Zinc Alginate Hydrogel-Coated Wound Dressings: Fabrication, Characterization, and Evaluation of Anti-Infective and In Vivo Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
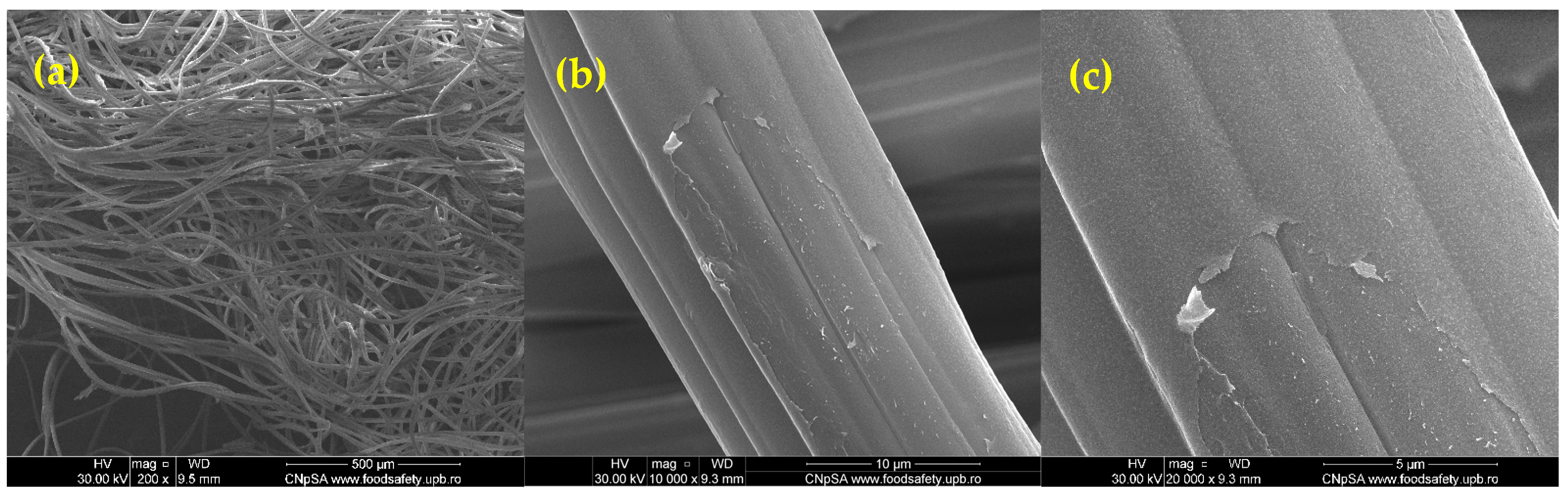
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
2.3. In Vivo Evaluation of Wound Healing in a Wistar Rat Burn Mode
Macroscopic Evaluation of Burn Wound Healing Following Topical Treatment
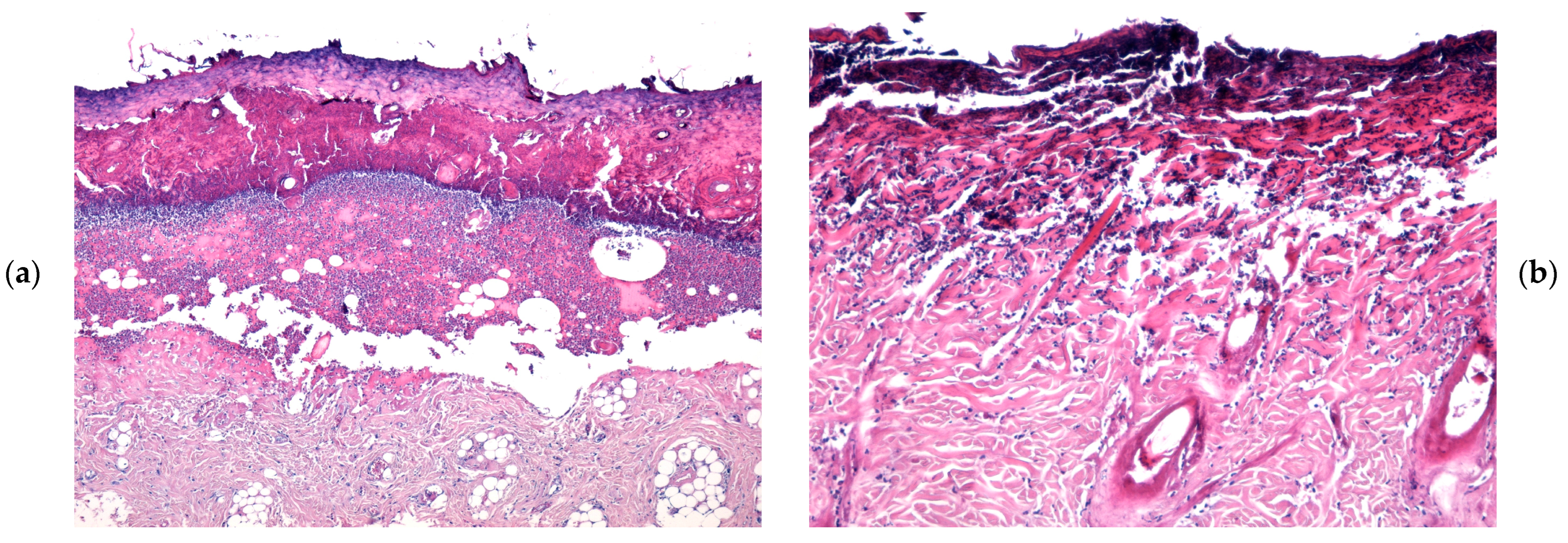
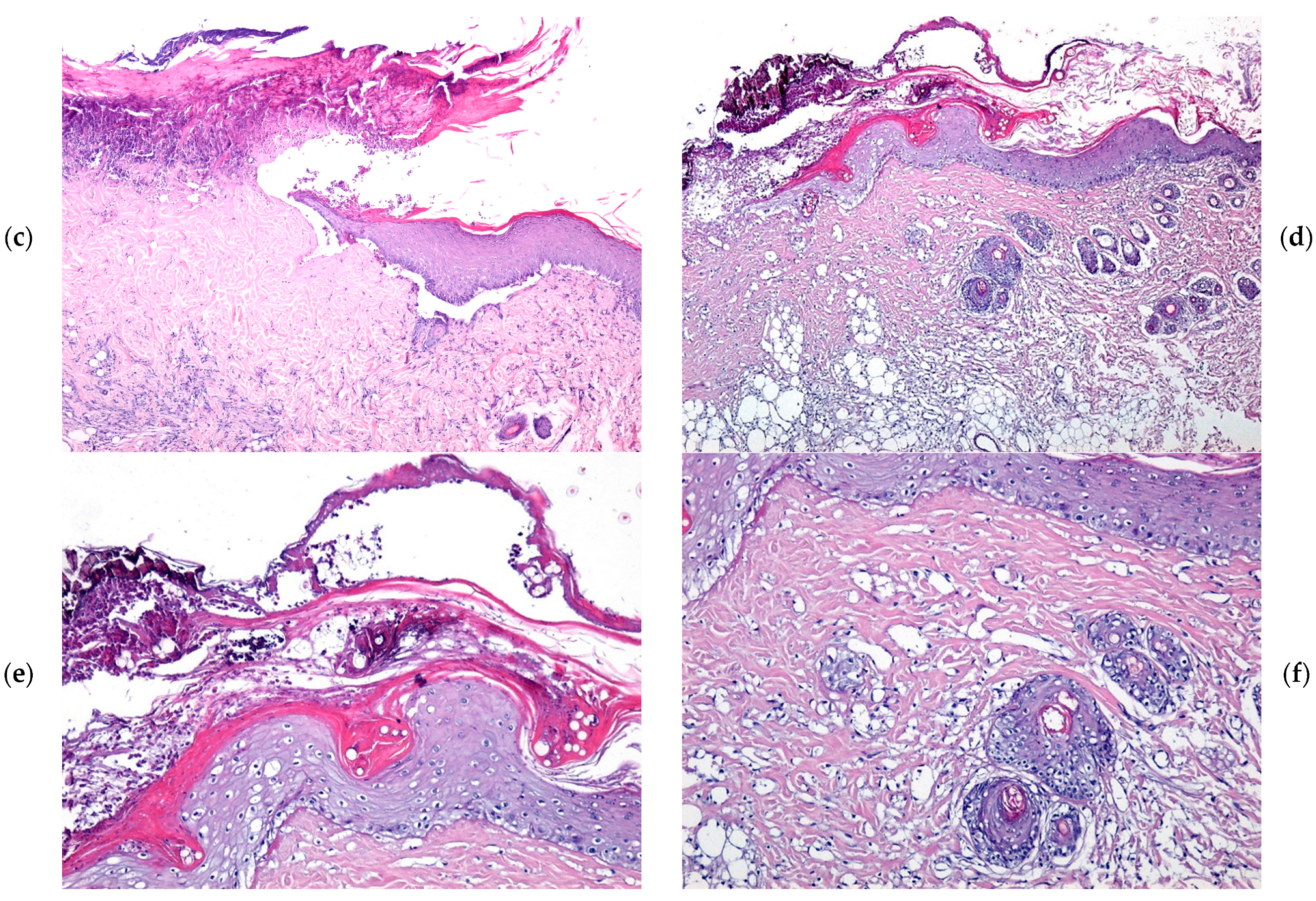
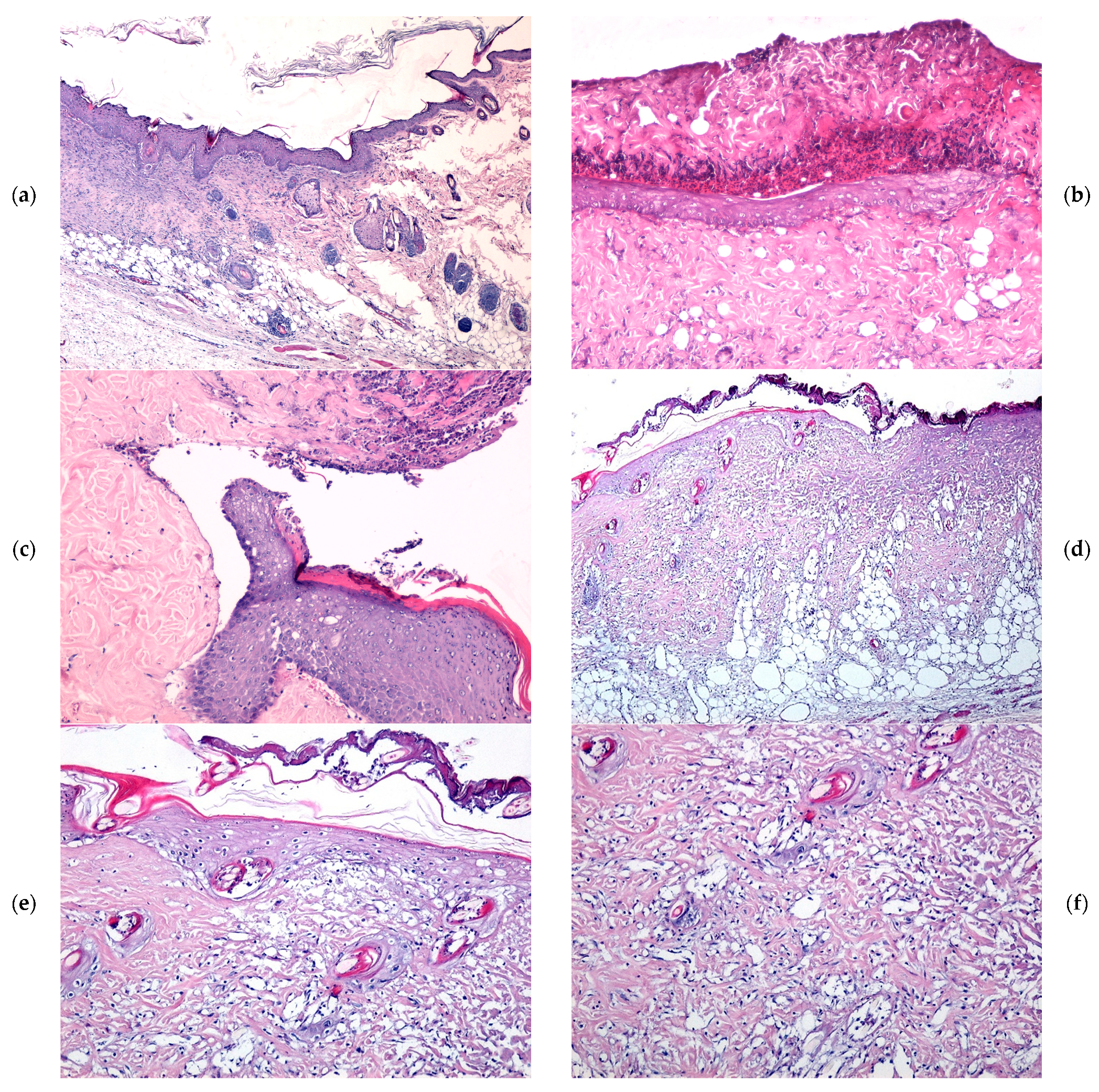
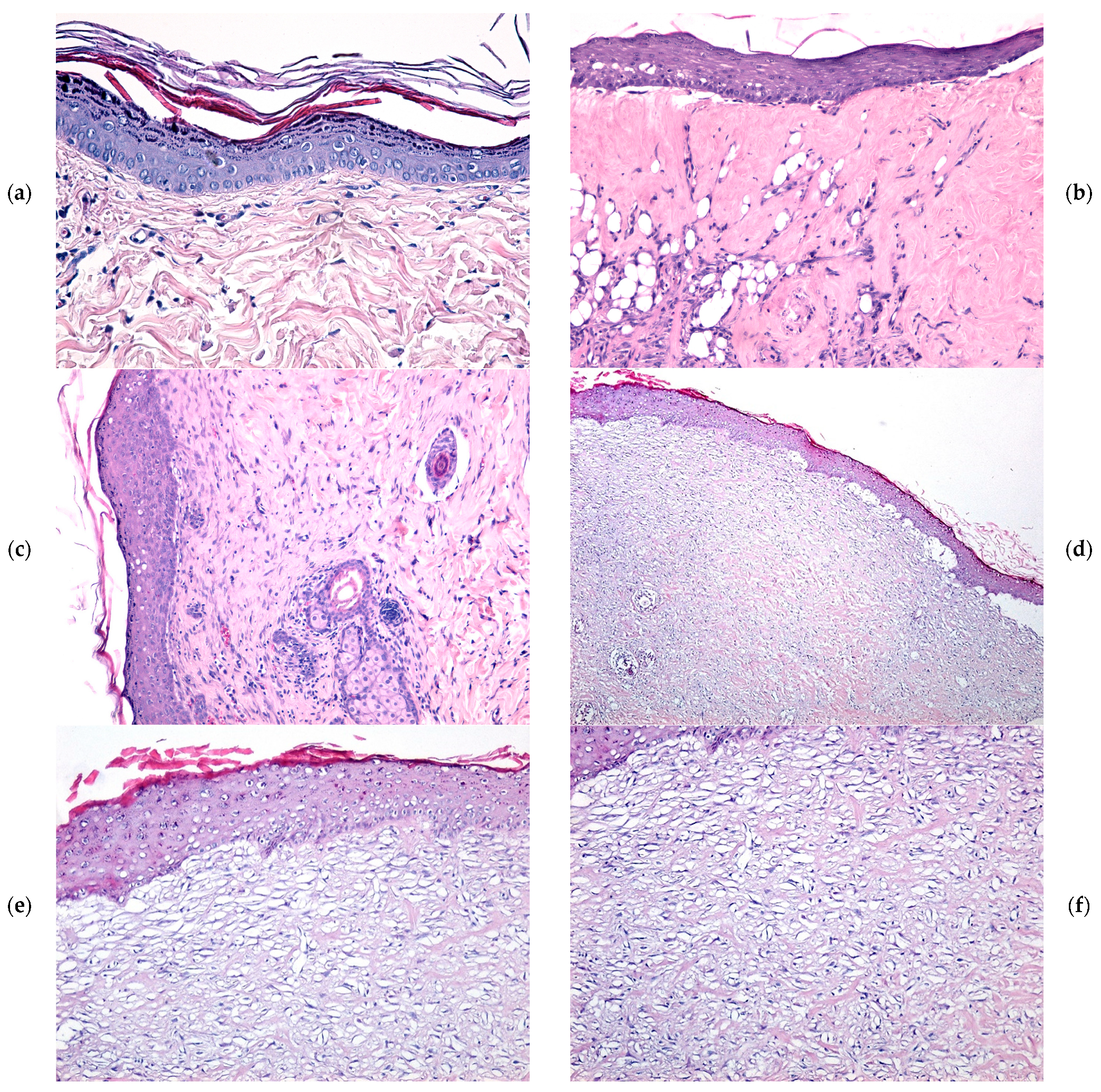
2.4. Microscopic Evaluation of Burn Wound Healing
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Zinc Alginate-Coated Wound Dressings
4.3. Physicochemical Characterization Methods
4.4. In Vivo Experimental Model
4.5. Animal Model and Experimental Design
4.6. Wound-Healing Monitoring
4.7. Histological Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
4.9. Antimicrobial Activity
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le, V.A.T.; Trinh, T.X.; Chien, P.N.; Giang, N.N.; Zhang, X.-R.; Nam, S.-Y.; Heo, C.-Y. Evaluation of the Performance of a ZnO-Nanoparticle-Coated Hydrocolloid Patch in Wound Healing. Polymers 2022, 14, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bâldea, I.; Soran, M.-L.; Stegarescu, A.; Opriș, O.; Kacso, I.; Tripon, S.; Adascalitei, A.; Fericel, I.G.; Decea, R.; Lung, I. Lilium candidum Extract Loaded in Alginate Hydrogel Beads for Chronic Wound Healing. Gels 2025, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atepileva, A.; Ogay, V.; Kudaibergen, G.; Kaukabaeva, G.; Nurkina, A.; Mukhambetova, A.; Balgazarov, S.; Batpen, A.; Saginova, D.; Ramazanov, Z.; et al. Exploring the Antibacterial and Regenerative Properties of a Two-Stage Alginate Wound Dressing in a Rat Model of Purulent Wounds. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayyif, S.M.I.; Mohammed, H.B.; Curuțiu, C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Dițu, L.M.; Lazăr, V.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Mihăescu, G.; et al. ZnO Nanoparticles-Modified Dressings to Inhibit Wound Pathogens. Materials 2021, 14, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsawy, H.; Sedky, A.; Abou Taleb, M.F.; El-Newehy, M.H. Antidiabetic Wound Dressing Materials Based on Cellulosic Fabrics Loaded with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Solid-State Method. Polymers 2022, 14, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rata, D.M.; Cadinoiu, A.N.; Daraba, O.M.; Gradinaru, L.M.; Atanase, L.I.; Ichim, D.L. Influence