Exploration of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption from Composite Hydrogel Beads—Adsorbent Reusability, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
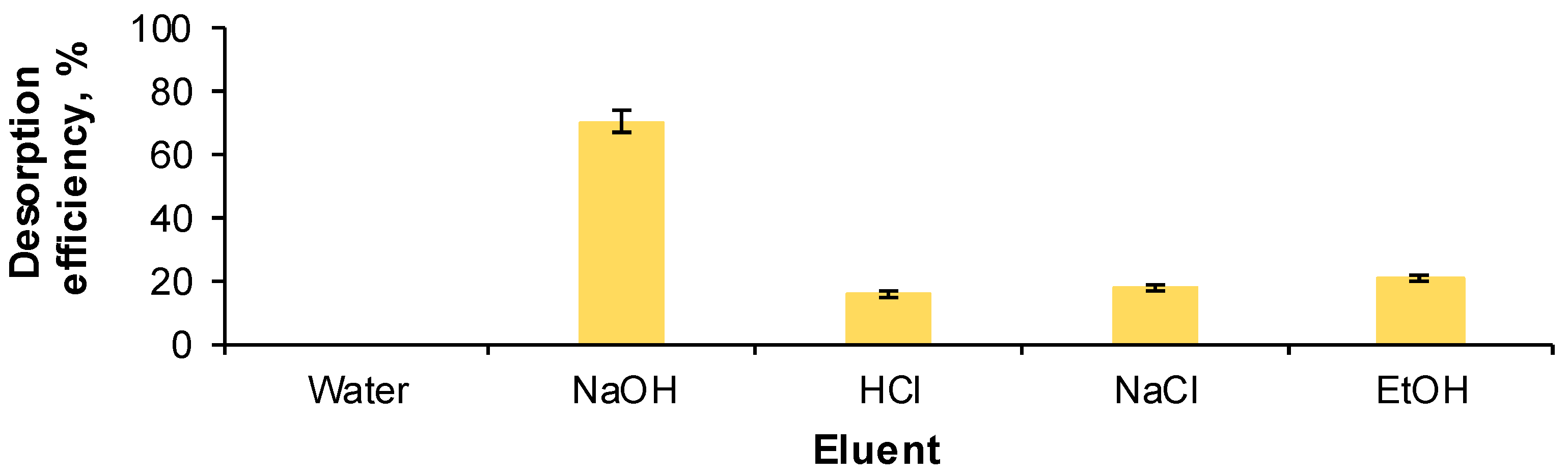
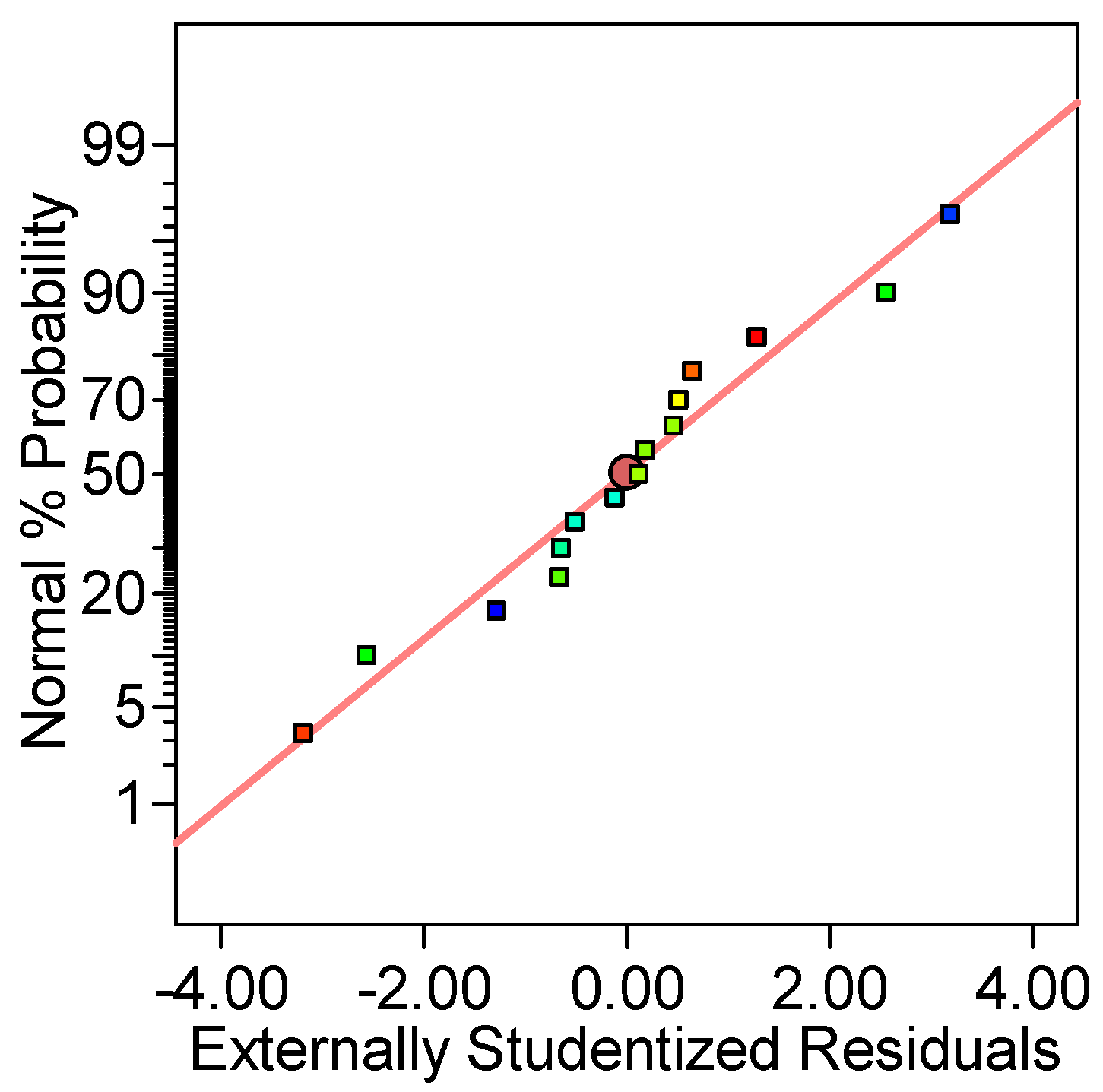
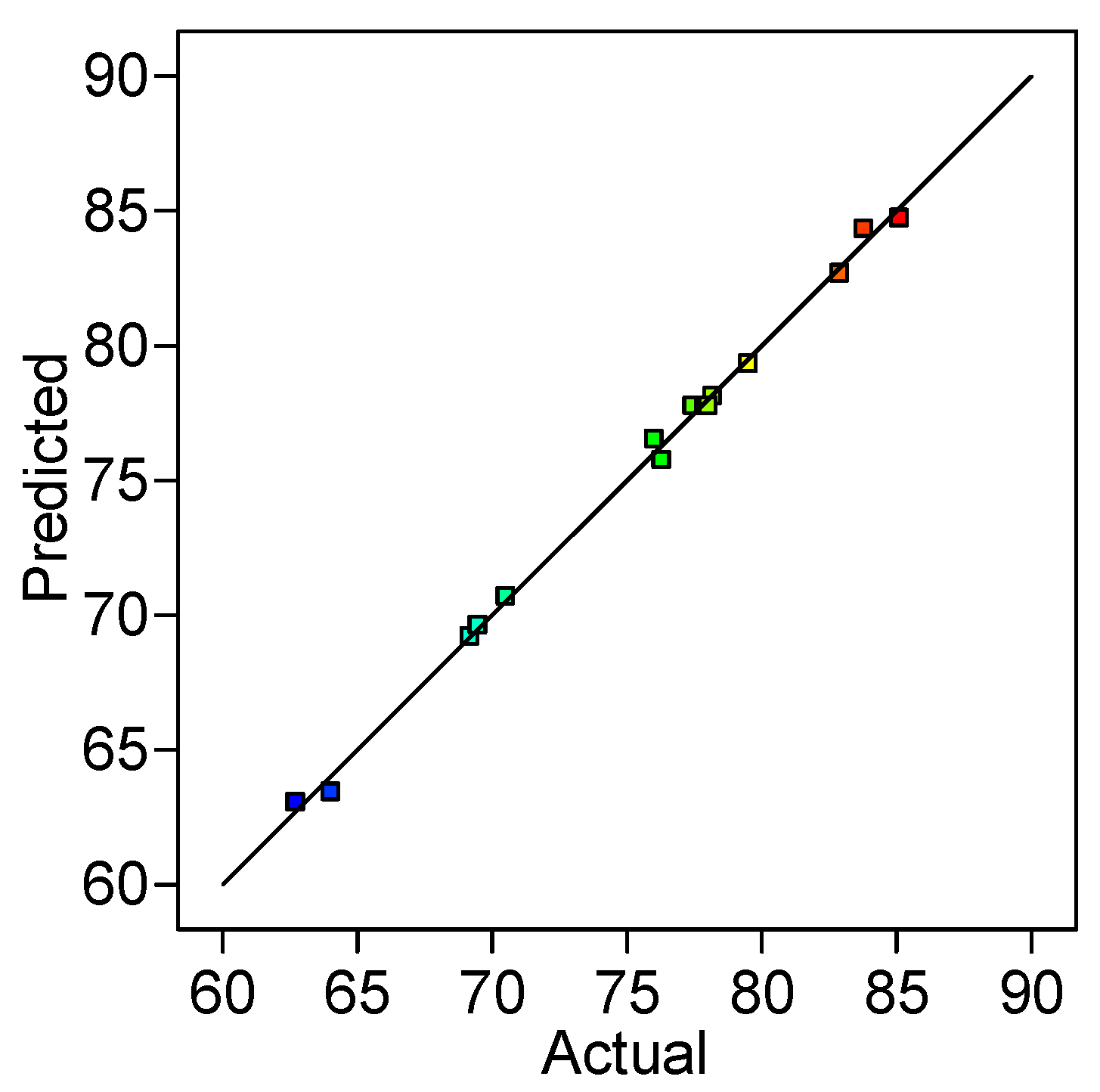
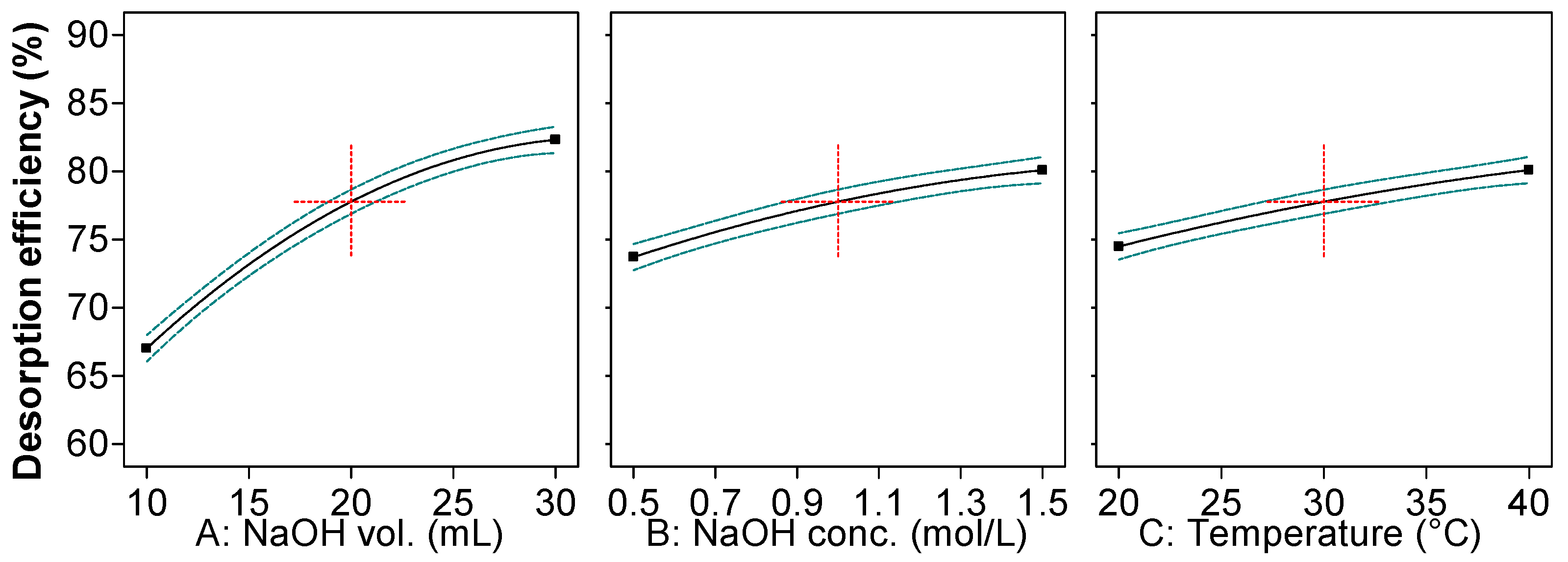
2.1. Optimization of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption by Response Surface Methodology
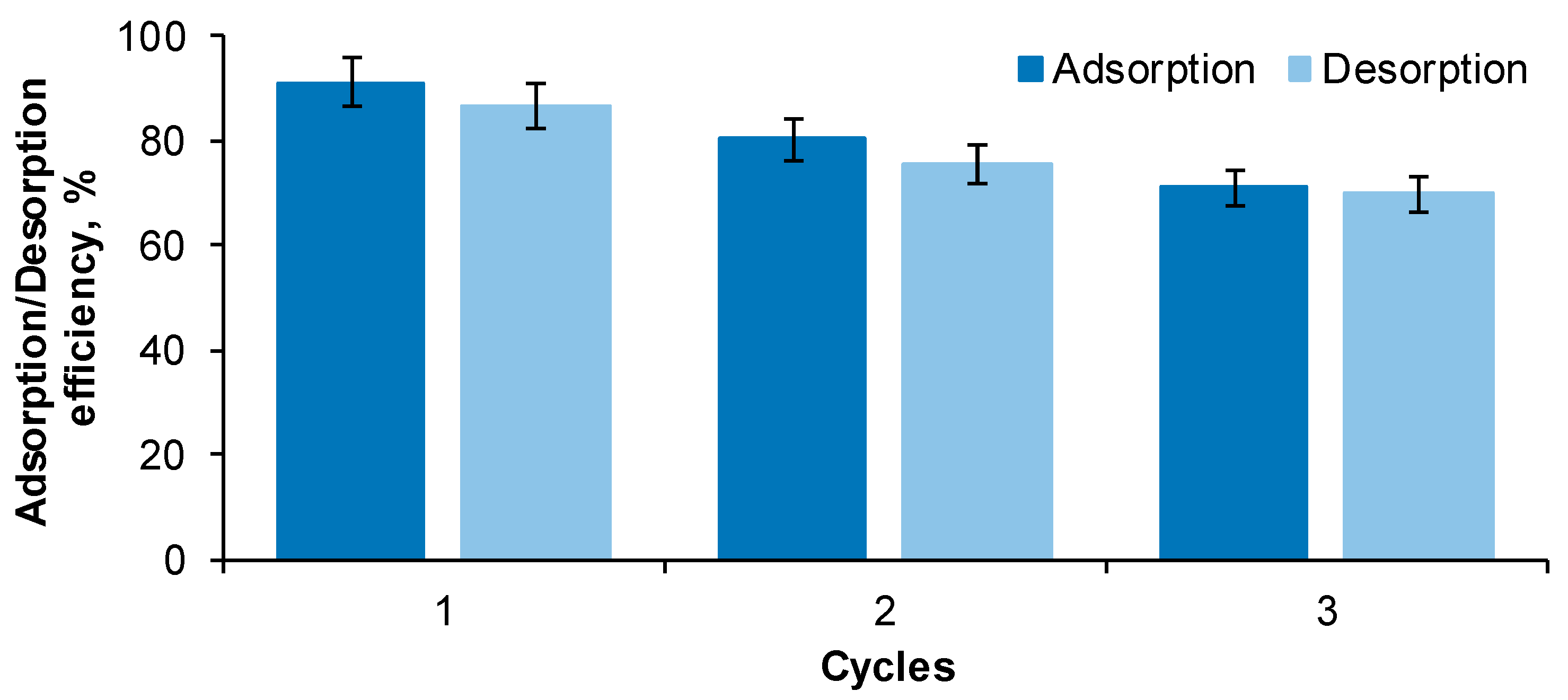
2.2. Adsorbent Reusability
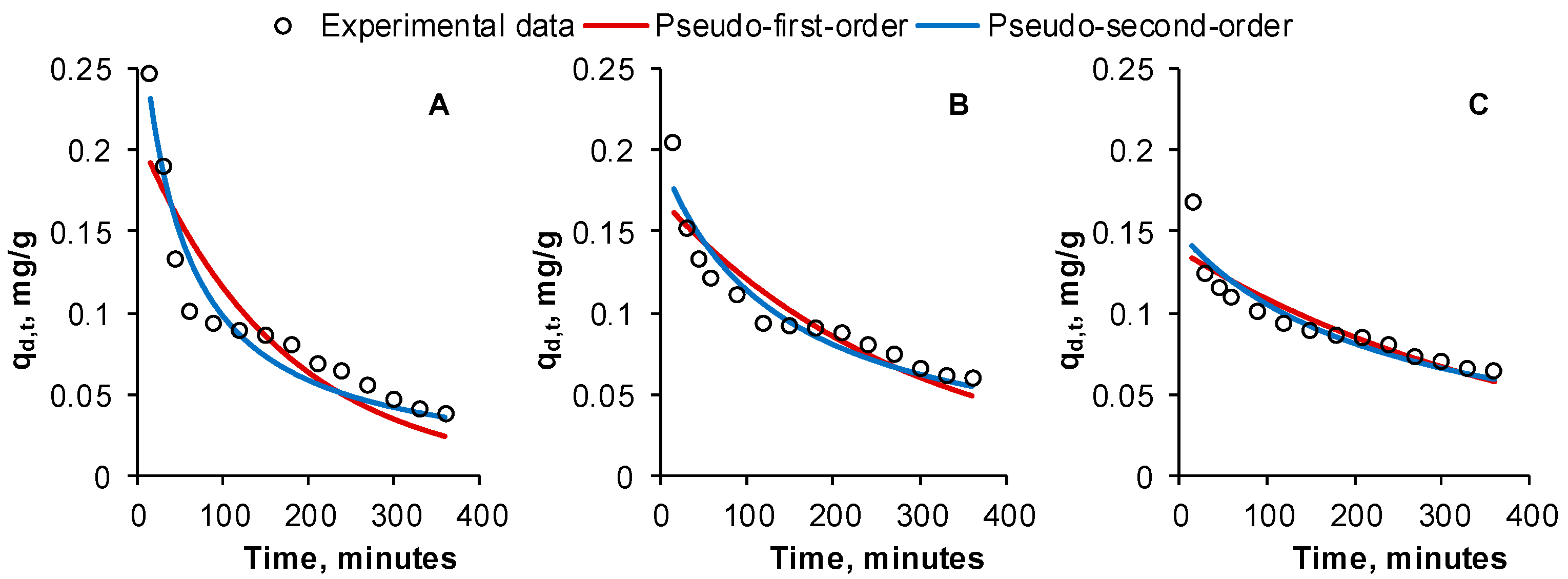
2.3. Impact of Contact Time on Reactive Black 5 Desorption. Kinetic Studies
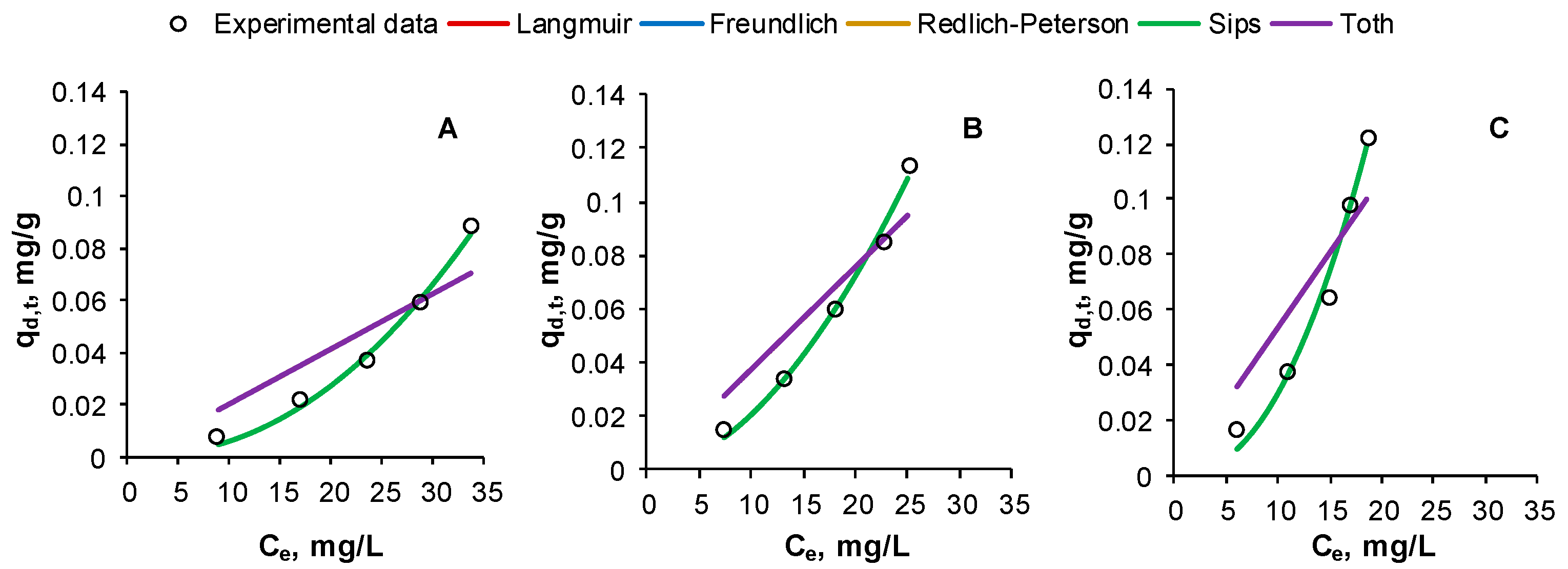
2.4. Influence of Reactive Black 5 Initial Concentration on Desorption. Equilibrium Isotherms
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Reagents
4.2. Analytical Procedure
4.3. Batch Adsorption–Desorption of Reactive Black 5 Dye
4.4. Adsorbent Reusability
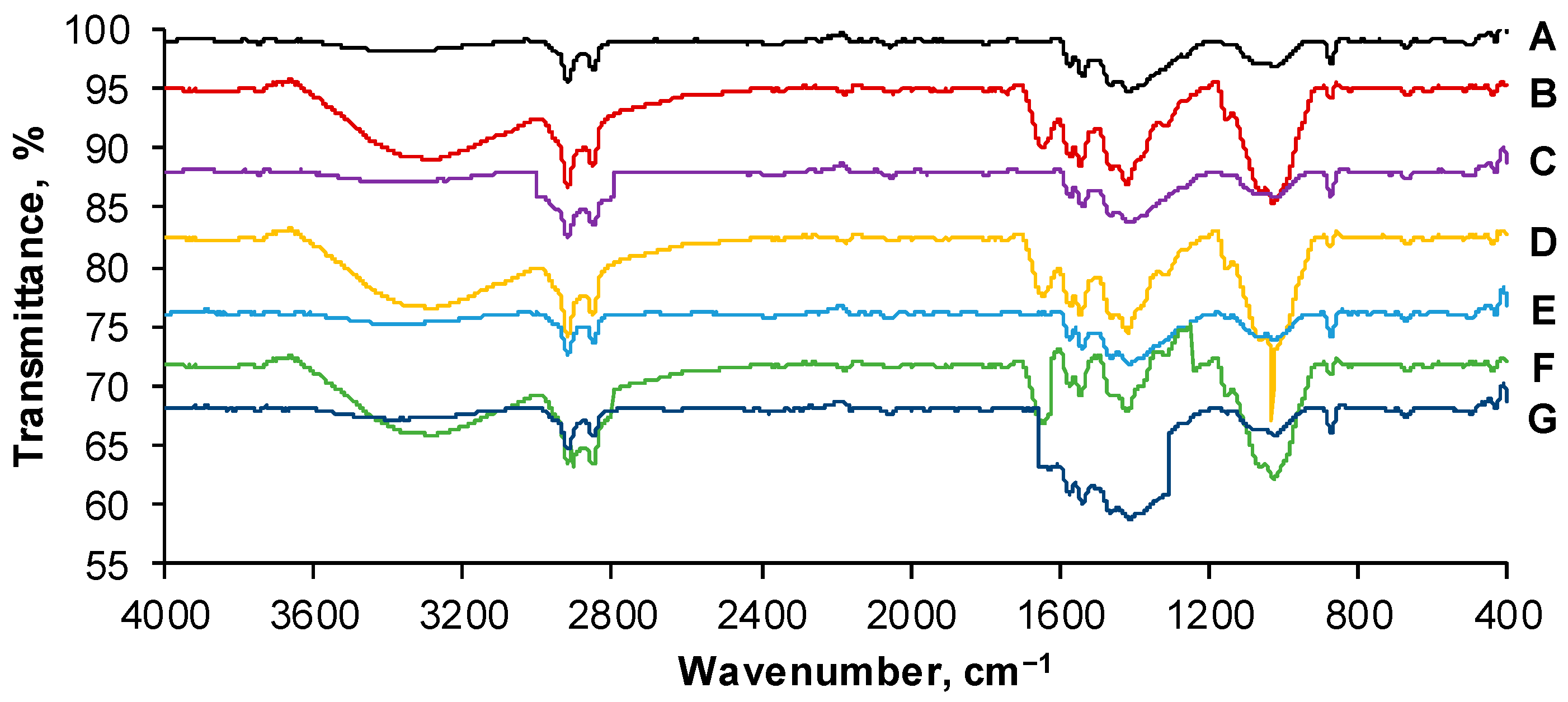
4.5. Adsorbent Characterization
4.6. Desorption Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sauvé, S.; Bernard, S.; Sloan, P. Environmental sciences, sustainable development and circular economy: Alternative concepts for trans-disciplinary research. Environ. Dev. 2016, 17, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. A review on selective dye adsorption by different mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osagie, C.; Othmani, A.; Ghosh, S.; Malloum, A.; Kashitarash Esfahani, Z.; Ahmadi, S. Dyes adsorption from aqueous media through the nanotechnology: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2195–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, E.D.V.; Oliveira, M.G.; Spaolonzi, M.P.; Costa, H.P.S.; Silva, T.L.d.; Silva, M.G.C.d.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of pharmaceutical products from aqueous solutions on functionalized carbon nanotubes by conventional and green methods: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; He, M.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wan, Z.; Hou, D.; Alessi, D.