An Advanced Adhesive Electrolyte Hydrogel Intended for Iontophoresis Enhances the Effective Delivery of Glycolic Acid Via Microbeads
Abstract
1. Introduction
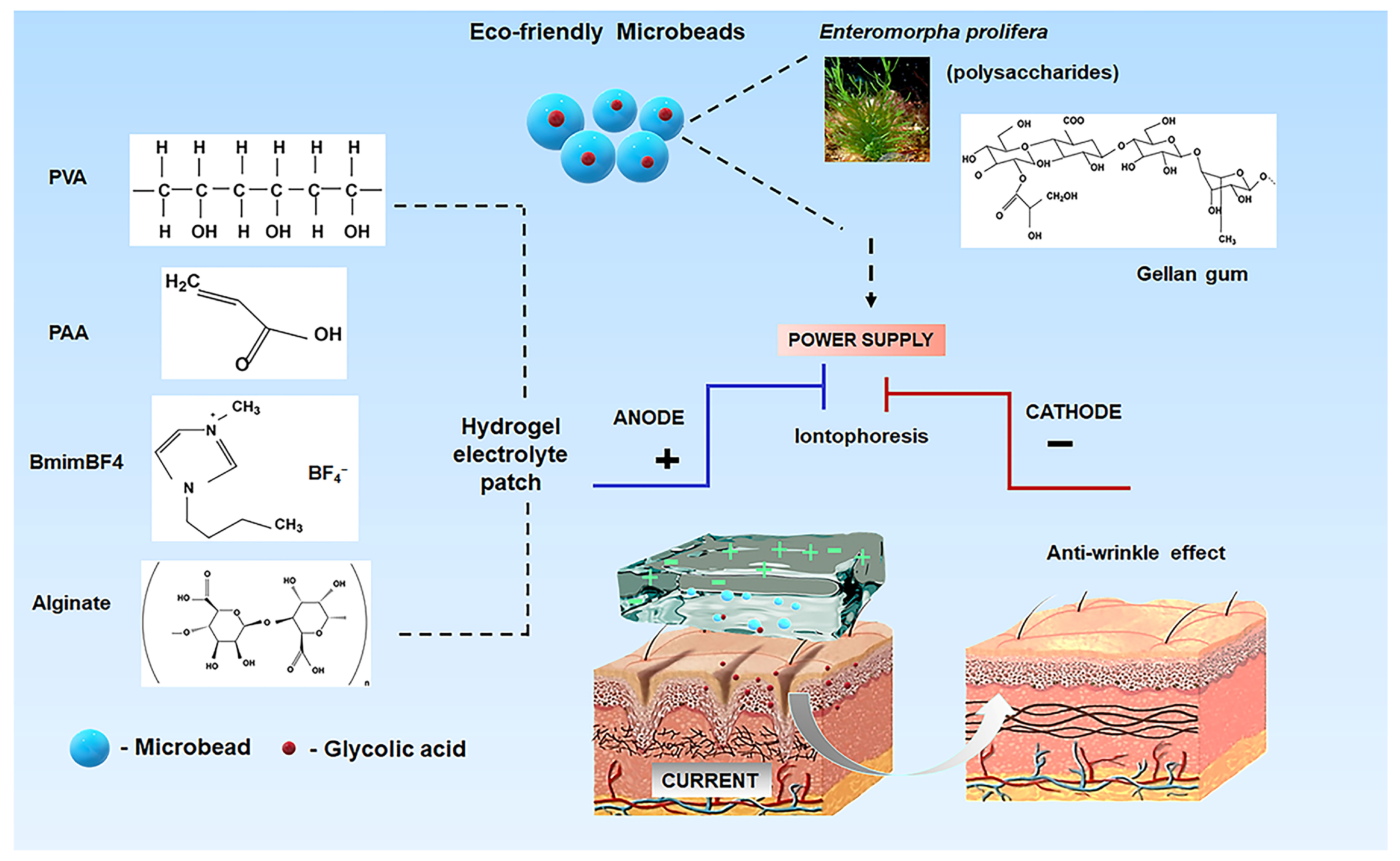
2. Results and Discussion
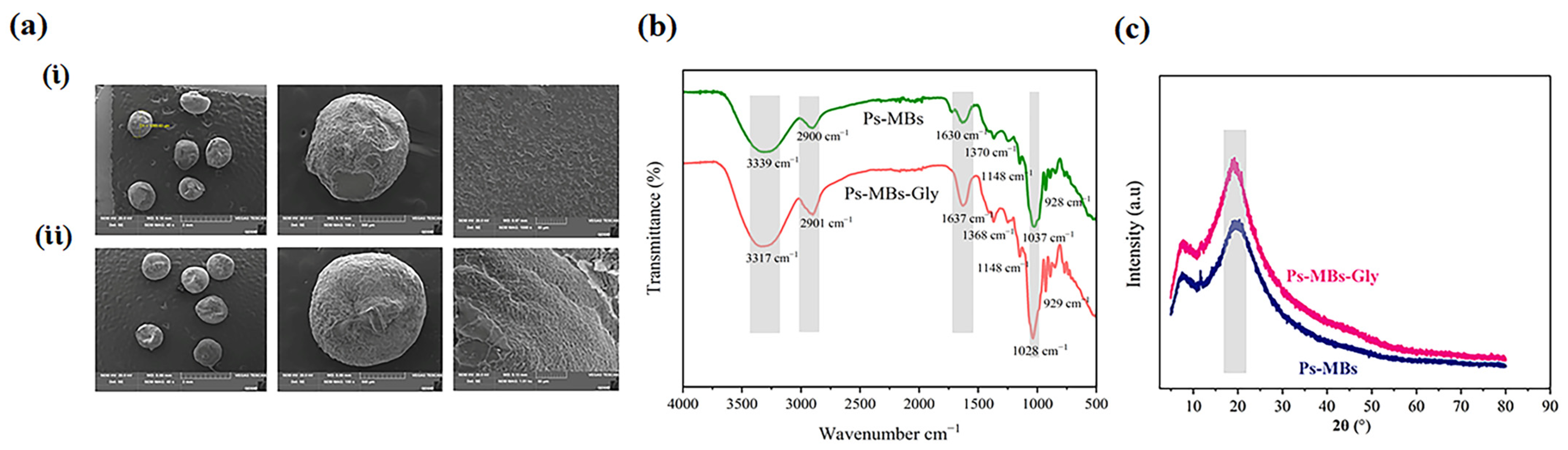
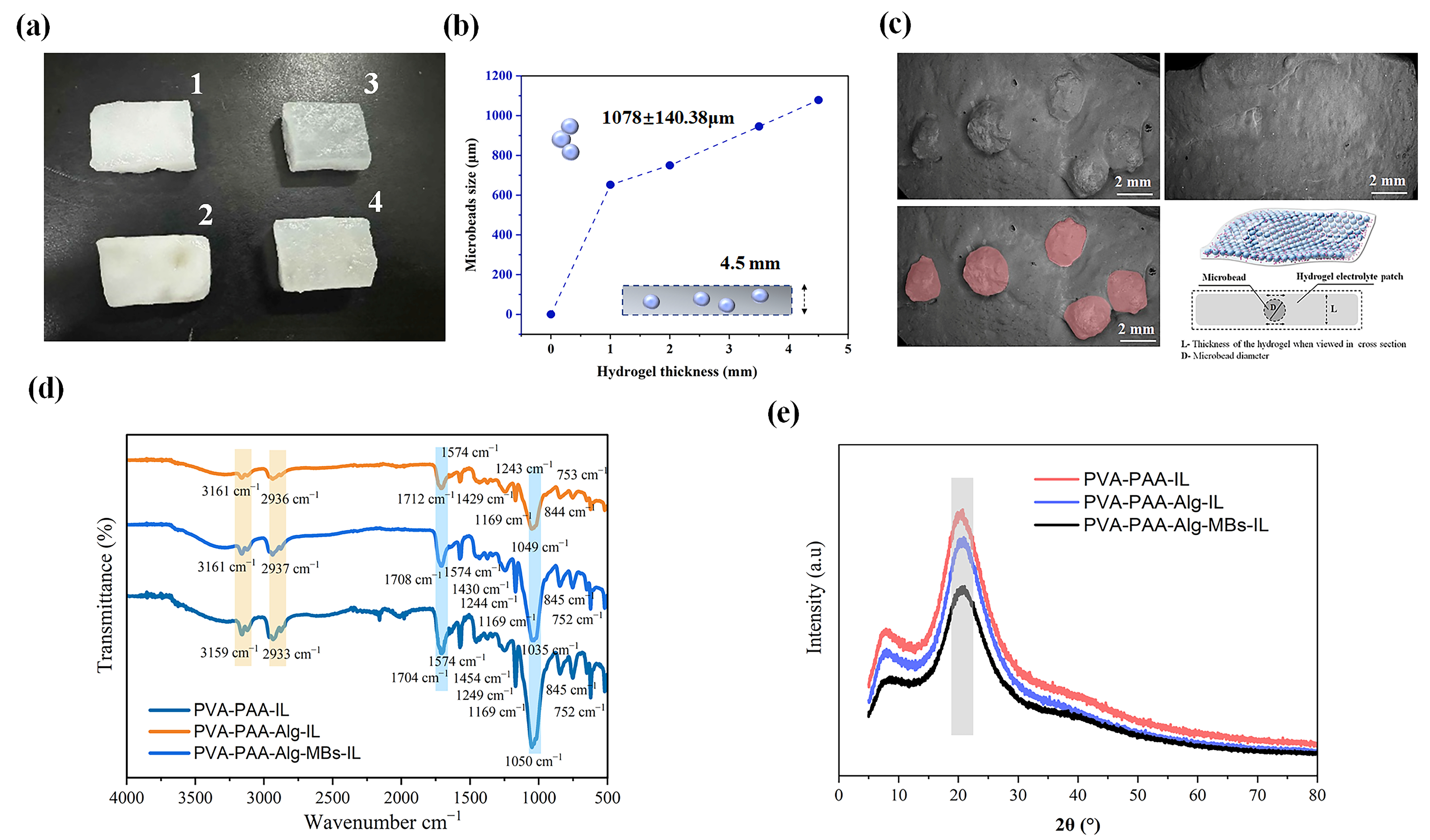
2.1. Characterization of Polysaccharide Microbeads and Electrolyte Hydrogel
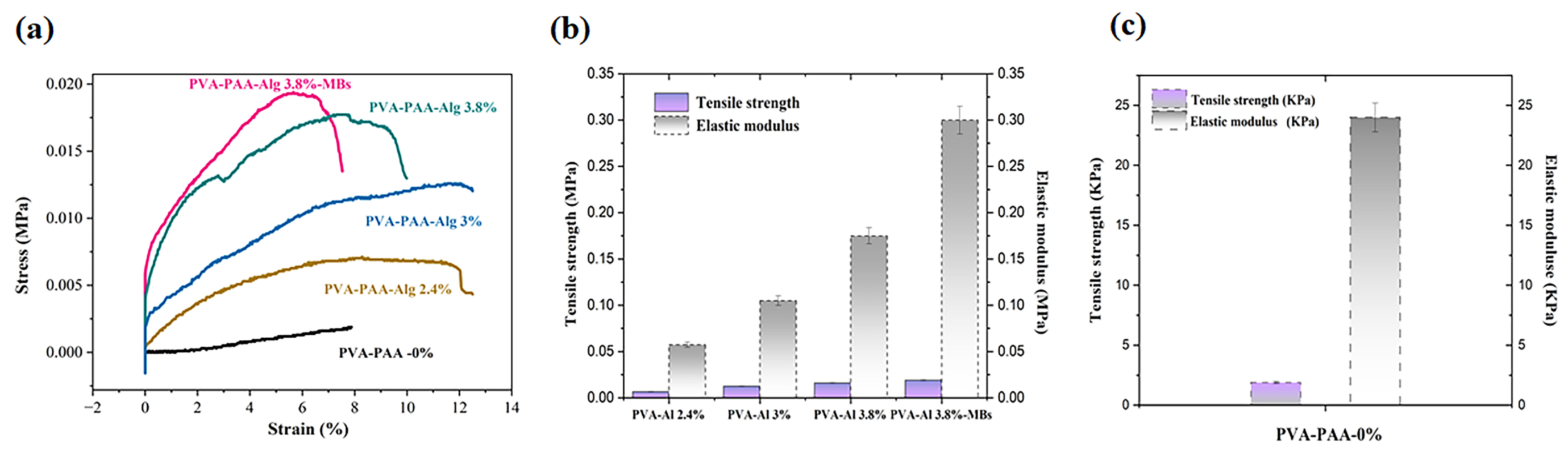
2.2. Mechanical Properties of Hydrogels
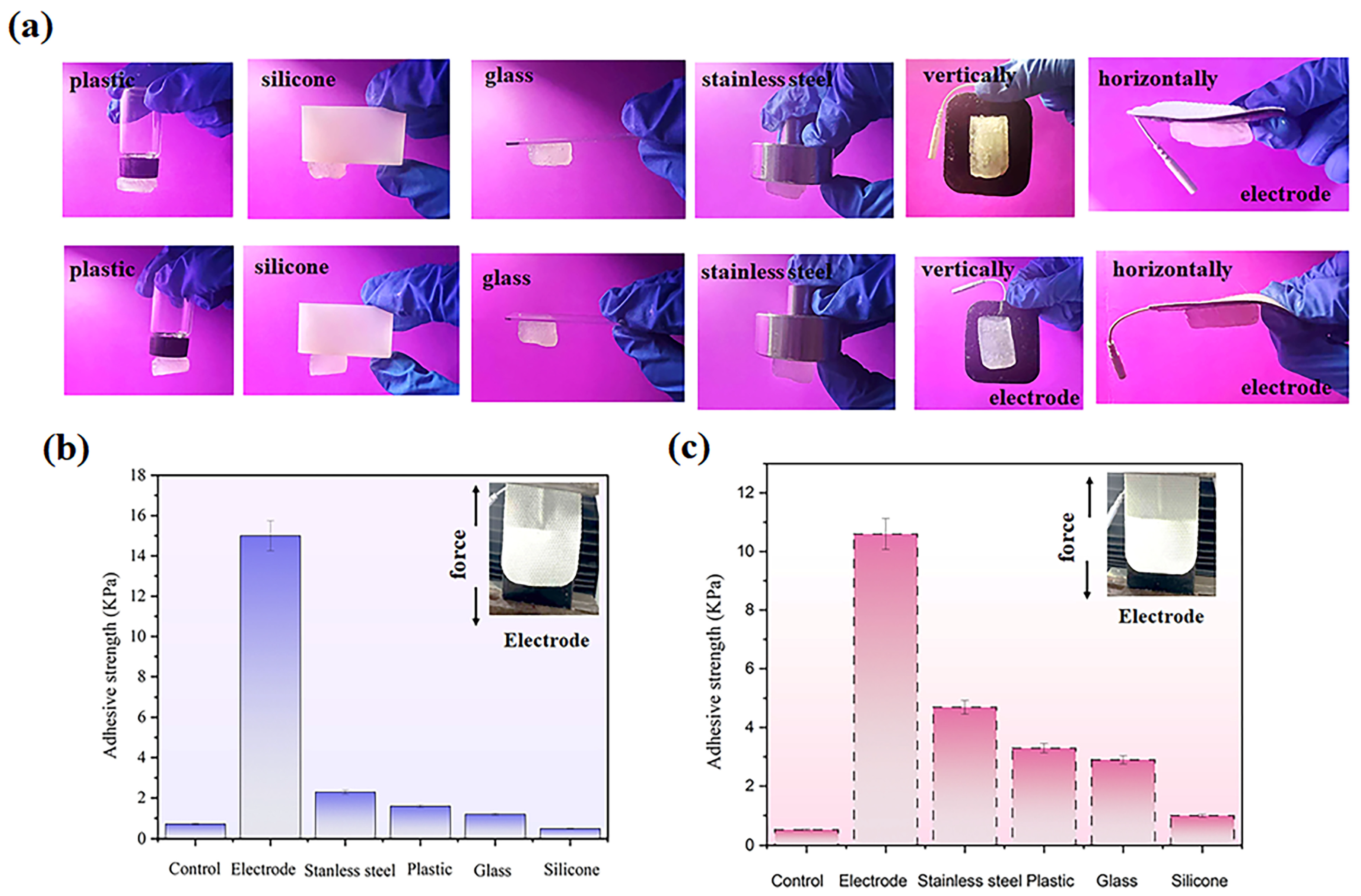
2.3. Adhesive Properties
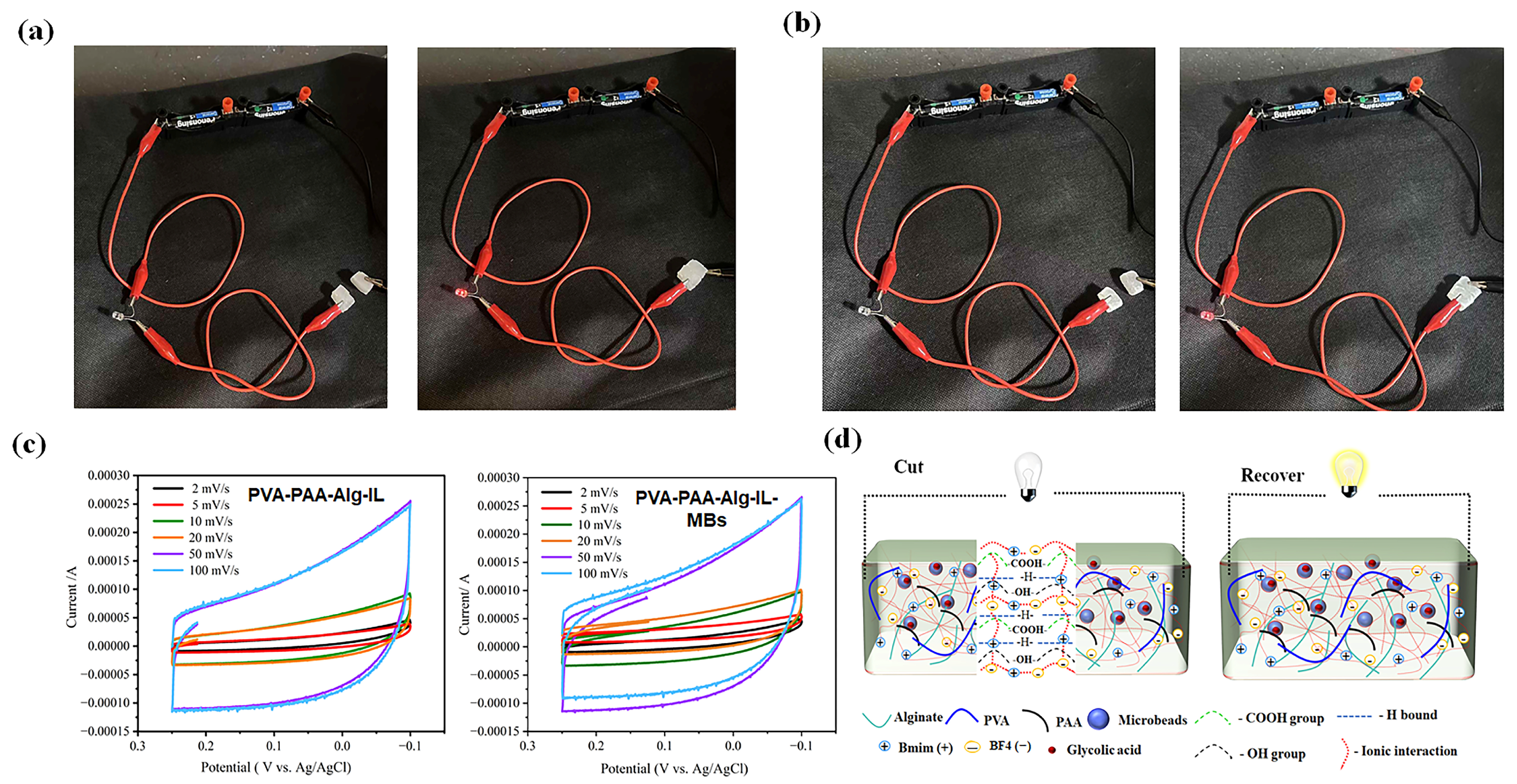
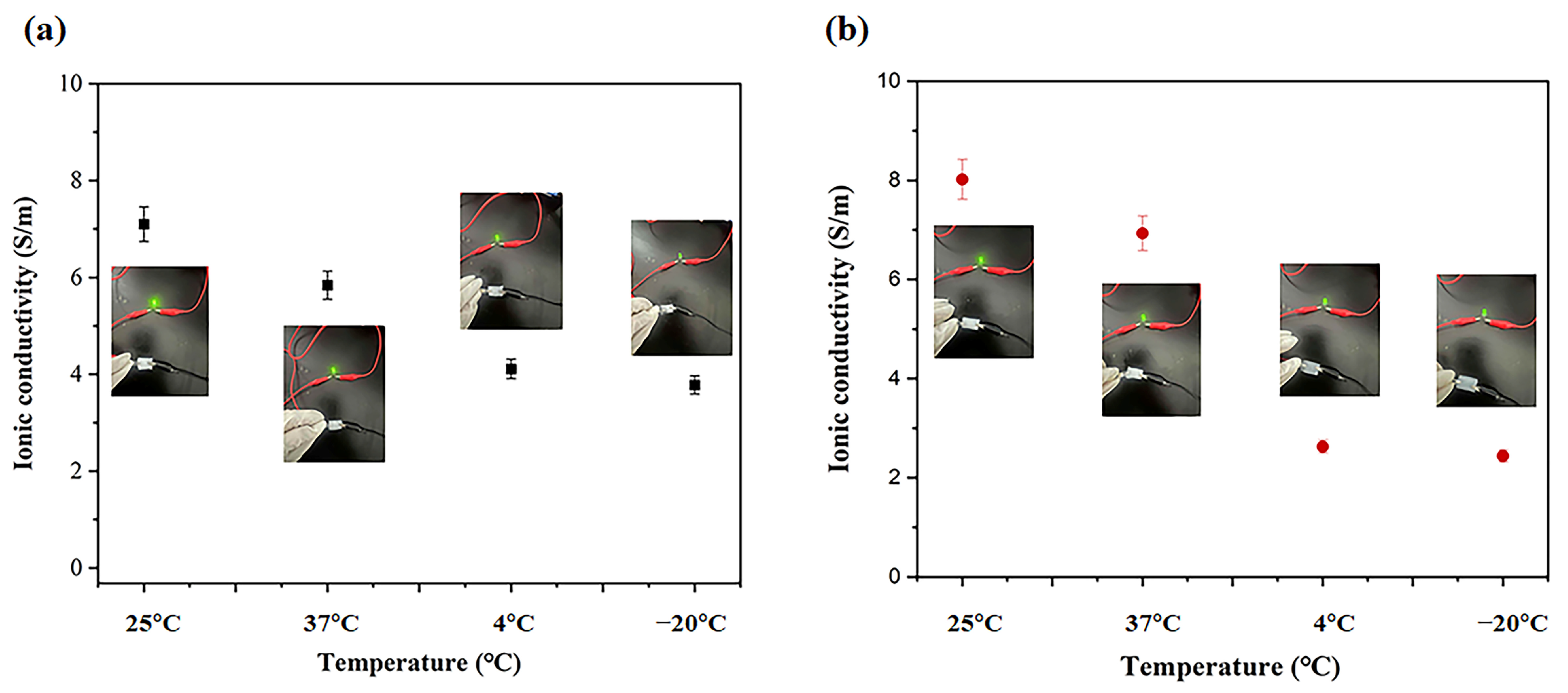
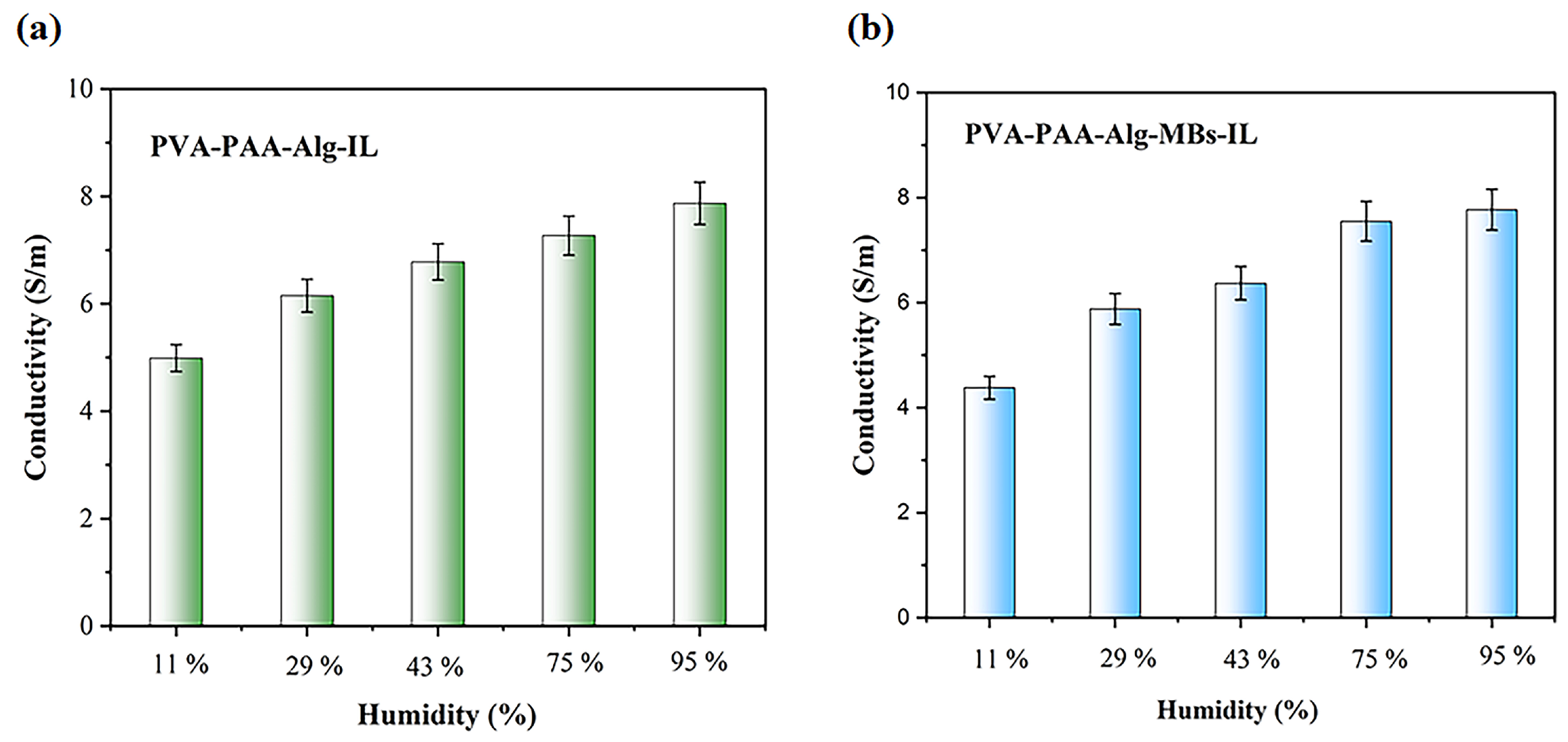
2.4. Conductive and Electrochemical Characterizations
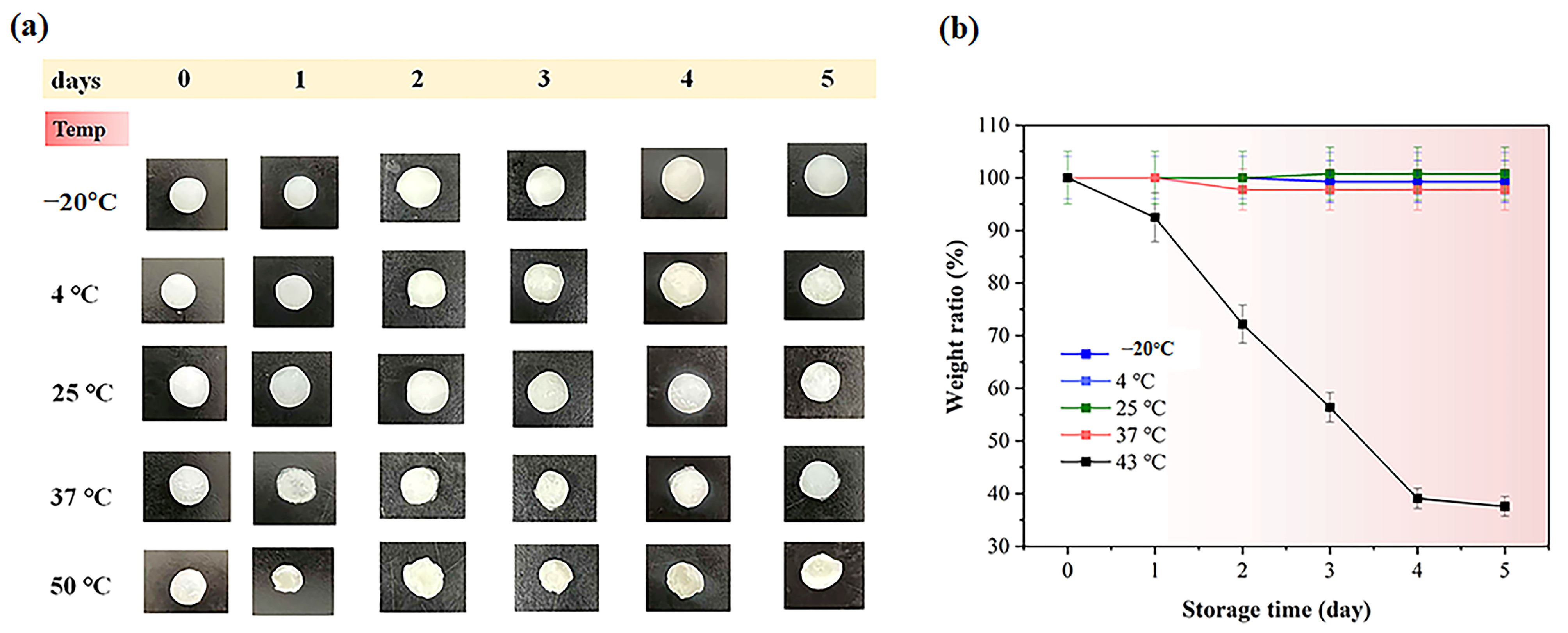
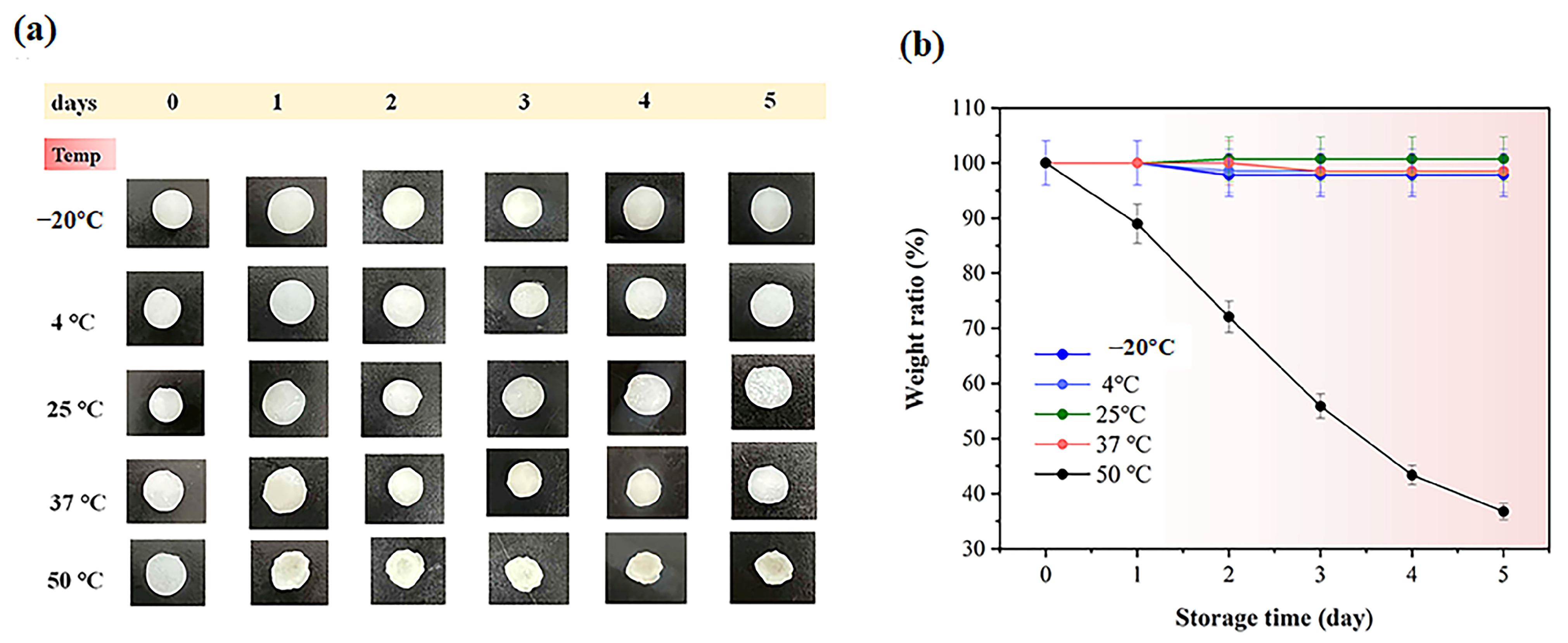
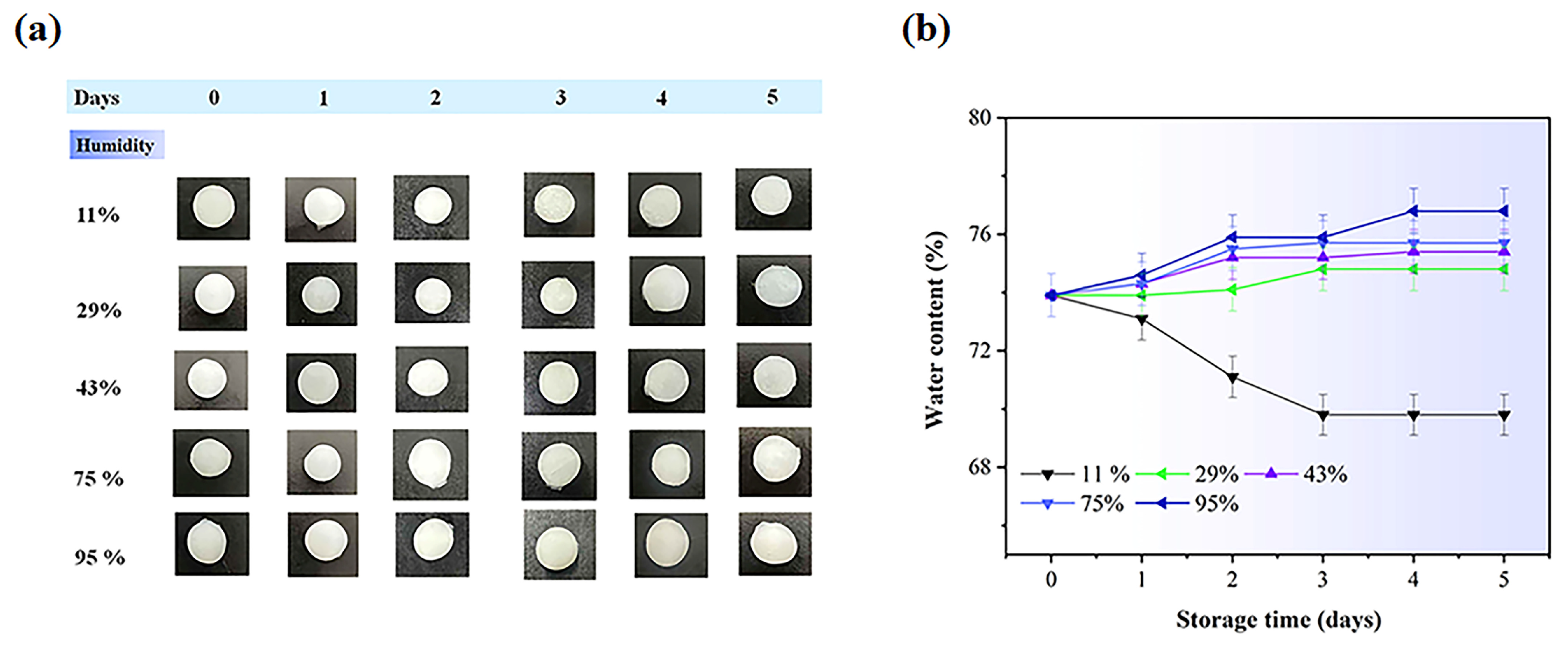
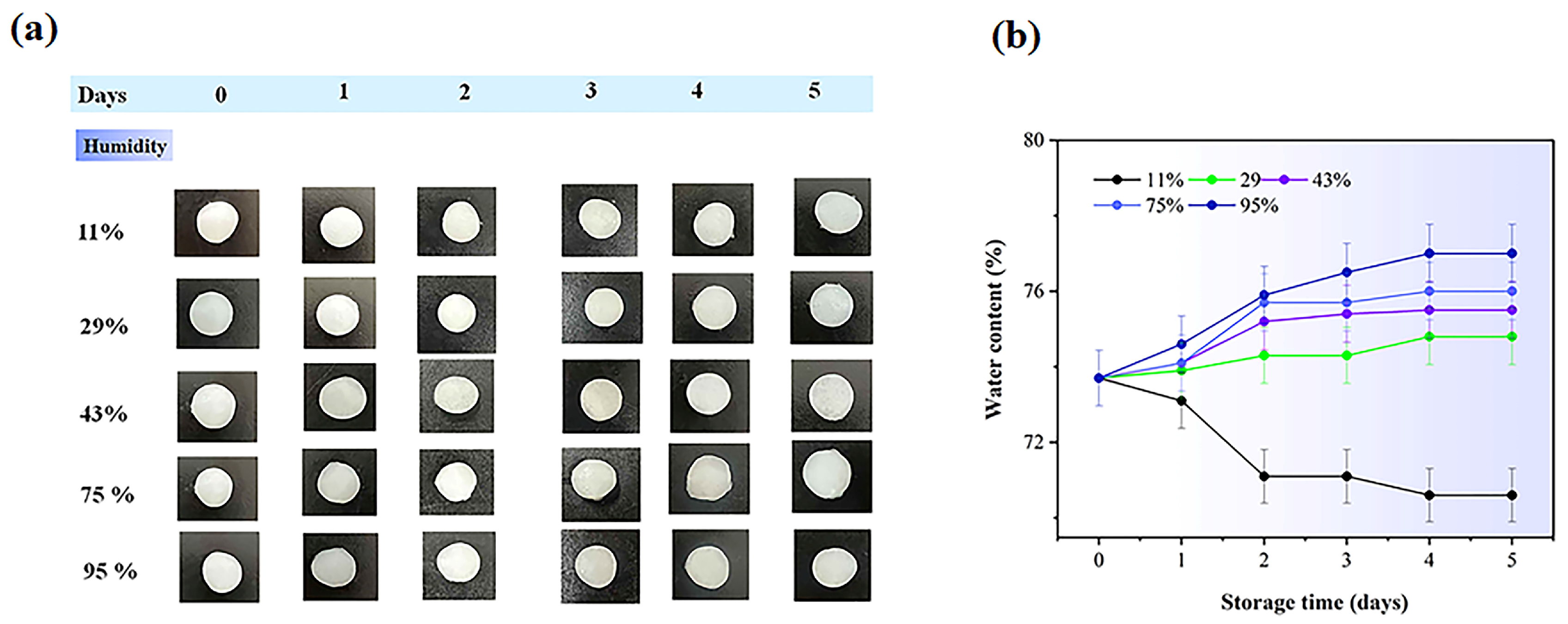
2.5. Stability of the Hydrogel Under Various Storage Conditions
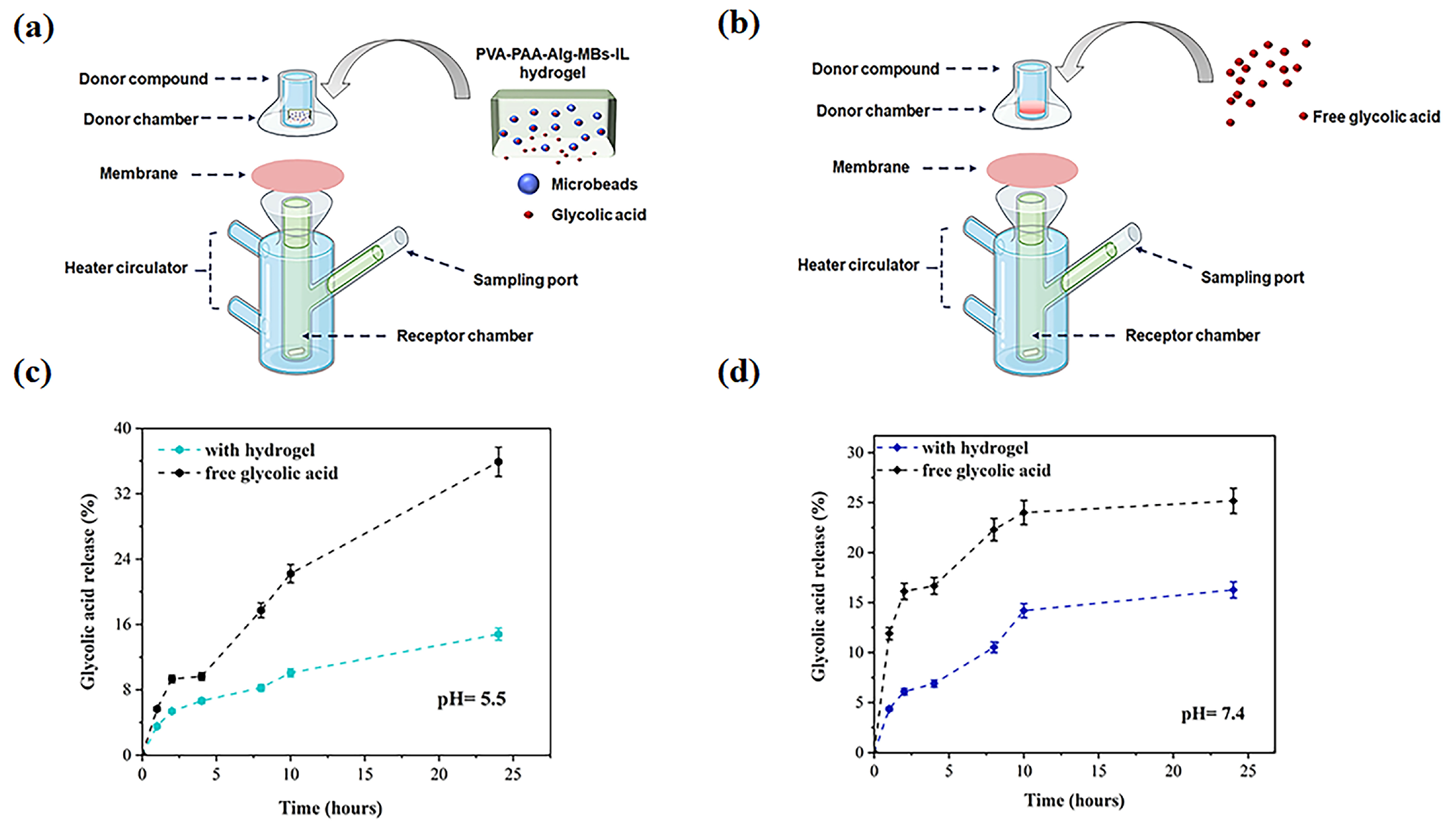
2.6. In Vitro Permeability Study
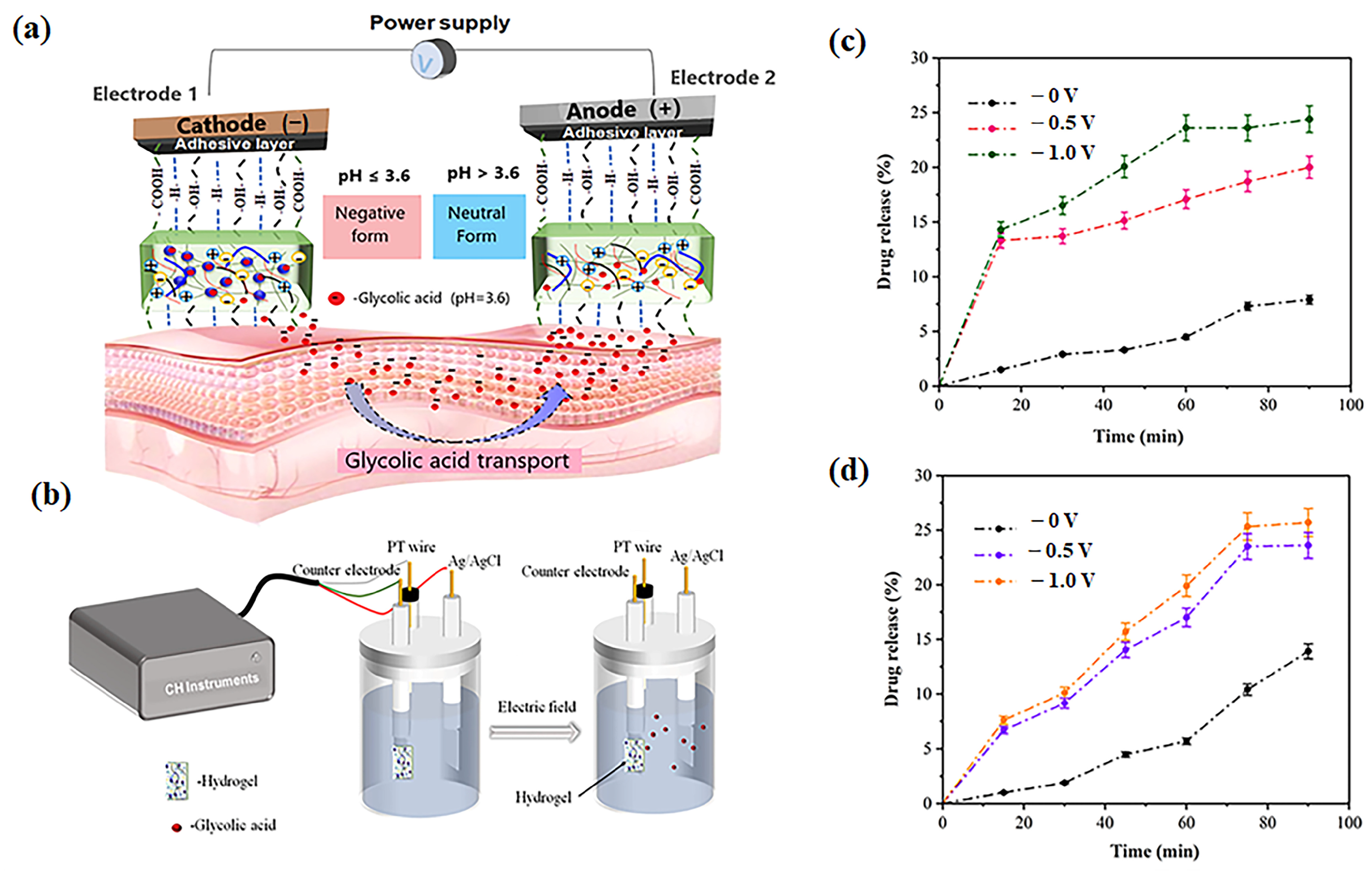
2.7. In Vitro Glycolic Acid Release Under Different Voltaged
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Synthesis of the Electrolyte Hydrogels
4.3. Characterizations of Hydrogels
4.3.1. FT-IR, X-Ray, and SEM Analysis
4.3.2. Mechanical Measurements
4.3.3. Adhesive Measurements
4.3.4. Storage Stability of Electrolytes Hydrogels Under Temperatures and Hymidity Conditions
4.3.5. The In Vitro Glycolic Acid Release from Electrolyte Hydrogel PVA-PAA-Alg-MBs-IL
4.3.6. Electrical and Electrochemical Measurements
4.4. Statistical Method