of ZnO Nanoparticles on the Properties of Ibuprofen-Loaded Alginate-Based Biocomposite Hydrogels with Potential Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.; Moldoveanu, E.T.; Niculescu, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Hydrogels for Wound Dressings: Applications in Burn Treatment and Chronic Wound Care. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikovych, O.; Pasetto, P.; Nosova, N.; Kudina, O.; Ostapiv, D.; Samaryk, V.; Varvarenko, S. Functional Properties of Gelatin–Alginate Hydrogels for Use in Chronic Wound Healing Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathya Seeli, D.; Das, A.; Prabaharan, M. Zinc Oxide–Incorporated Chitosan–Poly(methacrylic Acid) Polyelectrolyte Complex as a Wound Healing Material. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, S.; Padma, V.V.; Santhini, E. Wound dressings-a review. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.; Bratu, A.G.; Niculescu, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Collagen-Based Wound Dressings: Innovations, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.A.; Swogger, E.; Wolcott, R.; Pulcini, E.; Secor, P.; Sestrich, J.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S. Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, S.P.; Sequeira, R.S.; Moreira, A.F.; Cabral, C.S.D.; Mendonça, A.G.; Ferreira, P.; Correia, I.J. An overview of electrospun membranes loaded with bioactive molecules for improving the wound healing process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.; Tudorache, D.-I.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Advancements in Wound Dressing Materials: Highlighting Recent Progress in Hydrogels, Foams, and Antimicrobial Dressings. Gels 2025, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.A.; Rastegarpanah, H.; Ansari, N.; Dortaj, H.; Shafaghi, S.; Ghorbani, F.; Shafaghi, M. Preparation and in vivo Evaluation of an Astragalus Gummifer Hydrogel-Based Dressing for Excisional Wound. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2024, 14, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Bîrcă, A.C.; Minculescu, M.A.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Hudiță, A.; Holban, A.M.; Alberts, A.; Grumezescu, A.M. Nanoparticle-Enhanced Collagen Hydrogels for Chronic Wound Management. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, B.A.; Buyana, B. Alginate in Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Luo, T.; Liu, H.; Luo, Z. A Zn2+ cross-linked sodium alginate/epigallocatechin gallate hydrogel scaffold for promoting skull repair. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 239, 113971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yang, F.; Yu, D.; Shi, C.; Zhao, D.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. Double Network Physical Cross-linked Hydrogel for Healing Skin Wounds: New Formulation Based on Polysaccharides and Zn2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S. Alginate dressings in surgery and wound management—Part 1. J. Wound Care 2000, 9, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Feky, G.S.; El-Banna, S.T.; El-Bahy, G.S.; Abdelrazek, E.M.; Kamal, M. Alginate coated chitosan nanogel for the controlled topical delivery of Silver sulfadiazine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, S.L.; Babić Radić, M.M.; Vuković, J.S.; Filipović, V.V.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Vukomanović, M. Alginate-Based Hydrogels and Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.H.; Sermersheim, M.; Li, H.; Lee, P.H.U.; Steinberg, S.M.; Ma, J. Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation. Nutrients 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.M.; Yu, M.M. Molecular mechanisms of wound healing: The role of zinc as an essential microelement. Res. Results Pharmacol. 2023, 9, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Fulindi, R.B.; Rodrigues, J.D.; Barbosa, T.W.L.; Garcia, A.D.G.; Porta, F.d.A.L.; Pratavieira, S.; Chiavacci, L.A.; Junior, J.P.A.; Costa, P.I.d.; Martinez, L.R. Zinc-Based Nanoparticles Reduce Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04831-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Biofilm therapy for chronic wounds. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, A.Y.; Felix, J.C.; Silvestre, R.G.M.; Lipinski, L.C.; Carletto, B.; Kawahara, F.A.; Pereira, A.V. Evaluation of wound healing effect of alginate film containing Aloe vera gel and cross-linked with zinc chloride. Acta Cir. Bras. 2020, 35, e202000507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, V.; Grey, J.E.; Harding, K.G. Wound dressings. Bmj 2006, 332, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, S.; Chang, J.; Ning, C.; Dong, C.; Yan, D. Surface modification of polycaprolactone membrane via layer-by-layer deposition for promoting blood compatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Yang, J.H.; Huang, H.T. Chitosan/polyanion