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Insights into the adsorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) on biochar and activated carbon with the aid of machine learning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wen, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. Surface functional groups determine adsorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products on polypropylene microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Rangasamy, G.; Prasannamedha, G.; Kanmani, S. A review on the applicability of adsorption techniques for remediation of recalcitrant pesticides. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Ladino, C.R.; Mekonnen, T.H. Cationic modification of cellulose as a sustainable and recyclable adsorbent for anionic dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, P.; Agarwal, M. Adsorption of cationic dye by using metal industry solid waste as an adsorbent. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 78, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Nayagam, J.O.; Prasanna, K. Utilization of shell-based agricultural waste adsorbents for removing dyes: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, O.; Panahandeh, S. Fabrication of different adsorbents based on zirconium oxide, graphene oxide, and dextrin for removal of green malachite dye from aqueous solutions. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Min, D.; Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Du, J.; Tao, Y.; Wang, H. Design of bionic amphoteric adsorbent based on reed root loaded with amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for heavy metal ions removal. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohaizad, A.; Mohd Hir, Z.A.; Kamal, U.A.A.M.; Aspanut, Z.; Pam, A.A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Allium sativum extract assisted by solar irradiation in a composite with graphene oxide as potent adsorbents. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamasbi, N.; Mohammadi Ziarani, G.; Mohajer, F.; Darroudi, M.; Badiei, A.; Varma, R.S.; Karimi, F. Silica-coated modified magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2@(BuSO3H)3) as an efficient adsorbent for Pd2+ removal. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harikishore Kumar Reddy, D.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Kim, J.A.; Yun, Y.-S. Valorisation of post-sorption materials: Opportunities, strategies, and challenges. