Sodium Alginate/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Microbeads for Antibiotic Adsorption in Single and Binary Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
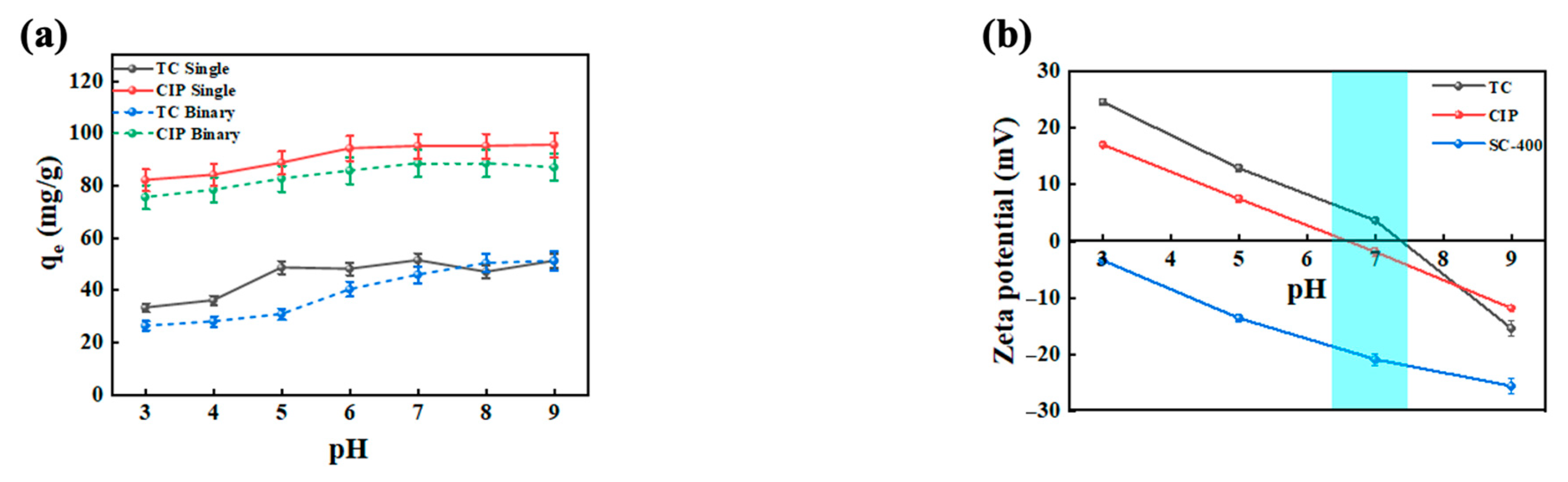
2.1. Effect of pH on the Antibiotic Adsorption
2.2. Effect of Temperature on Antibiotic Adsorption
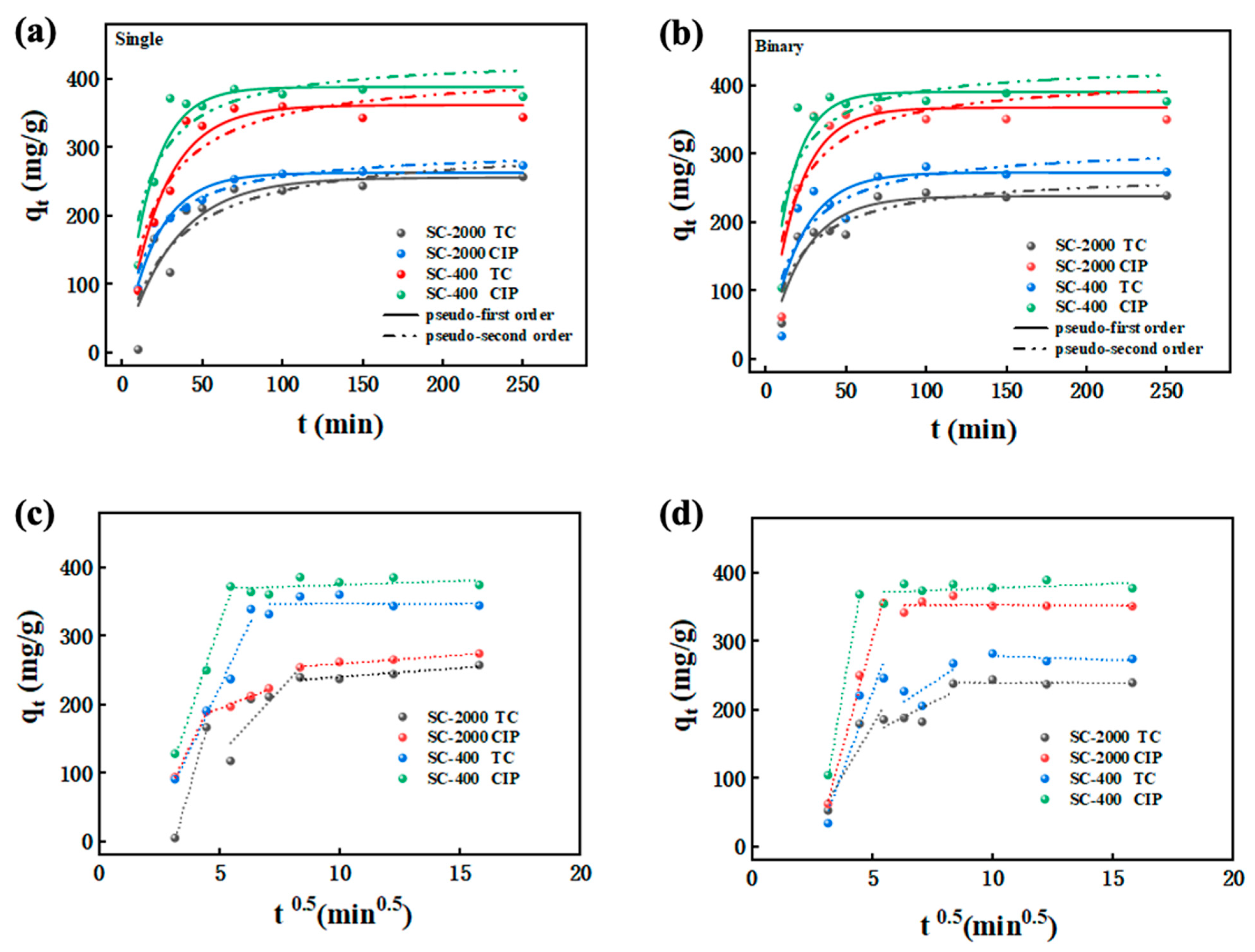
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
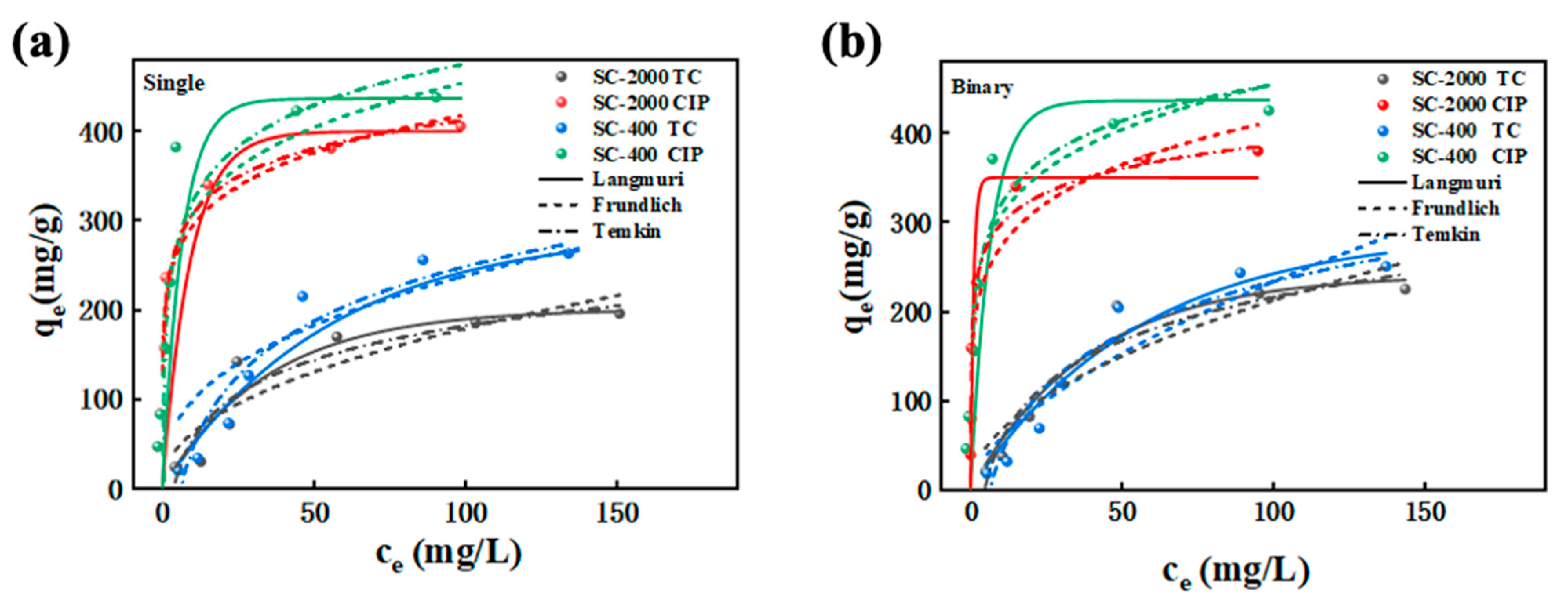
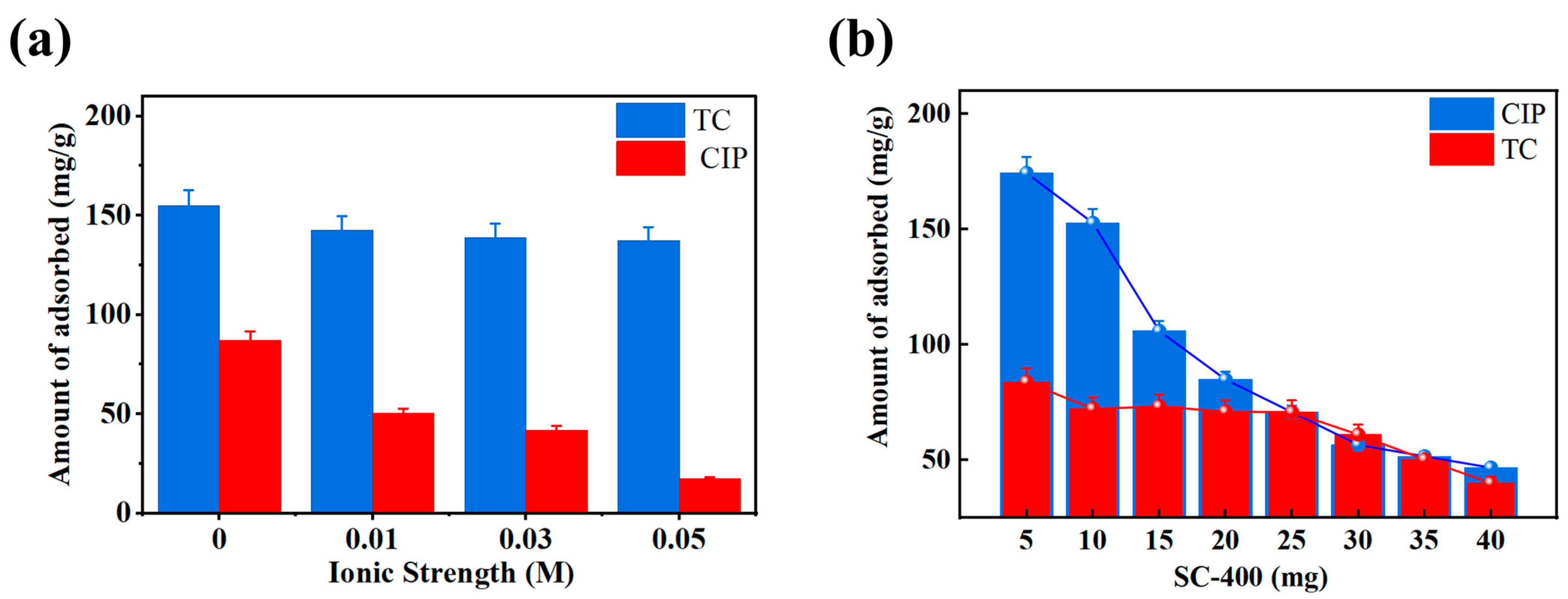
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
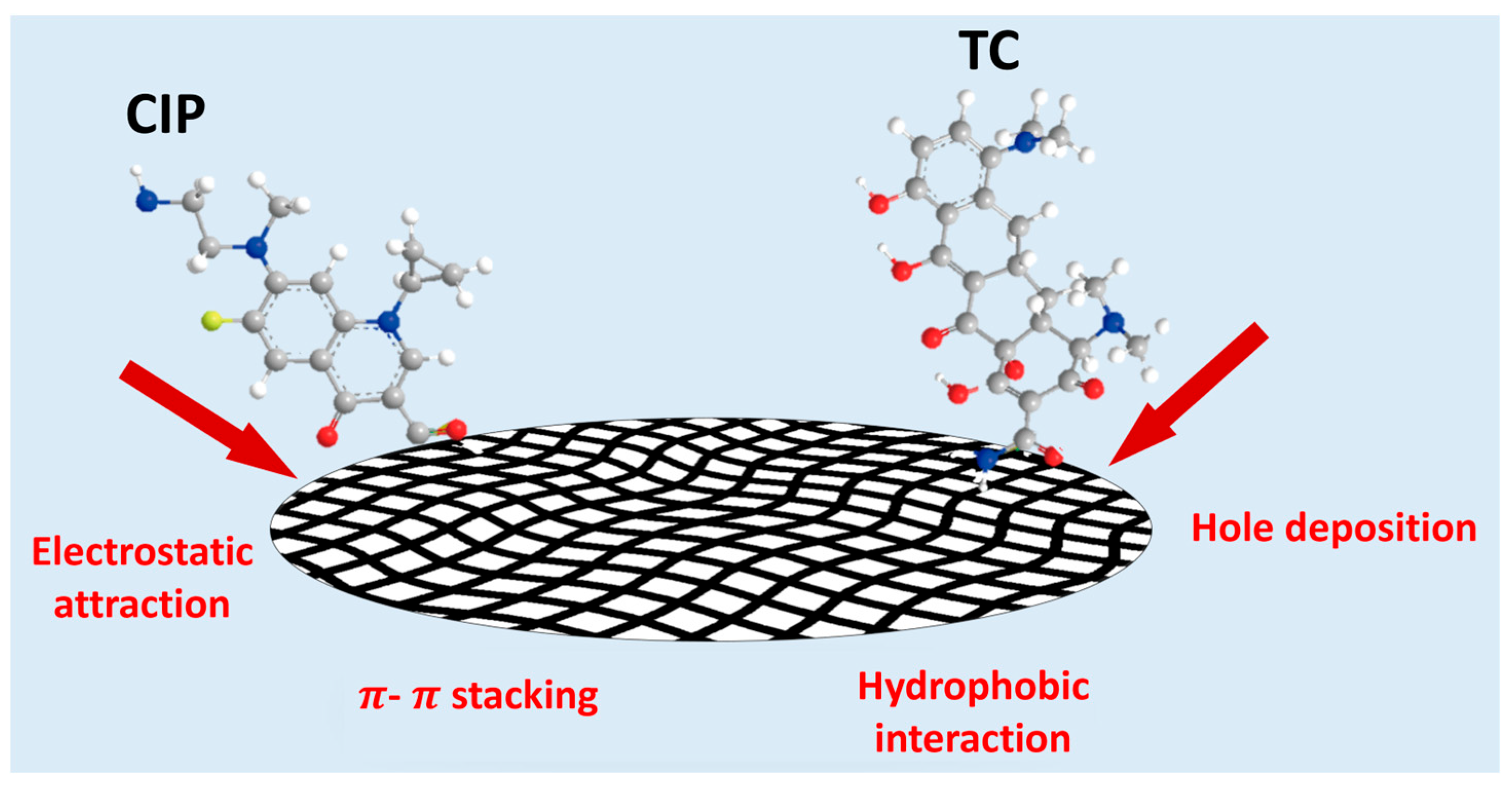
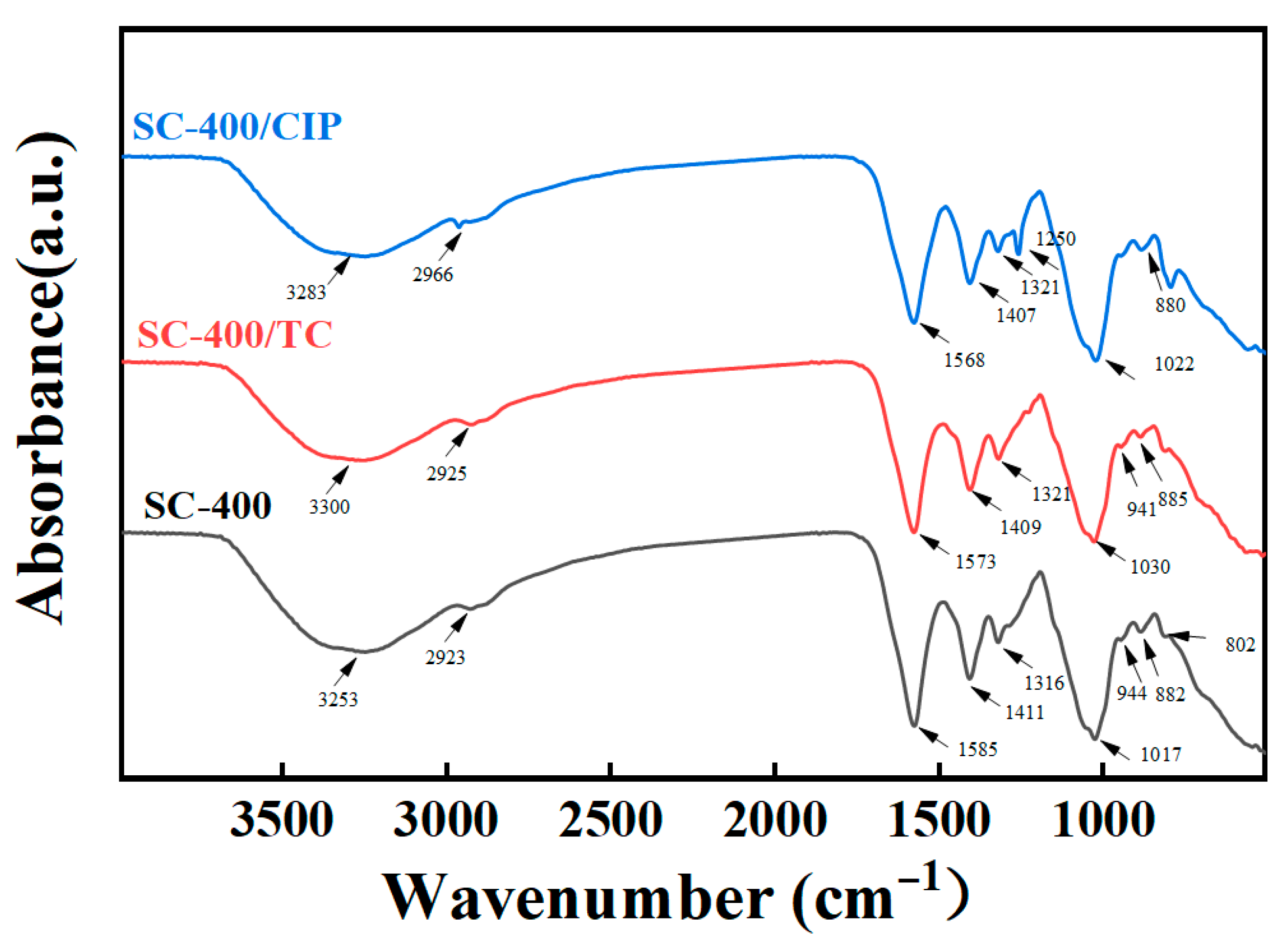
2.5. Characterization and Adsorption Mechanisms
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material
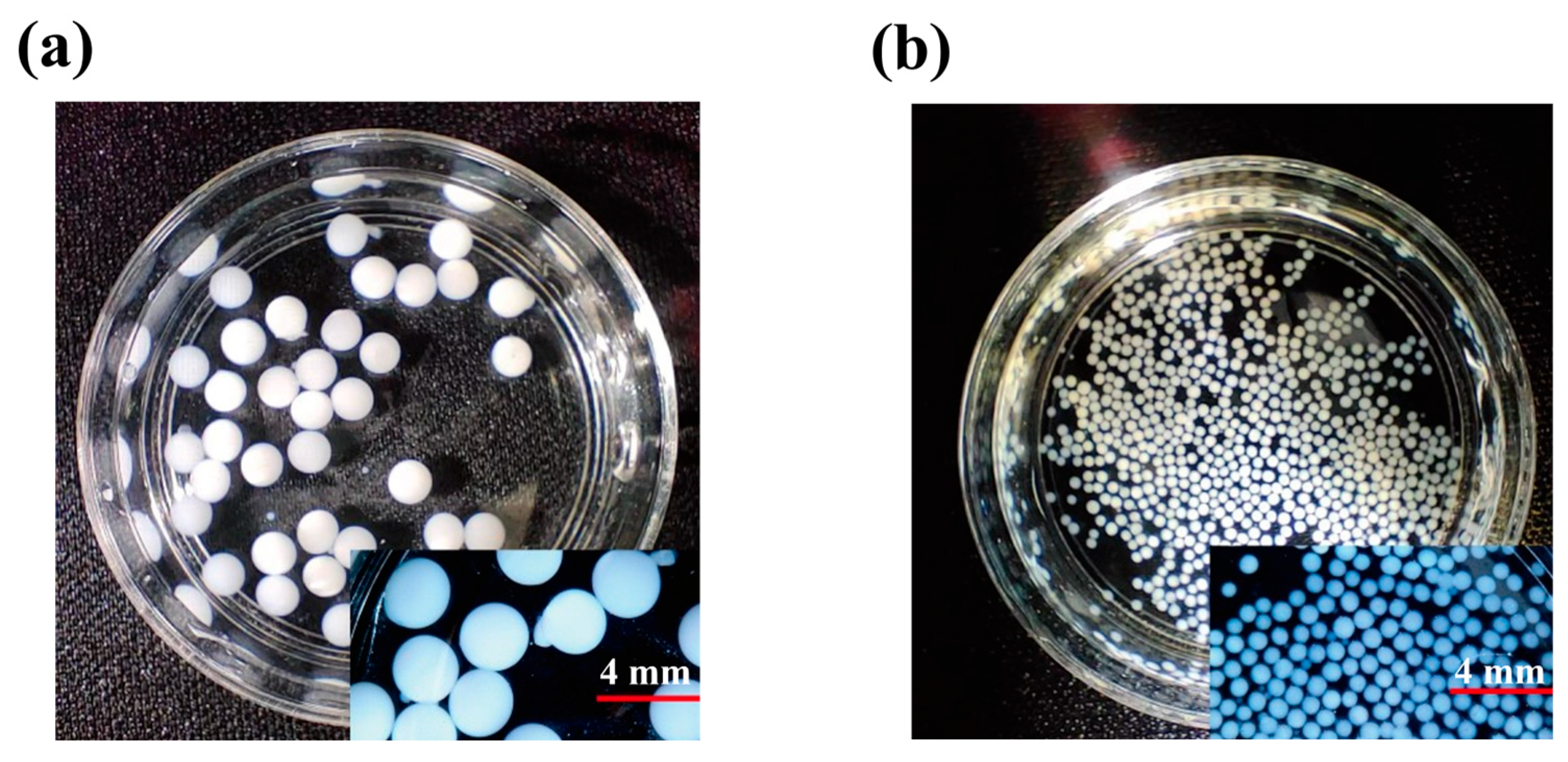
4.2. Preparation of the SA/CMCS Microbeads Using Electrostatic Spraying Method
4.3. Adsorption Study
4.4. Characterization of Sorbents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SA | Sodium alginate |
| CMC | Carboxymethyl cellulose |
| TC | Tetracycline |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
References
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Yacoub, M.H. Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: Progress and challenges. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2013, 2013, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinadha, M.R.; Phanindra, C.; Yamini, M.; Prasad, C.H. Hydrogels The Three Dimensional Networks: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2021, 13, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasalizadeh, F.; Moghaddam, S.V.; Alizadeh, E.; Akbari, E.; Kashani, E.; Fazljou, S.M.B.; Torbati, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Alginate-based hydrogels as drug delivery vehicles in cancer