Poloxamer-Driven Drug Delivery System for Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Approach
Abstract
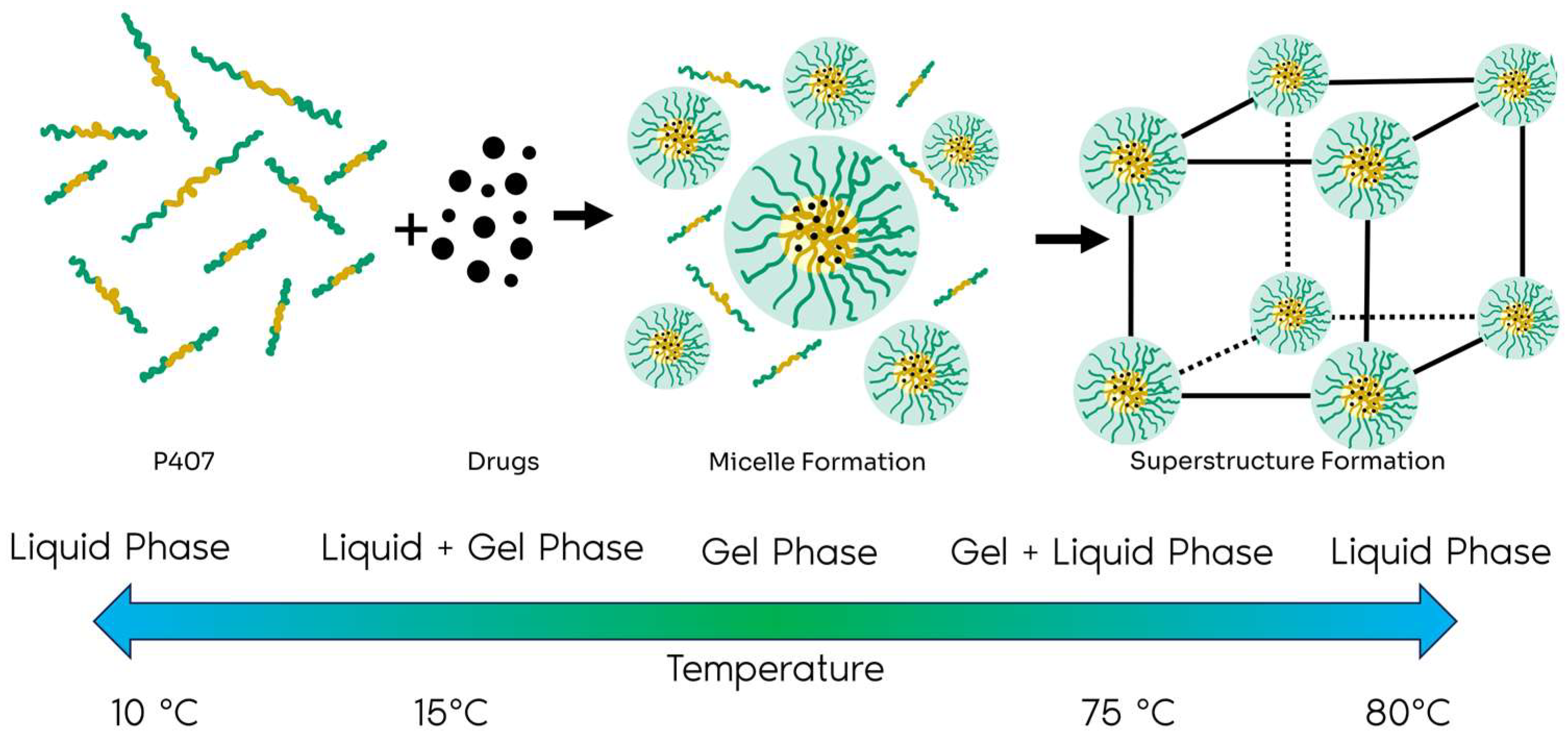
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
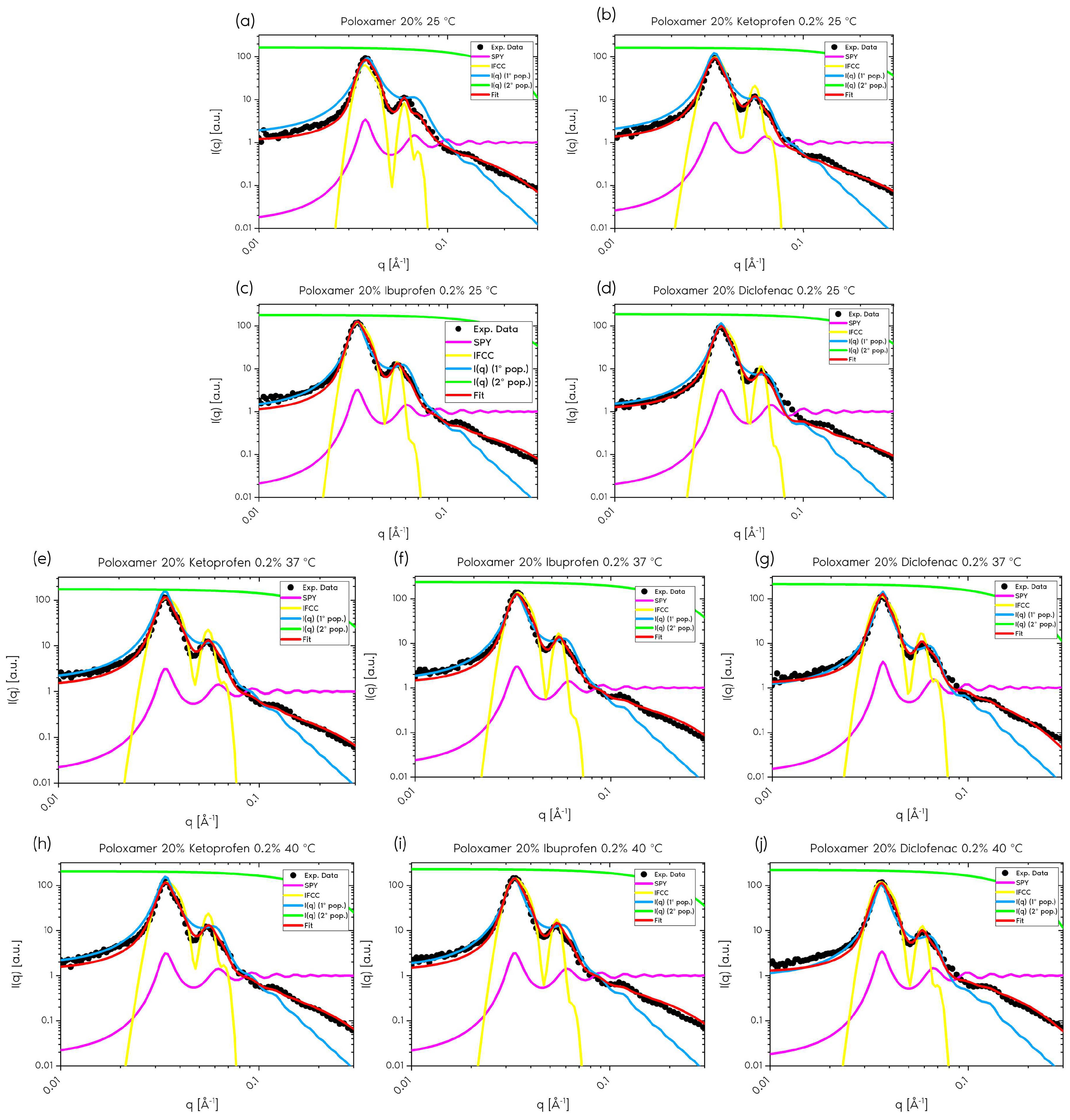
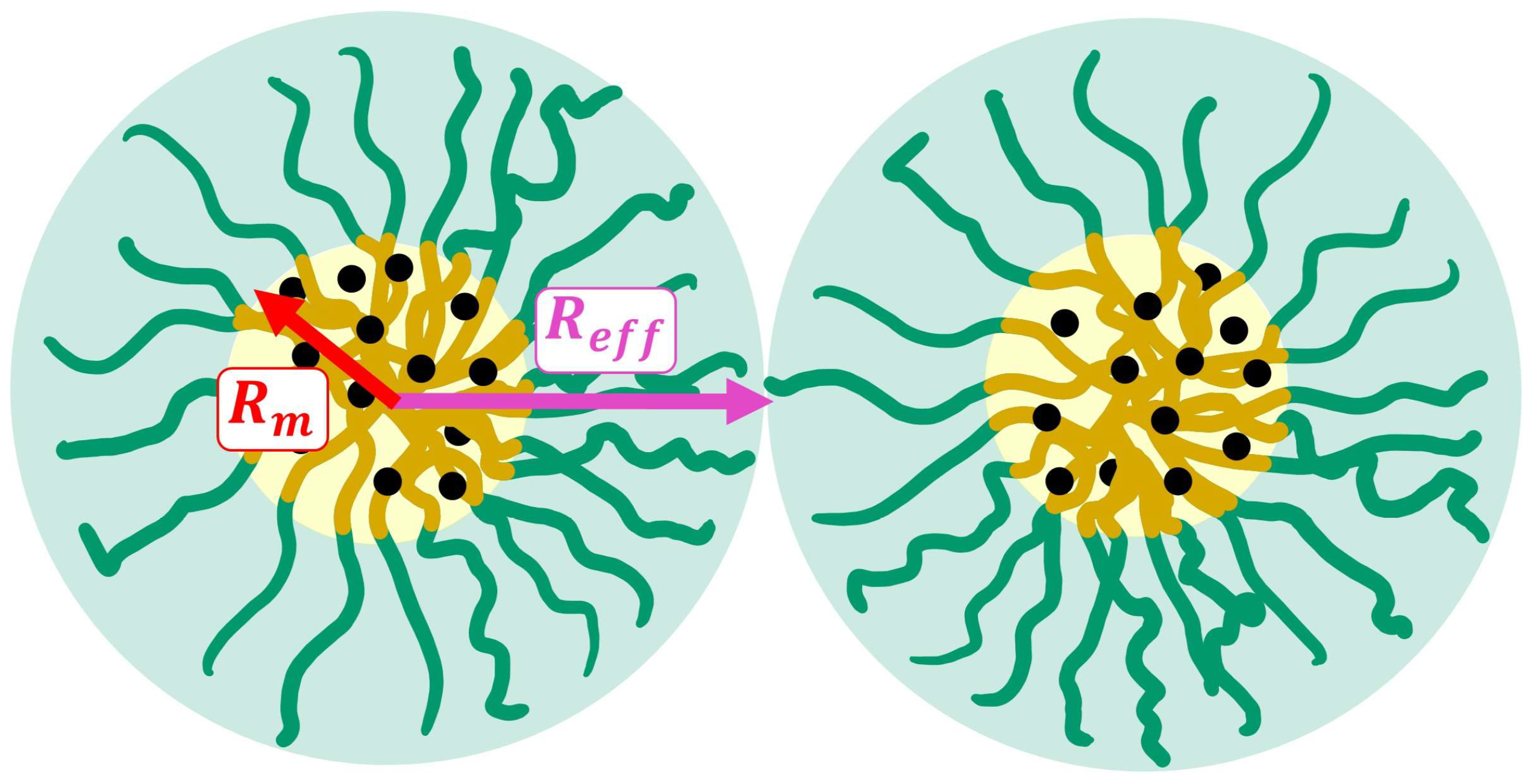
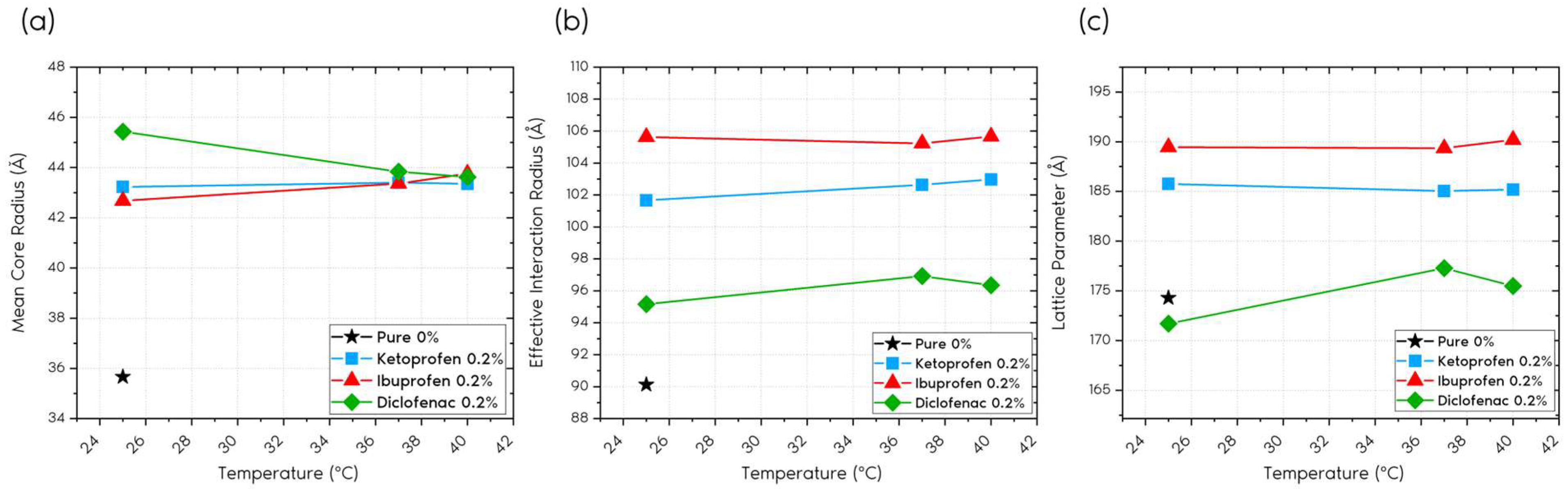
2.1.1. Form Factor
2.1.2. Structure Factor
2.1.3. Polydispersity
2.1.4. Ordered Contribution
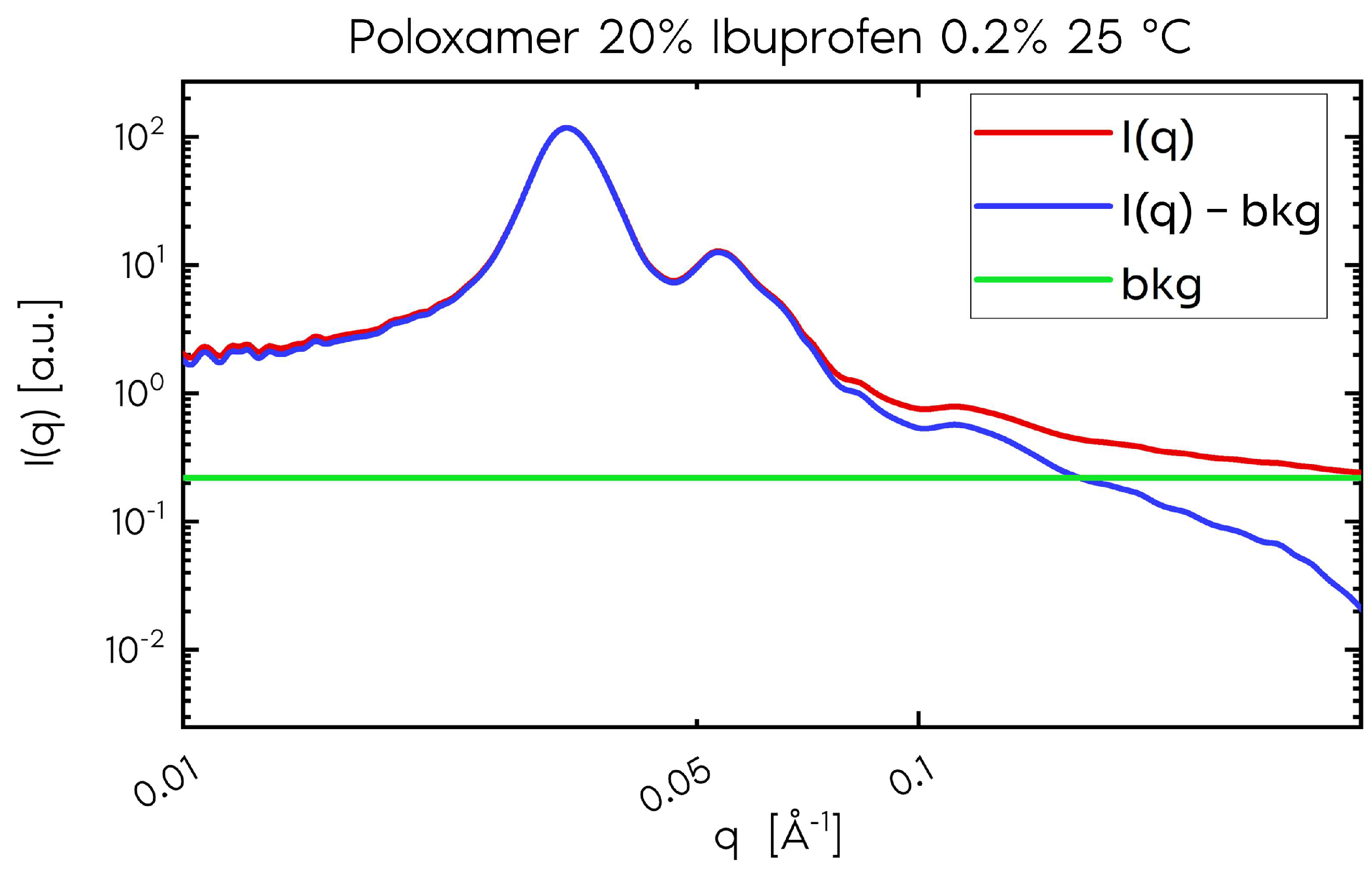
2.1.5. Porod Constant
2.2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
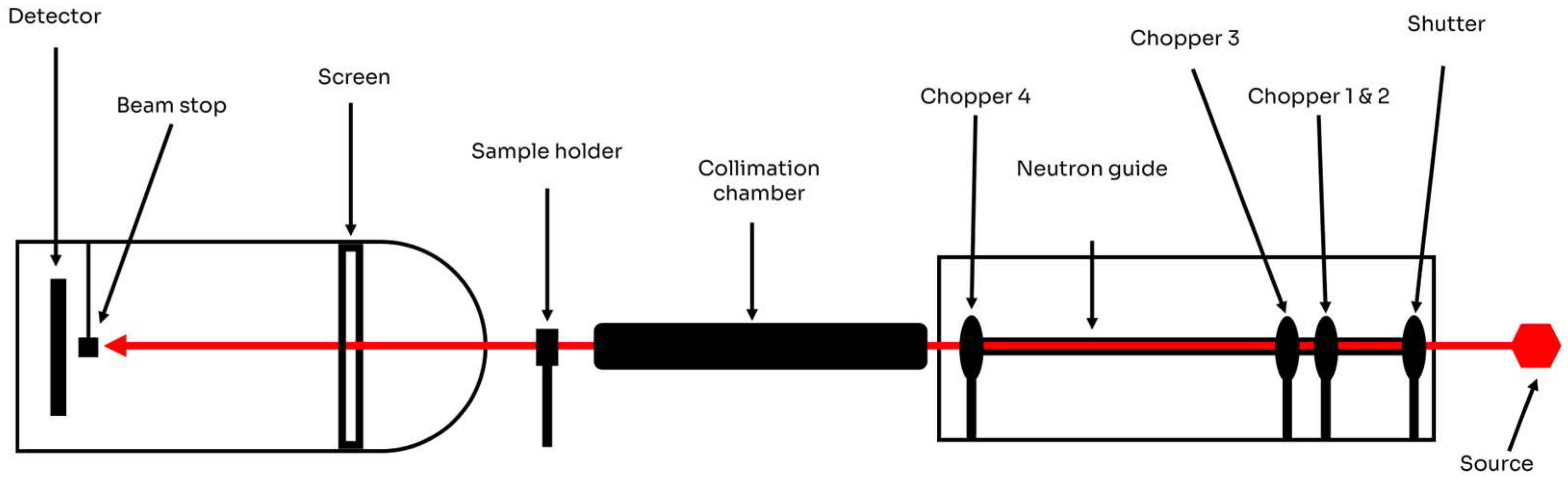
4.2. Experimental Setup
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarrintaj, P.; Ramsey, J.D.; Samadi, A.; Atoufi, Z.; Yazdi, M.K.; Ganjali, M.R.; Amirabad, L.M.; Zangene, E.; Farokhi, M.; Formela, K.; et al. Poloxamer: A versatile tri-block copolymer for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 110, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodratti, A.M.; Alexandridis, P. Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, H.; Miyata, K.; Osada, K.; Kataoka, K. Block Copolymer Micelles in Nanomedicine Applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6844–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, D.H.; Anggadiredja, K.; Rachmawati, H. Mini-review of poloxamer as a biocompatible polymer for advanced drug delivery. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 58, e21125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, Y.M.; Ghaly, E.S. Modified drug release of poloxamer matrix by including water-soluble and water-insoluble polymer. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, D.; Burgalassi, S.; Rossato, M.