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 242, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabruś, E.; Tabero, P.; Aleksandrzak, T. A study of the thermal regeneration of carbon and zeolite adsorbents after adsorption of 1-hexene vapor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 216, 119065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyravi, A.; Feizbakhshan, M.; Hashisho, Z.; Crompton, D.; Anderson, J.E. Purge gas humidity improves microwave-assisted regeneration of polymeric and zeolite adsorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, F.; Gagnon, L.R.; Mulmi, S.; Roberts, E.P.L. Electrochemical regeneration of a reduced graphene oxide/magnetite composite adsorbent loaded with methylene blue. Water Res. 2017, 114, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoraș, C.-G.; Simion, A.-I.; Favier, L.; Drob, C.; Gavrilă, L. Performance of Dye Removal from Single and Binary Component Systems by Adsorption on Composite Hydrogel Beads Derived from Fruits Wastes Entrapped in Natural Polymeric Matrix. Gels 2022, 8, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, D.; Kupka, D.; Vaclavikova, M.; Ivanicova, L.; Gallios, G. Degradation of Reactive Black 5 by electrochemical oxidation. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Toxicological Assessment and UV/TiO2-Based Induced Degradation Profile of Reactive Black 5 Dye. Environ. Manag. 2018, 61, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, L.A.; Mohd Yusoff, A.R.; Hadibarata, T.; Khudhair, A.B. Biodegradation of Bis-Azo Dye Reactive Black 5 by White-Rot Fungus Trametes gibbosa sp. WRF 3 and Its Metabolite Characterization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Industrial Chemicals Introduction Scheme. Available online: https://www.industrialchemicals.gov.au/chemical-information (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bruns, R.E.; Ferreira, H.S.; Matos, G.D.; David, J.M.; Brandão, G.C.; da Silva, E.G.P.; Portugal, L.A.; dos Reis, P.S.; Souza, A.S.; et al. Box-Behnken design: An alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, E.; Vazirzadeh, A.; Niazi, A.; Kousha, M.; Naushad, M.; Bhatnagar, A. Desorption of Methylene blue dye from brown macroalga: Effects of operating parameters, isotherm study and kinetic modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.-L.; Lu, Y.