HyperArcTM Dosimetric Validation for Multiple Targets Using Ionization Chamber and RT-100 Polymer Gel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. End-to-End Tests with Ionization Chamber
2.2. End-to-End Tests with Polymer Gels
3. Results
3.1. Ionization Chamber Measurements
3.2. Polymer Gel Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kraft, J.; Zindler, J.; Minniti, G.; Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N. Stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases. Curr. Treat. Option. Neurol. 2019, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Tago, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Toyoda, T.; Hatano, K.; Kenjyo, M.; Oya, N.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kased, N.; Huang, K.; Nakamura, J.L.; Sahgal, A.; Larson, D.A.; McDermott, M.W.; Sneed, P.K. Gamma knife radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: The UCSF experience. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 86, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, B.E. Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas: Indications and results. Neurosurg. Focus 2003, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldebawy, E.; Mousa, A.; Reda, W.; Elgantiry, M. Stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy in benign intracranial meningioma. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 23, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vermeulen, S.; Kim, E. The stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of common benign brain tumors: Pituitary adenomas, vestibular schwannoma and meningiomas. Transl. Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, B.C.; Hamlyn, P.J.; Zakrzewska, J.M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for primary trigeminal neuralgia: State of the evidence and recommendations for future reports. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benedict, S.H.; Yenice, K.M.; Followill, D.; Galvin, J.M.; Hinson, W.; Kavanagh, B.; Keall, P.; Lovelock, M.; Meeks, S.; Papiez, L.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: The report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4078–4101, Erratum in Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahgal, A.; Ma, L.; Chang, E.; Shiu, A.; Larson, D.A.; Laperriere, N.; Yin, F.F.; Tsao, M.; Menard, C.; Basran, P.; et al. Advances in technology for intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 8, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kocher, M.; Wittig, A.; Piroth, M.D.; Treuer, H.; Seegenschmiedt, H.; Ruge, M.; Grosu, A.L.; Guckenberger, M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases. A report of the DEGRO Working Group on Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergalasova, I.; Liu, H.