Biofunctional Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Incorporating Hyaluronic Acid and RGD Peptides for Accelerated Wound Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fabrication of CMCS Hydrogels
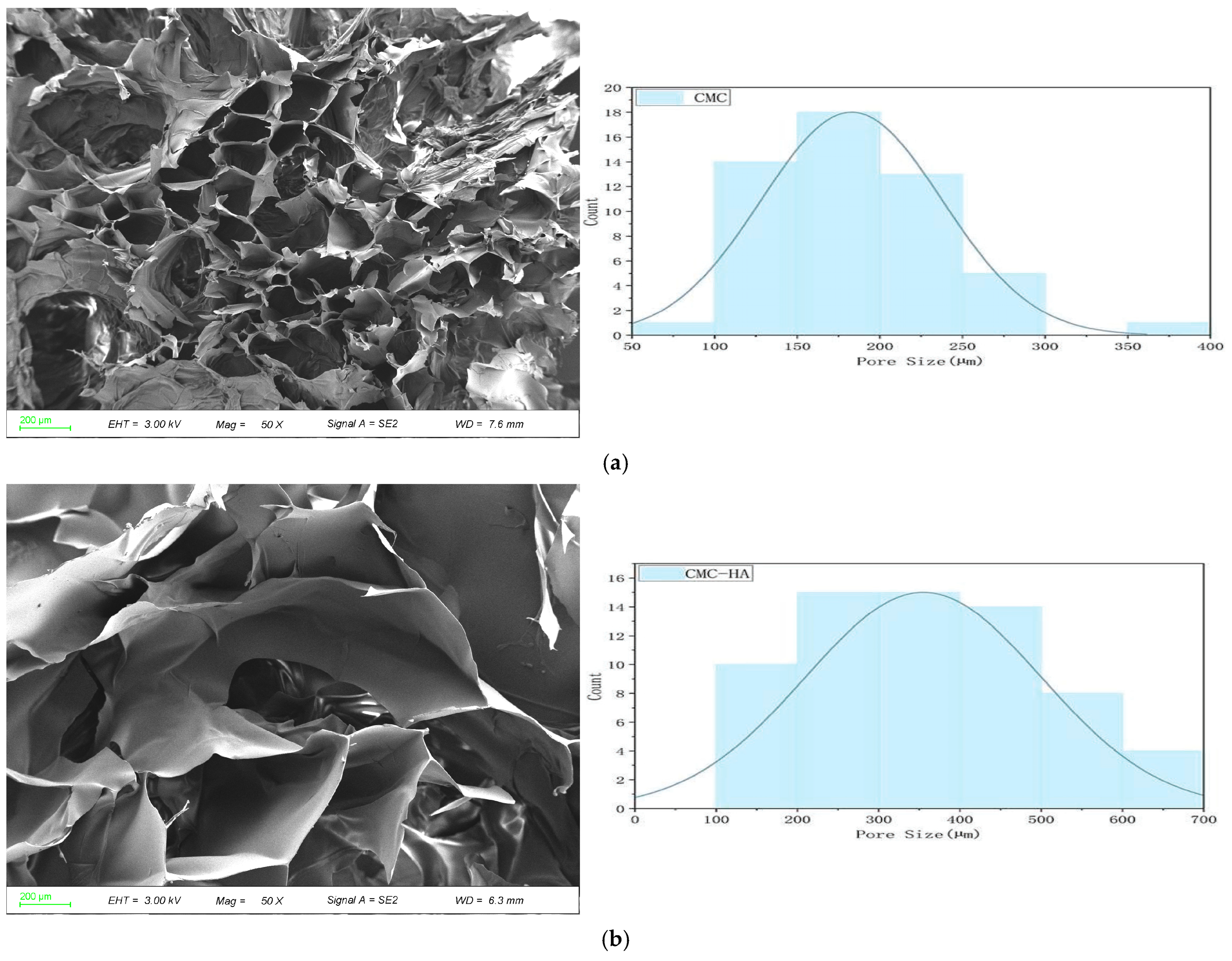
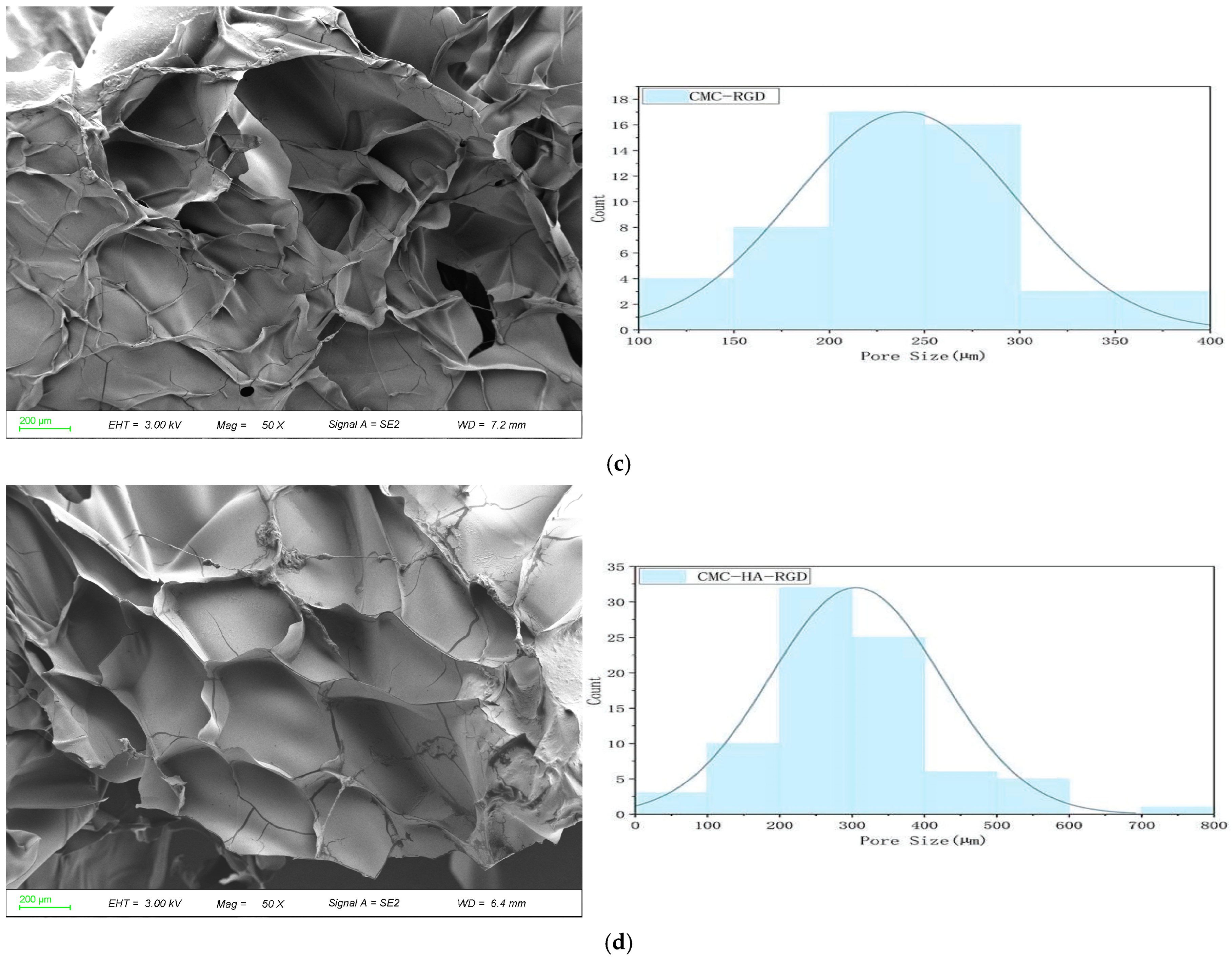
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. Physicochemical Properties
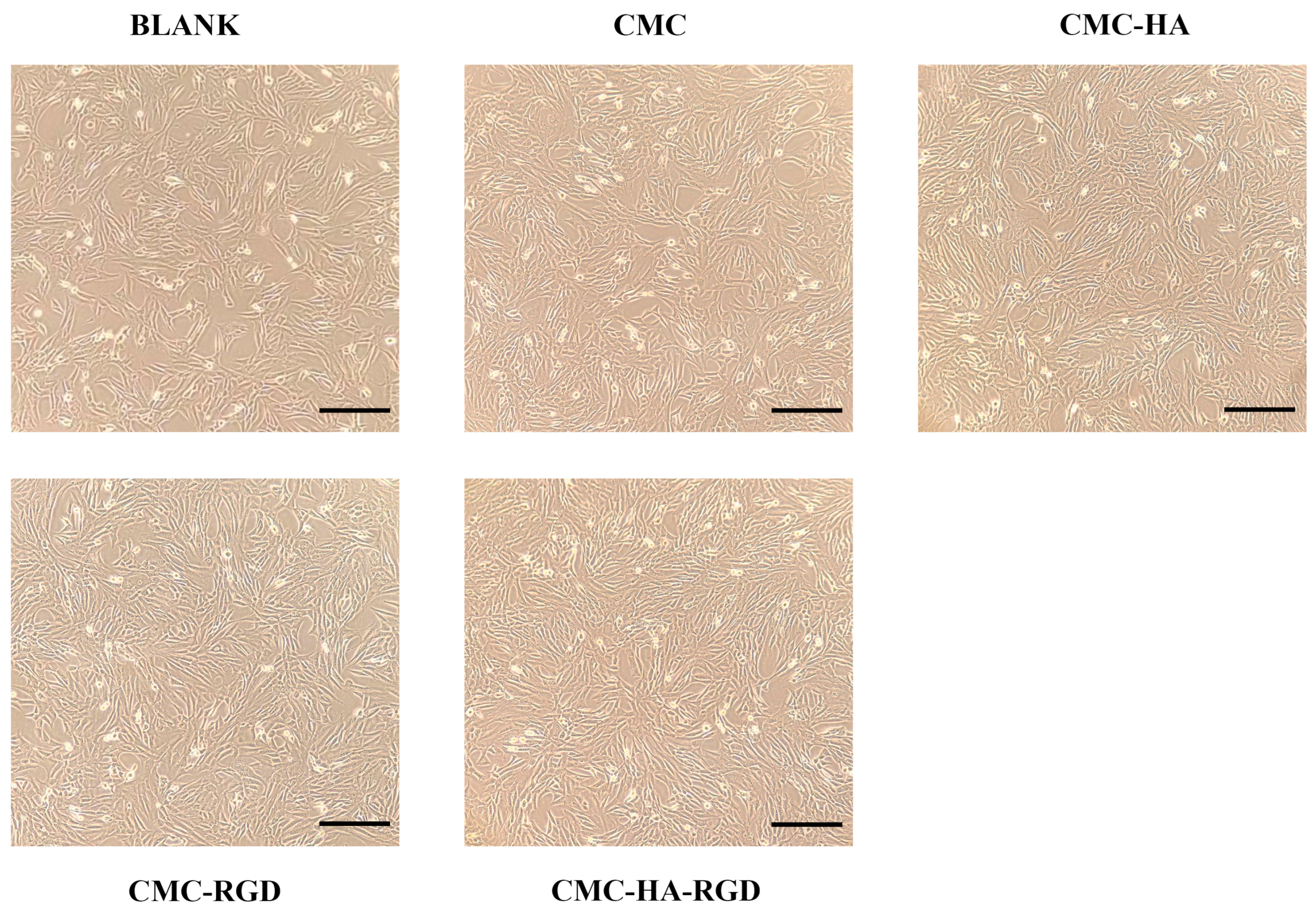
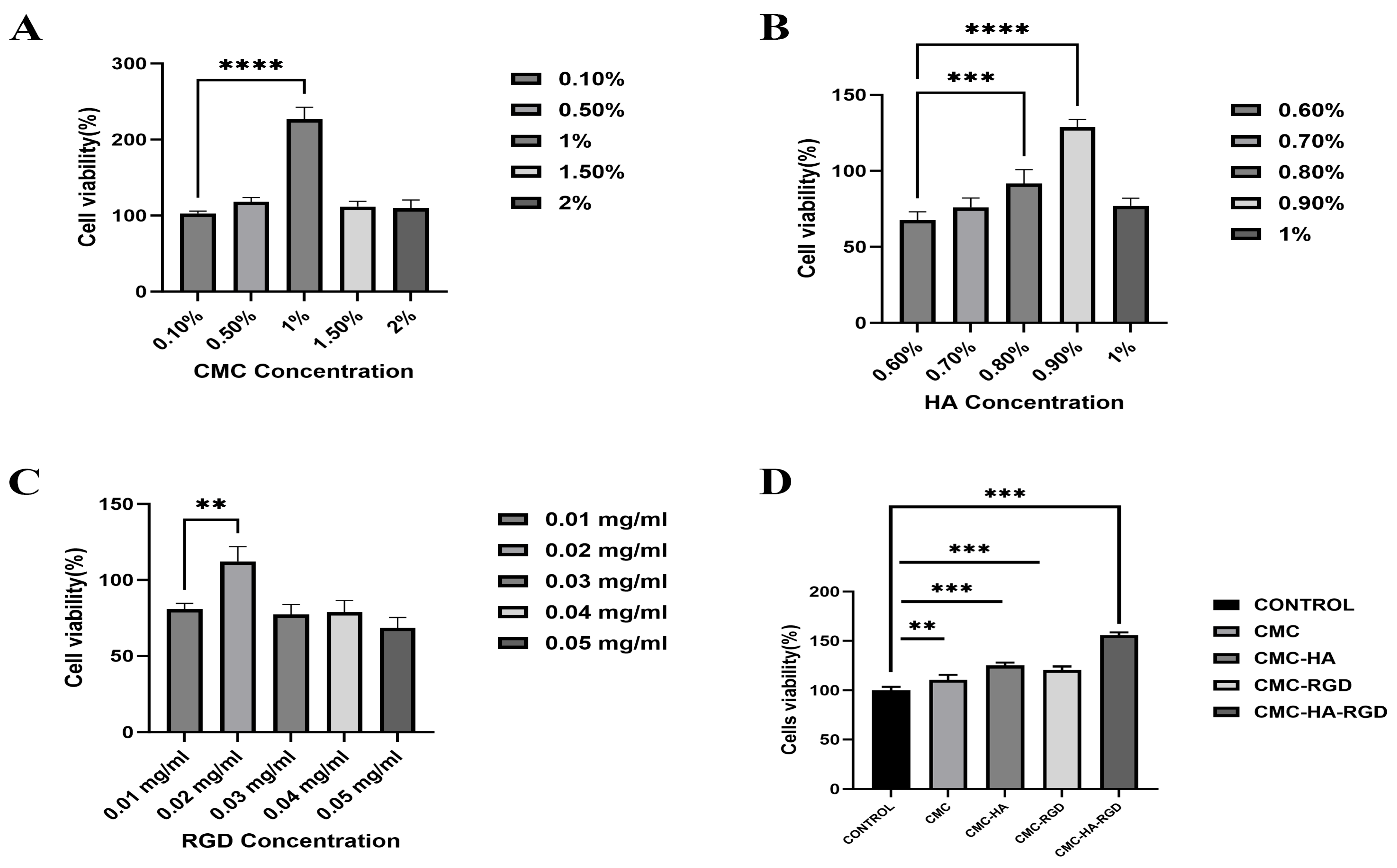
2.4. Cell Proliferation
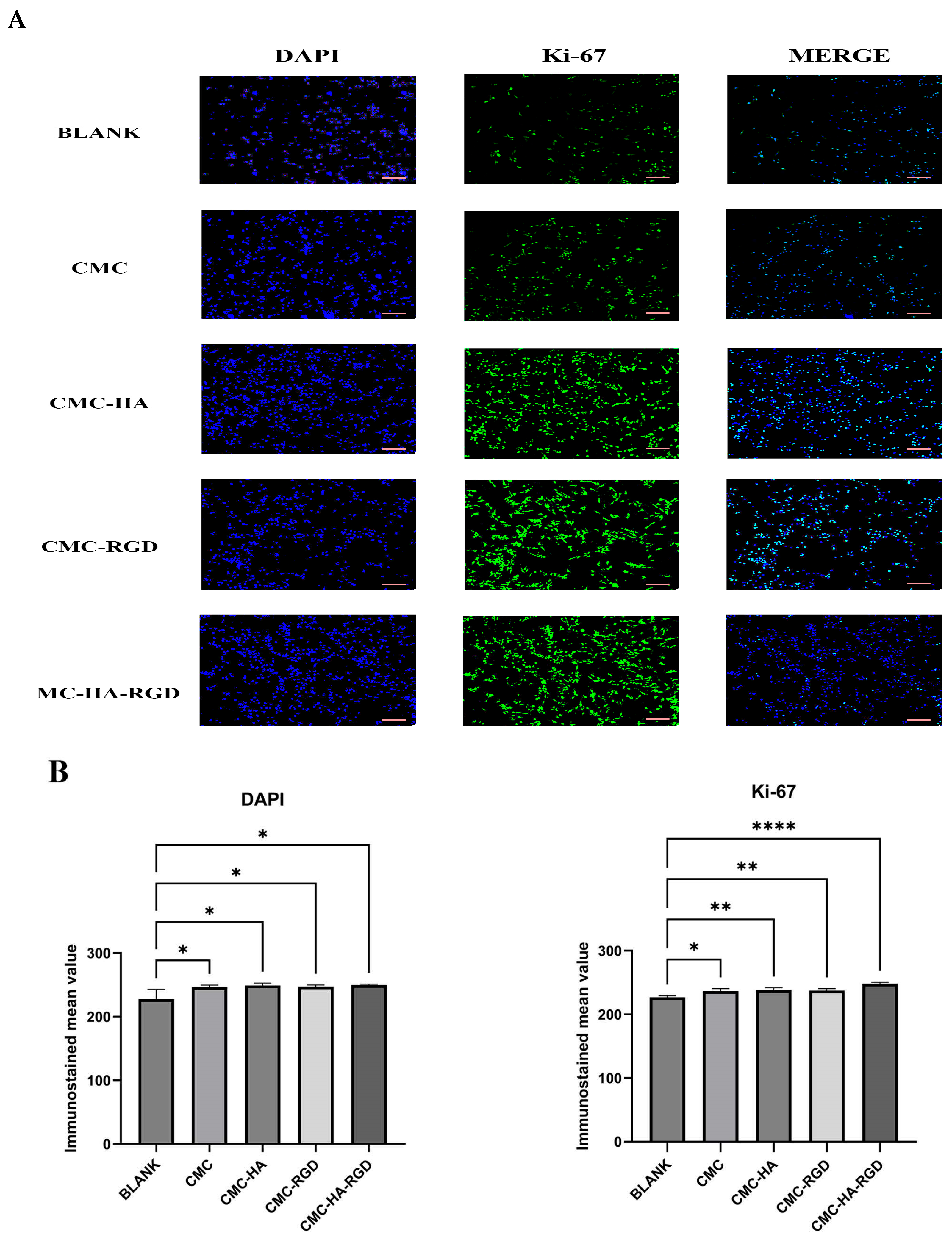
2.5. Fluorescence Staining
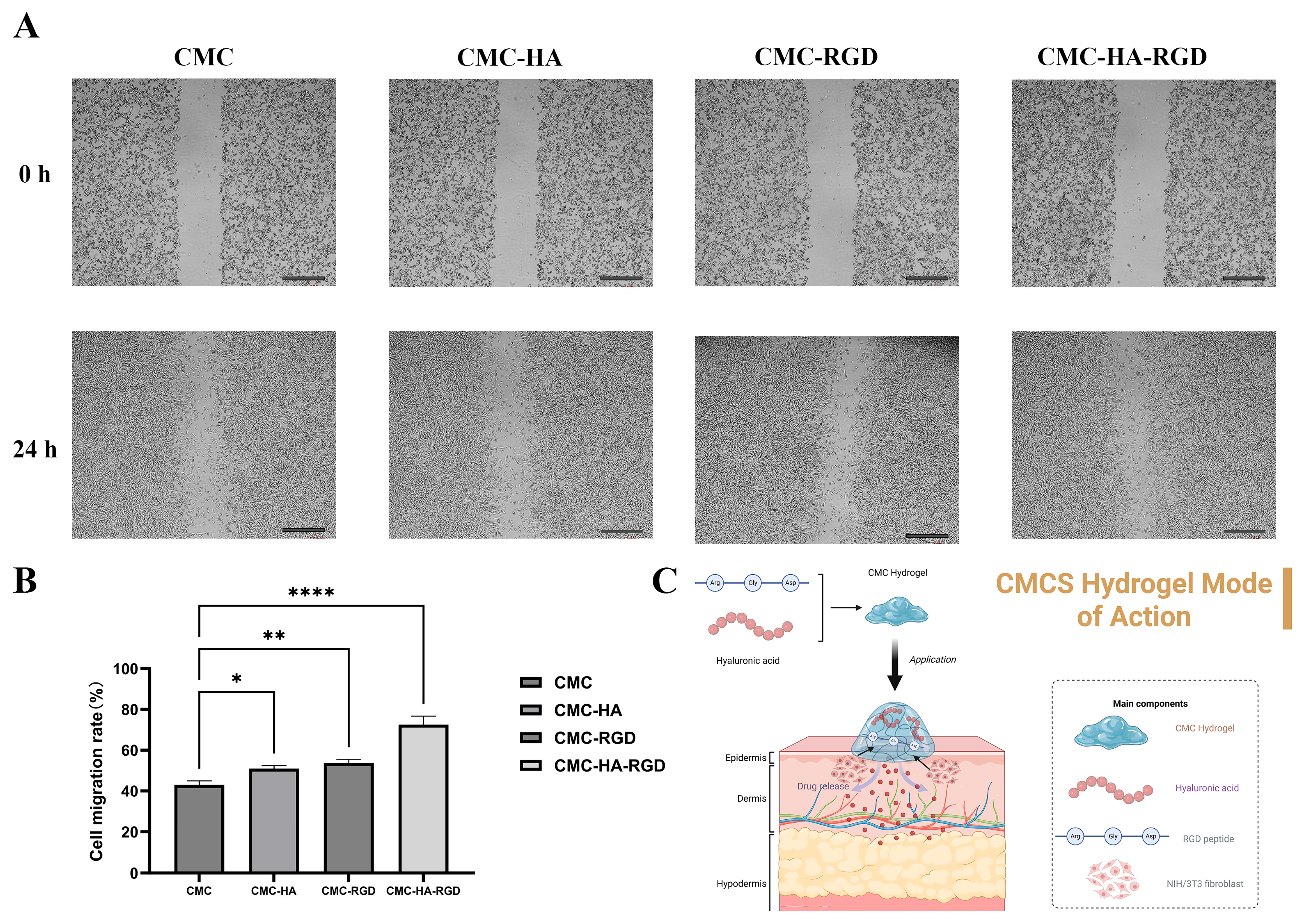
2.6. Cell Migration
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Optimization of CMCS Hydrogels
4.2. Fabrication Method of CMCS Hydrogels
4.3. Morphological Analysis of CMCS Hydrogels
4.4. Zeta Potential Measurement of CMCS Hydrogels
4.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of CMCS Hydrogels
4.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of CMCS Hydrogels
4.7. In Vitro Experiment
4.8. Hydrogel Sterilization for Cell Culture
4.9. Proliferation
4.10. Ki-67 Immunocytochemistry
4.11. Scratch Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, R.F.; Bártolo, P.J. Traditional Therapies for Skin Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 208–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Jin, S.H.; Peng, K.L.; Yang, Z.M.; Li, P.W.; Chen, Y. Preparation and properties of a fast curing carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel for skin care. Polym. Test. 2022, 113, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, G.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z. Photo-induced adhesive carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogels with antibacterial and antioxidant properties for accelerating wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 119000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevithan, L.; Shuyue, W.; Thomas, S.; de Val, J.E.M.S.; Wu, W.; Elango, J. Stem cell-mediated bone regeneration of marine-derived fibrinolytic compound (FGFC-1) loaded carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogels. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 188, 118162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; McConnell, M.; Cabral, J.; Ali, M.A. Chitosan hydrogels in 3D printing for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cui, Z.