Janus Hydrogels: Design, Properties, and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of Janus Hydrogels
2.1. Double Layer
2.2. Multilayers
3. Design of Janus Hydrogels
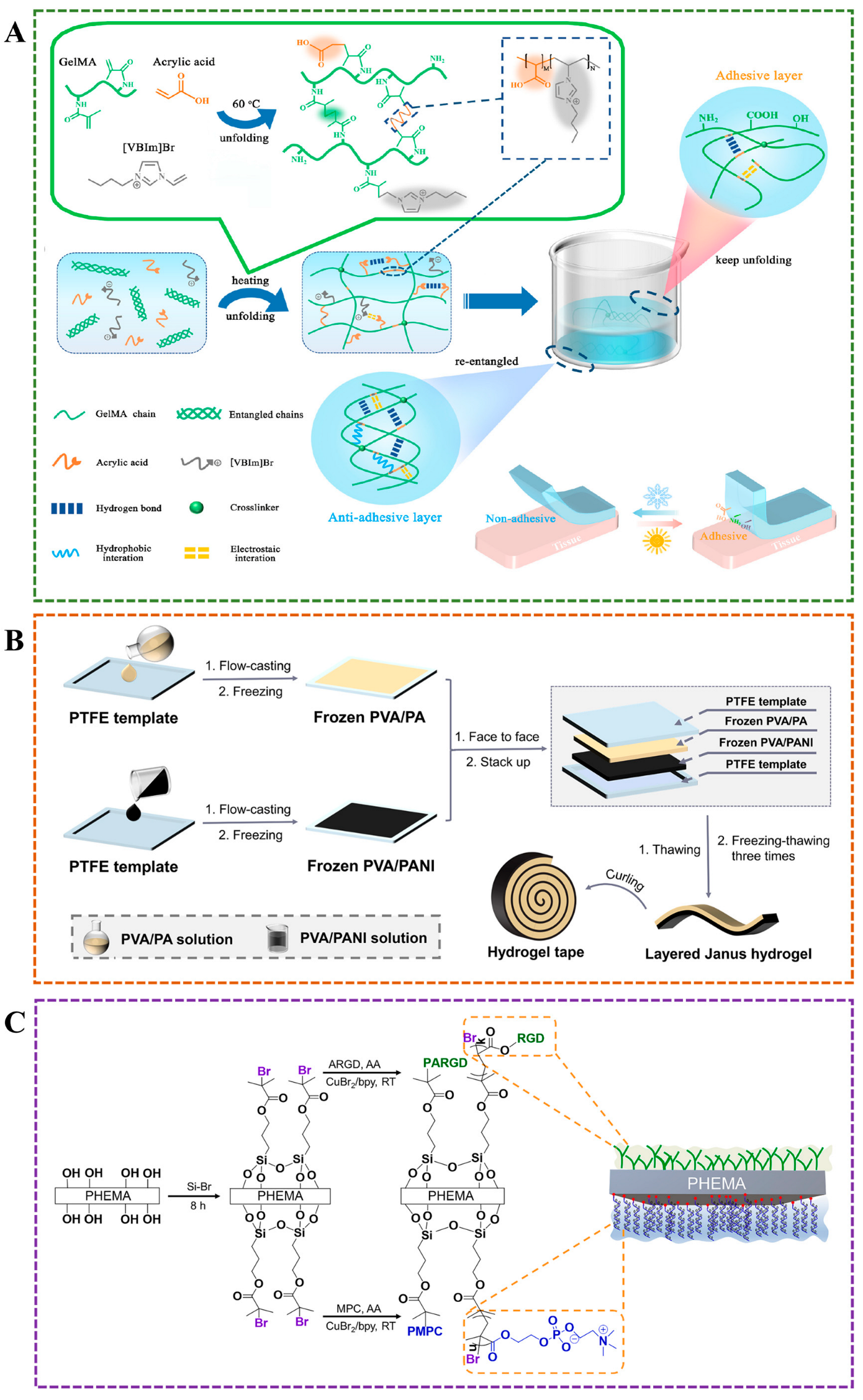
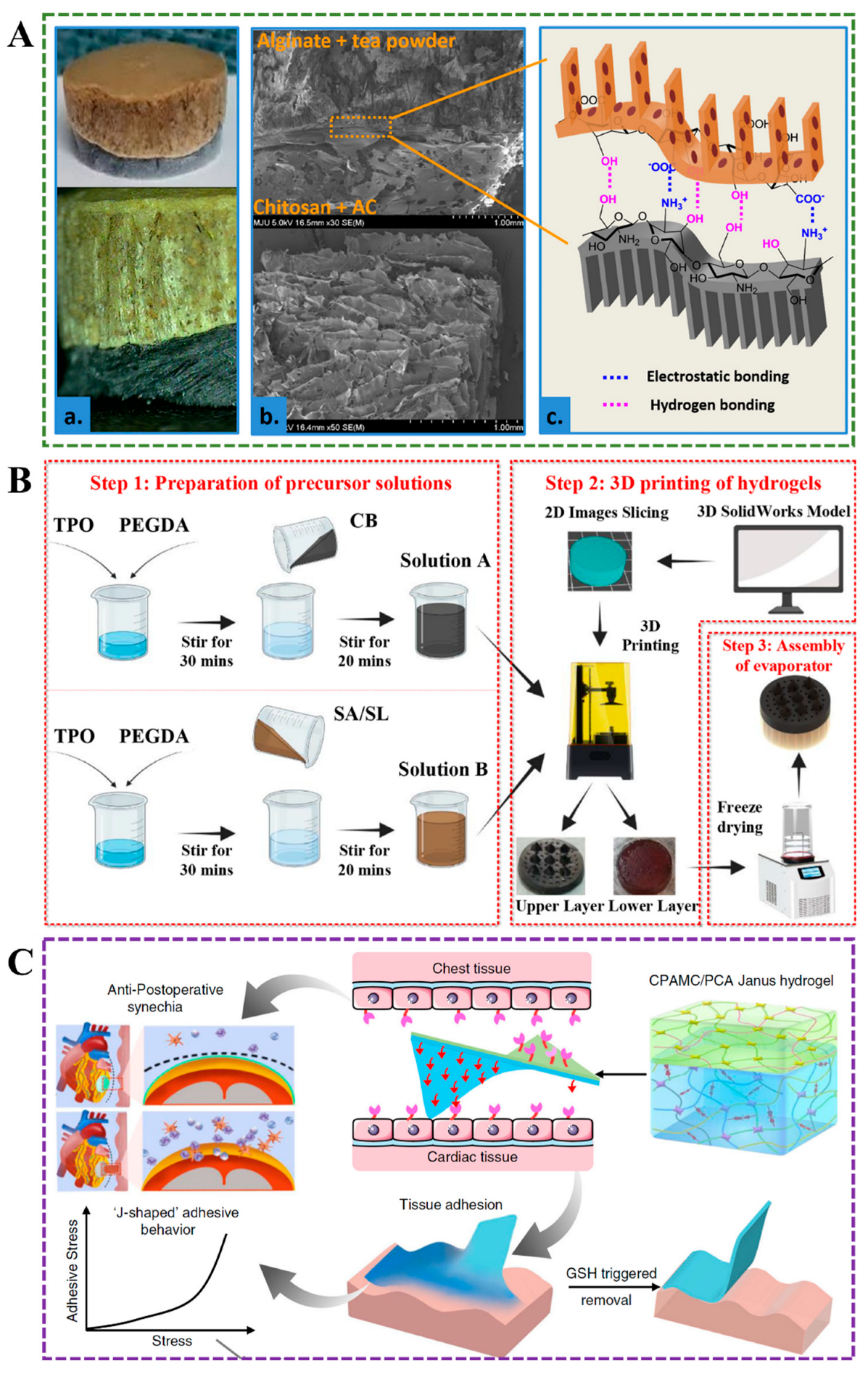
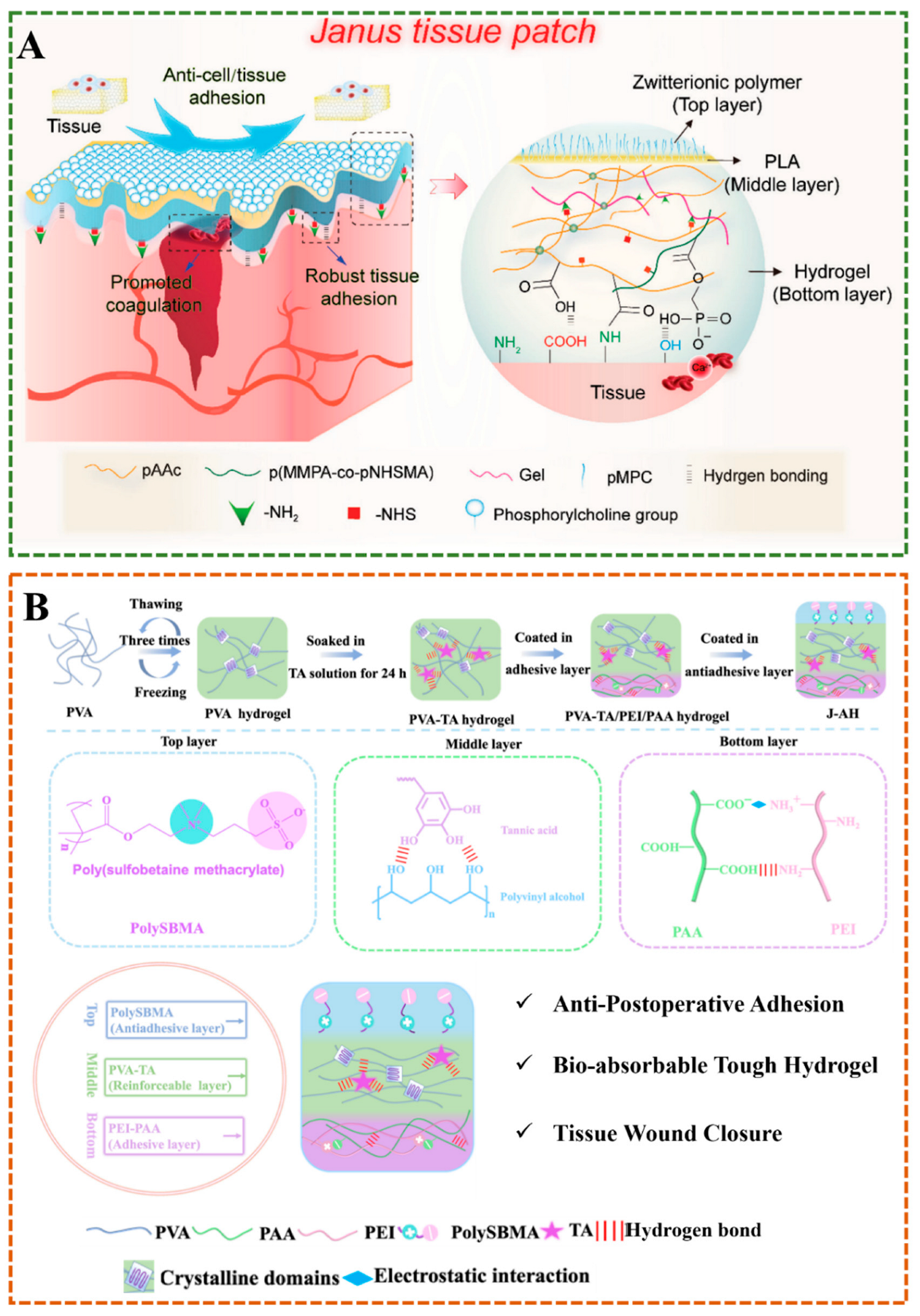
3.1. Layer-by-Layer Method
3.2. One-Pot Method
3.3. Self-Assembly Method
3.4. Electrospinning
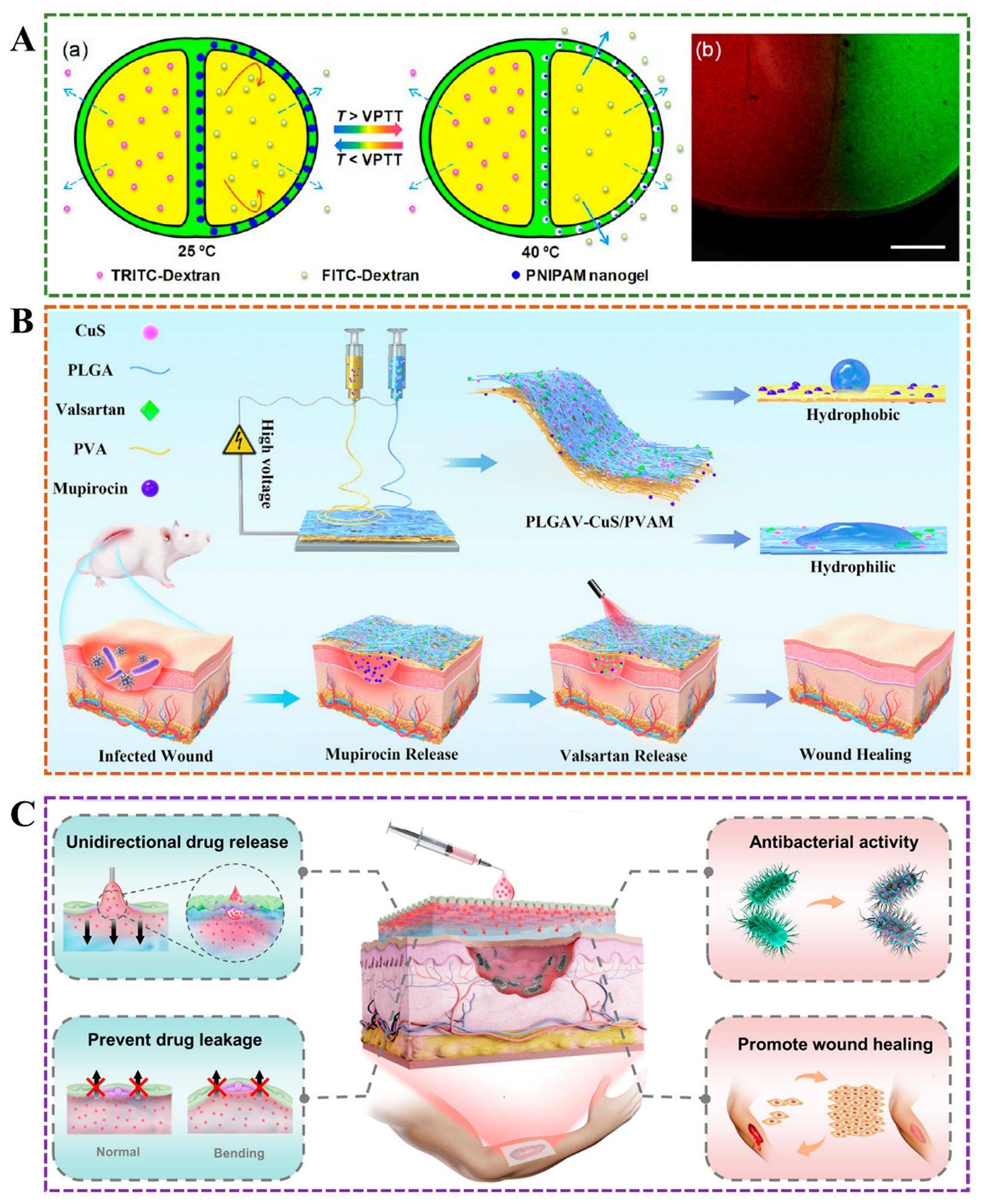
3.5. External Factor-Induced Method

3.6. Others
4. Desired Properties of JANUS Hydrogels
4.1. Efficient Drug Delivery
4.2. Biofluid Transport Capability
4.3. Mechanical Performance
4.4. Antibacterial Properties
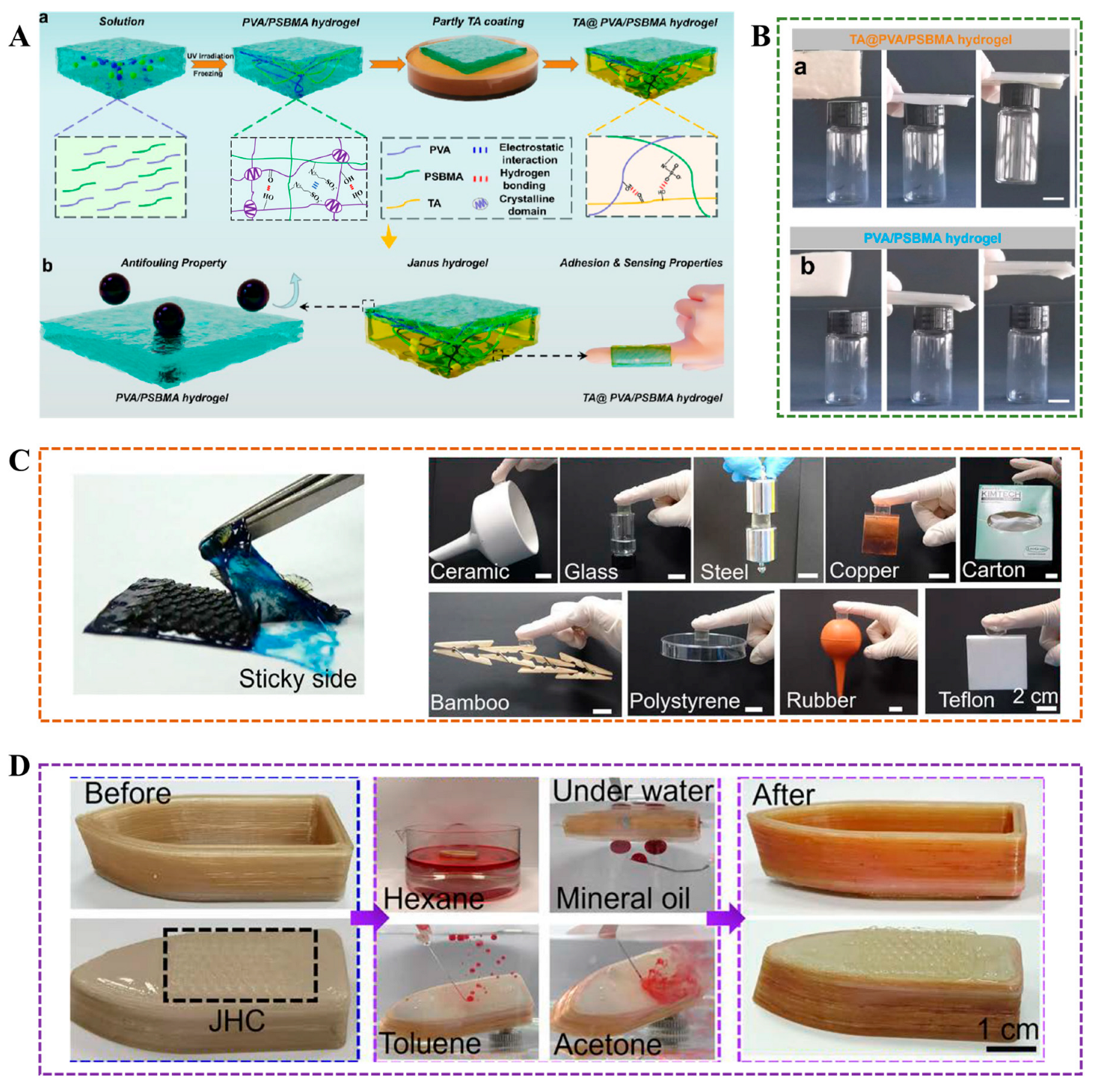
4.5. Self-Adhesive Properties and Antifouling Properties
4.6. Conductive Properties
4.7. Biocompatibility
4.8. Others
5. Janus Hydrogel Applications
5.1. Wound Healing
5.2. Internal Bioadhesion
5.3. Gastric Perforation Repair
5.4. Wearable Devices and Sensors
5.5. Postoperative Tumor Prevention
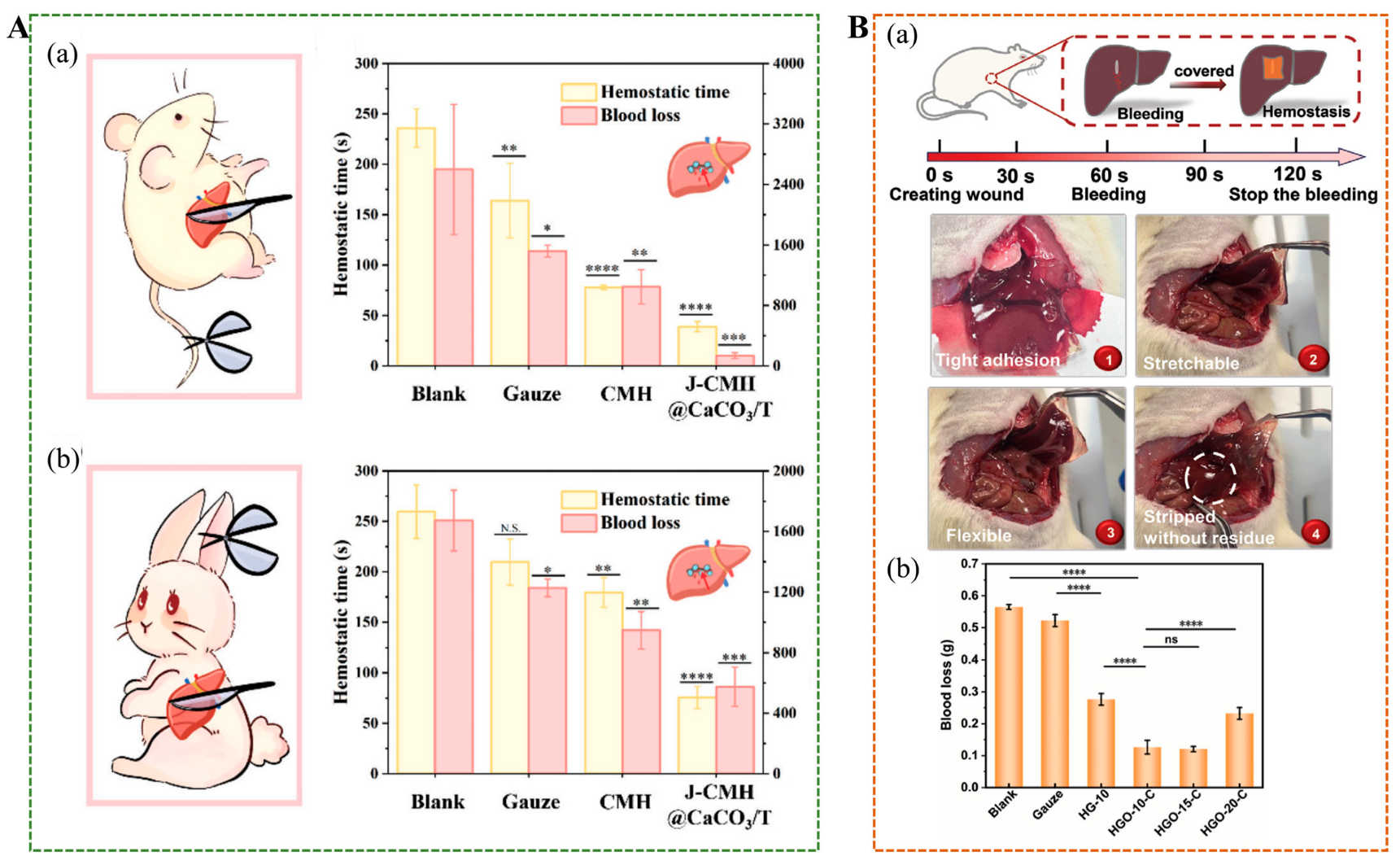
5.6. Rapid Bleeding Control
5.7. Cardiac Tissue Repair
5.8. Articular Cartilage Regeneration
5.9. Soft Actuators
5.10. Biomarker Detection
5.11. Personal Moisture Management
5.12. Smart Textile Fabrication
5.13. Cosmetics Production
5.14. Solar Desalination (Solar Water Evaporation)
5.15. Solar Thermal Desorption
5.16. Supercapacitors
5.17. Human–Machine Interfaces
5.18. Others
6. Future Outlook
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.C.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z.K. Janus Membranes: Exploring Duality for Advanced Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 13398–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Lee, K.-W. Morphology of latex particles formed by poly(methyl methacrylate)-seeded emulsion polymerization of styrene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 1903–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Guo, Q.; Ji, F.; Tian, X.; Cui, J.; Song, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Thermoresponsive polysaccharide-based composite hydrogel with antibacterial and healing-promoting activities for preventing recurrent adhesion after adhesiolysis. Acta Biomater. 2018, 74, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Jin, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, M.; Bian, Y. An anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic Janus hydrogel for preventing postoperative peritoneal adhesion. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-F.; Luo, S.; Li, J.; Bi, S.; Wei, F.; Xu, C.; Fu, L.; Lin, B. In Situ Ultrafast Construction of Polysaccharide-Based Janus Hydrogel Films by Asymmetric Cross-Linking for On-Demand Sterilization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 10905–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wan, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Cai, D.; Lu, H. Janus structure hydrogels: Recent advances in synthetic strategies, biomedical microstructure and (bio)applications. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 3003–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Janus hydrogels: Merging boundaries in tissue engineering for enhanced biomaterials and regenerative therapies. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 2504–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Carneiro, J.; Campos, J.B.L.M.; Miranda, J.M. Production of hydrogel microparticles in microfluidic devices: A review. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xia, T.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; Wang, T.; Li, X. Enzyme-powered Janus nanomotors launched from intratumoral depots to address drug delivery barriers. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Jing, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ma, Q.; Dong, X.; Mahadevan, C.K. Electrospun green fluorescent-highly anisotropic conductive Janus-type nanoribbon hydrogel array film for multiple stimulus response sensors. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2025, 288, 111933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvalilou, S.; Khoei, S.; Khoee, S.; Soleymani, M.; Shirvaliloo, M.; Ali, B.H.; Mahabadi, V.P. Dual-drug delivery by thermo-responsive Janus nanogel for improved cellular uptake, sustained release, and combination chemo-thermal therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 653, 123888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Yi, A.; Jiao, R.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Li, A. Excellent solar-driven interface evaporation by an oil repellence Janus photothermal membrane for oily wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Deng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Janus gels for biomedical applications: Progress and future prospective. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 155, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Shui, T.; Zhao, Z.; Xiang, L.; Yan, B.; Gu, N.; Zeng, H. Engineered Janus hydrogels: Biomimetic surface engineering and biomedical applications. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, F.; Zong, Z. A novel strategy for addressing post-surgical abdominal adhesions: Janus hydrogel. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 249, 114511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Q. Novel Structural Janus Hydrogels for Battery Applications: Structure Design, Properties, and Prospects. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Cheng, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Multifunctional Janus Hydrogels: Surface Design Strategies for Next-Generation Clinical Solutions. Gels 2025, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Li, J.; Gong, W.; Liu, Y.; Ai, Y.; He, A.; Nie, H. A multi-responsive actuator with sensing capability based on poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide)/poly (sodium acrylate) Janus hydrogels. Compos. Struct. 