pH-Responsive Nanogels from Bioinspired Comb-like Polymers with Hydrophobic Grafts for Effective Oral Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Characterization of pH-Responsive Comb-like Polymers
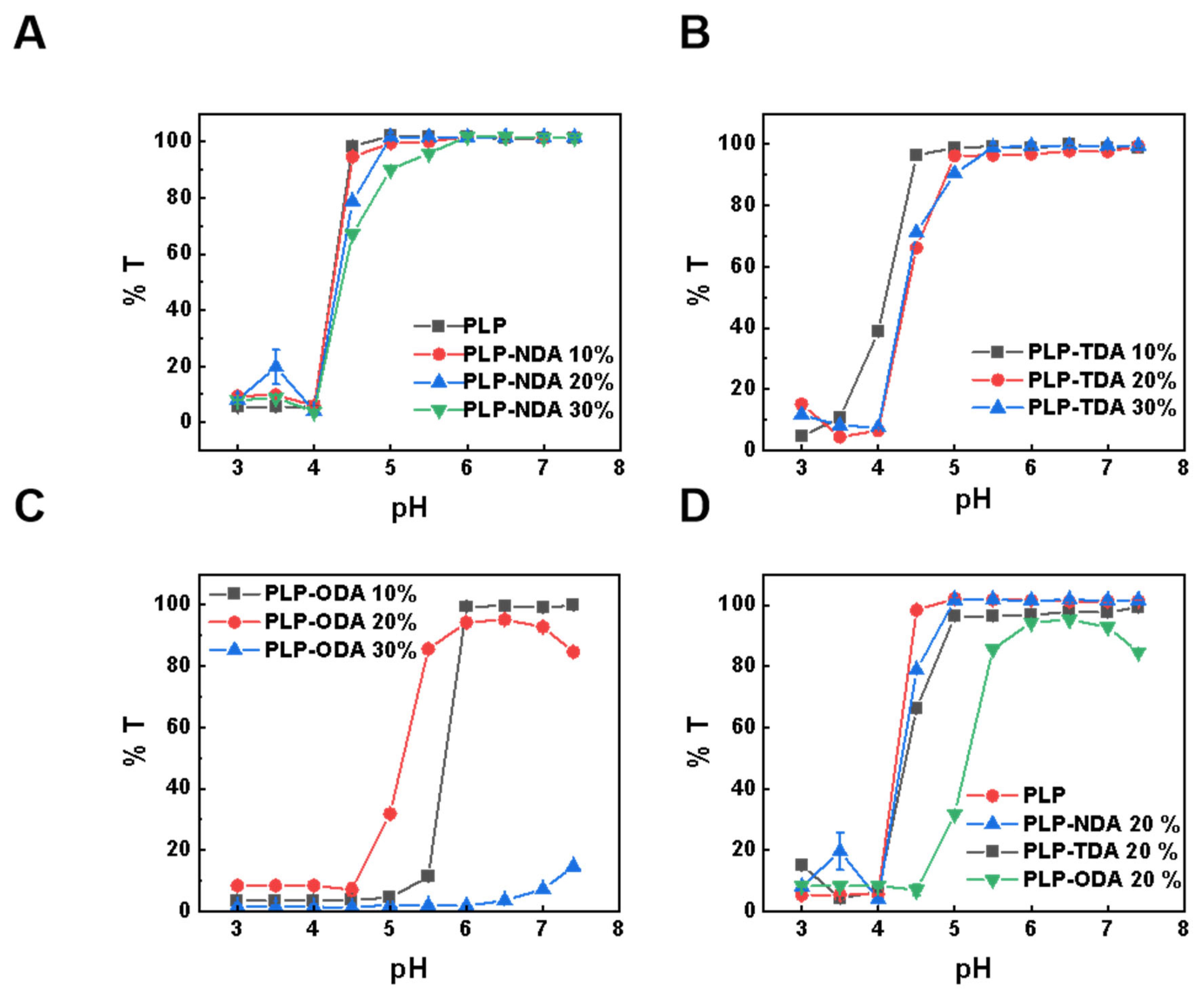
2.2. Aqueous Solution Properties
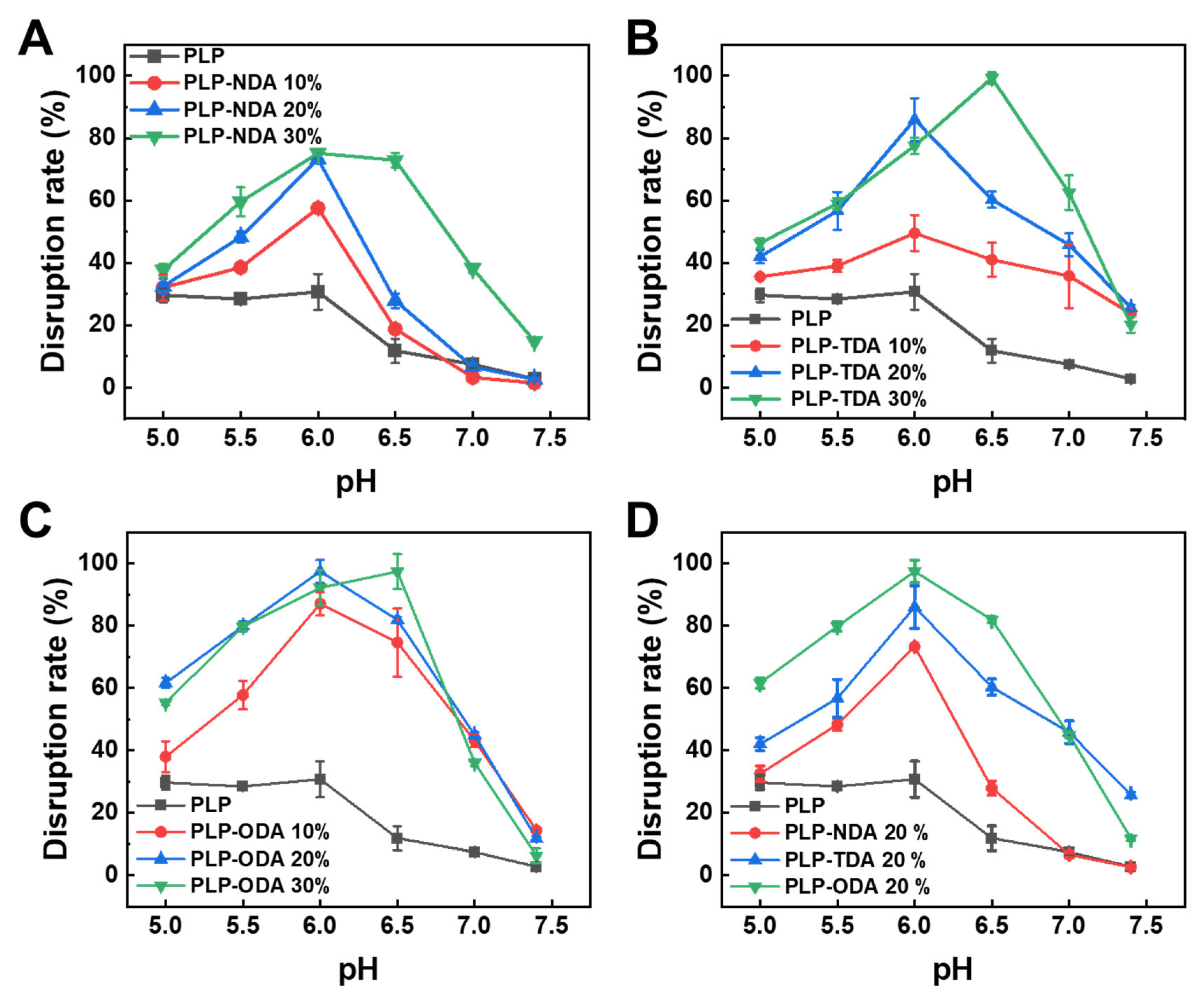
2.3. pH-Responsive Membrane Destabilization
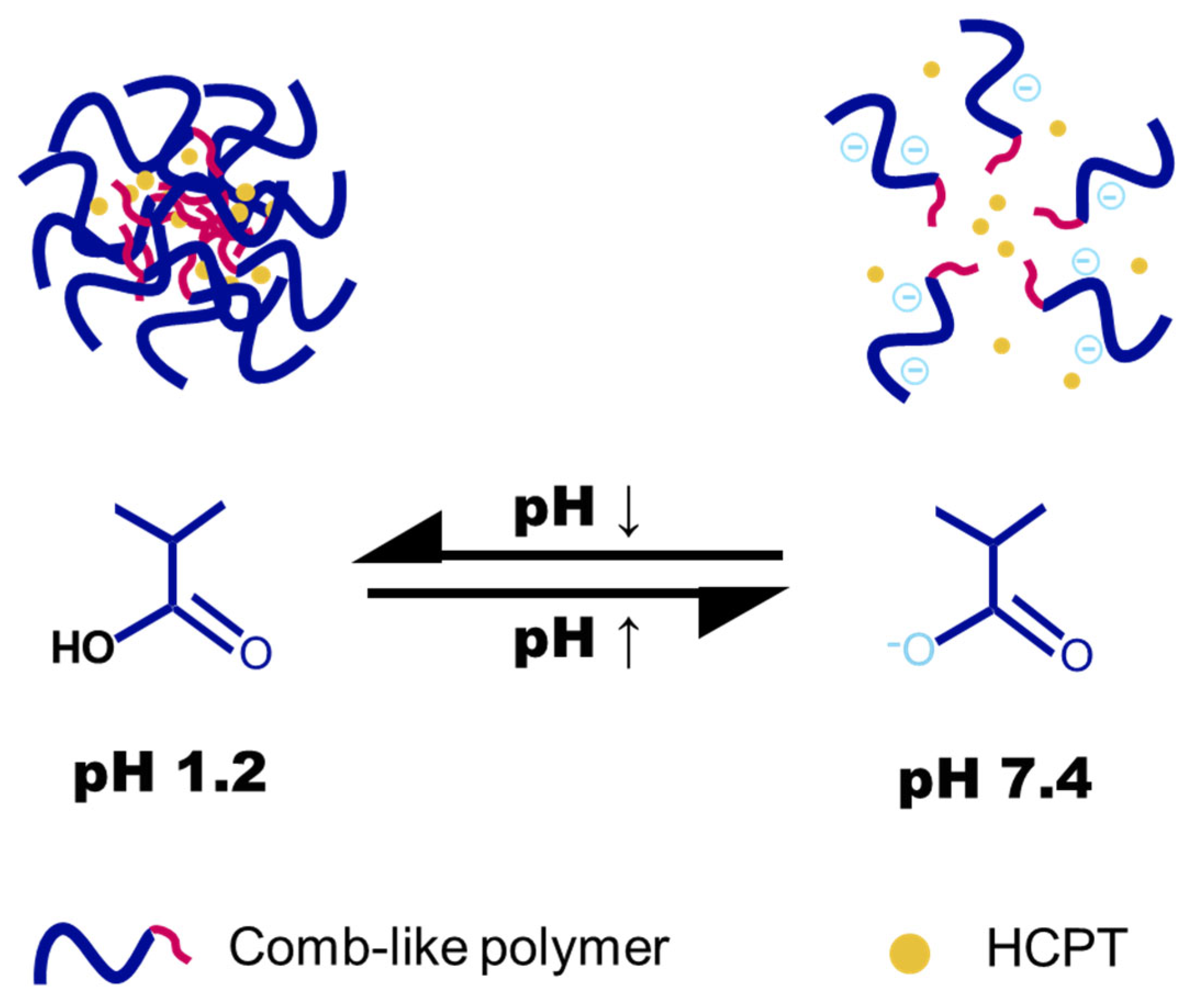
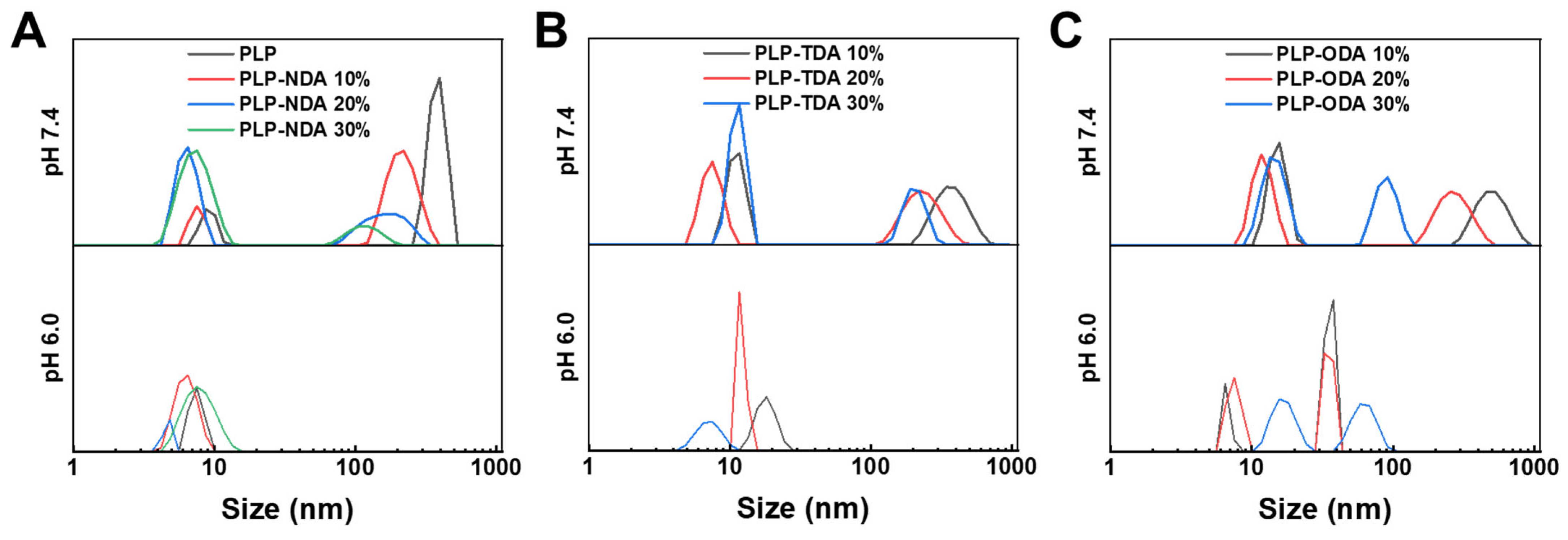
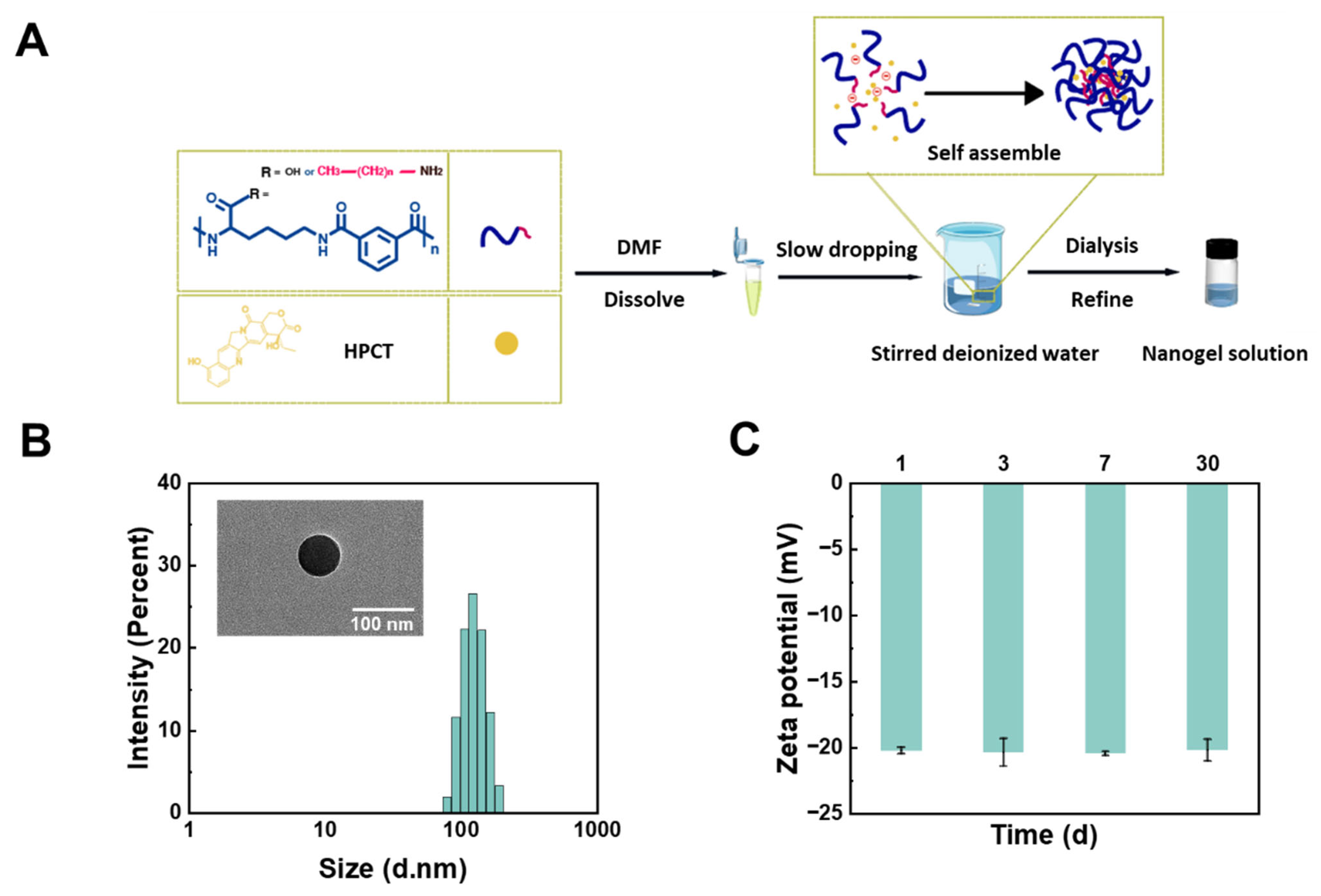
2.4. Preparation and Characterization of Nanogels
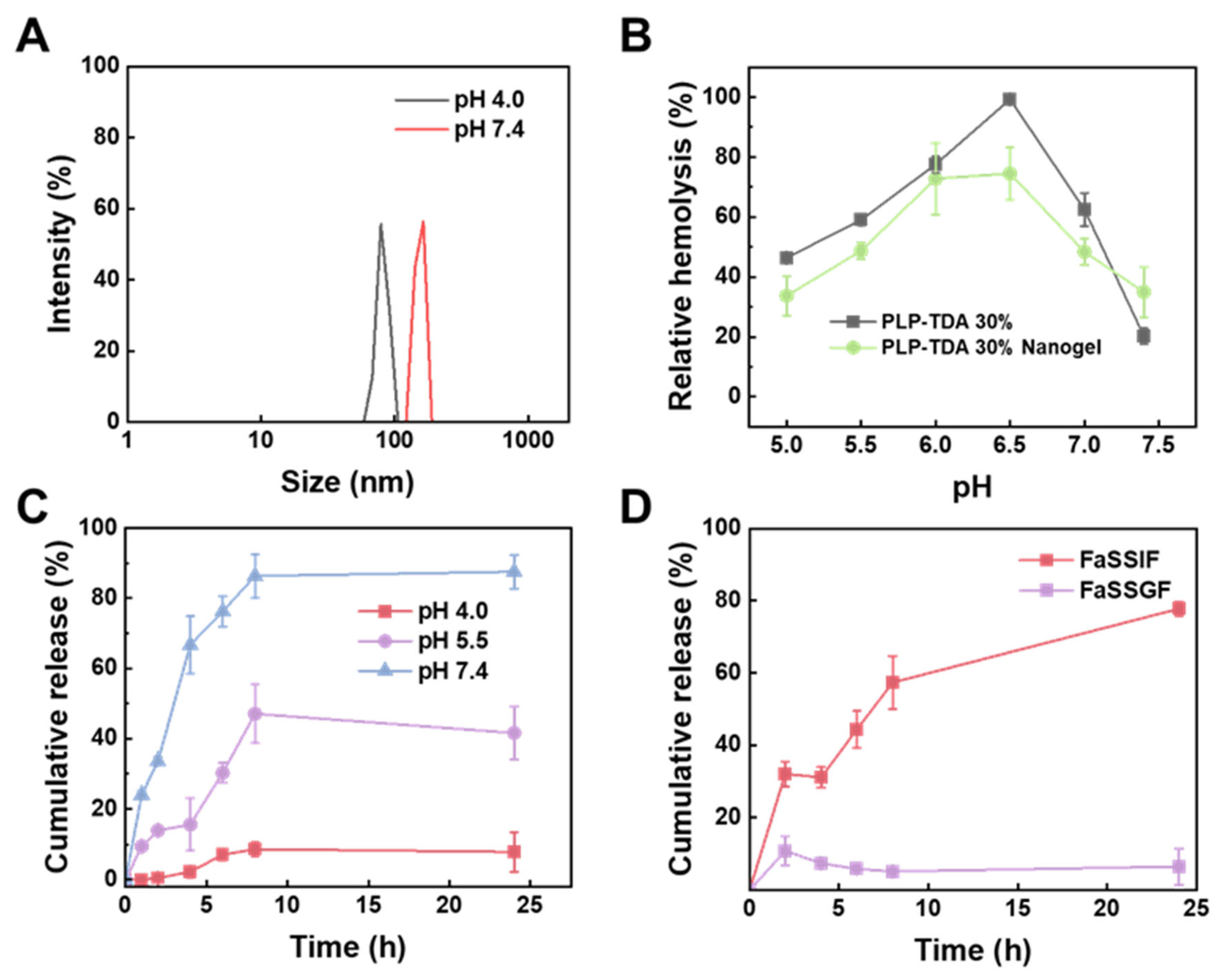
2.5. pH-Responsiveness of Nanogel
2.6. Cellular Uptake
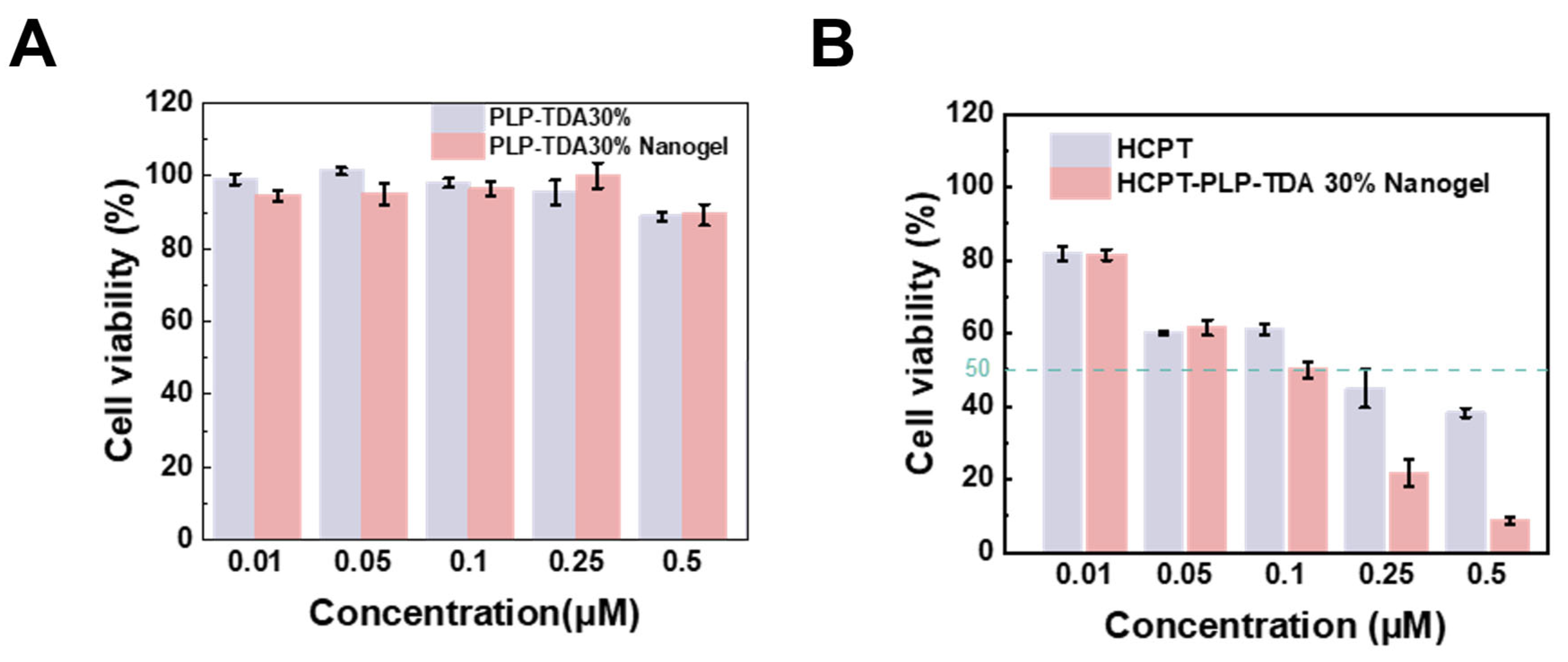
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of pH-Responsive Comb Polymers
4.3. Structural Characterization
4.4. Turbidity Measurement
4.5. CAC Determination
4.6. pH-Responsive Membrane Destabilization Assay
4.7. Preparation of Nanogels
4.8. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurement
4.9. EE and DL
4.10. In Vitro Drug Release
4.11. Cell Culture
4.12. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4.13. Cellular Uptake
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, A.; Castro, F.; Resende, C.; Lúcio, M.; Schwartz, S.; Sarmento, B. Oral Delivery of Camptothecin-Loaded Multifunctional Chitosan-Based Micelles Is Effective in Reduce Colorectal Cancer. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Arora, M.; Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. Oral Drug Delivery Technologies—A Decade of Developments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinholz, J.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V. The Challenges of Oral Drug Delivery via Nanocarriers. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejazi, S.A.; Louisthelmy, R.; Maisel, K. Mechanisms of Nanoparticle Transport across Intestinal Tissue: An Oral Delivery Perspective. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 13044–13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kuhar, S.; Seo, J.