-K.; Fan, J.; Fartash, A.; Aghaloo, T.L.; Lee, M. Photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogels functionalized with the RGD peptide and phosphoserine to enhance osteogenesis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5289–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yu, R.; Guo, B. Dual-Dynamic-Bond Cross-Linked Antibacterial Adhesive Hydrogel Sealants with On-Demand Removability for Post-Wound-Closure and Infected Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7078–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qiao, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, P.; Xie, F.; Zhang, B. Biofunctional chitosan-biopolymer composites for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2024, 159, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Raziyeva, K.; Tabyldiyeva, L.; Berikova, K.; Zhumagul, D.; Temirkhanova, K.; Saparov, A. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-B.; Chen, Y.-R.; Liu, H.-L.; Lai, J.-Y. Fabrication of UV-crosslinked chitosan scaffolds with conjugation of RGD peptides for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Lang, X.; Kong, M.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Chen, X. Surface fluid-swellable chitosan fiber as the wound dressing material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, K.; Malik, A.K.; Setia, A.; Randhave, N.V.; Verma, N.; Kumar, V.; Vaishali; Deshmukh, K.; Muthu, M.S. Chitosan and its derivatives as nanotheranostics in multiple diseases management: A clinical perspective. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 366, 123852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragostin, O.-M.; Tatia, R.; Samal, S.K.; Oancea, A.; Zamfir, A.S.; Dragostin, I.; Lisă, E.-L.; Apetrei, C.; Zamfir, C.L. Designing of Chitosan Derivatives Nanoparticles with Antiangiogenic Effect for Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahariah, P.; Másson, M. Antimicrobial Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives: A Review of the Structure-Activity Relationship. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3846–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Santos, B.; Chorilli, M. An overview of carboxymethyl derivatives of chitosan: Their use as biomaterials and drug delivery systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia, Z. Carboxymethyl chitosan: Properties and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120 Pt B, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Huang, W.; Jin, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, S. Effect of molecular structure and ionization state on aggregation of carboxymethyl chitosan: A molecular dynamics study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 119993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yi, J.; Tong, J.; Zhou, X.; Ge, H.; Zou, S.; Wen, H.; Nie, M. Preparation and characterization of oxidized konjac glucomannan/carboxymethyl chitosan/graphene oxide hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosiński, K.K.; Wach, R.A.; Girek-Bąk, M.K.; Rokita, B.; Kołat, D.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Kłosińska, B.; Duda, Ł.; Pasieka, Z.W. Biocompatibility and Mechanical Properties of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels. Polymers 2022, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lan, X.; Xiong, Y. In Situ Growth of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-L in Macroporous PVA/CMC/PEG Composite Hydrogels with Synergistic Antibacterial and Rapid Hemostatic Functions for Wound Dressing. Gels 2022, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isık, S.; Taşkapılıoğlu, M.Ö.; Atalay, F.O.; Dogan, S. Effects of cross-linked high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid on epidural fibrosis: Experimental study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 22, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J.-P.; Kan, Y.; Zhang, T. Methods for determining the structure and physicochemical properties of hyaluronic acid and its derivatives: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Gadomska, M.; Musiał, K.; Piątek, J. Hyaluronic Acid as a Component of Natural Polymer Blends for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Kim, B.S.; Jang, J.; Cho, D.-W. Recent Strategies in Extrusion-Based Three-Dimensional Cell Printing toward Organ Biofabrication. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 1150–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.M.A.; Silva, M.; Gershovich, P.; Betta, S.; Babo, P.; Caridade, S.G.; Mano, J.F.; Motta, A.