Circulating MicroRNAs as Specific Biomarkers in Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
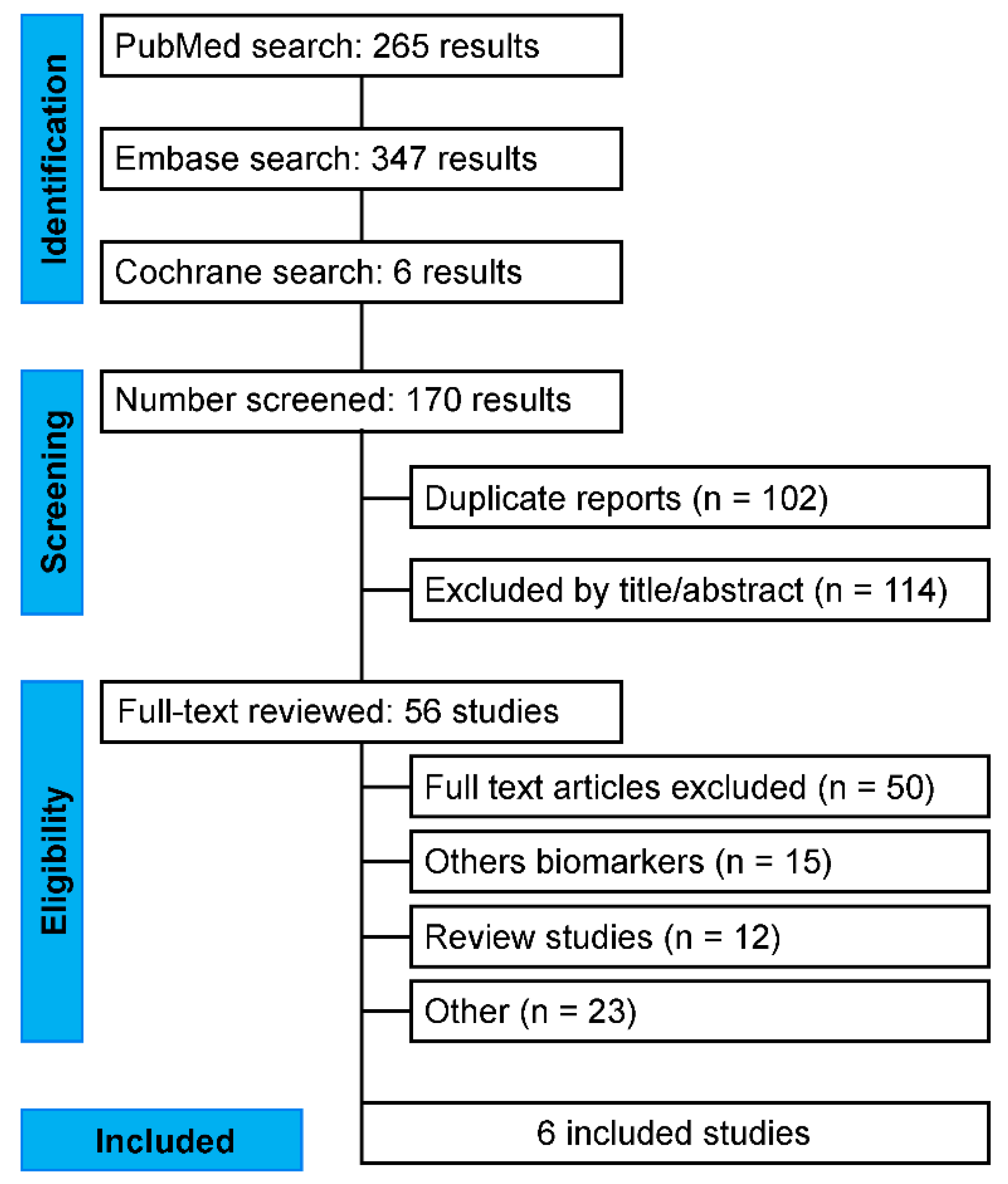
2.3. Literature Search Strategy
2.4. Data Extraction and Result Definition
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Selected Studies
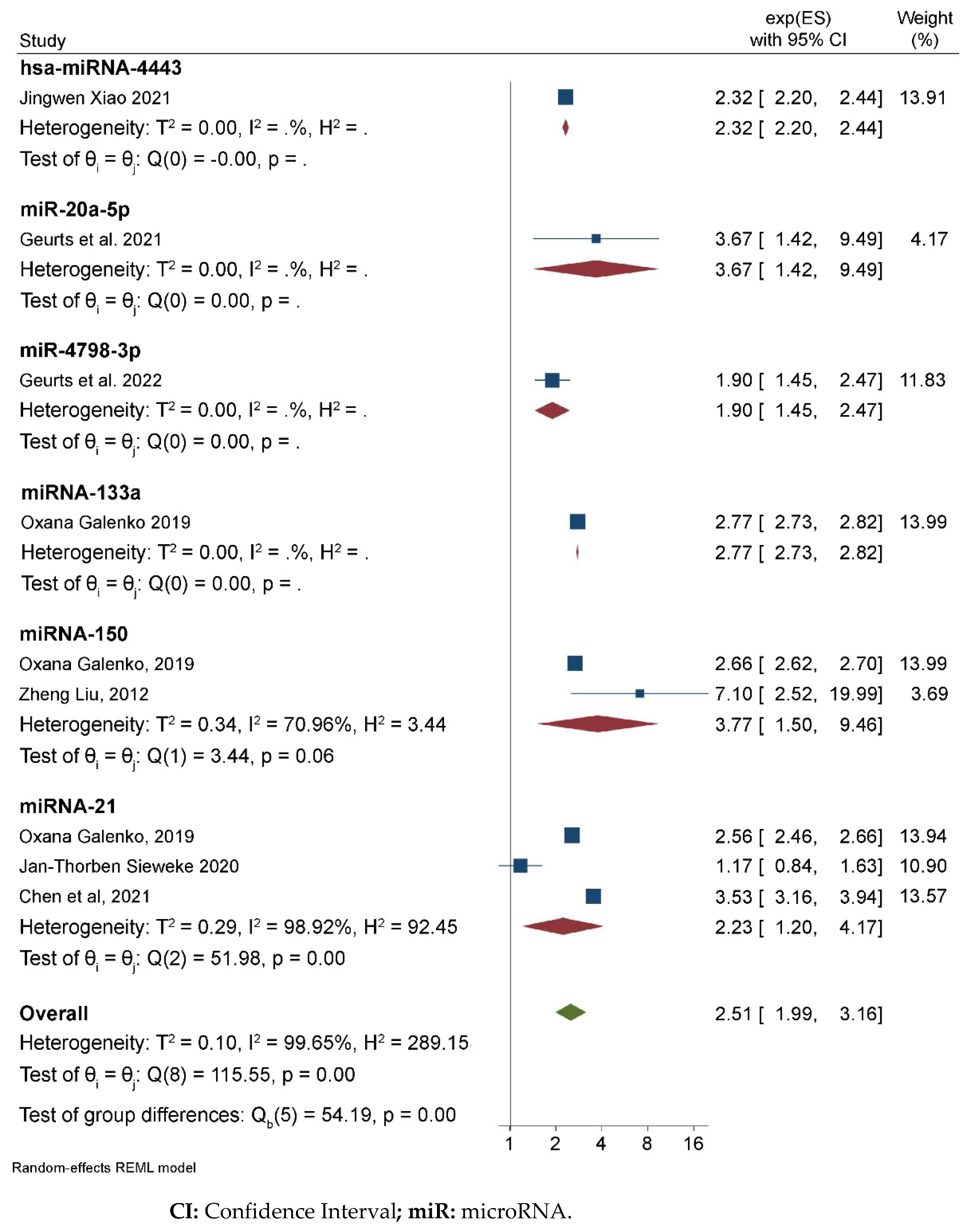
3.2. Meta-Analysis Results
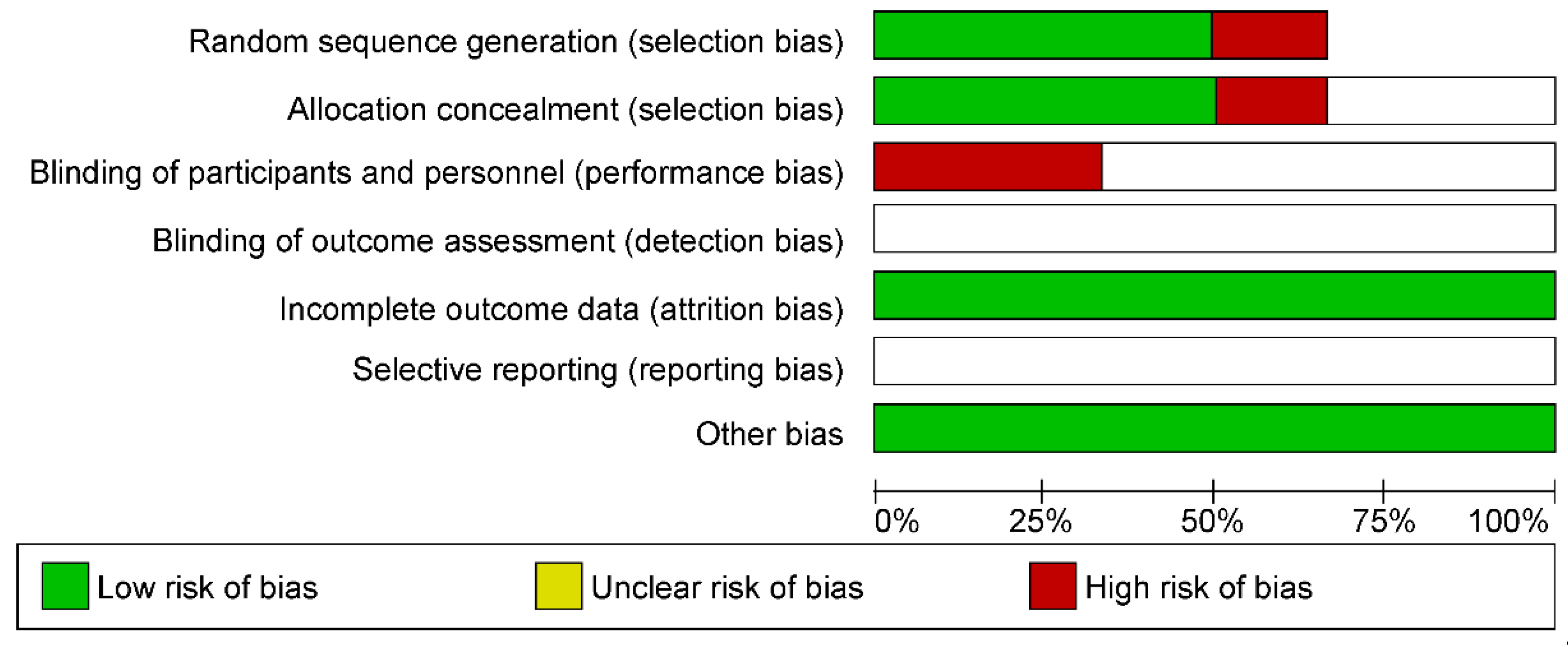
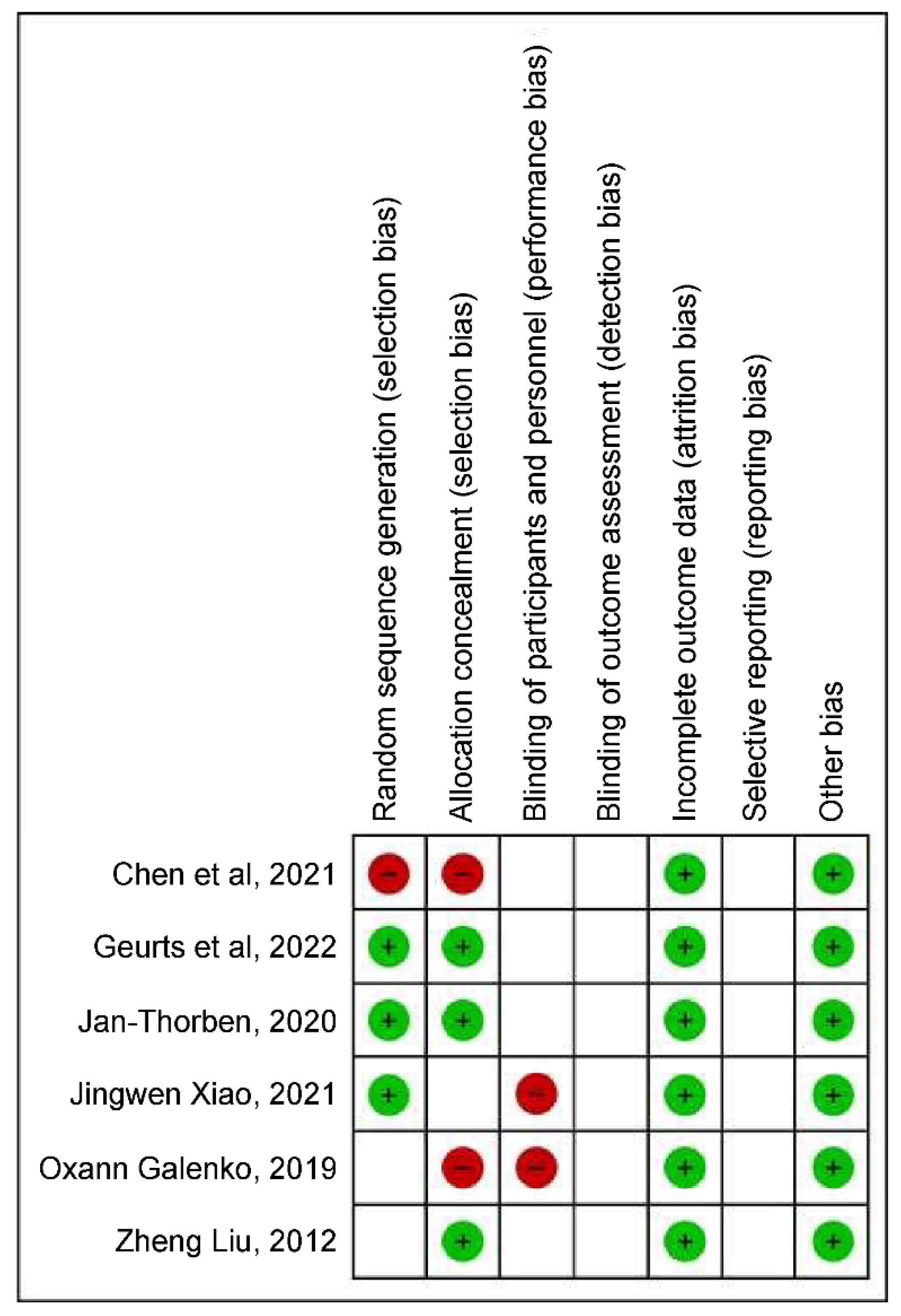
3.3. Evaluation of Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| DGCR8: | DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 |
| ECG: | electrocardiography |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| miRNAs | microRNAs; |
| OR | odds ratio |
| pre-miRs | precursor miRs |
| pri-miRs | primary miRs |
| qRT-PCR | reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-beta |
References
- Cintra, F.D.; Figueiredo, M.J.O. Atrial fibrillation (Part 1): Pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic basis. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Velasco, E.; Franco, D.; Aranega, A.; Daimi, H. Genetics and epigenetics of atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimetbaum, P. Atrial fibrillation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 166, ITC33–ITC48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Hu, L.L.; Dong, Q.B.; Hu, F.; Zhu, L.J.; Liang, Q.; Yu, L.; Bao, H.; Cheng, X. Potential target genes in the development of atrial fibrillation: A comprehensive bioinformatics analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e928366. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Shi, K.H.; Yang, J.J.; Li, J. Epigenetic mechanisms in atrial fibrillation: New insights and future directions. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 26, 306–318. