Urinary miRNA Expression in Pre-Eclampsia During Early and Mid-Pregnancy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. MiRNA Isolation and Library Preparation for Sequencing
2.4. Illumina Sequencing
2.5. Clinical Data Analysis
2.6. Sequencing Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Objectives
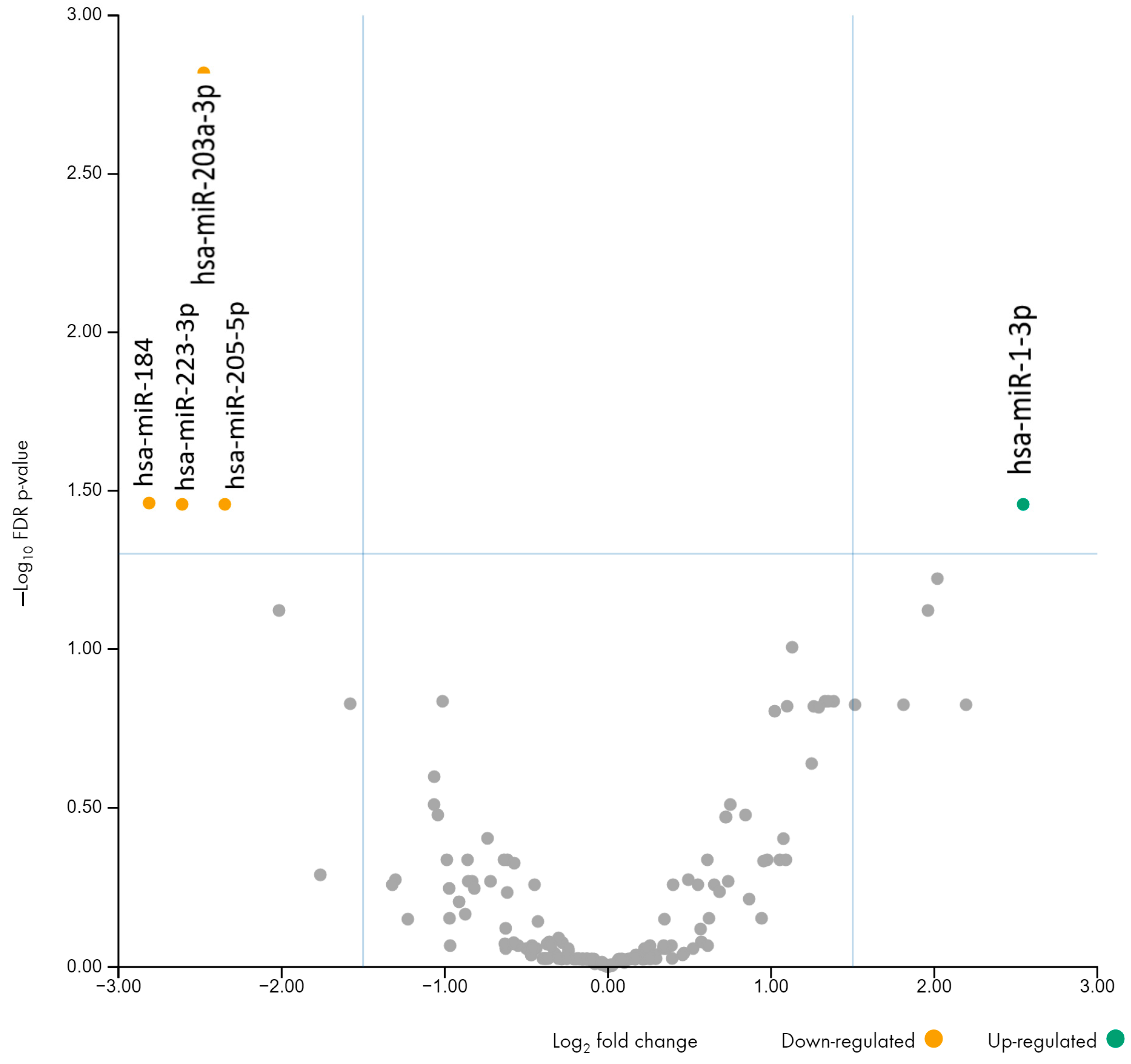
3.2. Comparison of miRNA Profiles in Urine Between Pre-Eclampsia and Control Groups
3.3. Target Prediction and Gene Ontology Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macedo, T.C.C.; Montagna, E.; Trevisan, C.M.; Lorençone, B.R.; Barbosa, C.P.; Ferreira, S.M.; Fraietta, R.; Bianco, B. Prevalence of Preeclampsia and Eclampsia in Adolescent Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 291,247 Adolescents Worldwide since 1969. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 248, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Agrifoglio, O.; Gallo, G.; Scalisi, A.; Agodi, A. The Role of miRNAs as Biomarkers for Pregnancy Outcomes: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 8067972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, C.; Ruano, C.S.M.; Méhats, C.; Miralles, F.; Vaiman, D. The Role of Epigenetics in Placental Development and the Etiology of Preeclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondracka, A.; Jaszczuk, I.; Koczkodaj, D.; Kondracki, B.; Frąszczak, K.; Oniszczuk, A.; Rybak-Krzyszkowska, M.; Staniczek, J.; Filip, A.; Kwaśniewska, A. Analysis of Circulating C19MC MicroRNA as an Early Marker of Hypertension and Preeclampsia in Pregnant Patients: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Weiss, D.; Nyhan, K.; Dewan, A.; Jukic, A.M.Z. Circulating miRNAs in the First Trimester and Pregnancy Complications: A Systematic Review. Epigenetics 2023, 18, 2152615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannubilo, S.R.; Cecati, M.; Marzioni, D.; Ciavattini, A. Circulating miRNAs and Preeclampsia: From Implantation to Epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igaz, I.; Igaz, P. Diagnostic Relevance of MicroRNAs in Other Body Fluids Including Urine, Feces, and Saliva. Exp. Suppl. 2015, 106, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, C.; Rocke, D.M.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Weiss, R.H. Stability of miRNA in Human Urine Supports Its Biomarker Potential. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, M.; Poojary, S.S.; Seshan, V.; Pinto, M.J.; Abraham, A. Urine miRNA Signature as a Potential Non-Invasive Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Cervical Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, A.M.; Lapucci, C.; Salvatore, M.; Incoronato, M.; Ferrari, M. Urinary miRNAs as a Diagnostic Tool for Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inno, R.; Laan, M. Urinary MicroRNA Profiling in Pregnant Women Identifies Placental MicroRNAs That Are Candidate Biomarkers for Monitoring Placental Health. FEBS Lett. 2023, 597, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Van Oostdam, A.S.; Toro-Ortíz, J.C.; López, J.A.; Noyola, D.E.; García-López, D.A.; Durán-Figueroa, N.V.; Martínez-Martínez, E.; Portales-Pérez, D.P.; Salgado-Bustamante, M.; López-Hernández, Y. Placental Exosomes Isolated from Urine of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Exhibit a Differential Profile Expression of MicroRNAs across Gestation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Liu, Z.; Wei, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Xiao, X. MiR-210 and MiR-155 as Potential Diagnostic Markers for Pre-Eclampsia Pregnancies. Medicine 2017, 96, e7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting Effective MicroRNA Target Sites in Mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tastsoglou, S.; Skoufos, G.; Miliotis, M.; Karagkouni, D.; Koutsoukos, I.; Karavangeli, A.; Kardaras, F.S.