Evaluation of the Effect of Honey-Containing Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels on Wound Healing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. In Vitro Characterization of Chitosan/HA/Honey Hydrogels
2.1.1. Viscosity
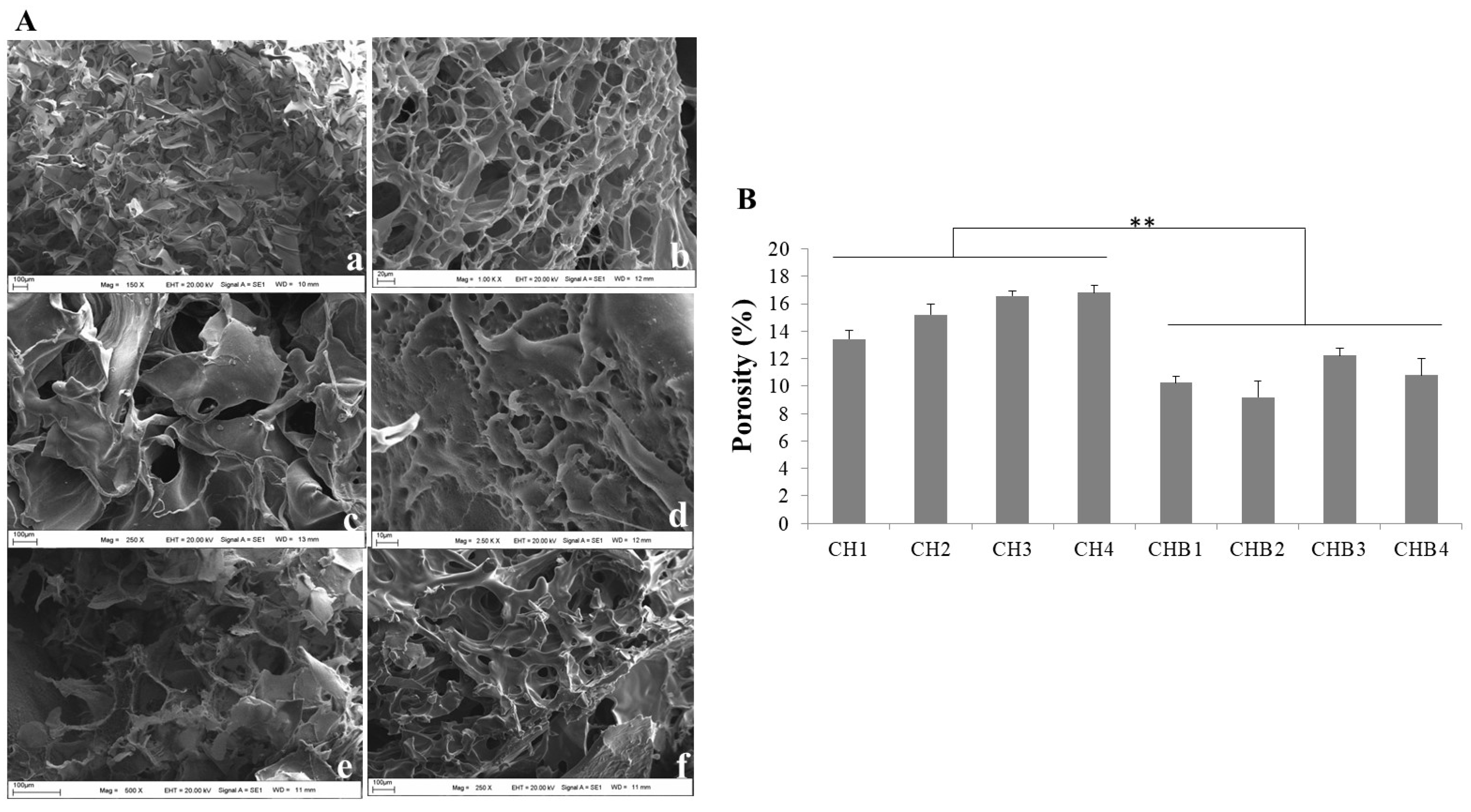
2.1.2. Morphology and Porosity
2.1.3. Swelling Ratio
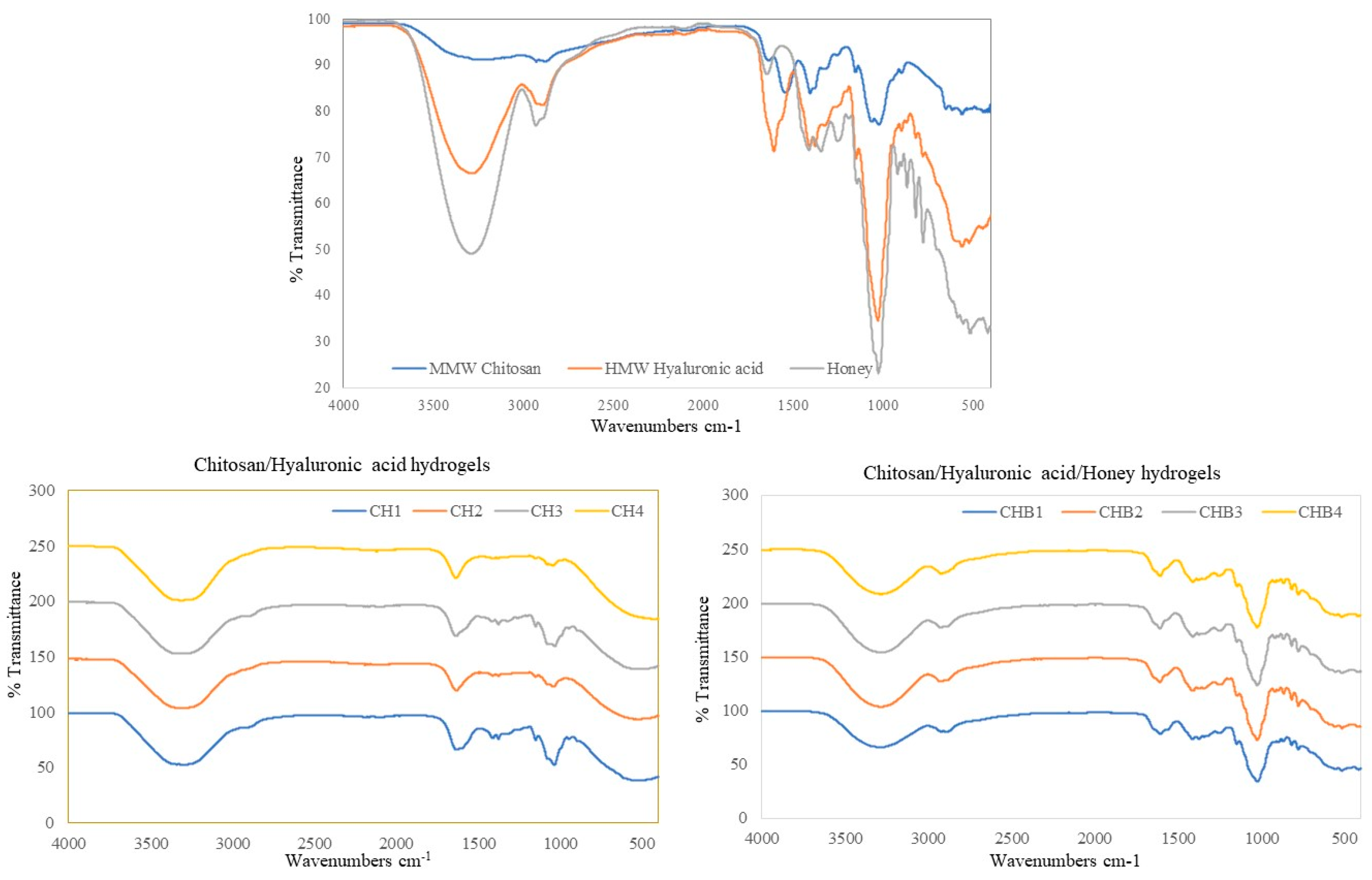
2.1.4. FT-IR Analyses
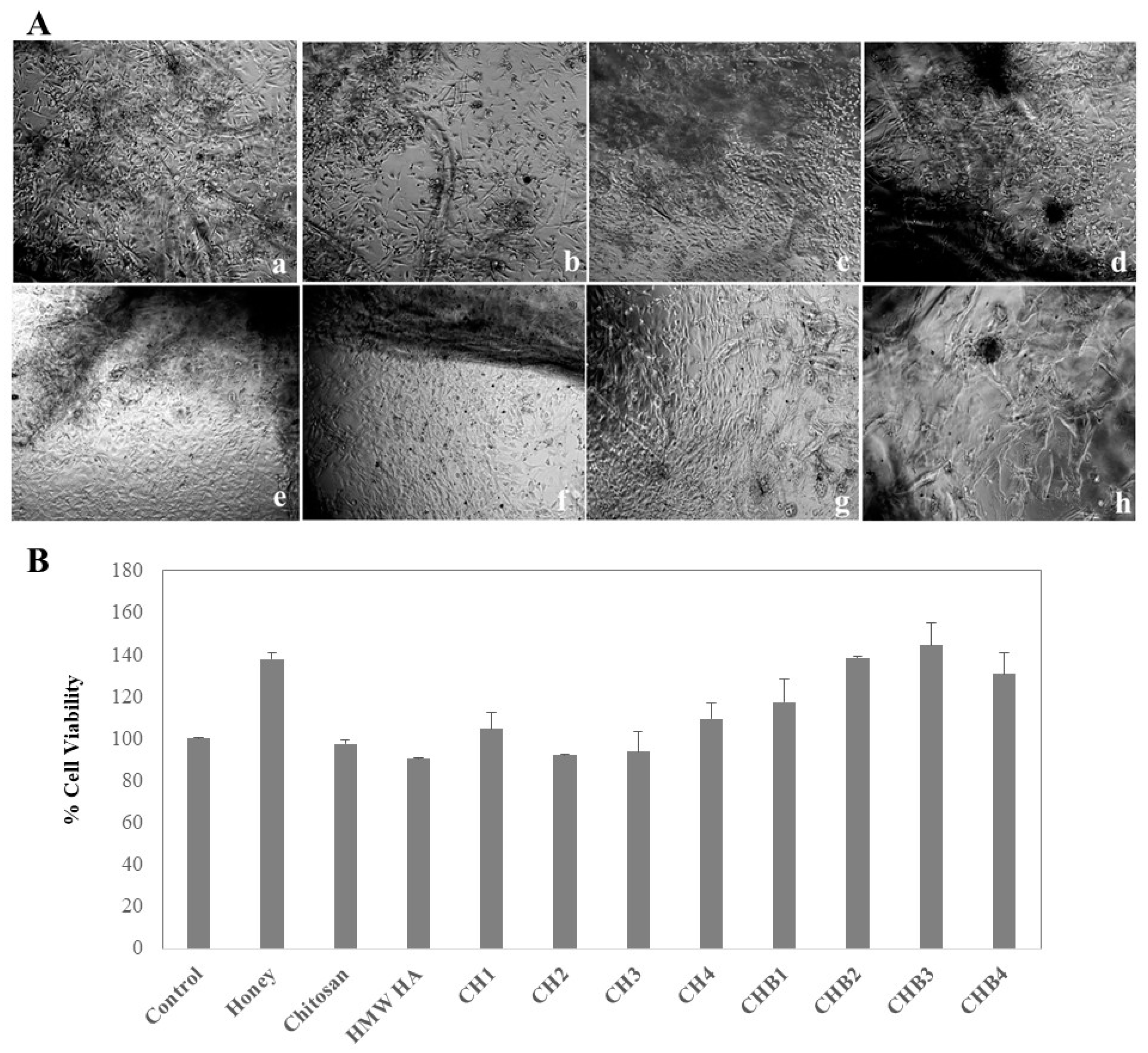
2.1.5. Cell Attachment of Hydrogels, Cell Viability, and Proliferation
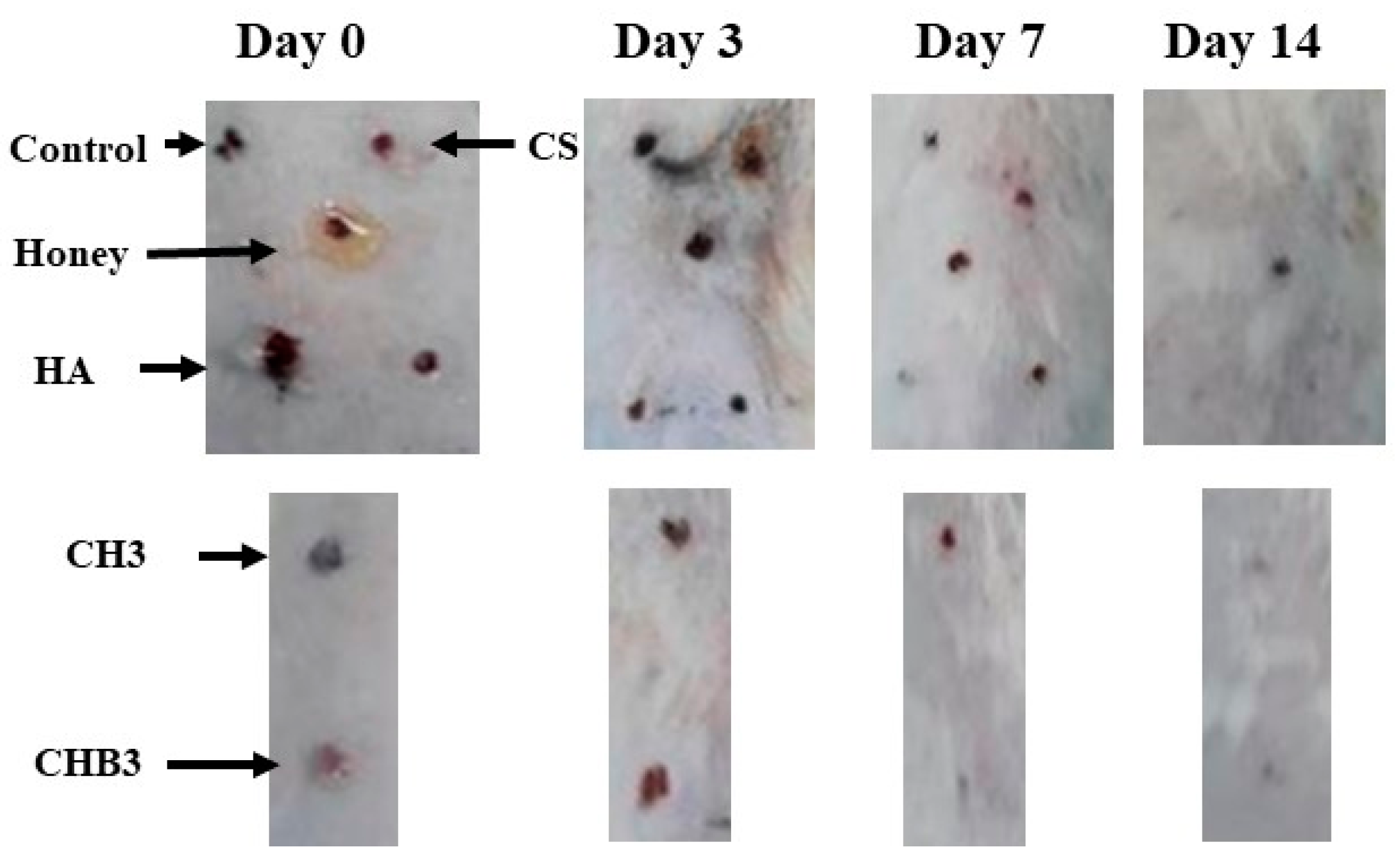
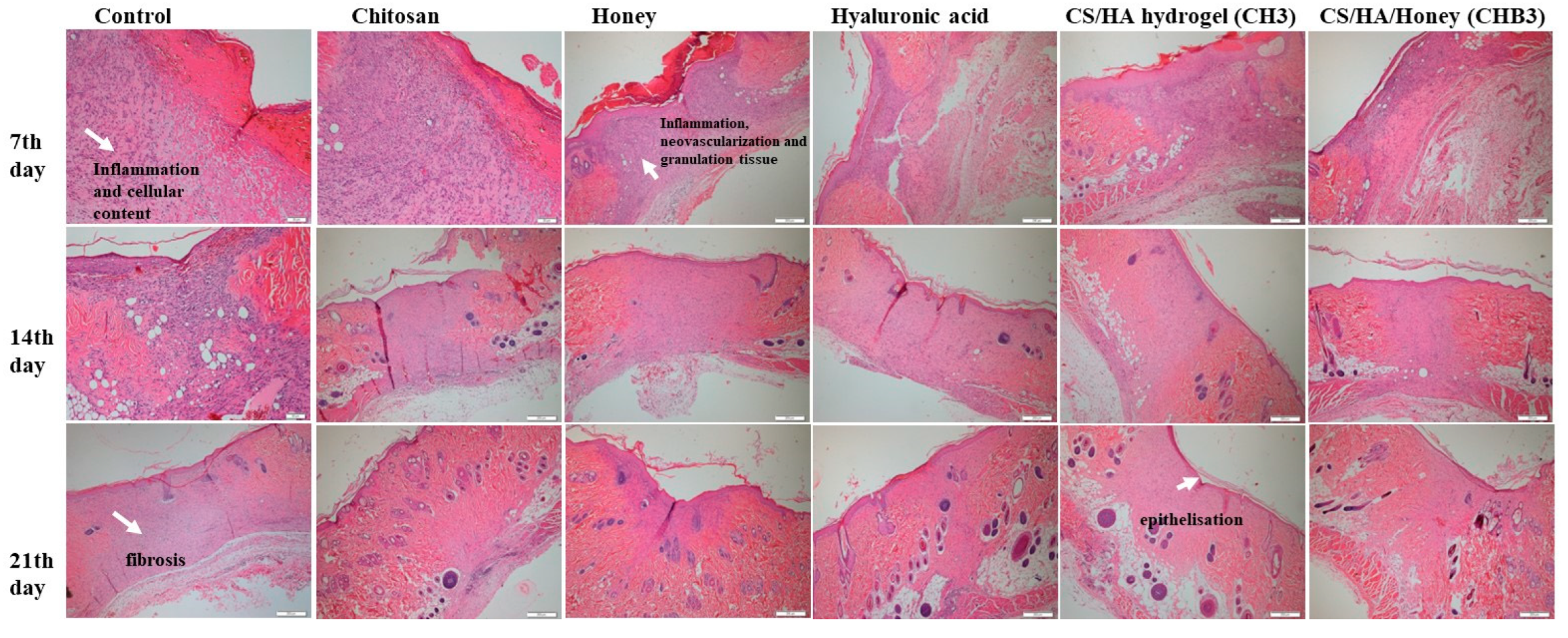
2.1.6. In Vivo Wound Healing
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid-Honey Hydrogels
4.2.2. Viscosity Study
4.2.3. Morphology Study
4.2.4. Porosity Measurements of Hydrogels
4.2.5. Determination of Water Content
4.2.6. Swelling Control
4.2.7. Ph Sensitivity Study
4.2.8. Characterization of Hydrogels by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.2.9. Adhesion of Cells to Hydrogels and the Effect on Proliferation
4.2.10. In vivo studies
4.2.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.C.; Xiao, C.; Tan, H.P.; Hu, X.H. Covalently crosslinked hyaluronic acid-chitosan hydrogel containing dexamethasone as an injectable scaffold for soft tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, S.; Sivashanmugam, A.; Mohandas, A.; Janarthanan, R.; Iyer, S.