Structural and Physical Characteristics of Mixed-Component Oleogels: Natural Wax and Monoglyceride Interactions in Different Edible Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Oleogel Appearance
2.2. Polarized Microscopy
2.2.1. Polarized Light Micrographs of MG Oleogels
2.2.2. Polarized Light Micrographs of Wax-Based Oleogels
2.2.3. Polarized Light Micrographs of Mixed Oleogels
2.3. Textural Properties
2.3.1. Single-Component Oleogels
2.3.2. RBW and MG Oleogels
2.3.3. BW and MG Oleogels
2.3.4. CDW and MG Oleogels
2.3.5. SW and MG Oleogels
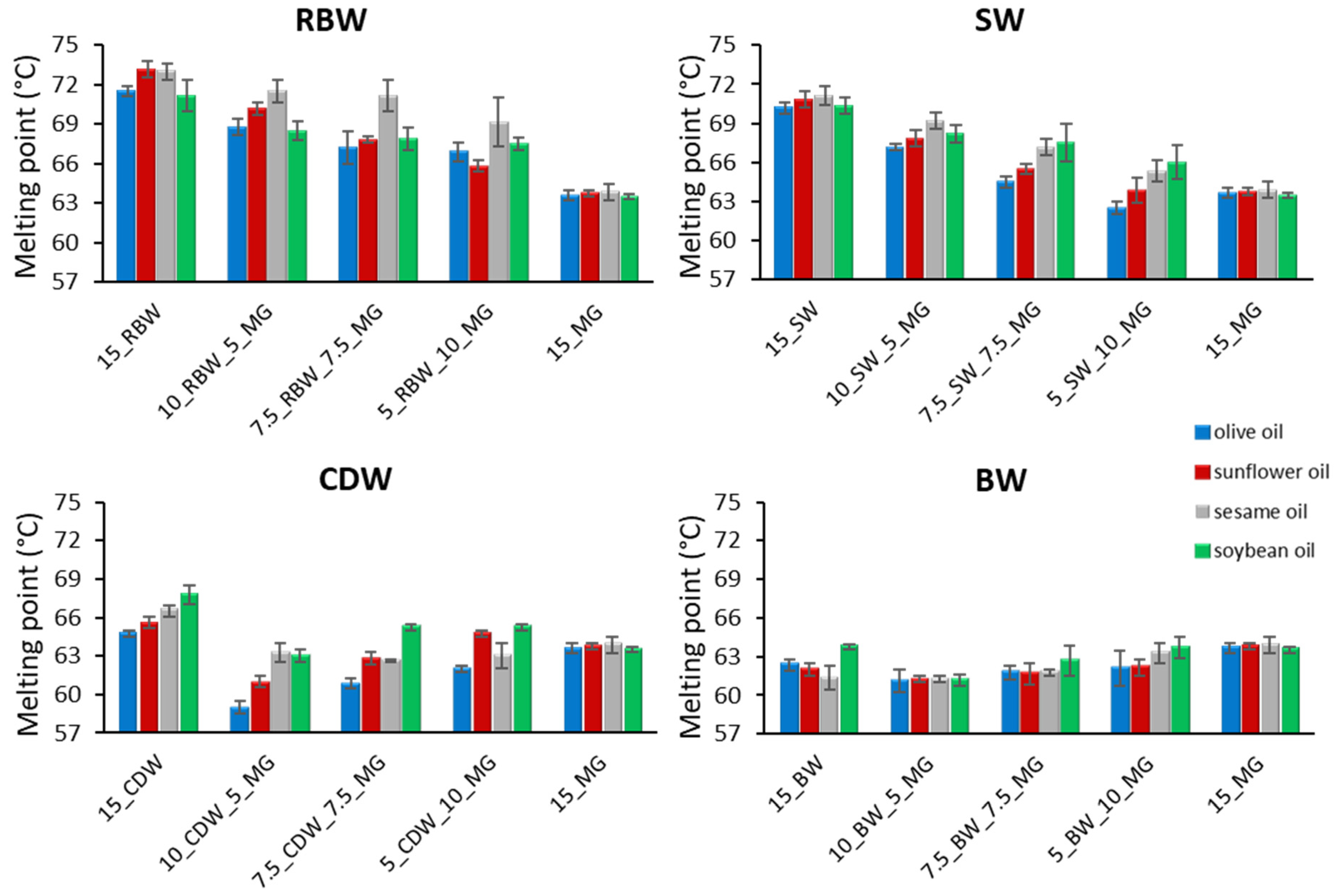
2.4. Melting Point
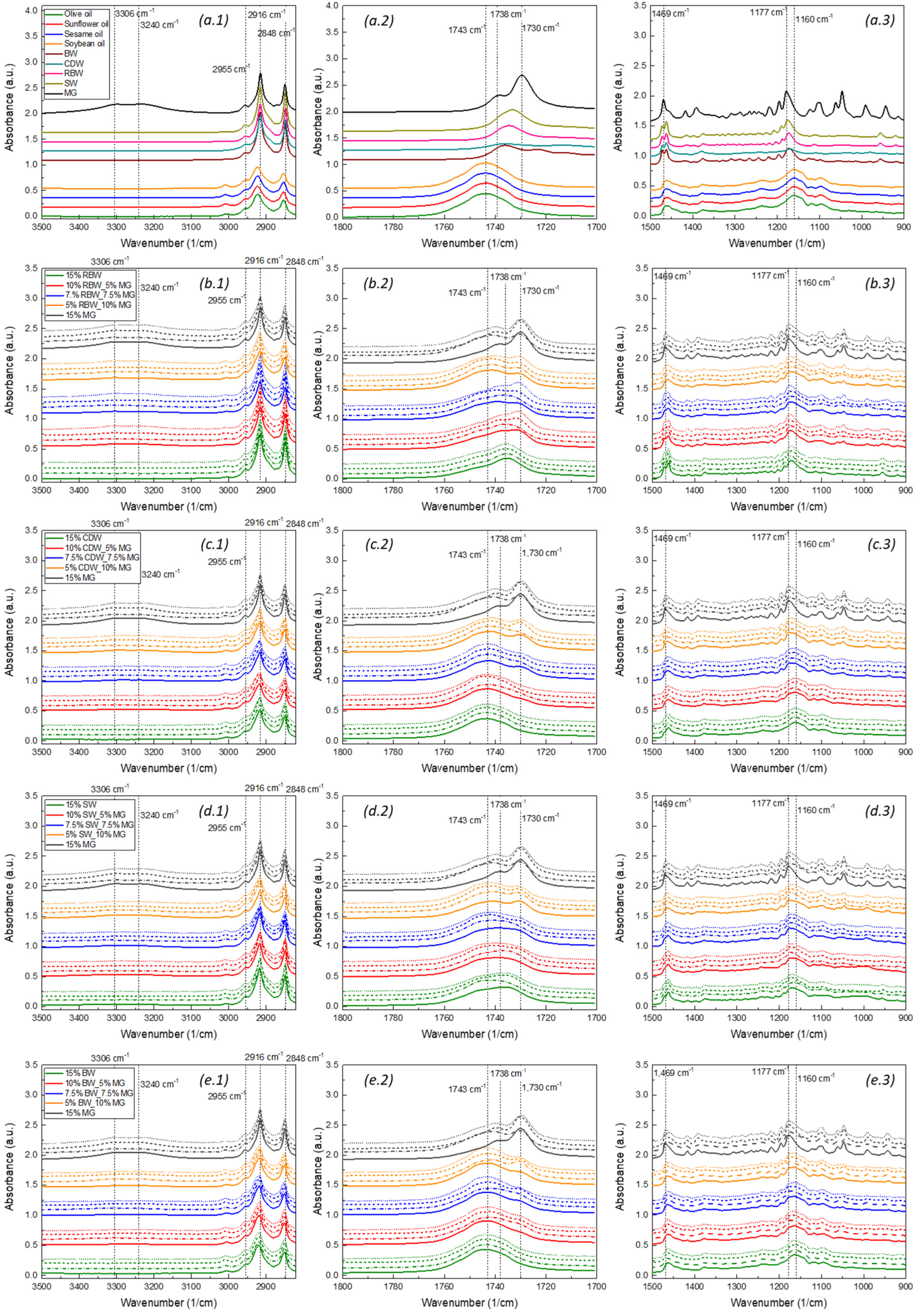
2.5. FTIR Measurements
2.6. Mixed-Component Oleogels in Foods As a Fat Substitute
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Raw Materials
4.2. Oleogel Preparation
4.3. Color Measurement
4.4. Optical Microscopy
4.5. Texture Analysis
4.6. Melting Point Determination
4.7. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Fats and Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition: Report of an Expert Consultation; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010; pp. 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Aro, A.; Willett, W.C. Health effects of trans-fatty acids: Experimental and observational evidence. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, S5–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivanoğlu, H.; Demirci, M.; Toker, O.S.; Konar, N.; Karasu, S.; Sagdic, O. Oleogels, a promising structured oil for decreasing saturated fatty acid concentrations: Production and food-based applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Healthy Diet. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Doan, C.D.; Tavernier, I.; Okuro, P.K.; Dewettinck, K. Internal and external factors affecting the crystallization, gelation and applicability of wax-based oleogels in food industry. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnprecha, K.; Aryusuk, K.; Santiwattana, P.; Sonwai, S.; Rousseau, D. Structure and rheology of oleogels made from rice bran wax and rice bran oil. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terech, P.; Weiss, R.G. Low molecular mass gelators of organic liquids and the properties of their gels. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 3133–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, E.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Organogels: An alternative edible oil-structuring method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 749–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, L.S.K.; Kodali, D.R.; Ueno, S. Formation of oleogels based on edible lipid materials. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface 2011, 16, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Dewettinck, K. Edible oil structuring: An overview and recent updates. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaberi, R.; Pedram Nia, A.; Naji-Tabasi, S.; Elhamirad, A.H.; Shafafi Zenoozian, M. Rheological and structural properties of oleogel base on soluble complex of egg white protein and xanthan gum. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, A.G.; Garti, N. Edible Oleogels: Structure and Health Implications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Palla, C.A.; Dominguez, M.; Carrín, M.E. An overview of structure engineering to tailor the functionality of monoglyceride oleogels. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 2587–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Dusemund, B.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; et al. Re-evaluation of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids (E 471) as food additives. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e05045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampouni, K.; Soniadis, A.; Dimakopoulou-Papazoglou, D.; Moschakis, T.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Katsanidis, E. Modified fermented sausages with olive oil oleogel and NaCl–KCl substitution for improved nutritional quality. LWT 2022, 158, 113172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanelaki, A.; Zampouni, K.; Mourtzinos, I.; Katsanidis, E. Hydrogels, oleogels and bigels as edible coatings of sardine fillets and delivery systems of rosemary extract. Gels 2022, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin Sintang, M.D.; Rimaux, T.; Van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R. Oil structuring properties of monoglycerides and phytosterols mixtures. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1500517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampouni, K.; Soniadis, A.; Moschakis, T.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Lazaridou, A.; Katsanidis, E. Crystalline microstructure and physicochemical properties of olive oil oleogels formulated with monoglycerides and phytosterols. LWT 2022, 154, 112815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzounis, D.; Lazaridou, A.; Katsanidis, E. Partial replacement of animal fat by oleogels structured with monoglycerides and phytosterols in frankfurter sausages. Meat Sci. 2017, 130, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, A.K.; Pérez-Martínez, J.D.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A.; Toro-Vazquez, J.F.; Ornelas-Paz, J.J. Rheological properties of ethyl cellulose-monoglyceride-candelilla wax oleogel vis-a-vis edible shortenings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martínez, A.; Charó-Alonso, M.A.; Marangoni, A.G.; Toro-Vazquez, J.F. Monoglyceride organogels developed in vegetable oil with and without ethylcellulose. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.L.T.; Arellano, D.B.; Martini, S. Physical properties of candelilla wax, monoacylglycerols, and fully hydrogenated oil oleogels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, N.G.; Okuro, P.K.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Cunha, R.L. Tailoring properties of mixed-component oleogels: Wax and monoglyceride interactions towards flaxseed oil structuring. Gels 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öǧütcü, M.; Yılmaz, E. Oleogels of virgin olive oil with carnauba wax and monoglyceride as spreadable products. Grasas Aceites 2014, 65, e040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.D.; To, C.M.; De Vrieze, M.; Lynen, F.; Danthine, S.; Brown, A.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R. Chemical profiling of the major components in natural waxes to elucidate their role in liquid oil structuring. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolova, Y.; Sarkisyan, V.; Sobolev, R.; Makarenko, M.; Semin, M.; Kochetkova, A. The influence of edible oils’ composition on the properties of beeswax-based oleogels. Gels 2022, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisyan, V.; Frolova, Y.; Sobolev, R.; Kochetkova, A. On the role of beeswax components in the regulation of sunflower oil oleogel properties. Food Biophys. 