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yue, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, P. Uncovering Key Mechanisms and Intervention Therapies in Aging Skin. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 79, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Chen, J.; Chevalier, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Sheng, L.; et al. Holistic investigation of the anti-wrinkle and repair efficacy of a facial cream enriched with C-xyloside. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 4017–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yuan, M.; Gao, P.; Wang, L.; Qi, Y.; Chen, J.; Bai, K.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X. Microemulsion-Based Keratin–Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin. Gels 2023, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thy, L.T.M.; Duy, H.K.; Dat, N.M. Applications of lecithin in emulsion stabilization and advanced delivery systems in cosmetics: A mini-review. Results Surf. Interfaces 2025, 19, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, L. Effects of electrical stimulation on skin surface. Acta Mech. Sin. 2021, 37, 1843–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragit, R.; Fulzele, P.; Rathi, N.V.; Thosar, N.R.; Khubchandani, M.; Malviya, N.S.; Das, S. Iontophoresis as an Effective Drug Delivery System in Dentistry: A Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, A.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, Q.; Guo, W. Dual network conductive hydrogel for robust epidermal electrode patches. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 45, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R. Elastic and conductive hydrogel electrodes. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ai, Z.; Wu, J.; Lin, Z.; Huang, M.; Gao, Y.; Bai, H. A robust polyaniline hydrogel electrode enables superior rate capability at ultrahigh mass loadings. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Tao, W.; Tang, Z.; Hu, X. Conductive electronic skin coupled with iontophoresis for sensitive skin treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yun, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, F. Boosting Electronic Charge Transport in Conductive Hydrogels via Rapid Ion-Electron Transduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202506560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Kumar, N.; Chattopadhyay, S. Electrically conductive “Smart” hydrogels for on-demand drug delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 20, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ma, X.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liang, Q.; Jia, X.; Chao, D. A viologen-based conductive hydrogel enables iontophoresis devices powered by Mg biobattery. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Jiang, H. Lidocaine-Loaded Iontophoresis-Driven Fiber-Based Microneedle Patch for Controllable and Long-Lasting Transdermal Local Analgesia. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 7, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parvin, N.; Joo, S.W.; Mandal, T.K.; Park, S.S. Great Carbon Nano Materials based Composites for Electronic Skin: Intelligent Sensing, and Self-Powered Nano Generators. Nano Energy 2025, 137, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Chen, S.-W.; Tu, Q.; Yuan, M.-S.; Wang, J. Liquid Metal-Doped Conductive Hydrogel for Construction of Multifunctional Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 3811–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Hu, Y.; Abdiryim, T.; Xu, F.; You, J.; Tan, Y.; Tan, Z.; et al. Polyanionic hydrogel electrolytes to regulate ion transport behavior in long cycle life