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Rodriguez, L.; Chetoni, P. Poloxamer 407 microspheres for orotransmucosal drug delivery. Part II: In vitro/in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.P.; Rai, V.K.; Pradhan, D.; Halder, J.; Rajwar, T.K.; Mahanty, R.; Saha, I.; Mishra, A.; Dash, P.; Dash, C.; et al. A doxorubicin loaded chitosan–poloxamer in situ implant for the treatment of breast cancer. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33952–33967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. The mechanism of action of aspirin. Thrombosis Res. 2003, 110, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelidou, A.S.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): A comparative QSAR study. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3235–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainsford, K.D. Ibuprofen: Pharmacology, efficacy, and safety. Inflammopharmacology 2009, 17, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, G.A. Cardiovascular pharmacology of nonselective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and coxibs: Clinical considerations. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazaleuskaya, L.L.; Theken, K.N.; Gong, L.; Thorn, C.F.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB summary: Ibuprofen pathways. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2025, 25, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiffen, P.J.; Xia, J. Systematic review of topical diclofenac for the treatment of acute and chronic musculoskeletal pain. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 36, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Atzeni, F.; Lanata, L.; Bagnasco, M.; Colombo, M.; Fischer, F.; D’Imporzano, M. Pain and ketoprofen: What is its role in clinical practice. Reumatismo 2010, 62, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjoribanks, J.; Ayeleke, R.; Farquhar, C.; Proctor, M. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for dysmenorrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, 4, CD001751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, J.; Afrose, A.; Islam, N. Formulation and delivery strategies of ibuprofen: Challenges and opportunities. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drini, M. Peptic ulcer disease and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aust. Prescr. 2017, 40, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Huang, J. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity: Pathogenic mechanisms, biomarkers and prevention strategies. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, C.; Varas-Lorenzo, C.; Castellsague, J.; Rodriguez, L.G. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of first hospital admission for heart failure in the general population. Heart 2006, 92, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Donnan, P.T.; Bell, S.; Guthrie, B. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced acute kidney injury in the community dwelling general population and people with chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Sabzwari, S.R.A.; Vargova, V. Cardiovascular risk of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: An under-recognized public health issue. Cureus 2017, 9, e1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanas, A.; Hunt, R. Prevention of anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal damage: Benefits and risks of therapeutic strategies. Ann. Med. 2006, 38, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedaya, M.; Bandarkar, F.; Nada, A. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ibuprofen nanosuspensions for enhanced oral bioavailability. Med. Princ. Pract. 2021, 30, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Sahani, V.; Patil, S. Review on Ketoprofen (Anti-Inflammatory Drug). J. Res. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 3, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, N.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: Structure, preparation and application. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaylov, V.; Tosheva, M.; Petrov, V.; Titeva, S. Technological approaches to increase the bioavailability of Ibuprofen. Pharmacia 2025, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamroży, M.; Kudłacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Drabczyk, A.; Krzan, M. Advanced drug carriers: A review of selected protein, polysaccharide, and lipid drug delivery platforms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A review of liposomes as a drug delivery system: Current status of approved products, regulatory environments, and future perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alem, C.M.A.; Metselaar, J.M.; van Kooten, C.; Rotmans, J.I. Recent advances in liposomal-based anti-inflammatory therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinozzi, F.; Alcaraz, J.-P.; Ortore, M.G.; Gayet, L.; Radulescu, A.; Martin, D.K.; Maccarini, M. Small-angle neutron scattering reveals the nanostructure of liposomes with embedded OprF porins of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Langmuir 2022, 38, 15026–15037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, L.; Mishra, H.; Semalty, M.; Semalty, A. Small angle Neutron scattering in drug discovery research: A novel tool for advanced study of structures of biological macromolecules. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2023, 20, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Lowe, J.P.; Schweins, R.; Edler, K.J. Small angle neutron scattering studies on the internal structure of poly (lactide-co-glycolide)-block-poly (ethylene glycol) nanoparticles as drug delivery vehicles. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinier, A.; Fournet, G. Small Angle Scattering of X-Rays; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Jaclsch, S. Small-Angle Scattering. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.07353. [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim, M. Exact solution of the Percus-Yevick integral equation for hard spheres. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1963, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinning, D.J.; Thomas, E.L. Hard-sphere interactions between spherical domains in diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, N.W.; Lekner, R.J. Structure and resistivity of liquid metals. Phys. Rev. 1966, 145, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletto, V.; Caillet, C.; Fundin, J.; Hamley, I.W.; Yang, Z.; Kelarakis, A. The liquid–solid transition in a micellar solution of a diblock copolymer in water. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 10947–11095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, F.; Higashi, K.; Ueda, K.; Morita, T.; Iohara, D.; Hirayama, F.; Moribe, K. Effect of Acetaminophen on Poloxamer 407 Micelles and Hydrogels: The Relationship between Structural and Physical Properties. Langmuir 2024, 40, 15610–15620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepulveda, A.F.; Kumpgdee-Vollrath, M.; Franco, M.K.; Yokaichiya, F.; de Araujo, D.R. Supramolecular structure organization and rheological