Physicochemical, Pasting, and Thermal Properties of Native Corn Starch–Mung Bean Protein Isolate Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
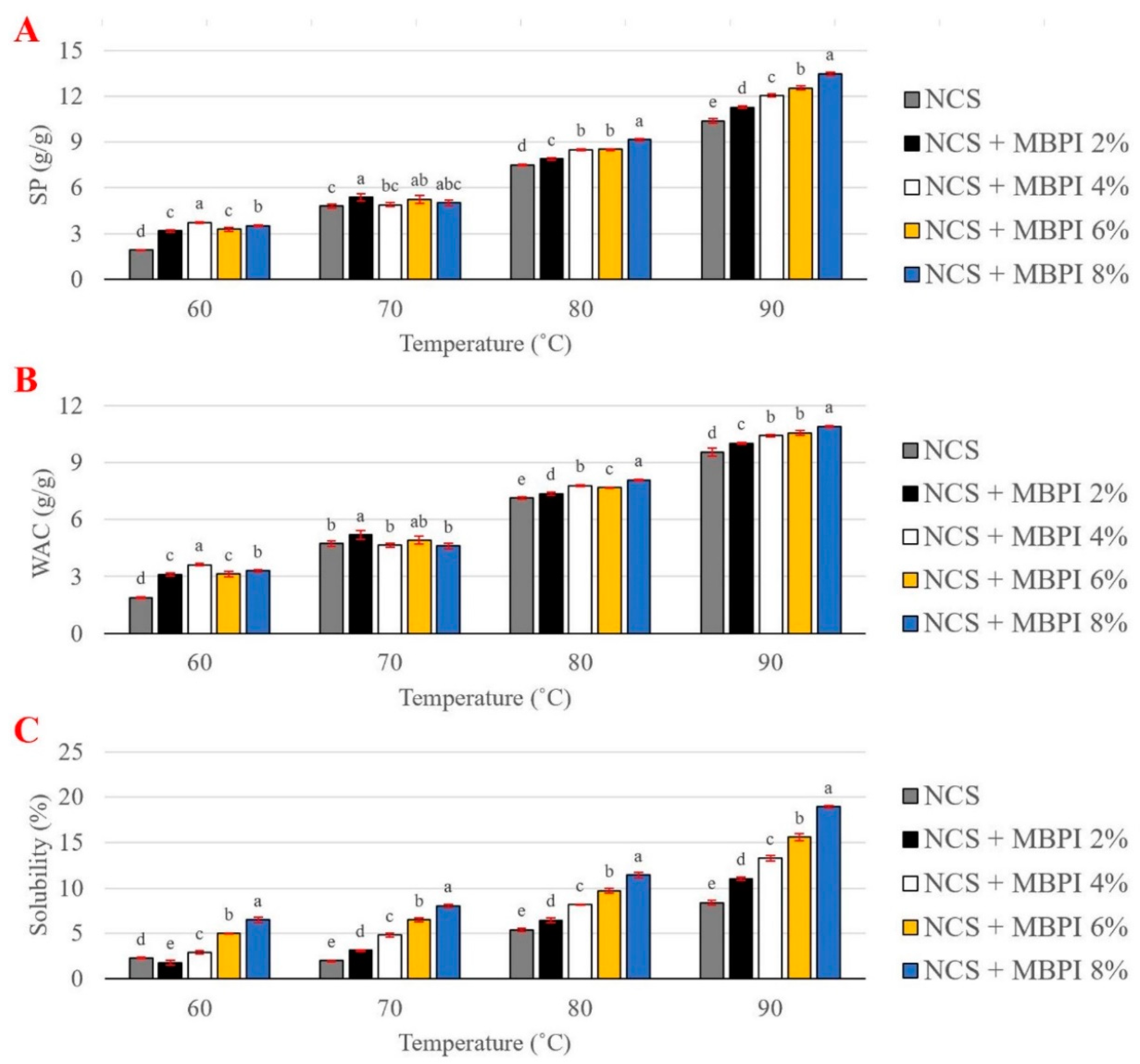
2.1. Swelling Power, Water Absorption Capacity, and Solubility
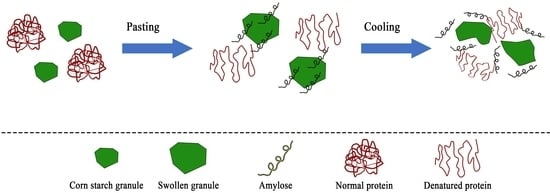
2.2. Pasting Properties
2.3. Thermal Properties
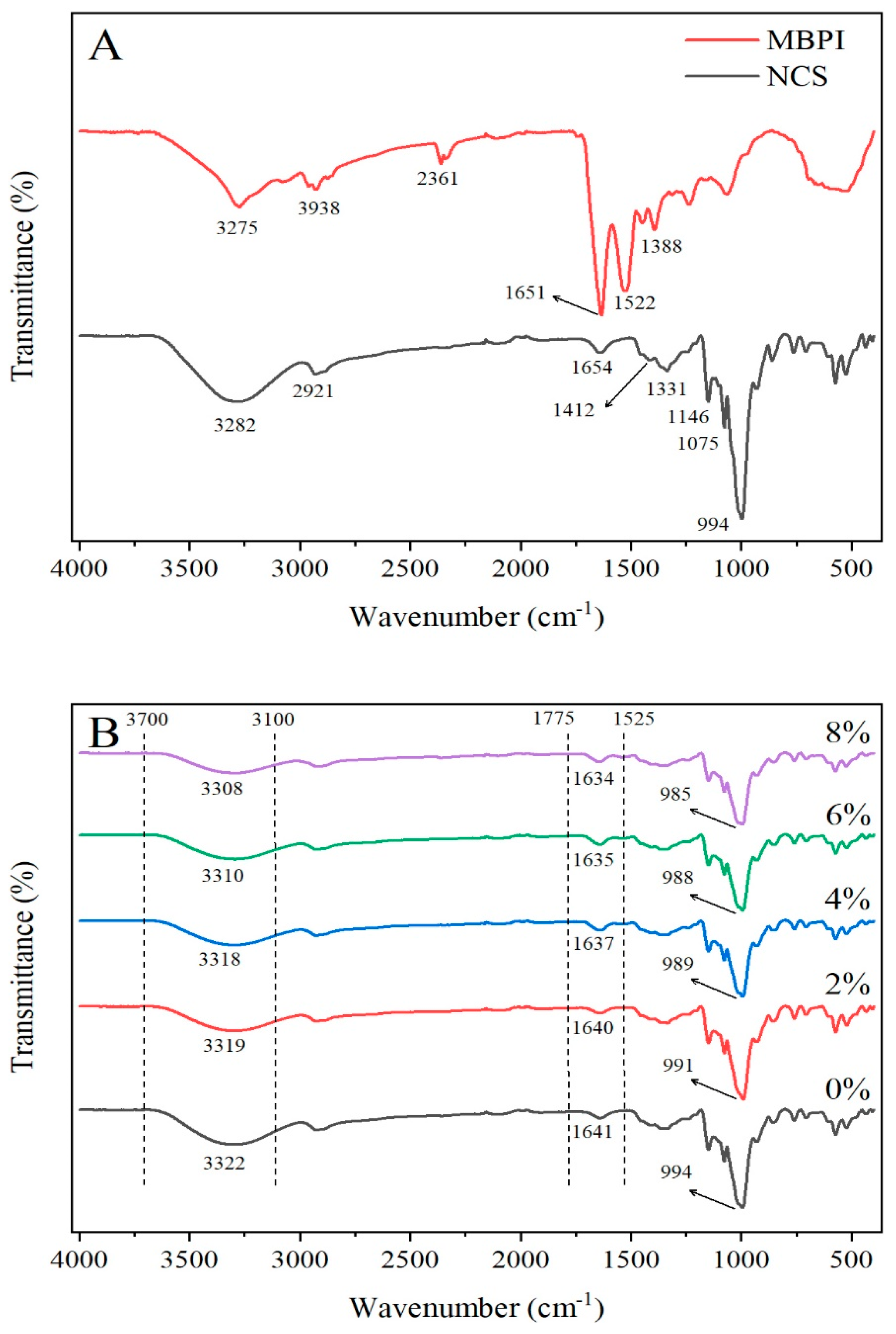
2.4. FT-IR Spectroscopy Analysis
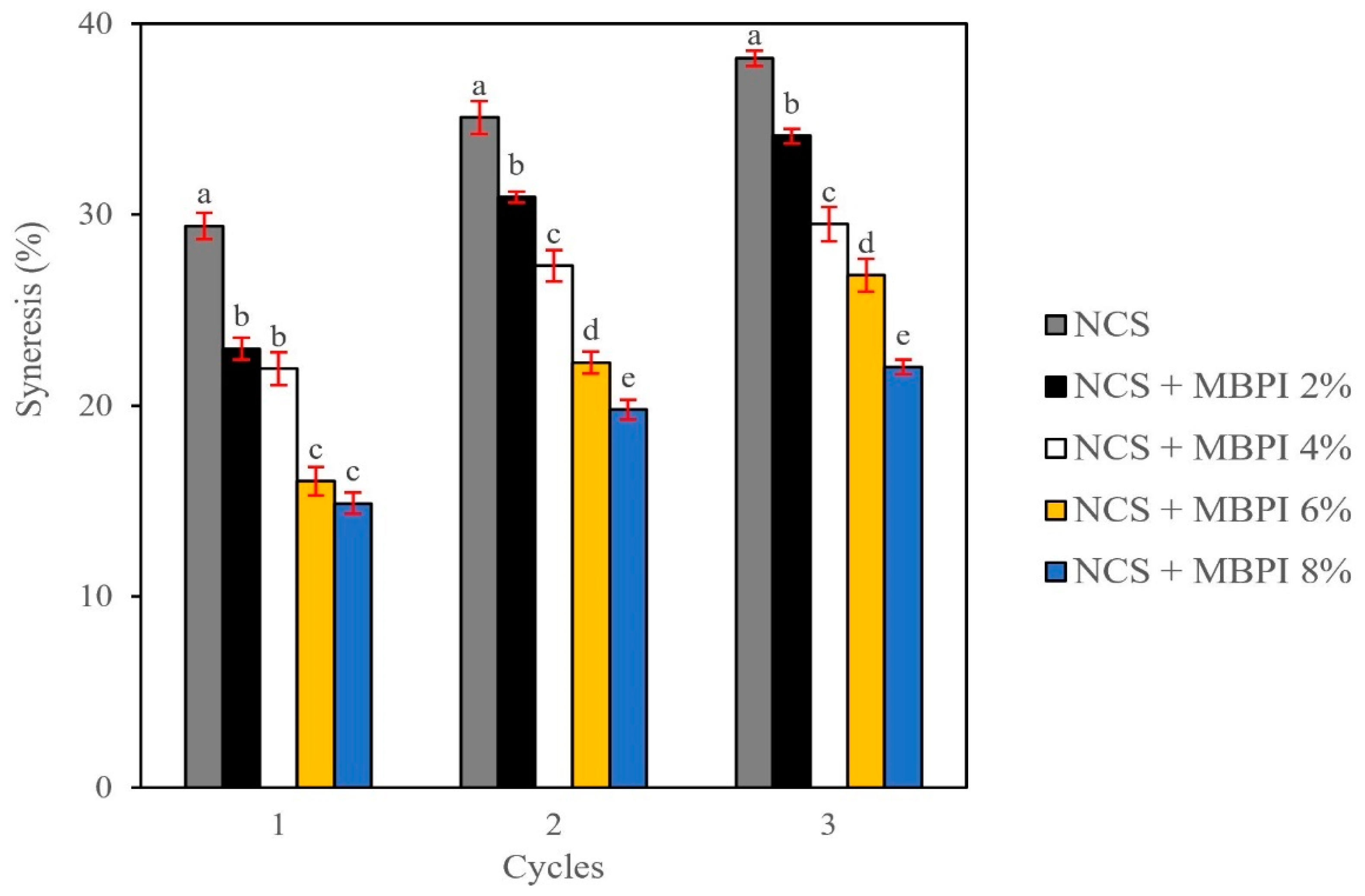
2.5. Freeze-Thaw Stability
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Isolation of Mung Bean Protein
4.3. Preparation of NCS/MBPI Blends
4.4. Swelling Power (SP), Water Absorption Capacity (WAC), and Solubility
4.5. Rapid Visco Analyzer (RVA) Measurements
4.6. Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
4.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
4.8. Evaluation of Freeze-Thaw Stability
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dome, K.; Podgorbunskikh, E.; Bychkov, A.; Lomovsky, O. Changes in the Crystallinity Degree of Starch Having Different Types of Crystal Structure after Mechanical Pretreatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.-N.; Zhang, B.; Chen, B.; Chen, H.-Q. Effects of oligosaccharides on pasting, thermal and rheological properties of sweet potato starch. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams-Abadi, S.T.; Razavi, S.M.A. Cress seed gum improves rheological, textural and physicochemical properties of native wheat starch-sucrose mixture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E. Understanding Starch Structure: Recent Progress. Agronomy 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Han, Q.; Cao, C.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B. Short-term retrogradation behaviour of corn starch is inhibited by the addition of porcine plasma protein hydrolysates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Shen, M.; Xie, J. Effects of Mesona chinensis Benth polysaccharide on physicochemical and rheological properties of sweet potato starch and its interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M. Effects of konjac glucomannan on pasting and rheological properties of corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Geveke, D.J.; Yadav, M.P. Improvement of rheological, thermal and functional properties of tapioca starch by using gum arabic. LWT 2017, 80, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso, J.O.; Brennan, C. Whey and Pea Protein Fortification of Rice Starches: Effects on Protein and Starch Digestibility and Starch Pasting Properties. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 1700315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhong, F.; Goff, H.D.; Li, Y. Study on starch-protein interactions and their effects on physicochemical and digestible properties of the blends. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, M.; Yadav, B.S.; Yadav, R.B.; Dangi, N. Assessing the influence of lentil protein concentrate on pasting and rheological properties of barley starch. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Lin, N.; Liu, J. Effect of adding zein, soy protein isolate and whey protein isolate on the physicochemical and in vitro digestion of proso millet starch. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhao, T.; Gong, T.; Zou, L.; Guo, Y. Young apple polyphenols postpone starch digestion in vitro and in vivo. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 56, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.-R.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Zhu, Y.-M. Effects of Cordyceps polysaccharides on pasting properties and in vitro starch digestibility of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B. DSC study on the thermal properties of soybean protein isolates/corn starch mixture. J. Therm. Anal. 2014, 115, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Fu, X.; Li, L.; Huang, Q. Structure, physicochemical and in vitro digestion properties of ternary blends containing swollen maize starch, maize oil and zein protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Brennan, M.; Zheng, H.; Brennan, C. The effects of dairy ingredients on the pasting, textural, rheological, freeze-thaw properties and swelling behaviour of oat starch. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.; Aldred, P.; Panozzo, J.; Kasapis, S.; Adhikari, B. Rheological and microstructural characteristics of lentil starch–lentil protein composite pastes and gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribotta, P.D.; Colombo, A.; León, A.E.; Añón, M.C. Effects of Soy Protein on Physical and Rheological Properties of Wheat Starch. Starch-Stärke 2007, 59, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekle, M.; Mühlberger, K.; Becker, T. Starch–gluten interactions during gelatinization and its functionality in dough like model systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Ai, L.; Xiong, W. Insight into protein-starch ratio on the gelatinization and retrogradation characteristics of reconstituted rice flour. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.