An Eco-Friendly Antheraea Pernyi Silk Gland Protein/Sodium Alginate Multiple Network Hydrogel as Potential Drug Release Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis Drug Loaded Hydrogels
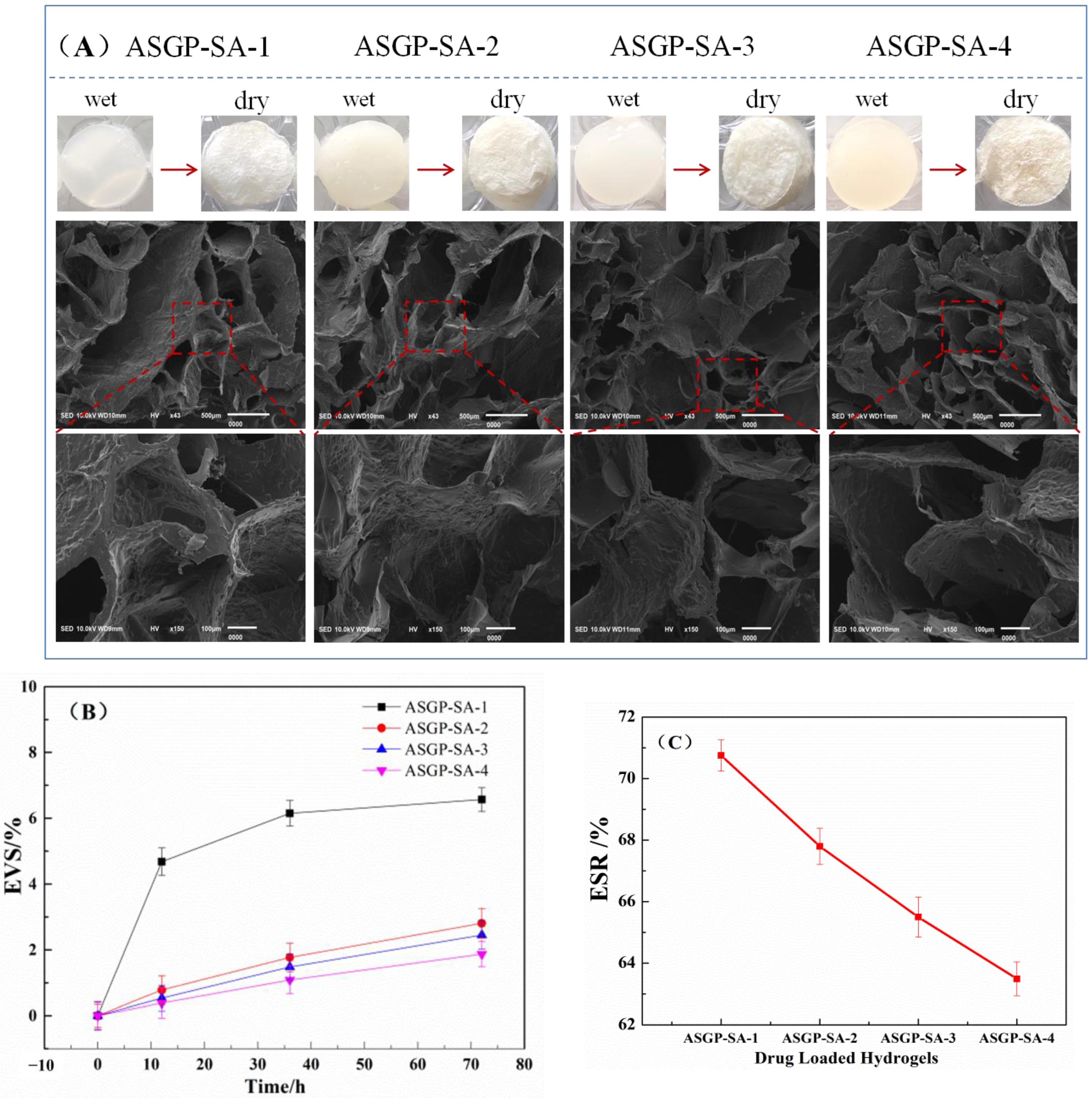
2.2. Morphological Observation
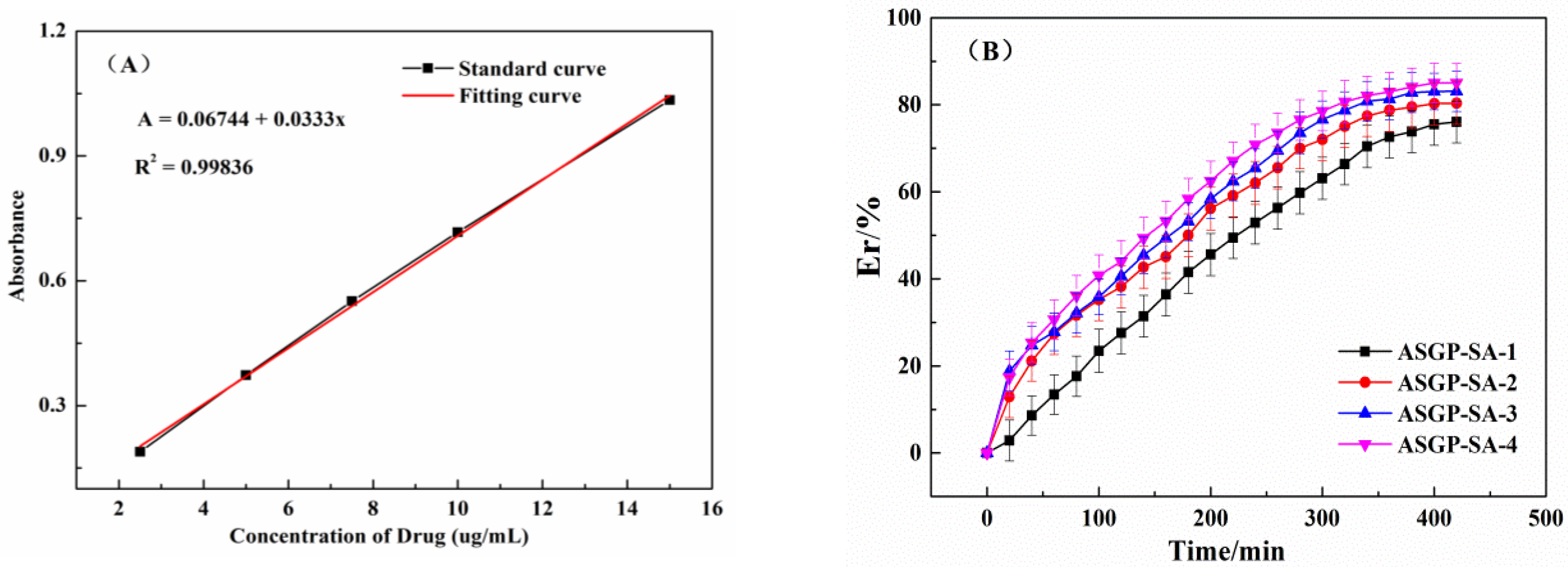
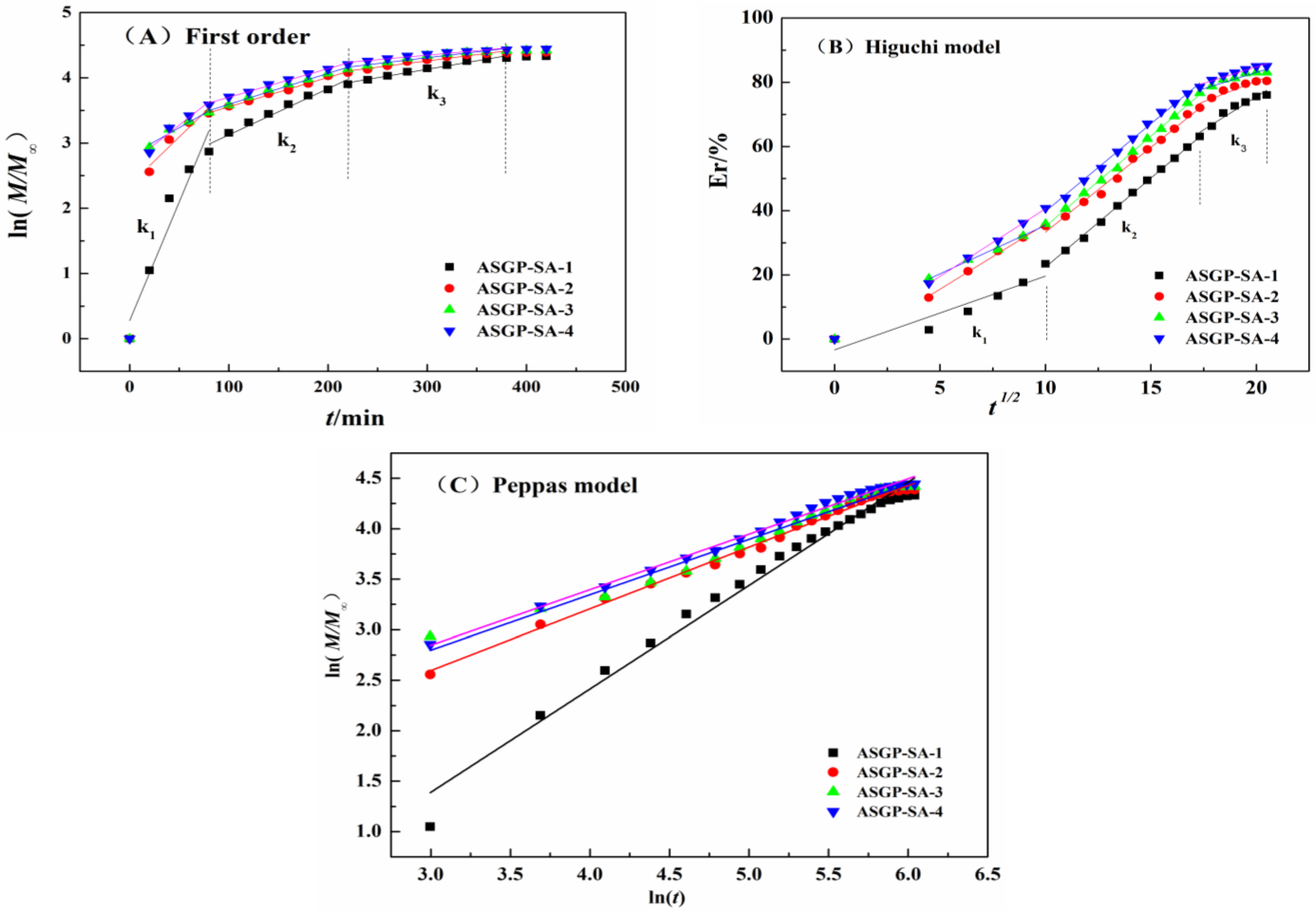
2.3. In Vitro Drug Release of Drug Loaded Hydrogels
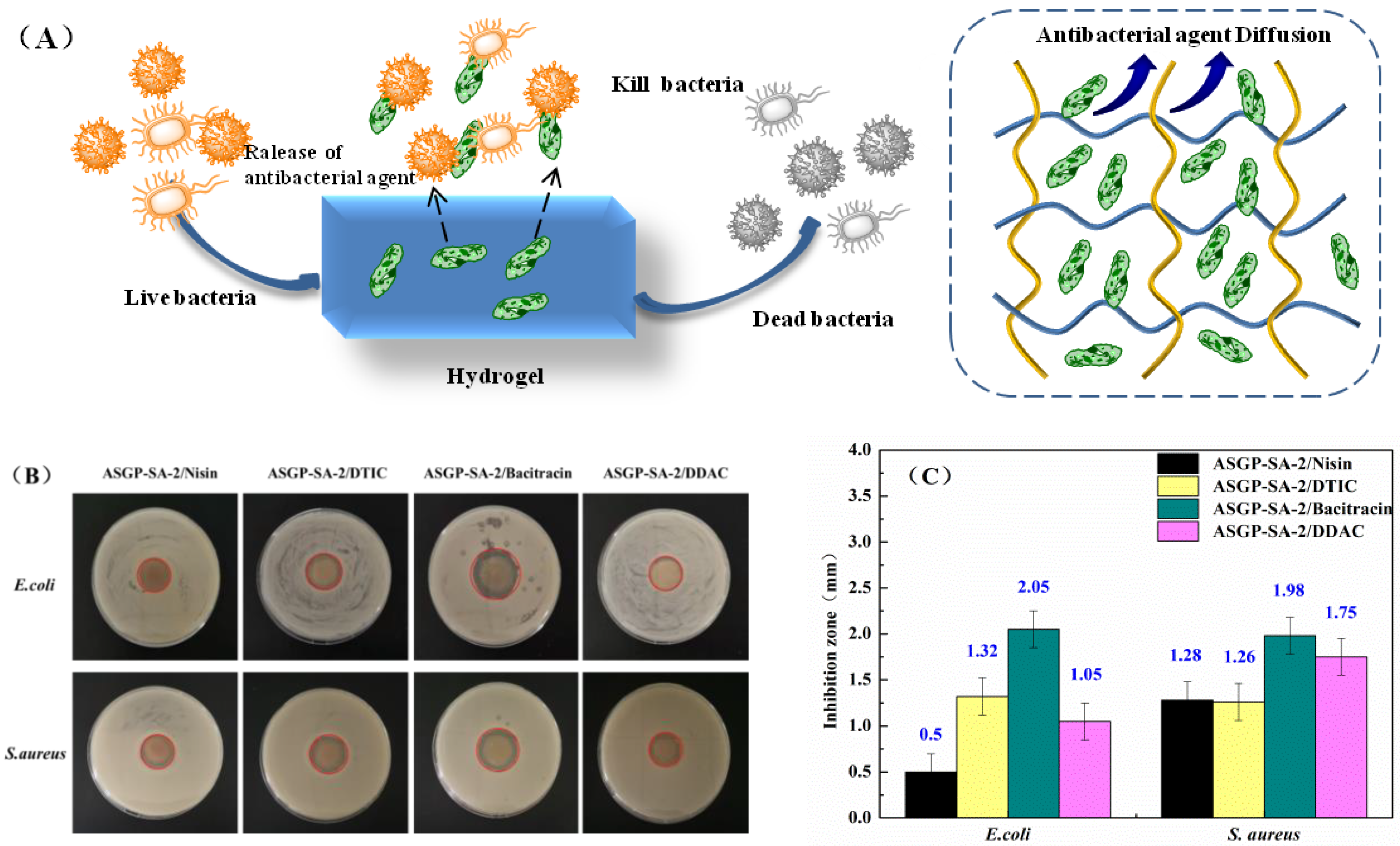
2.4. Anti-Bacterial Activity Assay
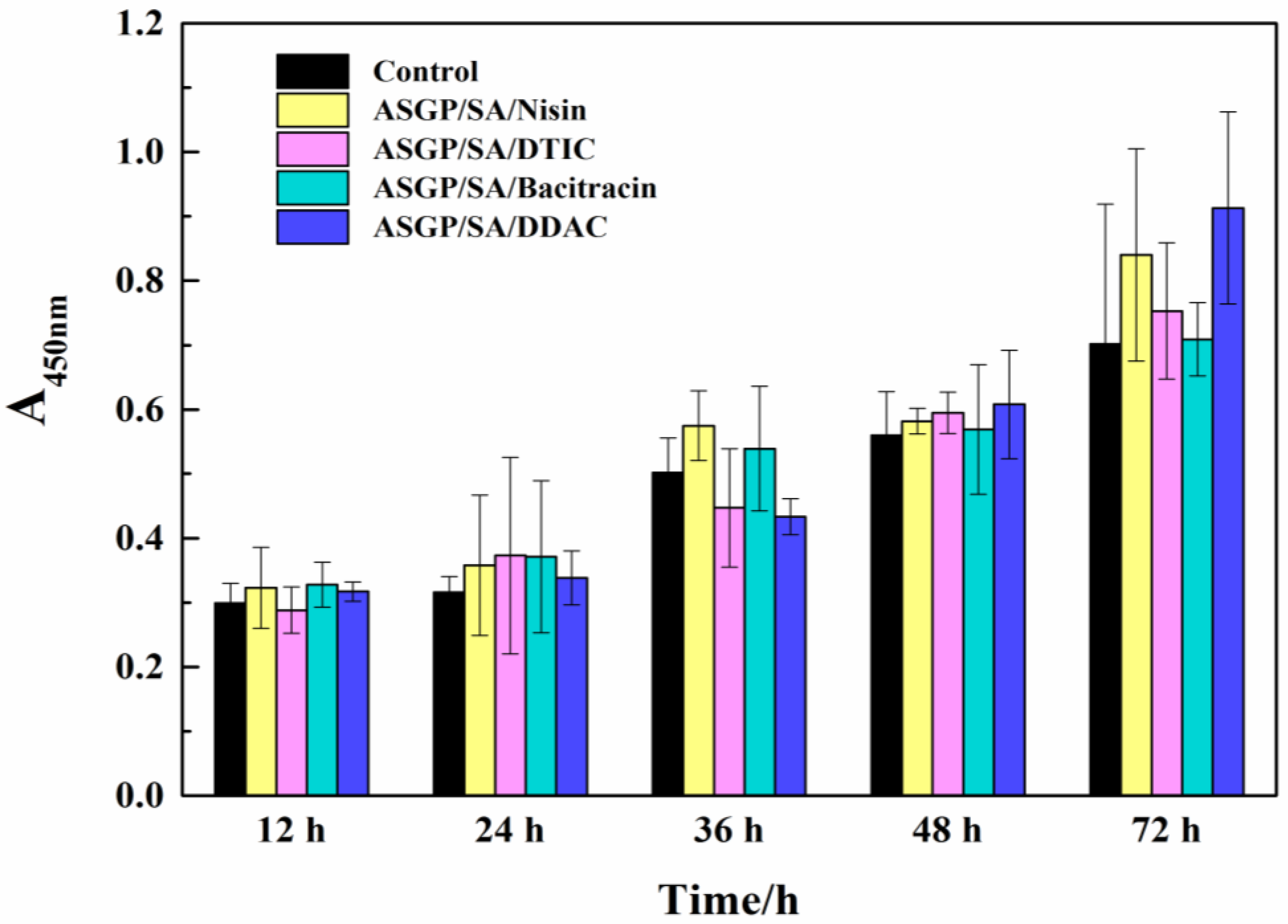
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Extraction of Antheraea pernyi Silk Gland Protein
4.3. Preparation of Drug Loaded Bio-Hydrogels
4.4. Preparation of Antibacterial Drug Loaded Bio-Hydrogels
4.5. Morphology of Dried Drug-Loaded Hydrogel
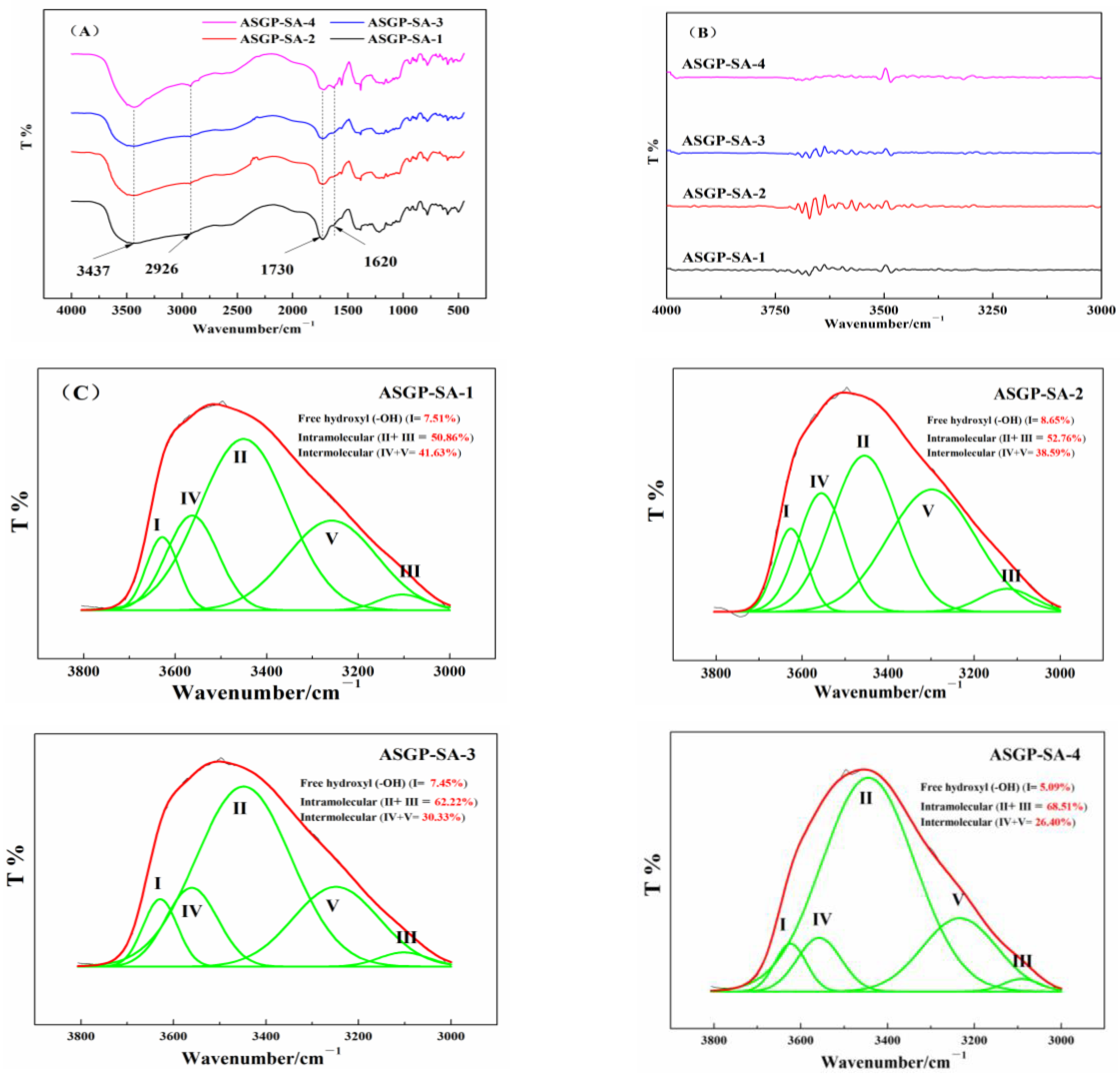
4.6. FT-IR Analysis
4.7. Swelling Ratio and Volume Stability Test
4.8. Anti-Bacterial Activity
4.9. UV-Vis Assay
4.10. CCK-8 Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, H.-T.; Zhao, J.-M.; Cao, M.; Wang, S.-D. Review on Fabrication and Application of Regenerated Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin Materials. Autex Res. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Dan, A.K.; Sengupta, A.; Das, M.; Bindhani, B.K.; Das, D.; Parhi, P.K. Extraction of Silk Fibroin with Several Sericin Removal Processes and its Importance in Tissue Engineering: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 2222–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Kurokawa, M.; Asakura, T. Design of silk-like biomaterials inspired by mussel-adhesive protein. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askarzadeh, N.; Nazarpak, M.H.; Mansoori, K.; Farokhi, M.; Gholami, M.; Mohammadi, J.; Mottaghitalab, F. Bilayer Cylindrical Conduit Consisting of Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers and DSC Cross-Linked Sodium Alginate Hydrogel to Bridge Peripheral Nerve Gaps. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, e2000149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Singh, N. Silk fibroin-alginate based beads for human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation in 3D. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4687–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Choi, D.; Hong, J. Multilayered Controlled Drug Release Silk Fibroin Nanofilm by Manipulating Secondary Structure. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3096–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Muthana, M.; Mukherjee, J.; Falconer, R.J.; Biggs, C.A.; Zhao, X. Magnetic-Silk Core–Shell Nanoparticles as Potential Carriers for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, A.M.; Löwik, W.D.; Hest, J.V. Peptide- and protein-based hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, S.; Kundu, S.C. Silk protein-based hydrogels: Promising advanced materials for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Han, X.; Lu, Q.; Qi, X.; Guo, C.; Wu, X. Rhein incorporated silk fibroin hydrogels with antibacterial anti-inflammatory efficacy to promote healing of bacteria-infected burn, w.o.u.n.d.s. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 201, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Davoudi, Z.; Xing, X.; Yu, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, H.; Wang, Q. Advanced Silk Fibroin Biomaterials for Cartilage Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2704–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Damoogh, S.; Reis, R.L.; Kundu, S.C.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Farokhi, M. Dual drug delivery system based on pH-sensitive silk fibroin/alginate nanoparticles entrapped in PNIPAM hydrogel for treating severe infected burn wound. Biofabrication 2020, 13, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Takano, R.; Hirabayashi, K. Production of soluble fibroin powder by hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid and physical properties. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericol. 2010, 60, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.S.; Ajiteru, O.; Lee, O.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.W.; Park, J.W.; Kim, K.Y.; Choi, K.Y.; et al. Biocompatible fluorescent silk fibroin bioink for digital light processing 3D printing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Ki, C.S.; Oh, H.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C. Molecular weight distribution and solution properties of silk fibroins with different dissolution conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. Effect of Various Dissolution Systems on the Molecular Weight of Regenerated Silk Fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Duan, L.; Sun, J.; Gou, S.; Chen, F.; Liang, Y.; Dai, F.; Xiao, B. Oral nanotherapeutics based on Antheraea pernyi silk fibroin for synergistic treatment of ulcerative colitis. Biomaterials 2022, 282, 121410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. Non-mulberry silk gland fibroin protein 3-D scaffold for enhanced differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into osteocytes. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2579–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, B.C.; Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. Silk gland sericin protein membranes: Fabrication and characterization for potential biotechnological applications. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 144, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augst, A.D.; Kong, H.J.