The Sorting Nexin Genes ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Are Required for Reproductive Development, Stress Adaption and Virulence in Cochliobolus heterostrophus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains and Plant Materials
2.2. Identification of ChSNX4 and ChSNX41
2.3. Construction of Snx4 and Snx41 Mutants and Complementation Strains, and PCR Verification
2.4. Phenotypic Analysis
2.5. Virulence Test
2.6. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) Assay
2.7. Response to Stress and ROS Detection
2.8. Expression Level Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
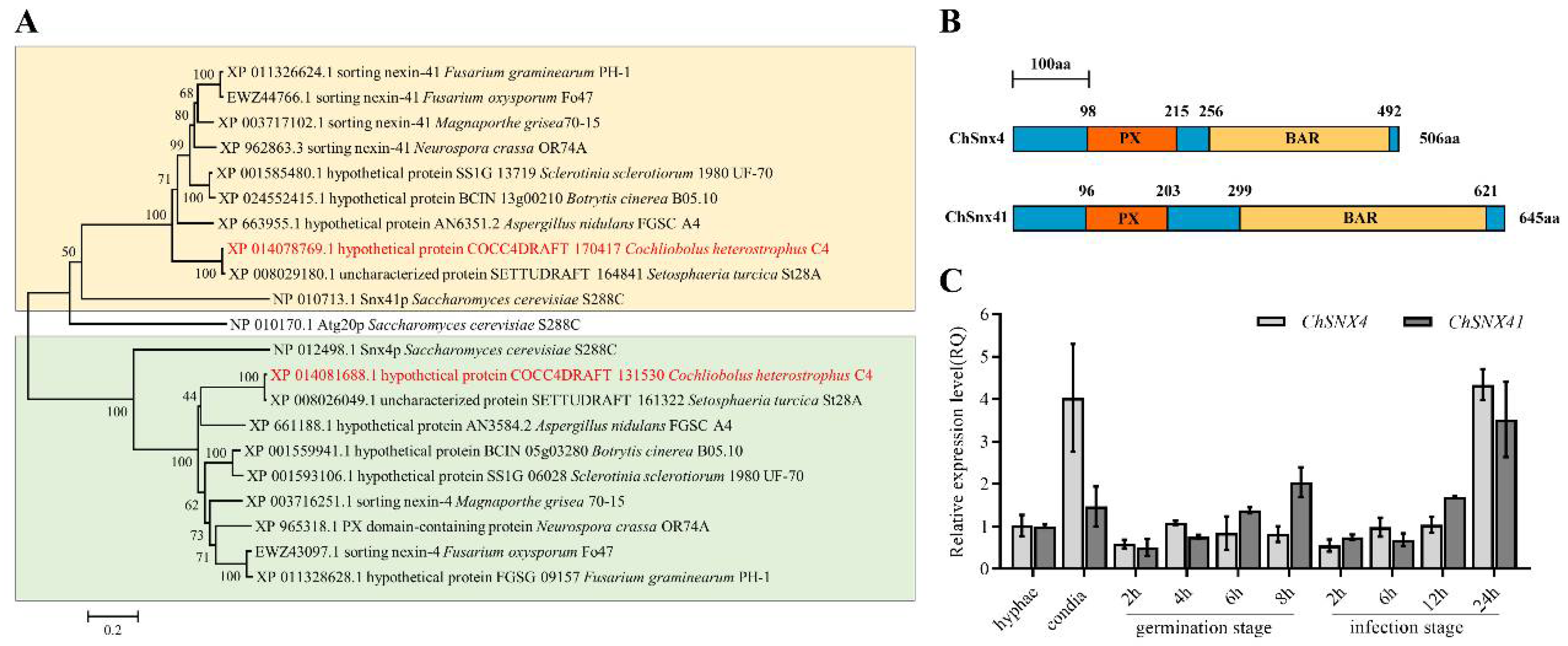
3.1. Identification of SNX4 and SNX41 in C. heterostrophus
3.2. ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Were Required for Proper Vegetative Growth
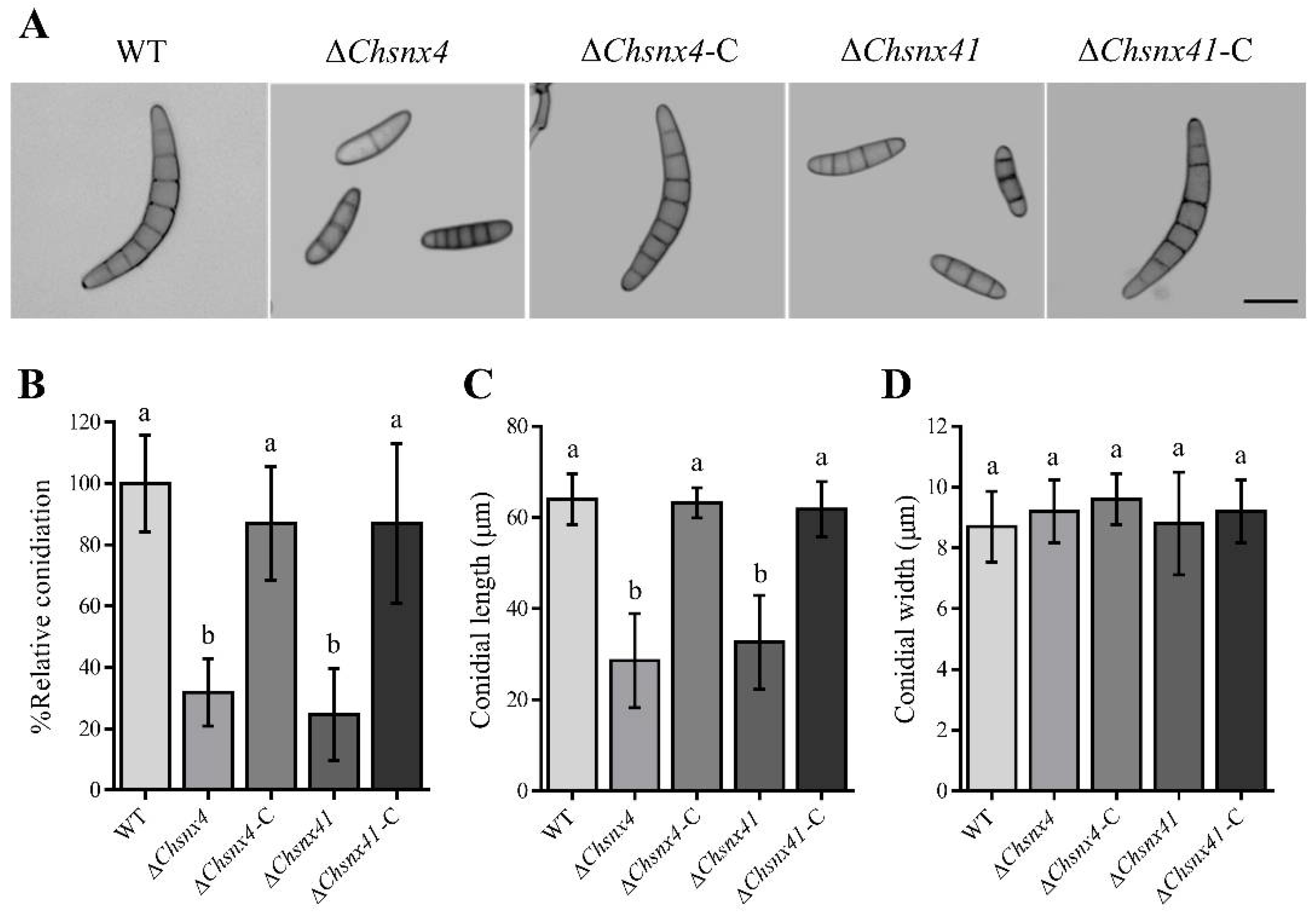
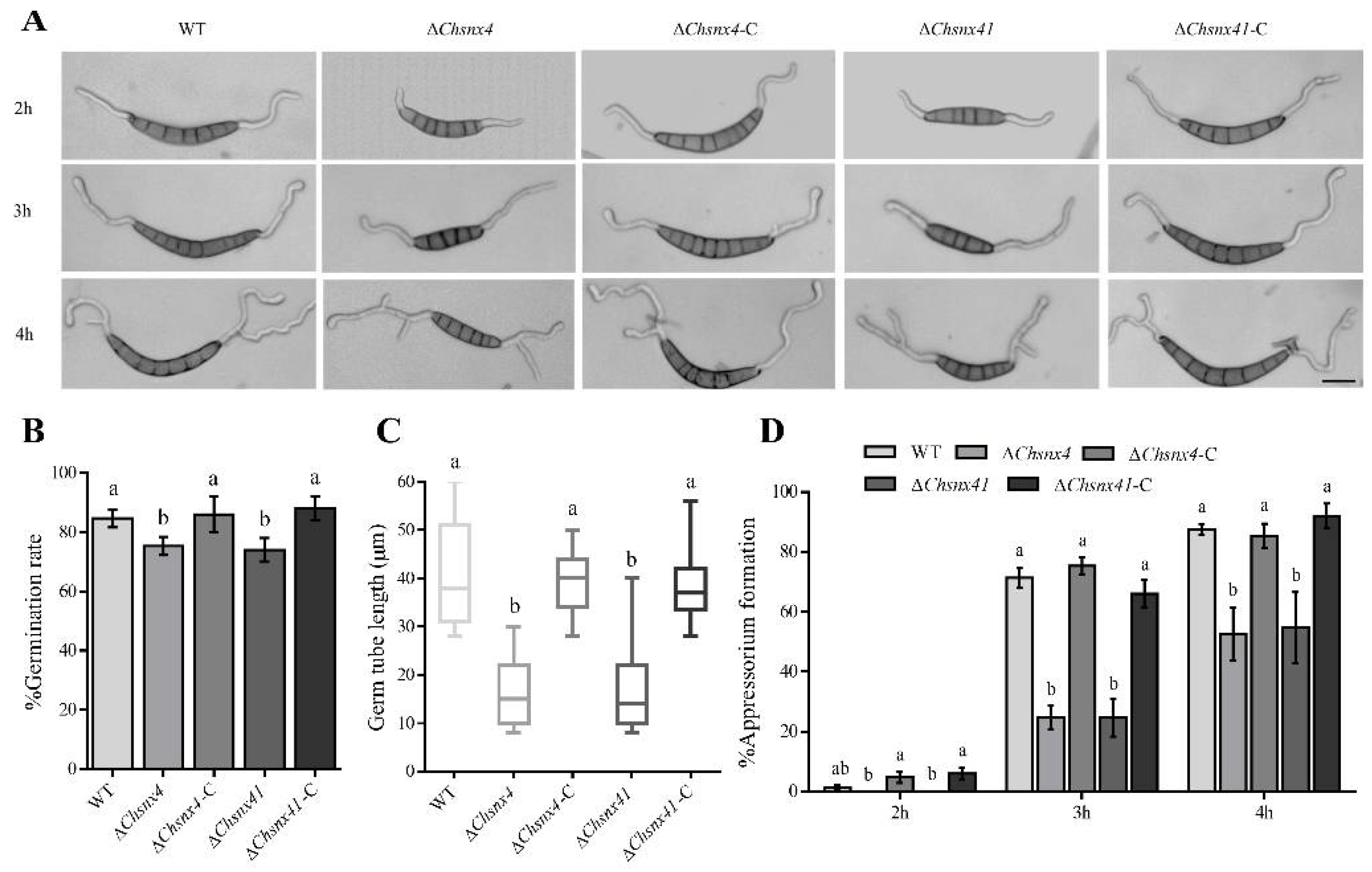
3.3. ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Disruption Caused Defects in Asexual Reproduction
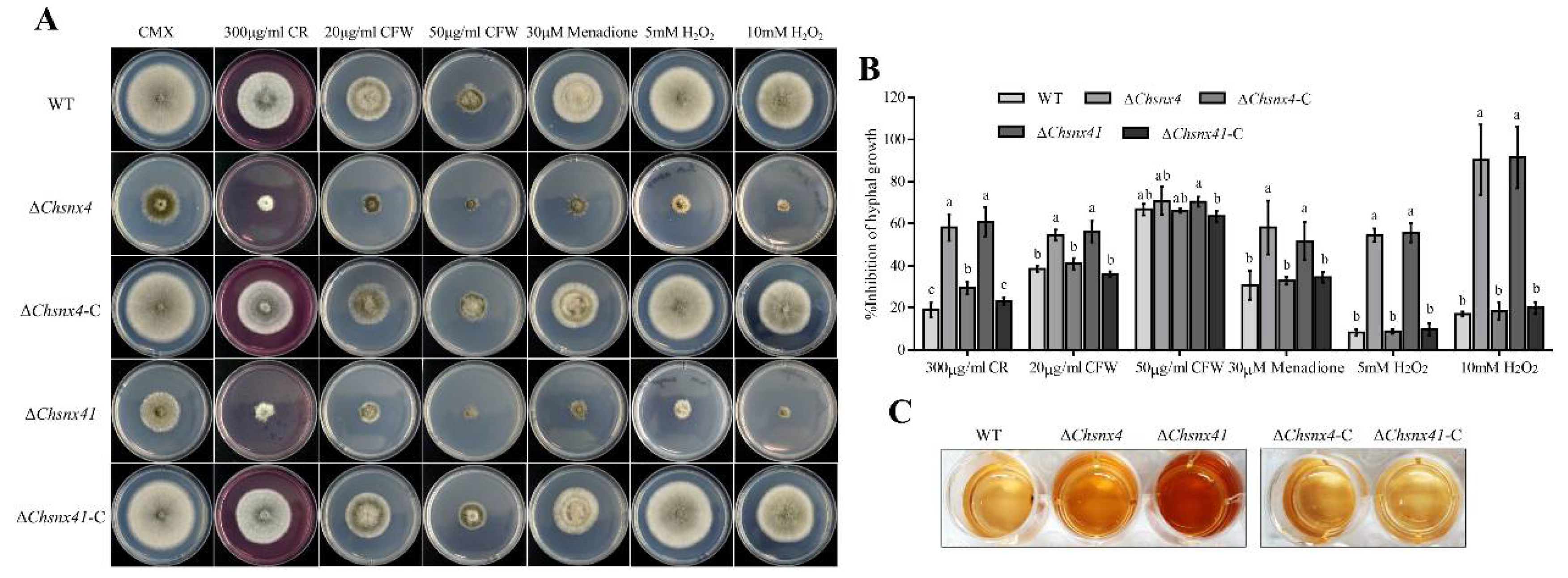
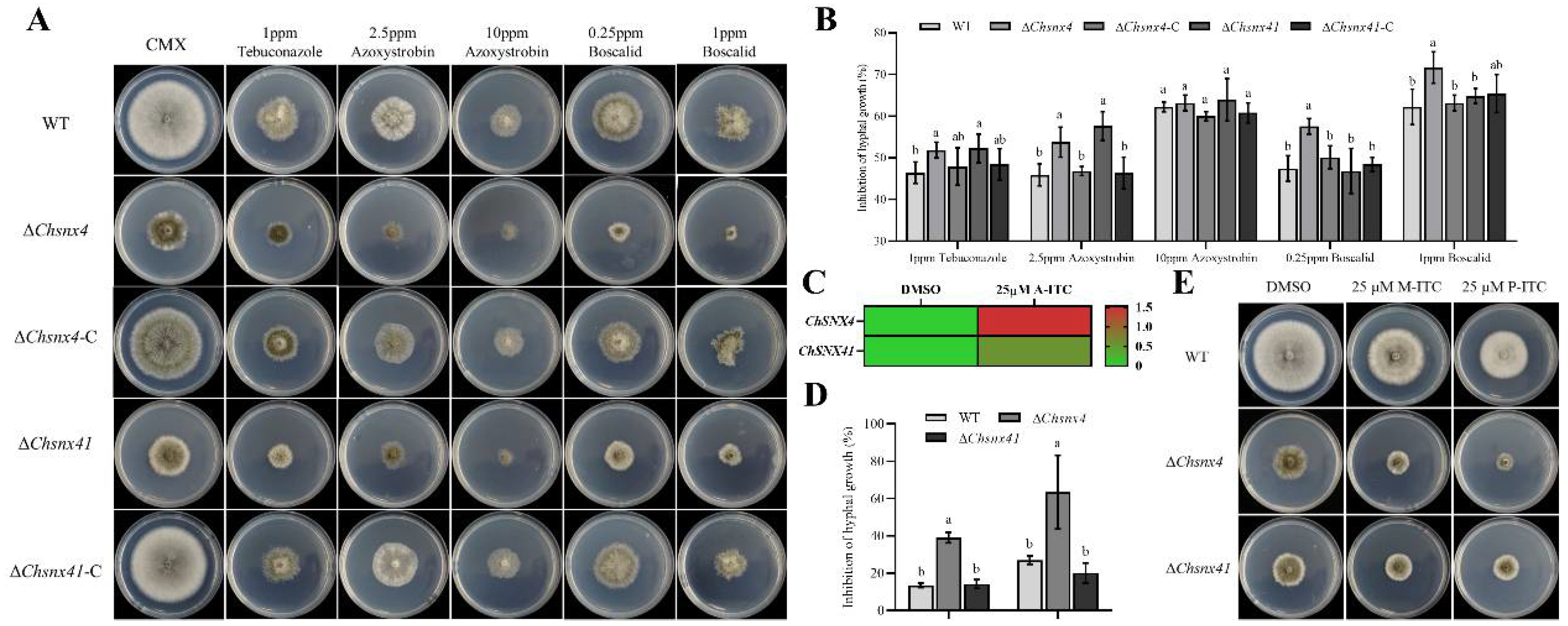
3.4. ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Are Necessary for Stress Adaption
