Viscoelastic Properties and Enzymatic Degradation of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid for Deep Dermal Filler Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Commercial Sample | BtHCROSS 2%® | Juvederm Voluma® | Belotero Soft® | Restylane Refyne® | Teosyal® Ultimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lot | 1738/24 | 1000648978 | B00041590 | 11512 | 23361BM1 |
| HA mg/mL | 20 mg/mL | 20 mg/mL | 20 mg/mL | 20 mg/mL | 22 mg/mL |
| Volume/Syringe | 1 mL | 1 mL | 1 mL | 1 mL | 1 mL |
| Lidocaine | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Crosslinking Technology | SARE® [19] | VYCROSS® [15] | CPM® [16] | XpresHAn® [17] | RHA® [18] |
| Composition (IFU) | Sodium hyaluronate cross-linked 20 mg, disodium phosphate dihydrate 0.6 mg, sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate 0.05 mg, sodium chloride 8 mg q.s. 1 mL | Hyaluronic acid gel 20 mg, lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate 3 mg, phosphate buffer pH 7.2 q.s. 1 mL | Cross-linked sodium hyaluronate 20 mg, lidocaine hydrochloride 3 mg, phosphate buffer pH 7.0 q.s. 1 mL | Cross-linked hyaluronic acid 20 mg, Lidocaine hydrochloride, Phosphate-buffered saline pH 7.0 q.s. 1 mL | Crosslinked hyaluronic acid 22 mg, Lidocaine hydrochloride 3 mg, phosphate buffer pH 7.3 q.s. 1 mL |
2. Results and Discussion
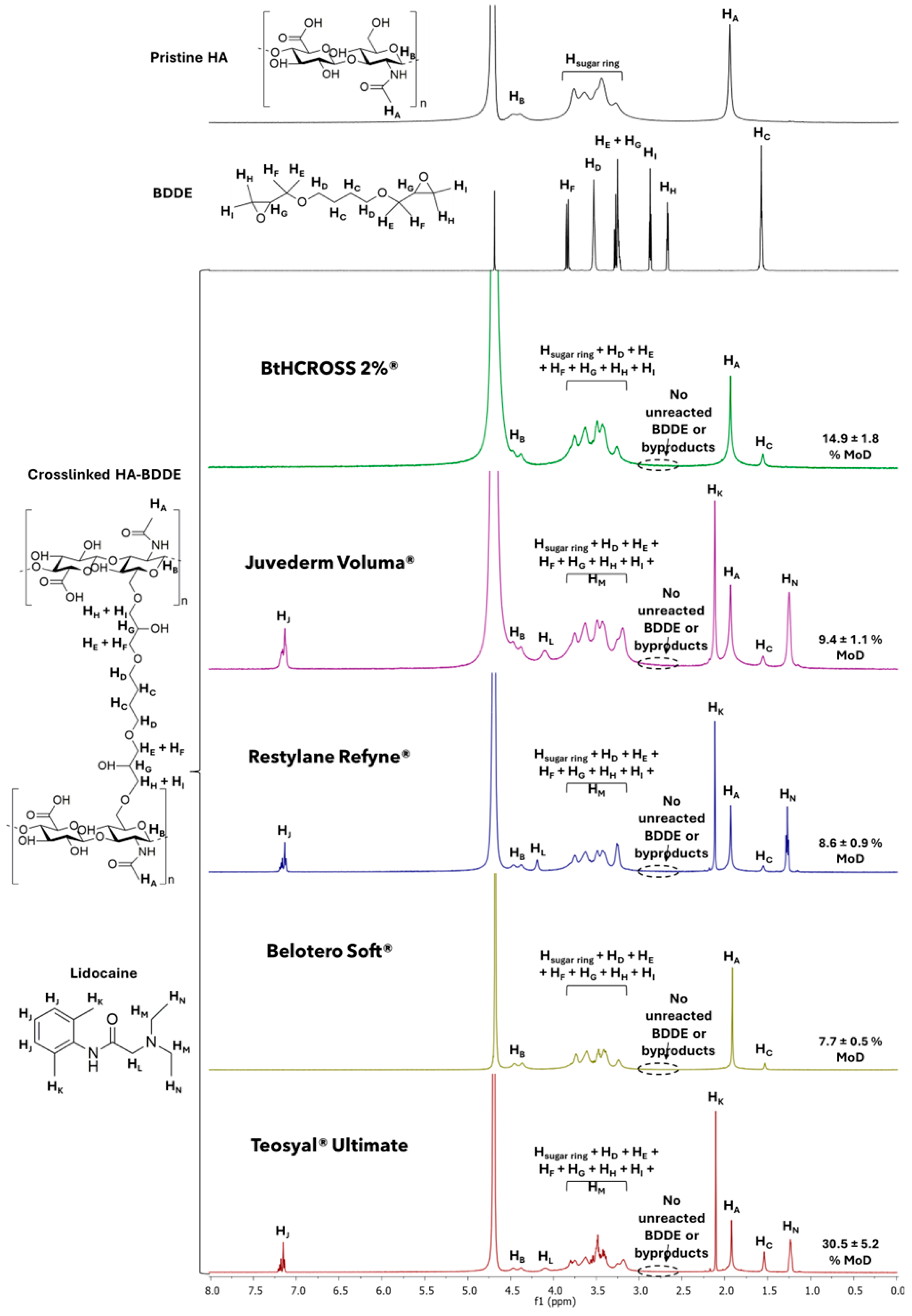
2.1. Chemical Composition and Degree of Modification
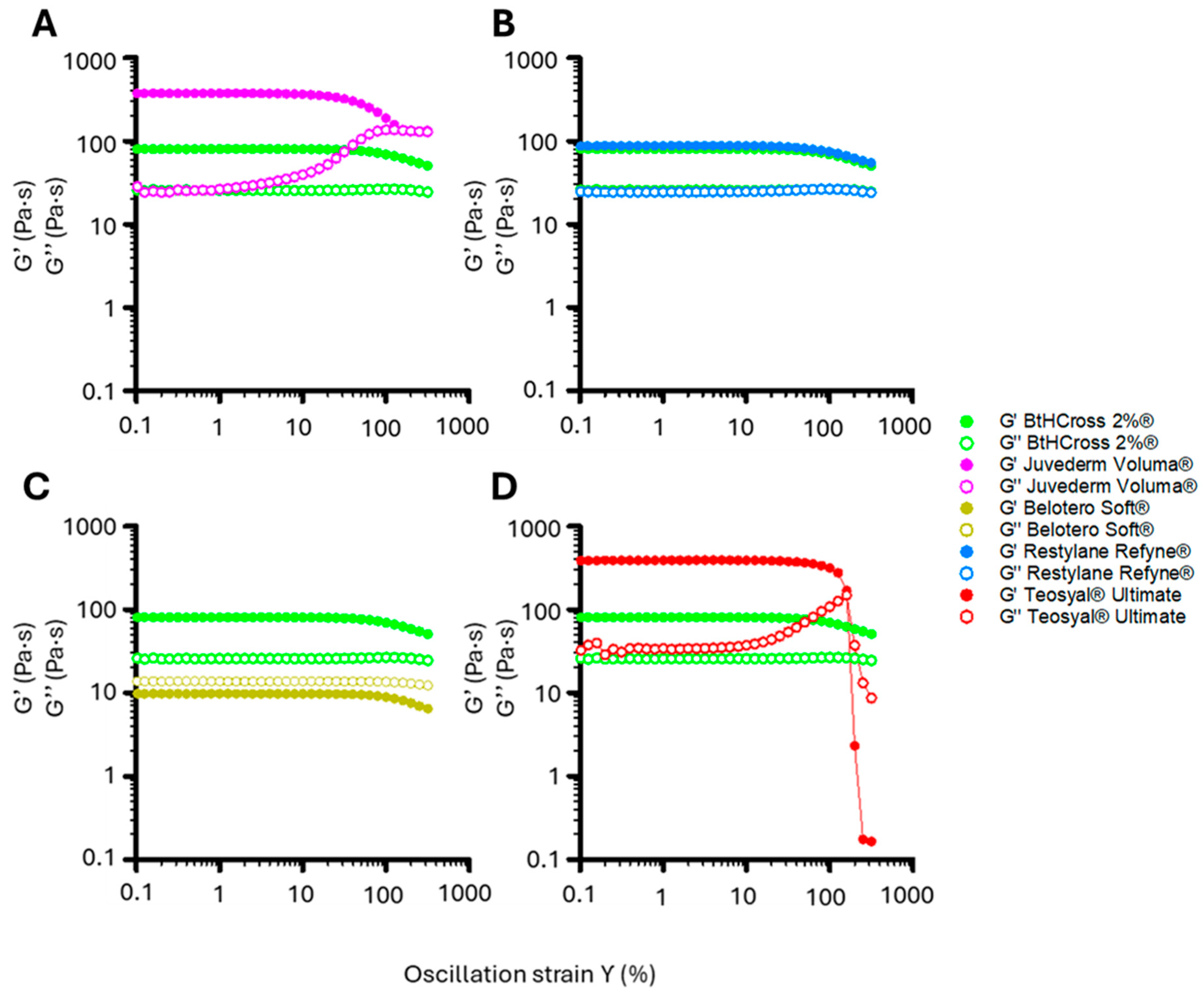
2.2. Rheological Characterisation
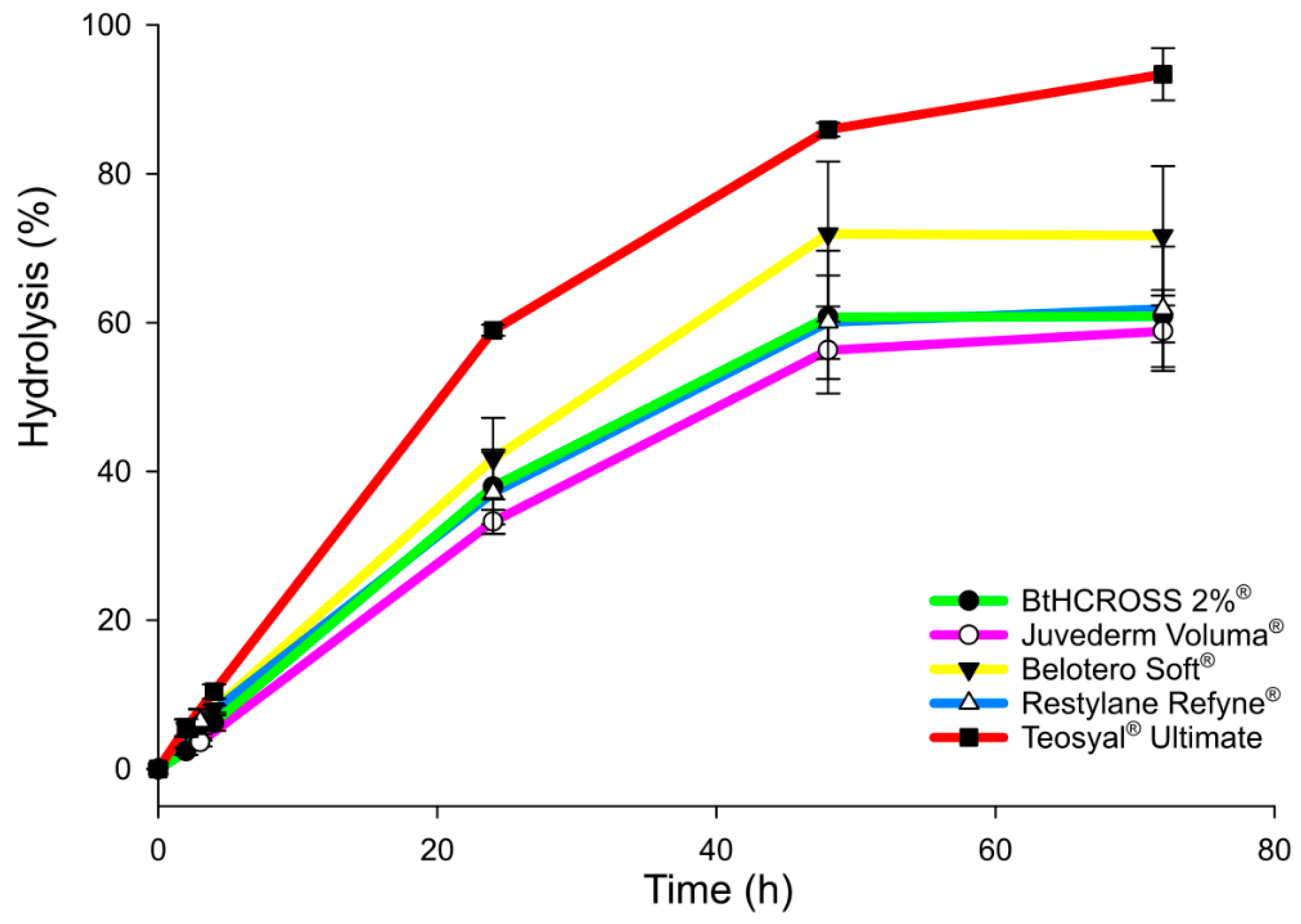
2.3. Enzymatic Degradation Assay
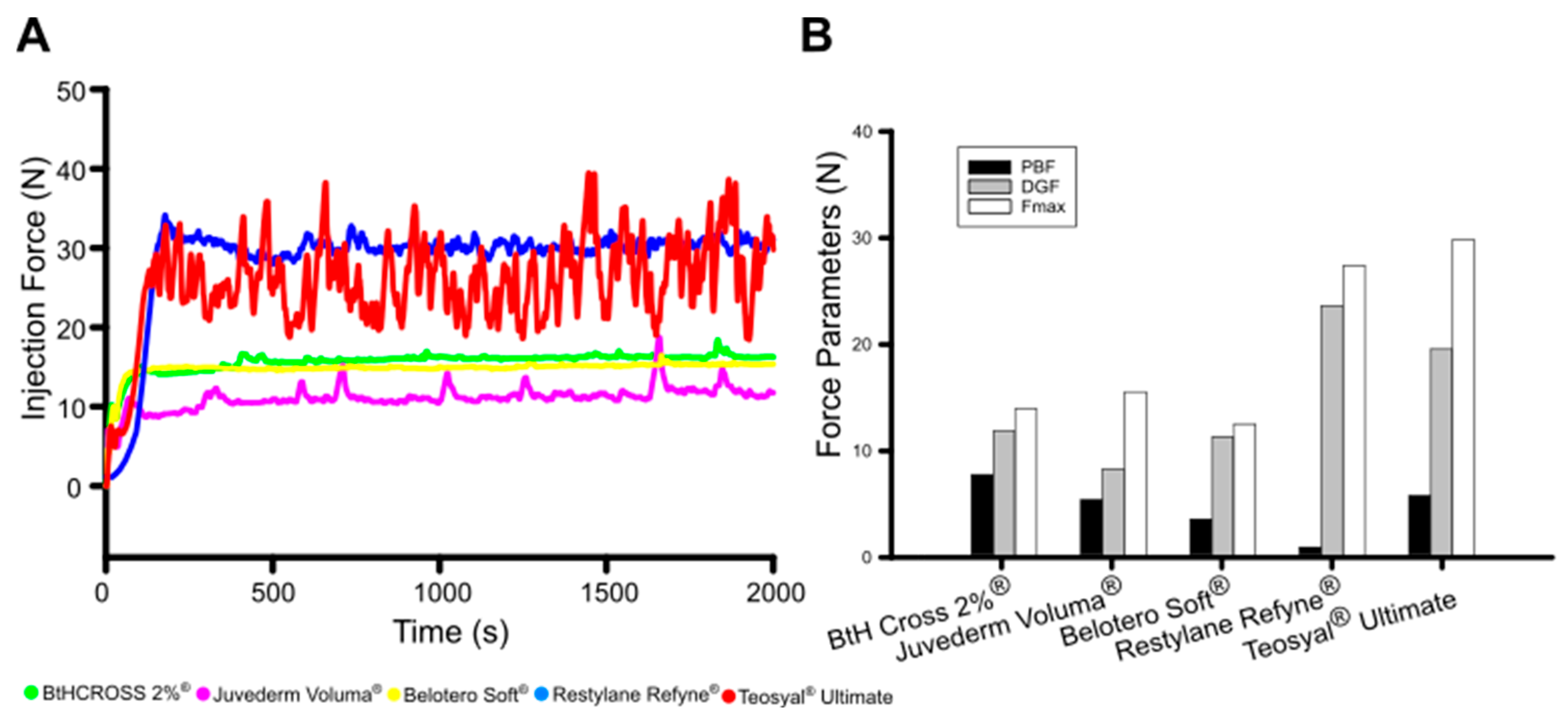
2.4. Injectability
2.5. Linking Microstructure to Rheology, Injectability, and Degradation in Crosslinked HA Fillers
2.6. Safety Considerations:Lidocaine-Free Dermal Filler and Biological Safety
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Characterisation
4.2.1. Chemical Composition and Degree of Modification (MoD)