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate hydrogels as biomaterials. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 6, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidarra, S.J.; Barrias, C.C.; Granja, P.L. Injectable alginate hydrogels for cell delivery in tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1646–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Wang, T.; Feng, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Cui, L.; Yin, J. Injectable In Situ Self-Cross-Linking Hydrogels Based on Poly(l-glutamic acid) and Alginate for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 4495–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikka, M.P.; Rao, S.V.; Garg, S. Silk biomaterial for skeletal tissue engineering. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2022, 47, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.-X.; Cheng, D.-H.; Lu, Y.-H. Eco-Friendly Bio-Hydrogels Based on Antheraea pernyi Silk Gland Protein for Cell and Drug Delivery. Gels 2022, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Cheng, J.; Wu, N.; Shi, W.; Zhao, F.; Shao, Z.; Meng, Q.; Chen, H.; et al. Cryo-self-assembled silk fibroin sponge as a biodegradable platform for enzyme-responsive delivery of exosomes. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 8, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Wang, Y.; Dai, W. Silk fibroin-based biomaterials for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierholz, J.M.; Yücel, N.; Rump, A.; Beuth, J.; Pulverer, G. Antiinfective and encrustation-inhibiting materials—Myth and facts. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2002, 19, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Cervantes, S.D.; Pagán, A.; Candel, M.J.; Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Cenis, J.L. Silkworm Gut Fibres from Silk Glands of Samia cynthia ricini—Potential Use as a Scaffold in Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M.H.B.