Advances in Nanohybrid Hydrogels for Wound Healing: From Functional Mechanisms to Translational Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Hydrogels in Wound Healing
2.1. Introduction to Traditional Hydrogels
2.2. Common Materials Used in Traditional Hydrogels
2.2.1. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels
2.2.2. Synthetic Polymer-Based Hydrogels
2.3. Limitations of Traditional Hydrogels in Wound Healing
2.4. Fabrication Techniques for Hydrogel-Based Wound Dressings: From Traditional Approaches to 3D Printing
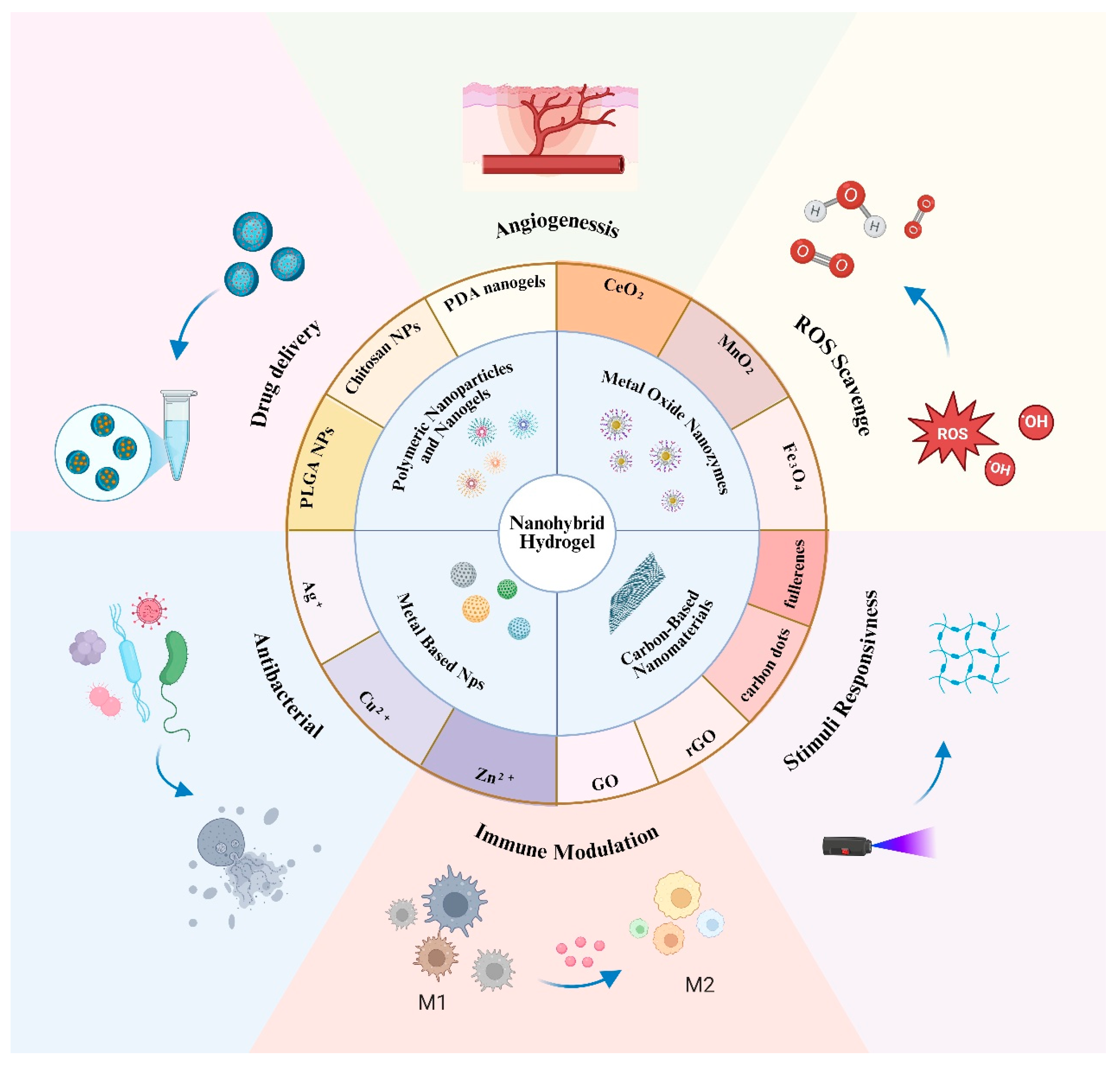
3. Emergence of Nanohybrid Hydrogels
3.1. Definition and Design Principles
3.2. Functional Advantages in Wound Healing
3.2.1. Antibacterial Activity
3.2.2. Antioxidant and ROS Scavenging
3.2.3. Angiogenesis Promotion
3.2.4. Immune Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
3.2.5. Stimuli-Responsive Behavior
3.3. Representative Nanomaterials in Nanohybrid Hydrogels
3.3.1. Metal-Based Nanoparticles
3.3.2. Metal Oxide Nanozymes
3.3.3. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials
3.3.4. Polymeric Nanoparticles and Nanogels
3.3.5. Emerging Hybrid Nanostructures
3.4. Summary of Representative Nanomaterials
4. Research Prospects
4.1. Rational Material Design and Standardization
4.2. Bioactivity-Biocompatibility Trade-Offs
4.3. Smart, Responsive, and Feedback-Controlled Systems
4.4. Clinical Translation and Regulatory Pathways
4.5. Interdisciplinary Integration and Emerging Technologies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.; Young, A.; McNaught, C.-E. The physiology of wound healing. Surgery 2017, 35, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; DiPietro, L.A. Factors Affecting Wound Healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falanga, V.; Isseroff, R.R.; Soulika, A.M.; Romanelli, M.; Margolis, D.; Kapp, S.; Granick, M.; Harding, K. Chronic wounds. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Shankar, R.; Yadav, A.K.; Pratap, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Srivastava, V. Burden of Chronic Nonhealing Wounds: An Overview of the Worldwide Humanistic and Economic Burden to the Healthcare System. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2024, 0, 15347346241246339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Díaz, E.C.; Varghese, S. Hydrogels as Extracellular Matrix Analogs. Gels 2016, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chan, H.-P.; Chung, T.-W.; Shu, C.-W.; Chuang, K.-P.; Duh, T.-H.; Yang, M.-H.; Tyan, Y.-C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Wang, X.; Yong, P.W.; Young, D.J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Li, Z.; Loh, X.J. Hydrogels as Emerging Materials for Translational Biomedicine. Adv. Ther. 2019, 2, 1800088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Noruzi, S.; Kesharwani, P.; Sahebkar, A. Hydrogel-based dressing for wound healing: A systematic review of clinical trials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-X.; Young, D.J.; Li, Z.; Loh, X.J. Going Beyond Traditional Applications? The Potential of Hydrogels. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyen, M.L. Mechanical characterisation of hydrogel materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhang, J.; Lai, J.; Deng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, Z.; Zhong, C.; Feng, X.; Hu, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Prussian blue nanohybrid hydrogel combined with specific far-infrared based on graphene devices for promoting diabetic wound healing. Mater. Des. 2025, 253, 113839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Javanbakht, S.; Mohammadi, R.; Ghorbani, M. Alginate/magnetic hydroxyapatite bio-nanocomposite hydrogel bead as a pH-responsive oral drug carrier for potential colon cancer therapy. Results Chem. 2025, 15, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Y.; Pang, Q.; Du, T.; Song, B.; Zhong, J.; Hu, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, J.; et al. Nanohybrid Hydrogel with Dual Functions: Controlled Low-Temperature Photothermal Antibacterial Activity and Promoted Regeneration for Treating MRSA-Infected Bone Defects. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2500092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-E.; Shamiya, Y.; Luo, W.; Paul, A. NIR-Responsive ZIF-8 Metal-Organic Framework Nanohybrids with Photothermal, Antimicrobial, and Osteoinductive Properties to Prevent Implant Infection. Macromol. Biosci. 2025, 25, 2400594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Ruan, M.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, K.; Du, S.; et al. Poly-tannic acid coated PLGA nanoparticle decorated with antimicrobial peptide for synergistic bacteria treatment and infectious wound healing promotion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Luo, M.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Lei, B. Sprayable Nanocomposites Hydrogel for Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2402549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Mei, X.; Hu, K.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y. Nanohybrid Double Network Hydrogels Based on a Platinum Nanozyme Composite for Antimicrobial and Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 17612–17626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Yacoub, M.H. Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: Progress and challenges. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2013, 2013, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyashri, G.; Badhe, R.V.; Sadanandan, B.; Vijayalakshmi, V.; Kumari, M.; Ashrit, P.; Bijukumar, D.; Mathew, M.T.; Shetty, K.; Raghu, A.V. Applications of hydrogel-based delivery systems in wound care and treatment: An up-to-date review. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 2025–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhang, S. Engineered hydrogel platform for diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhillar, A.; Jaiswal, A. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Self-Healing Hydrogels for Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2404255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovatlarnporn, C.; Basit, A. Chapter 20—Commercially available and recently approved hydrogels for clinical applications. In Natural and Synthetic Hydrogels; Narain, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 563–588. [Google Scholar]