4.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy with Attenuated Total Reflectance Methodology (FTIR-ATR)
4.2.3. In Vitro Enzymatic Degradation
4.2.4. Rheological Characterisation
4.2.5. Injectability
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDDE | 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| HA | Hyaluronic Acid |
| 1H-NMR | Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| LVR | Linear Viscoelastic Regime |
| MoD | Degree of chemical modification |
References
- Gosain, A.K.; Klein, M.H.; Sudhakar, P.V.; Prost, R.W. A Volumetric Analysis of Soft-Tissue Changes in the Aging Midface Using High—Resolution MRI: Implications for Facial Rejuvenation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 115, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargaran, D.; Zoller, F.; Zargaran, A.; Weyrich, T.; Mosahebi, A. Facial Skin Ageing: Key Concepts and Overview of Processes. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2022, 44, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.W.; Elson, M.L. The History of Substances for Soft Tissue Augmentation. Dermatol. Surg. 2000, 26, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, K.M.; Saputra, D.I.; Porter, C.E.; Colucci, L.; Stone, C.; Brenninkmeijer, E.E.A.; Sloane, J.; Sayed, K.; Winaya, K.K.; Bertossi, D. Treating Aging Changes of Facial Anatomical Layers with Hyaluronic Acid Fillers. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.A.; Hernández, R.; Alonso, J.M.; Pérez-González, R.; Sáez-Martínez, V. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Crosslinked in Physiological Conditions: Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.T.; Kam, J.; Bloom, J.D. Hyaluronic Acid Basics and Rheology. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 30, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.M.; Del Olmo, J.A.; Gonzalez, R.P.; Saez-martinez, V. Injectable Hydrogels: From Laboratory to Industrialization. Polymers 2021, 13, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongprasert, P.; Dreiss, C.A.; Murray, G. Evaluating Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Critique of Current Characterization Methods. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, M.W.; Wee, A.G.; Marx, D.B.; Ridgway, L.; Simetich, B.; De Sousa, T.C.; Vakilzadian, K.; Schulte, J. Viscoelastic Properties of Human Facial Skin and Comparisons with Facial Prosthetic Elastomers. Materials 2023, 16, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lateef, A.; Snyder, A.; Schlesinger, T. Restylane: What We Know. Dermatol. Rev. 2023, 4, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, T. Rheology of Hyaluronic Acid and Dynamic Facial Rejuvenation: Topographical Specificities. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, H.; Cassuto, D. Biophysical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Soft-Tissue Fillers and Their Relevance to Aesthetic Applications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 5S–21S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, M.C.A.; Viana, R.M.M.; Mendes, P.R.S.; Naccache, M.F.; Varges, P.R.; Castaño, E.P.M.; Palermo, E. Analysis of Morphologic and Rheological Properties of Hyaluronic Acid Gel Fillers to Body Contouring and Its Clinical Correlation. Gels 2025, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, G.J.; Swift, A.; Remington, B.K. Current Concepts in the Use of Voluma, Volift, and Volbella. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 139S–148S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, A.D.; Prager, W.; Rubin, M.G.; Moretti, E.A.; Nikolis, A. Hyaluronic Acid Fillers with Cohesive Polydensified Matrix for Soft-Tissue Augmentation and Rejuvenation: A Literature Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 9, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.; Öhrlund, A. Flexibility Measurements of Injectable Gels. Patent number WO2018104426A1, 7 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Hebel, C.; Snyder, A.; Schlesinger, T. Other