Preparation of a Nanomaterial–Polymer Dynamic Cross-Linked Gel Composite and Its Application in Drilling Fluids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Hybrid Nanoparticle SiO2@KH550 and P(AM-AAC)
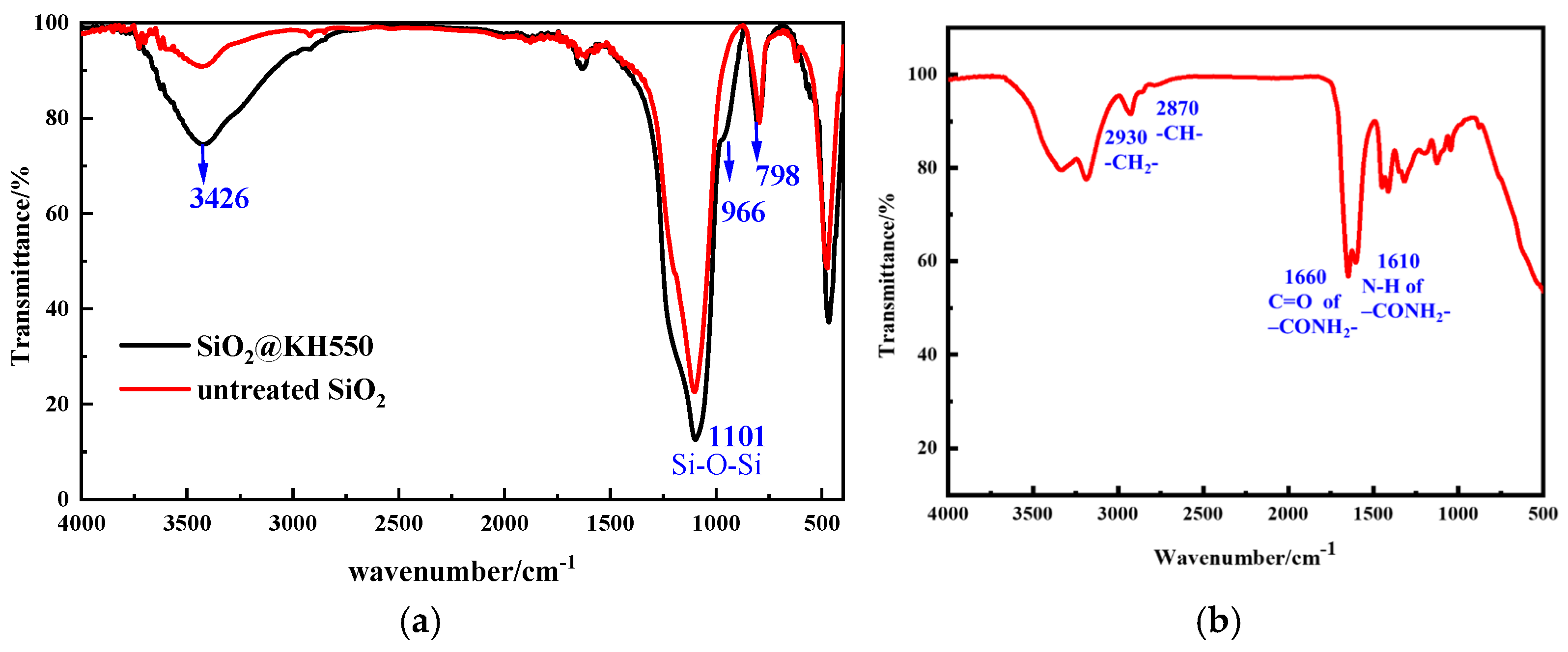
2.1.1. FTIR Spectra
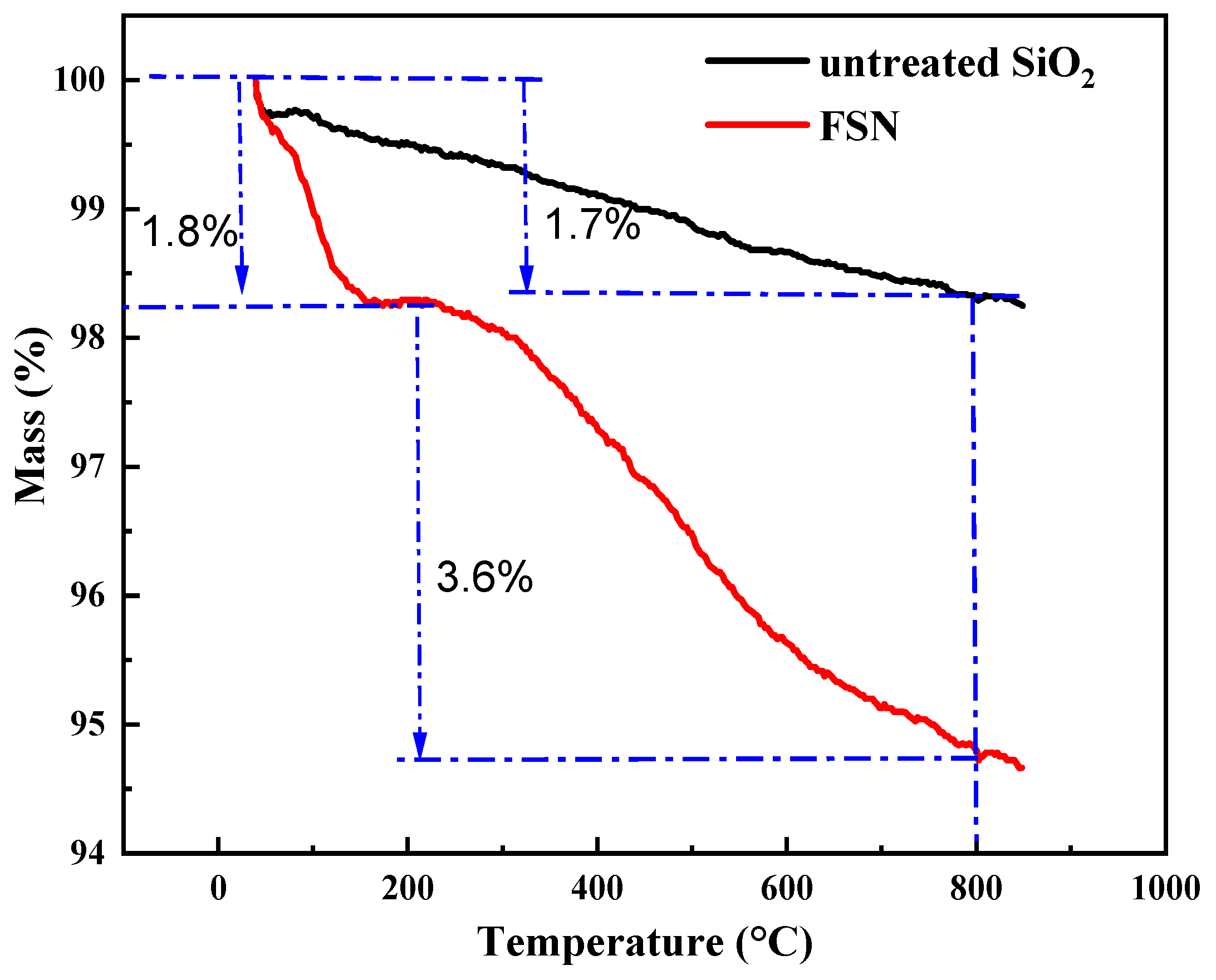
2.1.2. TGA
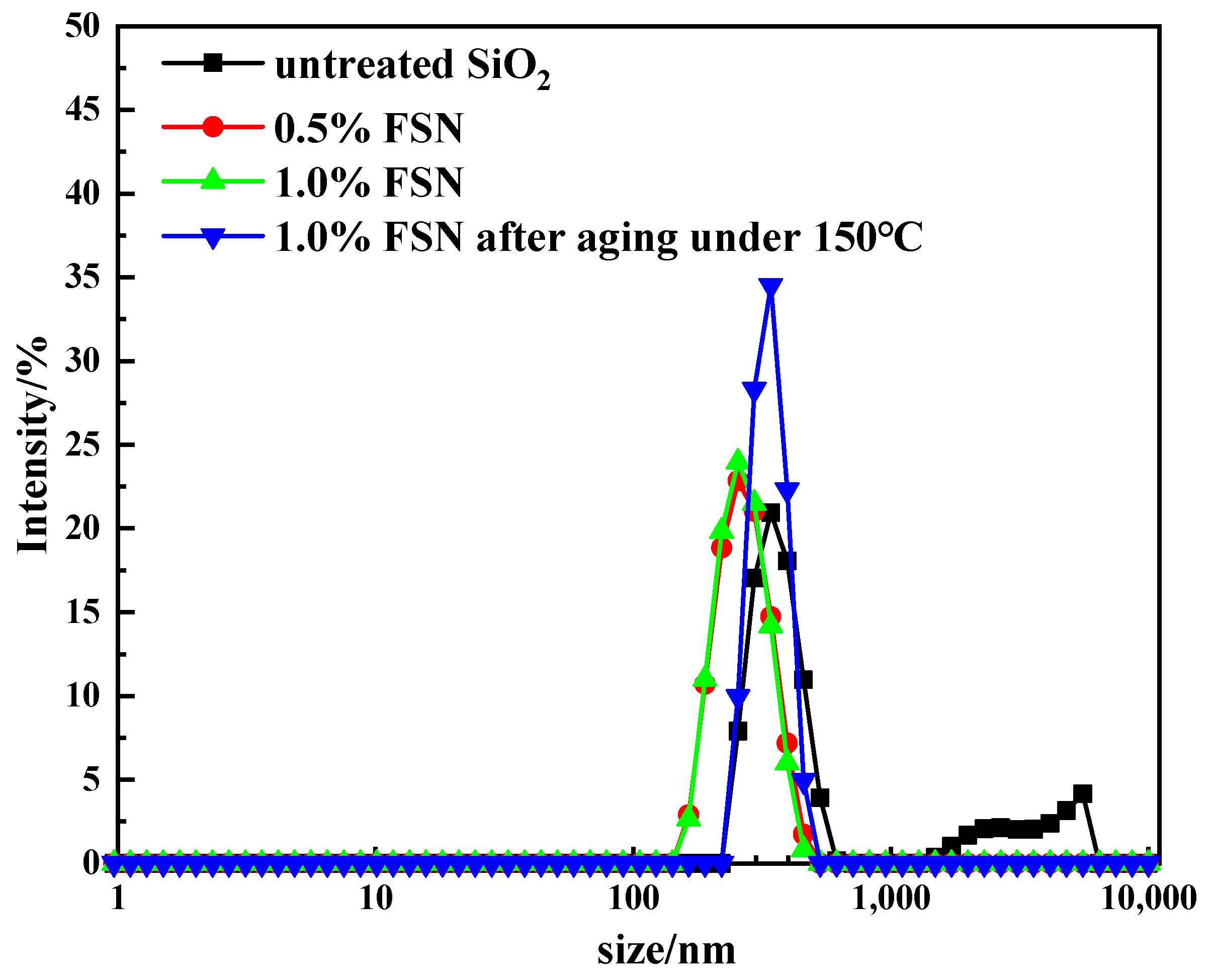
2.1.3. Particle Dispersibility
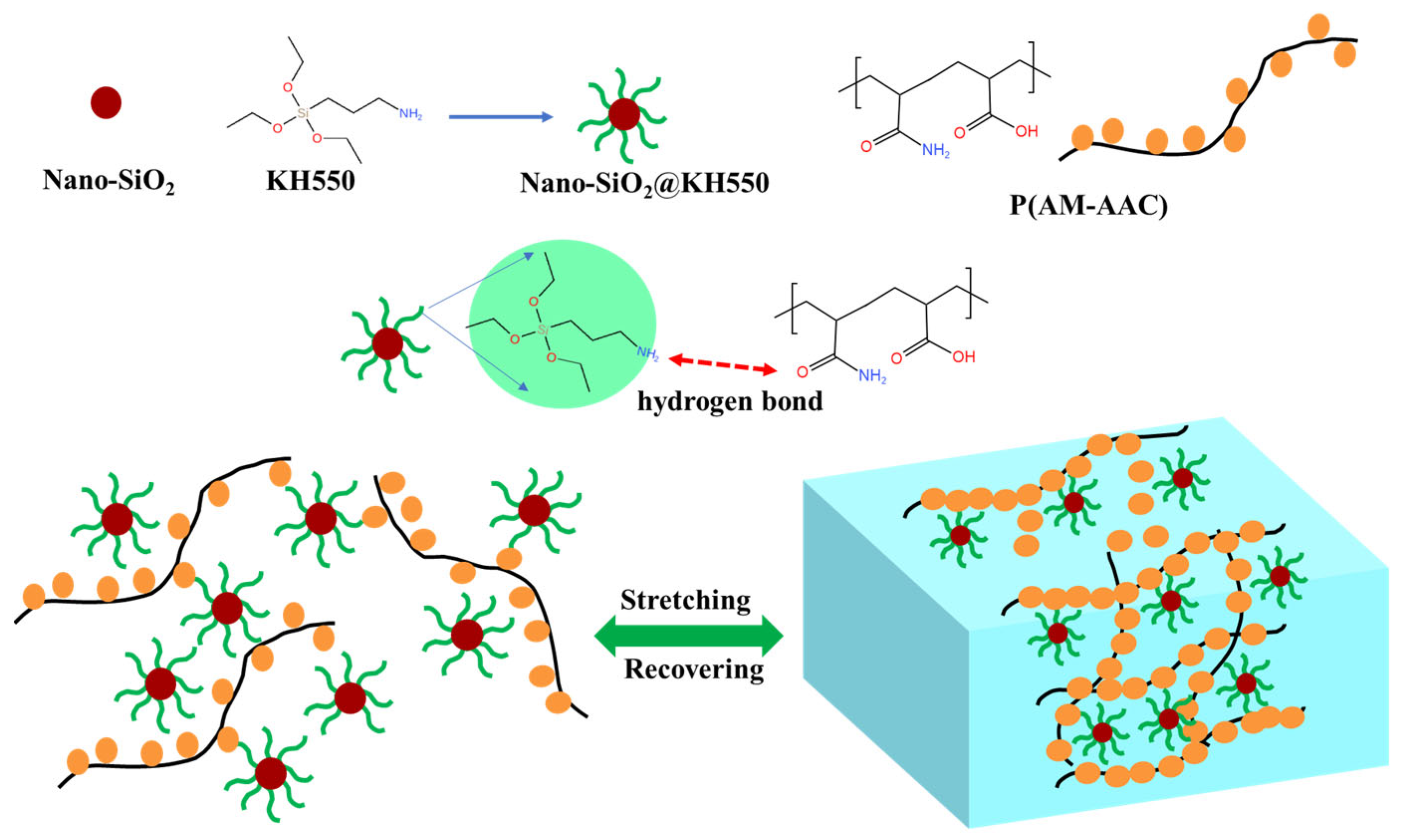
2.1.4. Preparation of the Dynamic Cross-Linked P(AM-AAC)/SiO2@KH550 Nanocomposite Gel