zinc-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2025, 143, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qu, M.; Wang, R.; Wan, L.; Lei, D.; Li, Z. High adhesion hydrogel electrolytes enhanced by multifunctional group polymer enable high performance of flexible zinc-air batteries in wide temperature range. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ou, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Mwakitawa, I.M.; Li, F.; Chen, R.; Yue, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Self-adhesive and biocompatible dry electrodes with conformal contact to skin for epidermal electrophysiology. Interdiscip. Mater. 2024, 3, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-S.; Yao, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Xing, C.; Song, X.; Su, P.; Zhang, H.-T. Recognition of Ionic Liquids as High-Voltage Electrolytes for Supercapacitors. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biji, C.A.; Balde, A.; Kim, S.-K.; Nazeer, R.A. Optimization of alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan microbeads for the sustained release of celecoxib and attenuation of intestinal inflammation in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassanelli, M.; Norton, I.; Mills, T. Effect of alcohols on gellan gum gel structure: Bridging the molecular level and the three-dimensional network. Food Struct. 2017, 14, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Yin, J.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y. Applications of infrared spectroscopy in polysaccharide structural analysis: Progress, challenge and perspective. Food Chem. 2021, 12, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Al-Sahlany, S.T.G. Gellan Gum as a Unique Microbial Polysaccharide: Its Characteristics, Synthesis, and