Metal Oxide Hydrogel Composites for Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Wastewater: Principal Component Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
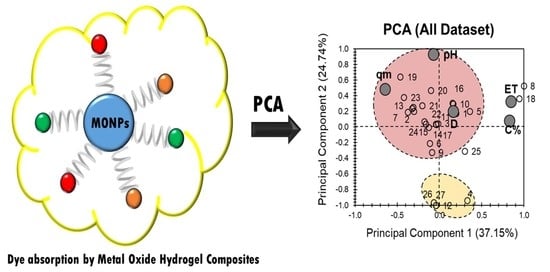
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Methodology
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ismail, M.; Akhtar, K.; Khan, M.I.; Kamal, T.; Khan, M.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Seo, J.; Khan, S.B. Pollution, Toxicity and Carcinogenicity of Organic Dyes and Their Catalytic Bio-Remediation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3645–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderete, B.L.; da Silva, J.; Godoi, R.; da Silva, F.R.; Taffarel, S.R.; da Silva, L.P.; Garcia, A.L.H.; Júnior, H.M.; de Amorim, H.L.N.; Picada, J.N. Evaluation of Toxicity and Mutagenicity of a Synthetic Effluent Containing Azo Dye after Advanced Oxidation Process Treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q. Pollution and Treatment of Dye Waste-Water. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 514, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, I.G.C.; Neves, R.A.M.D.; Nascimento, S.S.D.C.; Maciel, B.L.L.; Morais, A.H.D.A.; Passos, T.S. Artificial Dyes: Health Risks and the Need for Revision of International Regulations. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Pellicer, J.A.; Gómez-Morte, T.; Auñón, D.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Yáñez-Gascón, M.J.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á.; Cerón-Carrasco, J.P.; Crini, G.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; et al. Removal of an Azo Dye from Wastewater through the Use of Two Technologies: Magnetic Cyclodextrin Polymers and Pulsed Light. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, N.; Abdennouri, M.; Makhfouk, M.E. Removal of Methylene Blue and Eriochrome Black T from Aqueous Solutions by Biosorption on Scolymus Hispanicus L.: Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, I.; Saxena, A.; Bharti; Khurana, J.M.; Rai, P.K. Removal of Dyes Using Graphene-Based Composites: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, P.A.; Umbuzeiro, G.A.; Oliveira, D.P.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Assessment of Water Contamination Caused by a Mutagenic Textile Effluent/Dyehouse Effluent Bearing Disperse Dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of Various Recent Wastewater Dye Removal Methods: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.B.; Rodrigues, F.H.A.; Paulino, A.T.; Martins, A.F.; Fajardo, A.R. Recent Advances on Composite Hydrogels Designed for the Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Water and Wastewater: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaviya, P.; Singh, A. Physicochemical Technologies for Remediation of Chromium-Containing Waters and Wastewaters. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 1111–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, K.S.; Ramesh, S.T. Removal of Dyes Using Agricultural Waste as Low-Cost Adsorbents: A Review. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Ji, J.; Cai, Y.-F.; Li, H.; Ran, R. Robust, Anti-Fatigue, and Self-Healing Graphene Oxide/Hydrophobically Associated Composite Hydrogels and Their Use as Recyclable Adsorbents for Dye Wastewater Treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17445–17458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Bai, H.; Li, L. Graphene Oxide–Chitosan Composite Hydrogels as Broad-Spectrum Adsorbents for Water Purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Zhong, C.; Wang, H.-S.; Hu, X.-H.; Chu, L.-Q. Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Hydrogels Containing Metal Ions and Metals/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Polymers 2017, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, W.-J.; Tan, L.-L.; Ng, Y.H.; Yong, S.-T.; Chai, S.-P. Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C 3 N 4)-Based Photocatalysts for Artificial Photosynthesis and Environmental Remediation: Are We a Step Closer To Achieving Sustainability? Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7159–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannert, C.; Stokke, B.T.; Dias, R.S. Nanoparticle-Hydrogel Composites: From Molecular Interactions to Macroscopic Behavior. Polymers 2019, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Chaudhary, J.; Kumar, V.; Thakur, V.K. Progress in Pectin Based Hydrogels for Water Purification: Trends and Challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangia, S.; Warkar, S.; Katyal, D. A Review on Environmental Applications of Chitosan Biopolymeric Hydrogel Based Composites. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2018, 55, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, N.; Murshid, N.; Campbell, P.; Kitaev, V. Selective Plasmonic Sensing and Highly Ordered Metallodielectrics via Encapsulation of Plasmonic Metal Nanoparticles with Metal Oxides. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6514–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningthoujam, R.; Singh, Y.D.; Babu, P.J.; Tirkey, A.; Pradhan, S.; Sarma, M. Nanocatalyst in Remediating Environmental Pollutants. Chem. Phys. Impact 2022, 4, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Astruc, D. Nanocatalysts and Other Nanomaterials for Water Remediation from Organic Pollutants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 408, 213180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Cao, M.; Ren, X.; Jiang, J.; An, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Functionalized Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Magnetic Composite Hydrogel as an Efficient Adsorbent for Chromium (VI) Removal. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 121, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Liu, W.; Zhu, F.; Liang, Q.; Zhu, W.; You, W.; et al. Development of Magnetic Nanocomposite Hydrogel with Potential Cartilage Tissue Engineering. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6182–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Wang, H. Shape Changing Hydrogels and Their Applications as Soft Actuators. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.; Safronov, A.P.; Mikhnevich, E.A.; Beketov, I.V.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Ferrogels Based on Entrapped Metallic Iron Nanoparticles in a Polyacrylamide Network: Extended Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek Consideration, Interfacial Interactions and Magnetodeformation. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 3359–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Du, J. Recent Advances in Magnetic Hydrogels. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C. A Recyclable and Regenerable Magnetic Chitosan Absorbent for Dye Uptake. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhtady, O.; Obeid, E.; Abu-samha, M.; Younes, K.; Murshid, N. Evaluation of the Adsorption Efficiency of Graphene Oxide Hydrogels in Wastewater Dye Removal: Application of Principal Component Analysis. Gels 2022, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, K.; Moghrabi, A.; Moghnie, S.; Mouhtady, O.; Murshid, N.; Grasset, L. Assessment of the Efficiency of Chemical and Thermochemical Depolymerization Methods for Lignin Valorization: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Approach. Polymers 2022, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, K.; Grasset, L. The Application of DFRC Method for the Analysis of Carbohydrates in a Peat Bog: Validation and Comparison with Conventional Chemical and Thermochemical Degradation Techniques. Chem. Geol. 2020, 545, 119644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zheng, M.; Chen, N.; Wu, Z.; Xu, N.; Tang, J.; Teng, Z. Uniform Magnetic Chitosan Microspheres with Radially Oriented Channels by Electrostatic Droplets Method for Efficient Removal of Acid Blue. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 104, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Tang, K.; Zhang, K.; Zou, Z.; Gao, X. High-Strength Chitin Based Hydrogels Reinforced by Tannic Acid Functionalized Graphene for Congo Red Adsorption. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjiri, M.T.; Bagheri Marandi, G.; Kurdtabar, M. Adsorption of Methylene Blue, Brilliant Green and Rhodamine B from Aqueous Solution Using Collagen-g-p(AA-Co-NVP)/Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanocomposite Hydrogel. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangwansupamonkon, W.; Klaikaew, N.; Kiatkamjornwong, S. Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogel Composite, Self Degradation and Environmental Applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 107, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Bethi, B.; Sonawane, S.H. Investigation of Removal of Crystal Violet Dye Using Novel Hybrid Technique Involving Hydrodynamic Cavitation and Hydrogel. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolahi, G.; Dargahi, M.; Ghasemzadeh, H. Synthesis of Starch-g-Poly (Acrylic Acid)/ZnSe Quantum Dot Nanocomposite Hydrogel, for Effective Dye Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Studies. Cellulose 2020, 27, 6467–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, T.M.; Ajmal, M.; Saeed, S.; Naeem, H.; Ahmad, H.B.; Mahmood, K.; Farooqi, Z.H. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Poly(Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel Fabricated with Cobalt Nanoparticles for Adsorption and Catalytic Applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 2765–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halouane, F.; Oz, Y.; Meziane, D.; Barras, A.; Juraszek, J.; Singh, S.K.; Kurungot, S.; Shaw, P.K.; Sanyal, R.; Boukherroub, R.; et al. Magnetic Reduced Graphene Oxide Loaded Hydrogels: Highly Versatile and Efficient Adsorbents for Dyes and Selective Cr(VI) Ions Removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 507, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, G.R.; Mosallanezhad, A. Facile and Green Rout to Prepare Magnetic and Chitosan-Crosslinked κ-Carrageenan Bionanocomposites for Removal of Methylene Blue. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 10, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bée, A.; Obeid, L.; Mbolantenaina, R.; Welschbillig, M.; Talbot, D. Magnetic Chitosan/Clay Beads: A Magsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dye from Water. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 421, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengel, S.B.; Sahiner, N. Poly(Vinyl Phosphonic Acid) Nanogels with Tailored Properties and Their Use for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Hussain, S.A.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Ezzat, A.O.; Tawfeek, A.M.; Al-Otabi, T. In Situ Preparation of Magnetite/Cuprous Oxide/Poly(AMPS/NIPAm) for Removal of Methylene Blue from Waste Water. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Oh, Y.; Park, S.; Kan, E.; Lee, S.H. Cellulose/Carrageenan/TiO2 Nanocomposite for Adsorption and Photodegradation of Cationic Dye. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2017, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthiga Devi, G.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Sathish Kumar, K. Green Synthesis of Novel Silver Nanocomposite Hydrogel Based on Sodium Alginate as an Efficient Biosorbent for the Dye Wastewater Treatment: Prediction of Isotherm and Kinetic Parameters. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 27686–27699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, L. Facile Fabrication of Magnetic Carboxymethyl Starch/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Composite Gel for Methylene Blue Removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lu, G.