-W.; Hung, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. Adsorption kinetic, thermodynamic and desorption studies of C.I. Reactive Black 5 on a novel photoassisted Fenton catalyst. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 75, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.-J.; Kimura, S.; Wada, M. Highly enhanced adsorption of Congo red onto dialdehyde cellulose-crosslinked cellulose-chitosan foam. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Messaoudi, N.; El Khomri, M.; Chlif, N.; Chegini, Z.G.; Dbik, A.; Bentahar, S.; Lacherai, A. Desorption of Congo red from dye-loaded Phoenix dactylifera date stones and Ziziphus lotus jujube shells. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, J.-M.; Wu, C.-Y. Desorption of dye from activated carbon beds: Effects of temperature, pH, and alcohol. Water Res. 2001, 35, 4159–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Wang, J.J.; Meng, Y.; Wei, Z.; DeLaune, R.D.; Seo, D.-C. Adsorption/desorption behavior of cationic and anionic dyes by biochars prepared at normal and high pyrolysis temperatures. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 572, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.; Inaam-ul-Hassan, M.; Raza, A.; Tahir, M.; Yasin, T. Removal of copper using chitosan beads embedded with amidoxime grafted graphene oxide nanohybids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, T. Chitosan-coated sour cherry kernel shell beads: An adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI) from acidic solutions. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, A.; Singh, G.B. Biodecolorization of reactive black 5 using magnetite nanoparticles coated Bacillus sp. RA5. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksimović, K.; Kodranov, I.; Randjelović, D.; Slavković Beškoski, L.; Radulović, J.; Lješević, M.; Manojlović, D.; Beškoski, V.P. Microbial fuel cells as an electrical energy source for degradation followed by decolorization of Reactive Black 5 azo dye. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 145, 108088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Qiu, F.; Qin, J.; Zhao, H.; Yan, J.; Yang, D. A facile hydrothermal synthesis, adsorption kinetics and isotherms to Congo Red azo-dye from aqueous solution of NiO/graphene nanosheets adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramian, L.; El-Rassy, H. Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of azo-dye Orange II onto highly porous titania aerogel. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felista, M.M.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Ongera, G. Adsorption of anionic dye (Reactive black 5) using macadamia seed Husks: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, L.; Xu, Q. Preparation and swelling properties of graphene oxide/poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) super-absorbent hydrogel nanocomposites. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 401, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njikam, E.; Schiewer, S. Optimization and kinetic modeling of cadmium desorption from citrus peels: A process for biosorbent regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.N.; Safa, Y.; Yakout, S.M.; Shair, O.H.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A. Efficient removal of dyes using carboxymethyl cellulose/alginate/polyvinyl alcohol/rice husk composite: Adsorption/desorption, kinetics and recycling studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momina; Mohammad, S.; Suzylawati, I. Study of the adsorption/desorption of MB dye solution using bentonite adsorbent coating. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddeti, S.M.R.; Bhaumik, M.; Maity, A.; Ray, S.S. Removal of Congo red from aqueous solution by adsorption using gum ghatti and acrylamide graft copolymer coated with zero valent iron. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; McKay, G.; Porter, J.F. Adsorption isotherm models for basic dye adsorption by peat in single and binary component systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Physicochem. 1906, 57, 385. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Porter, J.F.; McKay, G. Equilibrium Isotherm Studies for the Sorption of Divalent Metal Ions onto Peat: Copper, Nickel and Lead Single Component Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 141, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D.L. A Useful Adsorption Isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J. Uniform interpretation of gas/solid adsorption. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 55, 1–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammad, N.A.; Zulkifli, M.