-H.; Pasricha, P.J.; Mittal, R. Computational Modeling of Drug Dissolution in the Human Stomach: Effects of Posture and Gastroparesis on Drug Bioavailability. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 81904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Ma, M.; Peng, X.; Xie, Y.; Xie, A.; Deng, B.; Ouyang, J.; Tao, W.; Yang, P.; He, W. Oral Delivery Strategies for Biological Drugs. Small Methods 2025, 8, 2401355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, G.; Cui, H.; Tian, Z.; Li, B.; Han, Y.; Wu, J.-X.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. Theoretical Basis, State and Challenges of Living Cell-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Theranostics 2024, 14, 5152–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, G. Challenges in the Therapeutic Exploitation of Chemokine Receptor-Mediated Internalization of Nanocarriers. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2024, 29, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, M.S.; Kazi, M.; Alsenaidy, M.A.; Ahmad, M.Z. Advances in Oral Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 618411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, B.; Ma, D.; Peng, M.; Mao, H.; Liu, W.; Gu, Z.; Chen, S. Virus Mimicking Liposomes Incorporated Microneedles Delivery Platform for Efficient Skin Penetration and Enhanced Cellular Uptake. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 99, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeva, L.; Yoncheva, K. Nanogels—Innovative Drug Carriers for Overcoming Biological Membranes. Gels 2025, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausig, F.; Sobotta, F.H.; Richter, F.; Harz, D.O.; Traeger, A.; Brendel, J.C. Correlation between Protonation of Tailor-Made Polypiperazines and Endosomal Escape for Cytosolic Protein Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35233–35247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, M.