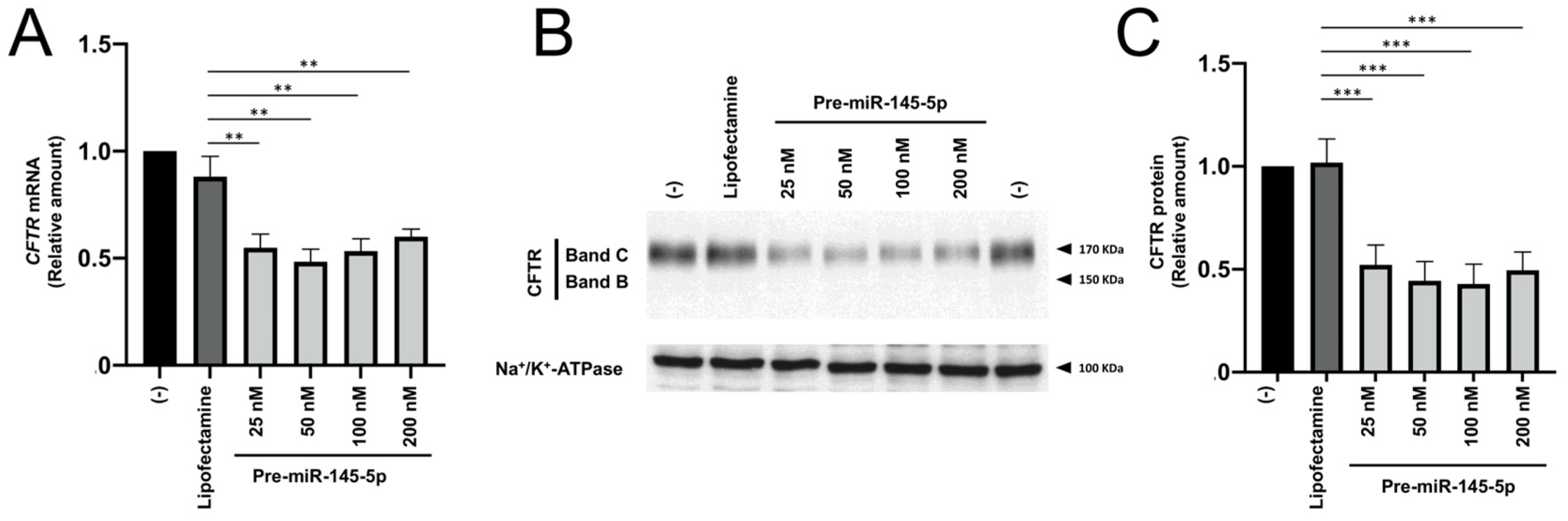
2.1. Effects of Treatment of Calu-3 Cells with Pre-miRNAs Regulating CFTR Expression
2.2. The Effects of Treatment of Calu-3 Cells with Pre-miR-145-5p Do Not Require Multiple Additions of the agomiR
2.3. Pre-miR-145-5p Inhibits CFTR Expression in the Intestinal Cell Line Caco-2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. Cell Treatments with agomiRNAs
4.3. RNA Extraction
4.4. Analysis of CFTR Expression: RT-qPCR
4.5. Analysis of CFTR Expression: Western Blotting
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontheimer, E.J.; Carthew, R.W. Silence from within: Endogenous siRNAs and miRNAs. Cell 2005, 122, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Garcia, I.; Miska, E.A. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development 2005, 132, 4653–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kowdley, K.V. MicroRNAs in common human diseases. Genomic. Proteom. Bioinform. 2012, 10, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, M.; Miao, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, W.; Cui, Q. An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Podder, S.; Ghosh, T.C. Insights into the miRNA regulations in human disease genes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Dru. Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Hossain, G.S.; Kocerha, J. The Potential for microRNA Therapeutics and Clinical Research. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, A.F.; Kaur, R.P.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, A.; Gupta, V.; Bansal, P. MicroRNA therapeutics: Discovering novel targets and developing specific therapy. Perspect. Clin Res. 2016, 7, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S. Therapeutic advances of miRNAs: A preclinical and clinical update. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 28, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ree, M.H.; de Vree, J.M.; Stelma, F.; Willemse, S.; van der Valk, M.; Rietdijk, S.; Molenkamp, R.; Schinkel, J.; vanNuenen, A.C.; Beuers, U.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and antiviral effect of RG-101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A phase 1B, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, S.; Parsley, T.B.; Yang, L.; Zeh, K.; van Doorn, L.J.; van der Veer, E.; Raney, A.K.; Hodges, M.R.; Patick, A.M. In vitro antiviral activity and preclinical and clinical resistance profile of miravirsen, a novel anti-hepatitis C virus therapeutic targeting the human factor miR-122. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnken, R.; Mishra, A. MicroRNAs in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma: The Future of Therapy. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillen, A.E.; Gosalia, N.; Leir, S.H.; Harris, A. MicroRNA regulation of expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. Biochem. J. 2011, 438, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megiorni, F.; Cialfi, S.; Dominici, C.; Quattrucci, S.; Pizzuti, A. Synergistic post-transcriptional regulation of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance Regulator (CFTR) by miR-101 and miR-494 specific binding. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.; Nuovo, G.J.; Crawford, M.; Boyaka, P.N.; Kirkby, S.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P.; Cormet-Boyaka, E. MiR-101 and miR-144 regulate the expression of the CFTR chloride channel in the lung. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Karp, P.H.; Jiang, P.; Ostedgaard, L.S.; Walz, A.E.; Fisher, J.T.; Keshavjee, S.; Lennox, K.A.; Jacobi, A.M.; Rose, S.D.; et al. A microRNA network regulates expression and biosynthesis of wild-type and DeltaF508 mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13362–13367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Karp, P.H.; Osterhaus, S.R.; Jiang, P.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Lennox, K.A.; Jacobi, A.M.; Praekh, K.; Rose, S.D.; Behlke, M.A.; et al. Post-transcriptional regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator expression and function by microRNAs. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglesby, I.K.; Chotirmall, S.H.; McElvaney, N.G.; Greene, C.M. Regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator by microRNA-145, -223, and -494 is altered in ΔF508 cystic fibrosis airway epithelium. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3354–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, E.; Tamanini, A.; Jakova, T.; Gasparello, J.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; Sabbioni, G.; Finotti, A.; Borgatti, M.; Lampronti, I.; et al. A Peptide Nucleic Acid against MicroRNA miR-145-5p Enhances the Expression of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) in Calu-3 Cells. Molecules 2017, 23, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Fabbri, E.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. Differential effects on the miRNome of the treatment of human airway epithelial Calu-3 cells with peptide-nucleic acids (PNAs) targeting microRNAs miR-101-3p and miR-145-5p: Next generation sequencing datasets. Data Brief. 2021, 35, 106718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finotti, A.; Gasparello, J.; Fabbri, E.; Tamanini, A.; Corradini, R.; Dechecchi, M.C.; Cabrini, G.; Gambari, R. Enhancing the Expression of CFTR Using Antisense Molecules against MicroRNA miR-145-5p. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1443–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, E.; Tamanini, A.; Jankova, T.; Gasparello, J.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; Finotti, A.; Borgatti, M.; Lampronti, I.; Munari, S.; et al. Treatment of human airway epithelial Calu-3 cells with a Peptide-Nucleic Acid (PNA) targeting the microRNA miR-101-3p is associated with increased expression of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanini, A.; Fabbri, E.; Jakova, T.; Gasparello, J.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; Finotti, A.; Borgatti, M.; Lampronti, I.; Munari, S.; et al. A Peptide-Nucleic Acid Targeting miR-335-5p Enhances Expression of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Gene with the Possible Involvement of the CFTR Scaffolding Protein NHERF1. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutful Kabir, F.; Ambalavanan, N.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Solomon, G.M.; Lal, C.V.; Mazur, M.; Halloran, B.; Szul, T.; Gerthoffer, W.T.; et al. MicroRNA-145 Antagonism Reverses TGF-beta Inhibition of F508del CFTR Correction in Airway Epithelia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.K.; Chinnapaiyan, S.; Rasmussen, L.; Raju, S.V.; Unwalla, H.J. A Neutralizing Aptamer to TGFBR2 and miR-145 Antagonism Rescue Cigarette Smoke- and TGF-beta-Mediated CFTR Expression. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, C.; Gasparello, J.; Zurlo, M.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; Cabrini, G.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. Combined Treatment of Bronchial Epithelial Calu-3 Cells with Peptide Nucleic Acids Targeting miR-145-5p and miR-101-3p: Synergistic Enhancement of the Expression of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Rozzi, A.; Gasparello, J.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; Papi, C.; Finotti, J.; Lampronti, I.; Reali, E.; Cabrini, G.; et al. A Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) Masking the miR-145-5p Binding Site of the 3’UTR of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) mRNA Enhances CFTR Expression in Calu-3 Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi, C.; Fernández Fernández, E.; Gaul, R.; Vencken, S.; Glasgow, A.; Oglesby, I.K.; Hurley, K.; Hawkins, F.; Mitash, N.; Mu, F.; et al. Precise Targeting of miRNA Sites Restores CFTR Activity in CF Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrat, M.; Wongdee, K.; Teerapornpuntakit, J.; Thongbunchoo, J.; Tanramluk, D.; Aeimlapa, R.; Thammayon, N.; Thonapan, N.; Wattano, P.; Charoenphandhu, N. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator contribute to the transepithelial calcium transport across intestinal epithelium-like Caco-2 monolayer. PLoS ONE. 2022, 17, e0277096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyi, P.; Seidler, U.; Kunzelmann, K. CFTR-beyond the airways: Recent findings on the role of the CFTR channel in the pancreas, the intestine and the kidneys. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2023, 22, S17–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, H.R.; Ardelean, M.C.; Bijvelds, M.J.C.; Vergani, P. Strategies for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator inhibition: From molecular mechanisms to treatment for secretory diarrhoeas. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 4085–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Yang, J.; Yin, J.; Cole, R.; Tse, M.; Berman, D.E.; Small, S.A.; Petsko, G.; Donowitz, M. Cholera toxin inhibits SNX27-retromer-mediated delivery of cargo proteins to the plasma membrane. J. Cell. Sci. 2018, 131, jcs218610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Lomazzi, M.; Papi, C.; D’Aversa, E.; Sansone, F.; Casnati, A.; Gaetano, D.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. Efficient Delivery of MicroRNA and AntimiRNA Molecules Using an Argininocalix[4]arene Macrocycle. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, G.B.; Elrggal, M.E.; Gaur, L.; Lerma, E.V. Update and review of adult polycystic kidney disease. Dis. Mon. 2020, 66, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidow, C.J.; Maser, R.L.; Rome, L.A.; Calvet, J.P.; Grantham, J.J. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mediates transepithelial fluid secretion by human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease epithelium in vitro. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Sonawane, N.D.; Zhao, D.; Somlo, S.; Verkman, A.S. Small-molecule CFTR inhibitors slow cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonum, K.; Chabang, N.; Fongsupa, S.; Chantawarin, S.; Jiarpinitnun, C.; Tuchinda, P.; Soodvilai, S. Pinostrobin inhibits renal CFTR-mediated Cl- secretion and retards cyst growth in cell-derived cyst and polycystic kidney disease rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 148, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeraphan, P.; Chavasiri, W.; Muanprasat, C.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Yuajit, C. A chalcone derivative retards renal cyst enlargement by inhibiting fluid secretion and cell proliferation in an in vitro model of polycystic kidney disease. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2021, 25, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuajit, C.; Muanprasat, C.; Homvisasevongsa, S.; Chatsudthipong, V. Steviol stabilizes polycystin 1 expression and promotes lysosomal degradation of CFTR and β-catenin proteins in renal epithelial cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Song, C.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. CFTR Functions as a Tumor Suppressor and Is Regulated by DNA Methylation in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 4261–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Than, B.L.; Linnekamp, J.F.; Starr, T.K.; Largaespada, D.A.; Rod, A.; Zhang, Y.; Bruner, V.; Abrahante, J.; Schumann, A.; Luczak, T.; et al. CFTR is a tumor suppressor gene in murine and human intestinal cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4179–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.; Tsang, K.S.; Liao, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. High cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator expression in childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia acts as a potential therapeutic target. Transl. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Dong, J.; Guo, J.; U, K.P.; Weng, Z.; Liu, S.; Chan, H.C.; Feng, H.; et al. CFTR promotes malignant glioma development via up-regulation of Akt/Bcl2-mediated anti-apoptosis pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 7301–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yong, M.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Yu, T.; Fu, X.; Hu, L. High level of CFTR expression is associated with tumor aggression and knockdown of CFTR suppresses proliferation of ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2227–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Shen, T.; Liu, P.; Fang, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, J. mir-145-5p is a suppressor of colorectal cancer at early stage, while promotes colorectal cancer metastasis at late stage through regulating AKT signaling evoked EMT-mediated anoikis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yu, G.; Peng, K.; Liu, S. MicroRNA-145-5p suppresses fascin to inhibit the invasion and migration of cervical carcinoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 5282–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, L.; Ye, X.; Tao, M.; Wu, J. miR-145-5p suppresses proliferation, metastasis and EMT of colorectal cancer by targeting CDCA3. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satitsri, S.; Pongkorpsakol, P.; Srimanote, P.