2024, 339, 118141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Shao, D.; Li, W.; Hu, X.; Tian, J.; Li, L.; Ding, S.; Zhou, C.; Lu, L. A Tough Janus Hydrogel Patch with Strong Wet Adhesion and Self-Debonding for Oral Ulcer Treatment. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 4976–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, S.; Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Liang, L.; Guo, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; et al. A Single-Component Janus Zwitterionic Hydrogel Patch with a Bionic Microstructure for Postoperative Adhesion Prevention. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 22900–22913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, C.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Che, L.B.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.S. A Conformable and Tough Janus Adhesive Patch with Limited 1D Swelling Behavior for Internal Bioadhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Han, M.; Peng, R.; Zhao, R.; Qin, M.; Li, T.; Yin, J.; Yu, L.; et al. A Sprayable Janus Hydrogel as an Effective Bioadhesive for Gastrointestinal Perforation Repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Niu, X.; Xie, W.; Yang, H.; Jiang, W.; Ma, M.; Yang, W. An integrated Janus hydrogel with different hydrophilicities and gradient pore structures for high-performance zinc-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 4126–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, W.; Mao, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Bioinspired colloidal crystal hydrogel pressure sensors with Janus wettability for uterus cervical canal tension perception. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 8941–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Fan, J.; Tian, W.; Ji, X.; Cui, Y.; Nan, Q.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J. Cellulose-Based pH-Responsive Janus Dressing with Unidirectional Moisture Drainage for Exudate Management and Diabetic Wounds Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2307449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Lv, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, Q.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, L.; et al. Dual-Janus Hydrogel Composite for Moisturizing and Antimicrobial Conservation of Bone Relics. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 10274–10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, F.; Shi, J.; Song, P.; Feng, F.; Cui, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J. Flexible Wood-Based Janus Hydrogel for Nasal Infection. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 8091–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Cao, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, M.; Qian, J.; Gong, C.; Shuang, X.; et al. Hydrogel coatings on universal medical devices with water-responsive Janus adhesion and acidity-triggered transformation for adaptive antibacterial treatment and fluorescence diagnosis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Yoshihara, D.; Tottori, S.; Nishizawa, M. Mussel-inspired thermo-switchable underwater adhesive based on a Janus hydrogel. NPG Asia Mater. 2024, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Xiong, Y.-H.; Song, W.; Sun, M.; Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Duan, S.; Xu, F.-J. Polysaccharide-based antibacterial nanocomposite hydrogels with Janus structure for treatment of infected extraction socket. Sci. China Mater. 2024, 67, 2550–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Tough and anisotropic Janus hydrogel for tendon injury repair with controlled release of bFGF in tendon microenvironment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, H.; Fang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H. A tough Janus poly(vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogel for wound closure and anti postoperative adhesion. Acta Biomater. 2024, 188, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yuan, H.; Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Gao, H.; Nie, Y. “Release-Occupy” strategy to fabricate an integrally formed Janus adhesive hydrogel for wearable sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Feng, J.; Zhou, J. A “Janus” Zwitterionic Hydrogel Patch for Tissue Repair and Prevention of Post-Operative Adhesions. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2404082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Liu, X.; Mao, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, H.; Cui, Z.; Zheng, Y.; et al. A Customized Janus Hydrogel with Robust Bio-Adhesion and Multi-Mode Disinfection for Rapid Recovery of Multi-Drug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus-Infected Open Wounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2420443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Ke, X.; Zhang, M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.; Li, J. A Janus Adhesive Hydrogel with Integrated Attack and Defense for Bacteria Killing and Antifouling. BME Front. 2024, 5, 0059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, M.W.; Ntiamoah, R.A.; Kim, H. Alginate/chitosan bi-layer hydrogel as a novel tea bag with in-cup decaffeination. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Bao, Y.Q.; Huang, A.; Qin, G.Z.; He, M.G. 3D printing double-layer hydrogel evaporator with surface structures for efficient solar steam generation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Li, Q.; Chen, P.; Duan, Q.X.; Zhan, J.M.A.; Cai, X.H.; Wang, L.Y.; Hou, H.H.; Qiu, X.Z. A smart adhesive Janus hydrogel for non-invasive cardiac repair and tissue adhesion prevention. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Liu, C.; Lai, Y.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Liu, P.S.; Shen, J. An Adhesive/Anti-Adhesive Janus Tissue Patch for Efficient Closure of Bleeding Tissue with Inhibited Postoperative Adhesion. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2301427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zeng, Y.J.; Meng, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. GelMA and aliphatic polyesters Janus nanofibrous membrane with lubrication/anti-fibroblast barrier functions for abdominal adhesion prevention. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 178, 111499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Continuous, Spontaneous, and Directional Water Transport in the Trilayered Fibrous Membranes for Functional Moisture Wicking Textiles. Small 2018, 14, e1801527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castleberry, S.A.; Almquist, B.D.; Li, W.; Reis, T.; Chow, J.; Mayner, S.; Hammond, P.T. Self-Assembled Wound Dressings Silence MMP-9 and Improve Diabetic Wound Healing In Vivo. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.H.; Huang, H.; Song, X.R.; Dong, T.; Yu, J.F.; Xu, J.Y.; Cheng, R.; Cui, T.T.; Li, J. Carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel-Janus nanofiber scaffolds with unidirectional storage-drainage of biofluid for accelerating full-thickness wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 331, 121870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Zheng, C.C.; Zhang, F.S.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.J. One-step synthesis of Janus hydrogel via heterogeneous distribution of sodium α-linoleate driven by surfactant self-aggregation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Q.; Ma, H.; Ma, X.L.; Ai, T.H.; Chai, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.R.; Li, F.W.; Wang, X.S.; Li, C.H.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Polymer crystallization regulation in liquid phase enables wearable full-featured thermoplastic-based smart Janus film. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Fei, X.; Zhao, W.H.; Tian, J.; Xu, L.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. A Janus supramolecular hydrogel prepared by one-pot method for wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Chi, C.Y.; Jiang, S.; Qin, W.B.; Zhang, Y.C.; Liu, H.Q.; Chen, Q.H. PAA-PU Janus Hydrogels Stabilized by Janus Particles and its Interfacial Performance During Hemostatic Processing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2303802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nummelin, S.; Liljeström, V.; Saarikoski, E.; Ropponen, J.; Nykänen, A.; Linko, V.; Seppälä, J.; Hirvonen, J.; Ikkala, O.; Bimbo, L.M.; et al. Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Janus Dendrimers into Mechanically Robust Supramolecular Hydrogels for Sustained Drug Release. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14433–14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessberger, T.; Braun, L.B.; Zentel, R. Interfacial Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Dual Temperature Responsive Actuating Janus Particles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, T. Scalable fabrication of free-standing, stretchable CNT/TPE ultrathin composite films for skin adhesive epidermal electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6666–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohata, S.; Dey, K.; Bhunia, S.; Thomas, N.; Gowd, E.B.; Ajithkumar, T.G.; Reddy, C.M.; Banerjee, R. Dual Nanomechanics in Anisotropic Porous Covalent Organic Framework Janus-Type Thin Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.-H.; Dong, Z.-T.; Chen, G.-H.; Ma, C.; Wang, H.-Y. Preparation of PVA/GO/h-BN Janus Film with High Thermal Conductivity and Excellent Flexibility via a Density Deposition Self-assembly Method. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 42, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, G.; Karimi, M.; Ashtiani, F.Z. Hybrid electrospun membrane based on poly(vinylidene fluoride)/poly(acrylic acid)-poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel for waterproof and breathable applications. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 1558–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Zha, X.L.; Liu, G.X.; Zhao, H.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Zha, L.S. Injectable extracellular matrix-mimetic hydrogel based on electrospun Janus fibers. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 13, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimna, C.; Bauer, M.G.; Lutz, T.M.; Mansi, S.; Akyuz, E.; Doganyigit, Z.; Karakol, P.; Mela, P.; Lieleg, O. Multifunctional “Janus-Type” Bilayer Films Combine Broad-Range Tissue Adhesion with Guided Drug Release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2105721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Yu, N.; Ren, Q.; Niu, S.N.; Zhu, L.Q.; Hong, L.; Cui, K.L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.Z.; Wen, M.; et al. Janus Nanofiber Membranes with Photothermal-Enhanced Biofluid Drainage and Sterilization for Diabetic Wounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2315020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Fan, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. Fabrication of Tough Hydrogel Composites from Photoresponsive Polymers to Show Double-Network Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37139–37146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.D.; Sun, K.Y.; Huang, L.Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Xia, F. Magneto-Induced Janus Adhesive-Tough Hydrogels for Wearable Human Motion Sensing and Enhanced Low-Grade Heat Harvesting. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 10556–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Cheang, U.K.; Liu, Y.G.; Kim, H.; Rogowski, L.; Sheckman, S.; Patel, P.; Sun, W.; Kim, M.J. Fabrication and magnetic control of alginate-based rolling microrobots. Aip Adv. 2016, 6, 125205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, M.; Tsuchiya, M.; Itai, S.; Murayama, T.; Kurashina, Y.; Heo, Y.J.; Onoe, H. Janus Hydrogel Microbeads for Glucose Sensing with pH Calibration. Sensors 2021, 21, 4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Shi, Z.X.; Yin, J.; Tian, M.; Qu, R.J. Shape Reconfiguration of a Biomimetic Elastic Membrane with a Switchable Janus Structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. An Injectable Asymmetric-Adhesive Hydrogel as a GATA6+ Cavity Macrophage Trap to Prevent the Formation of Postoperative Adhesions after Minimally Invasive Surgery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, P.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Yang, Q.; Long, M.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; et al. Injectable photocurable Janus hydrogel delivering hiPSC cardiomyocyte-derived exosome for post-heart surgery adhesion reduction. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, G.P.; Zhao, Y.J. 3D-Printed Janus Piezoelectric Patches for Sonodynamic Bacteria Elimination and Wound Healing. Research 2023, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Gu, Z.; Zhou, L.P.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhang, P.X.; Wen, Y.Q. Janus mucosal dressing with a tough and adhesive hydrogel based on synergistic effects of gelatin, polydopamine, and nano-clay. Acta Biomater. 2022, 149, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Liang, J.D.; Chen, S.S.; Guo, W.C.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.Q. A Janus adhesive hydrogel sheet for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion of intestinal injuries. Rsc Adv. 2024, 14, 4416–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Lai, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kan, Z.; Dai, C.; Shen, J.; Liu, P. Charge balance transition enabled Janus hydrogel for robust wet-tissue adhesion and anti-postoperative adhesion. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 52, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.Y.; Lv, C.; Zhuang, X.S.; Wang, S. Fabrication of antibacterial Janus bandages with high wound healing performances by facile single-side electrospray PDMS coating. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Ye, Z.F.; Wang, H.T. Water-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Silica Janus Nanosheets. Small 2023, 19, 2206215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.D.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, H.; Hou, Z.Q.; Miao, X.; Miao, G.; Li, F.C.; Lu, J.W.; Ren, G.A.; Zhu, X.T. Janus Hydrogel with Both Sticky Adhesion and Slippery Antifouling Properties for Strain Sensing. Acs Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; Zhou, H.W.; Du, H.T.; Chen, L.; Zhao, G.X.; Liu, H.B.; Jin, X.L.; Chen, W.X.; Ma, A.J. A cyclic freezing-thawing approach to layered Janus hydrogel tapes with single-sided adhesiveness for wearable strain sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.D.; Zhang, K.X.; Rao, Z.L.; Chen, J.X.; Meng, Y.; Quan, D.P.; Bai, Y. A surface grafting strategy for antifouling/bioadhesive properties on a Janus-type polymeric thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 649, 159146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budai, L.; Budai, M.; Pápay, Z.E.F.; Szalkai, P.; Niczinger, N.A.; Kijima, S.; Sugibayashi, K.; Antal, I.; Kállai-Szabó, N. Viscoelasticity of Liposomal Dispersions. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.J.; Bian, F.K.; Chen, H.X.; Guo, J.H.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.J. Anisotropic Microparticles from Microfluidics. Chem. 2021, 7, 93–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, W.; He, X.H.; Yang, X.L.; Li, M.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.J.; Liu, Z.; Chu, L.Y. Controllable Multicompartmental Capsules with Distinct Cores and Shells for Synergistic Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8743–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.P.; Zhou, M.Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.T.; Wang, W.H.; Cheng, J.L.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.F. Janus amphiphilic nanofiber membranes synergistically drive antibacterial and anti-inflammatory strategies for skin wound healing. Mater. Des. 2023, 227, 111778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Guo, M.; Lyu, K.; Chu, T.; He, B. Intelligent Silk Fibroin Based Microneedle Dressing (i-SMD). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2006839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.R.; Luo, Y.; Song, Y.C.; He, X.C.; Xu, T.L.; Zhang, X.J. Hydrogel-Functionalized Bandages with Janus Wettability for Efficient Unidirectional Drug Delivery and Wound Care. Acs Nano 2024, 18, 3468–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, L.Y.; Guo, J.H.; Zhao, Y.J. Hierarchical Spinning of Janus Textiles with Anisotropic Wettability for Wound Healing. Research 2023, 6, 0129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.R.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, D.W.; Dong, B.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, C.; Shen, Z.J. Laser Ablated Janus Hydrogel Composite Membrane for Draining Excessive Blood and Biofluid around Wounds. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2200026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.B.; Zhang, X.