properties modulate the performance of hyaluronic acid-loaded thermosensitive hydrogels as drug-delivery systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 630, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Sun, Z.; An, L.; Huang, Q. Investigation of sol- gel transition in Pluronic F127/D2O solutions using a combination of small-angle neutron scattering and Monte Carlo simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 26424–26429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.; Hu, W.; Houston, J.E.; Dreiss, C.A. Solubilisation of salicylate in F127 micelles: Effect of pH and temperature on morphology and interactions with cyclodextrin. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.S. Determination of size distribution from small-angle scattering data for systems with effective hard-sphere interactions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1994, 27, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.S.; Gerstenberg, M.C. Scattering form factor of block copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 1363–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.S. Form factors of block copolymer micelles with spherical, ellipsoidal and cylindrical cores. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2000, 33, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, T. Targetable Biodegradable Nanoparticles for Delivery of Chemotherapeutic and Imaging Agents to Ovarian Cancer; The University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-549-34761-3. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.M.; Hwang, C.S.; Yoon, Y.S.; Park, I.J.; Yoo, M.W.; Kim, B.S. Novel temperature-responsive hydrogel injected to the incision site for postoperative pain relief in laparoscopic abdominal surgery: A single-blind, randomized, pivotal clinical trial. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 5794–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmolka, I.R. Artificial skin I. Preparation and properties of pluronic F-127 gels for treatment of burns. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1972, 6, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| BCC | FCC |
|---|---|
| Name | Concentration (%) | Temperature (°C) | Rm (Å) | Rm2 (Å) | bkg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure | 0 | 25 | 35.66 | 8.20 | 10.30 | 1.38 | 0.031 |
| Ketoprofen | 0.2 | 25 | 43.23 | 9.87 | 6.32 | 1.67 | 0.016 |
| 37 | 43.40 | 10.82 | 7.93 | 1.79 | 0.017 | ||
| 40 | 43.35 | 10.81 | 7.53 | 2.25 | 0.017 | ||
| Ibuprofen | 25 | 42.68 | 9.50 | 7.17 | 1.78 | 0.017 | |
| 37 | 43.36 | 9.60 | 7.65 | 1.80 | 0.017 | ||
| 40 | 43.76 | 9.88 | 7.60 | 1.90 | 0.018 | ||
| Diclofenac | 25 | 45.43 | 8.33 | 6.44 | 2.01 | 0.033 | |
| 37 | 43.83 | 9.52 | 8.87 | 2.69 | 0.010 | ||
| 40 | 43.62 | 8.41 | 10.23 | 1.89 | 0.024 |
| Name | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Reff (Å) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure | 174.29 | 90.12 | 0.46 | 0.0025 | 10.12 | 3.97 | 1.36 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| Ketoprofen | 185.76 | 101.66 | 0.48 | 0.0030 | 9.68 | 2.00 | 2.22 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 185.05 | 102.63 | 0.50 | 0.0030 | 9.83 | 4.00 | 2.15 | 0.08 | 0.10 | |
| 185.18 | 102.97 | 0.50 | 0.0029 | 9.83 | 3.96 | 2.13 | 0.07 | 0.09 | |