- Pirsa, S.; Khodaei, S.M.; Sani, I.K.; Ghasemi, Y.; Jawhar, Z.H.; Eghbaljoo, H. Hydrogels and biohydrogels: Investigation of origin of production, production methods, and application. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 10593–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Leng, J.; Li, K.; Xu, K.; Lin, C.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Tao, B.; Huang, T.J.; et al. A multifunctional hydrogel coating to direct fibroblast activation and infected wound healing via simultaneously controllable photobiomodulation and photodynamic therapies. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, M.; An, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, Q.; Song, L.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Freeze-Thawing Chitosan/Ions Hydrogel Coated Gauzes Releasing Multiple Metal Ions on Demand for Improved Infected Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Two-Pronged Strategy of Biomechanically Active and Biochemically Multifunctional Hydrogel Wound Dressing To Accelerate Wound Closure and Wound Healing. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9937–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, S.; Suo, Z.; Yang, W. Functional hydrogel coatings. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 8, nwaa254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatangelo, G.; Vindigni, V.; Avruscio, G.; Pandis, L.; Brun, P. Hyaluronic Acid: Redefining Its Role. Cells 2020, 7, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Zhang, F.; Wei, Q. The role of CD44 in pathological angiogenesis. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13125–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios de la Rosa, J.M.; Tirella, A.; Tirelli, N. Receptor-Targeted Drug Delivery and the (Many) Problems We Know of: The Case of CD44 and Hyaluronic Acid. Adv. Biosyst. 2018, 2, 1800049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.; Chung, J.E.; Xu, K.; Kurisawa, M. Injectable Degradation-Resistant Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Cross-Linked via the Oxidative Coupling of Green Tea Catechin. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
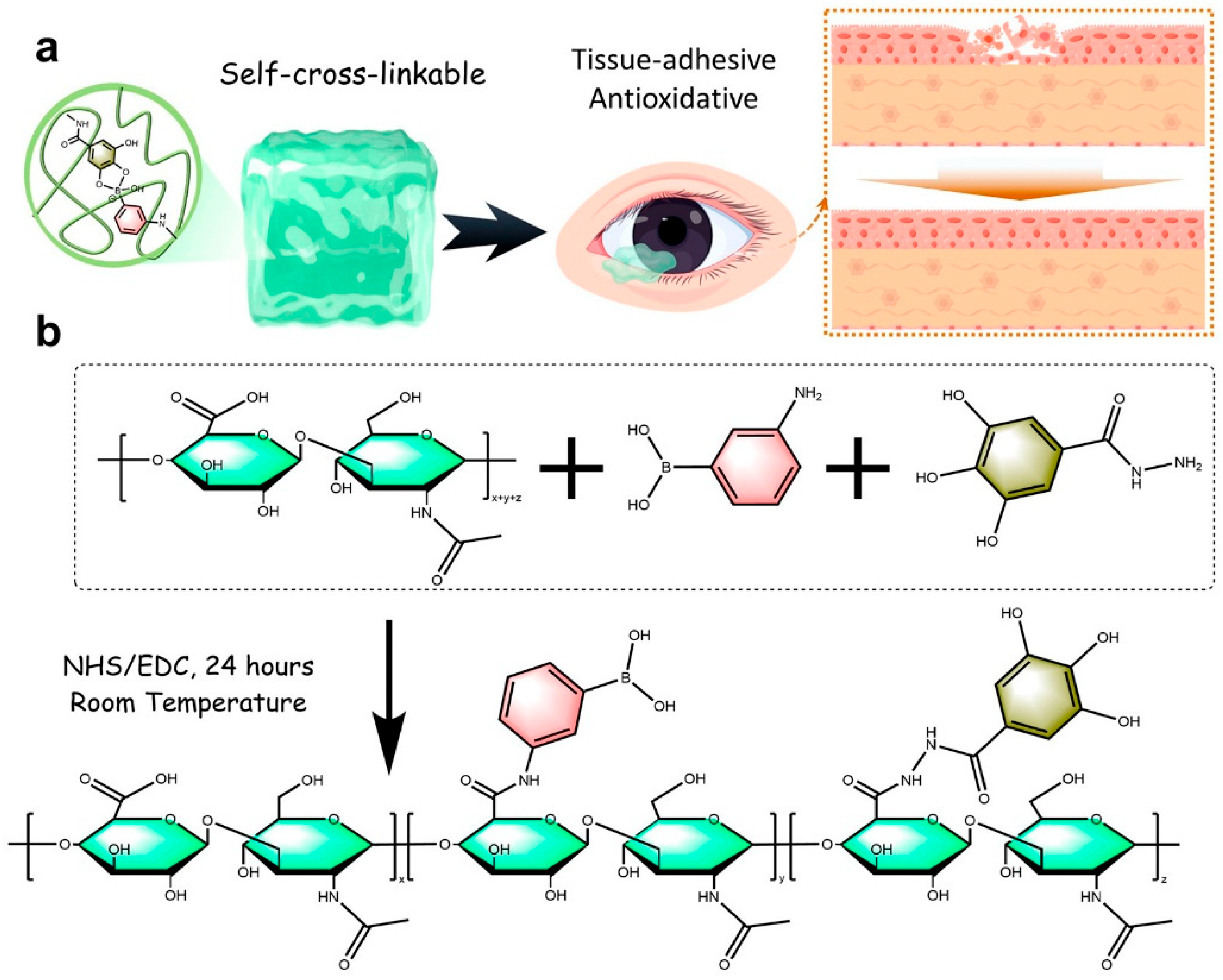
- Pan, X.-Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wu, X.-Q.; Guo, C.-R.; Yang, L.-X.; Liu, H.-R.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, W.-J.; Wang, J.-J.; Nan, K.-H.; et al. ROS scavenging and corneal epithelial wound healing by a self-crosslinked tissue-adhesive hydrogel based-on dual-functionalized hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 293, 139200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z. The chitosan hydrogels: From structure to function. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 17162–17180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Muzzarelli, C. Chitosan Chemistry: Relevance to the Biomedical Sciences. In Polysaccharides I: Structure, Characterization and Use; Heinze, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 151–209. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Guan, Y.L.; Yang, D.Z.; Li, Z.; De Yao, K. Antibacterial action of chitosan and carboxymethylated chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 79, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, H.; Mori, T.; Fujinaga, T. Topical formulations and wound healing applications of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 52, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Gou, D. Chitosan-based hydrogel wound dressing: From mechanism to applications, a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, V.; Asghari, M.; Dashti, A. A Review on Chitin and Chitosan Polymers: Structure, Chemistry, Solubility, Derivatives, and Applications. ChemBioEng Rev. 2015, 2, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, H.; Moradi, S.; Hudson, S.M.; Tonelli, A.E. Chitosan based hydrogels and their applications for drug delivery in wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosiński, K.K.; Wach, R.A.; Girek-Bąk, M.K.; Rokita, B.; Kołat, D.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Kłosińska, B.; Duda, Ł.; Pasieka, Z.W. Biocompatibility and Mechanical Properties of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels. Polymers 2023, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Tavakoli, E.; Motamedi, A.; Salimi, H. Facile synthesis of extremely biocompatible double-network hydrogels based on chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol) with enhanced mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
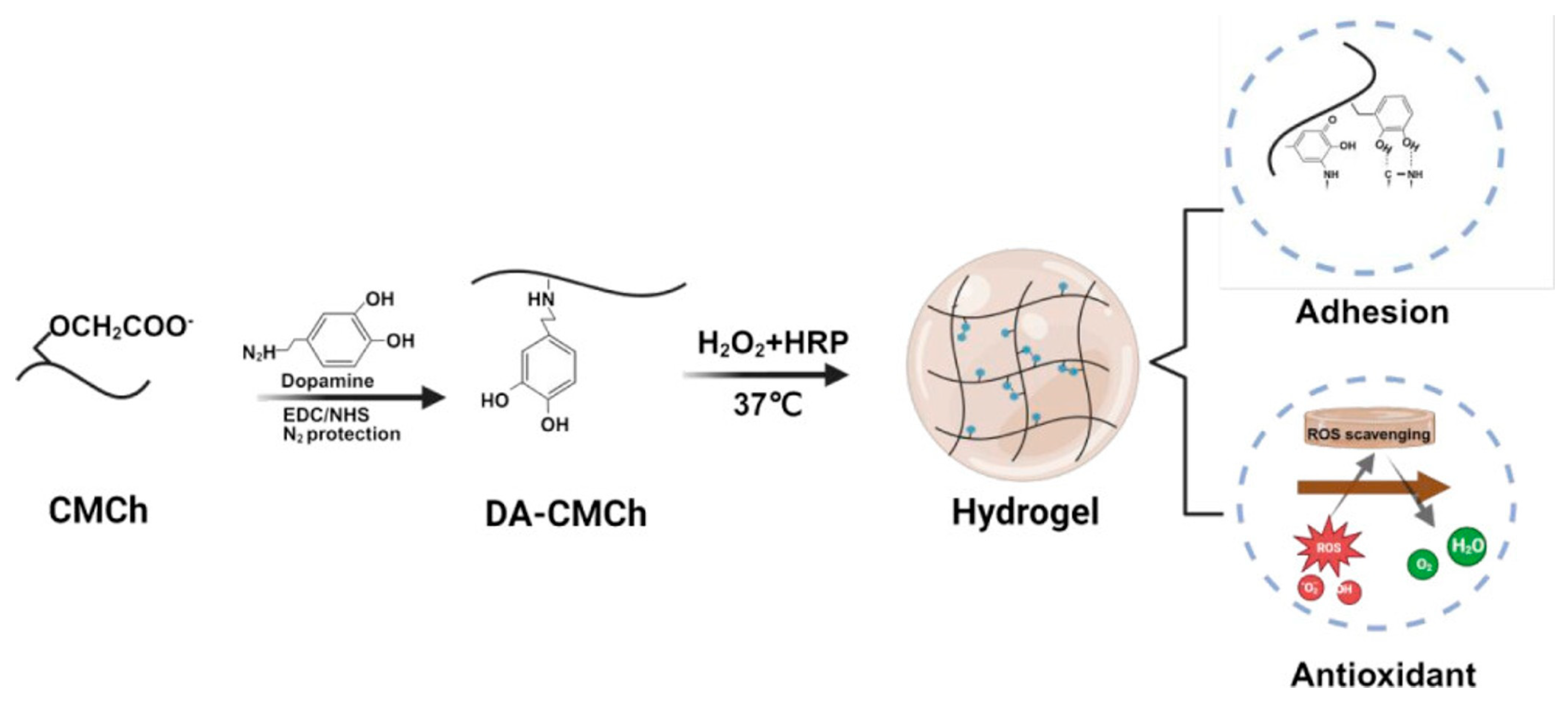
