Investigation on In Situ Carbon-Coated ZnFe2O4 as Advanced Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
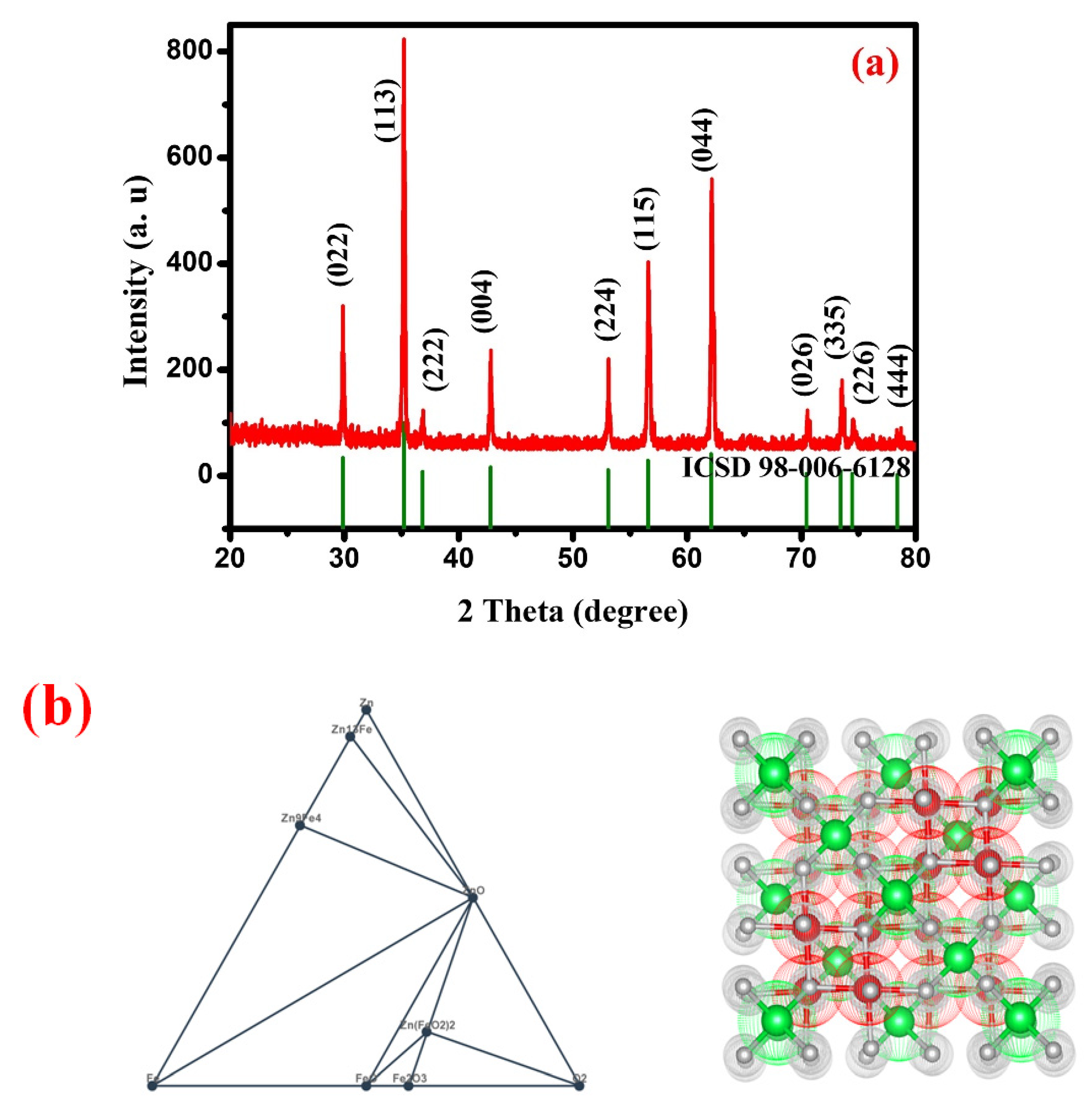
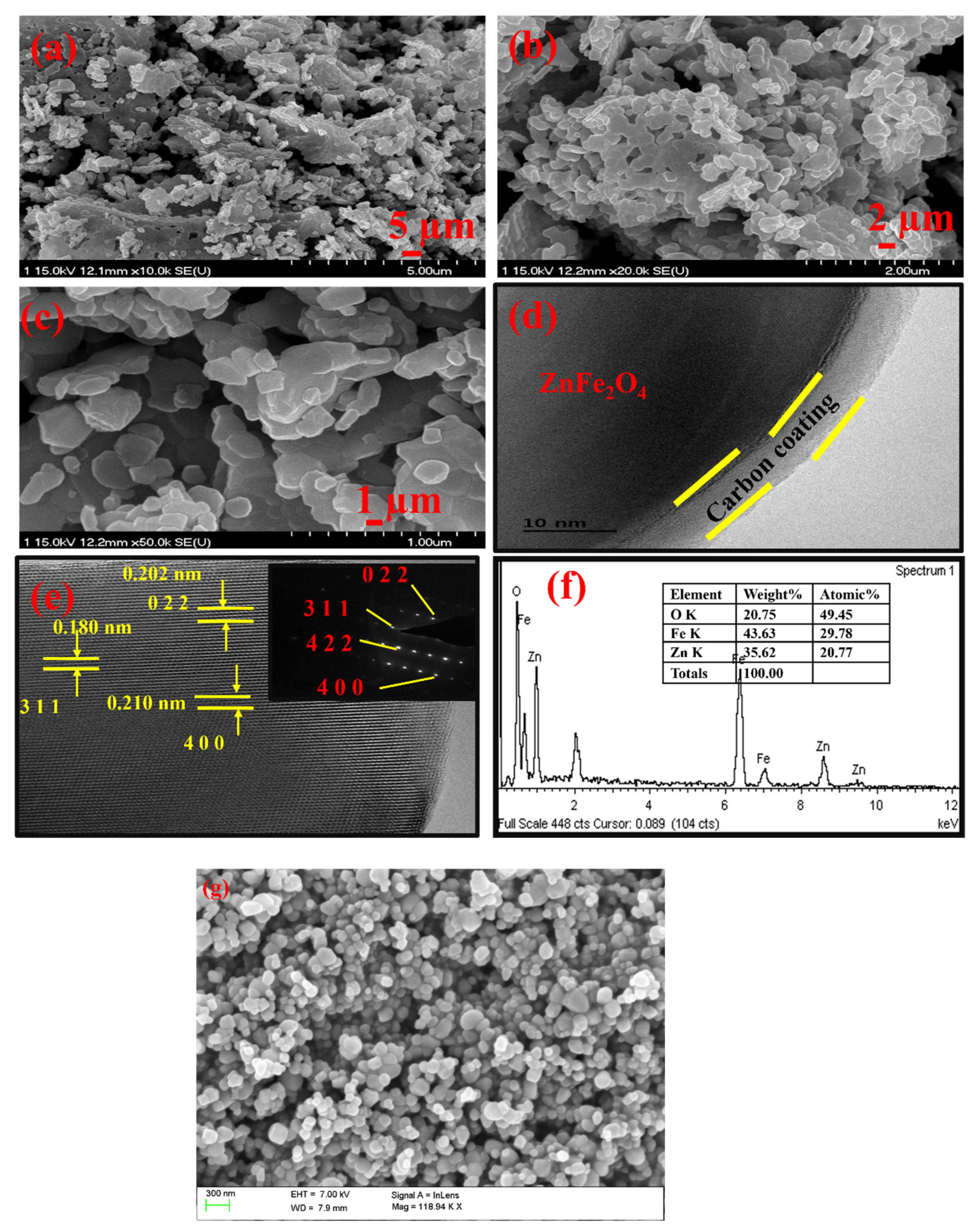
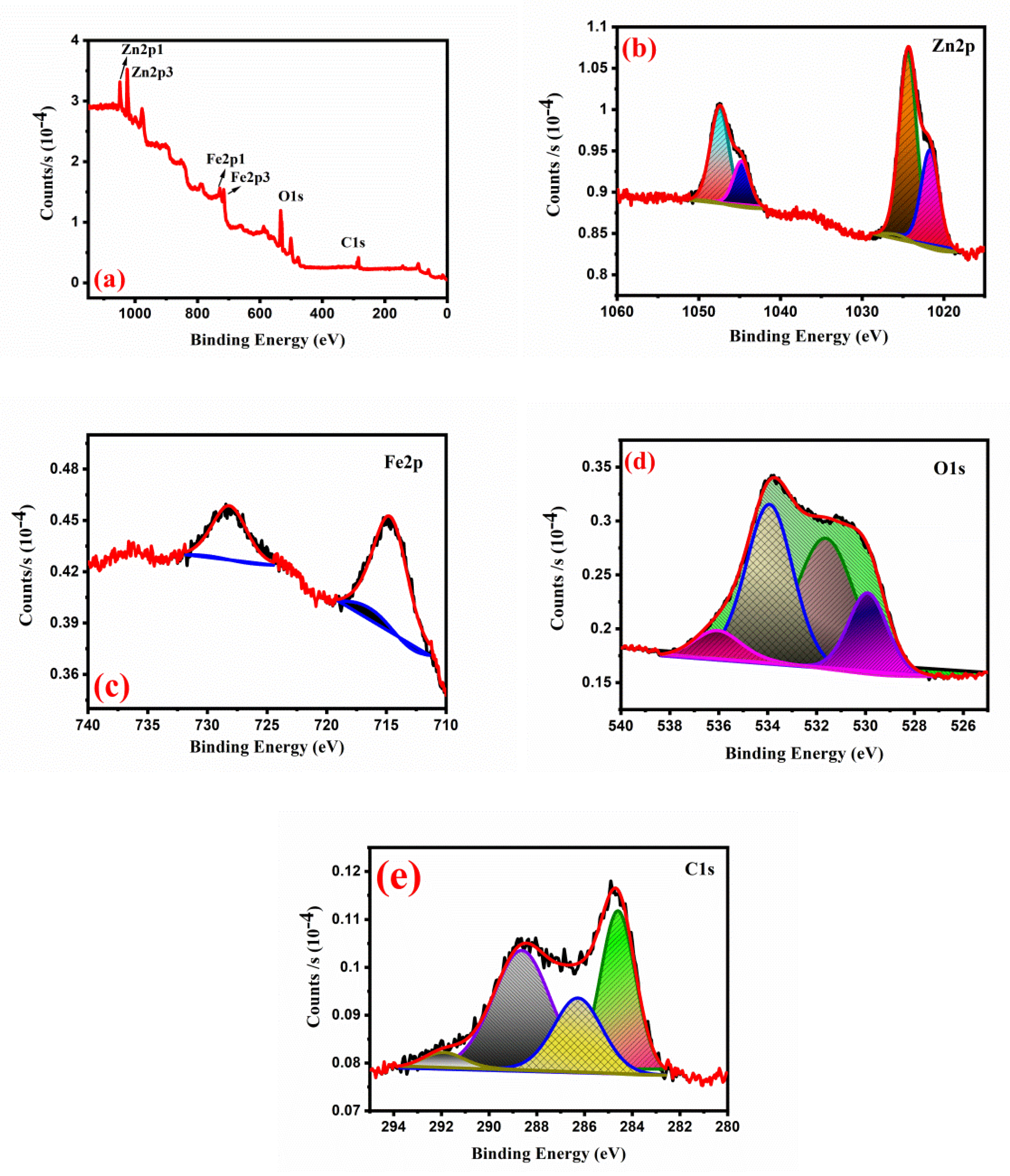
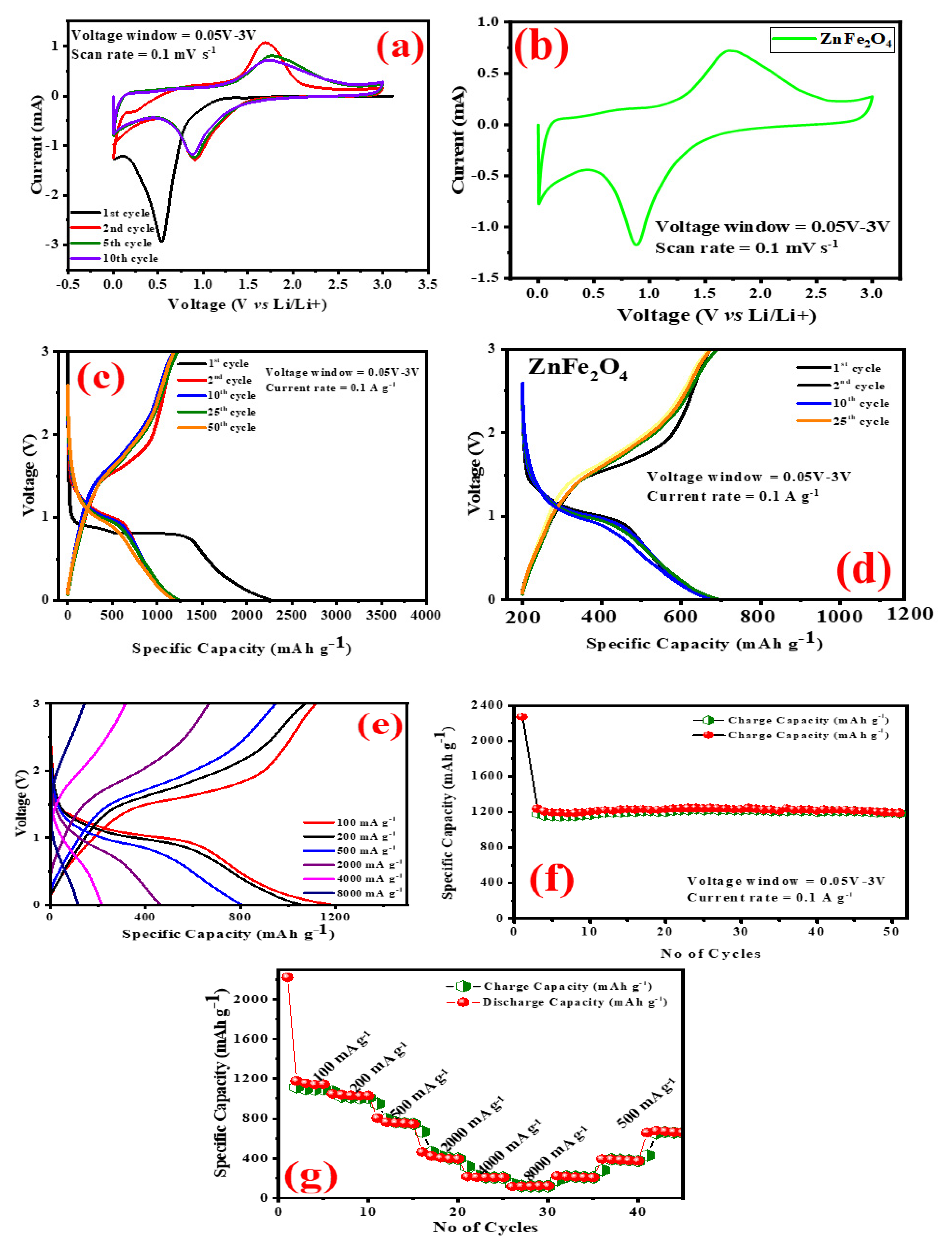
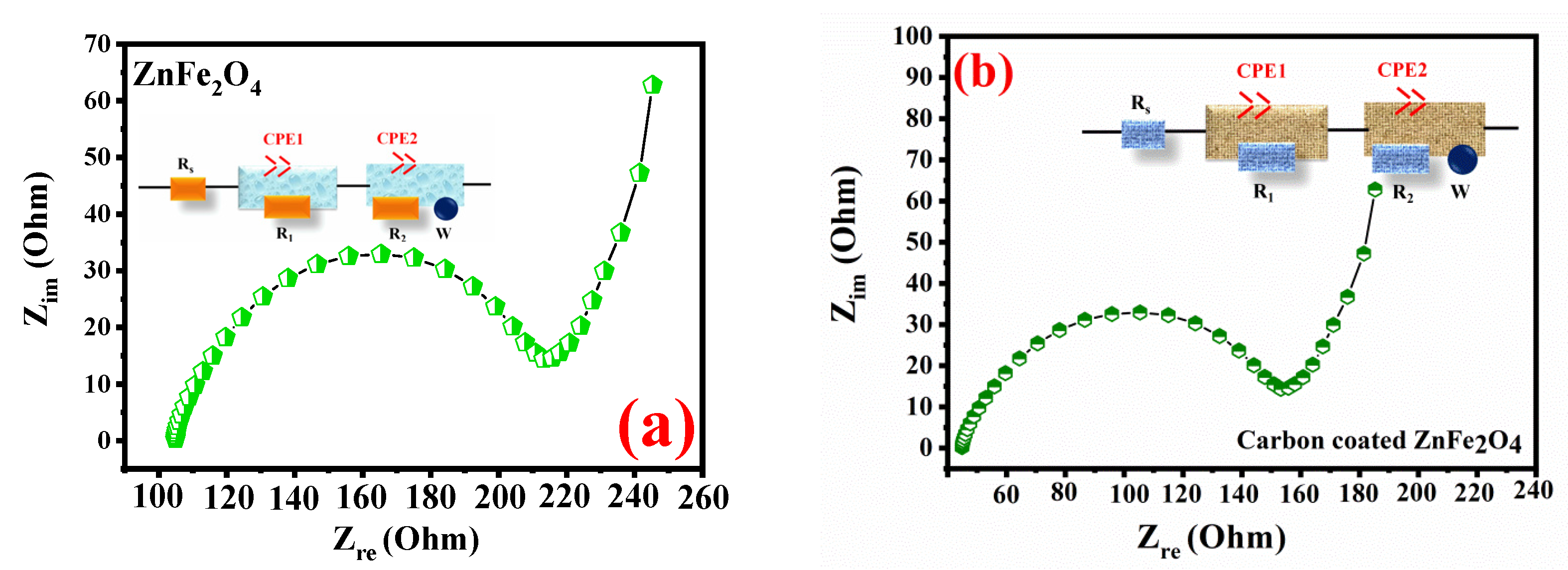
2. Results and Discussion
 LiZn (3) Zn0 + Li2O → ZnO + 2Li + 2e−
LiZn (3) Zn0 + Li2O → ZnO + 2Li + 2e−
3. Conclusions
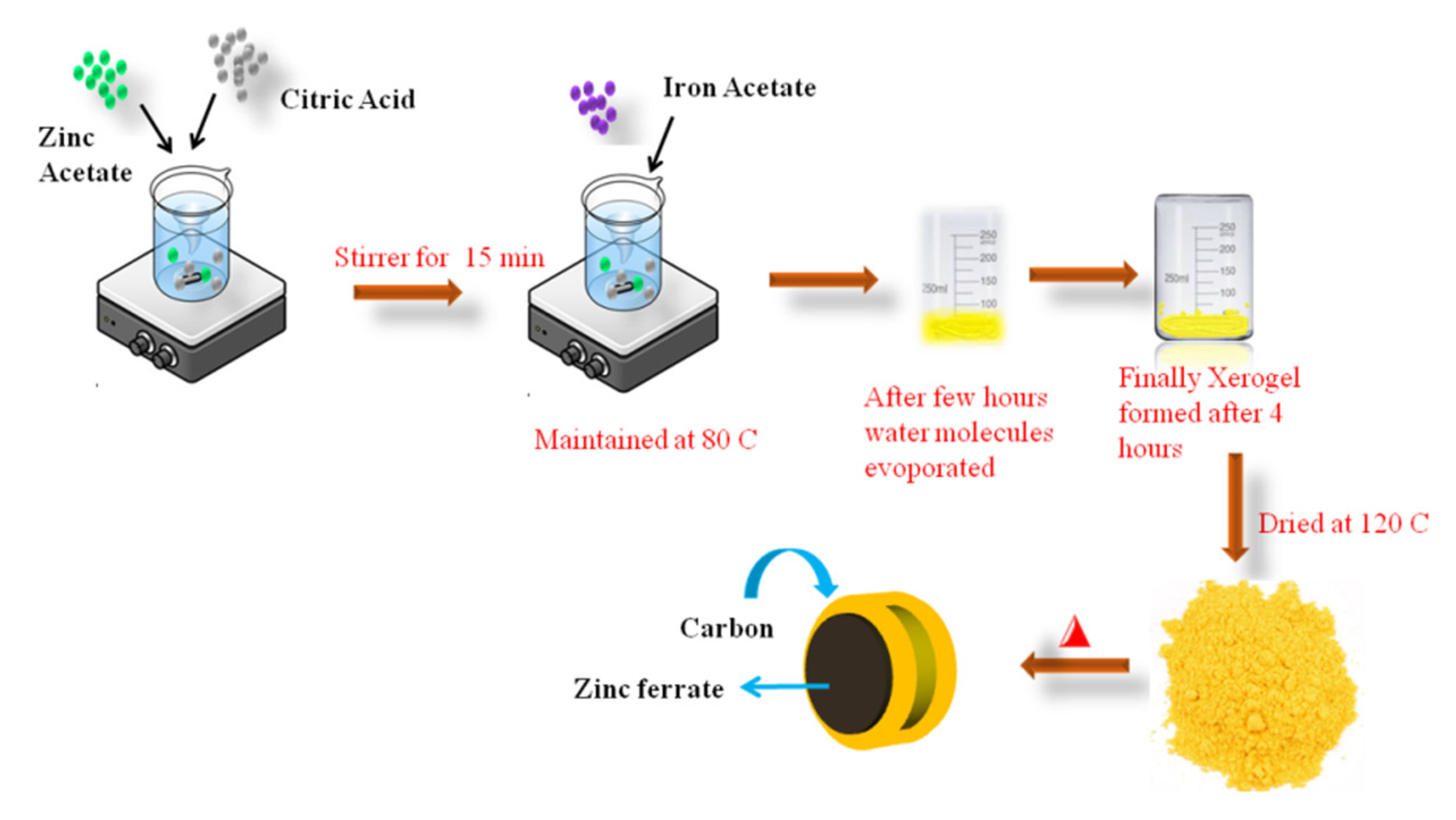
4. Experimental
4.1. The Electrochemical Studies
4.2. Characterization Details
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodenough, J.B.; Kim,, Y. Challenges for Rechargeable Li Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, J.R.; Maiyalagan, T.; Lee, Y.S.; Sivakumar, N. Advanced High Voltage Cathode Materials for Rechargeable Li Ion batteries; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; Volume 171. [Google Scholar]
- Armand, M.; Tarascon, J.M. Lithium Storage Mechanism in Purpurin based Organic Lithium ion Battery Electrodes. Nature 2008, 451, 637–652. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, P.G.; Scrosati, B.; Tarascon, J.M. Nanomaterials for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2930–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Jin, B.; Zhong, X.B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.X.; Liang, J.C.; Jiang, Q. One-Pot Synthesis and High Electrochemical Performance of CuS/Cu1.8S Nanocomposites as Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Pubmed. Cent. 2013, 277, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.R.; Lian, L.; Zhang, L.H.; Pang, G.; Yuan, C.Z.; Zhang, X.G. Ultrahigh-performance mesoporous ZnMn2O4 microspheres as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries and their in situ Raman investigation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yan, J.; Bin, H.; Li, Y.W.; Xiao, S.H. Nanoparticles-constructed spinel ZnFe2O4 anode material with superior lithium storage performance boosted by pseudocapacitance. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 104, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.B.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, L.L.; Jin, B.; Jin, E.M.; Jeong, S.; Jiang, Q. In-situ synthesized ZnFe2O4 firmly anchored to the surface of MWCNTs as a long-life anode material with high lithium storage performance. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2017, 425, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Xu, H.Y.; Chen, L.; Gu, X.