treatment and their applications in wound dressing and 3D bioprinting. J. Biol. Eng. 2020, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Ren, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Gou, D. Chitosan-based hydrogels: From preparation to applications, a review. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Tao, H.; Jin, L.; Wan, Z.; Dai, F.; Xiang, W.; Deng, H. Carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate-based micron-fibers fabricated by emulsion electrospinning for periosteal tissue engineering. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Lin, Z.; Tang, Z.; Lin, B. Carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate hydrogel films with good biocompatibility and reproducibility by in situ ultra-fast crosslinking for efficient preservation of strawberry. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 316, 121073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Lv, Z.; Meng, X.; Liang, Q.; Jiang, T.; Sun, S.; Li, Y.; Feng, J. Sodium alginate-carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogels loaded with difenoconazole for pH-responsive release to control wheat crown rot. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.Z.; Sun, X.F.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, S.G.; Javed, A. Enhancement of ciprofloxacin sorption on chitosan/biochar hydrogel beads. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamsi, E.B.; Reshma, M.; Devatha, C.P. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin antibiotic using chitosan graphene oxide hybrid beads. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J.; Chen, J. Enhanced adsorption removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions by modified alginate/graphene double network porous hydrogel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 507, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urkan, E.; Guler, H.; Kömekçi, F. A Review of Electrostatic Spraying for Agricultural Applications. J. Agric. Mach. Sci. 2016, 12, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, X.; Shang, B.; Yu, Y. Applications of electrostatic spray technology in food preservation. LWT 2023, 190, 115568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, I.; Choi, K.-H.; Lee, T.-M. Experimental Qualification of the Process of Electrostatic Spray Deposition. Coatings 2019, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Pan, G. Recent Advances in Bioactive Hydrogel Microspheres: Material Engineering Strategies and Biomedical Prospects. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Ren, L.-F.; Shao, J.; He, Y. Rapid preparation and mechanism investigation of covalent organic framework membranes by 3D printing based on electrostatic spraying. J. Memb. Sci. 2025, 715, 123487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.M.D.; Dinh, T.D.; Tran, T.M.H.; Nguyen, M.K.; Hoang, H.; Vu, L.K.; Vu, N.D.Q.; Pham, T.D. Adsorption characteristics of individual and binary mixtures of ciprofloxacin antibiotic and Cu(II) on nanosilica in water. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 398, 124298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; He, J.; He, J.; Cao, J. Removal of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2024, 9, 100717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Gao, M.; Chang, J.; Ma, H. Highly effective adsorption performance of carboxymethyl cellulose microspheres crosslinked with epichlorohydrin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricov, L.; Leontieș, A.R. Adsorption of Bisphenol A from Water Using Chitosan-Based Gels. Gels 