surface modification of styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer membrane for wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 34, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.; Bratu, A.G.; Niculescu, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M. New Perspectives of Hydrogels in Chronic Wound Management. Molecules 2025, 30, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, J.; Antunes, S.; Bonelli, R.; Backx, B. Development of Antimicrobial Dressings by the Action of Silver Nanoparticles Based on Green Nanotechnology. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2023, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellappan, L.K.; Manoharan, S. Fabrication of bioinspired keratin/sodium alginate based biopolymeric mat loaded with herbal drug and green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as a dual drug antimicrobial wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, G. Effect of Alginate Gelatin Hydrogel Composited with Nano-Zinc on Cesarean Section Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2022, 18, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolimi, P.; Narala, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Youssef, A.A.A.; Dudhipala, N. Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements. Cells 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Conductive Biomaterials as Bioactive Wound Dressing for Wound Healing and Skin Tissue Engineering. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, A.E.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Nanomaterials for Wound Dressings: An Up-to-Date Overview. Molecules 2020, 25, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumberg, V.; Astrelina, T.; Malivanova, T.; Samoilov, A. Modern Wound Dressings: Hydrogel Dressings. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Maleki, H.; Zavagna, L.; De la Ossa, J.G.; Linari, S.; Lazzeri, A.; Danti, S. Bio-Based Electrospun Fibers for Wound Healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.V.; Skardal, A.; Song, L.; Sutton, K.; Haug, R.; Mack, D.L.; Jackson, J.; Soker, S.; Atala, A. Solubilized Amnion Membrane Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Accelerates Full-Thickness Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz-Gospodarek, A.; Kozioł, M.; Tobiasz, M.; Baj, J.; Radzikowska-Büchner, E.; Przekora, A. Burn Wound Healing: Clinical Complications, Medical Care, Treatment, and Dressing Types: The Current State of Knowledge for Clinical Practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Li, G.; Cao, E.