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Injectable deferoxamine nanoparticles loaded chitosan-hyaluronic acid coacervate hydrogel for therapeutic angiogenesis. Colloid. Surf. B 2018, 161, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Patrulea, V.; Sublet, E.; Borchard, G.; Iyoda, T.; Kageyama, R.; Morita, A.; Seino, S.; Yoshida, H.; Jordan, O.; et al. Wound Healing Promotion by Hyaluronic Acid: Effect of Molecular Weight on Gene Expression and In Vivo Wound Closure. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight on Structural, Physical, Physico-Chemical, and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croisier, F.; Jérôme, C. Chitosan-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, S.H.; Narendrakumar, U.; Manjubala, I. Commercial hydrogels for biomedical applications. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiamingo, A.; Montembault, A.; Boitard, S.E.; Naemetalla, H.; Agbulut, O.; Delair, T.; Campana-Filho, S.P.; Menasché, P.; David, L. Chitosan Hydrogels for the Regeneration of Infarcted Myocardium: Preparation, Physicochemical Characterization, and Biological Evaluation. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xia, D.; Han, J.; Yuan, S.; Lin, H.; Zhao, C. Design and fabrication of porous chitosan scaffolds with tunable structures and mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuike, T.; Komoto, D.; Hashimoto, H.; Tamura, H. Preparation of chitosan hydrogel and its solubility in organic acids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita-López, M.L.; Fletes-Vargas, G.; Espinosa-Andrews, H.