-H.; Donner, E.; Yada, R.Y.; Liu, Q. Physicochemical properties and in vitro starch digestibility of potato starch/protein blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, S.O.; Ali, T.M.; Ahmed, J.; Shaikh, M.; Siddiq, M.; Uebersax, M.A. Physico-chemical and functional properties of legume protein, starch, and dietary fiber—A review. Legume Sci. 2022, 4, e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinma, C.E.; Ariahu, C.C.; Abu, J.O. Chemical composition, functional and pasting properties of cassava starch and soy protein concentrate blends. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qiao, D.; Zhao, S.; Lin, Q.; Wang, J.; Xie, F. Starch-based food matrices containing protein: Recent understanding of morphology, structure, and properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, N.; Yadav, M.; Kumar, S.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Singh, M.; Sharma, A.K. Review on health promoting biological activities of mungbean: A potent functional food of medicinal importance. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 2969–2975. [Google Scholar]
- Yi-Shen, Z.; Shuai, S.; FitzGerald, R. Mung bean proteins and peptides: Nutritional, functional and bioactive properties. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branch, S.; Maria, S. Evaluation of the functional properties of mung bean protein isolate for development of textured vegetable protein. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Yousaf, L.; Xue, Y.; Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; Feng, N.; Shen, Q. Mung bean (Vigna radiata L.): Bioactive polyphenols, polysaccharides, peptides, and health benefits. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adawy, T.A. Functional properties and nutritional quality of acetylated and succinylated mung bean protein isolate. Food Chem. 2000, 70, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Xie, J.; Gong, B.; Xu, X.; Tang, W.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Xie, M. Extraction, physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of Mung bean protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahi, M.; Hedayati, S.; Shahidi, F. Effects of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata) Protein Isolate on Rheological, Textural, and Structural Properties of Native Corn Starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayati, S.; Niakousari, M. Microstructure, pasting and textural properties of wheat starch-corn starch citrate composites. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Xiong, C.S.L. Functional and pasting properties of pea starch and peanut protein isolate blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, G. Effects of endogenous proteins and lipids on structural, thermal, rheological, and pasting properties and digestibility of adlay seed (Coix lacryma-jobi L.) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribotta, P.D.; Colombo, A.; Rosell, C.M. Enzymatic modifications of pea protein and its application in protein–cassava and corn starch gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lai, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Composites of Hydroxypropyl Tapioca Starch and Zein. Starch-Stärke 2020, 72, 1900204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejosano, F.P.; Corke, H. Effect of Amaranthus and buckwheat proteins on the rheological properties of maize starch. Food Chem. 1999, 65, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Ribotta, P.D.; León, A.E. Thermal and Rheological Behavior of Peanut Protein Concentrate and Starch Composites. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; León, A.E.; Ribotta, P.D. Rheological and calorimetric properties of corn-, wheat-, and cassava-starches and soybean protein concentrate composites. Starch-Stärke 2011, 63, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, S.; Shahidi, F.; Majzoobi, M.; Koocheki, A.; Farahnaky, A. Structural, rheological, pasting and textural properties of granular cold water swelling maize starch: Effect of NaCl and CaCl2. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; King, J. Pasting and Crystalline Property Differences of Commercial and Isolated Rice Starch with Added Amino Acids. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Salami, M.; Moghadam, M.; Amirsalehi, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Mung bean protein as a promising biopolymeric vehicle for loading of curcumin: Structural characterization, antioxidant properties, and in vitro release kinetics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.; Salami, M.; Mohammadian, M.; Khodadadi, M.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Development of antioxidant edible films based on mung bean protein enriched with pomegranate peel. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarani, N.M.; Razavi, S.M.A.; Taghizadeh, M. Impact of sage seed gum and whey protein concentrate on the functional properties and retrogradation behavior of native wheat starch gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.-N.; Xie, Y.; Chen, H.-Q. Effects of glutenin and gliadin modified by protein-glutaminase on pasting, rheological properties and microstructure of potato starch. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helrich, K. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Tarahi, M.; Shahidi, F.; Hedayati, S. A novel starch from bitter vetch (Vicia ervilia) seeds: A comparison of its physicochemical, structural, thermal, rheological, and pasting properties with conventional starches. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 6833–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, R.; Senanayake, S. Composition and physicochemical properties of oat starches. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MBPI (%) | Pasting Temperature (°C) | Viscosity (cP) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak | Breakdown | Setback | Final | ||
| 0 | 77.98 ± 0.02 a | 4691 ± 17 e | 1992 ± 20 e | 3063 ± 18 a | 5762 ± 15 a |
| 2 | 77.06 ± 0.03 b | 5002 ± 14 d | 2397 ± 25 d | 2738 ± 37 b | 5343 ± 25 b |
| 4 | 77.04 ± 0.01 b | 5282 ± 22 c | 2685 ± 22 c | 2612 ± 18 c | 5209 ± 13 c |
| 6 | 76.86 ± 0.06 c | 5578 ± 10 b | 3049 ± 23 b | 2475 ± 44 d | 5004 ± 12 d |
| 8 | 76.53 ± 0.06 d | 5648 ± 13 a | 3173 ± 19 a | 2400 ± 37 e | 4875 ± 28 e |
| MBPI (%) | Thermal Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) | |
| 0 | 69.69 ± 0.42 e | 73.45 ± 0.40 e | 77.75 ± 0.35 d | 10.85 ± 0.23 a |
| 2 | 70.43 ± 0.12 d | 74.71 ± 0.19 d | 80.78 ± 0.20 c | 9.77 ± 0.07 b |
| 4 | 71.24 ± 0.12 c | 75.36 ± 0.24 c | 81.17 ± 0.17 bc | 9.54 ± 0.11 b |
| 6 | 71.69 ± 0.14 b | 76.10 ± 0.16 b | 81.43 ± 0.19 b | 9.11 ± 0.09 c |
| 8 | 72.21 ± 0.20 a | 76.72 ± 0.15 a | 82.26 ± 0.24 a | 8.79 ± 0.15 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarahi, M.; Shahidi, F.; Hedayati, S. Physicochemical, Pasting, and Thermal Properties of Native Corn Starch–Mung Bean Protein Isolate Composites. Gels 2022, 8, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110693
Tarahi M, Shahidi F, Hedayati S. Physicochemical, Pasting, and Thermal Properties of Native Corn Starch–Mung Bean Protein Isolate Composites. Gels. 2022; 8(11):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110693
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarahi, Mohammad, Fakhri Shahidi, and Sara Hedayati. 2022. "Physicochemical, Pasting, and Thermal Properties of Native Corn Starch–Mung Bean Protein Isolate Composites" Gels 8, no. 11: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110693
APA StyleTarahi, M., Shahidi, F., & Hedayati, S. (2022). Physicochemical, Pasting, and Thermal Properties of Native Corn Starch–Mung Bean Protein Isolate Composites. Gels, 8(11), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110693