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E. Development of Injectable Hyaluronic Acid/Cellulose Nanocrystals Bionanocomposite Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.S.; Svechkarev, D.; Souchek, J.J.; Hill, T.K.; Taylor, M.A.; Natarajan, A.; Mohs, A.M. Impact of structurally modifying hyaluronic acid on CD44 interaction. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8183–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, S.; Pashkuleva, I.; Reis, C.A.; Reis, R.L.; Pires, R.A. Tunable layer-by-layer films containing hyaluronic acid and their interactions with CD44. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3880–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, S.G.; Jeong, Y.I.; Lee, H.C. Smart Nanoparticles Based on Hyaluronic Acid for Redox-Responsive and CD44 Receptor-Mediated Targeting of Tumor. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Qin, A.; Jin, Q.; Tang, B.Z.; Ji, J. Theranostic hyaluronic acid prodrug micelles with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for targeted drug delivery. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Roswandi, N.L.; Waqas, M.; Habib, H.; Hussain, F.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120 Pt B, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janarthanan, G.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, I.G.; Ji, P.; Chung, E.J.; Lee, C.; Noh, I. Self-crosslinking hyaluronic acid-carboxymethylcellulose hydrogel enhances multilayered 3D-printed construct shape integrity and mechanical stability for soft tissue engineering. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 045026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, N.; Jin, X.; Deng, R.; Nie, S.; Sun, L.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Gong, C. Biodegradable and injectable in situ cross-linking chitosan-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for postoperative adhesion prevention. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3903–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlian, T.; Cam, C.; Segura, T. Porous hyaluronic acid hydrogels for localized nonviral dna delivery in a diabetic wound healing model. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokatlian, T.; Cam, C.; Segura, T. Non-viral DNA delivery from porous hyaluronic acid hydrogels in mice. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laowpanitchakorn, P.; Zeng, J.; Piantino, M.; Uchida, K.; Katsuyama, M.; Matsusaki, M. Biofabrication of engineered blood vessels for biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2024, 25, 2330339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhu, W.; Nowicki, M.; Zhou, X.; Khademhosseini, A.; Zhang, L.G. Hierarchical Fabrication of Engineered Vascularized Bone Biphasic Constructs via Dual 3D Bioprinting: Integrating Regional Bioactive Factors into Architectural Design. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termeer, C.C.; Hennies, J.; Voith, U.; Ahrens, T.; Weiss, J.M.; Prehm, P.; Simon, J.C. Oligosaccharides of hyaluronan are potent activators of dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slevin, M.; Kumar, S.; Gaffney, J. Angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan induce multiple signaling pathways affecting vascular endothelial cell mitogenic and wound healing responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41046–41059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Hu, Y.; Boyer, C.; Xu, F.-J. Photo-responsive supramolecular hyaluronic acid hydrogels for accelerated wound healing. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Han, J.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, S.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X. Development of porous chitosan/tripolyphosphate scaffolds with tunable uncross-linking primary amine content for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 85, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cui, S.; Zhang, H.; Pei, X.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Cross-Linked Pectin Nanofibers with Enhanced Cell Adhesion. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, M.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X.; Feng, C. A thermosensitive RGD-modified hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel as a 3D scaffold for BMSCs culture on keloid treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.M.; Joung, Y.K.; Park, K.D.