Coulomb Driven Electro-Convection within Two Stacked Layers of Miscible Dielectric Liquids †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical and Numerical Models
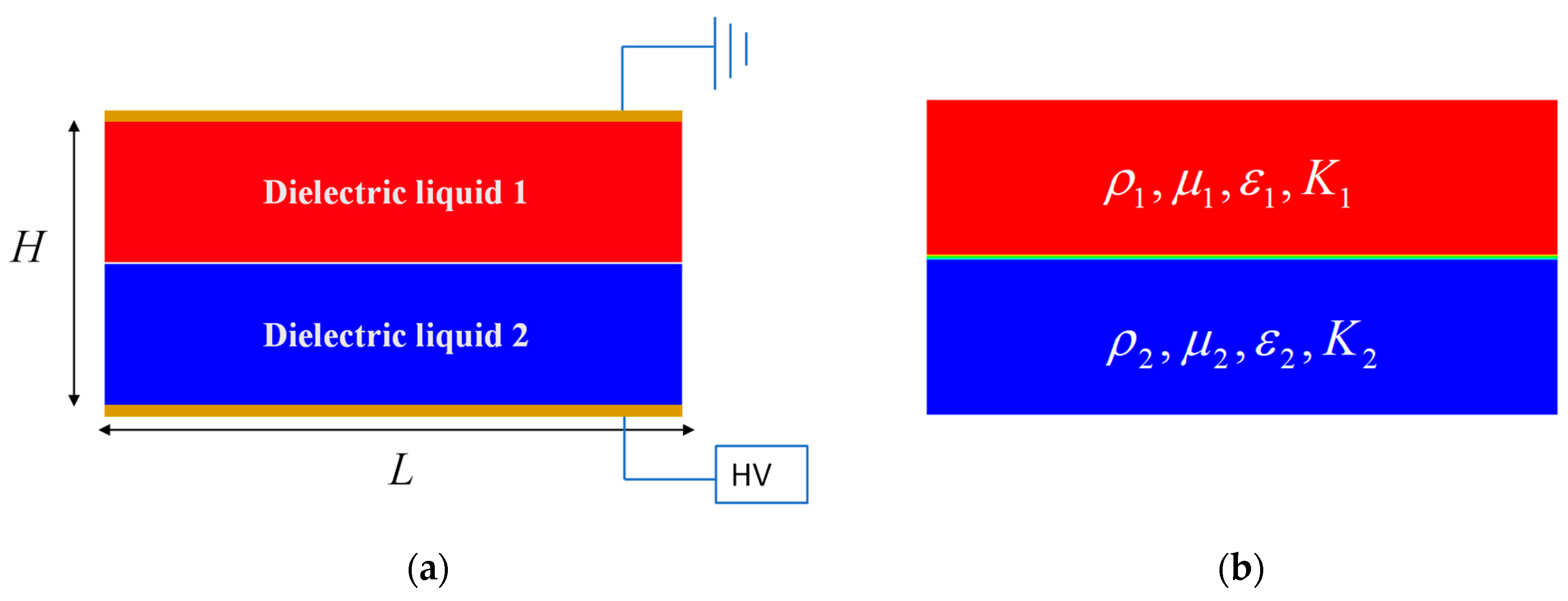
2.1. Problem Formuation
2.2. Governing Equations
2.3. Numerical Method
2.4. Initial and Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussions
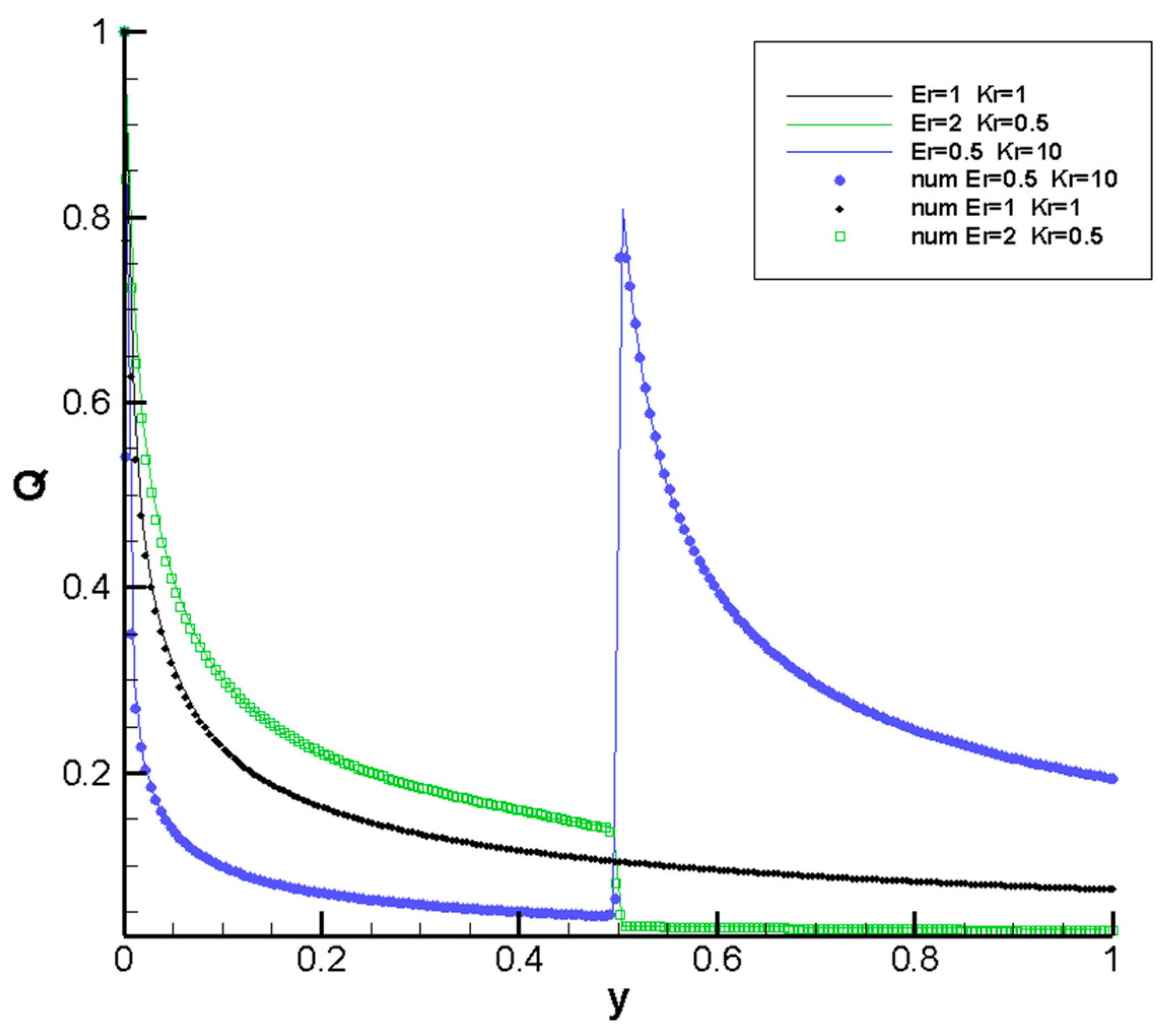
3.1. Code Validation
3.2. Mixture Controled by Electro-Convection
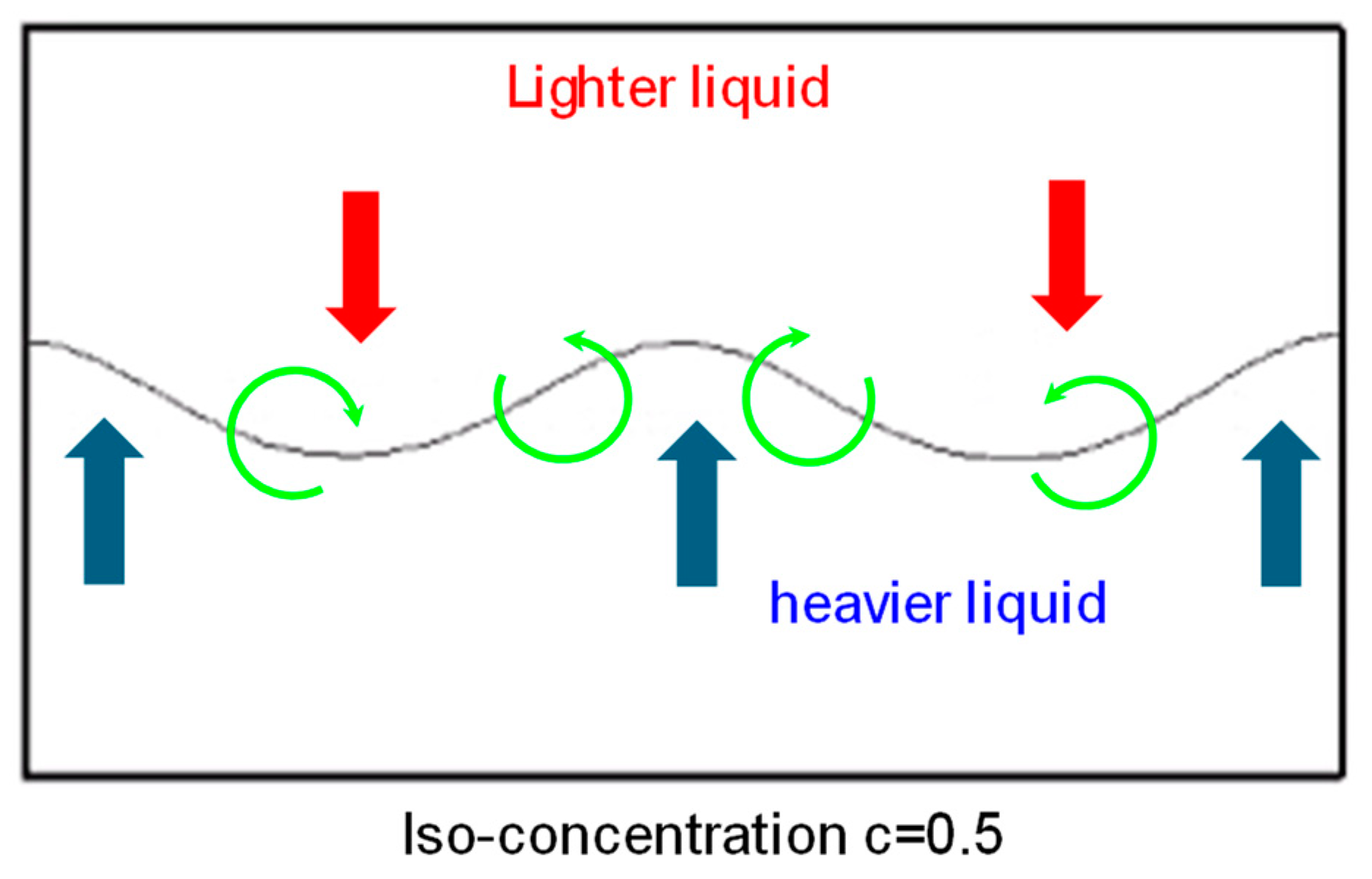
3.2.1. Effect of Electro-Convection on the Mixing
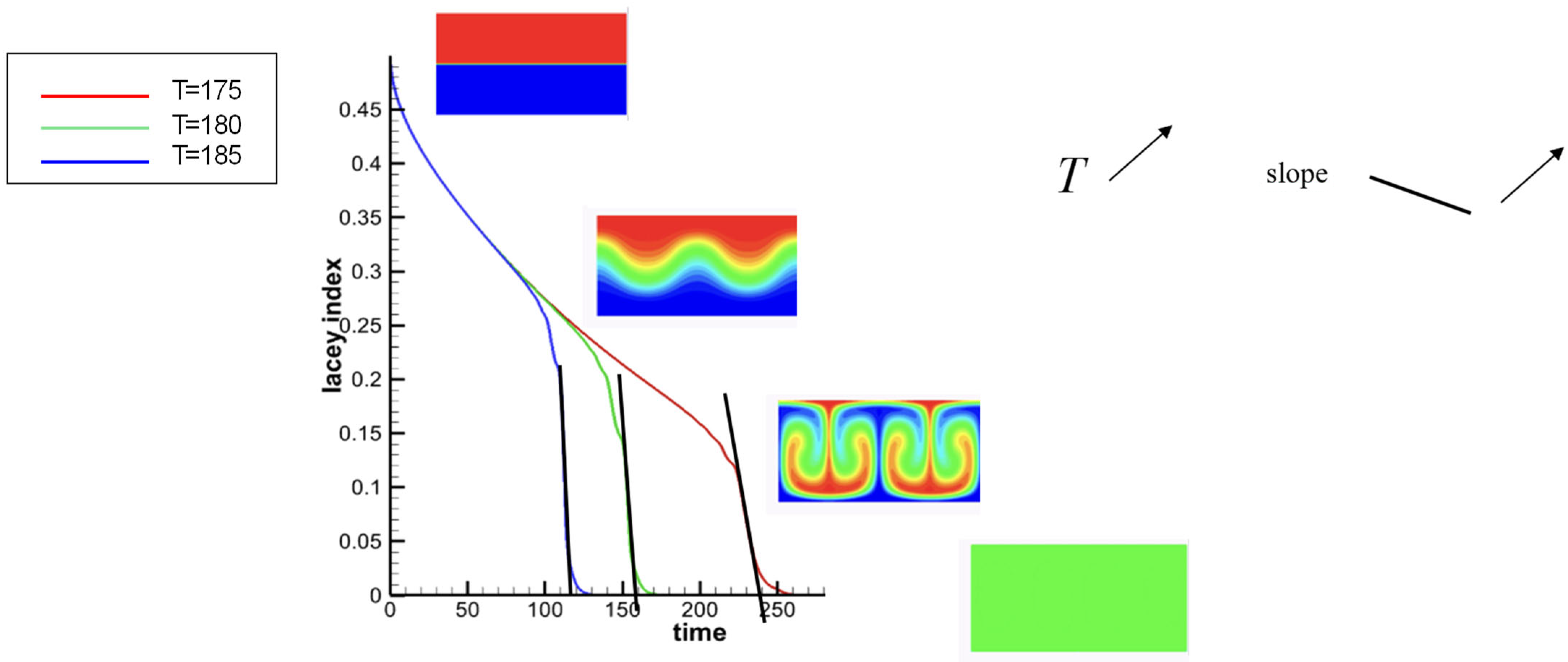
3.2.2. Effect of T on the Mixing
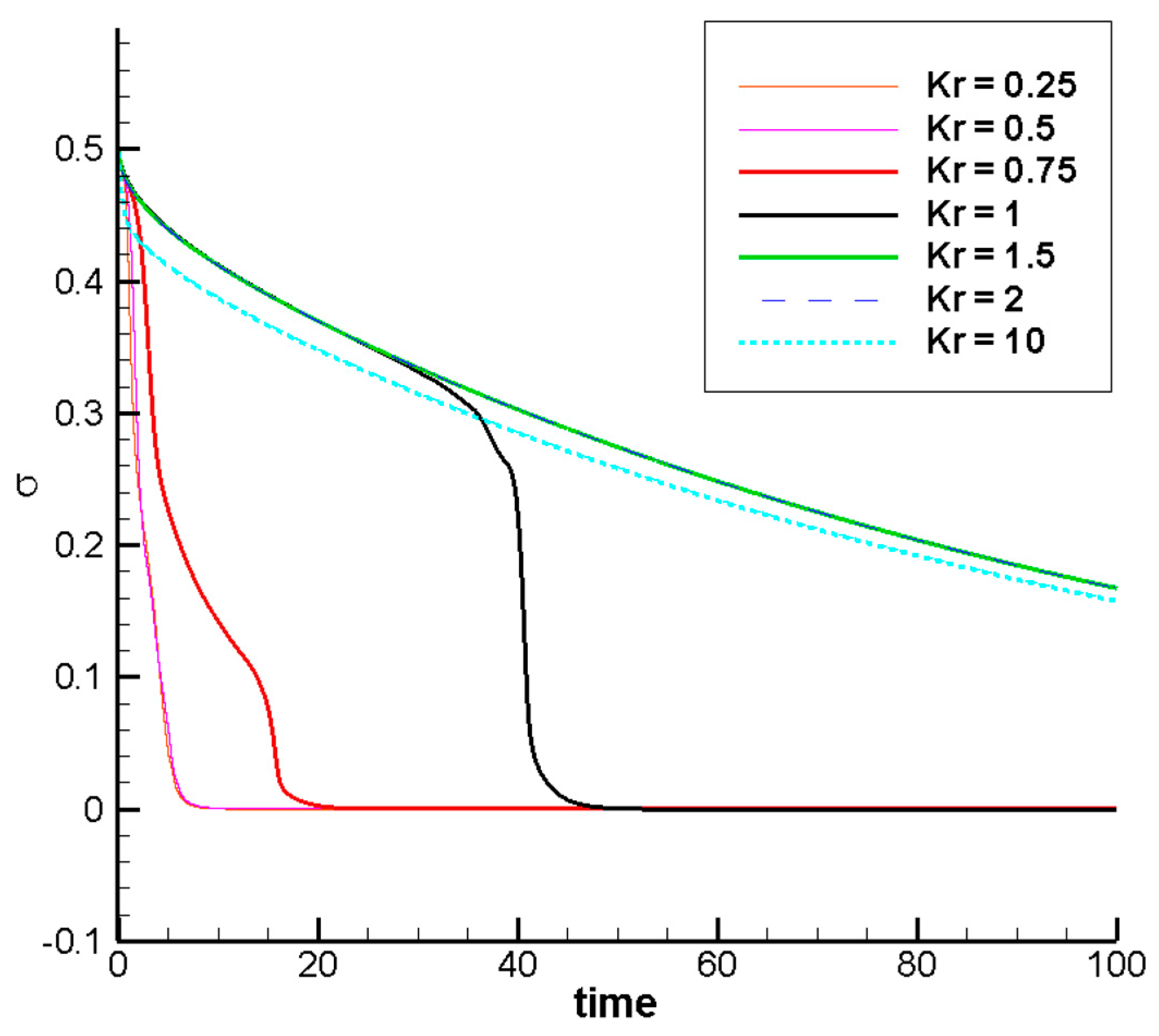
3.2.3. Effect of the Ionic Mobility Ratio on the Mixing
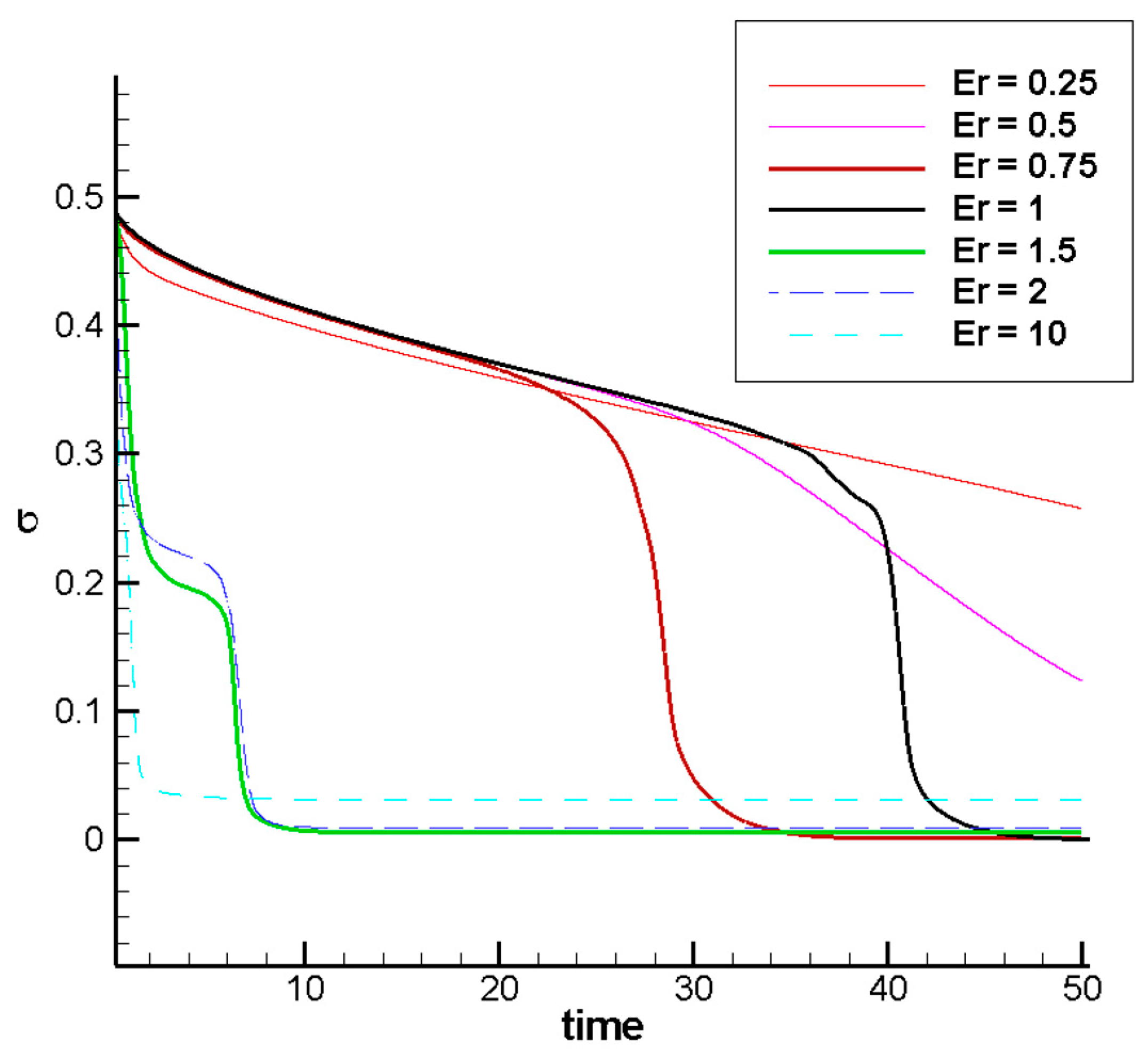