2.2. Plugging Performance Evaluation
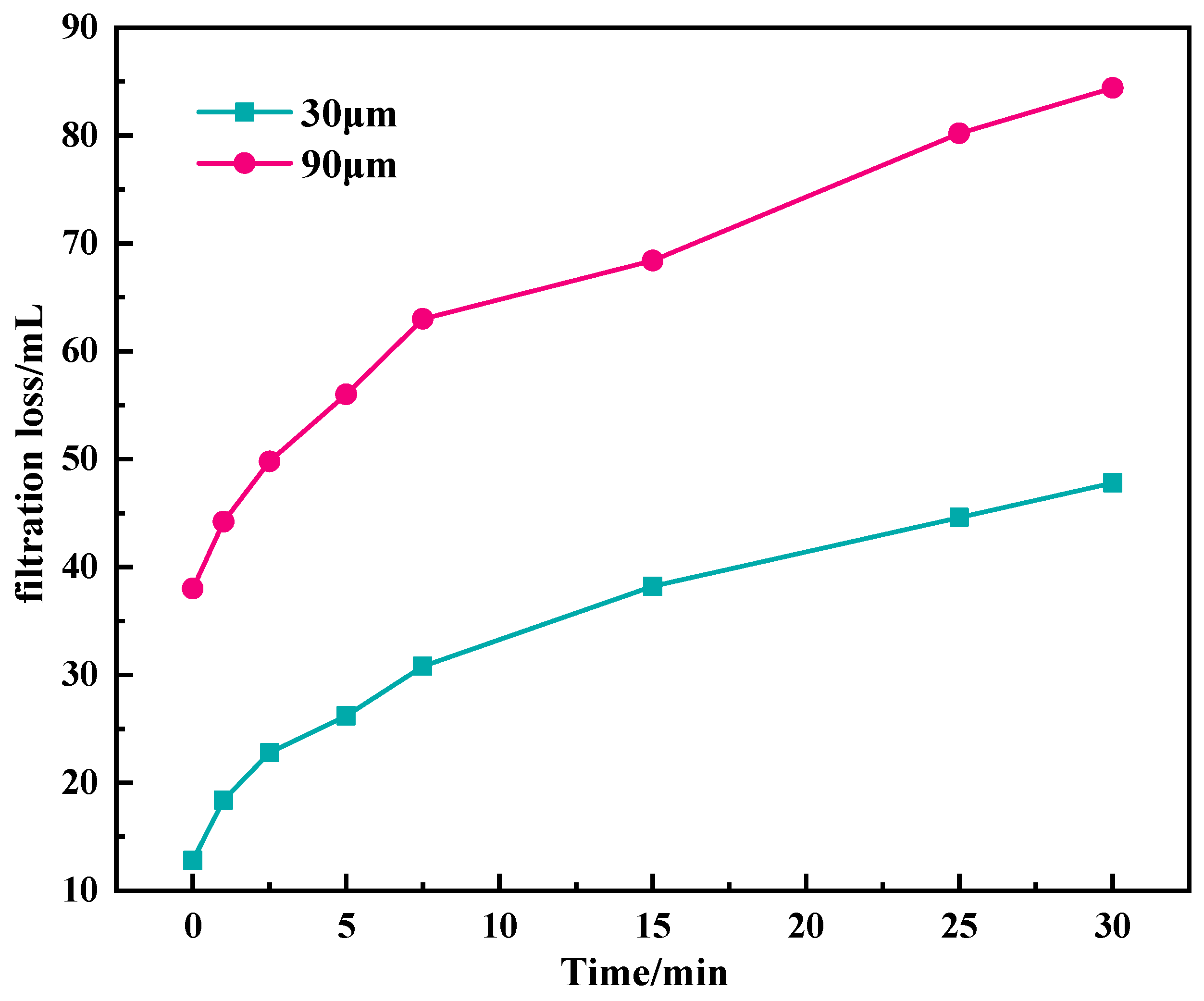
2.2.1. Penetration Plugging Apparatus
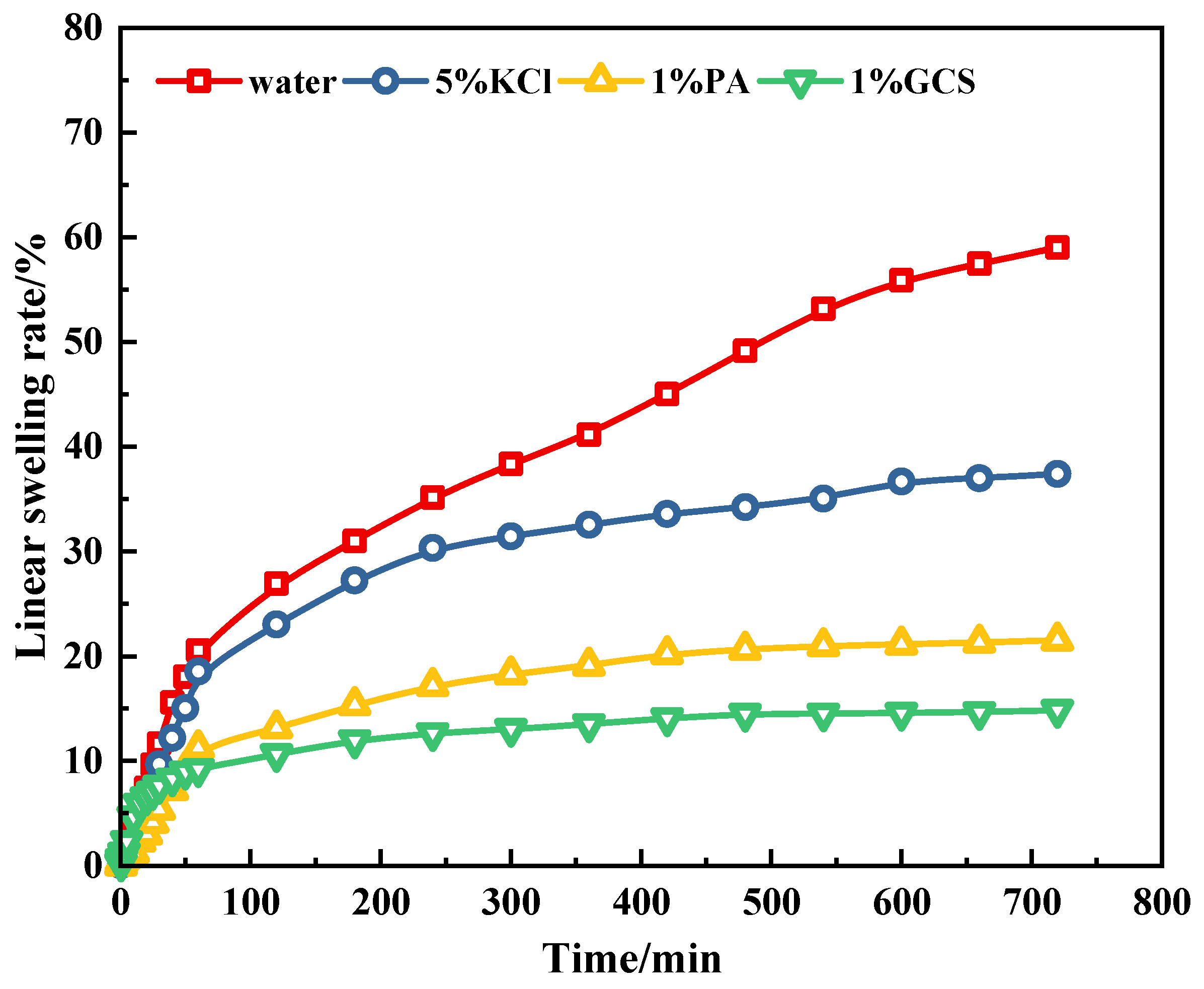
2.2.2. Linear Expansion Experiment
2.2.3. The Shale Rolling Recovery Test
2.3. Effect of GCS on Drilling Fluid Properties
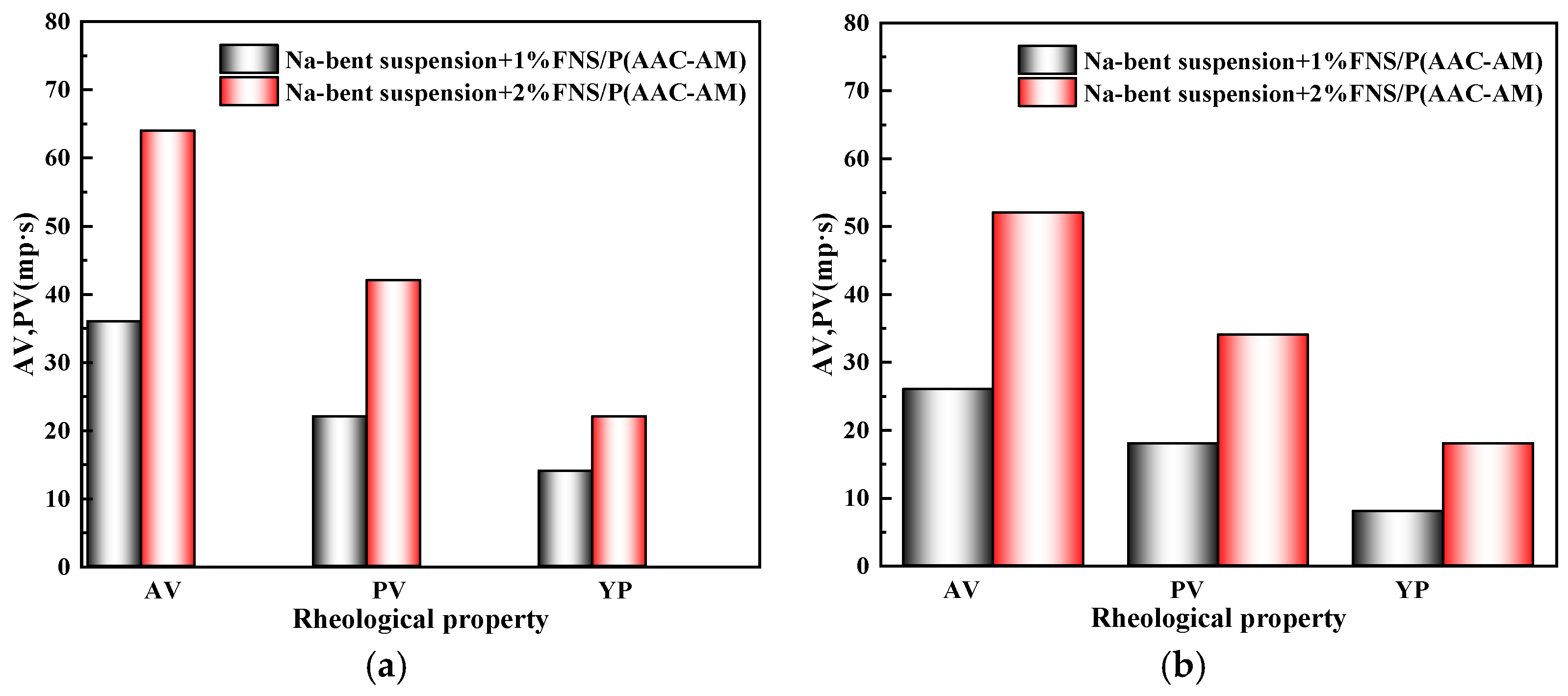
2.3.1. Effect of GCS on Rheological Properties of Drilling Fluid
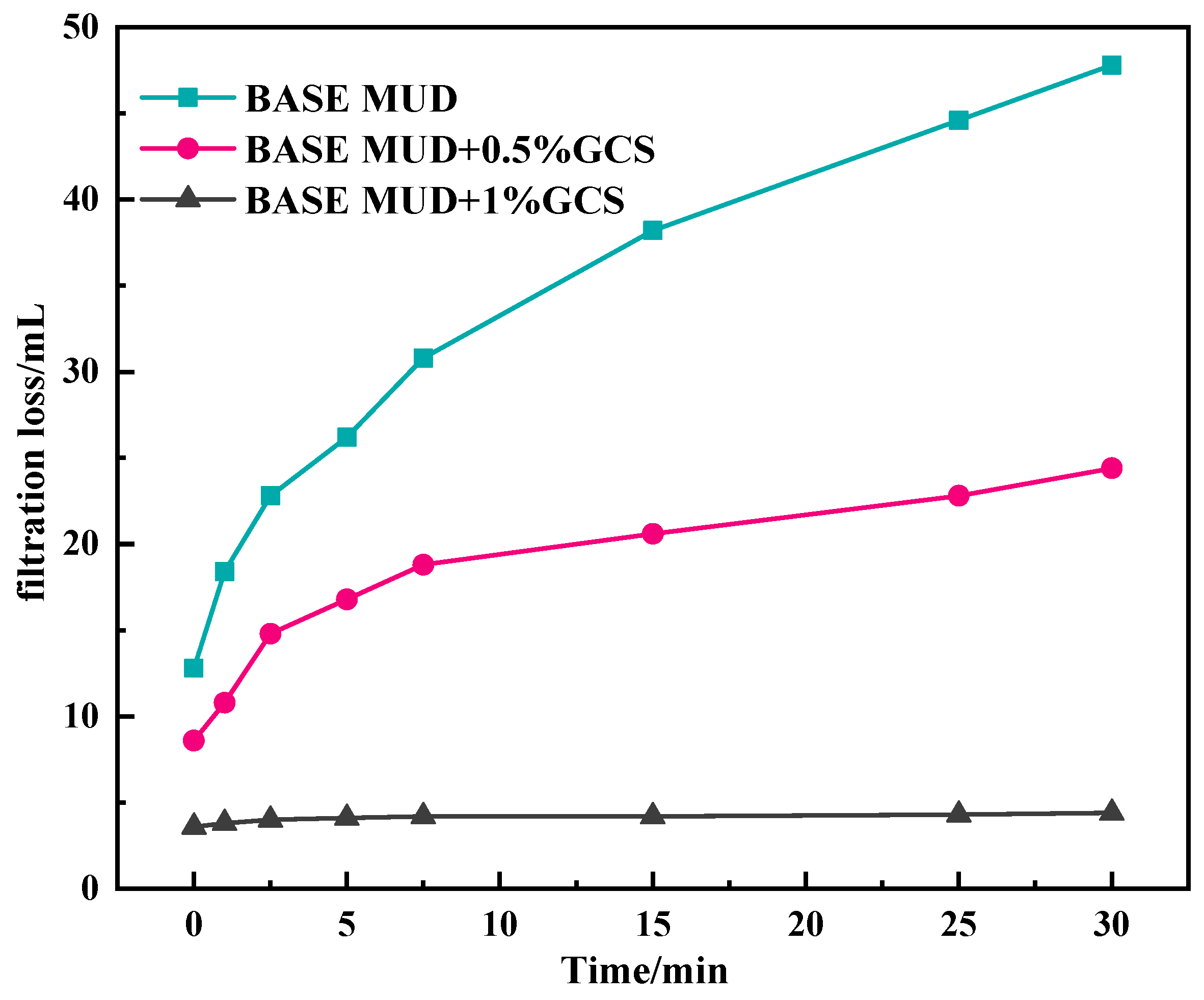
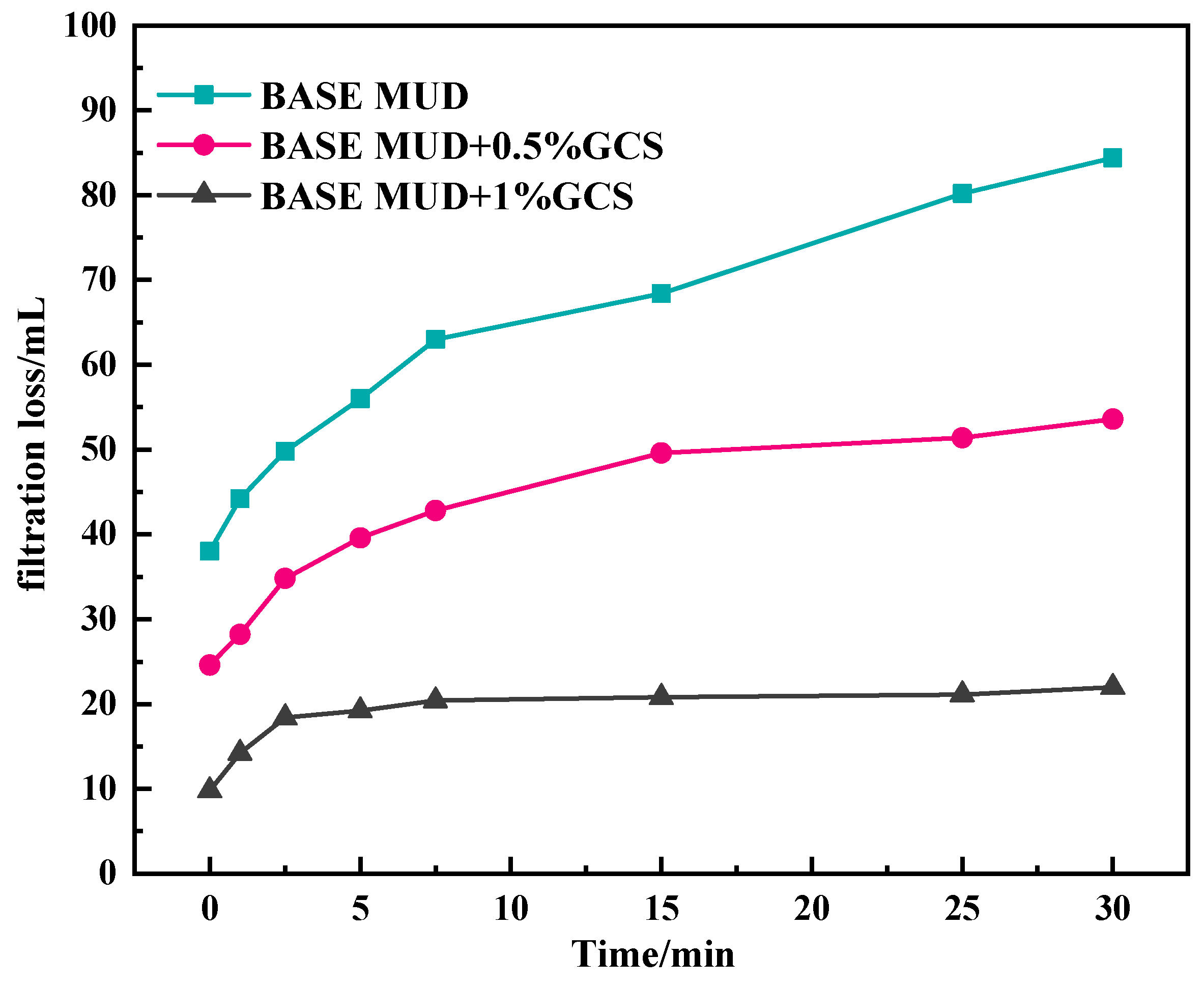
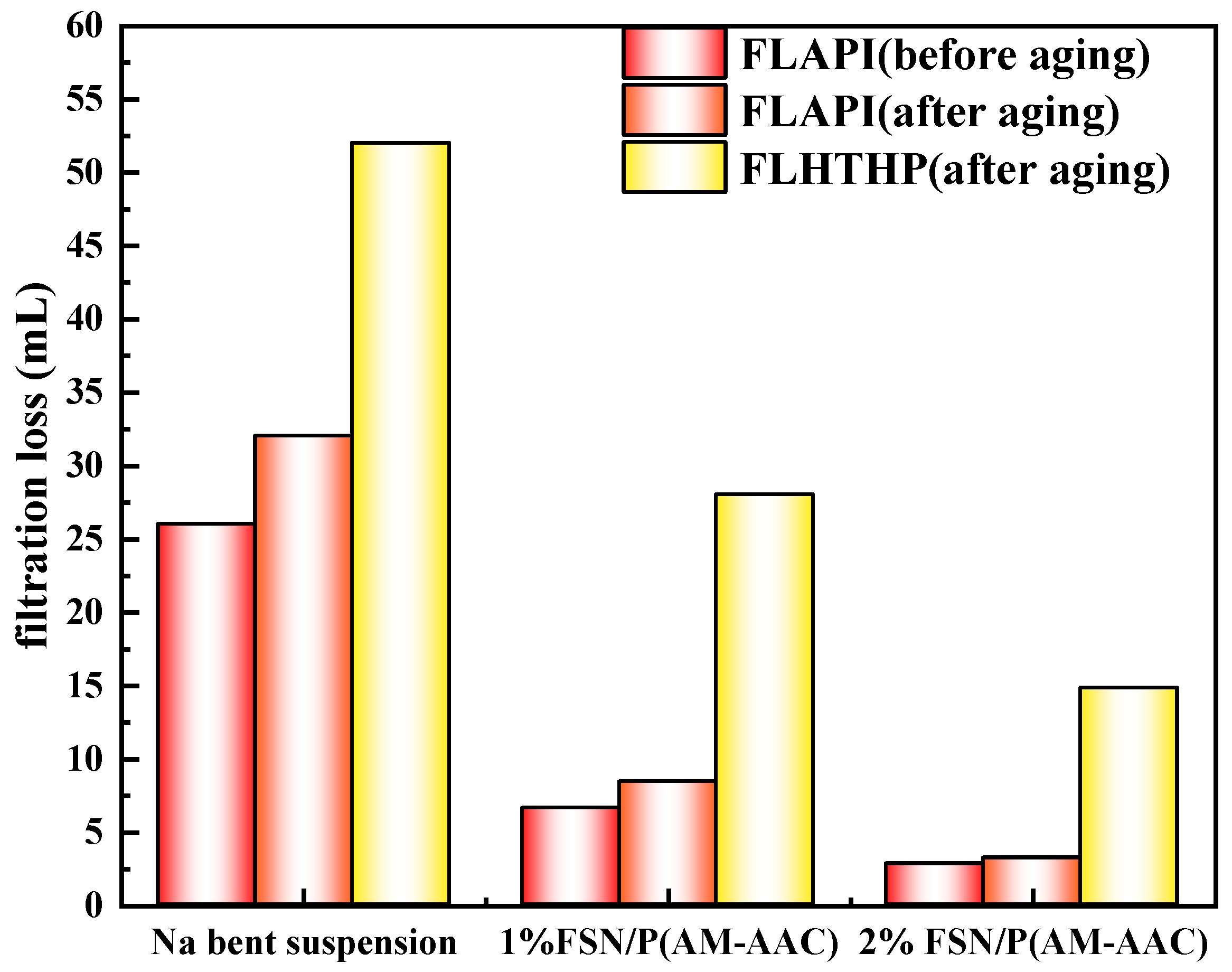
