Green and Low-Cost Modified Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gel Materials for Ecological Restoration: A Phase Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Distribution of Pisha Sandstone
3. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Precursors for Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gels
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties
3.2. Erosion Characteristics
4. Advances in the Ecological Restoration of Pisha Sandstone Region
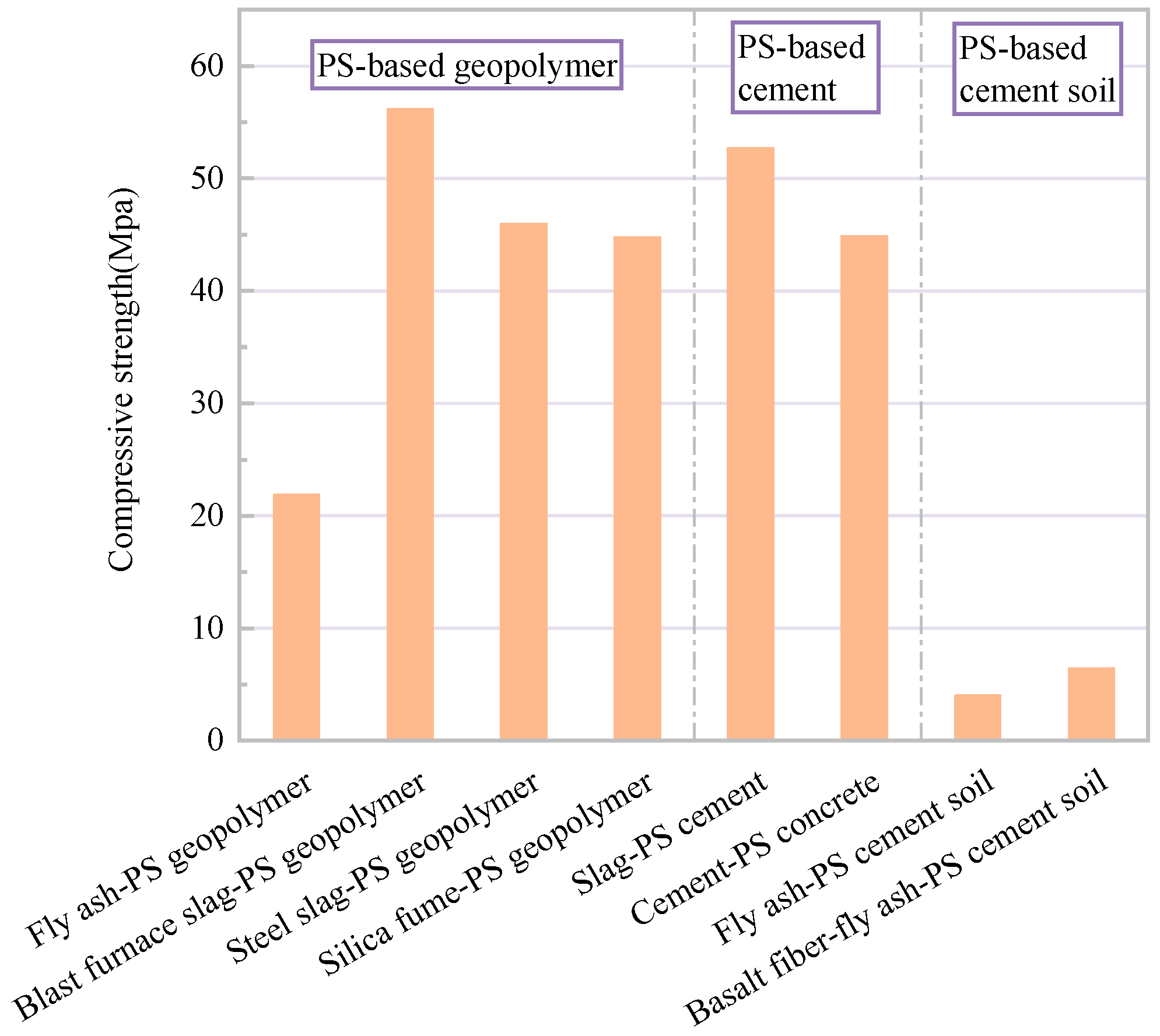
5. The Synthesis of Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gels
6. Ecological Restoration Applications of Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gels
6.1. Engineering Composite Materials
6.2. Mine Restoration Green Materials
7. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, X.; Deng, X. Current soil erosion assessment in the Loess Plateau of China: A mini-review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lv, G.; Chai, N.; Hu, J.; Jin, Z. Hydrochemistry and source apportionment of boron, sulfate, and nitrate in the Fen River, a typical loess covered area in the eastern Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Chen, H. Estimating soil erosion response to land use/cover change in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A. Modeling response of soil erosion and run off to changes in precipitation and cover. Catena 2005, 61, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Kumar, P.; Zlatic, M.; Nautiyal, R.; Panwar, V.P. Recent advances in assessment of soil erosion vulnerability in a watershed. Int. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 9, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andualem, T.G.; Hewa, G.A.; Myers, B.R.; Peters, S.; Boland, J. Erosion and Sediment Transport Modeling: A Systematic Review. Land 2023, 12, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, X.M. Loess Plateau soil erosion governance and runoff-sediment variation of Yellow River. Water. Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2020, 51, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, M. Research on Soil and Water Loss and Its Control Measures in the Pisha Sandstone Area; The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2007; ISBN 9787807342120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z. Research on Soil and Water Conservation and Development of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry in Pisha Sandstone Area; The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2003; ISBN 9787806215463. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Fang, D.; Bi, C.; Qiao, W.; Li, G.; Li, W. Study on the model of freeze-thaw and weathering erosion of smaller watershed in soft rock area. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2003, 2, 89–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cai, H.; Wei, M. Effect of Composition on Nutrient of Pisha Sandstone. Yellow River 2016, 38, 18–21+25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, C.; Lin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Yu, Q. Definition on Source Area of Centralized Coarse Sediment in Middle Yellow River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 8, 19–21+52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yao, W.; Noori, M.; Yang, C.; Xiao, P.; Leng, Y.; Deng, L. Pisha sandstone: Causes, processes and erosion options for its control and prospects. Int. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yao, W.; Liu, G.; Xiao, P.; Sun, W. Experimental study of sediment transport processes and size selectivity of eroded sediment on steep Pisha sandstone slopes. Geomorphology 2020, 363, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cao, M.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Bi, C. Simulation of sediment retention effects of the single seabuckthorn flexible dam in the Pisha Sandstone area. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, C.; Dong, J. Study on Distribution and Lithologic Characters of Feldspathic Sandstone. Yellow River 2013, 35, 91–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xiao, P.; Yao, W.; Liu, G.; Sun, W. Characteristics of sediment particle size distribution in the Pisha sandstone area of the middle Yellow River under the effects of vegetation and complex erosion. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2023, 48, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J. Speech at the symposium on ecological protection and quality development in the Yellow River Basin. China Water Resour. 2019, 20, 1–3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, K.; Baveye, P. Hysteresis in the binary exchange of cations on 2:1 clay minerals; a critical review. Clays Clay Miner. 1994, 42, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Study on Palaeo-Rock-Solution of Carbonate Rockof Ordovician and Its Reservoir. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, China, 2006. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Dang, B. The Tectonic and Sedimentary Evolution and its Relationship to Gas Accumulation of Lower Paleozoic in Ordos Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest University, Xi’an, China, 2003. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Techonic Evolution and Oil-Gas Reservoirs Distribution in Ordos Basin; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2002; ISBN 7-5021-3801-3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Basin Analyses and Simulation of Up-Paleozoicin Ordos Basin; Southwest Petroleum University: Chengdu, China, 2005; (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J. Research on Sedimentary System and Sequence Stratigraphy of Jurassic of the Ordos Basin; Southwest Petroleum University: Chengdu, China, 2007; (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kou, Q.; Min, D.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, R. Definition of arsenic rock zone borderline and its classification. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 5, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shi, M.; Cai, H.; Wu, Y. Experimental Study of the Physical Characteristics of the Pisha Sandstone on Its Erosion. Yellow River 2016, 38, 8–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Yao, W. Features and utilization of arsenic sandstone. China Water Resour. 2015, 8, 15–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Hou, H.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, Y. The Effect of Soft Rock Lithology upon Its Anti-erodibility. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2006, 27, 145–150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X. Mineral composition of soft rock in Mu Us sandy land in China. Land Dev. Eng. Res. 2018, 3, 29–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Ye, H.; Hou, H.; Bi, Z. The Internal Cause of the Erosion in “Pisha” Sandstone Area, Southern Inner Mongolia. