Digital Platform for Automatic Qualitative and Quantitative Reading of a Cryptococcal Antigen Point-of-Care Assay Leveraging Smartphones and Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
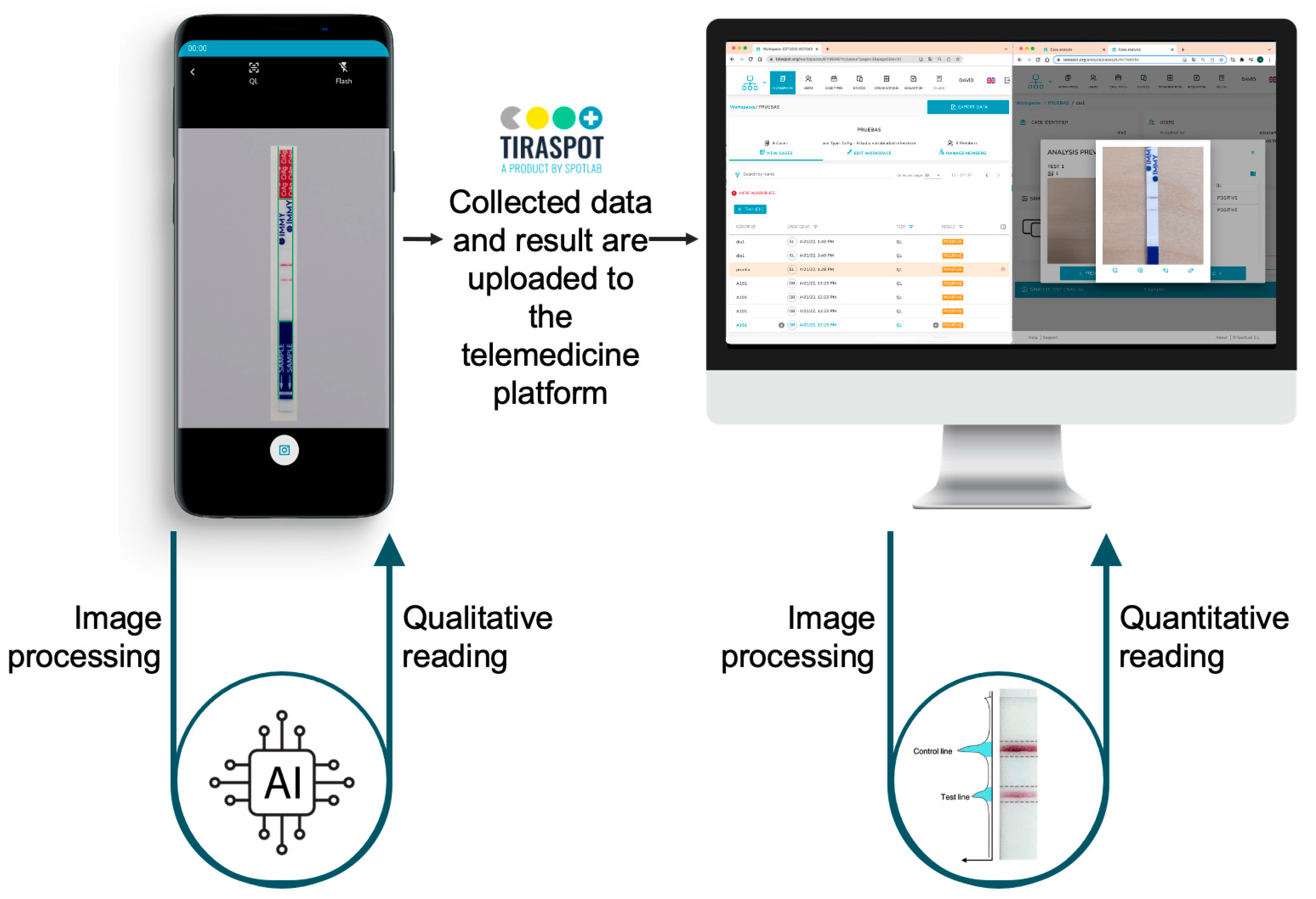
2.1. Experiment Design and Processing Pipeline
2.2. Sample Preparation and Data Acquisition
2.3. Mobile Application and Cloud Platform
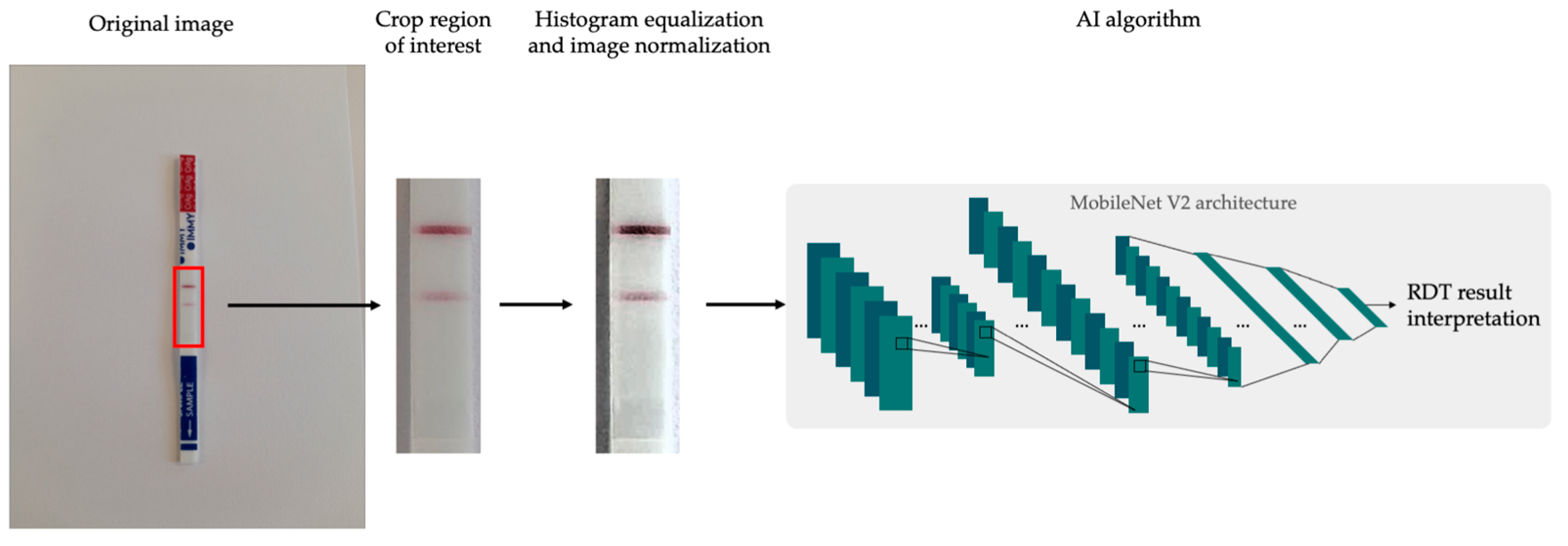
2.4. Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for POCT Qualitative Reading
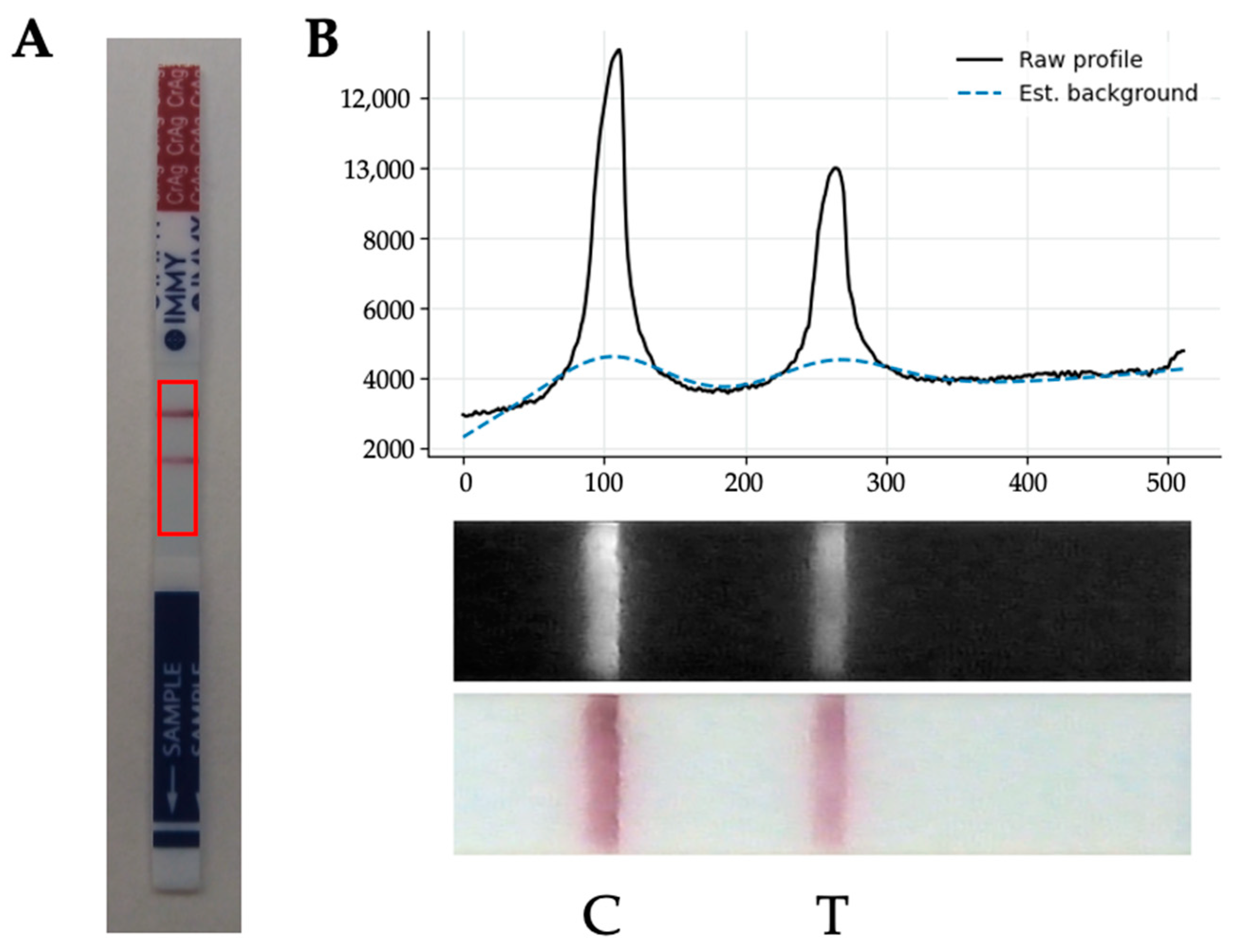
2.5. Artificial Intelligence Model for POCT Quantitative Reading
2.6. Validation Protocol and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
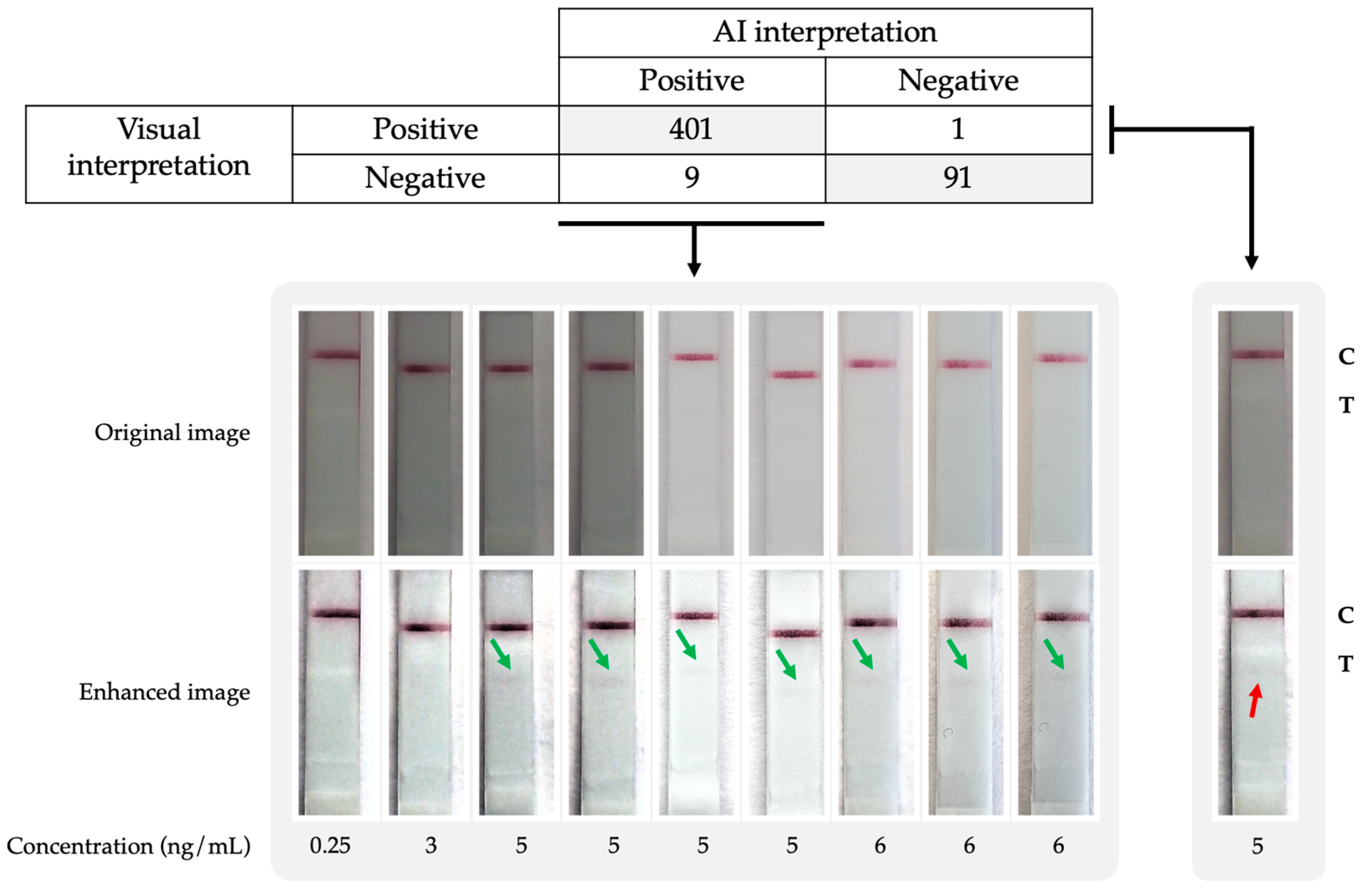
3.1. Real-Time AI-Assisted Reading of Qualitative CrAg LFA
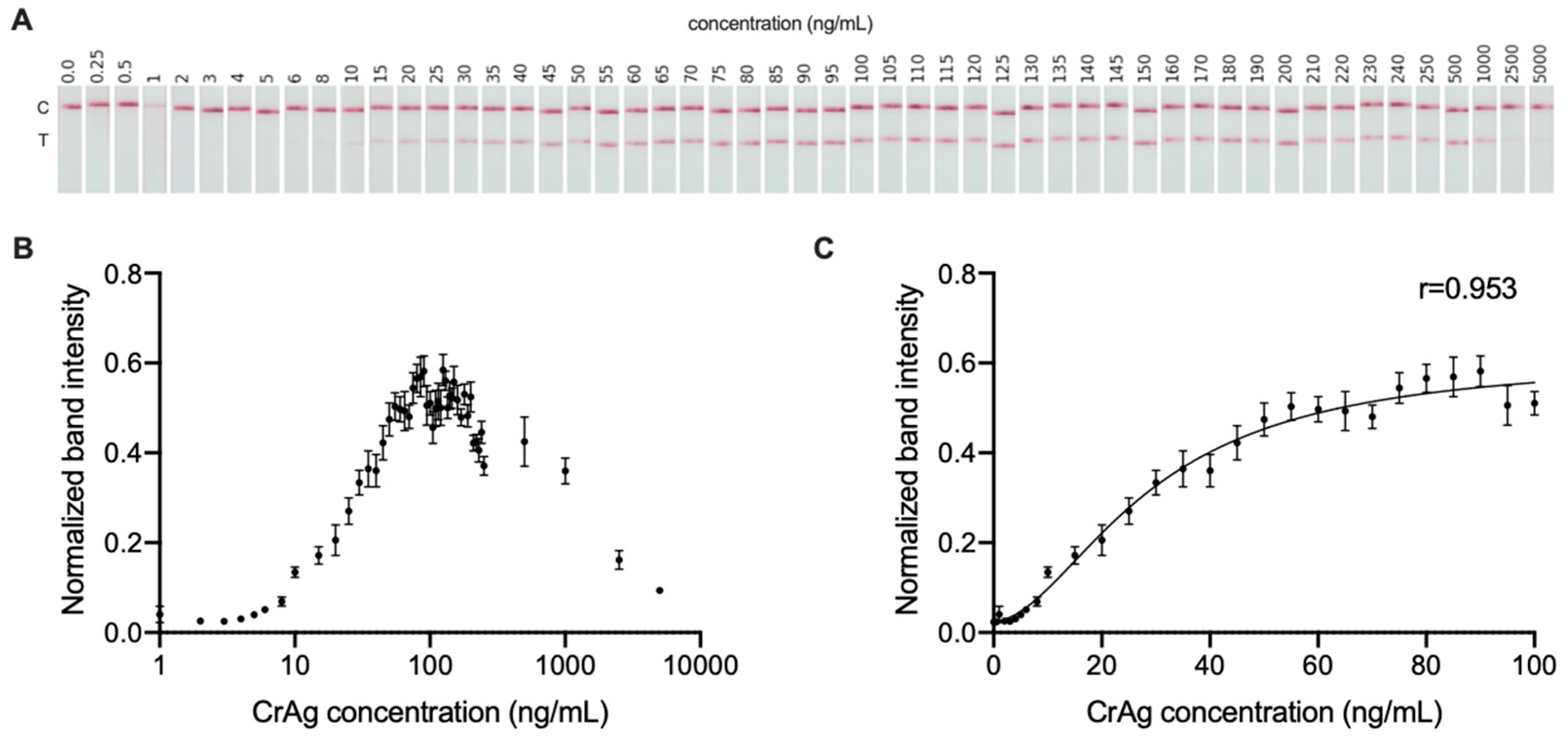
3.2. Quantitative Signal Measurement of CrAg LFA
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajasingham, R.; Govender, N.P.; Jordan, A.; Loyse, A.; Shroufi, A.; Denning, D.W.; Meya, D.B.; Chiller, T.M.; Boulware, D.R. The Global Burden of HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Infection in Adults in 2020: A Modelling Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wake, R.M.; Britz, E.; Sriruttan, C.; Rukasha, I.; Omar, T.; Spencer, D.C.; Nel, J.S.; Mashamaite, S.; Adelekan, A.; Chiller, T.M.; et al. High Cryptococcal Antigen Titers in Blood Are Predictive of Subclinical Cryptococcal