Hyaluronic Acid Fillers and Combination Fillers. Dermatol. Rev. 2023, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, J.A.; Martínez, V.S.; Cestafe, N.M.; Alonso, J.M.; Ibeas, C.G.; Heredia, M.U.L.; Cid, S.B.; González, R.P. Resistance to Enzymatic Degradation and Efficacy Evaluation of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Based Commercial Viscosupplements for Knee Osteoarthritis Treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 6, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.H.; Kim, D.H.; Yune, J.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Shin, D.M.; Sohn, H.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, B.; Kim, E.S.; Kang, J.H.; et al. In Vitro Toxicity Assessment of Crosslinking Agents Used in Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Filler. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 70, 105034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Olmo, J.A.; Pérez-álvarez, L.; Martínez, V.S.; Cid, S.B.; González, R.P.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Alonso, J.M. Drug Delivery from Hyaluronic Acid–BDDE Injectable Hydrogels for Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, J.; Pigweh, A.I.; Iehl, J.; Maffert, P.; Goekjian, P.; Bourdon, F. Crosslinking Hyaluronic Acid Soft-Tissue Fillers: Current Status and Perspectives from an Industrial Point of View. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2021, 18, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fundarò, S.P.; Salti, G.; Malgapo, D.M.H.; Innocenti, S. The Rheology and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Their Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, J.; Wu, K.; Gallet, M.; Sparrow, J.; Bourdon, F.; Gallagher, C.J. Comparison of Hyaluronidase-Mediated Degradation Kinetics of Commercially Available Hyaluronic Acid Fillers in Vitro. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2024, 44, NP402–NP410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yu, X.; Yi, X.