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, R. Physically cross-linked chitosan-based hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: A state-of-the-art review. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 145, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayitmazer, A.B.; Koksal, A.F.; Kilic Iyilik, E. Complex coacervation of hyaluronic acid and chitosan: Effects of pH, ionic strength, charge density, chain length and the charge ratio. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8605–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalevée, G.; David, L.; Montembault, A.; Blanchard, K.; Meadows, J.; Malaise, S.; Crépet, A.; Grillo, I.; Morfin, I.; Delair, T.; et al. Highly stretchable hydrogels from complex coacervation of natural polyelectrolytes. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6594–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, X.-K.; Xue, X.-T.; Wu, D.-Y. Hydrogel sheets of chitosan, honey and gelatin as burn wound dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Yao, Z.; Fang, Q.; Feng, L.; Guo, R.; Cheng, B. Preparation of Antimicrobial Hyaluronic Acid/Quaternized Chitosan Hydrogels for the Promotion of Seawater-Immersion Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibungu, C.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E. This Review Recent Advances in Chitosan and Alginate-Based Hydrogels for Wound Healing Application. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 681960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultankulov, B.; Berillo, D.; Sultankulova, K.; Tokay, T.; Saparov, A. Progress in the Development of Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Choi, B.; Hu, J.; Lee, M. Injectable chitosan hyaluronic acid hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4779–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Wei, G. Hyaluronan oligosaccharides promote excisional wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2010, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment Strategies for Infected Wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Javanbakht, S.; Asadi, N.; Ghorbani, M.; Milani, M.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Gholizadeh, P.; Akbarzadeh, A. Recent advances in honey-based hydrogels for wound healing applications: Towards natural therapeutics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kased, R.F.; Amer, R.I.; Attia, D.; Elmazar, M.M. Honey-based hydrogel: In vitro and comparative In vivo evaluation for burn wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Zohdi, R.; Abu Bakar Zakaria, Z.; Yusof, N.; Mohamed Mustapha, N.; Abdullah, M.N.H. Gelam (Melaleuca spp.) Honey-Based Hydrogel as Burn Wound Dressing. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 843025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfour, M.H.; Elmotasem, H.; Mostafa, D.M.; Salama, A.A.A. Chitosan based Pickering emulsion as a promising approach for topical application of rutin in a solubilized form intended for wound healing: In vitro and in vivo study. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, C.R.; Moreira-Teixeira, L.S.; Moroni, L.; Reis, R.L.