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, G. The therapeutic potential of microRNAs in atrial fibrillation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 3053520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalife, J.; Kaur, K. Atrial remodeling, fibrosis, and atrial fibrillation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 25, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nattel, S.; Harada, M. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: Recent advances and translational perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, N.W.E.; Kawasaki, M.; Berger, W.R.; Neefs, J.; Meulendijks, E.; Tijsen, A.J.; de Groot, J.R. MicroRNAs in atrial fibrillation: From expression signatures to functional implications. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2017, 31, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, L.P.; Figueiredo, M.J.O.; Cintra, F.D.; Saad, E.B.; Kuniyoshi, R.R.; Filho, A.M.L.; D’Avila, A.L.B.; de Paola, A.A.V.; Kalil, C.A.A.; Moreira, D.A.R.; et al. Executive summary of the II Brazilian guidelines for atrial fibrillation. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2016, 107, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, I.L.; Penna, K.G.B.D.; dos Santos Carneiro, M.A.; Libera, L.S.D.; Ramos, J.E.P.; Saddi, V.A. Tissue micro-RNAs associated with colorectal cancer prognosis: A systematic review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orenes-Piñero, E.; Montoro-García, S.; Patel, J.V.; Valdés, M.; Marín, F.; Lip, G.Y.H. Role of microRNAs in cardiac remodelling: New insights and future perspectives. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.N.; Zhang, Z.L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, J.; Gu, Z. Identification of microRNA biomarkers in atrial fibrillation: A protocol for systematic review and bioinformatics analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koniari, I.; Artopoulou, E.; Velissaris, D.; Ainslie, M.; Mplani, V.; Karavasili, G.; Kounis, N.; Tsigkas, G. Biomarkers in the clinical management of patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 908–951. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software; Release 16; College Station; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Galenko, O.; Jacobs, V.; Knight, S.; Taylor, M.; Cutler, M.J.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Carlquist, J.L.; Knowlton, K.U.; Bunch, T.J. The role of microRNAs in the development, regulation, and treatment of atrial fibrillation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2019, 55, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieweke, J.T.; Pfeffer, T.J.; Biber, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Weissenborn, K.; Grosse, G.M.; Hagemus, J.; Derda, A.A.; Berliner, D.; Lichtinghagen, R.; et al. Mir-21 and NT-proBNP correlate with echocardiographic parameters of atrial dysfunction and predict atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, S.; Mens, M.M.J.; Bos, M.M.; Ikram, M.A.; Ghanbari, M.; Kavousi, M. Circulatory microRNAs in plasma and atrial fibrillation in the general population: The Rotterdam study. Genes 2021, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Ye, P.; Miao, X.; Xia, J. The expression levels of plasma micoRNAs in atrial fibrillation patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44906. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Dai, H.; OuYang, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, M. Hsa-mir-4443 inhibits myocardial fibroblast proliferation by targeting THBS1 to regulate TGF-β1/α-SMA/collagen signaling in atrial fibrillation. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e10692. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yang, X.C. Relationship between circulating miRNA-21, atrial fibrosis, and atrial fibrillation in patients with atrial enlargement. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 12742–12749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thum, T.; Gross, C.; Fiedler, J.; Fischer, T.; Kissler, S.; Bussen, M.; Galuppo, P.; Just, S.; Rottbauer, W.; Frantz, S.; et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature 2008, 456, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barwari, T.; Eminaga, S.; Armstrong, P.C.; Chan, M.V.; Lu, R.; Barallobre-Barreiro, J.; Yin, X.; Pechlaner, R.; Langley, S.R.; Zampetaki, A.; et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates transforming growth factor beta-1 release from platelets: A novel mechanism for the anti-fibrotic effects of microRNA-21 inhibition. Circulation 2017, 136, A19935. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.; Modi, A.; Khokhar, M.; Sankanagoudar, S.; Yadav, D.; Sharma, S.; Purohit, P.; Sharma, P. MicroRNA 21 emerging role in diabetic complications: A critical update. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2021, 17, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Barana, A.; Matamoros, M.; Dolz-Gaitón, P.; Pérez-Hernández, M.; Amorós, I.; Núñez, M.; Sacristán, S.; Pedraz, Á.; Pinto, Á.; Fernández-Avilés, F. Chronic atrial fibrillation increases microRNA-21 in human atrial myocytes decreasing L-type calcium current. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 861–868. [Google Scholar]
- Goren, Y.; Meiri, E.; Hogan, C.; Mitchell, H.; Lebanony, D.; Salman, N.; Schliamser, J.E.; Amir, O. Relation of reduced expression of MiR-150 in platelets to atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic systolic heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komal, S.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, S.H.; Huang, C.Z.; Tao, H.L.; Dong, J.Z.; Han, S.; Zhang, L. MicroRNAs: Emerging biomarkers for atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tuazon, J.P.; Borlongan, C.V.; Yu, G. MicroRNA-133a and myocardial infarction. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, F.; Bian, H.; Tang, B.; Fang, X. MicroRNA-20a-5p suppresses tumor angiogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer through RRM2-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | MicroRNA Studied | RNA Extraction Method | MicroRNA Quantification Method | MicroRNA Quantification Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu [20] | miRNA-150 | mirVana™ PARIS™ kit (Invitrogen) | qRT-PCR | TaqMan |
| Galenko [17] | miRNA-133a | Norgen Biotek, Inc. (Thorold, ON, Canada) | qRT-PCR | TaqMan |
| Galenko [17] | miRNA-150 | Norgen Biotek, Inc. | qRT-PCR | TaqMan |
| Sieweke [18] | miRNA-21 | miRNeasy Mini kit | qRT-PCR | TaqMan |
| Xiao [21] | hsa-miRNA-4443 | miRCURY™ RNA isolation kit | Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 (Small RNA Analysis Chip; Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) | TaqMan |
| Chen et al. [22] | miRNA-21 | TRIzol reagent kit | qRT-PCR | TaqMan |
| Geurts et al. [19] | miR-20a-5p | Illumina NextSeq 500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) | HTG Molecular Diagnostics, Tuscon, AZ, USA | ------------------ |
| Geurts et al. [19] | miR-4798-3p | Illumina NextSeq 500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) | HTG Molecular Diagnostics, Tuscon, AZ, USA | ----------------- |
| Author/Year | MicroRNA Studied | Expression in Patients with AF |
|---|---|---|
| Galenko [17] | miRNA-133a | Hyperexpressed |
| Galenko [17] | miRNA-150 | Hypoexpressed |
| Sieweke [18] | miRNA-21 | Hypoexpressed |
| Xiao [21] | hsa-miRNA-4443 | Hypoexpressed |
| Chen et al. [22] | miRNA-21 | Hyperexpressed |
| Geurts et al. [19] | miR-20a-5p | Hyperexpressed |
| Geurts et al. [19] | miR-4798-3p | Hyperexpressed |