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Hao, Y.; Wang, W. Lidocaine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Adhesive Microneedle Patch for Oral Mucosal Topical Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Guardia, C.; Virno, A.; Musumeci, M.; Bernardin, A.; Silberberg, M.B. Rheologic and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Overview and Relationship to Product Performance. Facial Plast. Surg. 2022, 38, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkov, G.; Niyazov, Z.; Picchioni, F.; Bose, R.K. Relationship between Structure and Rheology of Hydrogels for Various Applications. Gels 2021, 7, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpowicz, M.I.; Klekotka, M.; Dąbrowski, J.R. The Effect of the Molecular Weight of Hyalyronic Acid on the Rheological and Tribological Properties of the Base for Artificial Synovial Fluid Preparations. Acta Mech. Autom. 2024, 18, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.W.; Hu, H.; Chang, K.; Park, Y.; Lee, K.W.A.; Chan, L.K.W.; Yi, K.H. Review of the Adverse Effects Associated with Dermal Filler Treatments: Part I Nodules, Granuloma, and Migration. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrlund, J.Å.; Edsman, K.L.M. The Myth of the “Biphasic” Hyaluronic Acid Filler. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41, S358–S364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, E.; Zoratto, N.; Mosca, L.; Cervoni, L.; Lallana, E.; Angelini, R.; Matassa, R.; Coviello, T.; Di Meo, C.; Matricardi, P. Halting Hyaluronidase Activity with Hyaluronan-Based Nanohydrogels: Development of Versatile Injectable Formulations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine (NLM) Lidocaine Viscous. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682701.html (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Bahar, E.; Yoon, H. Lidocaine: A Local Anesthetic, Its Adverse Effects and Management. Medicina 2021, 57, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Uchizono, J.A. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Anesthetics. In Essentials of Pharmacology for Anesthesia, Pain Medicine, and Critical Care; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 3–47. ISBN 9781461489481. [Google Scholar]
- Heydenrych, I.; Kapoor, K.M.; Boulle, K.; Goodman, G.; Swift, A.; Kumar, N.; Rahman, E. A 10-Point Plan for Avoiding Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Filler-Related Complications during Facial Aesthetic Procedures and Algorithms for Management. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 11, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranteas, T.; Mourouzis, C.; Koumoura, F.; Tesseromatis, C. Effects of Propranolol or Paracetamol on Lidocaine Concentrations in Serum and Tissues. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheels, P.; Porcello, A.; Bezzola, T.; Perrenoud, D.; Quinodoz, P.; Kalia, Y.; Allémann, E.; Laurent, A.; Jordan, O. Clinical Perspectives on the Injectability of Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Standardized Methodology for Commercial Product Benchmarking with Inter-Injector Assessments. Gels 2024, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15798:2022; International Standard Organization, Ophthalmic Implants—Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/79687.html (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Park, S.; Park, K.Y.; Yeo, I.K.; Cho, S.Y.; Ah, Y.C.; Koh, H.J.; Park, W.S.; Kim, B.J. Investigation of the Degradation-Retarding Effect Caused by the Low Swelling Capacity of a Novel Hyaluronic Acid Filler Developed by Solid-Phase Crosslinking Technology. Ann. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Commercial Sample | BtHCROSS 2%® | Juvederm Voluma® | Belotero Soft® | Restylane Refyne® | Teosyal Ultimate® |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| η at γ 1 s−1 (Pa·s) | 143.65 | 159.70 | 11.81 | 192.02 | 263.28 |