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2004, 25, 659–664. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cai, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z. Relationship between shear strength and structural characteristics of Pisha sandstone. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2019, 39, 21–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, G.; Hou, H.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, Y. Effect of chemical compositions of Pisha sandstone on the gravity erosion. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2006, 6, 5–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J.; Ye, H. Indoor Modeling the Effect of Water-Rock Interaction on the Weathering and Erosion of Pi-Sandstone. Yellow River 2013, 35, 45–47+68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ye, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y. Effect of Water-rock Interaction on the Weathering and Erosion of Pi-sandstone, Southern Inner Mongolia, China. Geoscience 2009, 23, 171–177. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. Pozzolanic Activity of Pisha Sandstone and Mechanical Properties of Alkali-activated Pisha Sandstone Materials. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 43, 1090–1098. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Properties of Pisha Sandstone in Inner Mongolia and Its Influence to Mechanical Properties of Cement. Soil Water Conserv. China 2015, 46–49+73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Yu, M. Characteristics and genesis of the bleached Pisha sandstone in Ordos Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2014, 35, 679–684. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Song, L.; Wang, L. Mineral composition and anti-erodibility of Pisha sandstone. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 13, 11–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Liu, H.; Liang, Z. A New Approach to Ecological Restoration in Pisha Sandstone Area—An Environment-Friendly Technique of Anti-Erosion and Vegetation-Promoting. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 118–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, Y.; Qi, X.; Liang, W. The Experimental Analysis Study of Soft Sandstone Soil Properties in the Plateau Hilly Region. J. Inn. Mong. Agric. Univ. 2011, 32, 315–318. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhai, T. The experimental research on mechanical properties of Pisha–Sandstone of Erdos. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2016, 30, 118–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ye, H.; Shi, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y. Indicator System Establishment of Sandstone Corrosion Resistance Inner Mongolia; Forum on Urban Geoenvironment and Sustainable Development: Shanghai, China, 2010; pp. 186–191. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Xie, W. Experimental research on mechanical properties and constitutive model of Pisha-sandstone remolded soil. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2019, 37, 909–914. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Shi, J.; Hou, H.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, J. Effect of the Lithologic Characters of Pisha Sandstone on Gravity Erosion in South Inner Mongolia. Arid Zone Res. 2008, 3, 402–405. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhai, T.; Zhang, Q. Experiment on mechanical properties of Pisha-sandstone at recurrent shear. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 154–159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Shi, P. A Study on the Soil Erosion Processses in the Semiarid Region of Inner Mongolia. J. Arid Land Resour. Emviron. 1987, 2, 55–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, F.; Yang, Z.; Li, L. Research progress on soil erosion mechanism and ecological restoration technology in feldspathic sandstone region. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2020, 42, 142–150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Li, J.; Peng, B. Study on microstructure characteristies of soft rocks in Ordos. Land Dev. Eng. Res. 2019, 4, 36–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.; Shi, J.; Ye, H.; Guo, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q. Quantitative characteristics of microstructure of Pisha-sandstone. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2007, 6, 597–602. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Wang, F. Research on soil erosion mechanism in soft rock regions. J. Sediment. Res. 2008, 1, 70–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. The Features of Sediment Production and the Analysis of Genesis by Erosion in Huangfuchuan Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1992, 2, 15–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G. Research on the Laws of Soil and Water Loss in Sand Rock Region, Inner Mongolia. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 4, 158–160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yao, W.; Liu, G.; Xiao, P. Dynamic characteristics of complex erosion in a typical small watershed of soft sandstone area. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 50, 1384–1391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Li, M. Deformation characteristics of red pisha-sandstone during freezing-thawing cycles in Ordos. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 14, 34–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Niu, G. Analysis on the influencing factors of soil erosion in the Pisha sandstone area. Inn. Mong. Water Resour. 2012, 3, 55–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Cai, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H. Study on Interaction Among Wind Erosion, Hydraulic Erosion and Gravity Erosion in Sediment-Rock Region of Inner Mongolia. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 2, 25–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y. Prospect and Research on the Erosion Mechanism of Pisha Sandstone. Yellow River 2018, 40, 1–7+65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Liang, Y. Water-holding Capability of Litter Layers of Artificial Seabuckthorn Stands in Arsenic Sandstone Area. Water Resour. Dev. Manag. 2007, 3, 10–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H. Creating a new model for managing World Bank financed Project-Brief introduction of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of Loess Plateau Watershed Rehabilitation Project. China Water Resour. 