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y.T. A general approach for MFe2O4 (M = Zn, Co, Ni) nanorods and their high performance as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Source 2014, 247, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zu, L.H.; Kong, B.; Chen, B.J.; He, H.L.; Lan, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.H.; Zhao, D.Y. Mesoporous TiO2/TiC@ C composite membranes with stable TiO2-C interface for robust lithium storage. Science 2018, 3, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.L.M.; Shaijumon, M.M.; Gowda, S.R.; Ajayan, P.M. Coaxial MnO2/Carbon Nanotube Array Electrodes for High-Performance Lithium Batteries. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, J.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Maiyalagan, T.; Nallamuthu, N.; Sivakumar, N. Na0.4(Mn0.33Co0.33Ni0.33)O2 surface grafted with SnO nanorods: A cathode materials for rechargeable sodium ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 856, 113633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachitra, J.; Balamurugan, A.; Joshua, J.R.; Sharmila, V. Enhancing the electrochemical performance by structural evolution in O3-NaFe1-xMgxO2 cathodes for sodium ion batteries. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 129, 108528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, V.; Parthibavarman, M. Lithium manganese phosphate associated with MWCNT: Enhanced positive electrode for lithium hybrid batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 157715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Bruce, P.G. Mesoporous Crystalline β-MnO2—A Reversible Positive Electrode for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Kim, J.; Kwon, H.; Song, H. Gram-Scale Synthesis of Cu2O Nanocubes and Subsequent Oxidation to CuO Hollow Nanostructures for Lithium-Ion Battery Anode Materials. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.P.; Bao, J.L.; Pan, G.L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Huang, P.X.; Wu, F.; Song, D.Y. Preparation and electrochemical performance of polycrystalline and single crystalline CuO nanorods as anode materials for Li ion battery. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 5547–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, X.L.; Shu, C.Y.; Guo, Y.G.; Wang, C.R. Synthesis of CuO/graphene nanocomposite as a high-performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10661–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.M.; Wu, X.L.; Hu, J.S.; Guo, Y.G.; Wan, L.J. Carbon Coated Fe3O4 Nanospindles as a Superior Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.S.; Liu, J.L.