Preparation and Characterization of Ultrasonically Modified Peanut Protein–Guar Gum Composite Emulsion Gels for 3D Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of the Chemical Composition of the PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels on Their 3D Printing Properties
2.1.1. Effects of Protein Content on 3D Printing Properties
2.1.2. Effects of the Oil Fraction on 3D Printing Properties
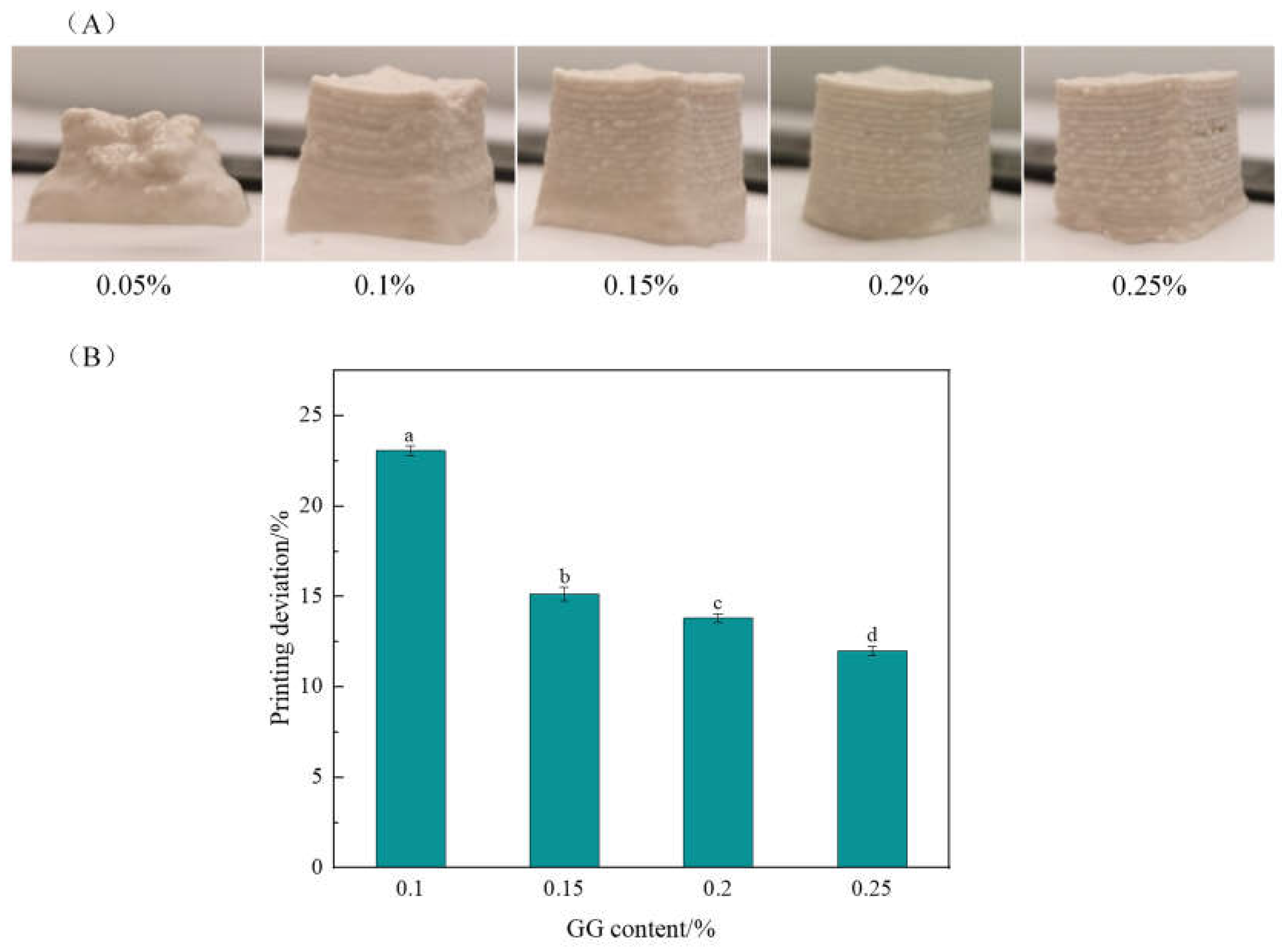
2.1.3. Effects of the GG Content on 3D Printing Properties
2.1.4. Orthogonal Experiments
2.2. Effects of US Modification of Peanut Proteins on the Physical Properties of PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels
2.2.1. Textural Properties
2.2.2. Rheological Properties
2.2.3. Microstructure
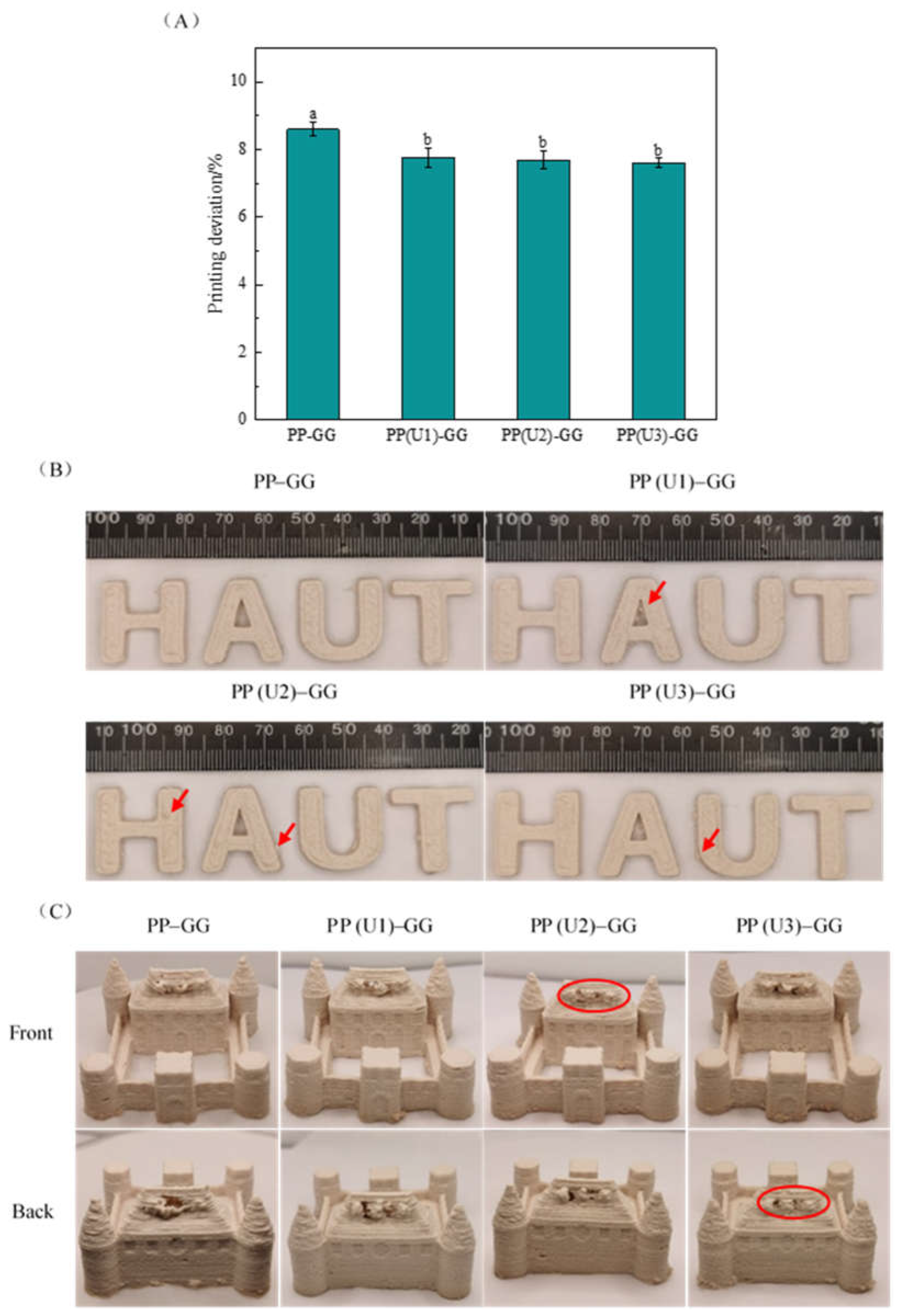
2.3. Effects of US Modification of Peanut Proteins on the 3D Printing Properties of PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Extraction of Peanut Proteins
4.3. Ultrasonic (US) Treatment of Peanut Proteins
4.4. Optimization of Preparation Conditions for PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels for 3D Printing
4.4.1. Preparation of PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels
4.4.2. Measurement of the Dimensional Printing Deviation of PP–GG Emulsion Gels
4.5. Preparation of Ultrasonically Modified PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels
4.6. Characterization of Ultrasonically Modified PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels
4.6.1. Textural Properties
4.6.2. Rheological Properties
Dynamic Viscoelastic Measurement
Rheological Properties of Emulsion Gels
- (1)
- Flow behavior test
- (2)
- Small-amplitude oscillatory shear (SAOS) test
- (3)
- Three interval thixotropy tests (3ITT)
4.6.3. Microstructure
4.7. Printability of Ultrasonically Modified PP–GG Composite Emulsion Gels
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, Y.; Cai, Q.; Huang, Q.; Lu, X. Application of LF-NMR to characterize the roles of different emulsifiers in 3D printed emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yin, Z.; Zeng, M. Construction of 3D printable Pickering emulsion gels using complexes of fiber polysaccharide-protein extracted from Haematococcus pluvialis residues and gelatin for fat replacer. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Guo, J.; Meng, Z. A review on food-grade-polymer-based O/W emulsion gels: Stabilization mechanism and 3D printing application. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lu, Q. A review of high internal phase Pickering emulsions: Stabilization, rheology, and 3D printing application. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 324, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Kelly, A.L.; Maidannyk, V.; Miao, S. Effect of structuring emulsion gels by whey or soy protein isolate on the structure, mechanical properties, and in-vitro digestion of alginate-based emulsion gel beads. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mao, L.; Hou, Z.; Miao, S.; Gao, Y. Development of Emulsion Gels for the Delivery of Functional Food Ingredients: From Structure to Functionality. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zheng, L.; Zou, Y.; Tong, Z.; Han, S.; Wang, S. 3D food printing: Main components selection by considering rheological properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2335–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Jiang, Y.S.; Zhang, S.Y.; Chen, L. Physical Properties of Peanut and Soy Protein-Based Emulsion Gels Induced by Various Coagulants. Gels 2022, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.Y.; Zhang, S.B.; Wang, Z.J. Effect of ultrasonic modification on the properties of peanut protein emulsion gels loaded with curcumin. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 45, 41–48+57. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Improving Freeze-Thaw Stability and 3D Printing Performance of Soy Protein Isolate Emulsion Gel Inks by Guar & Xanthan Gums. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108293. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, B.; Lv, W.; Mu, R.; Zhong, Y. Effect of Induction Mode on 3D Printing Characteristics of Whey Protein Isolate Emulsion Gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, B.; Lv, W.; Yang, L.; Xiao, H. Effect of κ-carrageenan on physicochemical and 3D printing properties of walnut protein-stabilized emulsion gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; An, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, H.; Mo, H.; Hati, S. Incorporation of Probiotics into 3D Printed Pickering Emulsion Gel Stabilized by Tea Protein/Xanthan Gum. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Jiao, A.; Wang, J.; Jin, Z. Preparation of High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsion Gels Stabilized by Glycyrrhizic Acid-Zein Composite Nanoparticles: Gelation Mechanism and 3D Printing Performance. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Nie, M.; Li, D.; Zhou, C.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. Rheological property, ?-carotene stability and 3D printing characteristic of whey protein isolate emulsion gels by adding different polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, C.; Mcclements, D.J.; Xu, X.; Sun, Q.; Jiao, B.; Wang, Q.; Dai, L. Improvement of 3D printing performance of pea protein isolate Pickering emulsion gels by regulating electrostatic interaction between protein and polysaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Naushad, M.; Ghfar, A.A.; Mola, G.T.; Stadler, F.J. Guar gum and its composites as potential materials for diverse applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Development of soy protein isolate emulsion gels as extrusion-based 3D food printing inks: Effect of polysaccharides incorporation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, L.; Dai, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yu, D. Improvement of 3D Printing Performance of Whey Protein Isolate Emulsion Gels by Regulating Rheological Properties: Effect of Polysaccharides Incorporation. In Food Bioprocess Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Song, L.; Bi, A.; Wu, C.; Ma, Y.; Du, M.; Zhu, B. High Internal Phase Emulsion for Food-Grade 3D Printing Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 45493–45503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zaky, A.A.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Su, W.; Wang, H.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Tan, M. High internal phase Pickering emulsion stabilized by sea bass protein microgel particles: Food 3D printing application. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Wang, Y. 3D printing: Printing precision and application in food sector. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Fan, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xia, S.; Huang, Q. Food-grade Pickering emulsions and high internal phase Pickering emulsions encapsulating cinnamaldehyde based on pea protein-pectin-EGCG complexes for extrusion 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.; Bao, Y.; Mac Regenstein, J.; Zhou, P. Fabrication of Gel-Like Emulsions with Whey Protein Isolate Using Microfluidization: Rheological Properties and 3D Printing Performance. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 1967–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.R.; Li-Sha, Y.J.; Chen, H.Q. The effects of basil seed gum on the physicochemical and structural properties of arachin gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z. 3D printing of food: Pretreatment and post-treatment of materials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achayuthakan, P.; Suphantharika, M. Pasting and rheological properties of waxy corn starch as affected by guar gum and xanthan gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, S.B. Structural and functional properties of self-assembled peanut protein nanoparticles prepared by ultrasonic treatment: Effects of ultrasound intensity and protein concentration. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Donkor, P.O.; Ren, X.F.; Wu, J.; Agyemang, K.; Ayim, I.; Ma, H. Effect of ultrasound pretreatment with mono-frequency and simultaneous dual frequency on the mechanical properties and microstructure of whey protein emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, R.A.; Cavallieri, Â.L.F.; Cunha, R.L. Gelation of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein. J. Food Eng. 2016, 175, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Shang, M.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Jiao, A.; Ji, H.; Qiu, C.; Jin, Z. Rheology and 3D printing characteristics of heat-inducible pea protein-carrageenan-glycyrrhizic acid emulsions as edible inks. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglarini, C.S.; Martini, S.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Physical properties of emulsion gels formulated with sonicated soy protein isolate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C. Dual extrusion 3D printing of mashed potatoes/strawberry juice gel. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 96, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuhongsung, P.; Zhang, M.; Devahastin, S. Investigation on 3D printing ability of soybean protein isolate gels and correlations with their rheological and textural properties via LF-NMR spectroscopic characteristics. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Luo, L.J.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z. Transglutaminase-set soy globulin-stabilized emulsion gels: Influence of soy β-conglycinin/glycinin ratio on properties, microstructure and gelling mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.; Jaeger, H.; Chen, J.; Ettelaie, R. Construction of 3D printed reduced-fat meat analogue by emulsion gels. Part II: Printing performance, thermal, tribological, and dynamic sensory characterization of printed objects. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, L.; Li, J. Extrusion-based 3D printing of high internal phase emulsions stabilized by co-assembled β-cyclodextrin and chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ban, Q. Development and characterization of a casein-hyaluronic acid emulsion gel with high water-holding capacity and excellent rheological properties for 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 140, 108632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Effects of flexibility and surface hydrophobicity on emulsifying properties: Ultrasound-treated soybean protein isolate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 142, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yan, R.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Jiao, A.; Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; et al. Development of emulsion-based edible inks for 3D printing applications: Pickering emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yu, J.; Gao, Y.; Mao, L. Tuning the rheological and tribological properties to simulate oral processing of novel high internal phase oleogel-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 130, 107757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.; Campbell, L.L.; Hanson, J.; Pantoya, M.L.; Christopher, G.F. Characterizing the feasibility of processing wet granular materials to improve rheology for 3D printing. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 13040–13053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.S.; Zhang, S.B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Peng, Y.X. Comparative study of high-intensity ultrasound and high-pressure homogenization on physicochemical properties of peanut protein-stabilized emulsions and emulsion gels. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootsma, K.; Fitzgerald, M.M.; Free BDimbath, E.; Conjerti, J.; Reese, G.; Konkolewicz, D.; Berberich, J.A.; Sparks, J.L. 3D printing of an interpenetrating network hydrogel material with tunable viscoelastic properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 70, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S.; Mantihal, S.; Zhang, M. Linking rheology and printability of a multicomponent gel system of carrageenan-xanthan-starch in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.J.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, X.Q. Effect of interfacial composition and crumbliness on aroma release in soy protein/sugar beet pectin mixed emulsion gels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4449–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Wang, K.; Lan, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, L. Effect of hybrid gelator systems of beeswax-carrageenan-xanthan on rheological properties and printability of litchi inks for 3D food printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Experimental Group | Factors | Printing Deviation/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: Protein Content/% | B: Oil Fraction/% | C: GG Content/% | ||
| 1 | 1 (4%) | 1 (30%) | 1 (0.15%) | 18.38 ± 0.76 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 (40%) | 2 (0.2%) | 15.83 ± 0.99 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 (50%) | 3 (0.25%) | 13.96 ± 0.40 |
| 4 | 2 (5%) | 1 | 2 | 17.34 ± 0.52 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 16.36 ± 0.36 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 12.55 ± 0.74 |
| 7 | 3 (6%) | 1 | 3 | 15.89 ± 0.40 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 15.03 ± 0.44 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 11.52 ± 0.34 |
| K1 | 48.17 | 51.61 | 45.96 | |
| K2 | 46.25 | 47.22 | 44.69 | |
| K3 | 42.44 | 38.03 | 46.21 | |
| R | 5.73 | 13.58 | 0.25 | |
| R order | B > A > C | |||
| Optimal conditions | A3B3C2 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.-Y.; Zhang, S.-B. Preparation and Characterization of Ultrasonically Modified Peanut Protein–Guar Gum Composite Emulsion Gels for 3D Printing. Gels 2024, 10, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120828
Yan H-Y, Zhang S-B. Preparation and Characterization of Ultrasonically Modified Peanut Protein–Guar Gum Composite Emulsion Gels for 3D Printing. Gels. 2024; 10(12):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120828
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Hong-Yan, and Shao-Bing Zhang. 2024. "Preparation and Characterization of Ultrasonically Modified Peanut Protein–Guar Gum Composite Emulsion Gels for 3D Printing" Gels 10, no. 12: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120828
APA StyleYan, H.-Y., & Zhang, S.-B. (2024). Preparation and Characterization of Ultrasonically Modified Peanut Protein–Guar Gum Composite Emulsion Gels for 3D Printing. Gels, 10(12), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120828