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Nie, K.; Shi, W.; Teo, B.K.; Yu, Y.; Yue, N.J.; et al. Multi-institutional dosimetric evaluation of modern-day stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) treatment options for multiple brain metastases. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, F.; Fiorentino, A.; Gregucci, F.; Corradini, S.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Romano, L.; Riley, K.O.; Markert, J.M.; Bredel, M.; Fiveash, J.B. First experience and clinical results using a new non-coplanar mono-isocenter technique (HyperArc™) for Linac-based VMAT radiosurgery in brain metastases. J. Cancer Res. Clin. 2019, 145, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popple, R.A.; Brown, M.H.; Thomas, E.M.; Willey, C.D.; Cardan, R.A.; Covington, E.L.; Riley, K.O.; Markert, J.M.; Bredel, M.; Fiveash, J.B. Transition from manual to automated planning and delivery of volumetric modulated arc therapy stereotactic radiosurgery: Clinical, dosimetric, and quality assurance results. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 11, e163–e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, R.; Naccarato, S.; Mazzola, R.; Ricchetti, F.; Corradini, S.; Fiorentino, A.; Alongi, F. Linac-based VMAT radiosurgery for multiple brain lesions: Comparison between a conventional multi-isocenter approach and a new dedicated mono-isocenter technique. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohira, S.; Ueda, Y.; Akino, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Masaoka, A.; Hirata, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Koizumi, M.; Teshima, T. HyperArc VMAT planning for single and multiple brain metastases stereotactic radiosurgery: A new treatment planning approach. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, T. Clinical three-dimensional Dosimetry in Modern Radiation Therapy. J. Med. Phys. 2019, 44, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, L.; Andratschke, N.; Blanck, O.; Brunner, T.B.; Combs, S.E.; Grosu, A.L.; Moustakis, C.; Schmitt, D.; Baus, W.W.; Guckenberger, M. ICRU report 91 on prescribing, recording, and reporting of stereotactic treatments with small photon beams: Statement from the DEGRO/DGMP working group stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2019, 195, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parwaie, W.; Refahi, S.; Ardekani, M.A.; Farhood, B. Different Dosimeters/Detectors Used in Small-Field Dosimetry: Pros and Cons. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2018, 8, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Prezado, Y.; Martinez-Rovira, I.; Thengumpallil, S.; Deman, P. Dosimetry protocol for the preclinical trials in white-beam minibeam radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 5012–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TRS; IAEA. 483-Dosimetry of Small Static Fields Used in External Beam Radiotherapy; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stasi, M.; Baiotto, B.; Barboni, G.; Scielzo, G. The behavior of several microionization chambers in small intensity modulated radiotherapy fields. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 2792–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhood, B.; Geraily, G.; Abtahi, S.M.M. A systematic review of clinical applications of polymer gel dosimeters in radiotherapy. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 143, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Deene, Y.; Vergote, K.; Claeys, C.; De Wagter, C. The fundamental radiation properties of normoxic polymer gel dosimeters: A comparison between a methacrylic acid based gel and acrylamide based gels. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyani Nezhad, Z.; Geraily, G. A review study on application of gel dosimeters in low energy radiation dosimetry. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2022, 179, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, C.; De Deene, Y.; Doran, S.; Ibbott, G.; Jirasek, A.; Lepage, M.; McAuley, K.B.; Oldham, M.; Schreiner, L.J. Polymer gel dosimetry. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, R1–R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, A.J. Radiation Chemistry: An Introduction; Longman: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Magee, J.L.; Chatterjee, A. Track reactions of radiation chemistry. In Kinetics of Nonhomogeneous Processes; Freeman, G.R., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Spinks, J.W.T.; Wodds, R.J. An Introduction to Radiation Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chernyshev, A.V.; Soini, A.E.; Surovtsev, I.V.; Maltsev, V.P.; Soini, E. A mathematical model of dispersion radical polymerization kinetics. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 1997, 35, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Deene, Y.; Hanselaer, P.; De Wagter, C.; Achten, E.; de Neve, W. An investigation of the chemical stability of a monomer/polymer gel dosimeter. Phys. Med. Biol. 2000, 45, 859–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, A.K. A discussion of the factors influencing the polymerization processes in polymer gel dosimeters. In Proceedings of the DOSGEL 2001, 2nd International Conference on Radiotherapy Gel Dosimetry, Brisbane, Australia, 18–21 November 2001; Baldock, C., de Deene, Y., Eds.; QUT: Brisbane, Australia, 2001; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lepage, M.; Whittaker, A.K.; Rintoul, L.; Bäck, S.A.; Baldock, C. The relationship between radiation-induced chemical processes and transverse relaxation times in polymer gel dosimeters. Phys. Med. Biol. Apr. 2001, 46, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.H.; Chang, T.H.; Lin, C.M.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, Y.J. Three-dimensional dose comparison of flattening filter (FF) and flattening filter-free (FFF) radiation therapy by using NIPAM gel dosimetry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parwaie, W.; Geraily, G.; Mehri-Kakavand, G.; Babaloui, S.; Rezvani, S.; Pursamimi, M. Dosimetry of small photon fields in the presence of bone heterogeneity using MAGIC polymer gel, Gafchromic film, and Monte Carlo simulation. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2022, 27, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadeh, P.; Amiri, S.; Mostaar, A.; Joybari, A.Y.; Paydar, R. Evaluation of MAGIC-f polymer gel dosimeter for dose profile measurement in small fields and stereotactic irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 194, 109991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrevicius, L.; Jaselske, E.; Adliene, D.; Rudzianskas, V.; Radziunas, A.; Tamasauskas, A. Application of 3D Gel Dosimetry as a Quality Assurance Tool in Functional Leksell Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Gels 2022, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaeh, K.A.; Issra’ME, H.; Eyadeh, M.M.; Aldweri, F.M.; Awad, S.I.; Oglat, A.A.; Shatnawi, M.T. Improved performance of N-(Hydroxymethyl) acrylamide gel dosimeter using potassium chloride for radiotherapy. Rad. Meas. 2021, 142, 106542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaeh, K.A.; Hammoudeh, I.M.E.; Oglat, A.A.; Eyadeh, M.M.; Abdel-Qader, A.J.; Aldweri, F.M.; Awad, S.I. Polymer gel containing N,N’-methylene-bis-acrylamide (BIS) as a single monomer for radiotherapy dosimetry. Rad. Phys. Chem. 2021, 187, 109522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyadeh, M.M.; Alshomali, L.S.; Rabaeh, K.A.; Oglat, A.A.; Diamond, K.R. Improvement on the performance N-(3-methoxypropyl) acrylamide polymer-gel dosimeter by the addition of inorganic salt for application in radiotherapy dosimetry. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2022, 331, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Absorbed Dose Determination in External Beam Radiotherapy; Technical Reports Series; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, E.; Maris, T.; Angelopoulos, A.; Paparigopoulou, M.; Sakelliou, L.; Sandilos, P.; Voyiatzi, S.; Vlachos, L. A new polymer gel for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) radiation dosimetry. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoutsaki, M.V.; Maris, T.G.; Pappas, A.E.; Papadakis, J. Damilakis Dosimetric characteristics of a new polymer gel and their dependence on post-preparation and post-irradiation time: Effect on X-ray beam profile measurements. Phys. Med. 2013, 29, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nierer, L.; Kamp, F.; Reiner, M.; Corradini, S.; Rabe, M.; Dietrich, O.; Parodi, K.; Belka, C.; Kurz, C.; Landry, G. Evaluation of an anthropomorphic ion chamber and 3D gel dosimetry head phantom at a 0.35 T MR-linac using separate 1.5 T MR-scanners for gel readout. Z. Med. Phys. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Low, D.A.; Harms, W.B.; Mutic, S.; Purdy, J.A. A technique for the quantitative evaluation of dose distributions. Med. Phys. 1998, 25, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, G.; Cavalli, N.; Bonanno, E.; Zirone, L.; Borzì, G.R.; Pace, M.; Girlando, A.; Gueli, A.M.; Marino, C. SBRT/SRS patient-specific QA using GAFchromicTM EBT3 and FilmQATM Pro software. J. Radiosurgery SBRT 2022, 8, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Miften, M.; Olch, A.; Mihailidis, D.; Moran, J.; Pawlicki, T.; Molineu, A.; Li, H.; Wijesooriya, K.; Shi, J.; Xia, P.; et al. Tolerance limits and methodologies for IMRT measurement-based verification QA: Recommendations of AAPM Task Group No. 218. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, e53–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awad, S.I.; Moftah, B.; Basfer, A.; Almousa, A.A.; Al Kafi, M.A.; Eyadeh, M.M.; Rabaeh, K.A. 3-D quality assurance in CyberKnife radiotherapy using a novel N-(3-methoxypropyl) acrylamide polymer gel dosimeter and optical CT. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 161, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorsen, P.H.; Cirino, E.; Das, I.J.; Garrett, J.A.; Yang, J.; Yin, F.F.; Fairobent, L.A. AAPM-RSS Medical Physics Practice Guideline 9.a. for SRS-SBRT. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2017, 18, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz, D.; Papanikolaou, N.; Zoros, E.; Pappas, E.; Reiner, M.; Chew, L.T.; Lim, H.Y.; Hancock, S.; Nebelsky, A.; Njeh, C.; et al. Robustness of single-isocenter multiple-metastasis stereotactic radiosurgery end-to-end testing across institutions. J. Radiosurgery SBRT 2021, 7, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Kwak, J.; Back, G.M.; Cho, B.; Min Yoon, S.; Lee, S.W. Evaluation of the Dosimetric Accuracy of Brain Stereotactic Radiotherapy by Using a Hybrid Quality Assurance (QA) Toolkit. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2019, 74, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bry, V.; Saenz, D.; Pappas, E.; Kalaitzakis, G.; Papanikolaou, N.; Rasmussen, K. End to end comparison of surface-guided imaging versus stereoscopic X-rays for the SRS treatment of multiple metastases with a single isocenter using 3D anthropomorphic gel phantoms. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
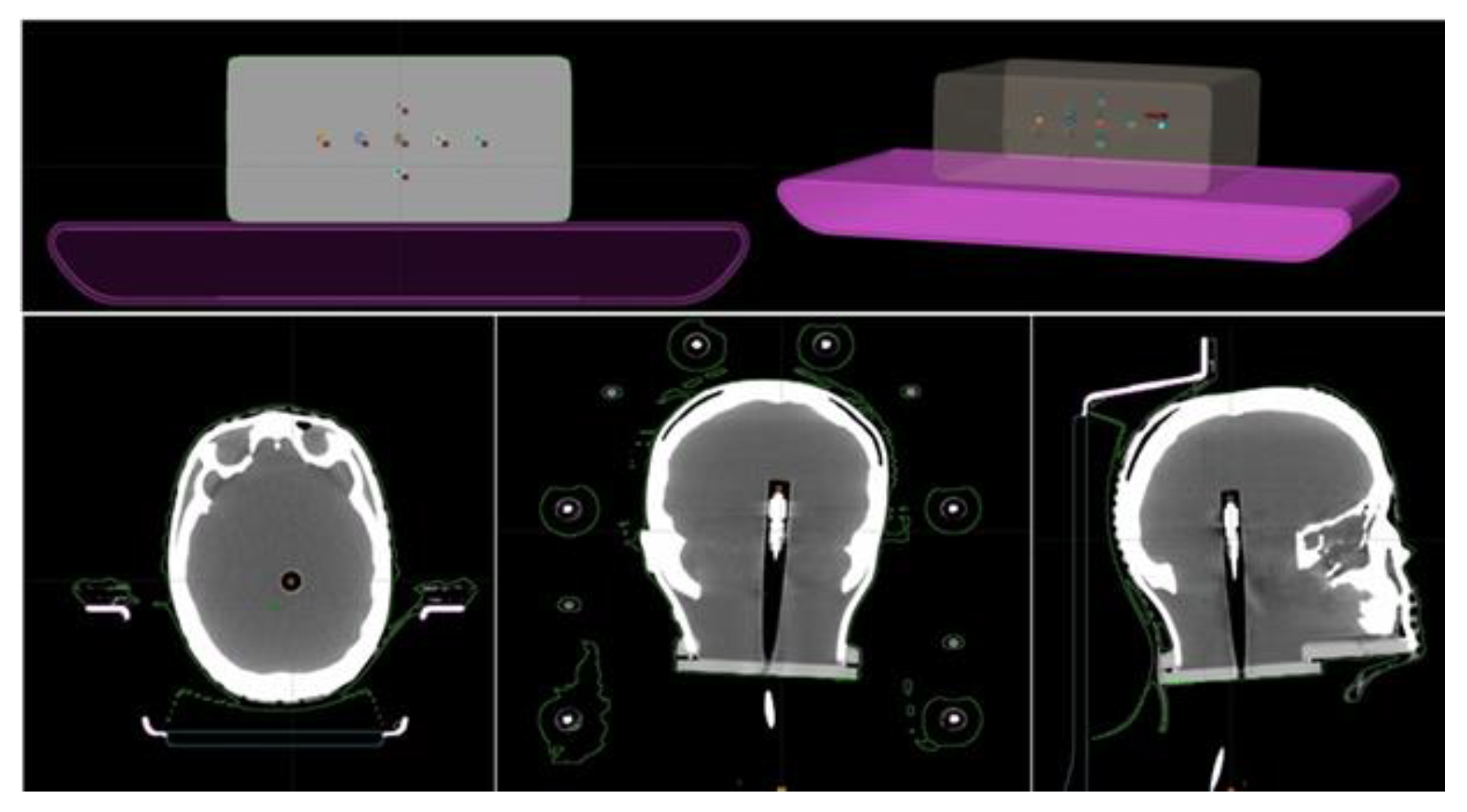
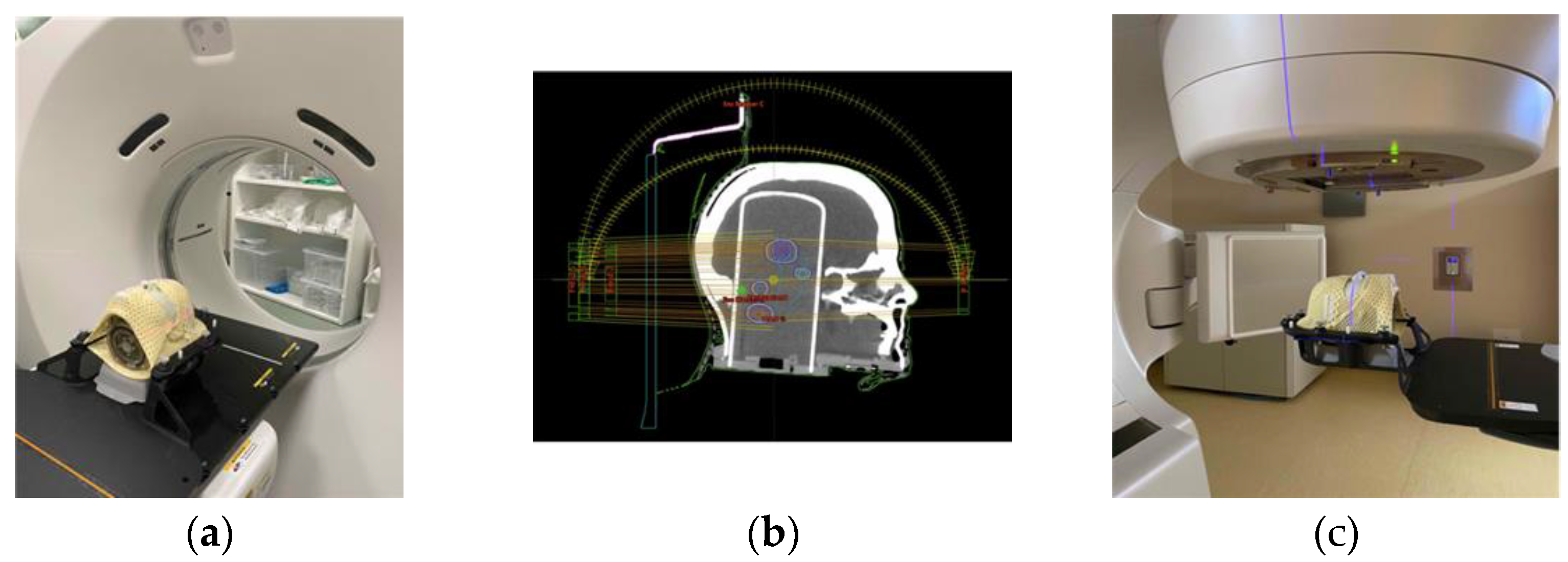


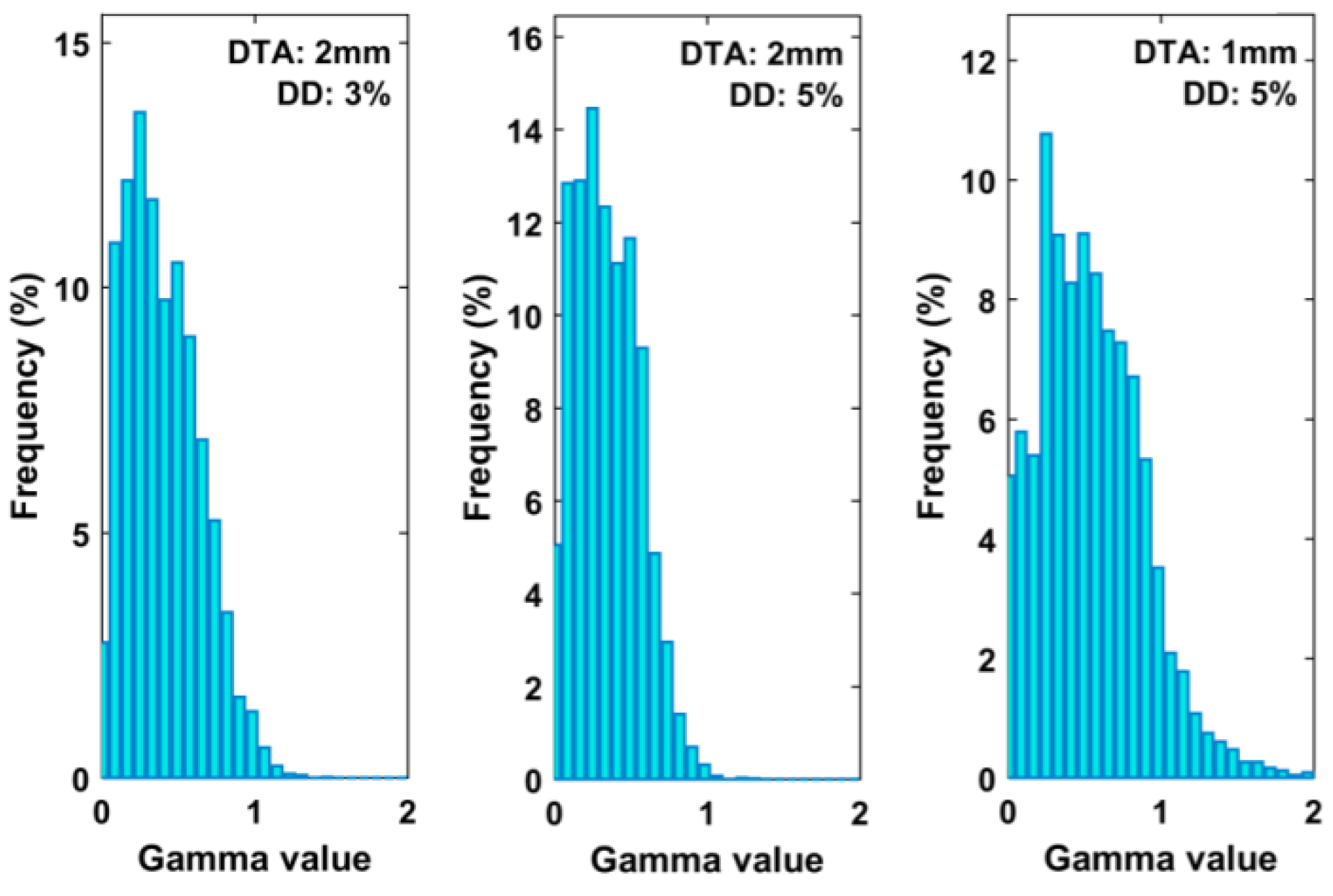
| ID | N° Target | Vtarget [cm3] | Dp [Gy] | Distance from ISO [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 3.37 | 20 | - |
| M1 | 2 | 0.47–0.93 | 20 | 21.8–22.9 |
| M2 | 3 | 0.29–2.32 | 20 | 3.3–19.9 |
| M3 | 4 | 1.49–1.57 | 21 | 28.00–68.21 |
| M4 | 5 | 0.15–3.94 | 15–22 | 15.93–28.29 |
| ID | N° Target | Vtarget [cm3] | Dp [Gy] |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 3.37 | 7 |
| M1 | 2 | 0.47–0.93 | 8 |
| M2 | 3 | 0.29–2.32 | 9 |
| M3 | 4 | 1.49–1.57 | 9 |
| M4 | 5 | 0.15–3.94 | 6–9 |
| ID | Target | DTPS (Gy) | DMVP (Gy) | Diff. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | PTV1 | 23.871 | 24.498 | 2.63 |
| M1 | PTV1 | 21.701 | 22.153 | 2.08 |
| PTV2 | 24.205 | 23.584 | −2.57 | |
| M2 | PTV1 | 23.755 | 24.008 | 1.07 |
| PTV2 | 24.129 | 23.944 | −0.77 | |
| PTV3 | 24.419 | 23.844 | −2.36 | |
| M3 | PTV1 | 25.491 | 24.721 | −2.13 |
| PTV2 | 27.471 | 26.779 | −2.52 | |
| PTV3 | 26.845 | 26.595 | −0.93 | |
| PTV4 | 27.871 | 27.425 | −1.60 | |
| M4 | PTV1 | 26.183 | 25.397 | −2.28 |
| PTV2 | 28.891 | 27.865 | −2.74 | |
| PTV3 | 20.257 | 19.671 | −2.89 | |
| PTV4 | 27.327 | 27.750 | 1.55 | |