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, M.C. RGD-Conjugated chitosan-pluronic hydrogels as a cell supported scaffold for articular cartilage regeneration. Macromol. Res. 2008, 16, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritchenkov, A.S.; Egorov, A.R.; Abramovich, R.A.; Kurliuk, A.V.; Shakola, T.V.; Kultyshkina, E.K.; Meza, M.J.B.; Pavlova, A.V.; Suchkova, E.P.; Thuy, G.L.N.; et al. Water-soluble triazole chitin derivative and its based nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, catalytic and antibacterial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, M.; Liu, L. Abortive ligation intermediate blocks seamless repair of double-stranded breaks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arıcı, Ş.; Kamali, A.R.; Ege, D. CMC/Gel/GO 3D-printed cardiac patches: GO and CMC improve flexibility and promote H9C2 cell proliferation, while EDC/NHS enhances stability. Biofabrication 2024, 17, 015025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Li, Z.; Xia, W.; Yang, N.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C. Preparation and properties of EDC/NHS mediated crosslinking poly (gamma-glutamic acid)/epsilon-polylysine hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, J.; Guan, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, K.; Li, J. Injectable multifunctional CMC/HA-DA hydrogel for repairing skin injury. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 14, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Shao, W. UV-mediated synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose/poly-N-isopropylacrylamide composite hydrogels with triple stimuli-responsive swelling performances. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, S.; Duan, H.; He, J.; Luo, Y. Removal of anionic and cationic dyes using porous chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels: Optimization, adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123213. [Google Scholar]
- Doane, T.L.; Chuang, C.H.; Hill, R.J.; Burda, C. Nanoparticle ζ-potentials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Paknia, S.; Izadi, Z.; Moosaipour, M.; Moradi, S.; Khalilzadeh, B.; Jaymand, M.; Samadian, H. Fabrication and characterization of electroconductive/osteoconductive hydrogel nanocomposite based on poly(dopamine-co-aniline) containing calcium phosphate nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 362, 119701. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, P. pH-Sensitive Polyampholyte Microgels of Poly(Acrylic Acid-co-Vinylamine) as Injectable Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Release. Polymers 2019, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manamoongmongkol, K.; Sriprom, P.; Narkrugsa, W.; Phumjan, L.; Permana, L.; Kaewbutra, S.; Assawasaengrat, P. Study on chemical structure stability and properties of chitosan-incorporated tamarind seed kernel xyloglucan hydrogels. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 702, 135114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, C.D.T.; Giacometti, J.A.; Job, A.E.; Ferreira, F.C.; Fonseca, J.L.C.; Pereira, M.R. Thermal Analysis of Chitosan Based Networks. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, L.; Witek, L.; Nayak, V.V.; Pereira, A.C.; Kim, E.; Good, J.; Liu, C.-J. Injectable hydrogel for sustained delivery of progranulin derivative Atsttrin in treating diabetic fracture healing. Biomaterials 2023, 301, 122289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, S.; Ding, Q.; Liu, W.; Ding, C. A poloxamer/hyaluronic acid/chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel that releases dihydromyricetin to promote wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 475–486. [Google Scholar]
- Santhamoorthy, M.; Kim, S.C. A Review of the Development of Biopolymer Hydrogel-Based Scaffold Materials for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanikireddy, V.; Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Karthikeyan, C.; Sadiku, R. Carboxymethyl cellulose-based materials for infection control and wound healing: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessanha, F.S.; de Oliveira, B.G.R.B.; Oliveira, B.C.; Deutsch, G.; Teixeira, F.L.; Bokehi, L.C.; Calomino, M.A.; de Castilho, S.R.; Thiré, R.M.d.S.M.; Teixeira, L.A.; et al. Effectiveness of Epidermal Growth Factor Loaded Carboxymethylcellulose (EGF-CMC) Hydrogel in Biofilm Formation in Wounds of Diabetic Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Gels 2023, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Saha, S.; Hanjaya-Putra, D. Biomimetic Hydrogels to Promote Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 