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, H. Recent progress of antibacterial hydrogels in wound dressings. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 19, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Gao, Y.; Xin, H.; Cao, C.; Ma, W.; Sun, W.; Ma, Q. A review on multifunctional calcium alginate fibers for full-time and multipurposed wound treatment: From fundamentals to advanced applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 290, 139133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straccia, M.; d’Ayala, G.; Romano, I.; Laurienzo, P. Novel zinc alginate hydrogels prepared by internal setting method with intrinsic antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Yu, D.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, W. Progress in Research on Metal Ion Cross-linking Alginate-Based Gels. Gels 2025, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhang, T.; Yang, K.; Tian, G.; Dang, Y.; Ma, J. Zn2+ ions cross-linking sodium alginate encapsulated bacterial cellulose/ZnO composite film for antibacterial application. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7853–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Lian, S.; Wu, Y.; Yan, L.; Quan, G.; Zhu, G. Zinc is an important inter-kingdom signal between the host and microbe. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Eckhard, U.; Delgado, L.M.; de Roo Puente, Y.J.D.; Hoyos-Nogués, M.; Gil, F.J.; Perez, R.A. Antibacterial approaches in tissue engineering using metal ions and nanoparticles: From mechanisms to applications. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4470–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, G.C.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Antibacterial Oxidative Therapies: Available Methods to Generate ROS and a Novel Option Proposal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, C.R.; Dilarri, G.; Forsan, C.F.; Sapata, V.d.M.R.; Lopes, P.R.M.; de Moraes, P.B.; Montagnolli, R.N.; Ferreira, H.; Bidoia, E.D. Antibacterial action and target mechanisms of zinc oxide nanoparticles against bacterial pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowiecka, A.; Strużyna, J.; Winiarska, A.; Korzeniowski, T. Hydrogels in Burn Wound Management—A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Xia, H.; Huang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Ye, Q.; Na, N.; Lu, A. Biocompatible, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory zinc ion cross-linked quaternized cellulose-sodium alginate composite sponges for accelerated wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Chengyong, W.; Yu, X.; Su, W.; Zhishan, Y. Chitosan/zinc nitrate microneedles for bacterial biofilm eradication. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 109, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, I.; Sivori, F.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Abril, E.; Pontone, M.; Di Domenico, E.G.; Pimpinelli, F. Bacterial Biofilm in Chronic Wounds and Possible Therapeutic Approaches. Biology 2024, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, D.A.; Carter, G.P.; Howden, B.P. Current and Emerging Topical Antibacterials and Antiseptics: Agents, Action, and Resistance Patterns. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 827–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartotto, R. Topical antimicrobial agents for pediatric burns. Burn. Trauma. 2017, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, R.; Mehta, R.K.; Mohanty, S.; Padhi, A.; Sengupta, M.; Vaseeharan, B.; Goswami, C.; Sonawane, A. Topical application of zinc oxide nanoparticles reduces bacterial skin infection in mice and exhibits antibacterial activity by inducing oxidative stress response and cell membrane disintegration in macrophages. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Chu, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, P. Research on the antibacterial properties of nanoscale zinc oxide particles comprehensive review. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1449614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, O.; Turunc, E.; Dogen, A.; Binzet, R. Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dot Zinc Oxide Nanocomposites: Assessment of their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2024, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Abka-Khajouei, R.; Tounsi, L.; Shahabi, N.; Patel, A.K.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlevanzadeh, F.; Mokhtari, H.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Emadi, R.; Kharaziha, M.; Valiani, A.; Poursamar, S.A.; Ismail, A.F.; RamaKrishna, S.; Berto, F. Recent Trends in Three-Dimensional Bioinks Based on Alginate for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salesa, B.; Sabater, I.S.R.