| Ibuprofen | 189.46 | 105.63 | 0.50 | 0.0026 | 10 | 4.00 | 1.30 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 189.34 | 105.23 | 0.49 | 0.0026 | 10 | 4.00 | 1.30 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 190.20 | 105.66 | 0.50 | 0.0026 | 10 | 4.00 | 1.30 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Diclofenac | 171.70 | 95.17 | 0.50 | 0.0029 | 10 | 4.00 | 1.30 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 177.28 | 96.92 | 0.53 | 0.0028 | 10.48 | 4.50 | 1.70 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| 175.47 | 96.35 | 0.51 | 0.0029 | 10.32 | 4.17 | 1.19 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Drug | Concentration (%) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | 0 | 25 |
| Diclofenac | 0.2 | 25, 37, 40 |
| Ketoprofen | 0.2 | 25, 37, 40 |
| Ibuprofen | 0.2 | 25, 37, 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rhinow, R.; Franco, M.K.K.D.; Vollrath, M.K.; Kellermann, G.; Yokaichiya, F. Poloxamer-Driven Drug Delivery System for Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Approach. Gels 2025, 11, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060410
Rhinow R, Franco MKKD, Vollrath MK, Kellermann G, Yokaichiya F. Poloxamer-Driven Drug Delivery System for Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Approach. Gels. 2025; 11(6):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060410
Chicago/Turabian StyleRhinow, Rodrigo, Margareth K. K. D. Franco, Mont Kumpugdee Vollrath, Guinther Kellermann, and Fabiano Yokaichiya. 2025. "Poloxamer-Driven Drug Delivery System for Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Approach" Gels 11, no. 6: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060410
APA StyleRhinow, R., Franco, M. K. K. D., Vollrath, M. K., Kellermann, G., & Yokaichiya, F. (2025). Poloxamer-Driven Drug Delivery System for Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Approach. Gels, 11(6), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060410