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Ng, C.F.; Ma, L.J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, J.Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Fan, H.J. Three-Dimensional Graphene Foam Supported Fe3O4 Lithium Battery Anodes with Long Cycle Life and High Rate Capability. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 6136–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Liu, A.H.; Liu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.Z.; Zhong, X.B.; Ma, X.Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.Y. Fe3O4–pyrolytic graphite oxide composite as an anode material for lithium secondary batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 90, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.M.; Wang, D.W.; Yin, L.C.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Cheng, H.M. Oxygen bridges between NiO nanosheets and graphene for improvement of lithium storage. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3214–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, B.; Reddy, M.V.; Yanwu, Z.; Lit, C.S.; Hoong, T.C.; Rao, G.V.S.; Chowdari, B.V.R.; Wee, A.T.S.; Lim, C.T.; Sow, C.H. Fabrication of NiO nanowall electrodes for high performance lithium ion battery. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3360–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, G.X.; Liu, J.; Qiao, S.Z.; Ahn, H.J. Highly ordered mesoporous NiO anode material for lithium ion batteries with an excellent electrochemical performance. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3046–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Ju, Z.C.; Yang, J.; Xu, H.Y.; Qian, Y.T. Spin-coated silicon nanoparticle/graphene electrode as a binder-free anode for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, P.F.; Pramana, S.S.; Sharma, Y.; Ko, Y.W.; Madhavi, S. Electrospun Zn1–xMnxFe2O4 Nanofibers As Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries and the Impact of Mixed Transition Metallic Oxides on Battery Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5461–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Majeed, A.; Yang, Z.; Yao, S.; Shen, X.; Li, T.; Qin, S. Porous N-doped carbon nanofibers assembled with nickel ferrite nanoparticles as efficient chemical anchors and polysulfide conversion catalyst for lithium-sulfur batteries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 601, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, M.; Liang, Y.; Majeed, A.; Yang, Z.; Shen, X. CoFe2O4 