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, S.B.; Naito, M.; Miyata, K. Recent Progress in the Endosomal Escape Mechanism and Chemical Structures of Polycations for Nucleic Acid Delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24, 2300366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Bon, A.; Gumerova, N.I.; Tanuhadi, E.; Ashjari, M.; Chen, Y.; Rompel, A.; Nau, W.M. All-inorganic Polyoxometalates Act as Superchaotropic Membrane Carriers. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2309219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donders, E.N.; Slaughter, K.V.; Dank, C.; Ganesh, A.N.; Shoichet, B.K.; Lautens, M.; Shoichet, M.S. Synthetic Ionizable Colloidal Drug Aggregates Enable Endosomal Disruption. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, L.P.; Lewis, J.S.; Evans, B.C.; Duvall, C.L.; Keselowsky, B.G. Formulation and Characterization of Poly(Propylacrylic Acid)/Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Blend Microparticles for pH-Dependent Membrane Disruption and Cytosolic Delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackey, C.A.; Press, O.W.; Hoffman, A.S.; Stayton, P.S. A Biomimetic pH-Responsive Polymer Directs Endosomal Release and Intracellular Delivery of an Endocytosed Antibody Complex. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.G.; De, P. pH Responsive Polymers with Amino Acids in the Side Chains and Their Potential Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Laurén, P.; Zini, J.; Gounani, Z.; Bi, J.; Yi, J.; Laaksonen, T. Amidated Pectin/Nanocellulose Hybrid Cryogel System with a pH-Responsive Release Profile for Small Intestinal Delivery. Gels 2025, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Omarova, M.; Zhang, M.; Hossain, I.; Chen, J.; Darvish, O.; John, V.T.; Zhang, D. Uncovering the Optimal Molecular Characteristics of Hydrophobe-Containing Polypeptoids to Induce Liposome or Cell Membrane Fragmentation. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Kopytynski, M.; Bachelet, M.; Chen, R. Membrane-Anchoring, Comb-Like Pseudopeptides for Efficient, pH-Mediated Membrane Destabilization and Intracellular Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8021–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wu, L.; Ren, J.; Bemmer, V.; Zajicek, R.; Chen, R. Comb-like Pseudopeptides Enable Very Rapid and Efficient Intracellular Trehalose Delivery for Enhanced Cryopreservation of Erythrocytes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, acsami.0c03260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Morrison, G.; Liu, W.; Kaur, A.; Chen, R. A pH-Responsive, Endosomolytic Liposome Functionalized with Membrane-Anchoring, Comb-like Pseudopeptides for Enhanced Intracellular Delivery and Cancer Treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 6718–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Whymark, K.D.; Sydenham, J.; Sneddon, H.F. A Solvent-Reagent Selection Guide for Steglich-Type Esterification of Carboxylic Acids. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 6405–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Bo, H.; Ma, D.; Peng, M.; Liu, Q.; Heng, Z.; Gu, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. pH and Glucose Dual-Responsive Phenylboronic Acid Hydrogels for Smart Insulin Delivery. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 8855–8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Y.; Li, T.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, F.; Jia, L.; Liu, W.; Gai, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, W.; Yang, X. pH-Sensitive and Folic Acid-Targeted MPEG-PHIS/FA-PEG-VE Mixed Micelles for the Delivery of PTX-VE and Their Antitumor Activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5863–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Selianitis, D.; Pispas, S. Thermo- and pH-Responsive Poly[(Diethylene Glycol Methyl Ether Methacrylate)- Co -(2-Diisopropylamino Ethyl Methacrylate)] Hyperbranched Copolymers: Self-Assembly and Drug-Loading. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo, E.; Grimau, M.; Bello, A.; López-Carrasquero, F. Segmental Dynamics in Nanophase Separated Comb-like Polymers with Long Side Chains. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 4324–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Matsumura, Y.; Yano, S.; Ochiai, B. pH-Responsive Charge-Conversional and Hemolytic Activities of Magnetic Nanocomposite Particles for Cell-Targeted Hyperthermia. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodszkij, E.; Hviid, M.J.; Ade, C.; Schattling, P.S.; Burmeister, M.; Szilagyi, S.; Gal, N.; Zhu, C.; Han, X.; Städler, B. Interaction of pH-Responsive Polyanions with Phospholipid Membranes. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 5992–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulón Marruecos, D.; Kienle, D.F.; Kaar, J.L.; Schwartz, D.K. Grafting Density Impacts Local Nanoscale Hydrophobicity in Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Brushes. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Deng, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, W. Self-Assembled Nanogels Based on Ionic Gelation of Natural Polysaccharides for Drug Delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 703559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Goswami, S.; Das, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bhaladhare, S. pH-Responsive, Stable, and Biocompatible Functional Nanogels Based on Chitosan (CS)/Poly Methacrylic Acid (PMAA) Polymers: Synthesis and Characterization. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannat, N.E.; Alam, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hossain, M.K.; Hossain, S.; Minami, H.; Ahmad, H. Carboxylic Acid Modified pH-Responsive Composite Polymer Particles. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellular Uptake Mechanism and Intracellular Fate of Hydrophobically Modified Pullulan Nanoparticles—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23674894/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Poudel, S.; Mattheolabakis, G. Passive and Active Nucleic Acid Delivery against Colon Cancer Cells Using a Novel Nanocarrier Aimed for Oral Administration. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Heng, Z.; Ma, D.; Hou, B.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.; Gu, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, S. Iontophoresis-Integrated Smart Microneedle Delivery Platform for Efficient Transdermal Delivery and on-Demand Insulin Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 70378–70391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, S.R.; Verma, P.; Singh, R.; Kumar, P. Self-Assembled Micellar Nanostructures of Ursolic Acid-Polyethylene Glycol (UA-PEG) Conjugate as Efficient Drug Transporter System. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2021, 26, 100688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Li, P.; Yu, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Tong, G. Dual Network Hydrogel with High Mechanical Properties, Electrical Conductivity, Water Retention and Frost Resistance, Suitable for Wearable Strain Sensors. Gels 2023, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana-Linares, A.C.; Barrera-Ocampo, A.; Salamanca, C.H. Determination of the Critical Aggregation Concentration of Phospholipids Widely Used in Nanoliposomal Development from Different Experimental Methodologies. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 417, 126677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Chen, D.; Luo, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, W. Microneedle Delivery Platform Integrated with Codelivery Nanoliposomes for Effective and Safe Androgenetic Alopecia Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 15701–15717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Liu, X. Preparation of HCPT-Loaded Nanoneedles with Pointed Ends for Highly Efficient Cancer Chemotherapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, M.; Cui, L.