Current Application Trends. Gels 2024, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Fu, J.; Feng, G. Progress on predicting the electrochemical stability window of electrolytes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 34, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, J.; Yan, C.; Sha, H.; Hong, M.; Fu, H. Self-Healing, Water-Retaining, Antifreeze, Conductive PVA/PAA-PAM-IS/GC Composite Hydrogels for Strain and Temperature Sensors. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan Aneem, T.; Firdous, S.O.; Anjum, A.; Wong, S.Y.; Li, X.; Arafat, M.T. Enhanced wound healing of ciprofloxacin incorporated PVA/alginate/PAA electrospun nanofibers with antibacterial effects and controlled drug release. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 38, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Park, J.M.; Oh, M.S.; Nguyen, T.L.; Shin, H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.; Park, H.S.; Kim, J. Superstrong, superstiff, and conductive alginate hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Quan, F. Multi-network PVA/SA aerogel fiber: Unveiling superior mechanical, thermal insulation, and extreme condition stability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 223, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić Gajić, I.M.; Savić, I.M.; Svirčev, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Alginate Hydrogels with High Water-Retaining Capacity. Polymers 2023, 15, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, T.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Qi, J.; Dong, Q.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, Z.; Si, C. Functionalities and properties of conductive hydrogel with nanocellulose integration. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 159872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothermund, M.A.; Koehler, S.J.; Vaissier Welborn, V. Electric Fields in Polymeric Systems. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 13331–13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.-T.; Guo, L.; Yin, C.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L. Eco-Friendly, Self-Healing Hydrogels for Adhesive and Elastic Strain Sensors, Circuit Repairing, and Flexible Electronic Devices. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Cui, X.; Qi, Z.; Yang, X. An injectable, self-healing, electroconductive hydrogel loaded with neural stem cells and donepezil for enhancing local therapy effect of spinal cord injury. J. Biol. Eng. 2023, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, R. Chemical Stability of Cosmetic Ingredients: Mechanisms of Degradation and Influencing Factors. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2025, 156, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Yan, S.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Gao, G. Wearable strain sensors based on casein- driven tough, adhesive and anti-freezing hydrogels for monitoring human-motion. J. Mat. Chem. 2019, 7, 5230–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Gu, K.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Poly (vinyl alcohol) Hydrogels with Integrated Toughness, Conductivity, and Freezing Tolerance Based on Ionic Liquid/Water Binary Solvent Systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29008–29020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.N.; Mo, K.; Liang, X.H.; Xie, J.S.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Gu, M.; Liu, X.R.; Lu, Y.; Ge, J. High Ion-Conductive Hydrogel: Soft, Elastic, with Wide Humidity Tolerance and Long-Term Stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 60992–61003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, W.; Lang, M. Natural UCST hydrogel with long-term stability, recyclability, thermoplasticity, frost resistance and adhesive properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 199, 112414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jia, X.; Pang, D.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, M.; Lu, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; Chao, D.; Wallace, G. An integrated Mg battery-powered iontophoresis patch for efficient and controllable transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Injectable antibacterial conductive hydrogels with dual response to an electric field and pH for localized “smart” drug release. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, A.; Pereira, C.; Martins, A.M.; Raposo, S.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Marto, J. Upgrading skin barrier Protection: Addition of active ingredients to a Gelatin/Tannic Acid-Based hydrogel patch for treating skin lesions related to Personal protective Equipment. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 669, 125110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, G.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; He, Z. Low-voltage/temperature double responsive N-isopropylacrylamide based shape-changing double network hydrogel with enhanced mechanical properties for controlled drug release and its mechanism. Mater. Des. 2025, 253, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Kou, X.; Yang, M.; Normakhamatov, N.; Alasmari, A.F.; Xin, B.; Tan, Y. Water-soluble polysaccharides extracted from Enteromorpha prolifera/PVA composite film