2025, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhasan, H.S.; Yasin, S.A.; Alahmadi, N.; Alkhawaldeh, A.K. The Application of Hydroxyapatite NPs for Adsorption Antibiotic from Aqueous Solutions: Kinetic, Thermodynamic, and Isotherm Studies. Processes 2023, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Sun, M.; Bi, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Removal of Ciprofloxacin by PAA-PAM Hydrogel: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism Studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 71, 107361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Cui, L.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Da, C.; Hirasaki, G.J.; Biswal, S.L. Adsorption of cationic and anionic surfactants on natural and synthetic carbonate materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 408, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Abidi, N.; Lucia, L. Smart superabsorbent alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan composite hydrogel beads as efficient biosorbents for methylene blue dye removal. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 159, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, S.; Abu-Khamsin, S.A.; Kamal, M.S.; Patil, S. Surfactant Adsorption Isotherms: A Review. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32342–32348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafin, J.; Dziejarski, B. Application of isotherms models and error functions in activated carbon CO2 sorption processes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 354, 112513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Adsorption behaviors and influencing factors of antibiotic norfloxacin on natural kaolinite-humic composite colloids in aquatic environment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Lundborg, C.S.; Diwan, V. Factors influencing the adsorption of antibiotics onto activated carbon in aqueous media. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 2260–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckmann, F.d.S.; Schnorr, C.E.; Salles, T.d.R.; Nunes, F.B.; Baumann, L.; Müller, E.I.; Silva, L.F.O.; Dotto, G.L.; Rhoden, C.R.B. Highly Efficient Adsorption of Tetracycline Using Chitosan-Based Magnetic Adsorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lu, T.; Qi, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Qi, Z.; Chen, W. Effect of phosphate on the adsorption of antibiotics onto iron oxide minerals: Comparison between tetracycline and ciprofloxacin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tiang, M.F.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Takriff, M.S.; Sajab, M.S.; Abdul, P.M.; Ding, G. Precisely controlled electrostatically sprayed sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel microbeads as super-adsorbent for adsorption of cationic dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
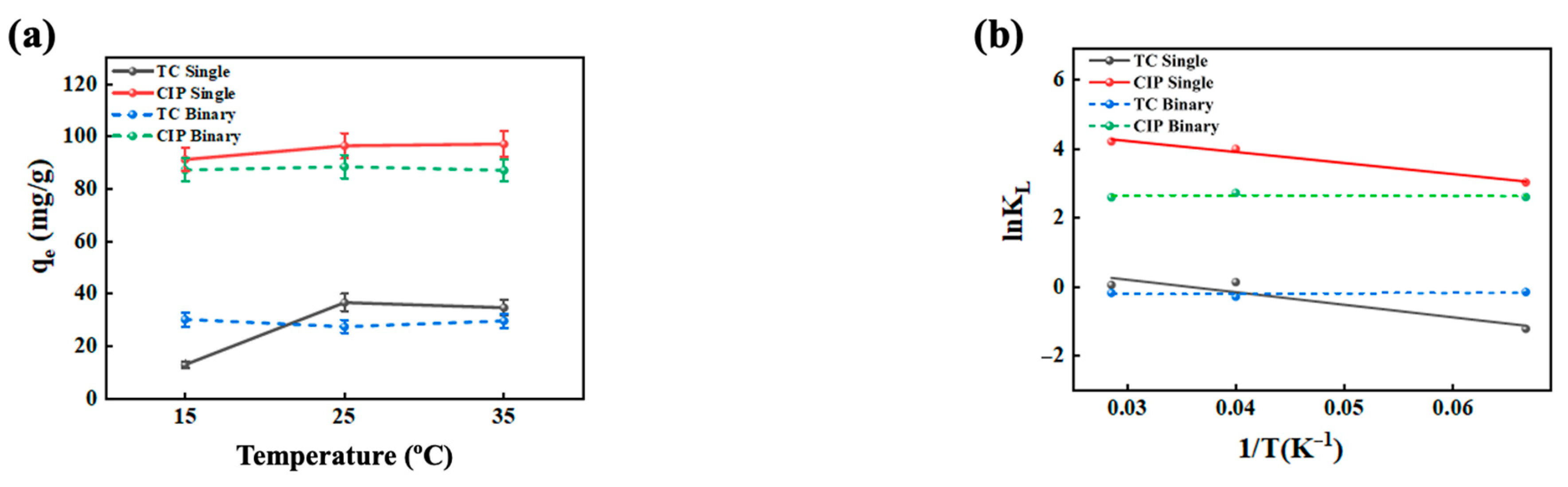
| Systems | Temperature, °C | Adsorption Equilibrium Constant, KL (L·mg) | Gibbs Free Energy ∆G (kJ·mol−1) | Enthalpy, ∆H (kJ·mol−1) | Entropy ∆S (J·mol−1K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single TC | 15 | 1.2998 ± 0.1040 | −0.628 ± 0.192 | 46.213 | 152.5 |
| 25 | 1.1611 ± 0.0929 | −0.370 ± 0.198 | |||
| 35 | 1.0665 ± 0.0853 | −0.165 ± 0.205 | |||
| Single CIP | 15 | 20.8865 ± 1.0443 | −7.281 ± 0.120 | 43.462 | 177.2 |
| 25 | 55.0970 ± 2.7549 | −9.938 ± 0.124 | |||
| 35 | 68.4252 ± 3.4213 | −10.826 ± 0.128 | |||
| Binary TC | 15 | 0.8700 ± 0.0870 | 0.334 ± 0.240 | 8.769 | 45.5 |
| 25 | 0.7598 ± 0.0760 | 0.681 ± 0.248 | |||