3.2.4. Effect of the Permittivity Ratio on the Mixing
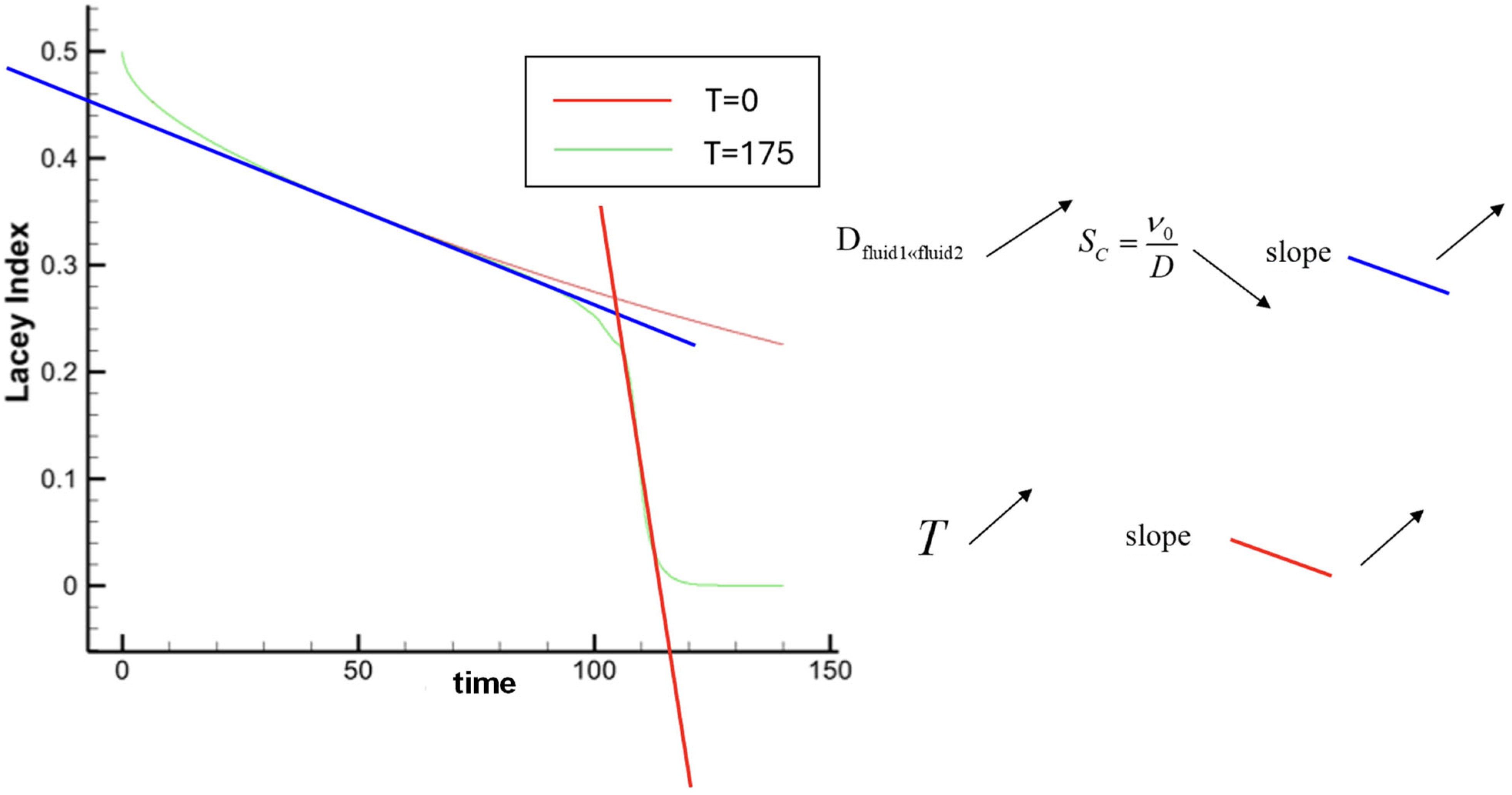
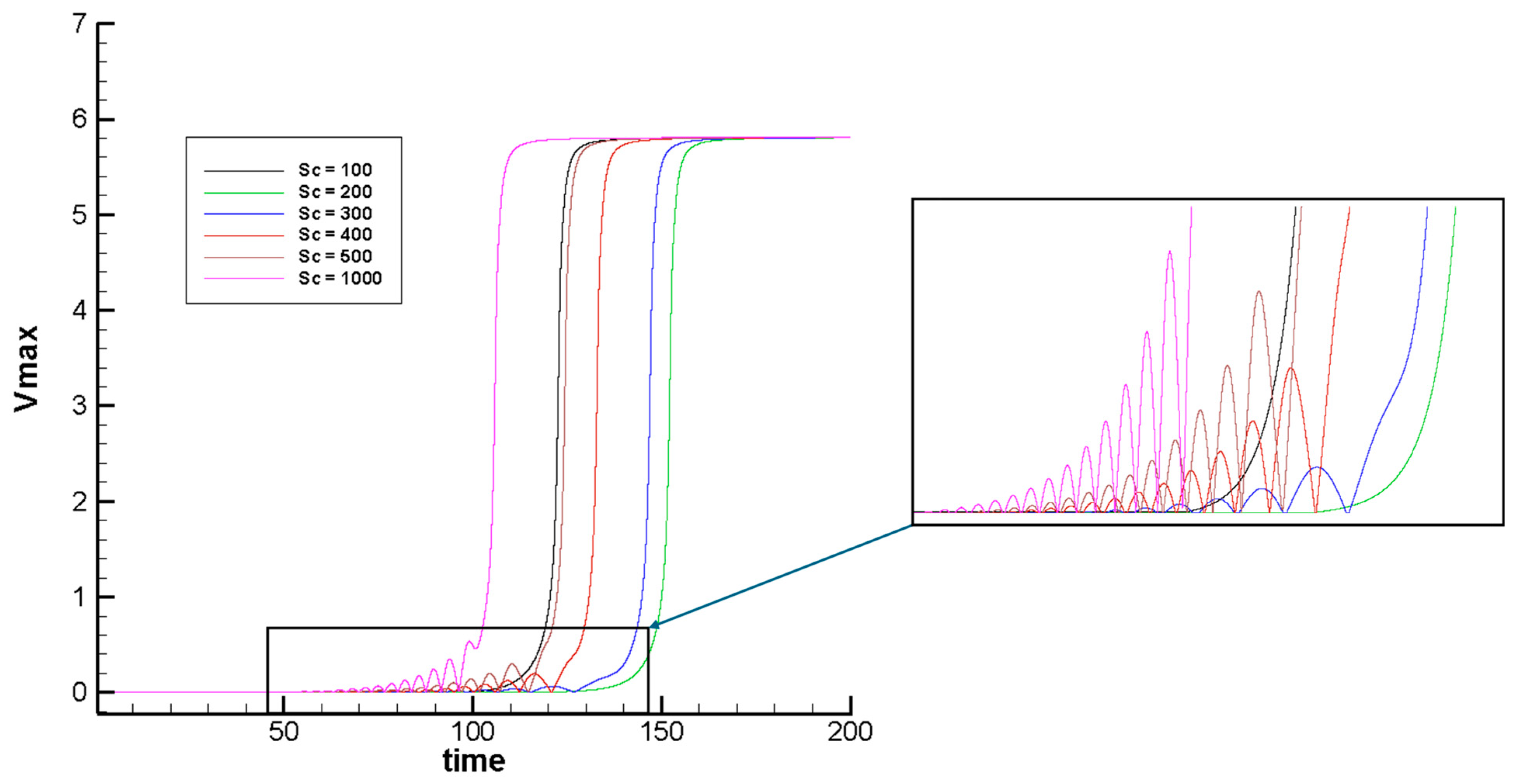
3.3. Impact of Mixing on Flow Stability
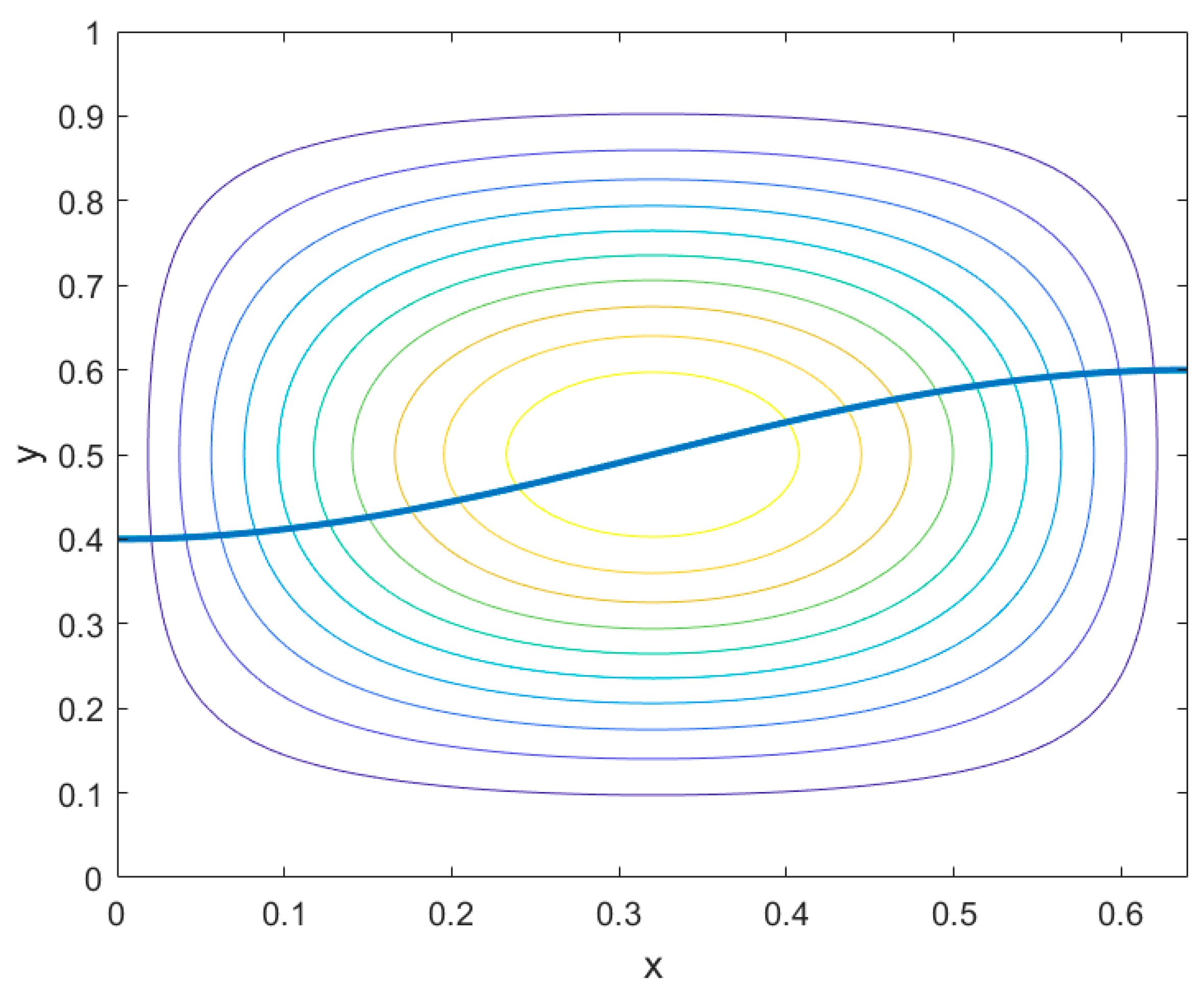
Oscillation of the Growing Instability
4. Semi-Analytical Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castellanos, A. Electrohydrodynamics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.S.; Kelly, A.J.; Crowley, J.M. Handbook of Electrostatic Processes, 2nd ed.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Traoré, P.; Pérez, A.T.; Koulova, D.; Romat, H. Numerical modelling of finite-amplitude electro-thermo convection in a dielectric liquid layer subjected to both unipolar injection and temperature gradient. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 658, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Traoré, P.; Zhang, M.; Pérez, A.T.; Vázquez, P.A. Charge injection enhanced natural convection heat transfer in horizontal concentric annuli filled with a dielectric liquid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 92, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Traoré, P.; Louste, C.; Pérez, A.T.; Vázquez, P.A. Numerical evaluation of heat transfer enhancement due to annular electroconvection induced by injection in a dielectric liquid. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaal, M.; Khorshidi, B.; Esmaeilzadeh, E. Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) mixing of two miscible dielectric liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, R.; Khosroshahi, A.R.; Sadri, B.; Esmaeilzadeh, E. The Electrohydrodynamic mixer for producing homogenous emulsion of dielectric liquids. Colloids and Surfaces A Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2019, 578, 123592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicon, R.; Castellanos, A.; Martin, E. Numerical Modelling of Coulomb-driven Convection in Insulating Liquids. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 344, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atten, P.; Moreau, R. Stabilité électrohydrodynamique des liquides isolants soumis à une injection unipolaire. J. Mécanique 1972, 11, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Atten, P.; Lacroix, J.C. Non-linear hydrodynamic stability of liquids subjected to unipolar injection. J. Mécanique 1979, 18, 469. [Google Scholar]
- Traoré, P.; Pérez, A.T. Two-dimensional numerical analysis of electroconvection in a dielectric liquid subjected to strong unipolar injection. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 037102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Ma, B.; He, K. Lattice Boltzmann modeling of double-diffusive convection of dielectric liquid in rectangular cavity subjected to unipolar injection. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 067106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Traoré, P. A finite-volume method for electrothermoconvective phenomena in a plane layer of dielectric liquid. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A 2015, 68, 471–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traoré, P.; Wu, J. On the limitation of Imposed Velocity Field strategy for Coulomb-driven electroconvection flow simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 727, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Traore, P.; Bhattacharya, A.; Perez, A.T.; Vasquez, P.A. Mass Transfer Enhancement Induced by Electro Soluto Convection within two Parallel Electrodes Due to unipolar Charge Injection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 21st International Conference on Dielectric Liquids (ICDL), Sevilla, Spain, 25 May–2 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Félici, N. Phenoménes hydro et aérodynamiques dans la conduction des diélectriques fluides. Rev. Gén. Electr. 1969, 78, 717–734. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, A. Coulomb driven convection in electrohydrodynamics. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1991, 26, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
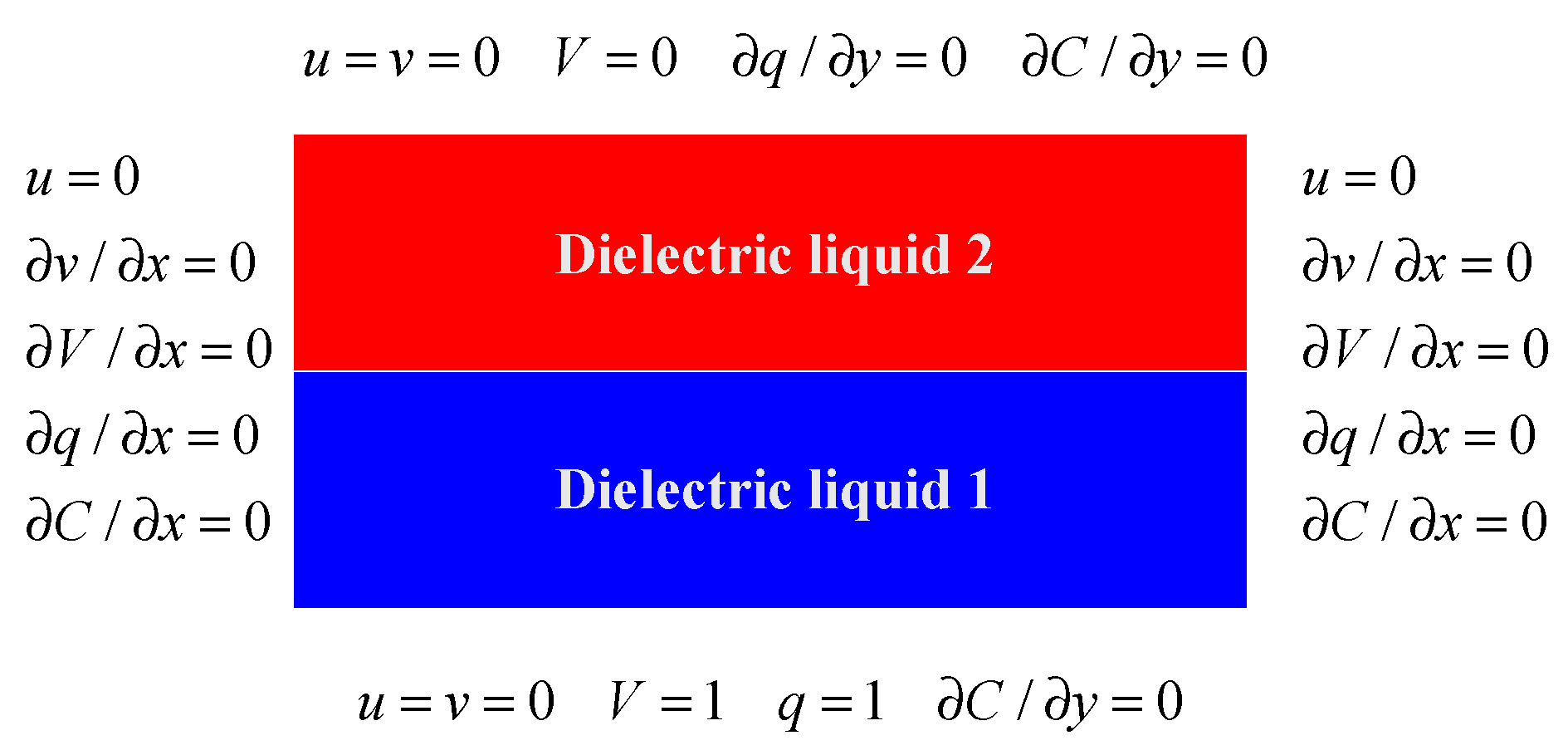



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Traore, P.; Pérez, A.T.; Mondal, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Vázquez, P.A.; Yan, Z. Coulomb Driven Electro-Convection within Two Stacked Layers of Miscible Dielectric Liquids. Fluids 2024, 9, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9090219
Traore P, Pérez AT, Mondal S, Bhattacharya A, Vázquez PA, Yan Z. Coulomb Driven Electro-Convection within Two Stacked Layers of Miscible Dielectric Liquids. Fluids. 2024; 9(9):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9090219
Chicago/Turabian StyleTraore, Philippe, Alberto T. Pérez, Subhadeep Mondal, Anandaroop Bhattacharya, Pedro A. Vázquez, and Zelu Yan. 2024. "Coulomb Driven Electro-Convection within Two Stacked Layers of Miscible Dielectric Liquids" Fluids 9, no. 9: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9090219
APA StyleTraore, P., Pérez, A. T., Mondal, S., Bhattacharya, A., Vázquez, P. A., & Yan, Z. (2024). Coulomb Driven Electro-Convection within Two Stacked Layers of Miscible Dielectric Liquids. Fluids, 9(9), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9090219