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Lan, J.Z.; Fan, B.S.; Shi, L.X.; Wang, S.T.; Wan, X.Z. Self-Pumping Janus Hydrogel with Aligned Channels for Accelerating Diabetic Wound Healing. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2200814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.Y.; Yang, T.T.; Zhao, Y.R.; Qi, M.Y.; Song, Z.N.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, L.; Qu, X.Z.; Liang, F.X.; Yang, Z.Z. Janus Nanoparticle Coupled Double-Network Hydrogel. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, 2200157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Lv, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, W.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Chong, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z. Au-Pt nanozyme-based multifunctional hydrogel dressing for diabetic wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137, 212869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Wu, M.M.; Lu, J.; He, Q.; Zhang, J. Janus Intelligent Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Chronic Wound Healing in Diabetes. Acs Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Li, L.J.; Wang, R.T.; Liu, J.W.; Lin, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, H.T.; Lei, Y.F.; Xiong, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Fish Skin-Inspired Janus Hydrogel Coating for Drag Reduction. Chin. J. Chem. 2024, 42, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Cheng, Z.A.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zou, D.; Zhong, Z.X. Engineering Janus PTFE composite membranes with high anti-fouling and anti-scaling performance for membrane desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Khlyustova, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, R. An imidazolium-based zwitterionic polymer for antiviral and antibacterial dual functional coatings. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Ai, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Surface-fragmenting hyperbranched copolymers with hydrolysis-generating zwitterions for antifouling coatings. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5434–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Pan, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Strong-adhesion and nonfouling self-generating zwitterionic Janus hydrogel paint. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Pan, D.W.; Fan, H.D.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.M.; Liu, Z.; Ju, X.J.; Xie, R.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.Y. Stretchable conductive Janus hydrogel with controllable porous structures for high-performance strain sensing. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 62, 3236–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhu, W.; Wu, P. A Bioinspired Mineral Hydrogel as a Self-Healable, Mechanically Adaptable Ionic Skin for Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Keplinger, C.; Whitesides, G.M.; Suo, Z. Ionic skin. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7608–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.; Gao, G. Skin-Contactable and Antifreezing Strain Sensors Based on Bilayer Hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8938–8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.W.; Xing, Y.C.; Ji, Q.; Ma, X.M.; Xia, Y.Z. Strain-sensitive alginate/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogels with Janus hierarchy and conductivity mediated by tannic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 212, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.X.; Qi, L.H.; Shi, X.W.; Deng, H.B.; Du, Y.M. One-step electrodeposition of Janus chitosan coating for metallic implants with anti-corrosion properties. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 641, 128498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Harimurti, S.; Inoue, D.; Nayeem, M.O.G.; Wang, J.; Okuda, C.; Hashizume, D.; Lee, S.; Fukuda, K.; Yokota, T.; et al. Janus Membrane-Based Wearable pH Sensor with Sweat Absorption, Gas Permeability, and Self-Adhesiveness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 27065–27074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.H.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, J.M.; Kim, S.L.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, J.S.; Im, S.G.; Lee, K.E.; et al. Hydrogel Functionalized Janus Membrane for Skin Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1600795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, A.; Sheng, N.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Luo, F.; Li, J.; Tan, H. Janus Polyurethane Adhesive Patch with Antibacterial Properties for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 15970–15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, J.; Yang, J.; Du, Z.; Zhao, W.; Guo, H.; Wen, C.; Li, Q.; Sui, X.; et al. A Multifunctional Pro-Healing Zwitterionic Hydrogel for Simultaneous Optical Monitoring of pH and Glucose in Diabetic Wound Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1905493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthis, A.H.C.; Abundo, M.P.; Neuer, A.L.; Tsolaki, E.; Rosendorf, J.; Rduch, T.; Starsich, F.H.L.; Weisse, B.; Liska, V.; Schlegel, A.A.; et al. Modular stimuli-responsive hydrogel sealants for early gastrointestinal leak detection and containment. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.C.; Cai, F.Y.; Zhao, X.K.; Zhu, X.T.; Wei, F.A.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Shi, X.A.; Yang, J.M. Bioinspired Microstructured Janus Bioadhesive for the Prevention of Abdominal and Intrauterine Adhesions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2314402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Yi, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q.A.; Ding, Y.H.