The Effect of Different Ratios of Starch and Freeze–Thaw Treatment on the Properties of Konjac Glucomannan Gels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rheological Analysis
2.1.1. Frequency Sweep
2.1.2. Temperature Sweep
2.1.3. Amplitude Sweep
2.2. TGA Analysis
2.3. DSC Analysis
2.4. XRD Analysis
2.5. FT–IR Analysis
2.6. Moisture Distribution in the Composite Gels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of KGM–CS Gels and Freeze–Thaw-Treated Gels (F–KGM–CS)
4.3. Rheological Measurements
4.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
4.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT–IR)
4.8. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF–NMR)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishinari, K.; Takahashi, R. Interaction in polysaccharide solutions and gels. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2002, 8, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M. Effects of konjac glucomannan on pasting and rheological properties of corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Xu, D.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y. Gelation of κ-carrageenan/Konjac glucommanan compound gel: Effect of cyclodextrins. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, N. Effect of konjac glucomannan with different molecular weights on physicochemical properties of corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroskenyi, B.; McCarthy, S.P. Synthesis of acetylated konjac glucomannan and effect of degree of acetylation on water absorbency. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Nishinari, K. Effect of degree of acetylation on gelation of konjac glucomannan. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Takahashi, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Kawase, T.; Nishinari, K. Gelation behavior of native and acetylated konjac glucomannan. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Sande, M.; Teijeiro-Osorio, D.