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M.; Mano, J.F. Chitosan scaffolds containing hyaluronic acid for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part. C Methods 2011, 17, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, P.; Alves, P.; Valente, T.A.; Santos, R.; Correia, I.J.; Ferreira, P. Sodium hyaluronate/chitosan polyelectrolyte complex scaffolds for dental pulp regeneration: Synthesis and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhasmana, A.; Singh, L.; Roy, P.; Chandra Mishra, N. Honey incorporated antibacterial acellular dermal matrix for full-thickness wound healing. Ann. Biotechnol. 2018, 1, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Lee, G.-H.; Chou, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-P.; Wu, T.-H.; Lin, H.-R. Stimulation of wound healing by PU/hydrogel composites containing fibroblast growth factor-2. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tan, J.; Zhu, H.; Lin, G.; Yin, F.; Wang, L.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Yi, W. Development of kartogenin-conjugated chitosan–hyaluronic acid hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A.; Yar, M.; Azzahari, A.D.; Selvanathan, V.; Sonsudin, F.; Abouloula, C.N. pH Sensitive Hydrogels in Drug Delivery: Brief History, Properties, Swelling, and Release Mechanism, Material Selection and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira de Souza, T.; Malmonge, S.M.; Santos, A.R., Jr. Development of a chitosan and hyaluronic acid hydrogel with potential for bioprinting utilization: A preliminary study. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 36, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jadi, A.M.; Kanyan Enchang, F.; Mohd Yusoff, K. The effect of Malaysian honey and its major components on the proliferation of cultured fibroblasts. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 44, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Vyver, M.; Boodhoo, K.; Frazier, T.; Hamel, K.; Kopcewicz, M.; Levi, B.; Maartens, M.; Machcinska, S.; Nunez, J.; Pagani, C.; et al. Histology Scoring System for Murine Cutaneous Wounds. Stem Cells Dev. 2021, 30, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Ren, J.; Chen, G.; Li, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, G.; Gu, G.; Li, J. Injectable in situ cross-linking chitosan-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for abdominal tissue regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majtan, J. Honey: An immunomodulator in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, W.A.; Azzazy, H.M.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Honey/Chitosan Nanofiber Wound Dressing Enriched with Allium sativum and Cleome droserifolia: Enhanced Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6379–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusto, G.; Vercelli, C.; Comino, F.; Caramello, V.; Tursi, M.; Gandini, M. A new, easy-to-make pectin-honey hydrogel enhances wound healing in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. Structural and biological investigation of chitosan/hyaluronic acid with silanized-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as an injectable reinforced interpenetrating network hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N.; Erum, A.; Zaman, M.; Tulain, U.R.; Shoaib, Q.U.; Majeed, A.; Rasool, M.F.; Imran, I.; Alshehri, S.; Noorani, B.; et al. pH-Responsive Nanocomposite Based Hydrogels for the Controlled Delivery of Ticagrelor; In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 6345–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, O.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.G.; Keidar, M. Biomimetic three-dimensional nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite and magnetically synthesized single-walled carbon nanotube chitosan nanocomposite for bone regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2087–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şalva, E.; Akbuğa, J. The effects to GM-CSF expression and fibroblast proliferation of pGM-CSF containing chitosan/PVP hydrogels. Marmara Pharm. J. 2017, 21, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yang, H.; Yang, J.; Peng, M.; Hu, J. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/gelatin/PVA hydrogel for wound dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, D.; Azamthulla, M.; Santhosh, S.; Dath, G.; Ghosh, A.; Natholia, R.; Anbu, J.; Teja, B.V.; Muzammil, K.M. Development and characterization of chitosan-based hydrogels as wound dressing materials. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