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Mohd Din, A.T. Desorption of chloramphenicol from ordered mesoporous carbon-alginate beads: Effects of operating parameters, and isotherm, kinetics, and regeneration studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Run | Variables—Actual and Coded Values | Desorption Efficiency, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | Observed | Predicted | |
| 1 | 10 (−1) | 0.5 (−1) | 30 (0) | 62.70 | 63.06 |
| 2 | 30 (+1) | 0.5 (−1) | 30 (0) | 78.17 | 78.13 |
| 3 | 20 (0) | 1.5 (+1) | 40 (+1) | 82.89 | 82.68 |
| 4 | 20 (0) | 1.5 (+1) | 20 (−1) | 76.01 | 76.54 |
| 5 | 30 (+1) | 1.5 (+1) | 30 (0) | 85.10 | 84.74 |
| 6 | 10 (−1) | 1 (0) | 20 (−1) | 64.01 | 63.44 |
| 7 | 10 (−1) | 1 (0) | 40 (+1) | 69.47 | 69.63 |
| 8 | 30 (+1) | 1 (0) | 40 (+1) | 83.77 | 84.34 |
| 9 | 20 (0) | 0.5 (−1) | 40 (+1) | 76.29 | 75.76 |
| 10 | 20 (0) | 1 (0) | 30 (0) | 77.87 | 77.77 |
| 11 | 30 (+1) | 1 (0) | 20 (−1) | 79.50 | 79.33 |
| 12 | 20 (0) | 1 (0) | 30 (0) | 78.02 | 77.77 |
| 13 | 20 (0) | 1 (0) | 30 (0) | 77.43 | 77.77 |
| 14 | 10 (−1) | 1.5 (+1) | 30 (0) | 69.17 | 69.21 |
| 15 | 20 (0) | 0.5 (−1) | 20 (−1) | 70.50 | 70.70 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 650.40 | 9 | 72.27 | 201.82 | <0.0001 |
| A—NaOH volume | 468.15 | 1 | 468.15 | 1307.43 | <0.0001 |
| B—NaOH concentration | 81.39 | 1 | 81.39 | 227.30 | <0.0001 |
| C—Temperature | 62.74 | 1 | 62.74 | 175.21 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 0.0538 | 1 | 0.0538 | 0.1503 | 0.7142 |
| AC | 0.3493 | 1 | 0.3493 | 0.9755 | 0.3687 |
| BC | 0.2943 | 1 | 0.2943 | 0.8219 | 0.4062 |
| A2 | 35.78 | 1 | 35.78 | 99.93 | 0.0002 |
| B2 | 2.84 | 1 | 2.84 | 7.93 | 0.0373 |
| C2 | 0.8376 | 1 | 0.8376 | 2.34 | 0.1867 |
| Residual | 1.79 | 5 | 0.3581 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 1.60 | 3 | 0.5339 | 5.66 | 0.1538 |
| Pure Error | 0.1887 | 2 | 0.0943 | ||
| Cor Total | 652.19 | 14 |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Desorption Cycle | 2nd Desorption Cycle | 3rd Desorption Cycle | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | qd,1 | 0.2103 | 0.1701 | 0.1387 |
| kd,1 | 0.0059 | 0.0034 | 0.0024 | |
| SSE | 0.007940 | 0.003271 | 0.001710 | |
| MSE | 0.000567 | 0.000234 | 0.000122 | |
| RMSE | 0.000662 | 0.000273 | 0.000142 | |
| ARE | 21.151430 | 10.657220 | 7.542603 | |