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, Q.W. An Integrally Formed Janus Hydrogel for Robust Wet-Tissue Adhesive and Anti-Postoperative Adhesion. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.B.; Feng, J.T.; Feng, Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Yang, Y.S.; Li, X.K.; Lei, M.; Guo, H.; Wei, Z.; Lv, Y.; et al. An endoscopically compatible fast-gelation powder forms Janus- adhesive hydrogel barrier to prevent postoperative adhesions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219024120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Lei, I.M.; Lin, J.; Xu, B.B.; Liu, J. Hydrogel Bioadhesives with Extreme Acid-Tolerance for Gastric Perforation Repairing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Q.; Wang, Z.H.; Xu, J.; Yu, L.; Qin, M.Y.; Li, J.F.; Liu, S.T.; Zheng, W.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Ouyang, J.; et al. Photocurable injectable Janus hydrogel with minimally invasive delivery for all-in-one treatment of gastric perforations and postoperative adhesions. Theranostics 2023, 13, 5365–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Xu, H.R.; Han, Q.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, J.D.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, X.F.; Yin, Z.H.; Guo, B.L. A Janus hydrogel sealant with instant wet adhesion and anti-swelling behavior for gastric perforation repair. Nano Today 2024, 54, 102105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, K.; Mu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Yao, T.; Zhao, K.; Gu, T.; Jia, P. A janus hydrogel with high strength, adhesive and conductive for wearable strain sensor. Polymer 2025, 323, 128210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Fu, J. Stretchable, self-healing and tissue-adhesive zwitterionic hydrogels as strain sensors for wireless monitoring of organ motions. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.K.; Liang, Z.J.; Fan, X.; Yu, J.; Bao, F.B. Bioinspired self-coiling Janus microfiber actuators for micro-lifter and humidity sensing. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2023, 394, 134344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Xiao, L.X.; Nie, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Bai, L.J.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.X.; Yang, H.W.; Wei, D.L. Fabrication of Janus-type nanocomposites from cellulose nanocrystals for self flexible sensors. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2022, 216, 112554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, M.X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Z.H. Janus-Inspired Core-Shell Structure Hydrogel Programmatically Releases Melatonin for Reconstruction of Postoperative Bone Tumor. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 2639–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Luo, Y.; He, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhou, X.S.; Hou, J.W.; Zhou, S.B. In-situ-sprayed therapeutic hydrogel for oxygen-actuated Janus regulation of postsurgical tumor recurrence/metastasis and wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Su, B.H.; Zhao, W.F.; Zhao, C.S. Janus Self-Propelled Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Spheres for Rapid Bleeding Control. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2205989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhou, J.; Lai, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, B.; Huang, R.; Zhang, L.M. Novel Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogel Patches with Janus Asymmetric-Adhesion for Emergency Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.H.; Guo, A.D.; Li, J.; Tang, Z.Q.; Luo, F.L. Janus Hydrogel to Mimic the Structure and Property of Articular Cartilage. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 35434–35443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zhao, Y.X.; Xu, D.N.; Li, D.P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.Z.; Huang, Y.W.; Long, S.J. Thermoresponsive double-network hydrogel/elastomer hybrid bilayer laminates with high interfacial toughness and controllable shape deformations. Polymer 2023, 286, 126381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Dual-gradient PNIPAM-based hydrogel capable of rapid response and tunable actuation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Jiang, X.; Gu, X. Mechanically Robust, Time-Programmable, Janus Hydrogel Actuator, and the Insights into Its Driving Principles. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 3670–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Sun, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Hou, Q.X. High performance and multifunctional Janus bio-nanocomposite film for underwater actuators with excellent sensitivity and controllability. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Hwang, J.S.; Seo, S.B.; Kang, B.; Jang, S.; Son, S.U.; Ki, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; et al. Janus hydrogel-based fuel stimulant powered amplification for multiple detections of miRNA biomarkers in gastric cancer. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Li, K.; Shi, L.; Wan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. Bioinspired Janus Textile with Conical Micropores for Human Body Moisture and Thermal Management. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1904113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, G.; Yu, H.; Qian, B.; Cheung, Y.H.; Wong, L.H.; Xin, J.H. Mussel-Inspired Design of a Self-Adhesive Agent for Durable Moisture Management and Bacterial Inhibition on PET Fabric. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Min, S.Q.; Zhan, T.H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, D.