2.3.2. The Influence of GCS on Filtration Performance of Na-Bent Base Fluid
2.4. Mechanism of FSN/P(AM-AAC)
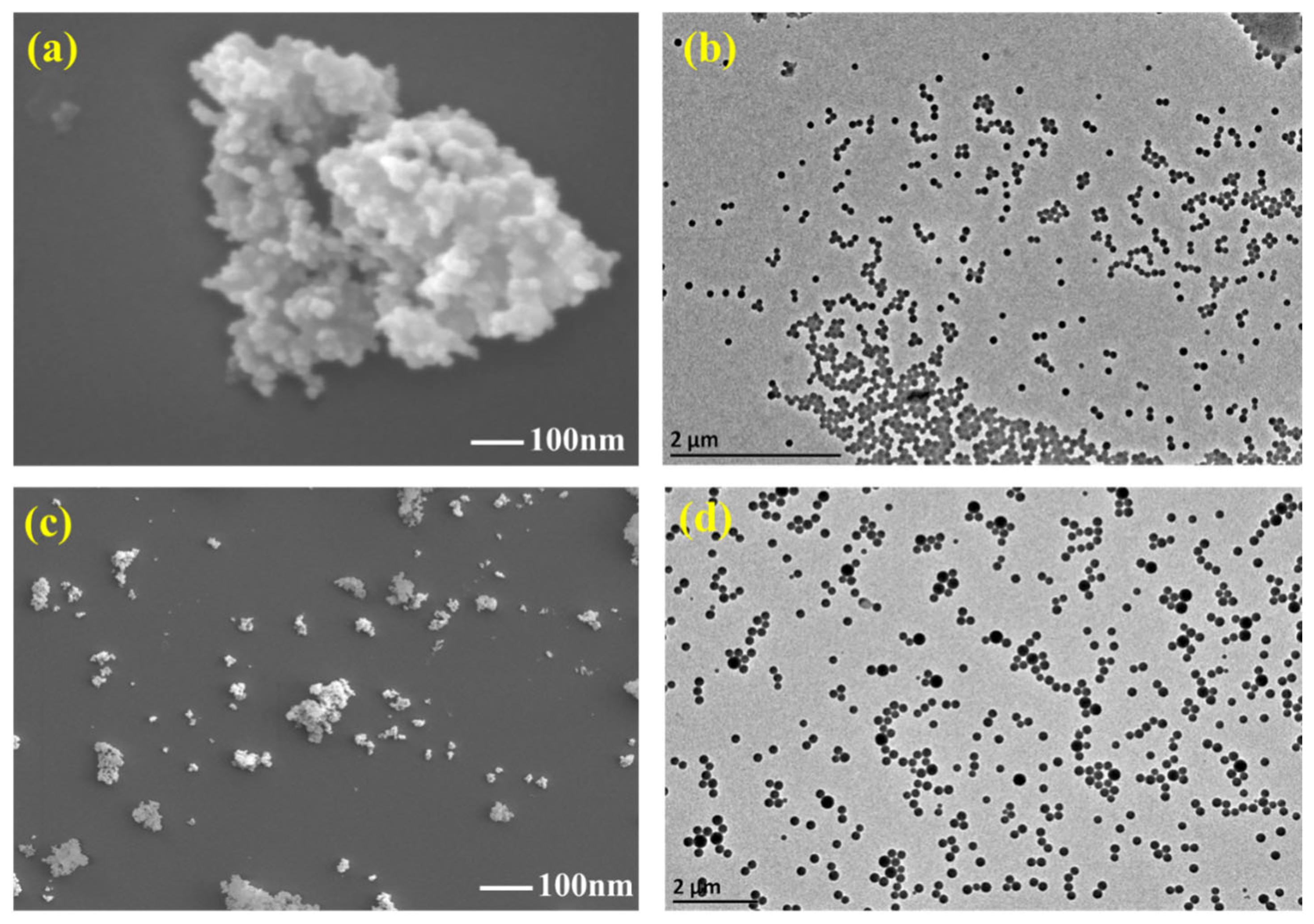
2.4.1. Micromorphology Analysis
2.4.2. Contact Angle
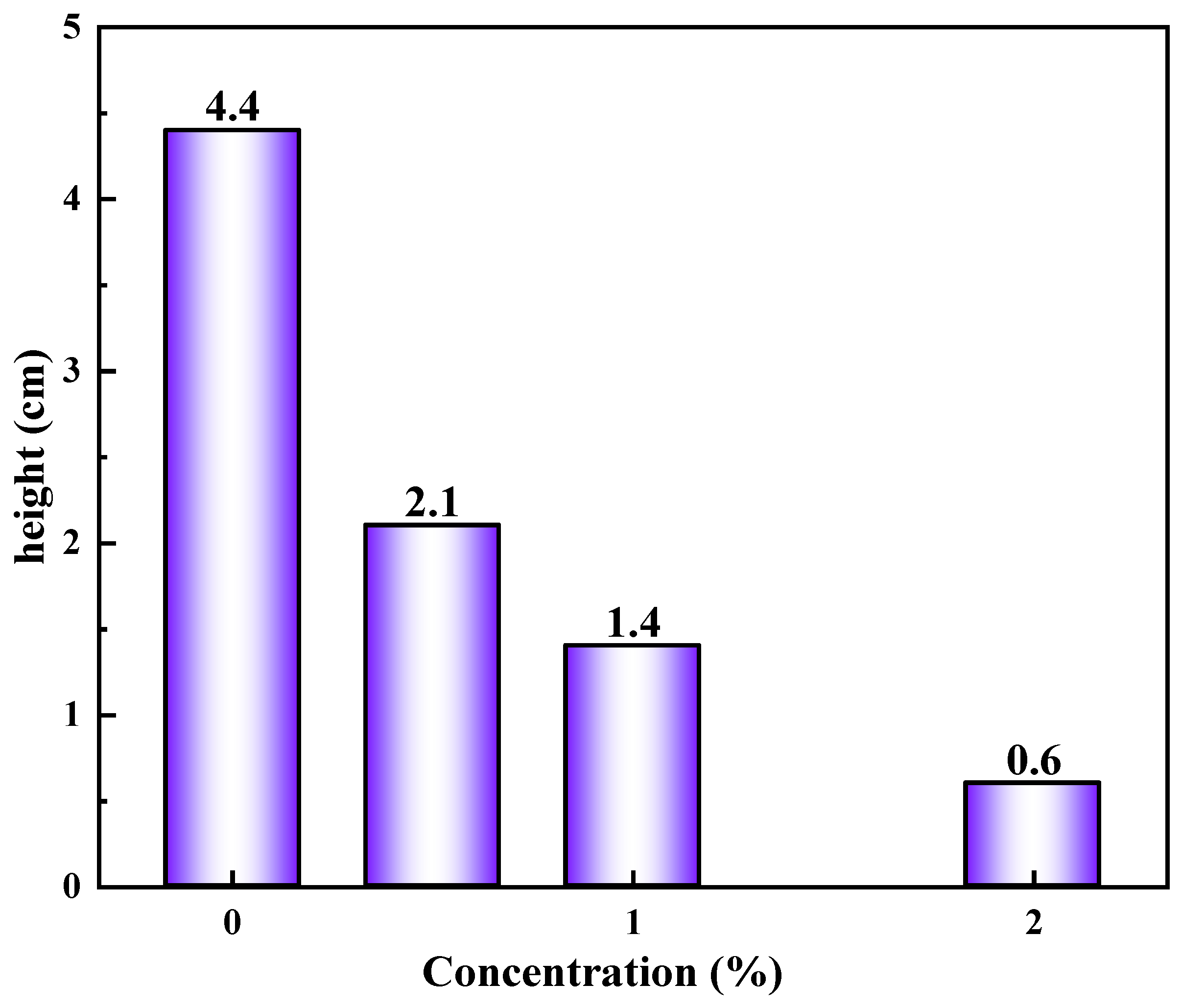
2.4.3. The Capillary Force Test
2.4.4. Mechanism Analysis
- (1)
- Physical blocking effect of nanoparticles
- (2)
- Reducing capillary force
- (3)
- Forming dynamic weak gel structure
3. Conclusions
- (1)
- Hydration inhibition: 1% GCS reduces linear expansion to 14.8% (vs. KCl: 38.2%; polyamine: 25.7%) and increases cuttings