| χ2 | 0.005771 | 0.025682 | 0.014560 | |
| R2 | 0.8228 | 0.8428 | 0.8294 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | qd,2 | 0.3051 | 0.1959 | 0.1497 |
| kd,2 | 0.0700 | 0.0369 | 0.0279 | |
| SSE | 0.003016 | 0.001788 | 0.001218 | |
| MSE | 0.000215 | 0.000128 | 0.000087 | |
| RMSE | 0.000251 | 0.000149 | 0.000101 | |
| ARE | 14.008901 | 8.579999 | 6.843968 | |
| χ2 | 0.032073 | 0.014693 | 0.010110 | |
| R2 | 0.9333 | 0.9110 | 0.8784 | |
| Isotherm | Parameters | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Desorption Cycle | 2nd Desorption Cycle | 3rd Desorption Cycle | ||
| Langmuir | QL | 3248.818 | 3286.657 | 3258.273 |
| KL | 6.394 × 10−7 | 1.184 × 10−6 | 1.643 × 10−6 | |
| SSE | 0.000752 | 0.000846 | 0.001425 | |
| MSE | 0.000150 | 0.000169 | 0.000285 | |
| RMSE | 0.000251 | 0.000282 | 0.000475 | |
| ARE | 49.542003 | 32.758021 | 40.071366 | |
| χ2 | 0.000762 | 0.000843 | 0.001425 | |
| R2 | 0.8130 | 0.8645 | 0.8073 | |
| Freundlich | KF | 4.141 × 10−5 | 3.025 × 10−4 | 1.832 × 10−4 |
| n | 0.460 | 0.547 | 0.451 | |
| SSE | 0.000035 | 0.000072 | 0.000113 | |
| MSE | 0.000007 | 0.000014 | 0.000022 | |
| RMSE | 0.000019 | 0.000024 | 0.000037 | |
| ARE | 13.420319 | 7.524428 | 12.111494 | |
| χ2 | 0.000033 | 0.000072 | 0.000114 | |
| R2 | 0.9911 | 0.9884 | 0.9847 | |
| Redlich–Peterson | KRP1 | 0.019 | 0.043 | 0.056 |
| KRP2 | 8.255 | 10.413 | 9.468 | |
| nRP | 4.079 × 10−15 | 5.724 × 10−17 | 1.379 × 10−15 | |
| SSE | 0.000752 | 0.000845 | 0.00145 | |
| MSE | 0.000150 | 0.000169 | 0.000285 | |
| RMSE | 0.000251 | 0.000282 | 0.000475 | |
| ARE | 49.543761 | 32.742932 | 40.072206 | |
| χ2 | 0.001125 | 0.001266 | 0.002136 | |
| R2 | 0.8130 | 0.8645 | 0.8073 | |
| Sips | QS | 101,770.961 | 8841.882 | 78,576.519 |
| KS | 4.806 × 10−5 | 8.274 × 10−5 | 1.294 × 10−4 | |
| nS | 2.175 | 1.829 | 2.221 | |
| SSE | 0.000035 | 0.000072 | 0.000113 | |
| MSE | 0.000007 | 0.000014 | 0.000022 | |
| RMSE | 0.000011 | 0.000024 | 0.000037 | |
| ARE | 13.427219 | 7.553481 | 12.150279 | |
| χ2 | 0.000051 | 0.000108 | 0.000168 | |
| R2 | 0.9911 | 0.9884 | 0.9847 | |
| Toth | QTO | 5.918 | 6.053 | 6.548 |
| KTO | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.007 | |
| nTO | 10.302 | 9.065 | 8.778 | |
| SSE | 0.000753 | 0.000849 | 0.001425 | |
| MSE | 0.000151 | 0.000170 | 0.000285 | |