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Situ-Forming, I. Adhesive, and Antioxidant Chitosan Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules 2025, 26, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Peppas, N.A.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augst, A.D.; Kong, H.J.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate Hydrogels as Biomaterials. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cong, H.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y. A review on the synthesis and development of alginate hydrogels for wound therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 2801–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.K.; Ma, P.X. Ionically crosslinked alginate hydrogels as scaffolds for tissue engineering: Part 1. Structure, gelation rate and mechanical properties. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacesa, P. Enzymic degradation of alginates. Int. J. Biochem. 1992, 24, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
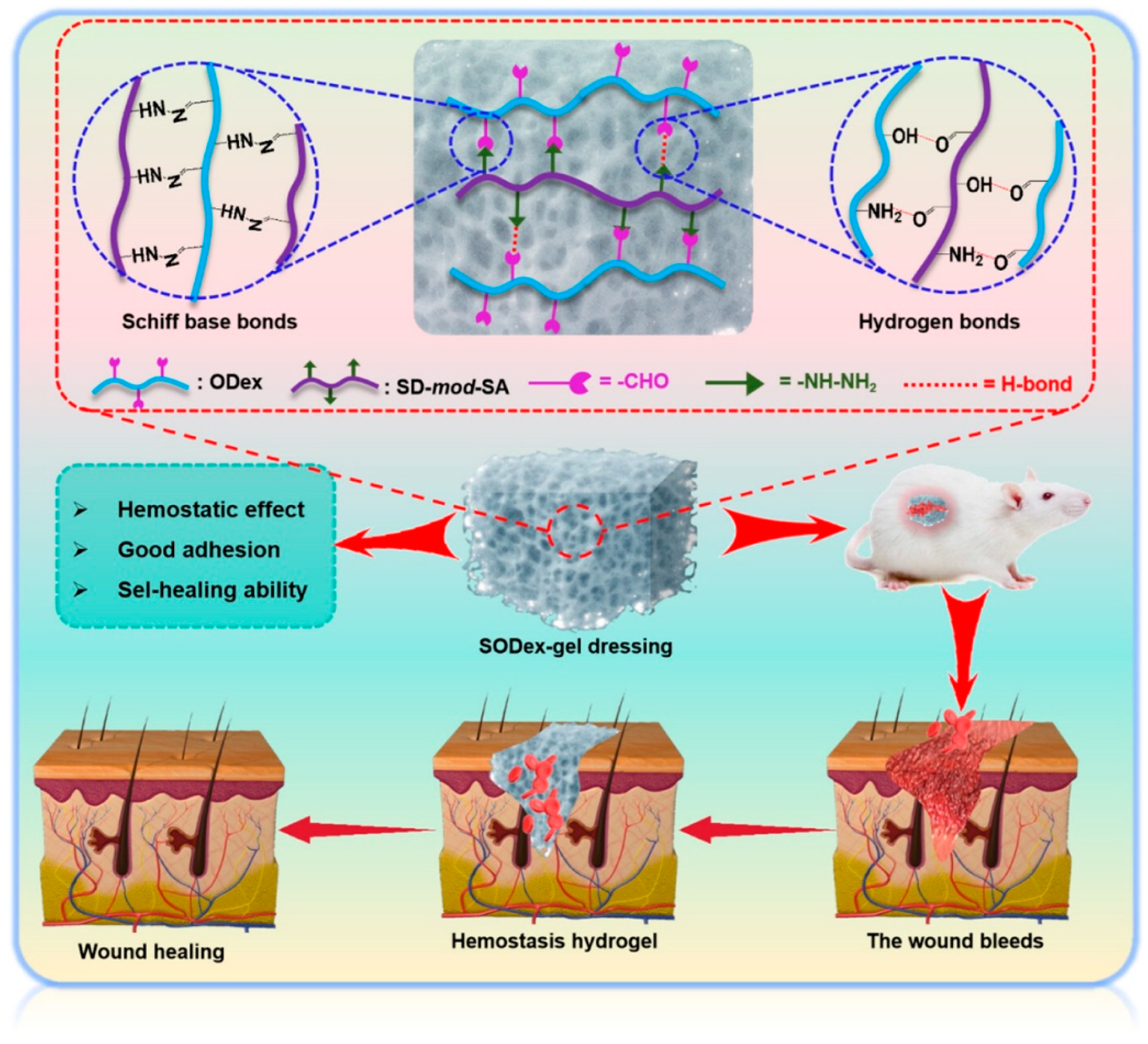
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.; Xu, T.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhuo, M.; Du, K.; Su, Y.; Han, X.; et al. Self-Healing Oxidized Dextran/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Dressing with Hemostatic Activity Speeds Up Wound Healing in Burn Injuries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 2940–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.B.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.; Park, H.; Lee, S.-H. Engineering and Functionalization of Gelatin Biomaterials: From Cell Culture to Medical Applications. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2020, 26, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, I.; Erezuma, I.; Maeso, L.; Zarate, J.; Desimone, M.F.; Al-Tel, T.H.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Orive, G. Progress in Gelatin as Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rýglová, Š.; Braun, M.; Suchý, T. Collagen and Its Modifications—Crucial Aspects with Concern to Its Processing and Analysis. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Werb, Z. How Matrix Metalloproteinases Regulate Cell Behavior. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 463–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathima, N.N.; Madhan, B.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U.; Ramasami, T. Interaction of aldehydes with collagen: Effect on thermal, enzymatic and conformational stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2004, 34, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Cai, B.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Natural blackcurrant extract contained gelatin hydrogel with photothermal and antioxidant properties for infected burn wound healing. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 26, 101113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnica-Palafox, I.M.; Sánchez-Arévalo, F.M. Influence of natural and synthetic crosslinking reagents on the structural and mechanical properties of chitosan-based hybrid hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Hernández, G.; Antunes-Ricardo, M.; Martínez-Morales, P.; Sánchez, M.L. Polyvinyl alcohol based-drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G. Production and Application of Biomaterials Based on Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as Wound Dressing. Chem. —Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, X.; Luo, X.; Wei, P.; Jing, W.; Zhao, B.; Su, J. A Constant Filgotinib Delivery Adhesive Platform Based on Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Hydrogel for Accelerating Wound Healing via Restoring Macrophage Mitochondrial Homeostasis. Small 2025, 21, 2408791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, C.; Zhong, X.; Shu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Yu, S.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, S.; Wang, P. Platelet-rich plasma polyacrylamide (PAM-PRP)-based hydrogel for wound healing via low-intensity ultrasound. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 18599–18618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Feng, W. PVA hydrogel properties for biomedical application. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradossi, G.; Cavalieri, F.; Chiessi, E.; Spagnoli, C.; Cowman, M.K. Poly(vinyl alcohol) as versatile biomaterial for potential biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhong, H.-J.; Ding, H.; Yu, B.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Chong, C.-M.; He, J. Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)-Based Hydrogels: Recent Progress in Fabrication, Properties, and Multifunctional Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács, T.; Abdelghafour, M.M.; Lamch, Ł.; Szenti, I.; Sebők, D.; Janovák, L.; Kukovecz, Á. Facile modification of hydroxyl group containing macromolecules provides autonomously self-healing polymers through the formation of dynamic Schiff base linkages. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 168, 111086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Wu, N.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Yan, C.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Y.; Sun, H. Phytic acid-loaded polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel promotes wound healing of injured corneal epithelium through inhibiting ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2024, 76, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’souza, A.A.; Shegokar, R. Polyethylene glycol (PEG): A versatile polymer for pharmaceutical applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1257–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-M.; Cheng, T.-L.; Roffler, S.R.; Immunogenicity, P.G. Clinical, and Practical Aspects of Anti-Polyethylene Glycol Antibodies. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14022–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Wei, G.; Su, Z. Recent Advances in Peptide Engineering of PEG Hydrogels: Strategies, Functional Regulation, and Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2200385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hove, A.H.; Burke, K.; Antonienko, E.; Brown, E.; Benoit, D.S.W. Enzymatically-responsive pro-angiogenic peptide-releasing poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels promote vascularization in vivo. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, C.; Kong, Q.; Luo, R.; Wang, Y. Peptide-/Drug-Directed Self-Assembly of Hybrid Polyurethane Hydrogels for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37147–37155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, M.R.; Turner, J.N.; Szarowski, D.; Martin, D.L. Biological functionalization and surface micropatterning of polyacrylamide hydrogels. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5883–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonyadi, S.Z.; Atten, M.; Dunn, A.C. Self-regenerating compliance and lubrication of polyacrylamide hydrogels. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 8728–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.A.; Murff, R.L.; Milam, V.T. Tailoring the mechanical properties of polyacrylamide-based hydrogels. Polymer 2010, 51, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olăreț, E.; Voicu, Ș.I.; Oprea, R.; Miculescu, F.; Butac, L.; Stancu, I.-C.; Serafim, A. Nanostructured Polyacrylamide Hydrogels with Improved Mechanical Properties and Antimicrobial Behavior. Polymers 2022, 14, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, X.; Gao, G.; Lou, J.; Wang, X.; Han, W. Double-network hydrogel dressing regulated by cationic polymer-grafted bacterial cellulose for promote rapid healing of infected wounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 353, 123257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Fortunata, V. Hydrogel Dressings in Wound Management: Advances, Applications, and Future Directions. Int. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res. Stud. 2023, 3, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, E. Challenges for Natural Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering. Gels 2019, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Clegg, J.R.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Hydrogels in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2020, 5, e10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F.; Harrison, I.D. The variation of mechanical properties in different areas of a healing wound. J. Biomech. 1977, 10, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gong, J.P. Fabrication of Bioinspired Hydrogels: Challenges and Opportunities. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S. Natural Polymers vs Synthetic Polymer. In Natural Polymer Drug Delivery Systems: Nanoparticles, Plants, and Algae; Bhatia, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 95–118. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Han, Z.-Y.; Yuan, Y.; Shao, Y.; Feng, X.-Q.; Weitz, D.A. Regulation of cell attachment, spreading, and migration by hydrogel substrates with independently tunable mesh size. Acta Biomater. 2022, 141, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyburz, K.A.; Anseth, K.S. Three-dimensional hMSC motility within peptide-functionalized PEG-based hydrogels of varying adhesivity and crosslinking density. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6381–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Abdeen, A.A.; Zhang, D.; Kilian, K.A. Directing stem cell fate on hydrogel substrates by controlling cell geometry, matrix mechanics and adhesion ligand composition. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8140–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borbolla-Jiménez, F.V.; Peña-Corona, S.I.; Farah, S.J.; Jiménez-Valdés, M.T.; Pineda-Pérez, E.; Romero-Montero, A.; Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; Bernal-Chávez, S.A.; Magaña, J.J.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Films for Wound Healing Fabricated Using a Solvent Casting Technique. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelnia, H.; Ensandoost, R.; Moonshi, S.S.; Gavgani, J.N.; Vasafi, E.I.; Ta, H.T. Freeze/thawed polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels: Present, past and future. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 164, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Pianella, L.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Ottonelli, M.; Castellano, M. Alginate-based hydrogels prepared via ionic gelation: An experimental design approach to predict the crosslinking degree. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Chopra, H.; Singh, I.; Emran, T.B. Physically and chemically crosslinked hydrogels for wound healing applications. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 106, 106915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.S.; Jung, H.D.; Pan, H.M.; Han, W.T.; Chen, S.; Song, J. 3D printing of hydrogel composite systems: Recent advances in technology for tissue engineering. Int. J. Bioprint 2018, 4, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, H.N.; Wu, B.M. Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials. J. Biol. Eng. 2015, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remaggi, G.; Bergamonti, L.; Graiff, C.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; Elviri, L. Rapid Prototyping of 3D-Printed AgNPs- and Nano-TiO2-Embedded Hydrogels as Novel Devices with Multiresponsive Antimicrobial Capability in Wound Healing. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafili, G.; Tamjid, E.; Niknejad, H.; Simchi, A. Development of printable nanoengineered composite hydrogels based on human amniotic membrane for wound healing application. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 12351–12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahroudi, S.; Parvinnasab, A.; Salahinejad, E.; Abdi, S.; Rajabi, S.; Tayebi, L. Efficacy of 3D-printed chitosan-cerium oxide dressings coated with vancomycin-loaded alginate for chronic wounds management. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 349, 123036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.; Li, X.; He, S.; Xu, D.; Yin, L.; Huang, X.; Deng, S.; Yue, W.; Zhong, W. Instant Self-Assembly Peptide Hydrogel Encapsulation with Fibrous Alginate by Microfluidics for Infected Wound Healing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 5001–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, K. Chapter 11—Fabrication of hydrogel micropatterns by soft photolithography. In Emerging Nanotechnologies for Manufacturing, 2nd ed.; Ahmed, W., Jackson, M.J., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Goudarzi, Z.M.; Zaszczyńska, A.; Kowalczyk, T.; Sajkiewicz, P. Electrospun Antimicrobial Drug Delivery Systems and Hydrogels Used for Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Yin, W.; Ni, L.; Wang, M. Photothermal nanohybrid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1066617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.D.; Mura, C.; Lampe, K.J. Stimuli-Responsive, Pentapeptide, Nanofiber Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4886–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, G.; Carrow, J.K.; Thakur, T.; Xavier, J.R.; Parani, M.; Bayless, K.J.; Gaharwar, A.K. Nanoengineered injectable hydrogels for wound healing application. Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, K.; Saleha, S.; Zhu, X.; Huo, L.; Basit, A.; Franco, O.L. Bacterial Contribution in Chronicity of Wounds. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Nakagami, G.; Kitamura, A.; Minematsu, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Suga, H.; Kurita, M.; Hayashi, C.; Kawasaki, A.; Sanada, H. Effectiveness of biofilm-based wound care system on wound healing in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Tang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, D.; Wang, S.; Tan, Q.; Maitz, J.; Maitz, P.K.; et al. Challenges and innovations in treating chronic and acute wound infections: From basic science to clinical practice. Burn. Trauma 2022, 10, 1066617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Release Strategies of Silver Ions from Materials for Bacterial Killing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3985–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linklater, D.P.; Baulin, V.A.; Le Guével, X.; Fleury, J.-B.; Hanssen, E.; Nguyen, T.H.P.; Juodkazis, S.; Bryant, G.; Crawford, R.J.; Stoodley, P.; et al. Antibacterial Action of Nanoparticles by Lethal Stretching of Bacterial Cell Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2005679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammari, N.; Lamouroux, E.; Boudier, A.; Duval, R.E. Current Knowledge on the Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Antimicrobial Properties of Metal-Based Nanoparticles. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.N.; Aldowairy, N.N.A.; Alorfi, H.S.S.; Aslam, M.; Bawazir, W.A.; Hameed, A.; Soomro, M.T.; Antimicrobial, E. Antioxidant, and Catalytic Activities of Medicinal Plant Aqueous Leaf Extract Derived Silver Nanoparticles. Processes 2022, 10, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Peng, Z.; Chen, X. Nanocomposite hydrogel with multiple metal ions coupling for effective treatment of bacteria infected wound via cascade catalysis and tissue regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 511, 161783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnill, C.; Patton, T.; Brennan, J.; Barrett, J.; Dryden, M.; Cooke, J.; Leaper, D.; Georgopoulos, N.T. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and wound healing: The functional role of ROS and emerging ROS-modulating technologies for augmentation of the healing process. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Shi, F.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, F.; Sun, M.-H.; Sun, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Zhao, R.-Z.; et al. M1 macrophage mediated increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) influence wound healing via the MAPK signaling in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 366, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.C.; Johnson, M.E.; Walker, M.L.; Riley, K.R.; Sims, C.M. Antioxidant Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Jia, L.; Zhang, X.; Ge, D.; Shi, W.; Sun, Y. Polydopamine-Based Nanocomposite as a Biomimetic Antioxidant with a Variety of Enzymatic Activities for Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 32901–32913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, I.; Anwar, A.; Imran, M.; Alvi, Z.I. Prospecting Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Harnessing Multienzyme-Like Activities. Top. Catal. 2024, 68, 823–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Yang, F.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Xia, D.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional Hydrogel with Photothermal ROS Scavenging and Antibacterial Activity Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2402236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnesen, M.G.; Feng, X.; Clark, R.A.F. Angiogenesis in Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2000, 5, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonkwo, U.A.; DiPietro, L.A. Diabetes and Wound Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ming, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, P.; Cai, R.; Yu, K.; et al. Biocompatible gellan gum/sericin hydrogels containing halloysite@polydopamine nanotubes with hemostasis and photothermal antibacterial properties for promoting infectious wound repair. Mater. Des. 2023, 227, 111744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Xu, P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, J.; Jin, F.; Li, Q.; You, J.; et al. Inflammation-Responsive Hydrogel Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing through Immunoregulation and Enhanced Angiogenesis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2400150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Barbul, A. Understanding the role of immune regulation in wound healing. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 187 (Suppl. S1), S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.S.; Mansbridge, J.N. The Innate Immune System in Acute and Chronic Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, M.; Tu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, H. Multifunctional hydrogel dressing promotes wound healing by reprogramming the infection-related wound microenvironment. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 16660–16677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Yao, N.; Wen, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Shen, C. A nanoenzyme-modified hydrogel targets macrophage reprogramming-angiogenesis crosstalk to boost diabetic wound repair. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, G.; Liang, X.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.-J. Hybrid Hydrogel with Photothermal Stimulation Elicits Immunomodulation-Mediated Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2419170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.; Xu, P.; Jing, X.; Cong, H.; Hu, H.; Yu, B.; Xu, F.-J. An NIR-responsive hydrogel loaded with polydeoxyribonucleotide nano-vectors for enhanced chronic wound healing. Biomaterials 2025, 314, 122789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yan, Z.; Ji, S.; Xiao, S.; Gao, J. Metal nanoparticle hybrid hydrogels: The state-of-the-art of combining hard and soft materials to promote wound healing. Theranostics 2024, 14, 1534–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hileuskaya, K.; Kraskouski, A.; Ihnatsyeu-Kachan, A.; Saichuk, A.; Pinchuk, S.; Nikalaichuk, V.; Ladutska, A.; Kulikouskaya, V.; Neves, M.C.; Freire, M.G.; et al. New insights into chitosan-Ag nanocomposites synthesis: Physicochemical aspects of formation, structure-bioactivity relationship and mechanism of antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 300, 140077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ya, J.; Sun, M.; Du, X.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Inhibition of the cGAS–STING pathway via an endogenous copper ion-responsive covalent organic framework nanozyme for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 7215–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; An, R.; Qian, Y. Magnetical scafford with ROS-scavenging for bone regeneration under static magnetic field. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, D.; Su, Z.; Guo, J.; Cui, L.; Su, H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B. Zinc-induced photocrosslinked konjac glucomannan/glycyrrhizic acid hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in diabetic mice through immune regulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, T.; Zhang, P.; Jing, X. Preparation and antibacterial effects of PVA-PVP hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, H.; Yan, L.; Yin, W.; Gu, Z. A Copper Peroxide Fenton Nanoagent-Hydrogel as an In Situ pH-Responsive Wound Dressing for Effectively Trapping and Eliminating Bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, A.Y.; Ganesana, M.; Trentini, J.F.; Olson, J.E.; Li, G.; Boateng, Y.O.; Lipps, J.M.; Yablonski, S.E.R.; Donnelly, W.T.; Leiter, J.C.; et al. Antioxidant Enzyme-Mimetic Activity and Neuroprotective Effects of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Stabilized with Various Ratios of Citric Acid and EDTA. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, M.S.; Berret, J.F.; Singh, S.; Vinu, A.; Karakoti, A.S. Redox Active Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Current Status and Burning Issues. Small 2021, 17, 2102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Shan, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Qian, H.; Cheng, L.; Chen, X.-L.; Wang, X. Bimetallic oxide Cu–Fe3O4 nanoclusters with multiple enzymatic activities for wound infection treatment and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2024, 173, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Lv, R.; Du, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, R.; Qi, Y. Multienzymatic Antioxidant Activity of Manganese-Based Nanoparticles for Protection against Oxidative Cell Damage. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; He, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, L.; Ji, X.; Yang, R.; Xie, J. Multifunctional Bioactive Nanozyme Systems for Enhanced Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2401580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z. MnO2@CeOx-GAMP radiosensitizer with oxygen vacancies depended mimicking enzyme-like activities for radiosensitization-mediated STING pathway activation. Biomaterials 2025, 314, 122797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yan, C.; Ma, R.; Dai, L.; Shu, W.; Asghar, A.