2005, 12, 45–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Analysis on the Sediment Reduction Effect of Seabuckthorn Ecological Project in the Concentrated Source Area of Yellow River Coarse Sediment. Soil Water Conserve. China 2016, 9, 86–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Li, G. Special functions of seabuckthorn in controlling soil erosion in arsenic sand areas. Express Water Resour. Hydropower Inf. 1998, 18, 2–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q. Study on Constructing Approach of Forest and Grass in Pisha Rock Aera. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 1997, 7, 2–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xue, S.; Gao, F. Effect, Experience, and Development Strategy of Seabuckthorn Control in Bare Arsenic Sandstone Areas. Hippophae 2002, 1, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; He, J.; Yin, L.; Zhao, X.; Xing, E.; Liu, T. Analysis on Community Structure and Plant Diversity of Artificial Hippophae rhamnoides in Soft Rock Region. Water Resour. Dev. Manag. 2011, 9, 24–29+33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Luo, L. Research on the Core Technology of Remixing Soil by Soft Rock and Sand in the Maowusu Sand Land Region. China Land Sci. 2012, 26, 87–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Wang, H.; Luo, L.; Han, J.; Ma, Z.; Tong, W.; Cheng, J. Farmland-building Technology of Turning Arsenic Rock and Sand into Soil. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 33, 242–246. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X. Pb (II) adsorption property of Pisha sandstone. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2014, 34, 2491–2499. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; She, X.; Wang, L. Remediation of lead contaminated soil by adding Pisha sandstone in resource-rich region of Shanxi, Shaanxi and Inner Mongolia. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2015, 35, 873–879. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Q.; She, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, F.; Zhang, X. Simulation of Infiltration Characteristics with Various Soil Configurations in Shanxi-Shaanxi-Inner Mongolia Energy Zone. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 90–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R. Effect of EN-1 on Shear Strength Characteristics of Pisha Sandstone Solidified Soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2013, 44, 86–90+67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Zhang, X. Effects of EN-1 Soil Stabilizer on Slope Runoff Hydraulic Characteristics of Pisha Sandstone Stabilized Soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2011, 42, 68–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yao, W.; Wang, L.; Shen, Z.; Liu, H.; Leng, Y. Research on properties of modified Yellow River Pisha sandstone dam construction materials. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2019, 39, 16–20+26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Yao, W.; Leng, Y. Mechanism of erosion resistance and vegetation promotion by W-OH in Pisha sandstone. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 47, 1160–1166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Shi, M.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, C. Experimental Study of the Physical Characteristics of the Pisha Sandstone on Its Erosion. Yellow River 2016, 38, 1–7+10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Xiao, P.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z. Research progress on soil erosion control technologies in Pisha sandstone areas. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2019, 39, 1–9+15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Song, L. Preparation of Geopolymeric Materials by Pisha Sandstone. J. Build. Mater. 2016, 19, 373–378. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhong, D.; Wu, B. Future trend of Yellow River sediment changes. China Water Resour. 2020, 1, 9–12+32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald, A.; Hohmann, M.; Posern, K.; Brendler, E. The suitability of thermally activated illite/smectite clay as raw material for geopolymer binders. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.; Heath, A.; Patureau, P.; Evernden, M.; Walker, P. Alkali activation behaviour of un-calcined montmorillonite and illite clay minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 166, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.; Bernal, S. Geopolymers and Related Alkali-Activated Materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 2014, 44, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondar, D.; Lynsdale, C.J.; Milestone, N.B.; Hassani, N.; Ramezanianpour, A.A. Effect of adding mineral additives to alkali-activated natural pozzolan paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2906–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. Mechanical properties and microstructure of alkali activated Pisha sandstone geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Yao, W.; Wang, L. Development of low cost supplementary cementitious materials utilizing thermally activated Pisha sandstone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Dong, J. Development of building material utilizing a low pozzolanic activity mineral. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. Effect of Dosage of Fly Ash and NaOH on Properties of Pisha Sandstone-Based Mortar. ACI Mater. J. 2016, 113, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Investigating the mechanical property and reaction mechanism of geopolymers cement with red Pisha Sandstone. Constr. Build. Mater 2019, 201, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T. Study on the strength development, hydration process and carbonation process of NaOH-activated Pisha Sandstone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Silica fume-reinforced alkali-activated uncalcined Pisha Sandstone-based geopolymer cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K.; Chai, J.; Qin, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, H. Collapse inhibition mechanism analysis and durability properties of cement-stabilized Pisha sandstone. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y. Synthesis of alkali-activated uncalcined Pisha sandstone cement composites. Compos. Eng. 2021, 225, 109311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Geng, K. Indoor experimental study on mechanical properties of composite fly ash and Pisha-sandstone cement soil. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2021, 39, 1230–1236. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Geng, K. Experimental study on mechanical properties of basalt fiber-Pisha sandstone cement soil. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2021, 39, 1264–1269+1290. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, Z.; Yin, H.