recovery to 96.7% (vs. KCl: 72%; polyamine: 85%)—exceeding API standards for recoverable shale integrity (>90%) 27.
- (2)
- Rheology-filtration balance: The gel network elevates drilling fluid viscosity (YP: 22 Pa at 2% dosage) while reducing API filtrate loss by 52% through dual pathways:
- (3)
- Thermal endurance: After aging (150 °C/16 h) YP retention ≥ 82% validates field applicability in deep reservoirs.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of GCS
4.3. Structural Characterizations of GCS
- (1)
- FT-IR
- (2)
- Thermogravimetric analyze
- (3)
- Particle size
- (4)
- Microscopic morphology observation
4.4. Method of Evaluation
4.4.1. Linear Expansion Experiment
4.4.2. The Shale Rolling Recovery Test
4.4.3. Penetration Plugging Apparatus
4.4.4. Compatibility Experiments
- (1)
- Rheological Property Evaluation: Utilize a 6-speed rotational viscometer to measure the apparent viscosity, plastic viscosity, and yield point of each drilling fluid sample at different shear rates and temperatures. This step is crucial for understanding how FSN affects the fluid’s ability to suspend cuttings and maintain stability during drilling.
- (2)
- Filtration Loss Evaluation: Use a standard API filtration cell to measure the filtrate loss of each drilling fluid sample under 0.7 MPa. Filtrate loss is a critical parameter for assessing the ability of the drilling fluid to form an effective filter cake and minimize fluid invasion into the formation.
4.5. Mechanism Analysis
4.5.1. SEM
4.5.2. Contact Angle
4.5.3. The Capillary Force Test
- ①
- Clean the capillary tube with alcohol cotton to remove grease or impurities.
- ②
- Soak the cleaned capillaries in different concentrations of FSN liquid, fully treat them for 24 h, and then dry the capillaries in the oven again to ensure that there is no residual liquid in the tube.
- ③
- Fix the capillary vertically on the support frame with clamps to ensure that the lower end is not tilted when immersed in liquid. Fill the beaker with an appropriate amount of liquid (such as pure water) and slowly insert it vertically into the capillary tube to avoid bubbles.