| 35 | 0.8475 ± 0.0848 | 0.424 ± 0.256 | |||
| Binary CIP | 15 | 13.7001 ± 0.4110 | −6.270 ± 0.072 | 4.342 | 20.6 |
| 25 | 15.3870 ± 0.4616 | −6.776 ± 0.074 | |||
| 35 | 13.5764 ± 0.4073 | −6.682 ± 0.077 |
| System | Kinetics | Parameter | SC-2000-TC | SC-400-TC | SC-2000-CIP | SC-400-CIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | qe experimental (mg·g−1) | 257.0453 ± 10.72 | 273.7004 ± 9.04 | 343.9326 ± 11.15 | 373.9326 ± 10.85 | |
| Pseudo-first order | qe (mg·g−1) | 255.9641 ± 1.08 | 262.9692 ± 10.73 | 361.6163 ± 17.68 | 388.0916 ± 14.15 | |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.0314 ± 0.003 | 0.0480 ± 0.005 | 0.0415 ± 0.004 | 0.0573 ± 0.006 | ||
| R2 | 0.8334 | 0.9483 | 0.9327 | 0.9130 | ||
| Pseudo-second order | qe (mg·g−1) | 305.1926 ± 48.14 | 297.4490 ± 23.74 | 413.3961 ± 69.46 | 432.6443 ± 58.71 | |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.000113 | 0.000218 | 0.000128 | 0.000187 | ||
| R2 | 0.7663 | 0.9461 | 0.8217 | 0.7725 | ||
| Intraparticle diffusion | ka (mgg−1min−0.5) | 123.2359 ± 12.32 | 72.8009 ± 7.28 | 74.5345 ± 7.45 | 104.6058 ± 10.46 | |
| Ra2 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9870 | 0.9970 | ||
| kb (mgg−1min−0.5) | 37.7781 ± 3.77 | 13.4903 ± 1.34 | 0.0601 ± 0.01 | 1.1654 ± 0.11 | ||
| Rb2 | 0.8756 | 0.9838 | 0.7666 | 0.8176 | ||
| kc (mgg−1min−0.5) | 2.5993 ± 0.25 | 2.5347 ± 0.25 | ||||
| Rc2 | 0.9372 | 0.9828 | ||||
| Binary | qe experimental (mg·g−1) | 239.1359 ± 7.47 | 273.7004 ± 13.11 | 350.2247 ± 14.16 | 376.6292 ± 10.37 | |
| Pseudo-first order | qe (mg·g−1) | 255.9641 ± 16.82 | 262.9692 ± 10.73 | 361.6163 ± 11.39 | 390.4361 ± 13.80 | |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.0314 ± 0.003 | 0.0480 ± 0.004 | 0.0415 ± 0.004 | 0.0693 ± 0.006 | ||
| R2 | 0.7663 | 0.9461 | 0.8217 | 0.7725 | ||