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, B.; Yang, J. Study of properties of cement mortars prepared of red pisha sandstone fine aggregate. Concrete 2015, 6, 112–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, Z.; Yin, H.; Lu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J. Study of erosion-wear of concrete prepared of Pisha sandstone fine aggregate. Concrete 2016, 6, 158–160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W. Compressive strength and microstructure of fly ash based geopolymer blended with silica fume under thermal cycle. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 78, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Kang, S.; Cheng, G.; Wu, W. The effect of slag and fly ash content on the properties of electric furnace nickel slag-based geopolymer used for repair materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Yao, W.; Shen, Z.; Jiao, P. Resistance to Erosion and Growth Promoting Technique of Pisha Sandstone Region in the Middle Yellow River. Soil Water Conserv. China 2016, 9, 73–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Geng, K. A Study of the Structural Evolution and Strength Damage Mechanisms of Pisha Sandstone Cement Soil Modified with Fly Ash. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 2241–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, X. Strength and microscopic mechanism analysis of CFBCA-based geopolymer–Pisha sandstone cement composite soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65197–65210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakor, P.; Chu, S.H.; Puzatova, A.; Dini, E. Review of binder jetting 3D printing in the construction industry. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 7, 643–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Sambucci, M.; Chougan, M.; Ghaffar, S.H. Composite alkali-activated materials with waste tire rubber designed for additive manufacturing: An eco-sustainable and energy saving approach. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 3098–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Jassim, M.; Ilcan, H.; Sahin, O.; Bayer, İ.R.; Sahmaran, M.; Koc, M. 3D printing of circular materials: Comparative environmental analysis of materials and construction techniques. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Pan, H.; Lin, C. A landscape approach towards ecological restoration and sustainable development of mining areas. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X. Microbially induced calcite precipitation and synergistic mineralization cementation mechanism of Pisha sandstone components. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, X. Effect of Pisha sandstone on water infiltration of different soils on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, J.; Njimou, J.R.; Abdus-Salam, N.; Panda, P.K.; Tripathy, B.C.; Ghosh, M.K.; Basu, S. Nanoscale ZnO-adsorbent carefully designed for the kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Rhodamine B. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 138, 109287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grba, N.; Baldermann, A.; Dietzel, M. Novel green technology for wastewater treatment: Geo-material/geopolymer applications for heavy metal removal from aquatic media. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2023, 38, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
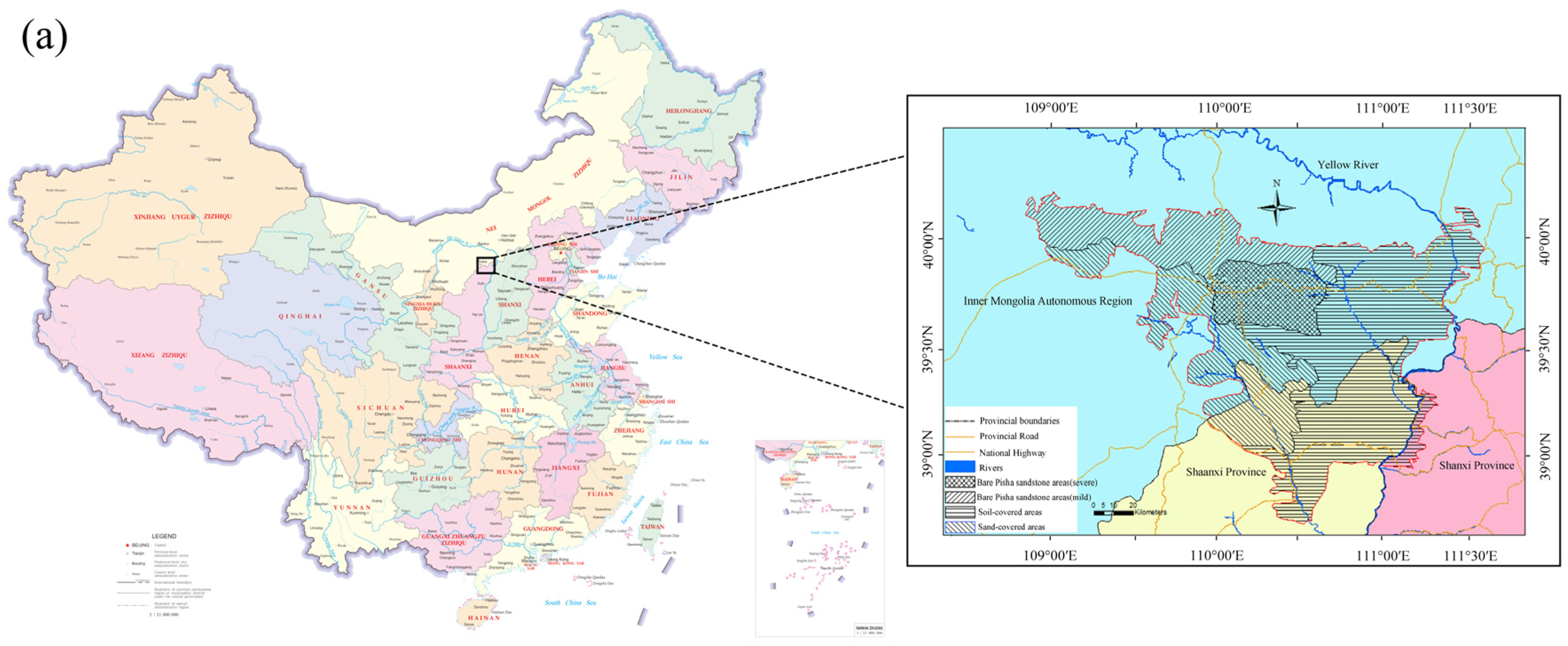

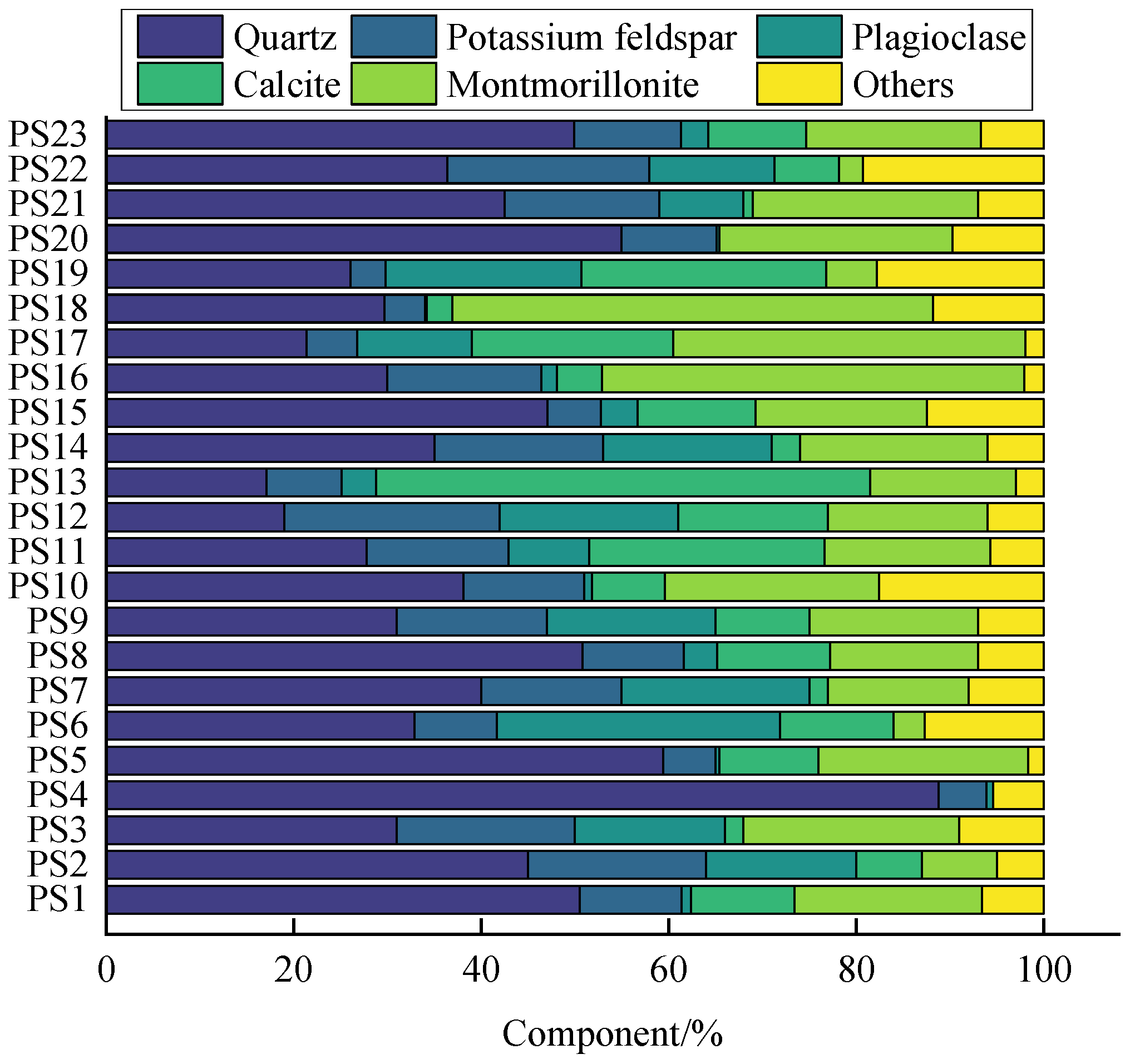
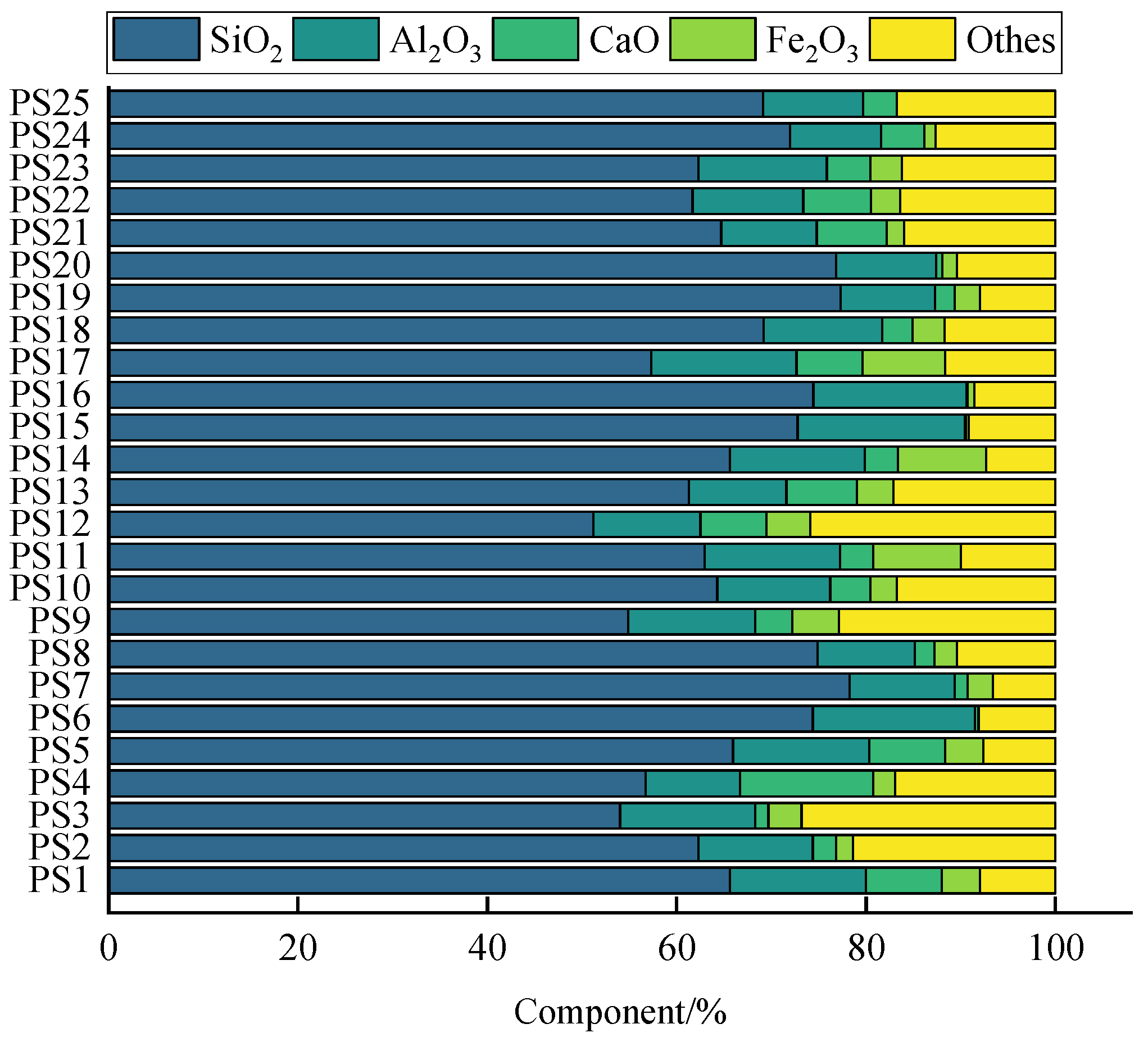