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; Yu, L. Combination of sodium alginate-based coating with L-cysteine and citric acid extends the shelf-life of fresh-cut lotus root slices by inhibiting browning and microbial growth. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 175, 111502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, N.; Sone, I.; Walsh, J.L.; Sivertsvik, M.; Fernández, E.N. Effect of citric acid and plasma activated water on the functional properties of sodium alginate for potential food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 29, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, B.; Peng, Y.; Ran, R. Fe3+-citric acid/sodium alginate hydrogel: A photo-responsive platform for rapid water purification. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.A.; Gosavi, P.; Athauda, T.J.; Ozer, R.R. In situ citric acid crosslinking of alginate/polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2013, 112, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zeng, S.; Yu, T.; Zhou, C. Synergistic effects of citric acid-sodium alginate on physicochemical properties of α-tricalcium phosphate bone cement. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Chu, W.B.; Jiang, N.; He, L. Influence of Hydrogen Bond and Sodium Alginate on Bovine Serum Albumin Adhesion on ZnSe Surface. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 21072–21078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Dang, G.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Y. Sodium alginate/feather keratin-g-allyloxy polyethylene glycol composite phase change fiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shen, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y. Low-temperature crosslinking of proteins using non-toxic citric acid in neutral aqueous medium: Mechanism and kinetic study. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 74, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, A.; Qiu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Bian, S.; Zeng, F.; Jin, Z. A combined enzymatic and ionic cross-linking strategy for pea protein/ sodium alginate double-network hydrogel with excellent mechanical properties and freeze-thaw stability. Food Hydrocolloid. 2022, 131, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Singh, S.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, P. Trivalent ion cross-linked pH sensitive alginate-methyl cellulose blend hydrogel beads from aqueous template. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 57, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Dang, G.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Y. A sodium alginate/feather keratin composite fiber with skin-core structure as the carrier for sustained drug release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, Z. Effects of cellulose nanocrystal polymorphs and initial state of hydrogels on swelling and drug release behavior of alginate-based hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 4401–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.K.; Pradhan, R.; Gupta, B.; Choi, J.Y.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Preparation and characterization of alginate gel core-lipid nanocapsules for co-delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic anti-cancer drugs. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 44, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwa, R.; Zandraa, O.; Capáková, Z.; Saha, N.; Sáha, P. Effect of Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles Impregnated Bacterial Cellulose on Overall Properties of Alginate/Casein Hydrogels: Potential Injectable Biomaterial for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyianta, A.J.; Castellano, M.; Dorris, M.; Williams, R.L.; Vicini, S. The effects of morpholine pre-treated and carboxymethylated cellulose nanofibrils on the properties of alginate-based hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A. Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1985, 60, 110–111. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Roseman, T.J.; Higuchi, W.I. Release of medroxyprogesterone acetate from a silicone polymer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 59, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, J.; Spasojević, J.; Radosavljević, A.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Đurić, M.; Kačarević-Popović, Z.; Popović, S. In vitro silver ion release kinetics from nanosilver/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels synthesized by gamma irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delves-Broughton, J.; Blackburn, P.; Evans, R.J.; Hugenholtz, J. Applications of the bacteriocin, nisin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1996, 69, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | EN (%) | DL (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| ASGP-SA-1 | 70.25 ± 1.05 | 450.3 ± 10.4 |
| ASGP-SA-2 | 72.81 ± 1.23 | 432.5 ± 12.7 |
| ASGP-SA-3 | 71.52 ± 1.20 | 425.3 ± 13.5 |
| ASGP-SA-4 | 72.27 ± 1.52 | 402.5 ± 14.3 |
| First Order | Higuchi Model | Korsmeyer Peppas Model | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R12 | k1 | R22 | k2 | R32 | k3 | R12 | k1 | R22 | k2 | R32 | k3 | R2 | n | |
| ASGP-SA-1 | 0.84 | 2.30 | 0.99 | 5.54 | 0.93 | 2.51 | 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.98 | 0.007 | 0.99 | 0.003 | 0.98 | 1.02 |