2022, 18, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J. Physicochemical properties and oxidative stability of oleogels made of carnauba wax with canola oil or beeswax with grapeseed oil. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, D.; Singh, A.; Prabhakar, P.K.; Meghwal, M.; Upadhyay, A. Optimization and characterization of soybean oil-carnauba wax oleogel. LWT 2022, 157, 113108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Vazquez, J.F.; Morales-Rueda, J.A.; Dibildox-Alvarado, E.; Charó-Alonso, M.; Alonzo-Macias, M.; González-Chávez, M.M. Thermal and textural properties of organogels developed by candelilla wax in safflower oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Becerril, M.; Marangoni, A.G.; Perea-Flores, M.J.; Cayetano-Castro, N.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, H.; Andraca-Adame, J.A.; Pérez-Martínez, J.D. Characterization of the micro and nanostructure of the candelilla wax organogels crystal networks. Food Struct. 2018, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, L.S.K.; Kodali, D.R.; Ueno, S.; Sato, K. Physical properties of rice bran wax in bulk and organogels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öğütcü, M.; Yılmaz, E. Characterization of hazelnut oil oleogels prepared with sunflower and carnauba waxes. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, D.; Kim, D.; Banerjee, I.; Rousseau, D.; Pal, K. Effects of sorbitan monostearate and stearyl alcohol on the physicochemical parameters of sunflower-wax-based oleogels. Gels 2022, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Gillman, J.D.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Kim, S.; Singh, M.; Byars, J.A.; Evangelista, R.L. Properties of oleogels formed with high-stearic soybean oils and sunflower wax. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Anderson, J.; Felker, F.C.; Hwang, H.-S. Physical properties of beeswax, sunflower wax, and candelilla wax mixtures and oleogels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Winkler-Moser, J.K. Properties of margarines prepared from soybean oil oleogels with mixtures of candelilla wax and beeswax. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3293–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernier, I.; Doan, C.D.; Van de Walle, D.; Danthine, S.; Rimaux, T.; Dewettinck, K. Sequential crystallization of high and low melting waxes to improve oil structuring in wax-based oleogels. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12113–12125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Herrero, A.M.; Herranz, B.; Álvarez, M.D.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Cofrades, S. Characterization of ethyl cellulose and beeswax oleogels and their suitability as fat replacers in healthier lipid pâtés development. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, G.; Polenghi, O.; Giardina, A.; Cerne, V.; Calligaris, S. Structural and rheological properties of medium-chain triacylglyceride oleogels. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 56, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelle, A.J.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Zetzl, A.K.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Influence of solvent quality on the mechanical strength of ethylcellulose oleogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestone, D. Olive oil. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products, 6th ed.; Shahidi, F., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 303–332. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, E.G.; Johnson, L.A.; Su, C.; Wang, T.; White, P.J. Soybean oil. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products, 6th ed.; Shahidi, F., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 577–654. [Google Scholar]
- Cerqueira, M.A.; Fasolin, L.H.; Picone, C.S.F.; Pastrana, L.M.; Cunha, R.L.; Vicente, A.A. Structural and mechanical properties of organogels: Role of oil and gelator molecular structure. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.C.; Okuro, P.K.; Badan, A.P.; Cunha, R.L. Role of the oil on glyceryl monostearate based oleogels. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.D.; Van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R. Evaluating the oil-gelling properties of natural waxes in rice bran oil: Rheological, thermal, and microstructural study. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.I.; Co, E.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Structure and physical properties of plant wax crystal networks and their relationship to oil binding capacity. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 2014, 91, 885–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, L.S.K.; Kodali, D.R.; Ueno, S.; Sato, K. Crystallization kinetics of organogels prepared by rice bran wax and vegetable oils. J. Oleo Sci. 2012, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.I.; Toro-Vazquez, J.F.; Hwang, H.-S. Wax oleogels. In Edible Oleogels; Marangoni, A.G., Garti, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 133–171. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, S.; Tan, C.Y.; Jana, S. Physical characterization of wax/oil crystalline networks. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C989–C997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ju, X.; Wang, Z.; He, R. Study of monoglycerides enriched with unsaturated fatty acids at sn-2 position as oleogelators for oleogel preparation. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holey, S.A.; Sekhar, K.P.C.; Mishra, S.S.; Kanjilal, S.; Nayak, R.R. Effect of oil unsaturation and wax composition on stability, properties and food applicability of oleogels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Kim, S.; Singh, M.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Liu, S.X. Organogel formation of soybean oil with waxes. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Öğütcü, M. Comparative analysis of olive oil organogels containing beeswax and sunflower wax with breakfast margarine. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E1732–E1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, A.; Antonella Miele, N.; Masi, P.; Aiello, A.; Cavella, S. Effect of fatty acid composition of vegetable oils on crystallization and gelation kinetics of oleogels based on natural wax. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öğütcü, M.; Yılmaz, E. Comparison of the pomegranate seed oil organogels of carnauba wax and monoglyceride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Öğütcü, M. Properties and stability of hazelnut oil organogels with beeswax and monoglyceride. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modupalli, N.; Thangaraju, S.; Naik, G.M.; Rawson, A.; Natarajan, V. Assessment of physicochemical, functional, thermal, and phytochemical characteristics of refined rice bran wax. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayaz, G.; Goli, S.A.H.; Kadivar, M. A novel propolis wax-based organogel: Effect of oil type on its formation, crystal structure and thermal properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2017, 94, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, A.C.S.; Martinez, M.A.G.; Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Advances in Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of biological tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2017, 52, 456–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.D.; Ferdaus, M.J.; Foguel, A.; da Silva, T.L.T. Oleogels as a fat substitute in food: A current review. Gels 2023, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, R.V.; Pessanha, M.D.F.; de Almeida, P.F.; Viana, C.L.; da Silva Lannes, S.C. Application of fats in some food products. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschakis, T.; Panagiotopoulou, E.; Katsanidis, E. Sunflower oil organogels and organogel-in-water emulsions (part I): Microstructure and mechanical properties. LWT 2016, 73, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
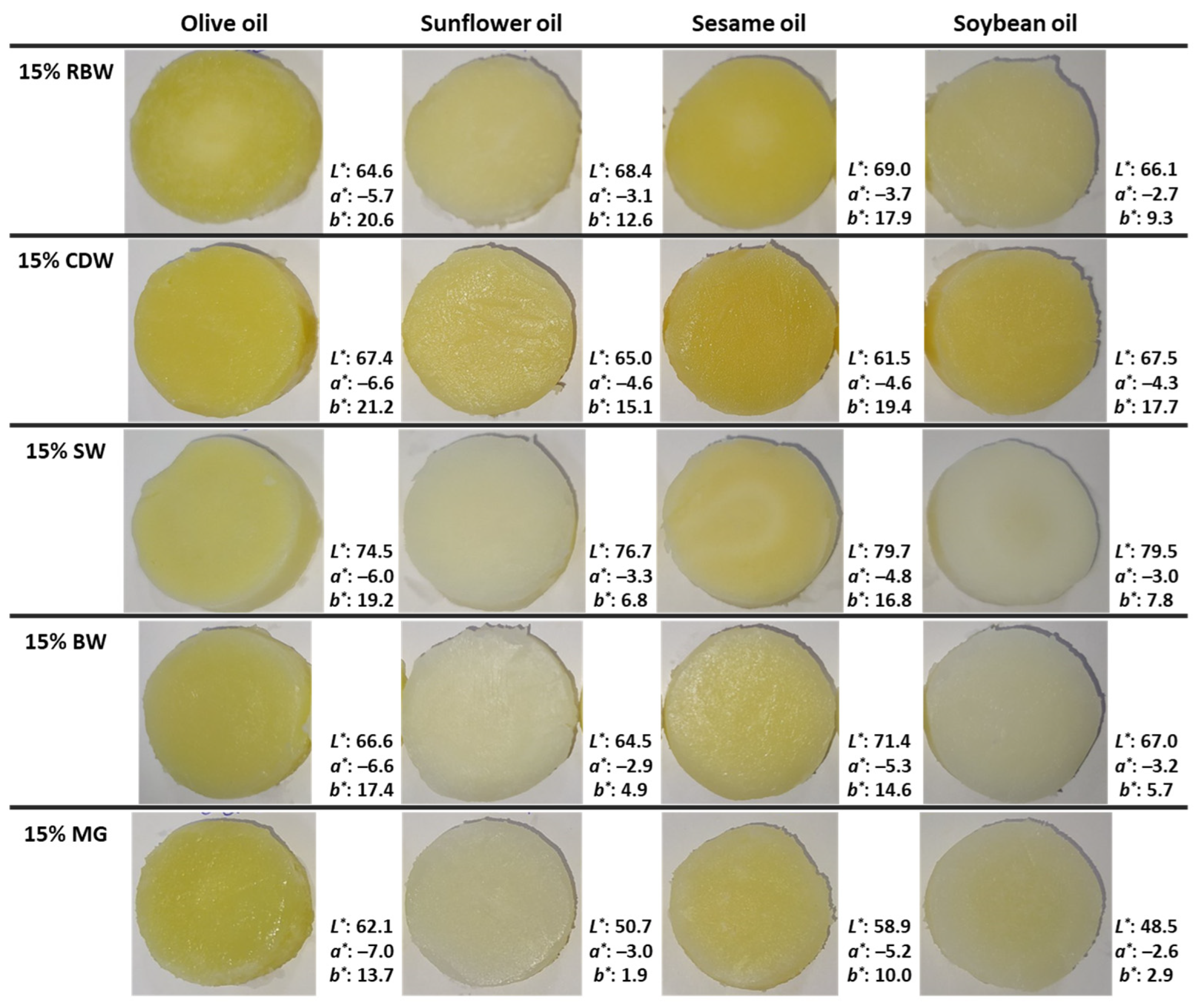
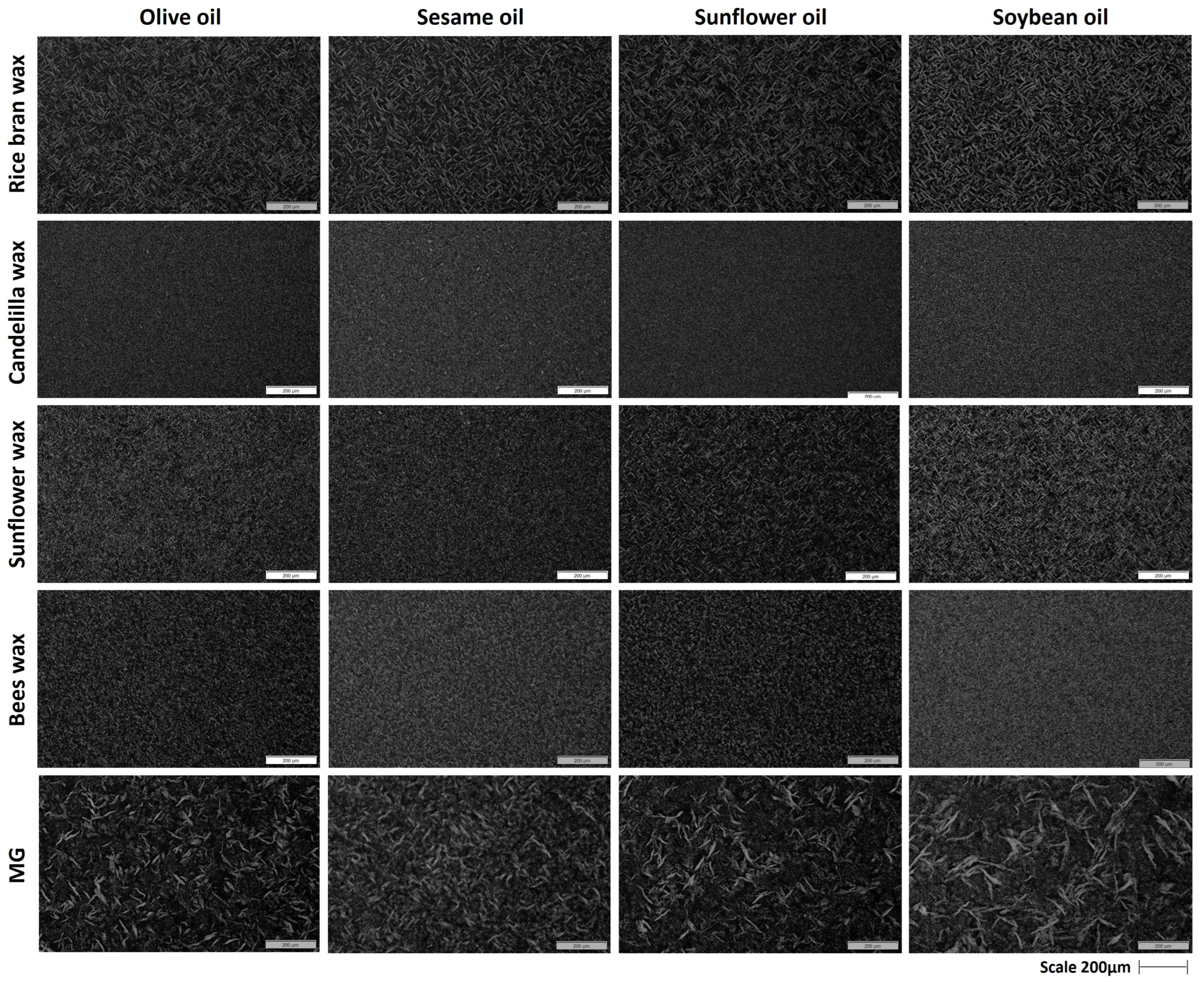
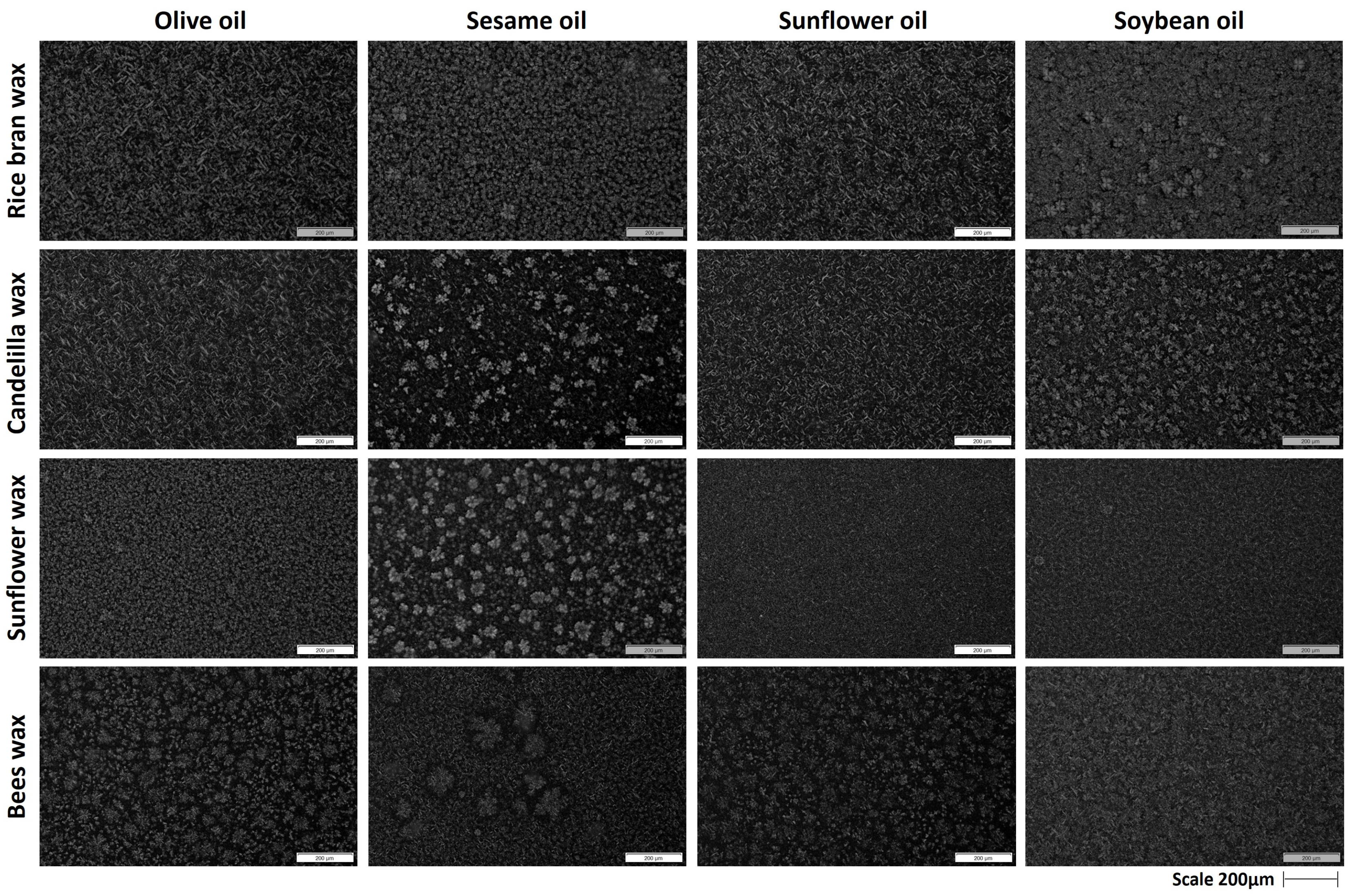

| Factors | Physicochemical Parameters | Color Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (N) | Gel Strength | Melting Point (°C) | L* | a* | b* | |
| Structural agent * | ||||||
| MGs | 1.91 c | 13.97 d | 64.53 c | 55.1 d | −4.4 a,b | 7.1 d |
| RBW | 2.34 b,c | 16.95 c,d | 69.23 a | 69.4 b | −4.3 a | 12.3 b |
| CDW | 2.87 b | 22.25 b | 63.59 c | 63.0 c | −5.1 c | 13.9 a |
| SW | 5.49 a | 43.04 a | 67.32 b | 74.1 a | −4.5 a,b | 10.5 c |
| BW | 2.24 c | 19.21 b,c | 61.55 d | 63.3 c | −4.8 b,c | 7.9 d |
| SE | 0.08 | 0.66 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Concentration of wax | ||||||
| 0.0% | 1.91 c | 13.97 c | 64.53 b | 55.06 d | −4.4 a | 7.1 e |