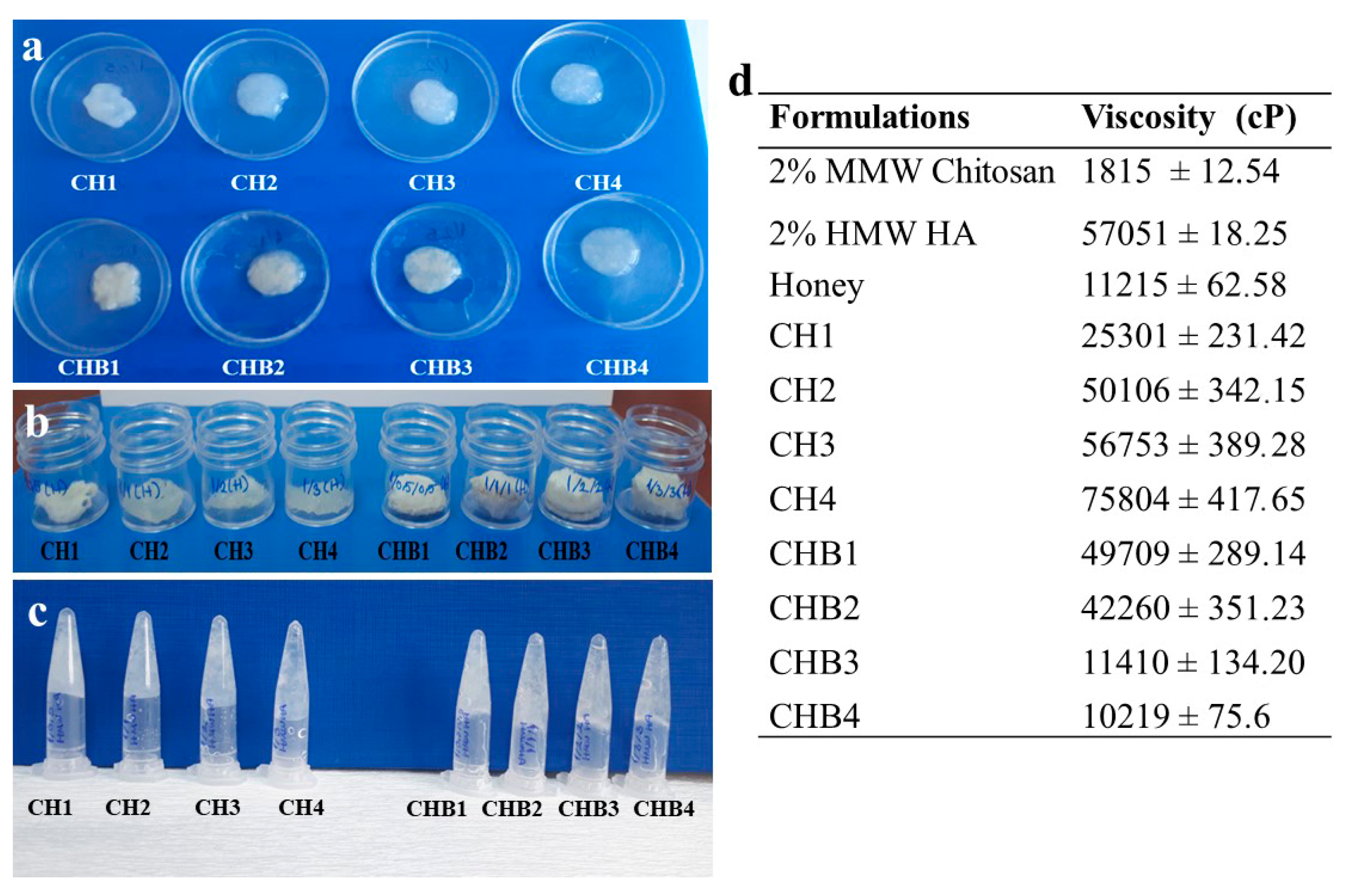


| Formulations | HMW Hyaluronic Acid | MMW Chitosan | Honey | CS/HA CS/HA/Honey (w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH1 | 1% | 2% | 1/0.5 | |
| CH2 | 2% | 1/1 | ||
| CH3 | 4% | 1/2 | ||
| CH4 | 6% | 1/3 | ||
| CHB1 | 1% | 1% | 1/0.5/0.5 | |
| CHB2 | 2% | 2% | 1/1/1 | |
| CHB3 | 4% | 4% | 1/2/2 | |
| CHB4 | 6% | 6% | 1/3/3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Şalva, E.; Akdağ, A.E.; Alan, S.; Arısoy, S.; Akbuğa, F.J. Evaluation of the Effect of Honey-Containing Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels on Wound Healing. Gels 2023, 9, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110856
Şalva E, Akdağ AE, Alan S, Arısoy S, Akbuğa FJ. Evaluation of the Effect of Honey-Containing Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels on Wound Healing. Gels. 2023; 9(11):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110856
Chicago/Turabian StyleŞalva, Emine, Ahmet Enes Akdağ, Saadet Alan, Sema Arısoy, and Fatma Jülide Akbuğa. 2023. "Evaluation of the Effect of Honey-Containing Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels on Wound Healing" Gels 9, no. 11: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110856
APA StyleŞalva, E., Akdağ, A. E., Alan, S., Arısoy, S., & Akbuğa, F. J. (2023). Evaluation of the Effect of Honey-Containing Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels on Wound Healing. Gels, 9(11), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110856