functionalized as ε-polylysine with improved mechanical and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.A.M.; Barik, A. Encapsulation of curcumin in alginate microbeads (AMB) for control release of curcumin. J. Chem. Sci. 2023, 135, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R.; Markova, N. 5-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline-containing Electrospun Materials Based on Poly (vinyl alcohol) and Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Their Cu2+ and Fe3+ Complexes with Diverse Biological Properties: Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticancer. Polymers 2023, 15, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazharskaia, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C. An Advanced Adhesive Electrolyte Hydrogel Intended for Iontophoresis Enhances the Effective Delivery of Glycolic Acid Via Microbeads. Gels 2025, 11, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090682
Kazharskaia M, Yu Y, Liu C. An Advanced Adhesive Electrolyte Hydrogel Intended for Iontophoresis Enhances the Effective Delivery of Glycolic Acid Via Microbeads. Gels. 2025; 11(9):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090682
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazharskaia, Mariia, Yu Yu, and Chenguang Liu. 2025. "An Advanced Adhesive Electrolyte Hydrogel Intended for Iontophoresis Enhances the Effective Delivery of Glycolic Acid Via Microbeads" Gels 11, no. 9: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090682
APA StyleKazharskaia, M., Yu, Y., & Liu, C. (2025). An Advanced Adhesive Electrolyte Hydrogel Intended for Iontophoresis Enhances the Effective Delivery of Glycolic Acid Via Microbeads. Gels, 11(9), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090682