| Author/Year | Effect | Result | IC Inferior | IC Superior | Subgroup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galenko [17] | OR | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.98 | miRNA-21 |
| Sieweke [18] | RR | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.7 | miRNA-21 |
| Chen et al. [22] | OR | 1.26 | 1.15 | 1.37 | miRNA-21 |
| Galenko [17] | OR | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.99 | miRNA-150 |
| Liu [20] | OR | 1.96 | 1.50 | 3.57 | miRNA-150 |
| Geurts et al., 2021 [19] | OR | 1.30 | 0.68 | 2.58 | miR-20a-5p |
| Geurts et al., 2022 | OR | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.97 | miR-4798-3p |
| Xiao [21] | ROC | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.87 | hsa-miRNA-4443 |
| Galenko [17] | OR | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.03 | miRNA-133a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menezes Junior, A.d.S.; Ferreira, L.C.; Barbosa, L.J.V.; Silva, D.d.M.e.; Saddi, V.A.; Silva, A.M.T.C. Circulating MicroRNAs as Specific Biomarkers in Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010013
Menezes Junior AdS, Ferreira LC, Barbosa LJV, Silva DdMe, Saddi VA, Silva AMTC. Circulating MicroRNAs as Specific Biomarkers in Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenezes Junior, Antônio da Silva, Lara Cristina Ferreira, Laura Júlia Valentim Barbosa, Daniela de Melo e Silva, Vera Aparecida Saddi, and Antonio Márcio Teodoro Cordeiro Silva. 2023. "Circulating MicroRNAs as Specific Biomarkers in Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010013
APA StyleMenezes Junior, A. d. S., Ferreira, L. C., Barbosa, L. J. V., Silva, D. d. M. e., Saddi, V. A., & Silva, A. M. T. C. (2023). Circulating MicroRNAs as Specific Biomarkers in Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. Non-Coding RNA, 9(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010013