nanoparticles loaded N-doped carbon nanofibers networks as electrocatalyst for enhancing redox kinetics in Li-S batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 560, 1449908. [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa, M.G.; Moustafa, M.S.S. Green fabrication of ZnAl2O4-coated LiFePO4 nanoparticles for enhanced electrochemical performance in Li-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, M.M.S.; Rashad, K.M.M. Enhancement of the electrochemical performance of hydrothermally prepared anatase nanoparticles for optimal use as high capacity anode materials in lithium ion. Powers Appl. Phys. A 2015, 118, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Shao, H.X. High Capacity ZnFe2O4 Anode. Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9433–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.B.; Yang, Z.Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Lu, L.; Jin, B.; Zha, M.; Jiang, Q.C. A novel approach to facilely synthesize mesoporous ZnFe2O4 nanorods for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Source 2016, 306, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.Y.; Kong, J.H.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, R.; Lu, X.H. Zinc ferrite nanorods coated with polydopamine-derived carbon for high-rate lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 146, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.F.; Wang, K.; Wu, H.W.; Zhang, N.; Fu, H.T. Synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene supported hollow ZnFe2O4 nanosphere composites for application in lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Su, Q.M.; Zhang, J.; Du, G.H. One-pot solvothermal synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanospheres/graphene composites with improved lithium-storage performance. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 65, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, P.F.; Sharma, Y.; Pramanac, S.S.; Srinivasan, M. Nanoweb anodes composed of one-dimensional, high aspect ratio, size tunable electrospun ZnFe2O4 nanofibers for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 14999–15008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Li, R.R.; Yu, Y.T.; Xia, Z.K.; Wang, L.J.; Wei, Q.F.; Chen, K.; Qiao, Q.Q. Fabrication of PANI-coated ZnFe2O4 nanofibers with enhanced electrochemical performance for energy storage. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 273, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.Q.; Wong, K.W.; Li, Y.; Ng, K.M. Novel nanosheets of ferrite nanoparticle arrays in carbon matrix from single source precursors: An anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 4456–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Dong, C.; Jin, B.; Wen, Z.; Jiang, Q. ZnFe2O4@ PPy core-shell structure for high-rate lithium-ion storage. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 851, 113442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NuLi, Y.N.; Chu, Y.Q.; Qin, Q.Z. Nanocrystalline ZnFe2O4 and Ag-Doped ZnFe2O4 Films Used as New Anode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.W.; Lu, X.; Fang, X.P.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Chen, L.Q.; Xu, X.X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.N. Lithium storage in hollow spherical ZnFe2O4 as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 847–850. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.H.; Zhang, R.P.; Jia, M.Q. Facile synthesis of ZnFe2O4-graphene aerogels composites as high-performance anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Hou, X.H.; Wang, X.Y.; He, G.N.; Shao, Z.P.; Hu, S.J. Corncob-shaped ZnFe2O4/C nanostructures for improved anode rate and cycle performance in lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 31807–31814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.B.; Han, C.P.; Li, B.; He, Y.J.; Lin, Z.Q. In-situ crafting of ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles impregnated within continuous carbon network as advanced anode materials. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2728–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.W.; Rooney, D.; Sun, K.N. Yolk-shell germanium@ polypyrrole architecture with precision expansion void control for lithium ion batteries. iScience 2018, 9, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, F.; Hu, X.L.; Li, Z.; Qie, L.; Hu, C.C.; Zeng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.H. MOF-derived porous ZnO/ZnFe₂O₄/C octahedra with hollow interiors for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6622–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Li, D.; Li, W.C.; Lei, C.; Sun, Q.; Lu, A.H. Nanoengineered polypyrrole-coated Fe2O3@C multifunctional composites with an improved cycle stability as lithium-ion anodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, J.J.; Liu, S.; Yuan, R. Sulfur-doped ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles with enhanced lithium storage capabilities. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 3566–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Yang, H.; Guo, X. 3-Dimensional hierarchically porous ZnFe2O4/C composites with stable performance as anode materials for Li-ion batteries 3-Dimensional hierarchically porous ZnFe2O4/C composites with stable performance as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X.D.; Yu, C.Z. Polypyrrole-coated zinc ferrite hollow spheres with improved cycling stability for lithium-ion batteries. Small 2016, 12, 3732–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.Q.; Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, Y.; Hou, L.R.; Yuan, C.Z. Core-shell N-doped carbon coated zinc ferrite nanofibers with enhanced Li-storage behaviors: A promising anode for Li-ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 2018, 224, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Deng, H.; Huang, Q.; Su, Q.; Du, G. Three-dimensional carbon-coated ZnFe2O4 nanospheres/nitrogen-doped graphene aerogels as anode for lithiumion batteries. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, T.; Yue, J.; Sheng, L.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, D.; Yuan, L.; Fan, Z. Ultra-small and highly crystallized ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles within double graphene networks for super-long life lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11188–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, M.; Tian, G.; Yue, H.; Feng, S.; Chen, G. Porous ZnFe2O4 nanospheres as anode materials for Li-ion battery with high performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Kloepsch, R.; He, X.; Evertz, M.; Nowak, S.; Li, J.; Winter, M.; Placke, T. Nanostructured ZnFe2O4 as anode material for lithium ion batteries: Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis and performance evaluation with special emphasis on comparative. Acta Chim. Slov. 2016, 63, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, P.K.; Zhang, K. Hierarchical porous acetylene black/ZnFe2O4@ carbon hybrid materials with high capacity and robust cycling performance for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, L.; Yan, W. Fabrication of the ZnFe2O4 Fiber-in-Tube and Tubular Mesoporous Nanostructures via Single-spinneret Electrospinning: Characterization, Mechanism and Performance as Anodes for Li-ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Pan, Q. ZnFe2O4@ C/graphene nanocomposites as excellent anode materials for lithium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chui, Y.; Cao, C.; Zapien, J.A. Self-assembled three-dimensional mesoporous ZnFe2O4-graphene composites for lithium ion batteries with significantly enhanced rate capability and cycling stability. J. Power Source 2015, 275, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Yu, M. Facile and large-scale fabrication of hierarchical ZnFe2O4/graphene hybrid films as advanced binder-free anodes for lithium-ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Hou, X.; Hu, S.