| RMSE | 0.000251 | 0.000283 | 0.000475 | |
| ARE | 49.572085 | 32.822459 | 40.072203 | |
| χ2 | 0.001125 | 0.002535 | 0.002136 | |
| R2 | 0.8130 | 0.8645 | 0.8073 | |
| Kinetic Model | Equation | Parameters Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-1st-order | kd,1—pseudo-first-order constant rate, min−1 | |
| Pseudo-2nd-order | kd,2—pseudo-2nd-order constant rate, g/(mg·min) |
| Equilibrium Isotherm | Equation | Parameters Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | QL—Langmuir maximum uptake, mg/g KL—Langmuir constant, L/mg | |
| Freundlich | KF—Freundlich constant, (mg/g) (L/mg)1/n n—Freundlich constant, dimensionless | |
| Redlich–Peterson | KRP1—Redlich–Peterson constant, L/g KRP2—Redlich–Peterson constant, L/mg nRP—Redlich–Peterson constant, dimensionless | |
| Sips | QS—Sips maximum uptake, mg/g KS—Sips constant, L/mg nS—Sips constant, dimensionless | |
| Toth | QTo—Toth maximum uptake, mg/g KTo—Toth constant, L/mg nTo—Toth constant, dimensionless |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigoraș, C.-G.; Simion, A.-I.; Favier, L. Exploration of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption from Composite Hydrogel Beads—Adsorbent Reusability, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms. Gels 2023, 9, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040299
Grigoraș C-G, Simion A-I, Favier L. Exploration of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption from Composite Hydrogel Beads—Adsorbent Reusability, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms. Gels. 2023; 9(4):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040299
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigoraș, Cristina-Gabriela, Andrei-Ionuț Simion, and Lidia Favier. 2023. "Exploration of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption from Composite Hydrogel Beads—Adsorbent Reusability, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms" Gels 9, no. 4: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040299
APA StyleGrigoraș, C.-G., Simion, A.-I., & Favier, L. (2023). Exploration of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption from Composite Hydrogel Beads—Adsorbent Reusability, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms. Gels, 9(4), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9040299