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, H.; Xia, Y.; Wen, X.; et al. Facile Preparation of Polyacrylamide/Chitosan/Fe3O4 Composite Hydrogels for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H. Green and Facile Fabrication of Pineapple Peel Cellulose/Magnetic Diatomite Hydrogels in Ionic Liquid for Methylene Blue Adsorption. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3825–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, L. Multi-Carboxylic Magnetic Gel from Hyperbranched Polyglycerol Formed by Thiol-Ene Photopolymerization for Efficient and Selective Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Methyl Violet Dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 529, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, F.; Ajmal, M.; Bibi, F.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Siddiq, M. Copper and Cobalt Nanoparticles Containing Poly(Acrylic Acid-Co-Acrylamide) Hydrogel Composites for Rapid Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Fast Removal of Malachite Green from Aqueous Medium. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 3187–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Arotiba, O. Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorption Studies of an Acrylic Acid-Grafted Sodium Alginate-Based TiO2 Hydrogel Nanocomposite. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, D. The Adsorption Behaviors of the Multiple Stimulus-Responsive Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Based Hydrogels for Removal of RhB Dye. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardajee, G.R.; Azimi, S.; Sharifi, M.B.A.S. Ultrasonically Accelerated Synthesis of Silver Nanocomposite Hydrogel Based on Salep Biopolymer: Application in Rhodamine Dye Adsorption. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, K.; Grasset, L. Analysis of Molecular Proxies of a Peat Core by Thermally Assisted Hydrolysis and Methylation-Gas Chromatography Combined with Multivariate Analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 124, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korichi, W.; Ibrahimi, M.; Loqman, S.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Younes, K.; Lemée, L. Assessment of Actinobacteria Use in the Elimination of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria of Ibn Tofail Hospital Wastewater (Marrakesh, Morocco): A Chemometric Data Analysis Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26840–26848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
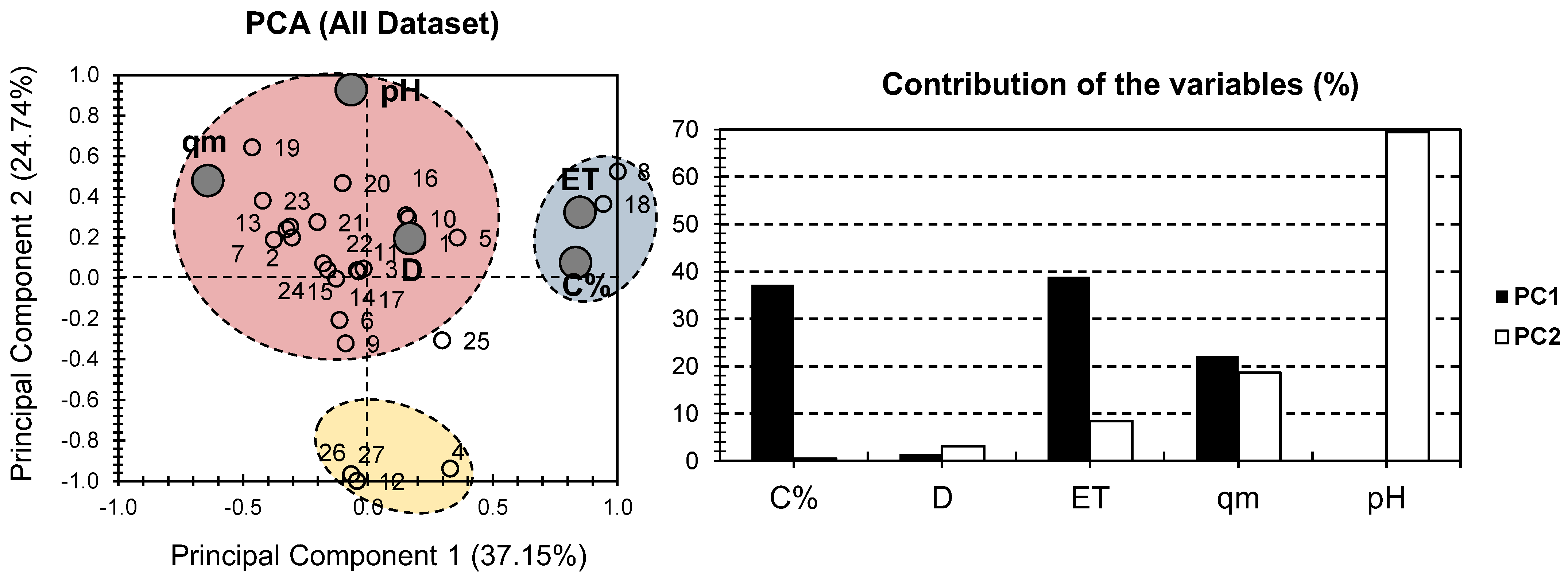
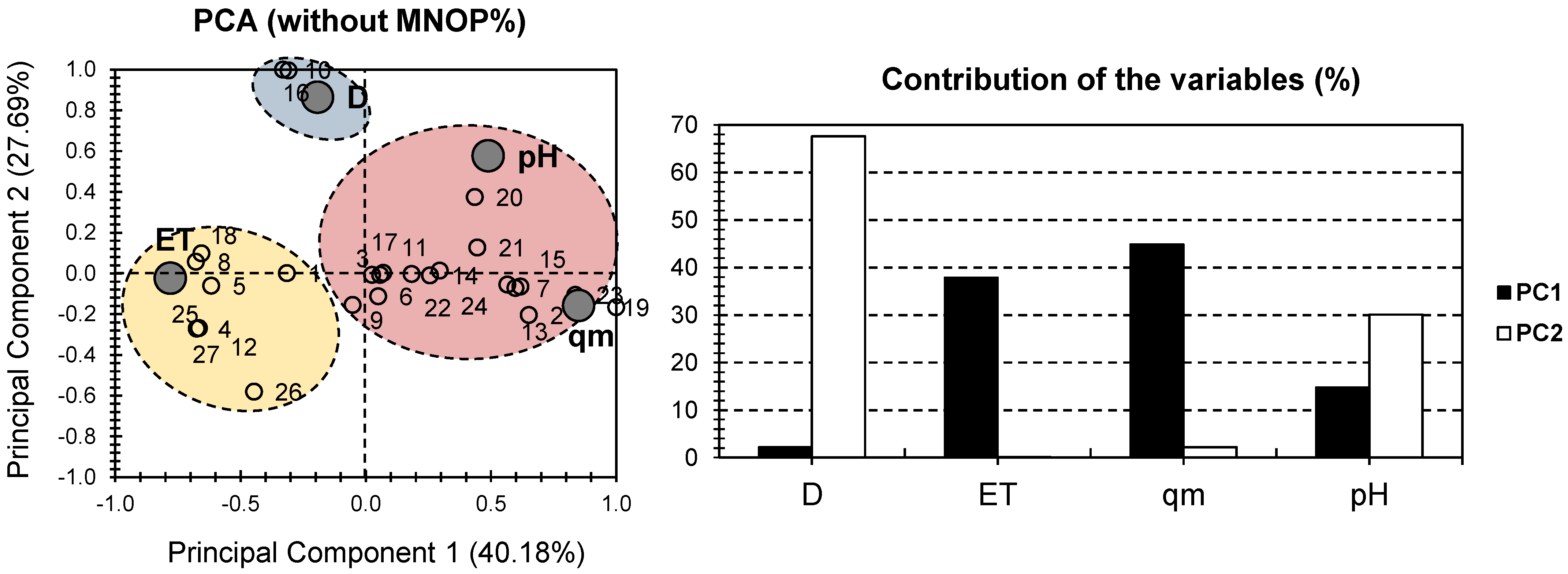
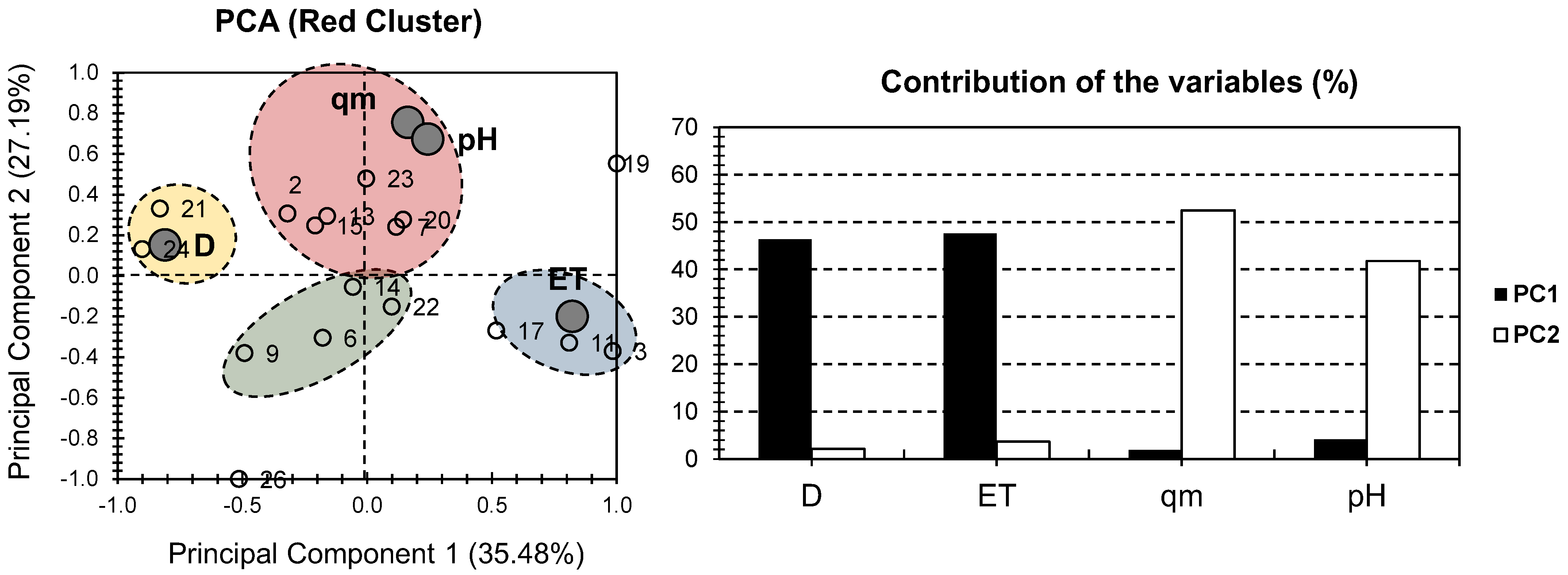

| MONPs Composite Hydrogel | Composite # | MONP% | D | ET | qm | pH | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTS@ Fe3O4 | 1 | - | 1 | 400 | 142 | 7 | [32] |