Meningitis Among Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyene, T.; Zewde, A.G.; Balcha, A.; Hirpo, B.; Yitbarik, T.; Gebissa, T.; Rajasingham, R.; Boulware, D.R. Inadequacy of High-Dose Fluconazole Monotherapy Among Cerebrospinal Fluid Cryptococcal Antigen (CrAg)–Positive Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Persons in an Ethiopian CrAg Screening Program. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 2126–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letang, E.; Müller, M.C.; Ntamatungiro, A.J.; Kimera, N.; Faini, D.; Furrer, H.; Battegay, M.; Tanner, M.; Hatz, C.; Boulware, D.R.; et al. Cryptococcal Antigenemia in Immunocompromised Human Immunodeficiency Virus Patients in Rural Tanzania: A Preventable Cause of Early Mortality. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.W.; Clemons, K.V.; Katzenstein, D.A.; Stevens, D.A. The Cryptococcal Antigen Lateral Flow Assay: A Point-of-Care Diagnostic at an Opportune Time. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Akay, A.; Wei, H.; Wang, S.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Erlandsson, B.-E.; Li, X.; Lee, W.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Advances in Smartphone-Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Michelini, E.; Zangheri, M.; Di Fusco, M.; Calabria, D.; Simoni, P. Smartphone-Based Biosensors: A Critical Review and Perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep Learning of HIV Field-Based Rapid Tests|Nature Medicine. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01384-9 (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Using Artificial Intelligence to Improve COVID-19 Rapid Diagnostic Test Result Interpretation | PNAS. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2019893118 (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Wang, W.; Stafford, J.W.; Banik, D.; Keller, M.D. Customization and Testing of a Mobile Reader App for an Open-Access SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Lateral Flow Assay. In Proceedings of the Optics and Biophotonics in Low-Resource Settings VIII–SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22 January–28 February 2022; Volume 11950, pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Mariakakis, A.; Yang, J.; Lassala, D.; Djiguiba, Y.; Keita, Y.; Diarra, H.; Wasunna, B.; Fall, F.; Gaye, M.S.; et al. Supporting Smartphone-Based Image Capture of Rapid Diagnostic Tests in Low-Resource Settings. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies and Development, New York, NY, USA, 17 June 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mudanyali, O.; Dimitrov, S.; Sikora, U.; Padmanabhan, S.; Navruz, I.; Ozcan, A. Integrated Rapid-Diagnostic-Test Reader Platform on a Cellphone. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.C.K.; Meshkinfamfard, S.; Turbé, V.; Whitaker, M.; Moshe, M.; Bardanzellu, A.; Dai, T.; Pignatelli, E.; Barclay, W.; Darzi, A.; et al. Machine Learning to Support Visual Auditing of Home-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay Self-Test Results for SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, T.; Liang, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, H. Region Growing Algorithm Combined With Fast Peak Detection for Segmenting Colloidal Gold Immunochromatographic Strip Images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 169715–169723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Huang, C.; Xu, F.; Yan, J.; Bian, H.; Fu, Q.; Xie, K.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y. A Simple and Compact Smartphone-Based Device for the Quantitative Readout of Colloidal Gold Lateral Flow Immunoassay Strips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paula Vaz Cardoso, L.; Dias, R.F.; Freitas, A.A.; Hungria, E.M.; Oliveira, R.M.; Collovati, M.; Reed, S.G.; Duthie, M.S.; Martins Araújo Stefani, M. Development of a Quantitative Rapid Diagnostic Test for Multibacillary Leprosy Using Smart Phone Technology. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hu, L.; Keller, M.D. Effects of Image Capture and Correction Approaches on Quantifying Results of Lateral Flow Assays with Mobile Phones. In Proceedings of the Optics and Biophotonics in Low-Resource Settings VII–SPIE, Online, 6–12 March 2021; Volume 11632, pp. 