| PTV5 | 29.793 | 29.322 | −1.58 |
| ID | Target | DTPS (Gy) | DPP (Gy) | Diff. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | PTV1 | 23.297 | 24.067 | 2.81 |
| M1 | PTV1 | 21.847 | 21.957 | 0.51 |
| PTV2 | 22.261 | 22.426 | 0.74 | |
| M2 | PTV1 | 23.654 | 24.269 | 2.60 |
| PTV2 | 22.672 | 22.769 | 0.43 | |
| PTV3 | 22.429 | 22.623 | 0.87 | |
| M3 | PTV1 | 24.808 | 24.264 | −2.19 |
| PTV2 | 26.101 | 25.738 | −1.39 | |
| PTV3 | 25.837 | 25.529 | −1.19 | |
| PTV4 | 26.778 | 26.408 | −1.38 | |
| M4 | PTV1 | 23.972 | 24.243 | 1.13 |
| PTV2 | 26.741 | 26.647 | −0.35 | |
| PTV3 | 19.009 | 19.007 | 0.01 | |
| PTV4 | 26.577 | 26.821 | 0.92 | |
| PTV5 | 28.495 | 28.478 | −0.06 |
| Passing Criteria | 2D Gamma Passing Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | SD (%) | Min (%) | Max (%) | |
| 3% 2 mm | 97.96 | 1.09 | 96.39 | 100.00 |
| 5% 2 mm | 99.78 | 0.55 | 97.89 | 100.00 |
| 5% 1 mm | 84.15 | 13.32 | 60.53 | 98.39 |
| Passing Criteria | 3D Gamma Passing Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | SD (%) | Min (%) | Max (%) | |
| 3% 2 mm | 97.92 | 2.28 | 92.76 | 100.00 |
| 5% 2 mm | 98.89 | 1.66 | 94.25 | 100.00 |
| 5% 1 mm | 91.38 | 10.24 | 73.28 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zirone, L.; Bonanno, E.; Borzì, G.R.; Cavalli, N.; D’Anna, A.; Galvagno, R.; Girlando, A.; Gueli, A.M.; Pace, M.; Stella, G.; et al. HyperArcTM Dosimetric Validation for Multiple Targets Using Ionization Chamber and RT-100 Polymer Gel. Gels 2022, 8, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080481
Zirone L, Bonanno E, Borzì GR, Cavalli N, D’Anna A, Galvagno R, Girlando A, Gueli AM, Pace M, Stella G, et al. HyperArcTM Dosimetric Validation for Multiple Targets Using Ionization Chamber and RT-100 Polymer Gel. Gels. 2022; 8(8):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080481
Chicago/Turabian StyleZirone, Lucia, Elisa Bonanno, Giuseppina Rita Borzì, Nina Cavalli, Alessia D’Anna, Rosaria Galvagno, Andrea Girlando, Anna Maria Gueli, Martina Pace, Giuseppe Stella, and et al. 2022. "HyperArcTM Dosimetric Validation for Multiple Targets Using Ionization Chamber and RT-100 Polymer Gel" Gels 8, no. 8: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080481
APA StyleZirone, L., Bonanno, E., Borzì, G. R., Cavalli, N., D’Anna, A., Galvagno, R., Girlando, A., Gueli, A. M., Pace, M., Stella, G., & Marino, C. (2022). HyperArcTM Dosimetric Validation for Multiple Targets Using Ionization Chamber and RT-100 Polymer Gel. Gels, 8(8), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080481