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Peng, J.; Liu, Z. Ginger Vesicle as a Nanocarrier to Deliver 10-Hydroxycamptothecin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Feng, T.; Yang, X.; Nie, C.; Yu, L.; Ding, R.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, X.; Li, P. Gastrointestinal Microenvironment Responsive Nanoencapsulation of Probiotics and Drugs for Synergistic Therapy of Intestinal Diseases. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 14718–14730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Ji, H.; Liu, Z.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, H.; Nie, S.-P.; Wan, H. Modified Prebiotic-Based “Shield” Armed Probiotics with Enhanced Resistance of Gastrointestinal Stresses and Prolonged Intestinal Retention for Synergistic Alleviation of Colitis. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 14775–14791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Xin, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Gao, H. Oral Delivery of Clostridium butyricum Using Selective Antibacterial Lipids for Enhanced Treatment of Fusobacterium nucleatum-Associated Intestinal Diseases. Nano Today 2025, 62, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md, S.; Abdullah, S.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Alharbi, W.S.; Ahmad, J.; Shaik, R.A.; Ansari, M.J.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Ali, J. Development, Optimization, and in Vitro Evaluation of Novel Oral Long-Acting Resveratrol Nanocomposite in-Situ Gelling Film in the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Gels 2021, 7, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, L.; Rudewicz, P.J. Analysis of Live Single Cells by Confocal Microscopy and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry to Study Drug Uptake, Metabolism, and Drug-Induced Phospholipidosis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 16005–16015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Days | 0 d | 7 d | 14 d | 30 d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Size (nm) | |||||