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Alonso, M.J. Glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide for biopharmaceutical purposes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Effect of degree of deacetylation on physicochemical and gelation properties of konjac glucomannan. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, M.; Nakao, Y.; Nara, K. Food Applications of Curdlan. In Food Hydrocolloids; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Mu, R.J.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Pang, J.; Wu, C. Effects of konjac glucomannan on the structure, properties, and drug release characteristics of agarose hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Mao, C.; Song, Z.; Liu, C. Preparation and characterization of konjac glucomannan and gum arabic composite gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, T.; Tuvikene, R.; Fang, Y.; Matsukawa, S.; Nishinari, K. Rheology of highly elastic iota–carrageenan/kappa–carrageenan/xanthan/konjac glucomannan gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tako, M.; Hizukuri, S. Gelatinization Mechanism of Rice Starch. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 1999, 18, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouni, E.; Petsi, T.; Kanellaki, M.; Bekatorou, A.; Koutinas, A. Tubular cellulose/starch gel composite as food enzyme storehouse. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadokawa, J.; Murakami, M.; Takegawa, A.; Kaneko, Y. Preparation of cellulose–starch composite gel and fibrous material from a mixture of the polysaccharides in ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, N.; Zielbauer, B.I.; Ghebremedhin, M.; Vilgis, T.A. Pre–gelatinized tapioca starch and its mixtures with xanthan gum and Ɩ–carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarge, C.; Journaux, L.; Bonnotte, A.; Lherminier, J.; Lee, J.A.; Bail, P.L.; Cayot, N. Trapping of carvacrol by konjac glucomannan–potato starch gels: Stability from macroscopic to microscopic scale, using image processing. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genevro, G.M.; Moraes, M.A.; Beppu, M.M. Freezing influence on physical properties of glucomannan hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Hatakeyama, T.; Hatakeyama, H. DSC and TMA studies on freezing and thawing gelation of galactomannan polysaccharide. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 532, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Wei, X.; Li, J. The influence of amylose and amylopectin on water retention capacity and texture properties of frozen–thawed konjac glucomannan gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solo-de-Zaldívar, B.; Herranz, B.; Borderías, A.J.; Tovar, C.A. Effect of freezing and frozen storage on restructured FISH prototypes made with glucomannan and FISH mince. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, W.; Chen, Z.; Wu, T. Freeze–thaw induced gelation of alginates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnkarnsujarit, N.; Kawai, K.; Suzuki, T. Impacts of freezing and molecular size on structure, mechanical properties and recrystallization of freeze–thawed polysaccharide gels. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantaro, P.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; Nishinari, K. Effect of heating–cooling on rheological properties of tapioca starch paste with and without xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, T.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Li, B. Preparation and characterization of heterogeneous deacetylated konjac glucomannan. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 40, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzababaee, S.M.; Ozmen, D.; Hesarinejad, M.A.; Toker, O.S.; Yeganehzad, S. A study on the structural, physicochemical, rheological and thermal properties of high hydrostatic pressurized pearl millet starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, H.; Hashimoto, R.; Lu, Y.; Hsieh, W.