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, X.; Yu, S. E-PL/MnO2 nanozymes/gellan gum/hyaluronic acid-based multifunctional hydrogel to promote diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, D.F. Graphene-Based Nanomaterials for Photothermal Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.K.F.D.; Júnior, A.A.M.P.; Filho, A.L.N.; Fonseca, C.J.N.; Isidorio, D.K.M.; Araújo, F.D.A.; Oliveira, P.H.A.; Júnior, V.F.D.V. Graphene and Natural Products: A Review of Antioxidant Properties in Graphene Oxide Reduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenzi, P.; Stagi, L. Carbon dots as oxidant-antioxidant nanomaterials, understanding the structure-properties relationship. A critical review. Nano Today 2023, 50, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, A.; Srdjenovic, B.; Seke, M.; Petrovic, D.; Injac, R.; Mrdjanovic, J. Review of Synthesis and Antioxidant Potential of Fullerenol Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 567073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Li, M.; Mu, L.; Huang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Guo, B. Photothermal/Photodynamic Synergistic Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressing with pH/Glucose Dual Responsive Pirfenidone Release for Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2416205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaudo, M.A.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Nanogels for regenerative medicine. J. Control. Release 2019, 313, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Maciel, D.; Rodrigues, J.; Shi, X.; Tomás, H. Biodegradable Polymer Nanogels for Drug/Nucleic Acid Delivery. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8564–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
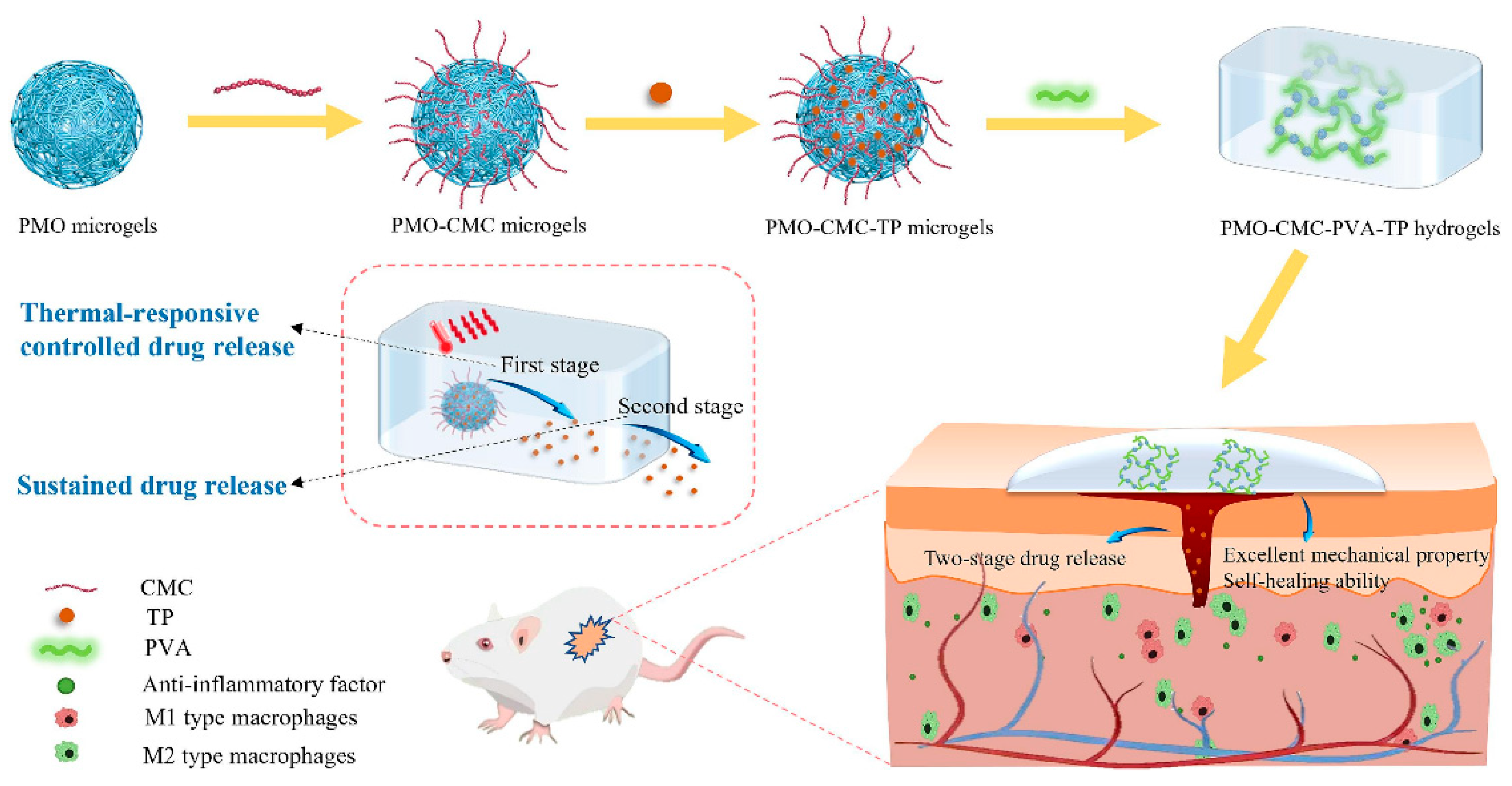
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, R.; Yun, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Hui, H.; Wu, L.; et al. Thermal-responsive microgels incorporated PVA composite hydrogels: Integration of two-stage drug release and enhanced self-healing ability for chronic wound treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 159813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.-W. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Applications. Small 2020, 16, 1906846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymaniha, M.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Rafieerad, A.R.; Maleki, A.; Amiri, A. Promoting Role of MXene Nanosheets in Biomedical Sciences: Therapeutic and Biosensing Innovations. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Li, Y.; Gu, N. Progress in Applications of Prussian Blue Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodyashkin, A.A.; Sergorodceva, A.V.; Kezimana, P.; Stanishevskiy, Y.M. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)—A Universal Material for Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Fan, C.; Ge, R.; Liu, G.; Su, L.; Dong, H. Visible light-activated Ti-MOF loaded metformin-hydrogel composite dressing for accelerated chronic diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello, E.A.; Mulko, L.E.; Balach, M.M.; Acevedo, D.; Barbero, C.A.; Lasagni, A.F.; Molina, M. Design and Development of Laser-Patterned Nanocomposites Based on Hydrogel Surfaces and Silver Clusters for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, L.; Ye, B.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Xue, P.; Yu, J.; Chen, K.; et al. Localized propranolol delivery from a copper-loaded hydrogel for enhancing infected burn wound healing via adrenergic β-receptor blockade. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 30, 101417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palem, R.R.; Kim, B.J.; Baek, I.; Choi, H.; Suneetha, M.; Shimoga, G.; Lee, S.-H. In situ fabricated ZnO nanostructures within carboxymethyl cellulose-based ternary hydrogels for wound healing applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, F. Engineered Au@MOFs silk fibroin-based hydrogel phototherapy platform for enhanced wound healing performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 297, 139872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, B.; Karadeniz, D.; Kalaycıoğlu, Z.; Kaygusuz, H.; Torlak, E.; Erim, F.B. Foam-based antibacterial hydrogel composed of carboxymethyl cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol/cerium oxide nanoparticles for potential wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 138924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Lin, L.; Wang, D.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, L. Injectable Hydrogel Incorporated with Iron-Doped Carbon Dots Exhibiting Peroxidase-Like Activity for Antibacterial Therapy and Wound Healing. Adv. Ther. 2024, 7, 2300368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Chang, X.; Ding, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, J. Peroxidase-like copper-doped carbon-dots embedded in hydrogels for stimuli-responsive bacterial biofilm elimination and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2025, 195, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Ma, Y.; Chen, A.; Cai, C.; Zhan, Q.; He, J.; Luo, J.; Zheng, J.; Lei, C. Fabrication of silver phosphate@carbon dots-embedded hydrogels with photodynamic and cationic synergistic antibacterial activity. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 310, 121548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-Y.; Lin, T.-Y.; Lai, Y.-J.; Chiu, T.-H.; Yeh, Y.-C. Engineering Multiresponsive Alginate/PNIPAM/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Hydrogels as On-Demand Drug Delivery Platforms. Small 2025, 21, 2407420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Knoedler, S.; Han, W.; Zha, K.; Li, H.; Panayi, A.C.; Alfertshofer, M.; Kim, B.-S.; Hu, W.; et al. Hybrid biomaterial hydrogel loading iRGD&PS double modified lipid nanoparticles ameliorates diabetic wound healing through promoting efferocytosis and glycolysis-related macrophage reprogramming. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154800. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.J.; Heydari, P.; Javaherchi, P.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Zarrabi, A. Alginate-based nanocomposite incorporating chitosan nanoparticles: A dual-drug delivery system for infection control and wound regeneration. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 107, 106755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, Z.; Che, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Tian, J.; Wang, C.; Li, G.; Jin, L. Near-Infrared Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogel Dressing with Anti-Inflammation and Pro-Angiogenesis for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 34720–34731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Hashem, M.; Fouad, H.; Albishi, H.M.; Eid, T.M.; Abdal-hay, A.; Hasan, A. Bioactive hydrogel (ZIF-8@CMC-PVA-SA) as dressing materials for wound healing applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodian, D.; Rashkhar, S.K.; Es-haghi, A. Harnessing the power of copper-based metal–organic framework (HKUST-1) nanostructures for advanced wound healing. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 2477–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, H.D.; Walton, S.P.; Chan, C. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery: A Design Perspective. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7004–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J.-Q.; Kumar, A. Multicomponent isoreticular metal-organic frameworks: Principles, current status and challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, B.; Qiu, L.; Qiao, X.; Yang, H. Dendrimer-based drug delivery systems: History, challenges, and latest developments. J. Biol. Eng. 2022, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidegger, S.; Gößl, D.; Schmidt, A.; Niedermayer, S.; Argyo, C.; Endres, S.; Bein, T.; Bourquin, C. Immune response to functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.; Chen, A.; Fu, C. Conductive hydrogels: Intelligent dressings for monitoring and healing chronic wounds. Regen. Biomater. 2024, 12, rbae127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun-Ur-Rashid, M.; Foyez, T.; Krishna, S.B.N.; Poda, S.; Imran, A.B. Recent advances of silver nanoparticle-based polymer nanocomposites for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 8480–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Naser, S.S.; Nandi, A.; Adhikari, A.; Prasad, A.; Sarkar, K.; Sinha, A.; Verma, S.K.; Dutt, A.; Chattopadhyay, D.; et al. Translational paradigm of MXene nanocomposites: Biophysical advancements to modern applications. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 909–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xu, P. Engineering functional natural polymer-based nanocomposite hydrogels for wound healing. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivunotko, E.; Koivuniemi, R.; Monola, J.; Harjumäki, R.; Pridgeon, C.S.; Madetoja, M.; Linden, J.; Paasonen, L.; Laitinen, S.; Yliperttula, M. Cellulase-assisted platelet-rich plasma release from nanofibrillated cellulose hydrogel enhances wound healing. J. Control. Release 2024, 368, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alinezhad, V.; Esmaeilzadeh, K.; Bagheri, H.; Zeighami, H.; Kalantari-Hesari, A.; Jafari, R.; Makvandi, P.; Xu, Y.; Mohammadi, H.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; et al. Engineering a platelet-rich plasma-based multifunctional injectable hydrogel with photothermal, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties for skin regeneration. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 5872–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Xiong, T.; Kang, Z.; Lei, S.; Wu, B.; Cheng, B. A composite hydrogel with antibacterial and promoted cell proliferation dual properties for healing of infected wounds. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 4467–4486. [Google Scholar]
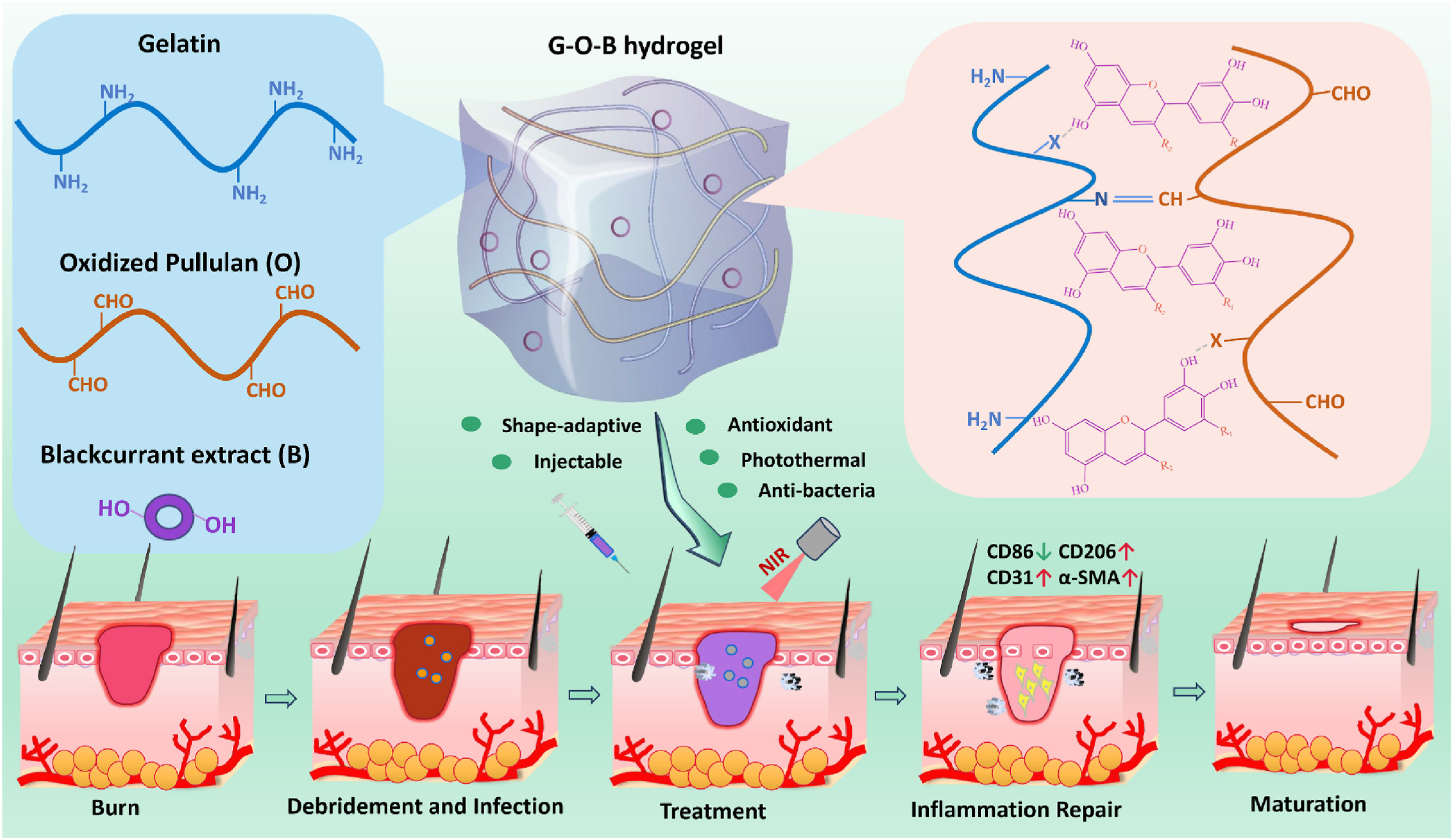
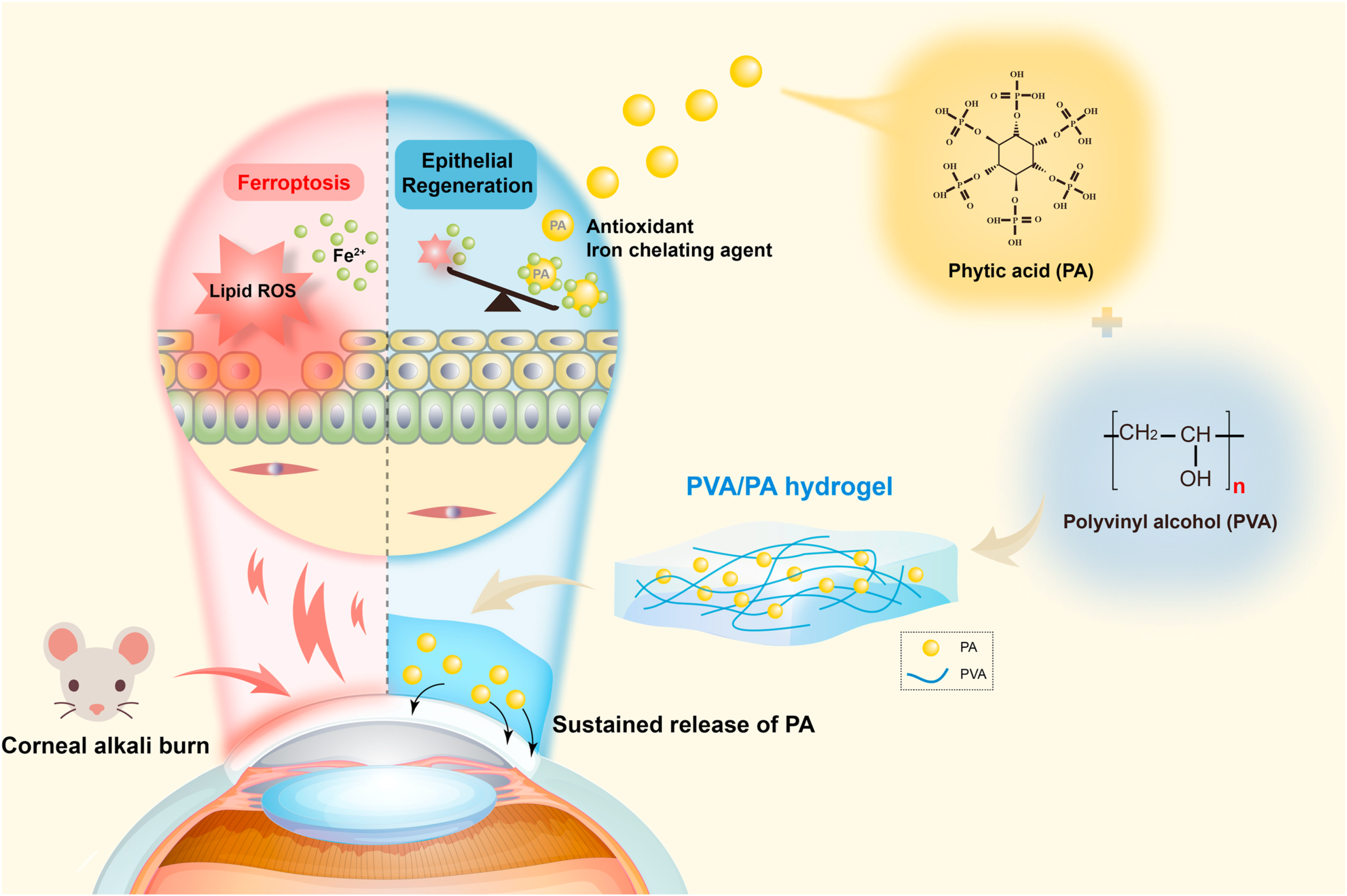
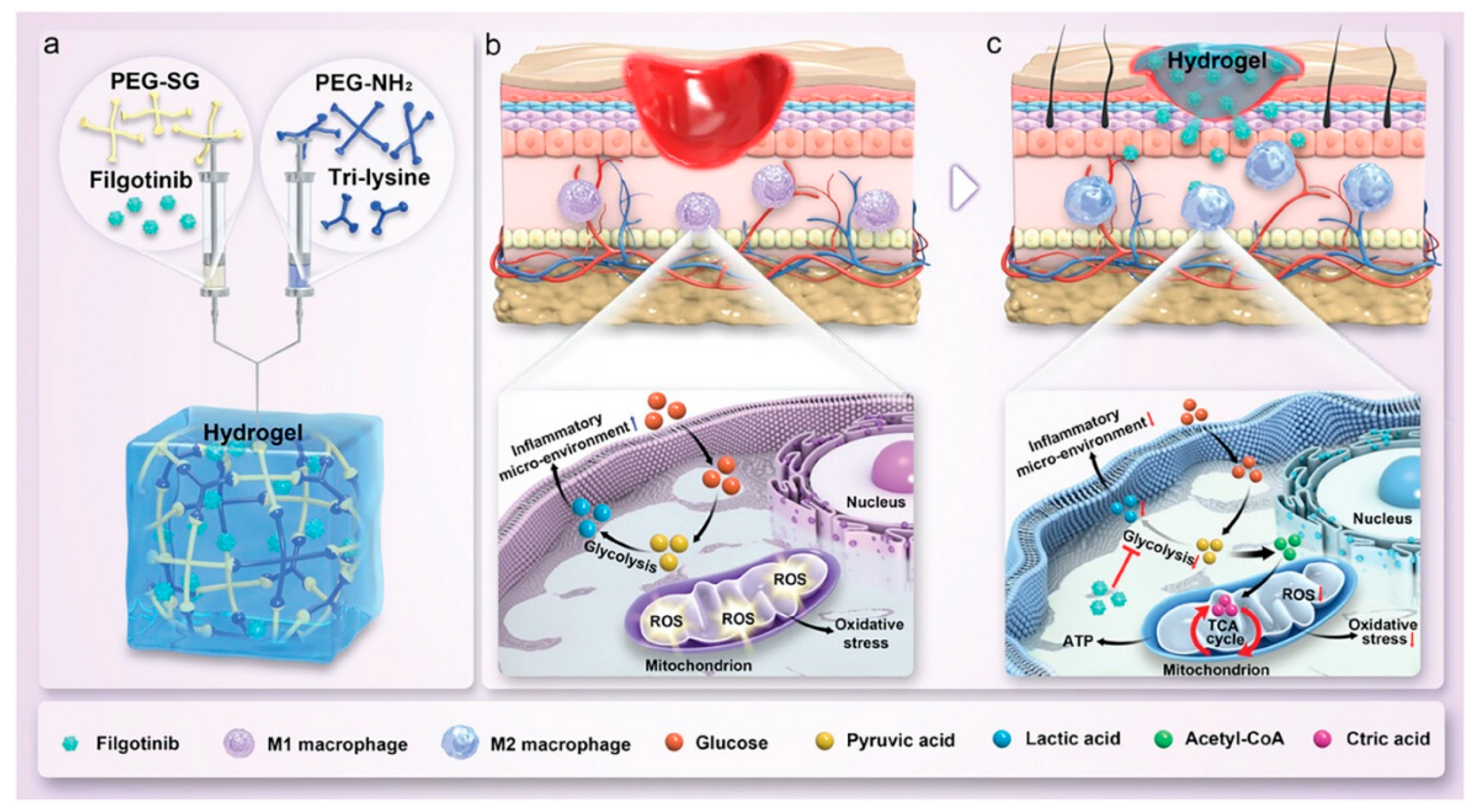
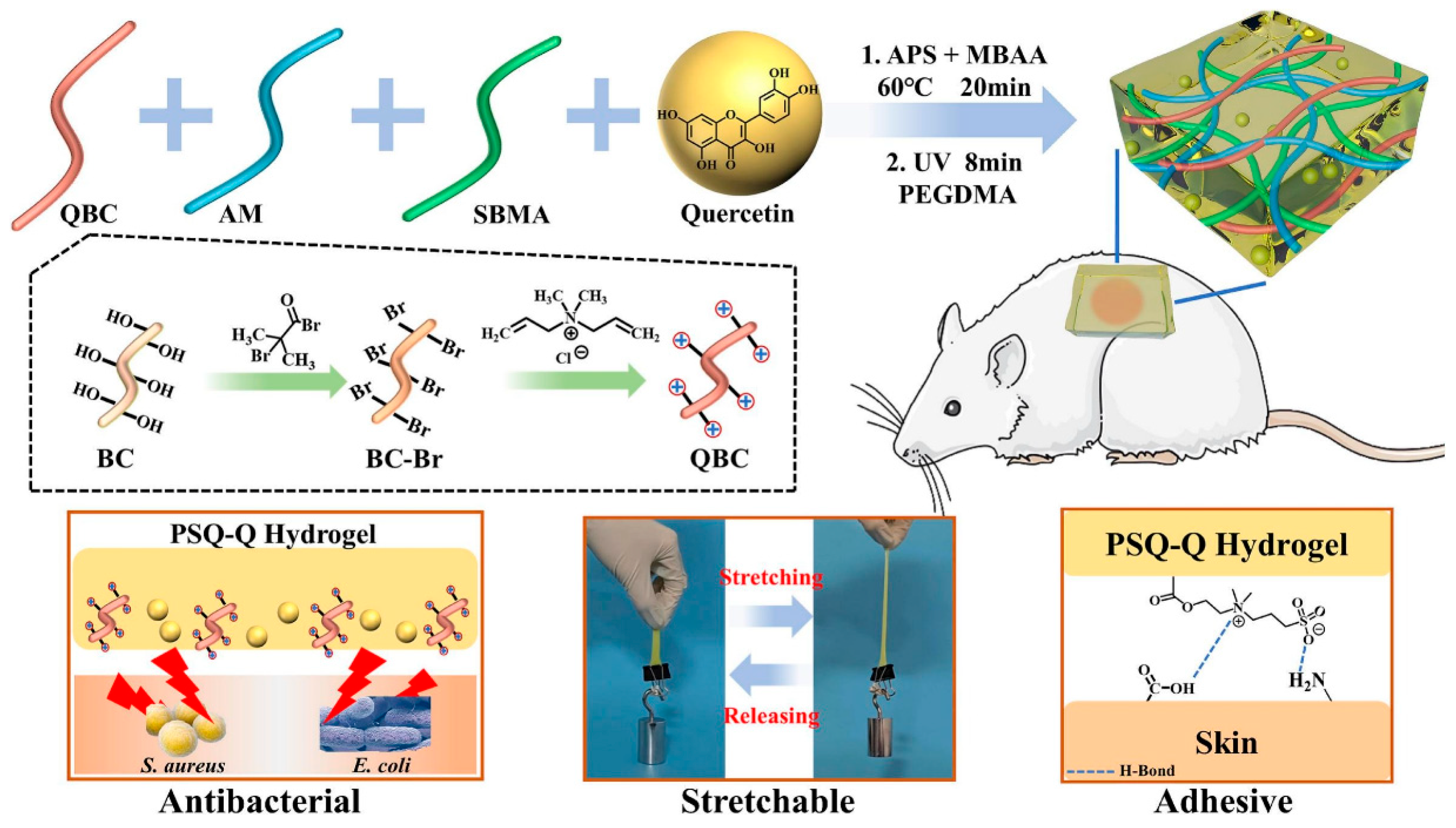
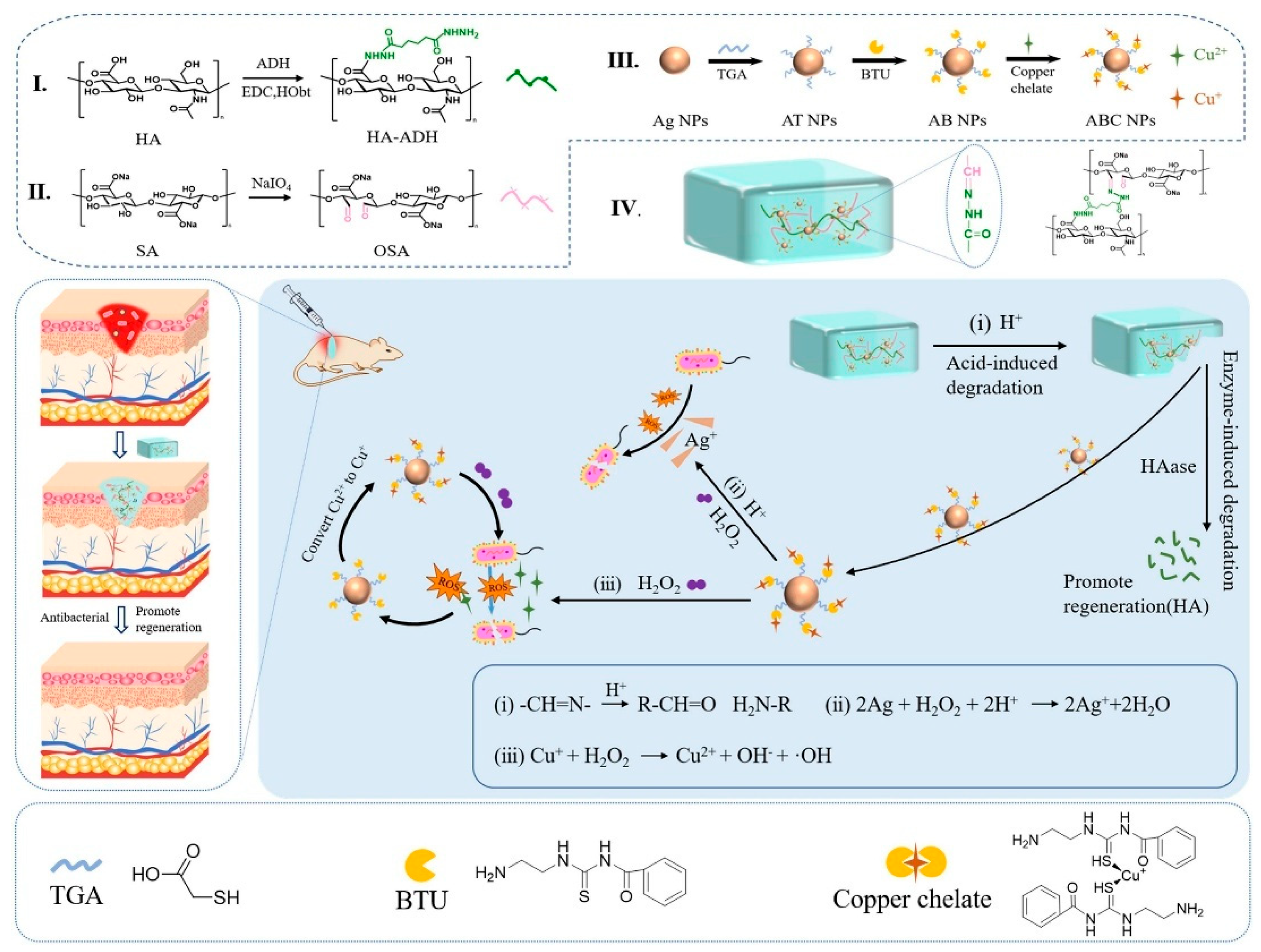
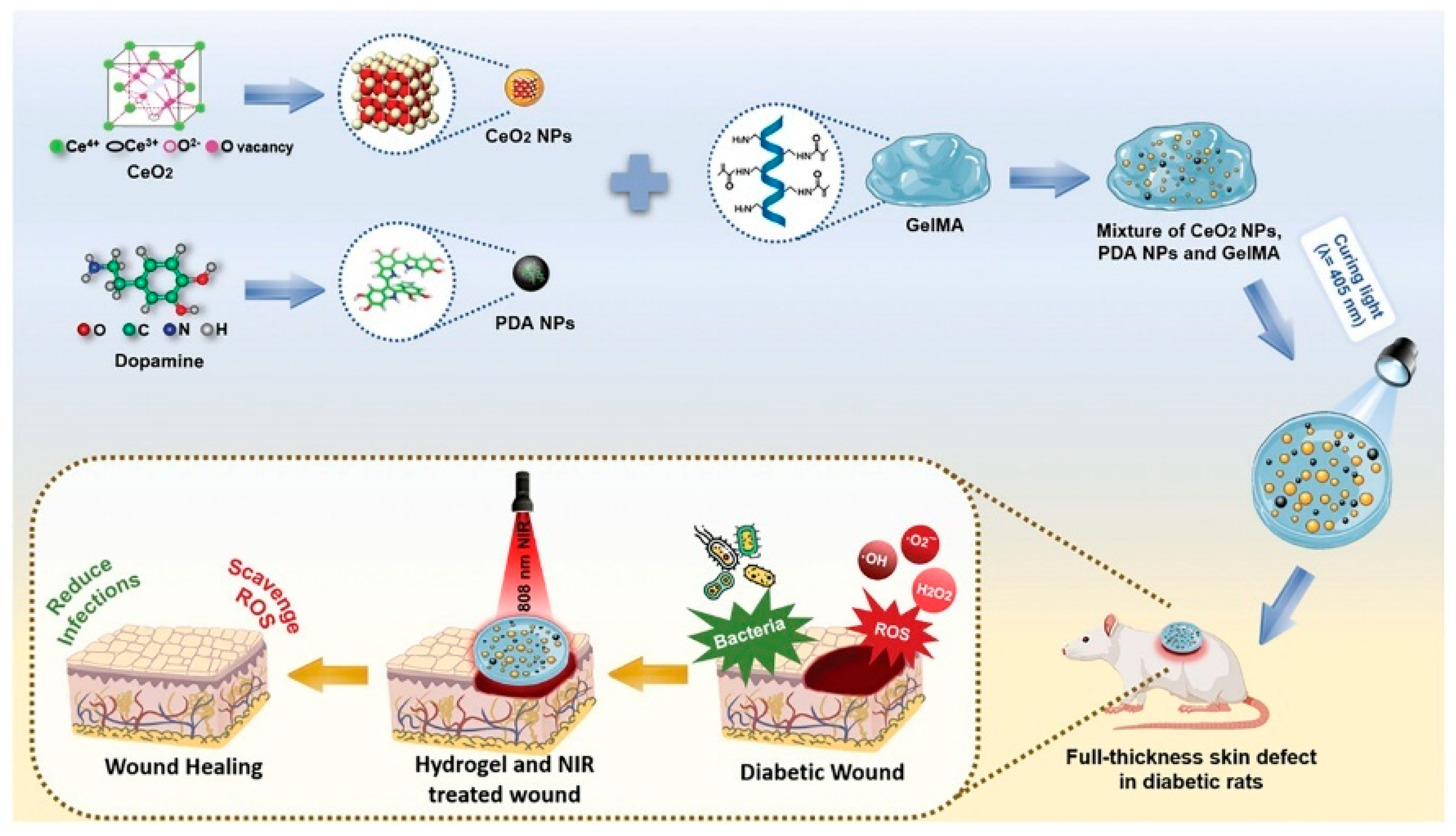
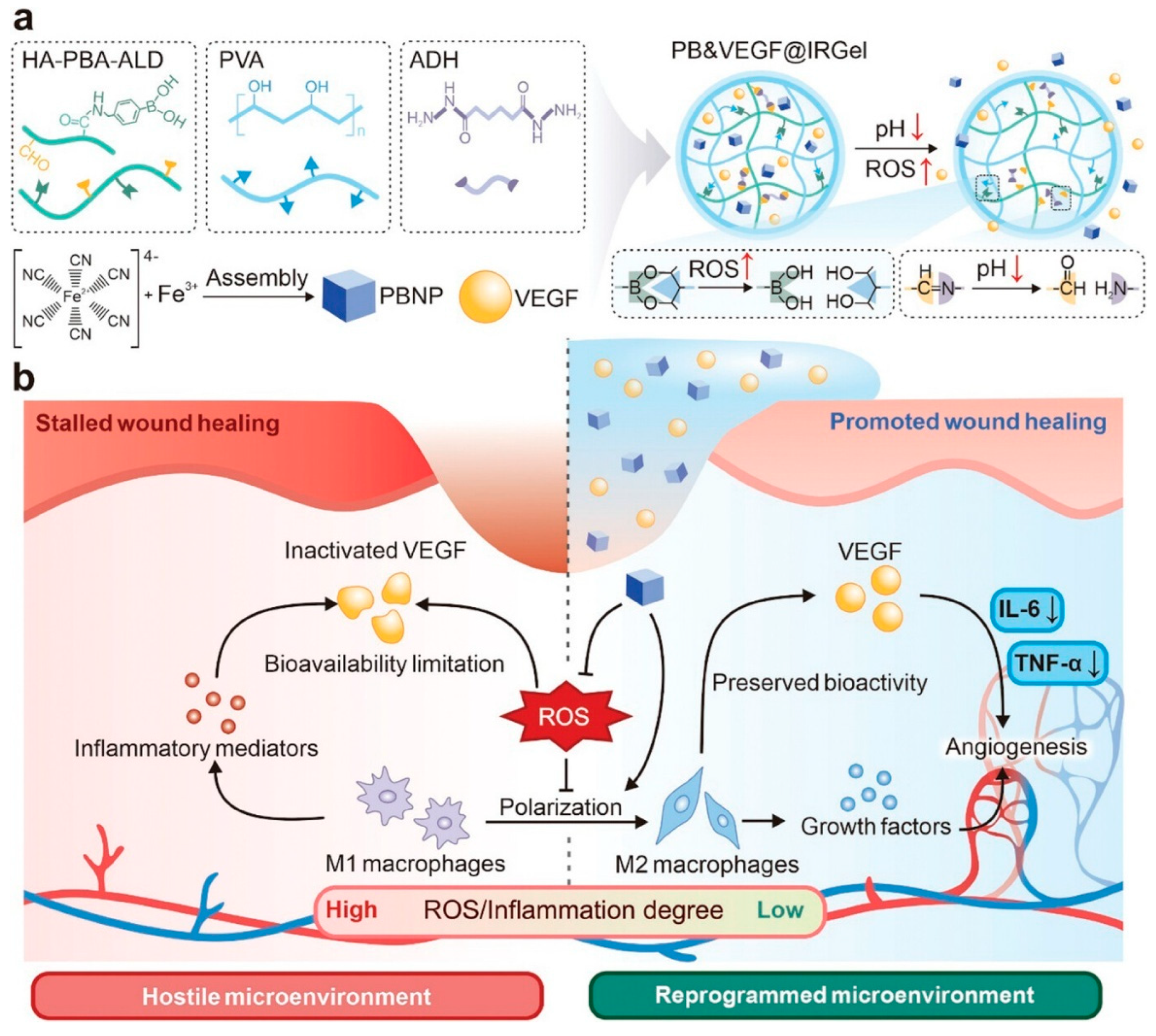

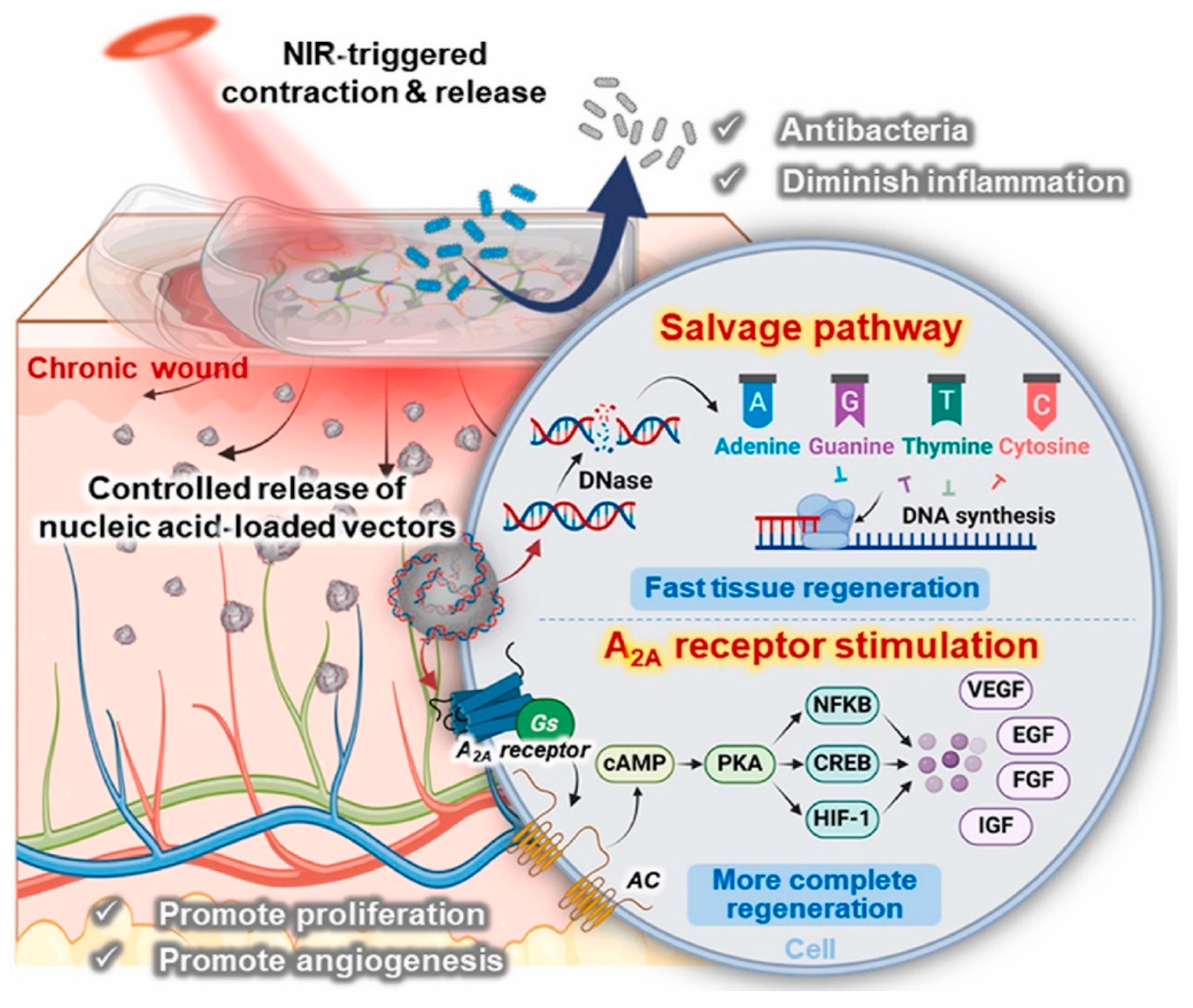
| Material Category | Nanomaterial Type | Hydrogel Matrix | Function | Wound Model | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| [154] |
|
|
|
| [155] | |
|
|
|
| [156] | |
|
|
|
| [157] | |
|
|
|
|
| [158] |
|
|
|
| [140] | |
|
|
|
| [159] | |
|
|
|
| [160] | |
|
|
|
|
| [145] |
|
|
|
| [161] | |
|
|
|
| [162] | |
|
|
|
|
| [163] |
|
|
|
| [164] | |
|
|
|
| [165] | |
|
|
|
|
| [166] |
|
|
|
| [167] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, W.; Niu, Y.; Sheu, C. Advances in Nanohybrid Hydrogels for Wound Healing: From Functional Mechanisms to Translational Prospects. Gels 2025, 11, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070483
Mo Y, Zhou T, Li W, Niu Y, Sheu C. Advances in Nanohybrid Hydrogels for Wound Healing: From Functional Mechanisms to Translational Prospects. Gels. 2025; 11(7):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070483
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Yunfei, Tao Zhou, Weichang Li, Yuqing Niu, and Chialin Sheu. 2025. "Advances in Nanohybrid Hydrogels for Wound Healing: From Functional Mechanisms to Translational Prospects" Gels 11, no. 7: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070483
APA StyleMo, Y., Zhou, T., Li, W., Niu, Y., & Sheu, C. (2025). Advances in Nanohybrid Hydrogels for Wound Healing: From Functional Mechanisms to Translational Prospects. Gels, 11(7), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070483