3.5. ChSnx4 and ChSnx41 Are Necessary for Virulence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Numrich, J.; Ungermann, C. Endocytic Rabs in membrane trafficking and signaling. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.H.; Zhou, J.; He, Y.L.; Xie, Q.R.; Chen, A.H.; Zheng, H.W.; Shi, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.K.; Huang, Q.P.; et al. Retromer is essential for autophagy-dependent plant infection by the rice blast fungus. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, R.D.; Loci, D.; Houghton, F.; Karlsson, L.; Gleeson, P.A. A large family of endosome-localized proteins related to sorting nexin 1. Biochem. J. 2001, 358, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worby, C.A.; Dixon, J.E. Sorting out the cellular functions of sorting nexins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlton, J.G.; Bujny, M.V.; Rutherford, A.; Cullen, P.J. Sorting nexins-Unifying trends and new perspectives. Traffic 2005, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, R.D.; Collins, B.M. Insights into the PX (phox-homology) domain and SNX (sorting nexin) protein families: Structures, functions and roles in disease. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaman, M.N.; McCaffery, J.M.; Emr, S.D. A membrane coat complex essential for endosome-to-Golgi retrograde transport in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettema, E.H.; Lewis, M.J.; Black, M.W.; Pelham, H.R. Retromer and the sorting nexins Snx4/41/42 mediate distinct retrieval pathways from yeast endosomes. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Stefan, C.; Rue, S.; Teis, D.; Emr, S. Two novel WD40 domain containing proteins, Ere1 and Ere2, function in the retromer-mediated endosomal recycling pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 4093–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nice, D.C.; Sato, T.K.; Stromhaug, P.E.; Emr, S.D.; Klionsky, D.J. Cooperative binding of the cytoplasm to vacuole targeting pathway proteins, Cvt13 and Cvt20, to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate at the pre-autophagosomal structure is required for selective autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30198–30207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traer, C.J.; Rutherford, A.C.; Palmer, K.J.; Wassmer, T.; Oakley, J.; Attar, N.; Carlton, J.G.; Kremerskothen, J.; Stephens, D.J.; Cullen, P.J. SNX4 coordinates endosomal sorting of TfnR with dynein-mediated transport into the endocytic recycling compartment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.Z.; Qu, Z.; Naqvi, N.I. The role of snx41-based pexophagy in magnaporthe development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.Z.; Qu, Z.; He, Y.; Naqvi, N.I. Sorting nexin Snx41 is essential for conidiation and mediates glutathione-based antioxidant defense during invasive growth in Magnaporthe oryzae. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.L.; Deng, Y.Z.; Naqvi, N.I. Atg24-assisted mitophagy in the foot cells is necessary for proper asexual differentiation in Magnaporthe oryzae. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Fang, W.Q.; Zhao, X.; Lou, Y.; Wang, G.H.; Zheng, H.W.; Liang, Q.F.; Abubakar, Y.S.; Olsson, S.; et al. The endosomal recycling of FgSnc1 by FgSnx41–FgSnx4 heterodimer is essential for polarized growth and pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.Y.; Xu, Z.; Talbot, N.; Wang, Z.Y. The sorting nexin FgAtg20 is involved in the Cvt pathway, non-selective macroautophagy, pexophagy and pathogenesis in Fusarium graminearum. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, V.; Schürmanns, L.; Brunner, M.; Hamann, A.; Osiewacz, H.D. Role of sorting nexin PaATG24 in autophagy, aging and development of Podospora anserine. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 186, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.; Lang, B.R.; Yoder, O.C. Methods for selection of mutants and in vitro culture of Cochliobolus heterostrophus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1982, 128, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Turgeon, B.G.; Condon, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, N. Protoplast transformation of filamentous fungi. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2010, 638, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Catlett, N.; Lee, B.N.; Yoder, O.; Turgeon, B.G. Split-marker recombination for efficient targeted deletion of fungal genes. Fungal Genet. Newsl. 2003, 50, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.W.; Lyngholm, L.; Yang, G.; Bronson, C.; Yoder, O.C.; Turgeon, B.G. Tagged mutations at the Tox1 locus of Cochliobolus heterostrophus using restriction enzyme mediated integration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12649–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shwab, E.K.; Juvvadi, P.R.; Shaheen, S.K.; John, A.I.; Waitt, G.; Soderblom, E.J.; Asfaw, Y.G.; Moseley, M.A.; Steinbach, W.J. Protein kinase A regulates autophagy-associated proteins impacting growth and virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sophie, L.; Benjamin, A.H. A mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway modulates the expression of two cellulase genes in Cochliobolus heterostrophus during plant infection. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 835–844. [Google Scholar]
- Kanki, T.; Klionsky, D.J. Mitophagy in yeast occurs through a selective mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 283, 32386–32393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Jia, W.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X. The Sorting Nexin Genes ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Are Required for Reproductive Development, Stress Adaption and Virulence in Cochliobolus heterostrophus. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080855
Yu H, Jia W, Li Z, Gao C, Pan H, Zhang X. The Sorting Nexin Genes ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Are Required for Reproductive Development, Stress Adaption and Virulence in Cochliobolus heterostrophus. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(8):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080855
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huilin, Wantong Jia, Zhongxiang Li, Chaofeng Gao, Hongyu Pan, and Xianghui Zhang. 2022. "The Sorting Nexin Genes ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Are Required for Reproductive Development, Stress Adaption and Virulence in Cochliobolus heterostrophus" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 8: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080855
APA StyleYu, H., Jia, W., Li, Z., Gao, C., Pan, H., & Zhang, X. (2022). The Sorting Nexin Genes ChSNX4 and ChSNX41 Are Required for Reproductive Development, Stress Adaption and Virulence in Cochliobolus heterostrophus. Journal of Fungi, 8(8), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080855