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tania, M.H.; Lwin, K.T.; Shabut, A.M.; Najlah, M.; Chin, J.; Hossain, M. Intelligent Image-Based Colourimetric Tests Using Machine Learning Framework for Lateral Flow Assays. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 139, 112843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the Areas under Two or More Correlated Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves: A Nonparametric Approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Fungal Priority Pathogens List to Guide Research, Development and Public Health Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-92-4-006024-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. Point of Care Testing for Infectious Diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2019, 493, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, P.; Sharma, P. POCT in Developing Countries. EJIFCC 2021, 32, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bermejo-Peláez, D.; Marcos-Mencía, D.; Álamo, E.; Pérez-Panizo, N.; Mousa, A.; Dacal, E.; Lin, L.; Vladimirov, A.; Cuadrado, D.; Mateos-Nozal, J.; et al. Smartphone-Based Platform Assisted by Artificial Intelligence for Reading and Reporting Rapid Diagnostic Tests: Application to SARS-CoV-2 Lateral Flow Immunoassays. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutakingirwa, M.K.; Kiiza, T.K.; Rhein, J. “False Negative” CSF Cryptococcal Antigen with Clinical Meningitis: Case Reports and Review of Literature. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2020, 29, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, M.A.S.B.; Araújo Filho, J.A.; Soares, R.B.A.; Vidal, J.E.; Turchi, M.D. False-Negative Result of Serum Cryptococcal Antigen Lateral Flow Assay in an HIV-Infected Patient with Culture-Proven Cryptococcaemia. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2019, 26, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| SN [95% CI] | SP [95% CI] | AUC [95% CI] | ACC [95% CI] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 0.998 [0.993–1] | 0.910 [0.885–0.935] | 0.997 [0.992–1] | 0.976 [0.963–0.989] |
| Samsung S9 | 1 [1–1] | 0.920 [0.887–0.953] | 0.997 [0.990–1] | 0.976 [0.957–0.995] |
| Motorola Moto E6 | 0.995 [0.986–1] | 0.900 [0.863–0.937] | 0.997 [0.990–1] | 0.976 [0.957–0.995] |
| Models Used for Evaluation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motorola E6 | Samsung S9 | Both | ||
| Model used for fitting | Motorola E6 | 0.961 [0.952–0.968] | 0.957 [0.947–0.965] | 0.953 [0.946–0.959] |
| Samsung S9 | 0.96 [0.951–0.967] | 0.957 [0.947–0.965] | 0.953 [0.946–0.959] | |
| Both | 0.96 [0.951–0.967] | 0.957 [0.947–0.965] | 0.953 [0.946–0.959] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bermejo-Peláez, D.; Medina, N.; Álamo, E.; Soto-Debran, J.C.; Bonilla, O.; Luengo-Oroz, M.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. Digital Platform for Automatic Qualitative and Quantitative Reading of a Cryptococcal Antigen Point-of-Care Assay Leveraging Smartphones and Artificial Intelligence. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020217
Bermejo-Peláez D, Medina N, Álamo E, Soto-Debran JC, Bonilla O, Luengo-Oroz M, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Alastruey-Izquierdo A. Digital Platform for Automatic Qualitative and Quantitative Reading of a Cryptococcal Antigen Point-of-Care Assay Leveraging Smartphones and Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020217
Chicago/Turabian StyleBermejo-Peláez, David, Narda Medina, Elisa Álamo, Juan Carlos Soto-Debran, Oscar Bonilla, Miguel Luengo-Oroz, Juan Luis Rodriguez-Tudela, and Ana Alastruey-Izquierdo. 2023. "Digital Platform for Automatic Qualitative and Quantitative Reading of a Cryptococcal Antigen Point-of-Care Assay Leveraging Smartphones and Artificial Intelligence" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020217
APA StyleBermejo-Peláez, D., Medina, N., Álamo, E., Soto-Debran, J. C., Bonilla, O., Luengo-Oroz, M., Rodriguez-Tudela, J. L., & Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. (2023). Digital Platform for Automatic Qualitative and Quantitative Reading of a Cryptococcal Antigen Point-of-Care Assay Leveraging Smartphones and Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Fungi, 9(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020217