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, B. Highly Durable Janus Fabrics Based on Transfer Prints for Personal Moisture Management. Small 2023, 19, 2302512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ge, D.; Yang, L. Enhanced IR Radiative Cooling of Silver Coated PA Textile. Polymers 2021, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.Q.; Zhu, L.L.; Liang, Y.Z.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Chen, S. Fiber-spinning Asymmetric Assembly for Janus-structured Bifunctional Nanofiber Films towards All-Weather Smart Textile. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, W.H.; Cao, D.L.G.; Guo, W.; Yu, L.; Ding, J.D. Intelligent Paper-Free Sprayable Skin Mask Based on an In Situ Formed Janus Hydrogel of an Environmentally Friendly Polymer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, A.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.; Shi, X.; Chen, J.; Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Sustainable Self-Cleaning Evaporators for Highly Efficient Solar Desalination Using a Highly Elastic Sponge-like Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 36116–36131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.; Ye, Z.D.; Chen, Y.; Lin, P.C. Robust seawater desalination and sewage purification enabled by the solar-thermal conversion of the Janus-type graphene oxide evaporator. Desalination 2022, 522, 115406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Chu, A.Q.; Yang, H.D.; Zhao, J.M.; Yang, M.; Fang, J.; Yang, Z.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, H. Self-Responsive Janus Hydrogel with Alternation of Day and Night for Highly Efficient Solar Evaporation. Sol. Rrl 2024, 8, 142944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.C.; Yang, K.; Cai, B.H.; Zhang, J.T.; Wei, C.Y.; Zhou, A.J. A magnetic nanostructure PAC@Fe3O4 driven design toward Janus hydrogel achieves highly efficient solar water evaporation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Song, F.; Huang, X.; Chen, D.; Nie, Z. Amphiphilic Janus patch-grafted hydrogels for salt-rejecting solar water desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 17142–17150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Zhou, W.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Feng, X.M.; Deng, Y.H.; Chen, X.C.; Xie, H.; Wu, T.; Qu, J.P. A Janus-type hygroscopic hydrogel for reusable robust dehumidification and efficient solar thermal desorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, M.; Ye, K.; Wang, G.L.; Zhou, L.M.; Cheng, K.; Cao, D.X. Janus-faced film with dual function of conductivity and pseudo-capacitance for flexible supercapacitors with ultrahigh energy density. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.Q.; Liu, S.; Feng, W.B.; Yang, W.T.; Peng, J.W.; Liu, R.X.; Fang, S.M.; Zhang, X.J. Janus POSS-based hydrogel electrolytes with highly stretchable and low-temperature resistant performances for all-in-one supercapacitors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; He, Y.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, G.; Zhao, B.X. Asymmetric “Janus” Biogel for Human-Machine Interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.; Tu, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Ni, Z.; Yang, J.; Dong, Y.; Zou, X.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; et al. One-Step Formed Janus Hydrogel with Time-Space Regulating Properties for Suture-Free and High-Quality Tendon Healing. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2411400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.L.; Yu, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Qin, C.X.; Liu, L.K.; Yang, H.; Cai, M.R.; Yu, B.; Pei, X.W.; Liu, Y.; et al. A Janus hydrogel material with lubrication and underwater adhesion. Giant 2023, 16, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Jin, X.; Zhong, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhong, M.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qi, X.; Guan, X.; et al. Difficult and complicated oral ulceration: An expert consensus guideline for diagnosis. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2022, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

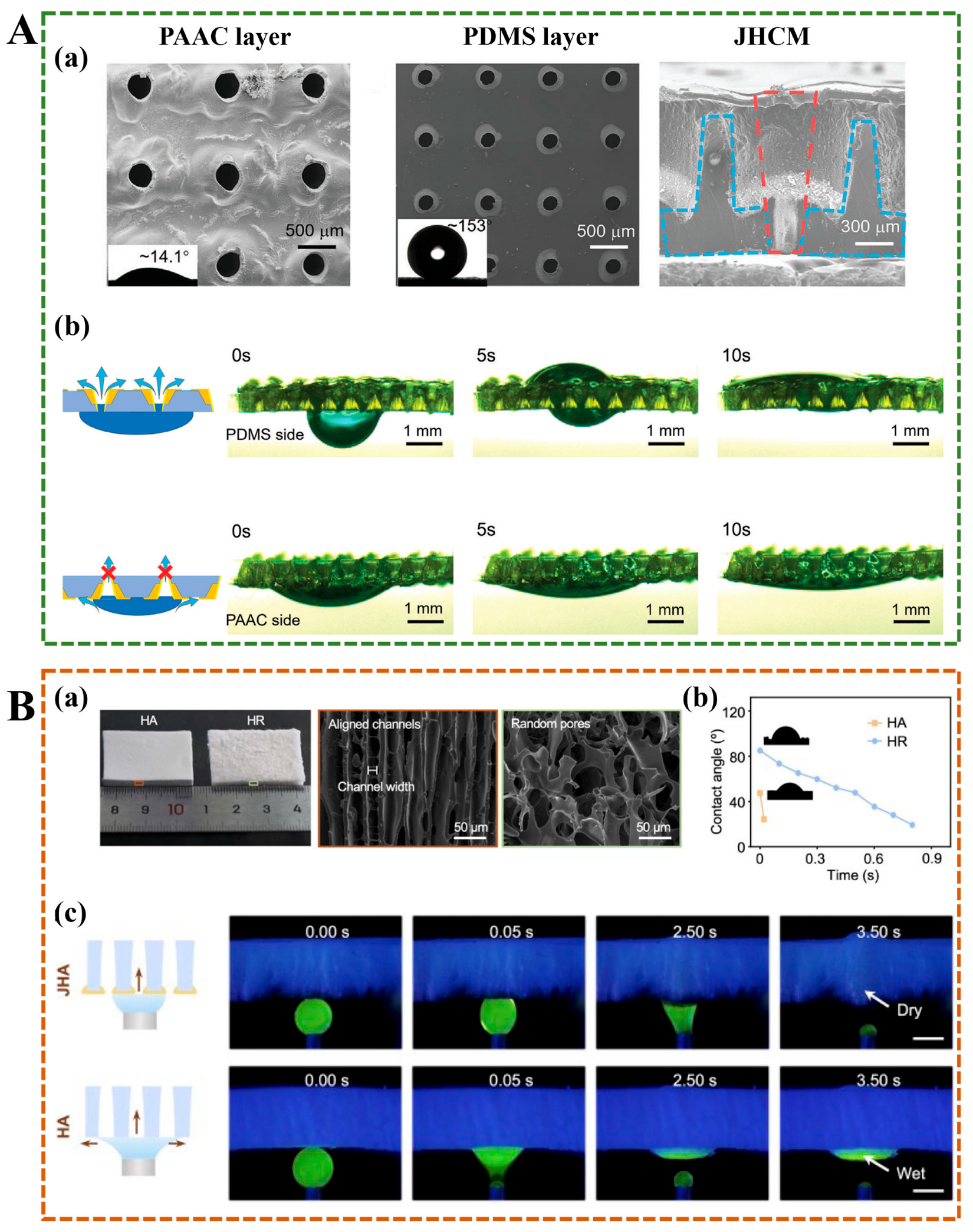
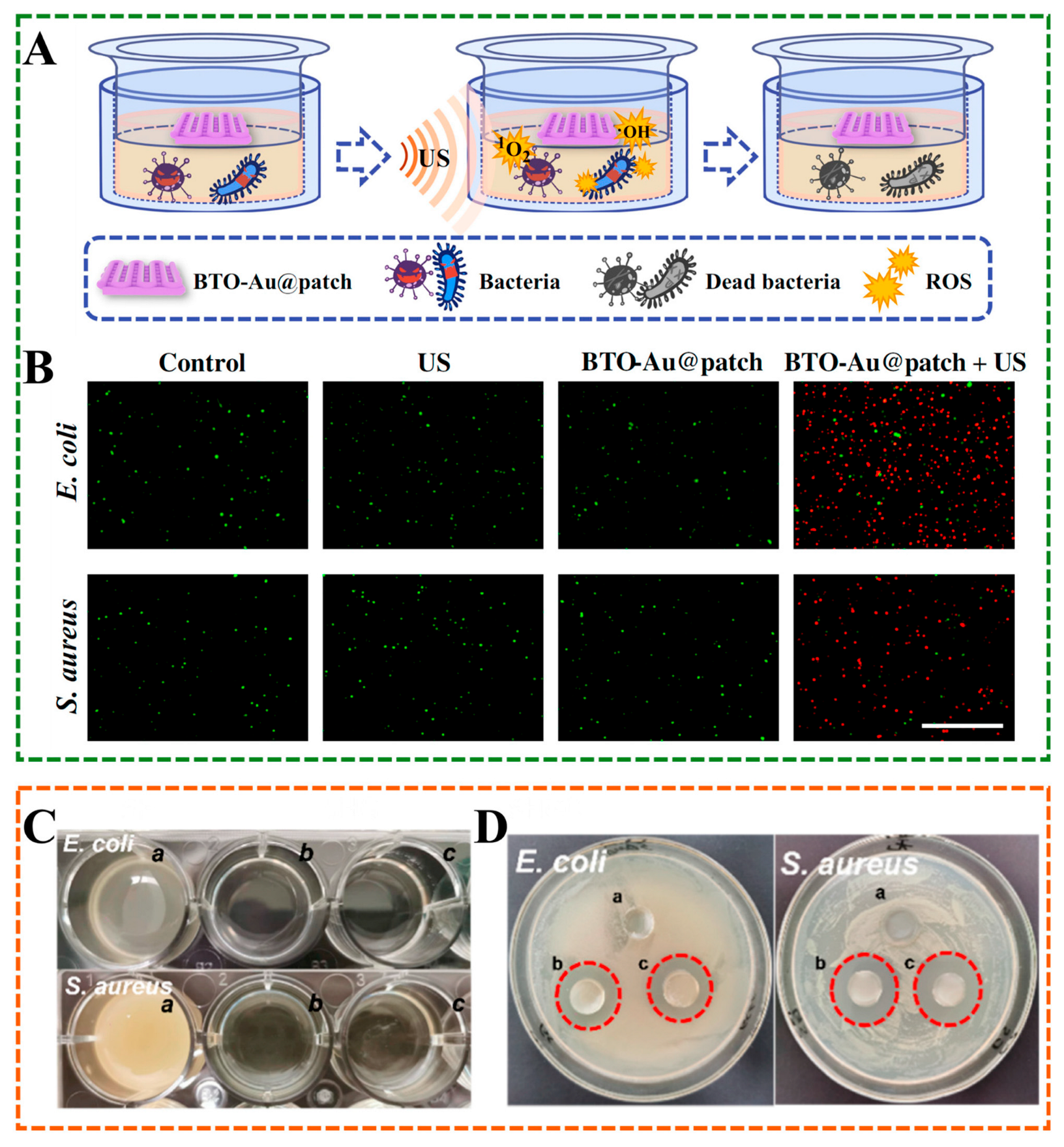

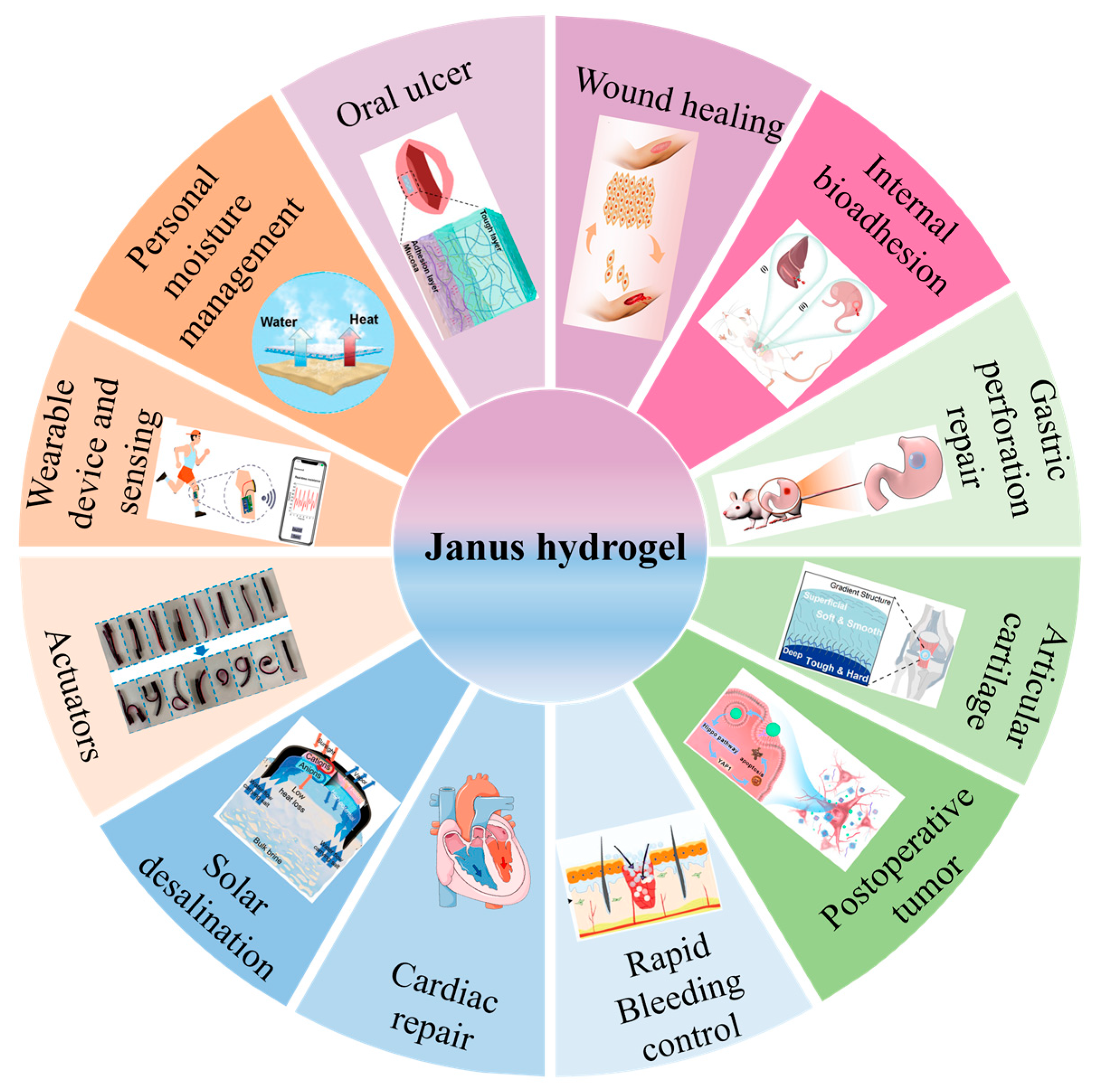

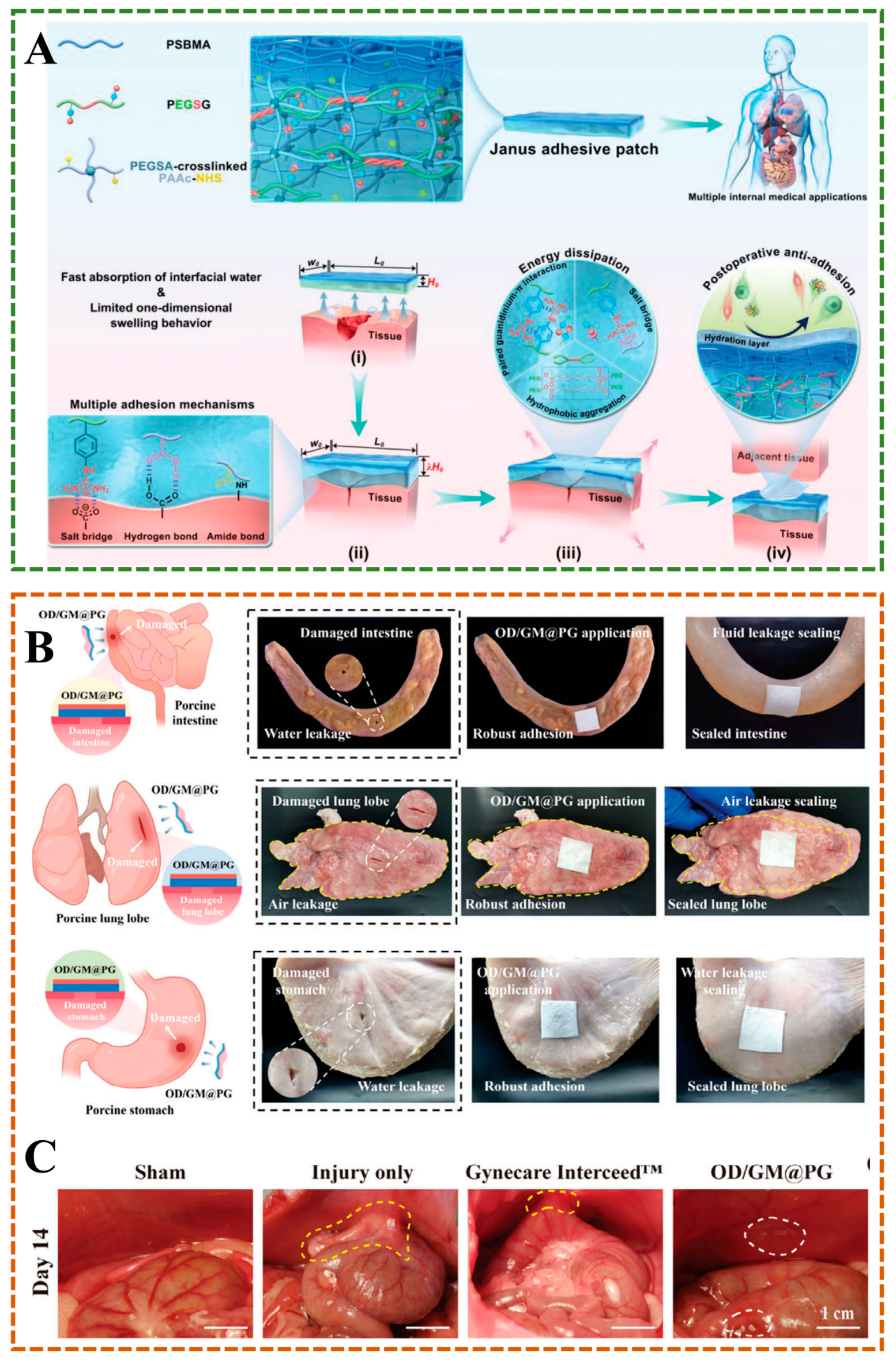

| Preparation | Component | Property | Cross-Linking Interaction | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer by layer | Poly (sodium acrylate)/poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PSA/PNIPAM) | Asymmetric swelling; multi-responsive | Network interpenetration | Actuator | [18] |
| Two-step process | N-[tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl]-acrylamide (THMA)/chitosan; poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) | Wet adhesion performance; self-deboning properties | Ultraviolet light crosslinking | Oral mucosal ulcers | [19] |
| Thermal polymerization | N’, N’-methylenebis(2-propenamide), sulfobetaine methacrylate | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; Hexagonal facet | Free radical polymerization | Prevent postoperative adhesion | [20] |
| Two-step, light-curing method | PEGS | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; Limited 1D swelling behavior | Monomer diffusion; | Internal bioadhesion | [21] |
| Two-step, cross-linking process, Light curing | Hyaluronic acid, Dopamine, Phenylboronic acid | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; inherent mechanical strength | Photo crosslinking | Gastrointestinal perforations | [22] |
| Copolymerization | Acrylamide (AM), Zinc acrylate (Zn-AC), Nisopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) and N, N’- methylenebisacrylamide (MBAA) | Higher hydrophilicity/lower hydrophilicity; gradient pores | copolymerization | Zinc-ion batteries | [23] |