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Ru, Q. An excellent performance anode of ZnFe2O4/flake graphite composite for lithium ion battery. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 585, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Kim, Y.; Noh, Y.; Kim, W.B. Formation of carbon-coated ZnFe2O4 nanowires and their highly reversible lithium storage properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, F.; Bresser, D.; Paillard, E.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S. Influence of the carbonaceous conductive network on the electrochemical performance of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Power Source 2013, 236, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Qian, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X. Graphene anchored with ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles as a high-capacity anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Sci. 2013, 17, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresser, D.; Paillard, E.; Kloepsch, R.; Krueger, S.; Fiedler, M.; Schmitz, R.; Baither, D.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S. Carbon Coated ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Advanced Lithium-Ion Anodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Zhang, C.; Hong, D.; Li, J.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Z.; Cai, W. Facile synthesis of MWCNT–ZnFe2O4 nanocomposites as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Cao, G.; Zhu, T.; Zhao, X. Self-assembly of a ZnFe2O4/graphene hybrid and its application as a high-performance anode material for Li-ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Electrode Materials | Synthesis Method | Current mA·g−1 | Cycle | Discharge Capacity mAh·g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Porous ZnFe2O4 | Sol–Gel | 1000 | 400 | 711 [45] |
| ZnFe2O4 Nanofibers | Electro Spinning | 50 | 50 | 1142 [46] |
| N-doped Carbon coated ZnFe2O4 | Electro Spinning | 200 | 200 | 881 [47] |
| ZnFe2O4 C/N Doped graphene | Hydrothermal Method | 100 | 100 | 952 [48] |
| ZnFe2O4/double graphene | Microwave irradiation | 1000 | 200 | 475 [49] |