| ALG@Yttrium | 2 | - | 2 | 30 | 1087 | 6 | [33] |
| Collagen-g-PAAc-co-NVP/Fe3O4@SiO2 | 3 | - | 0.05 | 150 | 199 | 7 | [34] |
| PAAm-co-AAc/TiO2 | 4 | 20 | 1 | - | 2.2 | - | [35] |
| PAAm/TiO2 | 5 | 0.5 | - | 600 | 132 | 6.5 | [36] |
| St-g-PAAc/ZnSe | 6 | - | 1 | 30 | 189 | 6 | [37] |
| PAAc/Co3O4 | 7 | - | 0.5 | 30 | 837 | - | [38] |
| PEGDMA-rGO/Fe3O4@cellulose | 8 | 30 | 2.5 | 720 | 112 | 7.4 | [39] |
| CTS/Fe3O4@κ-CARR | 9 | - | 2 | 30 | 123 | 5.5 | [40] |
| CTS/MMT/γFe2O3 | 10 | - | 100 | 180 | 82 | - | [41] |
| Collagen-g-PAAc-co-NVP/Fe3O4@SiO2 | 11 | - | 0.05 | 125 | 202 | 7 | [34] |
| PVPA/Fe3O4@SiO2 | 12 | 0 | 1.4 | - | 14 | - | [42] |
| AMPS/NIPAAm/Fe3O4 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 833 | 7 | [43] |
| AMPS/NIPAAm/Cu2O | 14 | 0 | 1 | 35 | 341 | 7 | [43] |
| AMPS/NIPAM/Fe3O4·Cu2O | 15 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 746 | 7 | [43] |
| Cellulose/κ-CARR/TiO2 | 16 | 0.7 | 115 | 7 | [44] | ||
| ALG/AgNPs | 17 | 1 | 120 | 214 | - | [45] | |
| CMSt/PVA/Fe3O4 | 18 | 10 | 600 | 24 | 7 | [46] | |
| PAAm/CTS/Fe3O4 | 19 | 0.1 | 125 | 1603 | 7 | [47] | |
| Cellulose/Fe3O4-diatomite | 20 | 0.7 | 30 | 102 | 10 | [48] | |
| HPG@Fe3O4 | 21 | 4 | 30 | 459 | 8 | [49] | |
| PAAc-co-AAm/Co3O4·Cu2O | 22 | 0.5 | 40 | 238 | 7 | [50] | |
| PAAc-g-ALG/TiO2 | 23 | 0.6 | 1157 | 7 | [51] | ||
| HPG@Fe3O4 | 24 | 4 | 30 | 400 | 7 | [49] | |
| PMOA/ATP/Fe3O4 | 25 | 3 | 400 | 1.7 | 4.6 | [52] | |
| PAAc-g-salep/AgNPs | 26 | 1 | 20 | 93 | 2 | [53] | |
| PVPA/Fe3O4@SiO2 | 27 | 1.4 | 16 | - | [42] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murshid, N.; Mouhtady, O.; Abu-samha, M.; Obeid, E.; Kharboutly, Y.; Chaouk, H.; Halwani, J.; Younes, K. Metal Oxide Hydrogel Composites for Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Wastewater: Principal Component Analysis. Gels 2022, 8, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110702
Murshid N, Mouhtady O, Abu-samha M, Obeid E, Kharboutly Y, Chaouk H, Halwani J, Younes K. Metal Oxide Hydrogel Composites for Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Wastewater: Principal Component Analysis. Gels. 2022; 8(11):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110702
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurshid, Nimer, Omar Mouhtady, Mahmoud Abu-samha, Emil Obeid, Yahya Kharboutly, Hamdi Chaouk, Jalal Halwani, and Khaled Younes. 2022. "Metal Oxide Hydrogel Composites for Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Wastewater: Principal Component Analysis" Gels 8, no. 11: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110702
APA StyleMurshid, N., Mouhtady, O., Abu-samha, M., Obeid, E., Kharboutly, Y., Chaouk, H., Halwani, J., & Younes, K. (2022). Metal Oxide Hydrogel Composites for Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Wastewater: Principal Component Analysis. Gels, 8(11), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110702