-C. Structural and Mechanical Properties of Konjac Glucomannan Gels and Influence of Freezing-Thawing Treatments on Them. Polymers 2022, 14, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, D.W.; Reich, L.; Lee, H.T. Degradation of polymers by thermal gravimetric techniques. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1965, 5, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, K.; Xiao, M.; Kuang, Y.; Corke, H.; Ni, X. Structural characterization and properties of konjac glucomannan and zein blend films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Takaya, T.; Nishinari, K. Rheological studies on mixtures of corn starch and konjac–glucomannan. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 35, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Song, R.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Shah, B.R.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Analysis of deacetylated konjac glucomannan and xanthan gum phase separation by film forming. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matignon, A.; Tecante, A. Starch retrogradation: From starch components to cereal products. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.M.; Bail, K.L.; Garnier, C.; Llamas, G.; Queveau, D.; Pontoire, B.; Srzednicki, G.; Bail, P.L. Available water in konjac glucomannan–starch mixtures. Influence on the gelatinization, retrogradation and complexation properties of two starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q. The gelatinization and retrogradation properties of wheat starch with the addition of stearic acid and sodium alginate. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, J. Physically crosslinked hydrogels from polysaccharides prepared by freeze-thaw technique. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BeMiller, J.N. Pasting, paste, and gel properties of starch–hydrocolloid combinations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 386–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, B. Preparation and characterization of konjac glucomannan microcrystals through acid hydrolysis. Food Res. Int. 2015, 67, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Properties of the konjac glucomannan and zein composite gel with or without freeze-thaw treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zhang, M.; Xia, X.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B. Effect of porcine plasma protein hydrolysates on long–term retrogradation of corn starch. Food Chem 2018, 239, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, W.S.; Jackson, D.S. A new insight into the gelatinization process of native starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xiao, C. Characterization of konjac glucomannan–quaternized poly(4-vinyl-N-butyl) pyridine blend films and their preservation effect. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, P.; Drábik, M.; Turjan, J. Characterization of starch and its mono and hybrid derivatives by thermal analysis and FT–IR spectroscopy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 99, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, J.; Xia, J.; Kennedy, J.F.; Yie, X.; Liu, T.G. Effect of gamma irradiation on the condensed state structure and mechanical properties of konjac glucomannan/chitosan blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chang, P.R. Structural characterization and properties of starch/konjac glucomannan blend films. Carbohydr Polym 2008, 74, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudianti, R.; Karina, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Azuma, J. DSC analysis on water state of salvia hydrogels. Macromol. Res. 2009, 17, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, J.; Tong, Q.; Jin, Z. Rapid, accurate, and simultaneous measurement of water and oil contents in the fried starchy system using low–field NMR. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, B.W.; Tan, M. Effect of hydrocolloid and processing potentiality on water migration in apple jellies of Yinduqing cultivar. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, J.; Ren, G.; Cui, G.; Liu, J. Effects of konjac glucomannan on the water distribution of frozen dough and corresponding steamed bread quality. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

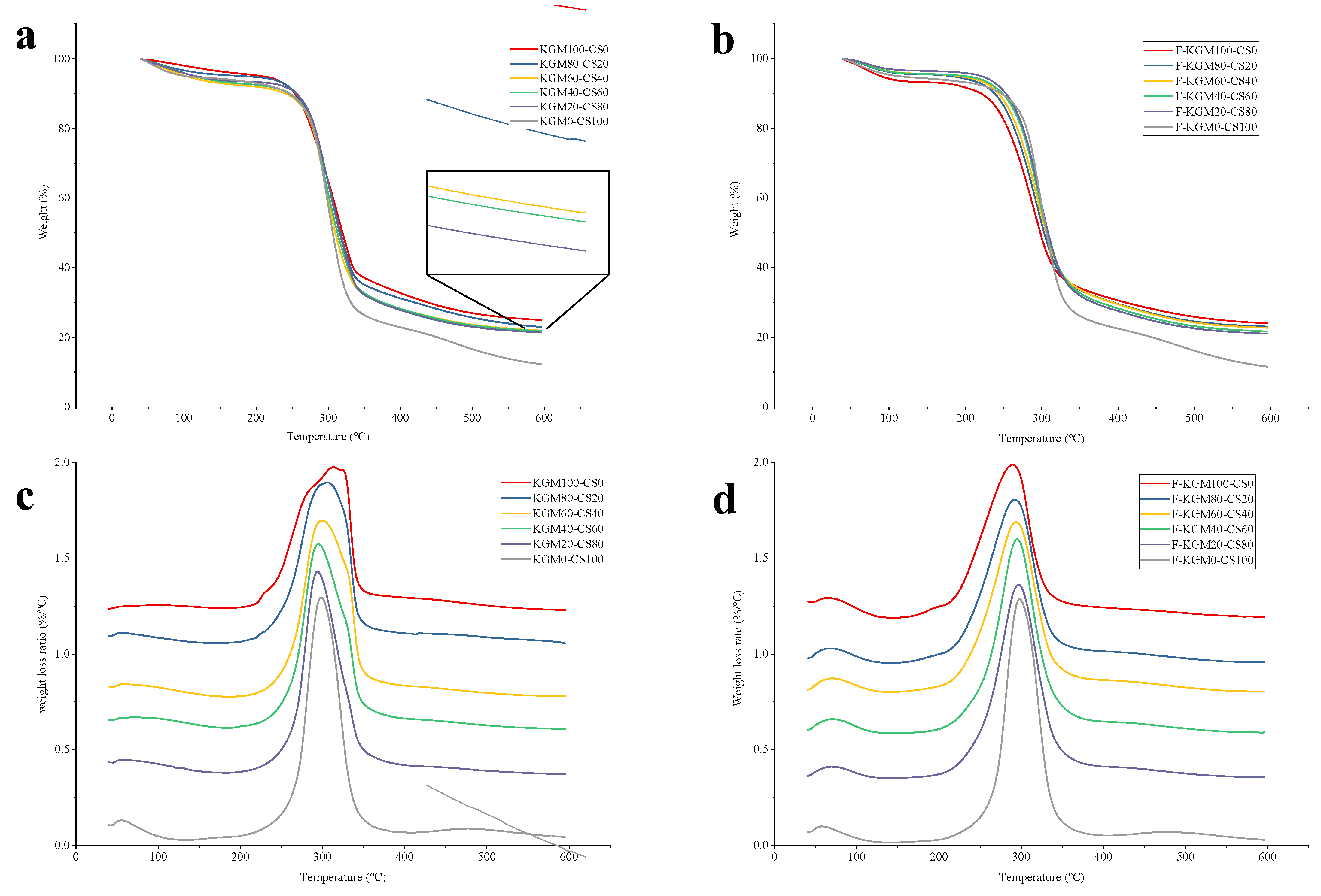
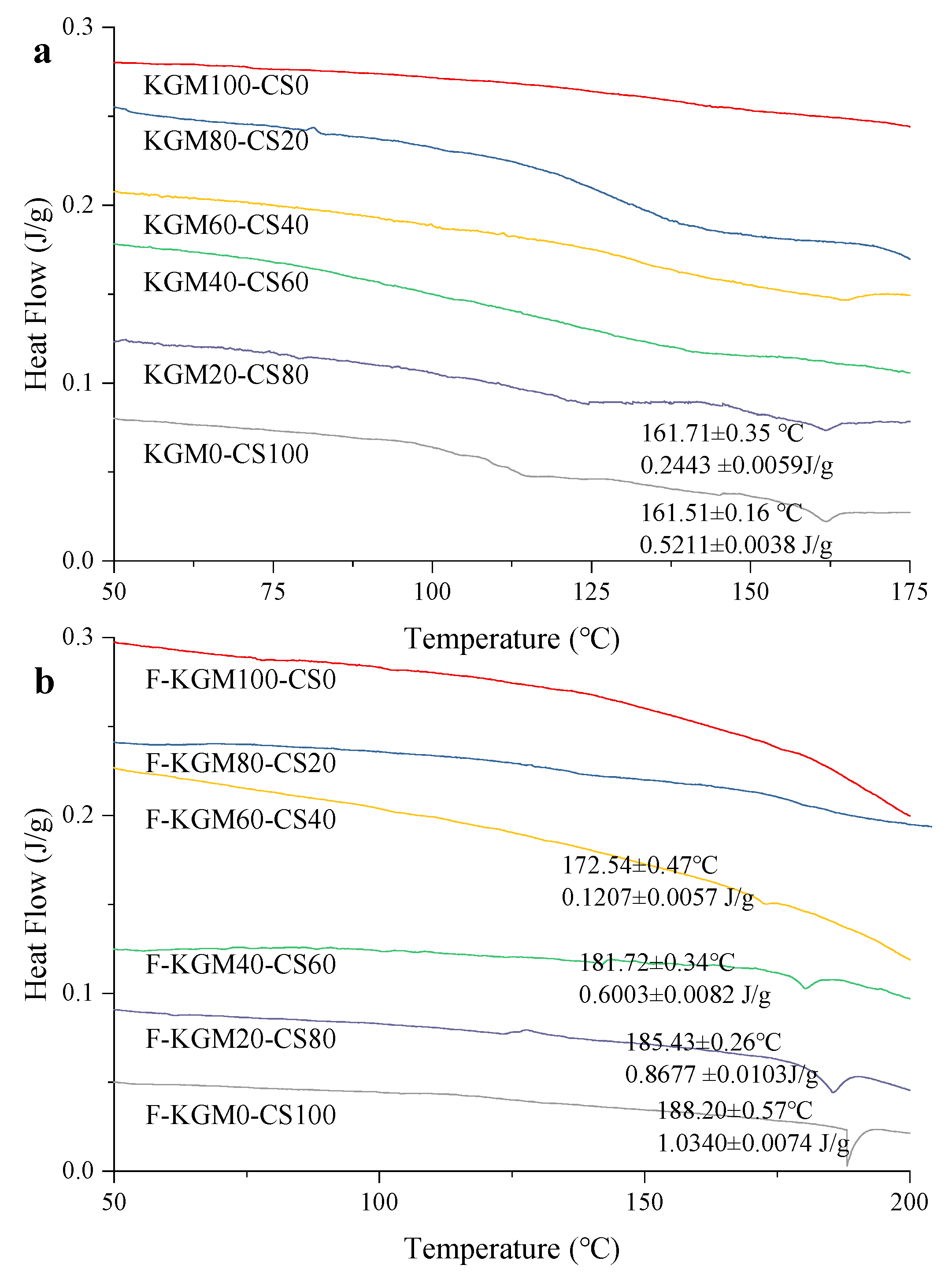

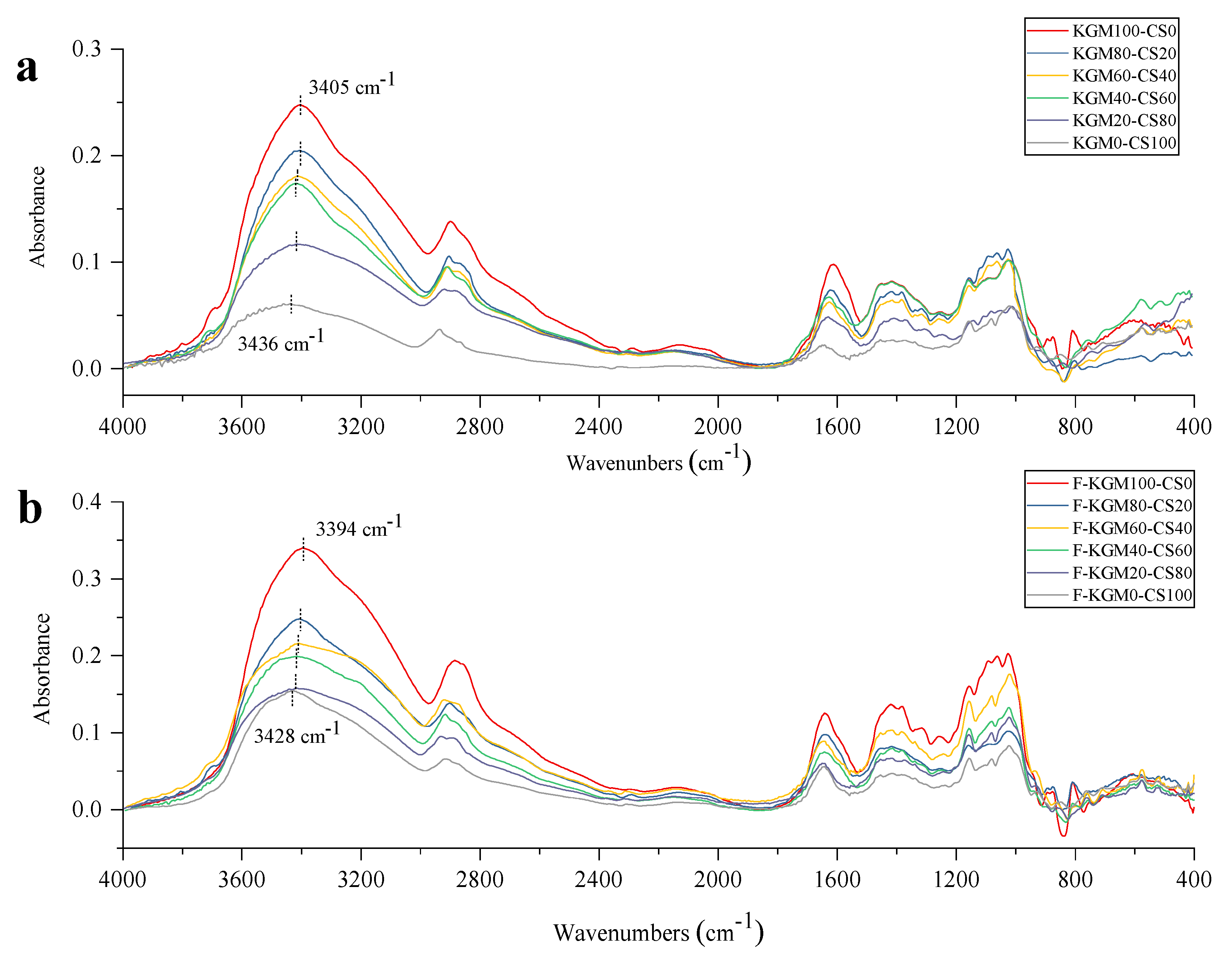
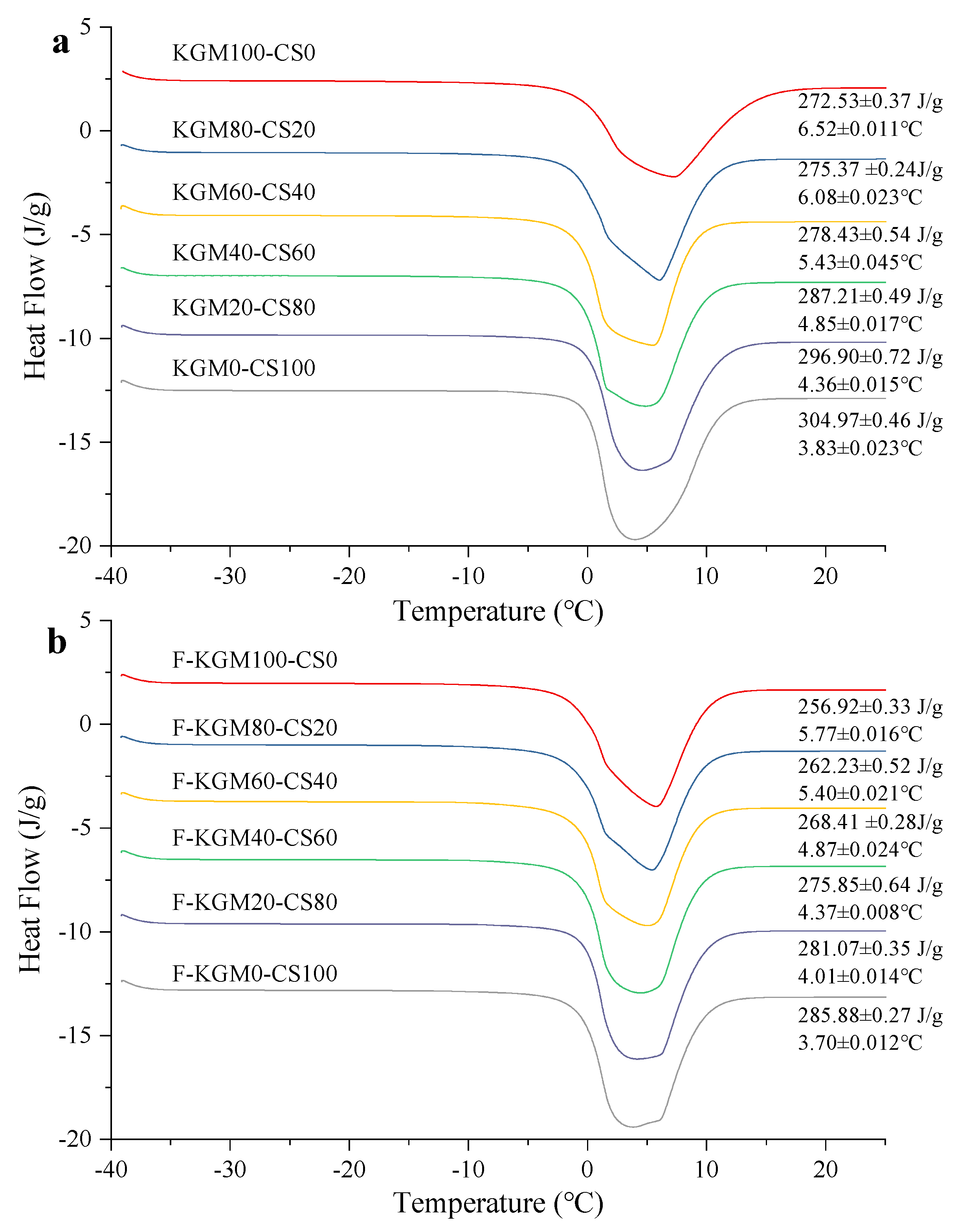

| KGM/CS Ratio | Crystallinity of KGM–CS Gels (%) | Crystallinity of F–KGM–CS Gels (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 100/0 | 19.8 ± 0.07 | 20.5 ± 0.03 |
| 80/20 | 19.5 ± 0.02 | 19.9 ± 0.05 |
| 60/40 | 19.3 ± 0.03 | 19.4 ± 0.09 |
| 40/60 | 18.6 ± 0.06 | 18.9 ± 0.07 |
| 20/80 | 17.9 ± 0.09 | 18.3 ± 0.13 |
| 0/100 | 16.5 ± 0.12 | 17.0 ± 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. The Effect of Different Ratios of Starch and Freeze–Thaw Treatment on the Properties of Konjac Glucomannan Gels. Gels 2023, 9, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020072
Wang Y, Liu J, Liu Y. The Effect of Different Ratios of Starch and Freeze–Thaw Treatment on the Properties of Konjac Glucomannan Gels. Gels. 2023; 9(2):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020072
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yangyang, Jie Liu, and Yawei Liu. 2023. "The Effect of Different Ratios of Starch and Freeze–Thaw Treatment on the Properties of Konjac Glucomannan Gels" Gels 9, no. 2: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020072
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, J., & Liu, Y. (2023). The Effect of Different Ratios of Starch and Freeze–Thaw Treatment on the Properties of Konjac Glucomannan Gels. Gels, 9(2), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9020072