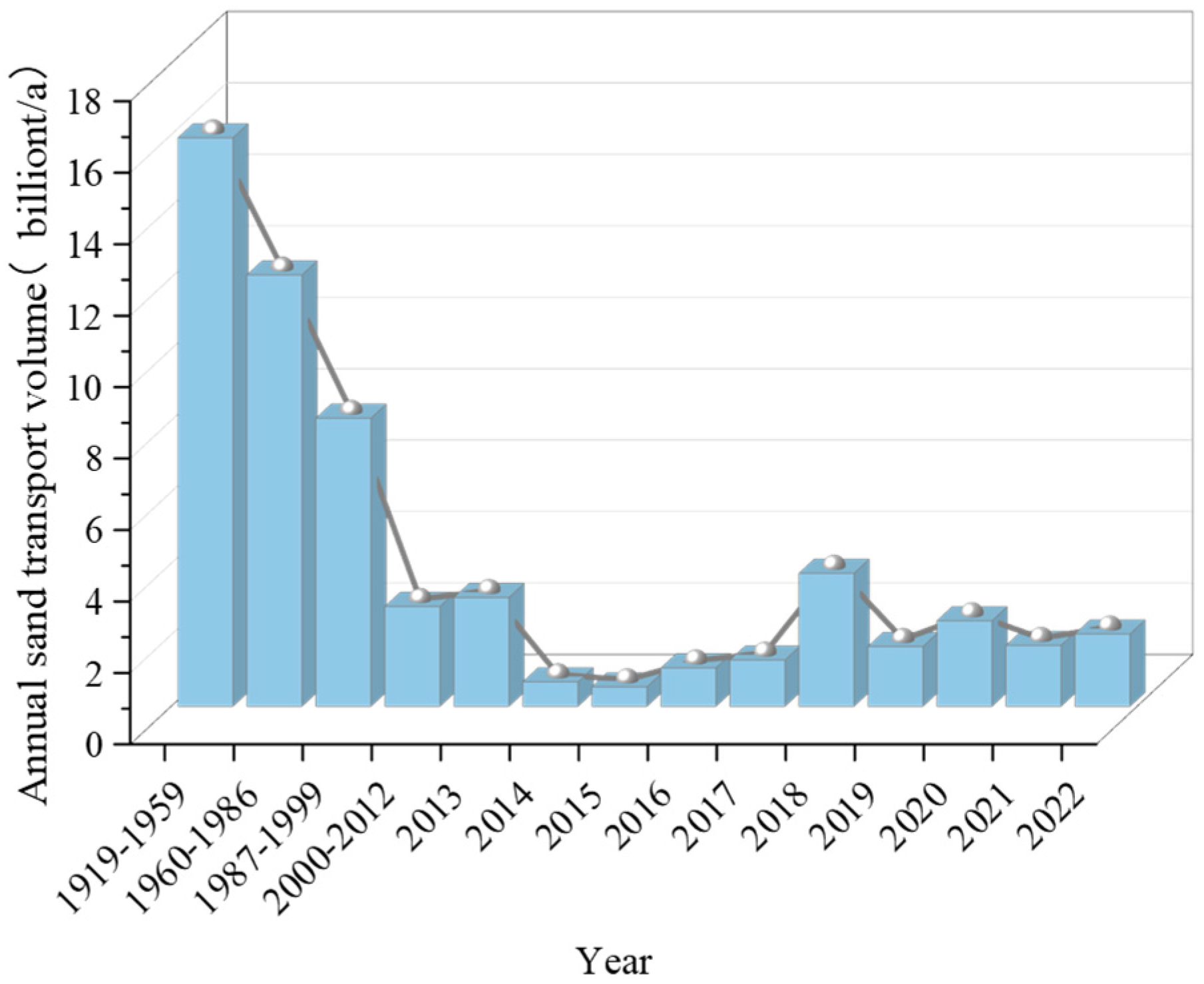
| Reference | Bare PS | Sand-Covered PS | Soil-Covered PS | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.84 | 1.66 |
| [9] | 0.63 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 1.20 |
| [10] | 0.63 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 1.17 |
| [11] | / | / | / | 3.20 |
| [12] | / | / | / | 1.97 ① |
| Reference | Sample Collection Site | Type | Softening Coefficient | Compressive Strength/MPa | Shear Strength/MPa | Tensile Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28,32] | Jungar Banner, Ordos | Gray-white, purple-red, gray-white with purple-red stripes | 0.05~0.42 | 5.19~39.70 (dry) | 0.09~4.15 | 0.06~0.74 |
| 18.72 (AVG) | ||||||
| 0.20 (AVG) | 1.00~8.69 (water-saturated) 3.73 (AVG) | 1.16 (AVG) | 0.21 (AVG) | |||
| [30] | Boldonggou, Shagedu town, Ordos | Gray-white, purple-red, gray-white with purple-red stripes | - | - | 0.090~0.470 (dry) | - |
| [38] | Erlaohuo gully, Shagedu town, Ordos | White | - | 0.40~1.20 | - | - |
| Red | - | 0.90~2.80 | - | - | ||
| [40] | Jungar Banner, Ordos | Brown red, light red | - | - | 0.072 (cohesive force) | - |
| [42] | Jungar Banner, Ordos | Gray-white with purple-red stripes | - | 7.30~10.90 | 0.0021~0.0082 | 0.0100~0.0430 |
| Gray-white | - | 13.70~20.10 | 0.0122~0.0210 | 0.0527~0.0896 | ||
| Purple-red | - | 23.20~27.60 | 0.0275~0.0393 | 0.1010~0.1696 | ||
| Pink | - | 30.30~30.60 | 0.0464~0.0674 | 0.2275~0.2627 | ||
| [49] | Jungar Banner, Ordos | - | - | 1.33~3.11 | - | 0.01~0.16 |
| Pisha Sandstone-Type Region | Distribution Region | Main Erosion Types | Main Composite Erosion Types | Average Erosion Modulus/[t/(km2·a)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare regions | Kuye River, Huangfuchuan Watershed, Ten Tributaries, etc. | Hydraulic erosion | Hydraulic erosion, wind erosion, freeze–thaw erosion | 2.1 |
| Soil-covered regions | Kuye River, Gushanchuan Watershed, Qingshui River, Huangfuchuan Watershed, Hun River, Ten Tributaries, etc. | Hydraulic erosion | Hydraulic erosion, wind erosion, gravity erosion, freeze–thaw erosion | 1.5 |
| Sand-covered regions | Kuye River, Gushanchuan Watershed, Ten Tributaries, etc. | Wind erosion | Hydraulic erosion, wind erosion | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Jia, D.; Liu, H. Green and Low-Cost Modified Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gel Materials for Ecological Restoration: A Phase Review. Gels 2024, 10, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050302
Li C, Fu Y, Cheng H, Wang Y, Jia D, Liu H. Green and Low-Cost Modified Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gel Materials for Ecological Restoration: A Phase Review. Gels. 2024; 10(5):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050302
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Changming, Yubing Fu, Haifeng Cheng, Yaozong Wang, Dongyang Jia, and Hui Liu. 2024. "Green and Low-Cost Modified Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gel Materials for Ecological Restoration: A Phase Review" Gels 10, no. 5: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050302
APA StyleLi, C., Fu, Y., Cheng, H., Wang, Y., Jia, D., & Liu, H. (2024). Green and Low-Cost Modified Pisha Sandstone Geopolymer Gel Materials for Ecological Restoration: A Phase Review. Gels, 10(5), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050302