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v4.0: Expanding Target-Based MiRNA Functional Analysis in Cell-Type and Tissue Contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W154–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, S.; Rusterholz, C.; Zanetti-Dällenbach, R.; Tercanli, S.; Holzgreve, W.; Hahn, S.; Lapaire, O. Potential Markers of Preeclampsia—A Review. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2009, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Han, T.; Hu, X.; Liu, D. Placental MiR-205-5p Downregulation Contributes to Preeclampsia by Targeting Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illarionov, R.A.; Pachuliia, O.V.; Vashukova, E.S.; Tkachenko, A.A.; Maltseva, A.R.; Postnikova, T.B.; Nasykhova, Y.A.; Bespalova, O.N.; Glotov, A.S. Plasma MiRNA Profile in High Risk of Preterm Birth during Early and Mid-Pregnancy. Genes 2022, 13, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashukova, E.S.; Glotov, A.S.; Fedotov, P.V.; Efimova, O.A.; Pakin, V.S.; Mozgovaya, E.V.; Pendina, A.A.; Tikhonov, A.V.; Koltsova, A.S.; Baranov, V.S. Placental MicroRNA Expression in Pregnancies Complicated by Superimposed Preeclampsia on Chronic Hypertension. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, H.; Long, L.; Hui, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. miR-1-3p inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by targeting fibronectin expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3116–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromadnikova, I.; Kotlabova, K.; Dvorakova, L.; Krofta, L. Postpartum profiling of microRNAs involved in pathogenesis of cardiovascular/cerebrovascular diseases in women exposed to pregnancy-related complications. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 291, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromadnikova, I.; Kotlabova, K.; Hympanova, L.; Krofta, L. Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease associated microRNAs are dysregulated in placental tissues affected with gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and intrauterine growth restriction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.; Chang, M.; Jiang, S.; Wang, T.; Sun, Q.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.; Li, T. Clinical value of serum miR-1-3p as a potential circulating biomarker for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2260395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.; Simpson, N.; Scott, E.; Forbes, K. miR-1-3p and miR-133-3p are altered in maternal serum EVs and placenta in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes with large-for-gestational age babies. Endocr. Abstracts 2019, 65, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, W.; Li, L. Altered serum miR-223 expression in women with preeclampsia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Lu, D. MicroRNA-223-3p downregulates the inflammatory response in preeclampsia placenta via targeting NLRP3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Wang, X.P.; Luoreng, Z.M.; Yang, J.; Jia, L.; Ma, Y.; Wei, D.W. miR-223: An effective regulator of immune cell differentiation and inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2308–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.L.; Jeong, D.U.; Noh, E.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Lee, D.C.; Kang, M.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.K.; Han, A.R.; Kang, J.; et al. Exosomal miR-205-5p Improves Endometrial Receptivity by Upregulating E-Cadherin Expression through ZEB1 Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Cao, G.; Zhao, Y. MicroRNA profiling in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia: Upregulation of miR-205-5p. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 87, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjas, J.; Sopić, M.; Stefanović, A.; Košir, R.; Ninić, A.; Joksić, I.; Antonić, T.; Spasojević-Kalimanovska, V.; Prosenc Zmrzljak, U. Non-coding RNAs in preeclampsia: Molecular mechanisms and diagnostic potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wei, C.; Ma, Q.; Wang, W. Hippo-YAP1 Signaling Pathway and Severe Preeclampsia (sPE) in the Chinese Population. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, K.; Nakayama, N.; Wang, Y.; McLennan, L. Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling in trophoblast cells: Implications for preeclampsia. Placenta 2019, 88, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, T.; Orisaka, M.; Miyazaki, Y.; Morichika, R.; Uesaka, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Yoshida, Y. Inhibition of YAP/TAZ-TEAD Activity Induces Cytotrophoblast Differentiation into Syncytiotrophoblast in Human Trophoblast. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2022, 28, gaac032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, R.; Brownfoot, F.C.; Pritchard, N.; Hannan, N.J.; Cannon, P.; Nguyen, V.; Palmer, K.; Beard, S.; Tong, S.; Kaitu’u-Lino, T.J. EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) Signaling and the Mitochondria Regulate sFlt-1 (Soluble FMS-Like Tyrosine Kinase-1) Secretion. Hypertension 2019, 73, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, N.; Jaramillo, S.; Wiggins, A.; Siu, E.; Jones, M.; Mangum, J.; Choi, A.; Zhang, M.; Sharma, A.; Harris, E. The Ras and Rap1 pathways in preeclampsia pathogenesis. Placenta 2020, 99, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, A.C.; Das, A.; Aitken, T.; Morgan, K.; Hodge, D.; Timmons, M.; Kamal, A.; Amarnath, V.; Van Duyne, R.; Guo, J. MAPK signaling in preeclampsia: Inflammatory response and vascular dysfunction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 5, 773–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthi, P.; Gonzalez, J.; Mackie, A.; Marks, K.; Joseph, K.; De Silva, S.; Kwan, K.; Parry, S.; Thangarajah, P.; Chatterjee, K. Targeting EGFR and MAPK pathways for therapeutic intervention in preeclampsia. Placenta 2021, 104, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | CTRL (n = 12) | PE (n = 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 30.67 ± 1.62 | 32.58 ± 1.38 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.60 ± 0.64 | 25.2 ± 1.19 |
| Symptoms during the manifestation of PE | ||
| Systolic blood pressure (SBP), mmHg | 122.0 ± 7.89 | 152.7 ± 4.88 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mmHg | 70.9 ± 7.01 | 96.82 ± 2.72 |
| Proteinuria | 0 (0.0%) | 12 (100%) |
| Edema | 2 (16.7%) | 12 (100%) |
| Outcomes of current pregnancy | ||
| Method of delivery (Cesarean section) | 3 (25.0%) | 6 (50.0%) |
| Gestational ages of delivery, weeks | 40.00 ± 0.21 | 36.76 ± 1.51 |
| Fetal weight, g | 3518.0 ± 116.4 | 2916.0 ± 262.4 |
| Fetal height, cm | 51.92 ± 0.40 | 48.18 ± 1.51 |
| Apgar score, 1 min | 8.17 ± 0.11 | 7.36 ± 0.31 |
| Apgar score, 5 min | 8.58 ± 0.19 | 7.82 ± 0.18 |
| miRNA | Fold Change | Adjusted p-Value (FDR) |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-184 | −7.02 | 0.035 |
| hsa-miR-223-3p | −6.10 | 0.035 |
| hsa-miR-203a-3p | −5.57 | 0.001 |
| hsa-miR-205-5p | −5.09 | 0.034 |
| hsa-miR-1-3p | 5.84 | 0.035 |
| miRNA | Fold Change | Adjusted p-Value (FDR) |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-205-5p | −5.63 | 0.002 |
| hsa-miR-223-3p | −9.45 | 0.010 |
| hsa-miR-9-5p | 6.03 | 0.034 |
| hsa-miR-206 | 8.27 | 0.039 |