| ASGP-SA-2 | 0.99 | 2.41 | 0.99 | 5.28 | 0.90 | 2.55 | 0.90 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.004 | 0.98 | 0.002 | 0.99 | 0.61 |
| ASGP-SA-3 | 0.99 | 3.01 | 0.99 | 5.62 | 0.90 | 2.04 | 0.94 | 0.01 | 0.98 | 0.004 | 0.96 | 0.002 | 0.98 | 0.55 |
| ASGP-SA-4 | 0.99 | 4.21 | 0.99 | 5.46 | 0.94 | 2.04 | 0.94 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.004 | 0.94 | 0.001 | 0.99 | 0.55 |
| Sample | ASGP/(g/mL) | SA/(g/mL) | MFH/(g/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASGP-SA-1 | 2 | 8 | 0.15 |
| ASGP-SA-2 | 4 | 6 | 0.15 |
| ASGP-SA-3 | 6 | 4 | 0.15 |
| ASGP-SA-4 | 8 | 2 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wang, B.-X.; Cheng, D.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Ji, X.-b.; Guo, J.; Lu, Y.-H. An Eco-Friendly Antheraea Pernyi Silk Gland Protein/Sodium Alginate Multiple Network Hydrogel as Potential Drug Release Systems. Gels 2023, 9, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010004
Li J, Wang B-X, Cheng D-H, Zhang Y, Yao Q, Ji X-b, Guo J, Lu Y-H. An Eco-Friendly Antheraea Pernyi Silk Gland Protein/Sodium Alginate Multiple Network Hydrogel as Potential Drug Release Systems. Gels. 2023; 9(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jia, Bo-Xiang Wang, De-Hong Cheng, Yue Zhang, Qiang Yao, Xin-bin Ji, Jing Guo, and Yan-Hua Lu. 2023. "An Eco-Friendly Antheraea Pernyi Silk Gland Protein/Sodium Alginate Multiple Network Hydrogel as Potential Drug Release Systems" Gels 9, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010004
APA StyleLi, J., Wang, B.-X., Cheng, D.-H., Zhang, Y., Yao, Q., Ji, X.-b., Guo, J., & Lu, Y.-H. (2023). An Eco-Friendly Antheraea Pernyi Silk Gland Protein/Sodium Alginate Multiple Network Hydrogel as Potential Drug Release Systems. Gels, 9(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010004