| Pseudo-second order | qe (mg·g−1) | 305.1926 ± 66.05 | 297.4490 ± 23.74 | 413.3961 ± 63.17 | 432.6443 ± 56.01 | |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.000113 | 0.000218 | 0.000128 | 0.000187 | ||
| R2 | 0.80958 | 0.94088 | 0.92309 | 0.74625 | ||
| Intraparticle diffusion | ka (mgg−1min−0.5) | 59.2387 ± 5.92 | 93.8703 ± 9.38 | 127.2468 ± 12.72 | 200.8108 ± 20.08 | |
| Ra2 | 0.9186 | 0.7540 | 0.9965 | 1.0000 | ||
| kb (mgg−1min−0.5) | 17.6819 ± 1.76 | 68.3053 ± 6.83 | −0.1538 ± −0.01 | 1.3127 ± 0.13 | ||
| Rb2 | 0.8179 | 0.7792 | 0.7792 | 0.7434 | ||
| kc (mgg−1min−0.5) | −0.1598 ± 0.015 | −1.1353 ± 0.11 | ||||
| Rc2 | 0.5686 | 0.9432 | ||||
| Systems | Isotherms | Parameters | SC-2000-TC | SC-400-TC | SC-2000-CIP | SC-400-CIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | Langmuir | qm (mg·g−1) | 200.3854 ± 10.0193 | 289.6927 ± 8.6908 | 399.4930 ± 19.9727 | 436.0794 ± 21.8040 |
| KL (L·g−1) | 0.0286 ± 0.0014 | 0.9821 ± 0.0295 | 0.8957 ± 0.0448 | 0.8569 ± 0.0429 | ||
| R2 | 0.8835 | 0.9378 | 0.8605 | 0.8517 | ||
| Freundlich | KF (mg1−N·LN·g−1) | 21.3941 ± 0.2139 | 40.5521 ± 0.4055 | 206.5262 ± 10.3263 | 207.8708 ± 10.3935 | |
| n | −0.4609 ± 0.0046 | −0.3839 ± 0.0038 | −0.1531 ± 0.0077 | −0.1697 ± 0.0085 | ||
| R2 | 0.9851 | 0.9801 | 0.8826 | 0.8435 | ||
| Temkin | b (J·mol−1) | 0.2678 ± 0.0134 | 0.1654 ± 0.0050 | 81.6424 ± 4.0821 | 12.1640 ±0.6082 | |
| (L·g−1) | 55.2808 ± 2.7640 | 88.3751 ± 2.513 | 45.7654 ± 2.2883 | 66.8990 ± 3.3450 | ||
| R2 | 0.8437 | 0.9035 | 0.8924 | 0.8740 | ||
| Binary | Langmuir | qm (mg·g−1) | 241.2161 ± 12.0608 | 289.6927 ± 8.6908 | 350.0511 ± 17.5026 | 436.0769 ± 21.8039 |
| KL (L·g−1) | 0.0256 ± 0.0013 | 0.0180 ± 0.0005 | 1.0318 ± 0.0516 | 0.1545 ± 0.0077 | ||
| R2 | 0.8472 | 0.9378 | 0.8495 | 0.8552 | ||