718377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorana, A.; Lenzuni, M.; Contardi, M.; Palumbo, F.S.; Cataldo, S.; Pettignano, A.; Catania, V.; Schillaci, D.; Summa, M.; Athanassiou, A.; et al. Schiff Base-Based Hydrogel Embedded with In Situ Generated Silver Nanoparticles Capped by a Hyaluronic Acid-Diethylenetriamine Derivative for Wound Healing Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 20186–20201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CMC | CMC-HA | CMC-RGD | CMC-HA-RGD | Functional Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 608.63 | 602.29 | 601.22 | 601.75 | C-O-C stretching |
| 1060.47 | 1059.91 | 1058.88 | 1060.37 | C-C skeletal vibrations |
| 1313.20 | 1312.40 | 1313.96 | 1317.08 | C-N stretching/-OH bending |
| 1411.50 | 1412.04 | 1411.42 | 1411.57 | -COO− symmetric stretching |
| 1620.81 | 1608.37 | 1615.55 | 1604.78 | Amide I band (mainly C=O stretching) |
| 2928.13 | 2926.98 | 2924.88 | -CH2- stretching | |
| 3446.06 | 3422.79 | 3444.76 | 3442.31 | -OH stretching |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, X.; Wu, W.; Elango, J.; Diao, X. Biofunctional Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Incorporating Hyaluronic Acid and RGD Peptides for Accelerated Wound Repair. Gels 2025, 11, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100765
Wang S, Yang Q, Xu J, Zhou Y, Tian X, Wu W, Elango J, Diao X. Biofunctional Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Incorporating Hyaluronic Acid and RGD Peptides for Accelerated Wound Repair. Gels. 2025; 11(10):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100765
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuyue, Qing Yang, Jiren Xu, Youshiqi Zhou, Xiaoqing Tian, Wenhui Wu, Jeevithan Elango, and Xiaozhen Diao. 2025. "Biofunctional Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Incorporating Hyaluronic Acid and RGD Peptides for Accelerated Wound Repair" Gels 11, no. 10: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100765
APA StyleWang, S., Yang, Q., Xu, J., Zhou, Y., Tian, X., Wu, W., Elango, J., & Diao, X. (2025). Biofunctional Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel Incorporating Hyaluronic Acid and RGD Peptides for Accelerated Wound Repair. Gels, 11(10), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100765