| 5.0% | 3.09 b | 25.23 b | 64.21 b | 64.34 c | −4.7 b | 9.0 d |
| 7.5% | 3.63 a | 28.40 a | 64.73 b | 67.30 b | −4.8 b | 10.2 c |
| 10.0% | 3.06 b | 23.62 b | 64.91 b | 68.85 a | −4.8 b | 11.3 b |
| 15.0% | 3.16 b | 24.20 b | 67.83 a | 69.34 a | −4.4 a | 14.2 a |
| SE | 0.09 | 0.74 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Edible oil | ||||||
| Olive oil | 2.79 b | 22.49 a,b | 65.26 a | 65.58 b | −6.7 c | 16.1 a |
| Sunflower oil | 3.14 a | 24.91 a | 65.34 a | 63.60 c | −3.5 a | 5.7 c |
| Sesame oil | 3.13 a | 22.48 b | 65.32 a | 67.04 a | −4.9 b | 13.9 b |
| Soybean oil | 2.82 b | 22.47 b | 65.05 a | 63.70 c | −3.4 a | 5.8 c |
| SE | 0.08 | 0.66 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.020 | 0.886 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Samples 1 | Wax (% w/w) | MG (% w/w) | Oil (% w/w) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15_W | 15.0 | 0.0 | 85.0 |
| 10_W_5_MGs | 10.0 | 5.0 | 85.0 |
| 7.5_W_7.5_MGs | 7.5 | 7.5 | 85.0 |
| 5_W_10_MGs | 5.0 | 10.0 | 85.0 |
| 15_MGs | 0.0 | 15.0 | 85.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimakopoulou-Papazoglou, D.; Giannakaki, F.; Katsanidis, E. Structural and Physical Characteristics of Mixed-Component Oleogels: Natural Wax and Monoglyceride Interactions in Different Edible Oils. Gels 2023, 9, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080627
Dimakopoulou-Papazoglou D, Giannakaki F, Katsanidis E. Structural and Physical Characteristics of Mixed-Component Oleogels: Natural Wax and Monoglyceride Interactions in Different Edible Oils. Gels. 2023; 9(8):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080627
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimakopoulou-Papazoglou, Dafni, Foteini Giannakaki, and Eugenios Katsanidis. 2023. "Structural and Physical Characteristics of Mixed-Component Oleogels: Natural Wax and Monoglyceride Interactions in Different Edible Oils" Gels 9, no. 8: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080627
APA StyleDimakopoulou-Papazoglou, D., Giannakaki, F., & Katsanidis, E. (2023). Structural and Physical Characteristics of Mixed-Component Oleogels: Natural Wax and Monoglyceride Interactions in Different Edible Oils. Gels, 9(8), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080627