| Freundlich | KF (mg1−N·LN·g−1) | 20.7733 ± 1.0387 | 14.1002 ± 0.7050 | 179.5854 ± 5.3875 | 207.8769 ± 10.3939 | |
| n | −0.5047 ± 1.0387 | −0.6093 ± 0.0305 | −0.1810 ± 0.0054 | −0.1697 ± 0.0085 | ||
| R2 | 0.8349 | 0.8608 | 0.9184 | 0.8435 | ||
| Temkin | b (J·mol−1) | 0.2154 ± 0.0065 | 0.1579 ± 0.0047 | 215.5266 ±6.4658 | 23.4658 ± 1.1733 | |
| (L·g−1) | 70.3573 ± 2.1107 | 84.5191 ± 2.5356 | 38.7629 ± 1.1629 | 58.5195 ± 2.9260 | ||
| R2 | 0.9156 | 0.9057 | 0.9414 | 0.8718 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Z.; Li, X.; Yan, G.; Chen, X.; Sajab, M.S.; Ding, G.; Wan Jusoh, W.N.L. Sodium Alginate/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Microbeads for Antibiotic Adsorption in Single and Binary Systems. Gels 2025, 11, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080646
Qian Z, Li X, Yan G, Chen X, Sajab MS, Ding G, Wan Jusoh WNL. Sodium Alginate/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Microbeads for Antibiotic Adsorption in Single and Binary Systems. Gels. 2025; 11(8):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080646
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Zhisong, Xinpeng Li, Gege Yan, Xiaoyong Chen, Mohd Shaiful Sajab, Gongtao Ding, and Wan Nazihah Liyana Wan Jusoh. 2025. "Sodium Alginate/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Microbeads for Antibiotic Adsorption in Single and Binary Systems" Gels 11, no. 8: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080646
APA StyleQian, Z., Li, X., Yan, G., Chen, X., Sajab, M. S., Ding, G., & Wan Jusoh, W. N. L. (2025). Sodium Alginate/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Microbeads for Antibiotic Adsorption in Single and Binary Systems. Gels, 11(8), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080646