| Ultraviolet irradiation | patterned polydimethylsiloxanes (PDMS), P(NiPAAmbis- AA) hydrogel film | Hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity | Ultraviolet light crosslinking | Pressure sensors, uterus cervical canal tension perception | [24] |
| Two-layer | Cellulose-anthocyanin; polycaprolactone-chlorhexidine | Hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity; pH-response; | Electrospinning | Diabetic wound healing | [25] |
| Three-layer | Polyacrylamide; brominated isobutylene isoprene rubber; polydimethylsiloxane | Moisturize; antimicrobial | Van der Waals force; hydrophobic interaction; hydrogen bond | Preservation of bone relics | [26] |
| Stacked under vacuum using cyclic freezing | DL-a-tocopherol; flexible wood; Poly(vinyl alcohol; Chitosan | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; flexibility; | Van der Waals force; | Nasal infection | [27] |
| Double-network | PAAm/SA/TA matrix, AgNPs, Chitosan/bovine serum-AuNPs | Water-responsive Janus adhesion, Adaptive antibacterial property, pH-responsive monitoring | Covalently cross-linking; Ionically cross-linking; Hydrogen bond | Diagnosis and treatment of catheters-associated infections | [28] |
| Interfacial polymerization at an air/solution interface | N-isopropyl acrylamide, Allylamine hydrochloride, Dopamine | Thermoresponsive; strong adhesion; on-demand adhesion | Cross-linking reaction | Underwater adhesives | [29] |
| Penetration cross-linking method | Oxidized sodium alginate, Carboxymethyl chitosan | Asymmetric structure; antibacterial; | Schiff base | Treatment of an infected extraction socket | [30] |
| Two-layer | Poly(vinyl) alcohol, Sodium alginate, Thioglycellulose chitosan, N, N’-bisacryloyl cysteamine, bFGF | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; Antibacterial; Precise release of drugs | Electrostatic bonding; Amide bonding; Disulfide bonding; Hydrogen bond | Tendon injury repair | [31] |
| Three-layer(layer-by-layer) | Sulfobetaine methacrylate; poly(vinyl) alcohol, tannic acid; polyacrylic acid, polyethyleneimine | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; anti-swelling | Hydrogen bond; Electrostatic interaction; Cation-Π interaction | Anti-postoperative adhesion; tissue adhesive | [32] |
| Release-Occupy strategy | Poly(vinyl) alcohol, Calcium alginate, Ionic liquids, Ethylene glycol | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; Conductivity; Mechanical and sensing stability | Hydrogen bond; | Wearable sensor | [33] |
| Unilateral graft modification | Methacrylated hyaluronate acid (HAMA); Poly sulfobetaine-type zwitterion (SBMA); Ketoglutarate (KA); Poly(acrylic acid-co- N-hydroxysuccinimide acrylate) [P(AA-co-AA-NHS)] | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; | Electrostatic interaction; Semi-interpenetrating | Tissue repair, Prevention of post-operative adhesions | [34] |
| Spin-coating process | Chitosan-gelatin/rhein-graphene oxide; poly(vinyl) alcohol (PVA)- poly(acrylic acid) (PAA)) | Adhesion/anti-adhesion; Antibacterial activity | Phase separation; hydrogen-bond | Prevent postoperative tissue adhesion; Multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected open wound | [35] |
| Preparation Method | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Layer by layer | High interface accuracy; high flexibility of components | Processing time, limited number of layers; difficulty in achieving scale |
| One-pot | Simple operation; short time consumption; easy scalability. | Blurry interface; poor structural controllability |
| Self-assembly | No external force required; low energy consumption; capable of forming complex topologies | Uncontrollable dynamics; poor reproducibility |
| Electrospinning | It can be used to prepare fibrous Janus structures High specific surface area | Weak interface adhesion; poor solvent compatibility |
| Unilateral dipping | Equipment is simple. low cost | Asymmetry is incomplete, Thickness is uneven |
| External field | Real-time dynamic regulation; fast response speed (magnetic/electrical field/pH/temperature) | Require special equipment; limited for use inside the body |
| Cyclic freeze–thaw | Enhance mechanical strength; no need for chemical crosslinking agents | Long cycle; uncontrolled aperture |
| 3D printing | Complex structure customization; multi-material integration; precise spatial distribution | Resolution limitation; The requirements for biological ink are extremely strict |
| Template strategy | Simple operation; high structural accuracy; compatible with hard/soft material composites | The template removal process is prone to leaving behind impurities; the removal of large-sized templates may lead to the collapse of the structure. |
| Unilateral graft modification | Chemical bonding interface; controllable thickness of the modified layer; gradient functionalization | Complex process; deep grafting efficiency decline; high-speed grafting may damage the substrate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Mirzaei, M.; Nie, L. Janus Hydrogels: Design, Properties, and Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090717
Guo W, Mirzaei M, Nie L. Janus Hydrogels: Design, Properties, and Applications. Gels. 2025; 11(9):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090717
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Wei, Mahta Mirzaei, and Lei Nie. 2025. "Janus Hydrogels: Design, Properties, and Applications" Gels 11, no. 9: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090717
APA StyleGuo, W., Mirzaei, M., & Nie, L. (2025). Janus Hydrogels: Design, Properties, and Applications. Gels, 11(9), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090717