- ④
- Measure the height of the liquid column: after the liquid level is stable, use a scale to measure the height difference between the liquid level outside the tube and the liquid level inside the capillary. Repeat the average 3 times to reduce the error.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karakul, H. The combined effect of drilling fluid, in-situ stresses and inclination on wellbore stability. Arab. J. Geosci. 2024, 17, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Bai, Y.; Lyu, K.; Liu, F. Research progress and development of deep and ultra-deep drilling fluid technology. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, D.Y.; Zhuang, G.Z.; Li, X.L. Advanced development of chemical inhibitors in water-based drilling fluids to improve shale stability: A review. Pet. Sci. 2025, 22, 1977–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, X.; Dong, T.; Xuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Q. A new inhibitor of P(AM-DMDAAC)/PVA intermacromolecular-complex for shale in drilling fluids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Deng, Y. Synthesis of an amphoteric polymer as a high-temperature-resistant shale stabilizer in water-based drilling fluids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Xuan, Y.; Zhu, L.; An, Y. Zwitterionic polymer grafted nano-SiO2 as fluid loss agent for high temperature water-based drilling fluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 417, 126542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaoji, C.O.; Hareland, G.; Husein, M.; Nygaard, R.; Zakaria, M.F. Wellbore Strengthening-Nano-Particle Drilling Fluid Experimental Design Using Hydraulic Fracture Apparatus. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 5–7 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Yan, P.; Liu, G.; Sun, K.; Mou, Q.; Zhang, C. Nano-SiO2/hydroxyethyl cellulose nanocomposite used for 210 °C sedimentation control of petroleum drilling fluid. J. Polym. Eng. 2022, 42, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Jin, G. Study on the Effect of Cations on the Surface Energy of Nano-SiO 2 Particles for Oil/Gas Exploration and Development Based on the Density Functional Theory. Molecules 2024, 29, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Xie, R.; Zhang, J.; Pi, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, T. Rheological and thermal property of KH570-modified nano-SiO2 grafted xanthan gum and its application in drilling fluid system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 351, 123013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotnes, M.F. The Impact of Nano-Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) on Property and Performance of the CMC Polymer/Salttreated Bentonite Drilling Fluid Systems. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.H.; Sun, J.S.; Lv, K.H.; Liu, J.P.; Shen, H.K.; Zhang, F. Application of core-shell structural acrylic resin/nano-SiO2 composite in water based drilling fluid to plug shale pores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 55, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, Q.M.; Yue, Q.S. Preparation and properties of cationic polyacrylamide flocculant for drilling fluid based on modified nano SiO2. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Bao, Y.; Zhu, Z. Synthesis and Application of Polyacrylate/Nano-SiO2 Composite Leather Finishing Agent with Polymerizable Surfactant. J. Macromol. Sci. Part D—Rev. Polym. Process. 2012, 51, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ding, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, Q. Nano-SiO2-embedded poly(propylene carbonate)-based composite gel polymer electrolyte for lithium-sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. Mater. Energy Sustain. 2018, 10, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.R.; Tripathi, S.K. Structural and Morphological Studies of Nano Composite Polymer Gel Electrolyte having SiO2. Comput. Eng. Dep. VIVA Inst. Technol. 2021, 1, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Asadizadeh, S.; Ayatollahi, S.; Zarenezhad, B. Fabrication of a highly efficient new nanocomposite polymer gel for controlling the excess water production in petroleum reservoirs andincreasing the performance of enhanced oil recovery processes. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wagner, M.H.; Xu, Z. Surface Treatment Mechanism of Nano-SiO2 and the Properties of PP/Nano-SiO2 Composite Materials. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2003, 281, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Dou, R. Preparation and Mechanism of EP-HMTA-SiO 2 Nanocomposite Polymer Gel for Enhancing Oil Recovery. Processes 2025, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Dwivedi, B.K.; Kumar, Y.; Bobade, S.M. Synthesis and performance assessment of silica dispersed nano-composite polymer gel electrolyte for high-performance solid-state supercapacitors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 948, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeño Mata, M.; Orpella, A.; Dominguez-Pumar, M.; Bermejo, S. Boosting the Sensitivity and Hysteresis of a Gel Polymer Electrolyte by Embedding SiO2 Nanoparticles and PVP for Humidity Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Lin, L.; Su, J. Amidocyanogen silanol as a high-temperature-resistant shale inhibitor in water-based drilling fluid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 184, 105396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, W. Inhibiting shale hydration and dispersion with amine-terminated polyamidoamine dendrimers. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2016, 28, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Miska, S.; Yu, M.; Dokhani, V.; Ozbayoglu, E.N. Takach, Experimental and numerical analysis of effective enhancement of wellbore stability in shales with nanoparticles. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2021, 95, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Zhou, L.; Wan, X.C.; Tang, Y.F.; Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Liao, J.B. Synthesis and characterization of a temperature sensitive microcapsule gelling agent for high-temperature acid release. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 20849–20858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.O.; Schechter, D.S. Wettability Alteration and Spontaneous Imbibition in Unconventional Liquid Reservoirs by Surfactant Additives. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2017, 20, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Perfect, E.; Cheng, C.L.; Hu, X. Generalized Modeling of Spontaneous Imbibition Based on Hagen–Poiseuille Flow in Tortuous Capillaries with Variably Shaped Apertures. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5142–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kang, Y.; Luo, P.; You, L.; Tang, Y.; Kong, L. Wettability modification by fluoride and its application in aqueous phase trapping damage removal in tight sandstone reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 133, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, C.; Lan, H.; Cao, M.; Jiang, L. Improved Interfacial Floatability of Superhydrophobic/Superhydrophilic Janus Sheet Inspired by Lotus Leaf. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1701466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, C.P. Study on mono-dispersed nano-size silica by surface modification for underfill applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 292, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.A.; Hassanajili, S.; Rahimpour, M.R. Synthesis of fluorinated nano-silica and its application in wettability alteration near-wellbore region in gas condensate reservoirs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Xu, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Preparation of a Nanomaterial–Polymer Dynamic Cross-Linked Gel Composite and Its Application in Drilling Fluids. Gels 2025, 11, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080614
Gao F, Xu P, Zhang H, Wang H, Zhao X, Li X, Zhang J. Preparation of a Nanomaterial–Polymer Dynamic Cross-Linked Gel Composite and Its Application in Drilling Fluids. Gels. 2025; 11(8):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080614
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Fei, Peng Xu, Hui Zhang, Hao Wang, Xin Zhao, Xinru Li, and Jiayi Zhang. 2025. "Preparation of a Nanomaterial–Polymer Dynamic Cross-Linked Gel Composite and Its Application in Drilling Fluids" Gels 11, no. 8: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080614
APA StyleGao, F., Xu, P., Zhang, H., Wang, H., Zhao, X., Li, X., & Zhang, J. (2025). Preparation of a Nanomaterial–Polymer Dynamic Cross-Linked Gel Composite and Its Application in Drilling Fluids. Gels, 11(8), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080614