| PLP-NDA 10% nanogel | 58.7 ± 0.7 | 63.4 ± 5.5 | 59.6 ± 2.2 | 60.0 ± 2.3 | |
| PLP-NDA 20% nanogel | 85.7 ± 3.0 | 85.2 ± 4.8 | 80.7 ± 4.0 | 78.4 ± 3.5 | |
| PLP-NDA 30% nanogel | 84.0 ± 4.5 | 84.4 ± 3.7 | 83.4 ± 2.6 | 83.0 ± 3.9 | |
| PLP-TDA 10% nanogel | 83.2 ± 0.7 | 78.7 ± 0.8 | 79.0 ± 1.3 | 83.5 ± 0.9 | |
| PLP-TDA 20% nanogel | 92.0 ± 0.4 | 82.6 ± 0.3 | 82.8 ± 1.6 | 96.7 ± 0.6 | |
| PLP-TDA 30% nanogel | 105.4 ± 1.8 | 101.0 ± 2.7 | 102.8 ± 1.8 | 105.1 ± 3.2 | |
| PLP-ODA 10% nanogel | 87.4 ± 6.7 | 82.4 ± 5.2 | 88.2 ± 8.8 | 91.0 ± 5.7 | |
| PLP-ODA 20% nanogel | 94.4 ± 9.2 | 101.7 ± 10.8 | 115.8 ± 11.5 | 106.3 ± 2.6 | |
| PLP-ODA 30% nanogel | 165.0 ± 13.2 | 177.7 ± 41.0 | 232.6 ± 61.9 | 252.5 ± 4.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Ma, D.; Cheng, H.; Yang, K.; Hou, B.; Heng, Z.; Qian, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, S. pH-Responsive Nanogels from Bioinspired Comb-like Polymers with Hydrophobic Grafts for Effective Oral Delivery. Gels 2025, 11, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100806
Liu Q, Ma D, Cheng H, Yang K, Hou B, Heng Z, Qian Y, Liu W, Chen S. pH-Responsive Nanogels from Bioinspired Comb-like Polymers with Hydrophobic Grafts for Effective Oral Delivery. Gels. 2025; 11(10):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100806
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qinglong, Dewei Ma, Haoze Cheng, Keke Yang, Bo Hou, Ziwen Heng, Yu Qian, Wei Liu, and Siyuan Chen. 2025. "pH-Responsive Nanogels from Bioinspired Comb-like Polymers with Hydrophobic Grafts for Effective Oral Delivery" Gels 11, no. 10: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100806
APA StyleLiu, Q., Ma, D., Cheng, H., Yang, K., Hou, B., Heng, Z., Qian, Y., Liu, W., & Chen, S. (2025). pH-Responsive Nanogels from Bioinspired Comb-like Polymers with Hydrophobic Grafts for Effective Oral Delivery. Gels, 11(10), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100806