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Zinc Chloride: Time-Dependent Cytotoxicity, Proliferation and Promotion of Glycoprotein Synthesis and Antioxidant Gene Expression in Human Keratinocytes. Biology 2021, 10, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; James, S.A.; de Jonge, M.D.; Turney, T.W.; Wright, P.F.; Feltis, B.N. Relating cytotoxicity, zinc ions, and reactive oxygen in ZnO nanoparticle-exposed human immune cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 136, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc in Human Health: Effect of Zinc on Immune Cells. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Mahajan, V.K.; Mehta, K.S.; Chauhan, P.S. Zinc therapy in dermatology: A review. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 709152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Su, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, B.; Tang, L.; Qin, Y.-X. Zinc regulates vascular endothelial cell activity through zinc-sensing receptor ZnR/GPR39. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2018, 314, C404–C414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawson, E.J.; Duran-Jimenez, B.; Surosky, R.; Brooke, H.E.; Spratt, S.K.; Tomlinson, D.R.; Gardiner, N.J. Engineered zinc finger protein-mediated VEGF-a activation restores deficient VEGF-a in sensory neurons in experimental diabetes. Diabetes 2010, 59, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Xiang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Song, J.; Huang, N.; Li, J.; Jin, G.; Cui, S.; Xu, P.; Le, X.; et al. Enhanced healing of burn wounds by dressings with alginate: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Regenesis Repair Rehabil. 2025, 1, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, S.A.; Krieg, T.; Davidson, J.M. Inflammation in Wound Repair: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor-Ibarguren, A.; Busca-Arenzana, C.; Robles-Marhuenda, Á. A Hypothesis for the Possible Role of Zinc in the Immunological Pathways Related to COVID-19 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases, Vascular Remodeling, and Vascular Disease. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 241–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolosowicz, M.; Prokopiuk, S.; Kaminski, T.W. The Complex Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, C.; Hübner, C.; Richter, C.; Lier, S.; Barthel, L.; Meyer, V.; Subrahmanyam, R.; Gurikov, P.; Smirnova, I.; Haase, H. Ca-Zn-Ag Alginate Aerogels for Wound Healing Applications: Swelling Behavior in Simulated Human Body Fluids and Effect on Macrophages. Polymers 2020, 12, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Abraham, T.E. Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: Alginate and chitosan—A review. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogoşanu, G.D.; Popescu, F.C.; Busuioc, C.J.; Pârvănescu, H.; Lascăr, I. Natural products locally modulators of the cellular response: Therapeutic perspectives in skin burns. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2012, 53, 249–262. [Google Scholar]


| Day | REF | SDA | WD_Control | WD@AlgZn |
| Burn Wound Area (mean ± SD) (cm2)/Healing Rate (%) | ||||
| 7 | 1.28 ± 0.15/15.33 ** | 1.18 ± 0.12/25.48 ** | 1.34 ± 0.15/19.75 ** | 1.32 ± 0.13/38.25 ** |
| 14 | 0.95 ± 0.14/28.66 ** | 0.68 ± 0.06/41.25 ** | 0.84 ± 0.10/36.33 ** | 0.56 ± 0.10/71.33 ** |
| 21 | 0.56 ± 0.08/37.25 * | 0.29 ± 0.02/52.32 * | 0.38 ± 0.02/46.58 * | 0.18 ± 0.02/90.75 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niculescu, A.-G.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Mogoşanu, G.D.; Rădulescu, M.; Holban, A.M.; Manuc, D.; Alberts, A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L. Zinc Alginate Hydrogel-Coated Wound Dressings: Fabrication, Characterization, and Evaluation of Anti-Infective and In Vivo Performance. Gels 2025, 11, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060427
Niculescu A-G, Bîrcă AC, Mogoşanu GD, Rădulescu M, Holban AM, Manuc D, Alberts A, Grumezescu AM, Mogoantă L. Zinc Alginate Hydrogel-Coated Wound Dressings: Fabrication, Characterization, and Evaluation of Anti-Infective and In Vivo Performance. Gels. 2025; 11(6):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060427
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiculescu, Adelina-Gabriela, Alexandra Cătălina Bîrcă, George Dan Mogoşanu, Marius Rădulescu, Alina Maria Holban, Daniela Manuc, Adina Alberts, Alexandru Mihai Grumezescu, and Laurenţiu Mogoantă. 2025. "Zinc Alginate Hydrogel-Coated Wound Dressings: Fabrication, Characterization, and Evaluation of Anti-Infective and In Vivo Performance" Gels 11, no. 6: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060427
APA StyleNiculescu, A.-G., Bîrcă, A. C., Mogoşanu, G. D., Rădulescu, M., Holban, A. M., Manuc, D., Alberts, A., Grumezescu, A. M., & Mogoantă, L. (2025). Zinc Alginate Hydrogel-Coated Wound Dressings: Fabrication, Characterization, and Evaluation of Anti-Infective and In Vivo Performance. Gels, 11(6), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060427