| η at γ 1000 s−1 (Pa·s) | 1.31 | 1.59 | 0.35 | 1.46 | 0.31 |
| η:γ ratio | 109.54 | 100.44 | 33.74 | 131.52 | 849.29 |
| G′ (Pa) | 83.49 | 378.22 | 12.63 | 93.06 | 404.86 |
| G″ (Pa) | 30.18 | 31.38 | 17.24 | 30.34 | 34.65 |
| tan δ | 0.36 | 0.08 | 1.37 | 0.33 | 0.09 |
| Elasticity (%) | 73.45 | 92.34 | 42.28 | 75.41 | 92.12 |
| LVR (γ%) | >300 | 181.20 | N.A. | >300 | 218.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melero, A.; Andrade del Olmo, J.; Martínez de Cestafe, N.; Goenaga Ibeas, C.; Ucelay López de Heredia, M.; Izaguirre, J.K.; Alonso, J.M.; Pérez González, R. Viscoelastic Properties and Enzymatic Degradation of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid for Deep Dermal Filler Use. Gels 2025, 11, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090754
Melero A, Andrade del Olmo J, Martínez de Cestafe N, Goenaga Ibeas C, Ucelay López de Heredia M, Izaguirre JK, Alonso JM, Pérez González R. Viscoelastic Properties and Enzymatic Degradation of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid for Deep Dermal Filler Use. Gels. 2025; 11(9):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090754
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelero, Alejandro, Jon Andrade del Olmo, Nagore Martínez de Cestafe, Claudia Goenaga Ibeas, Miguel Ucelay López de Heredia, Jon Kepa Izaguirre, José María Alonso, and Raúl Pérez González. 2025. "Viscoelastic Properties and Enzymatic Degradation of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid for Deep Dermal Filler Use" Gels 11, no. 9: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090754
APA StyleMelero, A., Andrade del Olmo, J., Martínez de Cestafe, N., Goenaga Ibeas, C., Ucelay López de Heredia, M., Izaguirre, J. K., Alonso, J. M., & Pérez González, R. (2025). Viscoelastic Properties and Enzymatic Degradation of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid for Deep Dermal Filler Use. Gels, 11(9), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090754