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Muanprasat, C. Pathophysiological mechanisms of diarrhea caused by the Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor variant: An in vivo study in mice. Virulence 2016, 7, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangnil, P.; Satitsri, S.; Tadpetch, K.; Saparpakorn, P.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Hannongbua, S.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Muanprasat, C. A fungal metabolite zearalenone as a CFTR inhibitor and potential therapy of secretory diarrheas. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 150, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Chávez, F.; Meader, B.T.; Akosman, S.; Koprivica, V.; Mekalanos, J.J. A Potent Inhibitor of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Blocks Disease and Morbidity Due to Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae. Toxins 2022, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patanayindee, J.; Muanprasat, C.; Soodvilai, S.; Chatsudthipong, V. Antidiarrheal efficacy of a quinazolin CFTR inhibitor on human intestinal epithelial cell and in mouse model of cholera. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2012, 44, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Awwal, N.; Dweik, F.; Mahdi, S.; El-Dweik, M.; Anderson, S.H. A Review of SARS-CoV-2 Disease (COVID-19): Pandemic in Our Time. Pathogens 2022, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzerri, V.; Lucca, F.; Volpi, S.; Cipolli, M. Does cystic fibrosis constitute an advantage in COVID-19 infection? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, V.; Merigo, F.; Lagni, A.; Di Clemente, A.; Ligozzi, M.; Bernardi, P.; Rossini, G.; Concia, E.; Plebani, R.; Romano, M.; et al. CFTR Modulation Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzerri, V.; Gentili, V.; Api, M.; Finotti, A.; Papi, C.; Tamanini, A.; Boni, C.; Baldisseri, E.; Olioso, D.; Duca, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral entry and replication is impaired in Cystic Fibrosis airways due to ACE2 downregulation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parray, A.; Mir, F.A.; Doudin, A.; Iskandarani, A.; Danjuma, M.M.; Kuni, R.A.T.; Abdelmajid, A.; Abdelhafez, I.; Arif, R.; Mulhim, M.; et al. SnoRNAs and miRNAs Networks Underlying COVID-19 Disease Severity. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chidekel, A.; Shaffer, T.H. Cultured Human Airway Epithelial Cells (Calu-3): A Model of Human Respiratory Function, Structure, and Inflammatory Responses. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 394578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodby, B.; Schiavone, M.L.; Pambianchi, E.; Mastaloudis, A.; Hester, S.N.; Wood, S.M.; Pecorelli, A.; Valacchi, G. Particulate Matter Decreases Intestinal Barrier-Associated Proteins Levels in 3D Human Intestinal Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Pre-miRTM miRNA Precursor | ID |
|---|---|
| has-pre-miR-145-5p | PM11480 |
| has-pre-miR-101-3p | PM11414 |
| has-pre-miR-335-5p | PM10063 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papi, C.; Gasparello, J.; Zurlo, M.; Cosenza, L.C.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Gene (CFTR) Is under Post-Transcriptional Control of microRNAs: Analysis of the Effects of agomiRNAs Mimicking miR-145-5p, miR-101-3p, and miR-335-5p. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020029
Papi C, Gasparello J, Zurlo M, Cosenza LC, Gambari R, Finotti A. The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Gene (CFTR) Is under Post-Transcriptional Control of microRNAs: Analysis of the Effects of agomiRNAs Mimicking miR-145-5p, miR-101-3p, and miR-335-5p. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020029
Chicago/Turabian StylePapi, Chiara, Jessica Gasparello, Matteo Zurlo, Lucia Carmela Cosenza, Roberto Gambari, and Alessia Finotti. 2023. "The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Gene (CFTR) Is under Post-Transcriptional Control of microRNAs: Analysis of the Effects of agomiRNAs Mimicking miR-145-5p, miR-101-3p, and miR-335-5p" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020029
APA StylePapi, C., Gasparello, J., Zurlo, M., Cosenza, L. C., Gambari, R., & Finotti, A. (2023). The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Gene (CFTR) Is under Post-Transcriptional Control of microRNAs: Analysis of the Effects of agomiRNAs Mimicking miR-145-5p, miR-101-3p, and miR-335-5p. Non-Coding RNA, 9(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020029