| hsa-miR-1-3p | 24.40 | 0.001 |
| Term Name | Term Genes | Target Genes (n) | miRNAs (n) | Adjusted p-Value (FDR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axon guidance | 186 | 93 | 4 | 1.6639 × 10−10 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 329 | 144 | 4 | 1.6639 × 10−10 |
| Ras signaling pathway | 241 | 112 | 4 | 2.6679 × 10−10 |
| Rap1 signaling pathway | 214 | 102 | 4 | 2.9114 × 10−10 |
| Hippo signaling pathway | 164 | 82 | 5 | 1.4889 × 10−9 |
| Pathways in cancer | 555 | 210 | 4 | 6.0789 × 10−9 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 224 | 100 | 4 | 2.9138 × 10−8 |
| Focal adhesion | 213 | 93 | 4 | 4.0345 × 10−7 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | 220 | 95 | 4 | 4.8956 × 10−7 |
| Calcium signaling pathway | 246 | 103 | 4 | 7.762 × 10−7 |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | 80 | 43 | 4 | 2.8427 × 10−6 |
| AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | 115 | 56 | 4 | 3.0074 × 10−6 |
| EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | 82 | 43 | 4 | 6.0919 × 10−6 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 124 | 58 | 4 | 8.8447 × 10−6 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 78 | 41 | 4 | 9.2329 × 10−6 |
| Term Name | Term Genes | Target Genes (n) | miRNAs (n) | Adjusted p-Value (FDR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rap1 signaling pathway | 214 | 71 | 5 | 4.56713 × 10−11 |
| Ras signaling pathway | 241 | 72 | 5 | 4.64624 × 10−9 |
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | 156 | 52 | 5 | 2.47369 × 10−8 |
| Pathways in cancer | 555 | 128 | 5 | 3.48636 × 10−8 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 224 | 65 | 5 | 6.71583 × 10−8 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 329 | 85 | 5 | 9.23522 × 10−8 |
| EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | 82 | 33 | 5 | 1.01508 × 10−7 |
| Axon guidance | 186 | 56 | 5 | 1.25819 × 10−7 |
| Adherens junction | 79 | 32 | 5 | 1.25819 × 10−7 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 177 | 54 | 5 | 1.28565 × 10−7 |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | 80 | 32 | 5 | 1.35575 × 10−7 |
| Breast cancer | 163 | 50 | 5 | 3.32511 × 10−7 |
| Hippo signaling pathway | 164 | 50 | 5 | 3.8429 × 10−7 |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 372 | 90 | 5 | 4.3087 × 10−7 |
| Gastric cancer | 162 | 49 | 5 | 6.16709 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Illarionov, R.A.; Maltseva, A.R.; Pachuliia, O.V.; Postnikova, T.B.; Vashukova, E.S.; Popova, A.K.; Nasykhova, Y.A.; Bespalova, O.N.; Glotov, A.S. Urinary miRNA Expression in Pre-Eclampsia During Early and Mid-Pregnancy. Non-Coding RNA 2024, 10, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10060061
Illarionov RA, Maltseva AR, Pachuliia OV, Postnikova TB, Vashukova ES, Popova AK, Nasykhova YA, Bespalova ON, Glotov AS. Urinary miRNA Expression in Pre-Eclampsia During Early and Mid-Pregnancy. Non-Coding RNA. 2024; 10(6):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10060061
Chicago/Turabian StyleIllarionov, Roman A., Anastasia R. Maltseva, Olga V. Pachuliia, Tatiana B. Postnikova, Elena S. Vashukova, Anastasiia K. Popova, Yulia A. Nasykhova, Olesya N. Bespalova, and Andrey S. Glotov. 2024. "Urinary miRNA Expression in Pre-Eclampsia During Early and Mid-Pregnancy" Non-Coding RNA 10, no. 6: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10060061
APA StyleIllarionov, R. A., Maltseva, A. R., Pachuliia, O. V., Postnikova, T. B., Vashukova, E. S., Popova, A. K., Nasykhova, Y. A., Bespalova, O. N., & Glotov, A. S. (2024). Urinary miRNA Expression in Pre-Eclampsia During Early and Mid-Pregnancy. Non-Coding RNA, 10(6), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10060061