| Porous ZnFe2O4 | Hydrothermal Method | 200 | 80 | 868 [50] |
| ZnFe2O4/C | Ionic Liquid | 500 | 190 | 1091 [51] |
| Acetylene Black/ZnFe2O4/C | Thermal Decomposition | 1000 | 200 | 430 [52] |
| ZnFe2O4/hollow fiber | Electro spinning | 200 | 260 | 1026 [53] |
| ZnFe2O4 Nanorods | Co-Precipitation | 100 | 50 | 983 [28] |
| ZnFe2O4@C/graphene | Hydrothermal Method | 250 | 180 | 705 [54] |
| 3D- ZnFe2O4/Graphene | Hydrothermal Method | 100 | 50 | 770 [55] |
| ZnFe2O4 Nanosphere/G | Solvothermal | 100 | 50 | 704 [31] |
| ZnFe2O4/Graphene | Cathodic Deposition | 200 | 200 | 881 [56] |
| ZnFe2O4/Nanoflake/g | Hydrothermal Method | 100 | 100 | 730 [57] |
| Carbon Coated ZnFe2O4 Nanowires | Micro-Emulsion | 100 | 100 | 1292 [58] |
| ZnFe2O4/C | Planetary Ball-Mill | 100 | 60 | 1100 [59] |
| ZnFe2O4/Graphene | Hydrothermal Method | 100 | 50 | 956 [60] |
| ZnFe2O4/C | Planetary Ball-Mill | 400 | 160 | 1300 [61] |
| MWCNT/ZnFe2O4 | High-Temperature | 60 | 50 | 1152 [62] |
| ZnFe2O4 Nano-Octahedral | Hydrothermal Method | 1000 | 300 | 730 [25] |
| ZnFe2O4/Graphene | Solvothermal | 400 | 90 | 398 [63] |
| ZnFe2O4 Nanofibers | Electro spinning | 60 | 30 | 733 [32] |
| In situ ZnFe2O4/C | Sol–Gel | 100 | 50 | 1312 (This Work) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, M.W.; BaQais, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Aamir, M.; Abuzir, A.; Mushtaq, S.; Amin, M.N.; Khan, M.S. Investigation on In Situ Carbon-Coated ZnFe2O4 as Advanced Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries. Gels 2022, 8, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050305
Alam MW, BaQais A, Rahman MM, Aamir M, Abuzir A, Mushtaq S, Amin MN, Khan MS. Investigation on In Situ Carbon-Coated ZnFe2O4 as Advanced Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries. Gels. 2022; 8(5):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050305
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Mir Waqas, Amal BaQais, Mohammed M. Rahman, Muhammad Aamir, Alaaedeen Abuzir, Shehla Mushtaq, Muhammad Nasir Amin, and Muhammad Shuaib Khan. 2022. "Investigation on In Situ Carbon-Coated ZnFe2O4 as Advanced Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries" Gels 8, no. 5: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050305
APA StyleAlam, M. W., BaQais, A., Rahman, M. M., Aamir, M., Abuzir, A., Mushtaq, S., Amin, M. N., & Khan, M. S. (2022). Investigation on In Situ Carbon-Coated ZnFe2O4 as Advanced Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries. Gels, 8(5), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050305








